Prevalence of the Gingival Phenotype in Adults and Associated Risk Factors: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recording the Protocol
2.2. Research Question and Eligibility Criteria
- i.
- A retrospective, cross-sectional, or prospective study assessing the quantity and quality of the gingival phenotype.
- ii.
- At the level of one or more dental sectors.
- iii.
- Including adult subjects in good general health, regardless of gender, with a healthy periodontium.
- iv.
- The articles must be written in English or French and published between 2011 (1 January 2011) and 29 January 2024.
2.3. Search Strategy and Equations
2.4. Selection of Articles
- −
- List 0 included all the articles obtained from the search equations.
- −
- List no. 1 included all the articles selected from list 0 after eliminating duplicates and reading the titles.
- −
- List no. 2 included all the articles selected from list no. 1 after reading the abstracts and then the full texts.
- −
- List no. 3 finally included all the articles from list no. 2 and the manual search after a full reading of the additional articles deemed relevant.
Data Extraction and Risk of Bias Assessment
- −
- Author, journal, and year of publication; type of study.
- −
- Objective(s).
- −
- Population (number of subjects, individual characteristics, teeth concerned).
- −
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
- −
- Materials and methods (intervention, protocol).
- −
- Results (prevalence, association).
- −
- Selection, confusion, and classification bias.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
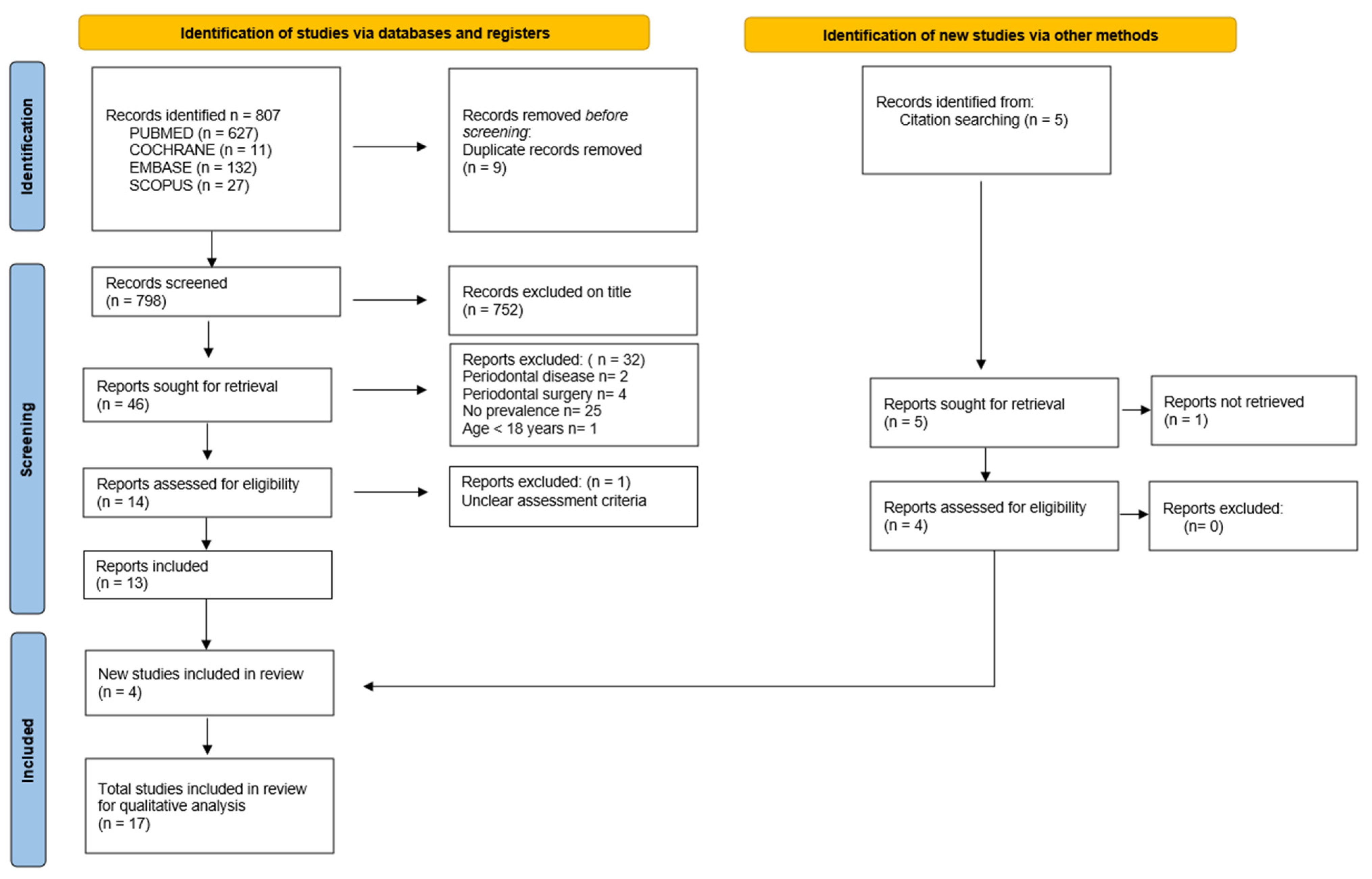
3.1. Article Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.2.1. General Characteristics
- Type of study.
- Geographical location of populations.
- Characteristics of subjects.
3.2.2. Protocol and Assessment Criteria
- Selection of subjects.
- Choice of dental sectors.
- Periodontal health assessment criterion.
- Gingival phenotype assessment criterion.
- Information about the investigators.
3.3. Main Results
- Overall assessment of gingival thickness, for all subjects, all types of teeth, and all means of assessment combined.
- Assessment of gingival thickness according to dental arch, all types of teeth, and means of assessment combined (Table 4).
- Assessment of gingival thickness as a function of tooth type, regardless of the method used (Table 5).
- Overall assessment of the height of the gum (or keratinized tissue).
- Association of gingival thickness and height of keratinized tissue (HTK).
3.4. Secondary Results
- Association between gingival thickness and gender.
- Association between gingival thickness and papillae height.
- Gingival thickness/dental morphology association.
- Gingival thickness/smoking association.
- Association with the dental angle class.
- Association with bone morphology.
- Association with gingival pigmentation.
- Association with the smile line.
- Geographical origin of populations.
3.5. Assessing Bias in Studies
- Selection bias (questions 1 and 4 of the MMAT tool): non-probabilistic or unspecified recruitment method; samples poorly distributed in relation to individual criteria; no information on the number or individual characteristics of patients who refused inclusion.
- Confounding bias (question 2 of the MMAT tool): periodontal condition not precisely indicated; known risk factors that can bias the assessment of gingival thickness, such as smoking, a physiological hormonal factor, or medication that causes gingival growth, are not taken into account.
- Classification bias (questions 3 and 5 of the MMAT tool): unspecified or unsuitable measurement instrument; uncalibrated examiner; no blinding; unspecified statistical method.
4. Discussion
- Assessment of the prevalence of gingival phenotypes.
- Indicators/risk factors for gingival phenotypes.
- Limitations.
- Clinical relevance.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cortellini, P.; Bissada, N.F. Mucogingival conditions in the natural dentition: Narrative review, case definitions, and diagnostic considerations. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S204–S213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweers, J.; Thomas, R.Z.; Slot, D.E.; Weisgold, A.S.; Van der Weijden, F.G. Characteristics of periodontal biotype, its dimensions, associations and prevalence: A systematic review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2014, 41, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpartida-Carrillo, V.; Tinedo-Lopez, P.L.; Guerrero, M.E.; Amaya-Pajares, S.P.; Özcan, M.; Rösing, C.K. Periodontal phenotype: A review of historical and current classifications evaluating different methods and characteristics. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2021, 33, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claffey, N.; Shanley, D. Relationship of gingival thickness and bleeding to loss of probing attachment in shallow sites following nonsurgical periodontal therapy. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1986, 13, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.; Wang, H.L. Flap Thickness as a Predictor of Root Coverage: A Systematic Review. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.; Almeida, R.; Dias, A.; Rodrigues, W.; Barceleiro, M.; Taba, M. Clinical Considerations on the Root Coverage of Gingival Recessions in Thin or Thick Biotype. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2016, 36, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, M.; Lindhe, J. Periodontal characteristics in individuals with varying form of the upper central incisors. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1991, 18, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.H.; Neiva, R.E.F.; Wang, H.L. Factors Affecting the Outcomes of Coronally Advanced Flap Root Coverage Procedure. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joss-Vassalli, I.; Grebenstein, C.; Topouzelis, N.; Sculean, A.; Katsaros, C. Orthodontic therapy and gingival recession: A systematic review. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2010, 13, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallikarjuna, D.; Shetty, M.; Fernandes, A.; Mallikarjuna, R.; Iyer, K. Gingival biotype and its importance in restorative dentistry: A pilot study. J. Interdiscip. Dent. 2016, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Park, J.S.; Jang, Y.H.; Son, J.H.; Kim, W.K.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, S.H. Accuracy of periodontal probe visibility in the assessment of gingival thickness. J. Periodontal. Implant Sci. 2021, 51, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachodimou, E.; Fragkioudakis, I.; Vouros, I. Is there an association between the gingival phenotype and the width of keratinized gingiva? A systematic review. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafizadeh, M.; Amid, R.; Tehranchi, A.; Motamedian, S.R. Evaluation of the association between gingival phenotype and alveolar bone thickness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2022, 133, 105287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Q.N.; Fàbregues, S.; Bartlett, G.; Boardman, F.; Cargo, M.; Dagenais, P.; Gagnon, M.P.; Griffiths, F.; Nicolau, B.; O’Cathain, A.; et al. The Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) version 2018 for information professionals and researchers. Educ. Inf. 2018, 34, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, K.H.; Al-Harthi, S.M.; Al-Zahrani, M.S. Prevalence of gingival biotype and its relationship to dental malocclusion. Saudi Med. J. 2012, 33, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.; Bhat, V. Prevalence of different gingival biotypes in individuals with varying forms of maxillary central incisors: A survey. J. Dent. Implant 2013, 3, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Sowmya, N.K.; Mehta, D.S. Prevalence of gingival biotype and its relationship to clinical parameters. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2015, 6, S167–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, A.; Marques, T.M.; Correia, A. Gingival biotype characterization—A study in a Portuguese sample. Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 2015, 10, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frost, N.A.; Mealey, B.L.; Jones, A.A.; Huynh-Ba, G. Periodontal Biotype: Gingival Thickness as It Relates to Probe Visibility and Buccal Plate Thickness. J. Periodontol. 2015, 86, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.R.; Richter, T.; Kebschull, M.; Petersen, N.; Fickl, S. On the relationship between gingival biotypes and gingival thickness in young Caucasians. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Rathod, V.J.; Rao, P.R.; Patil, A.A.; Langade, D.G.; Singh, R.K. Correlation of gingival thickness with gingival width, probing depth, and papillary fill in maxillary anterior teeth in students of a dental college in Navi Mumbai. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2016, 7, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.Z.; Ong, M.M.A.; Yeo, A.B. Gingival profiles in a select Asian cohort: A pilot study. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2018, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhajj, W.A. Gingival phenotypes and their relation to age, gender and other risk factors. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.R.; Pannuti, C.M.; Veras, K.; Ogando, G.; Brache, M. Gingival phenotype and its relationship with different clinical parameters: A study in a Dominican adult sample. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 4967–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.R.; Büchel, J.; Kauffmann, F.; Heumann, C.; Friedmann, A.; Schmidlin, P.R. Gingival phenotype distribution in young Caucasian women and men—An investigative study. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2022, 8, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.M.; Barreto, L.S.D.C.; Petersen, R.L.; Ferreira, V.; Cavalcante, D.M.; Barboza, E.D.S.P. Relationship between smile type and periodontal phenotype: A clinical and tomographic cross-sectional study. J. Dent. 2022, 122, 104160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nik-Azis, N.M.; Razali, M.; Goh, V.; Ahmad Shuhaimi, N.N.; Mohd Nazrin, N.A.S. Assessment of gingival thickness in multi-ethnic subjects with different gingival pigmentation levels. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2023, 50, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, G.; Ahmed, A.R.; Suleman, G.; Lal, A.; Rana, M.H.; Ahmed, N.; Arora, S. A Comparative Evaluation of Dentogingival Tissue Using Transgingival Probing and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Medicina 2022, 58, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.R.; Grill, E.; Jockel-Schneider, Y.; Bechtold, M.; Schlagenhauf, U.; Fickl, S. On the relationship between gingival biotypes and supracrestal gingival height, crown form and papilla height. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Yin, L.; Gu, J.; Wang, D.; Lu, W.; Sun, Y. Assessment of Periodontal Biotype in a Young Chinese Population using Different Measurement Methods. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.; Suragimath, G.; Zope, S.A.; Ashwinirani, S.R.; Varma, S.A. Comparison of gingival biotype between different genders based on measurement of dentopapillary complex. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, ZC40–ZC45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.J.; Wei, B.Y.; Ke, X.P.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, M.Y.; Luo, X.Y.; Sun, H.Q. Correlation between clinical parameters of crown and gingival morphology of anterior teeth and periodontal biotypes. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jepsen, S.; Caton, J.G.; Albandar, J.M.; Bissada, N.F.; Bouchard, P.; Cortellini, P.; Demirel, K.; de Sanctis, M.; Ercoli, C.; Fan, J.; et al. Periodontal manifestations of systemic diseases and developmental and acquired conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 3 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S237–S248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rouck, T.; Eghbali, R.; Collys, K.; de Bruyn, H.; Cosyn, J. The gingival biotype revisited: Transparency of the periodontal probe through the gingival margin as a method to discriminate thin from thick gingiva. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasperini, G.; Acunzo, R.; Cannalire, P.; Farronato, G. Influence of Periodontal Biotype on Root Surface Exposure During Orthodontic Treatment: A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2015, 35, 655–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, A.; Hefti, A.F. Defining periodontal health. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, N.P.; Bartold, P.M. Periodontal health. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S9–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.M.; Bassir, S.H.; Nguyen, T.T. Effect of gingival phenotype on the maintenance of periodontal health: An American Academy of Periodontology best evidence review. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshipura, K.J.; Kent, R.L.; DePaola, P.F. Gingival Recession: Intra-Oral Distribution and Associated Factors. J. Periodontol. 1994, 65, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Hartsfield, J.K.; Aps, J.; Naoum, S.; Lee, R.; Miranda, L.A.; Goonewardene, M.S. Effect of craniofacial morphology on gingival parameters of mandibular incisors. Angle Orthod. 2023, 93, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.T.; Huang, N.C.; Wong, A.; Cobb, C.; Lee, S.; Mikail, Y.; Kao, R.T. Periodontal Risk Assessment Based on Dental and Gingival Morphology: A Comparative Analysis of African Versus Asian American Cohorts. Clin. Adv. Periodontics 2020, 10, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saposnik, G.; Redelmeier, D.; Ruff, C.C.; Tobler, P.N. Cognitive biases associated with medical decisions: A systematic review. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2016, 16, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Database | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| PubMed (MEDLINE) | ((“healthy adults”) OR (“periodontal health”)) OR (“general population”)) OR (“epidemiological”)) OR (“clinical study”)) OR (“human study”))) AND ((“gingival biotype”)) OR (“periodontal biotype”)) OR (“gingival phenotype”)) OR (“periodontal phenotype”)) OR (“gingival width”)) OR (“gingival thickness”)) OR (“thick biotype”)) OR (“thin biotype”))) |
| The Cochrane Library | (“Periodontium” OR “Gingiva”) AND (“Morphotype” OR “Thickness” OR “thick” OR “Thin” OR “Biotype” OR “Flat”) |
| Embase | (“healthy adults” OR “periodontal health” OR “general population” OR “epidemiological” OR “clinical study” OR “human study”) AND “gingival biotype” OR “periodontal biotype” OR “gingival phenotype” OR “periodontal phenotype” OR “gingival width” OR “gingival thickness” OR “thick biotype” OR “thin biotype”) |
| Scopus | (KEY (periodontal AND phenotype) OR KEY (gingival AND biotype) OR KEY (gingival AND thickness) AND KEY (prevalence)) |
| Authors Year of Publication | Objectives | Population/Types of Teeth/Recruitment | Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria | Materials and Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zawawi et al. 2012 [16] | Primary: To assess the prevalence of gingival biotypes, and the association with the different types of malocclusions. Secondary: Assess the relationship with the smoking habits (current smoker/former smoker/never smoker). | 200 subjects (100 M, 100 F) 50% F (average age:31.7 years)/50% M (average age: 32.4 years) Max central incisors Recruitment: random successive mode at the dental faculty of King Abdulaziz University in Jeddah, (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia) | Inclusion criteria: 18 years or older Presence of all max anterior teeth Exclusion criteria: Dental crowns History of an orthodontic treatment Antibiotic treatment required for the examination Medicinal treatment with a known effect on the periodontal soft tissues, pregnant or breastfeeding women | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness Dental occlusion (angle classification or canine relationship) Tobacco consumption Protocol: A single calibrated examiner (superior reliability 93%) Williams periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) Transparent probe technique |
| Shetty and Bhat 2013 [17] | Primary: To assess gingival thickness (biotype). Secondary: Evaluate the prevalence of gingival biotypes of max central incisors as a function of gender, age, tooth shape, and papillary height. | 200 subjects (125 M, 75 F) 37.5% F/62.5% M 18–30 age group = 125 subjects, 30–50 age group = 75 subjects Max central incisors Inclusion following a visit to the outpatient department in Mangalore, Karnataka (India) | Inclusion criteria: Age between 18 and 50 Exclusion criteria: Catering/crowns Orthodontic treatment, dental malposition Periodontitis (PD > 3 mm) or recession Pregnant/lactating women | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness, papillary height Crown length/width ratio Protocol: A single calibrated examiner (kappa not quoted) Type of periodontal probe not quoted Transparent probe technique |
| Fischer et al. 2014 [30] | Primary: Determine the correlation between the gingival biotype, the supracrestal vestibular, and the interproximal gingival height. Secondary: Assess the correlation between the gingival biotype and the crown shape or the correlation between the gingival biotype and the papilla height. | 80 subjects (34 M, 46 F) 57.5% F/42.5% M (mean age 25.8 years) Max central incisors Inclusion in the Julius-Maximilians University in Wuerzburg (Germany) without further details | Inclusion criteria: Presence from 13 to 23 Exclusion criteria: Restoration/crown, severe attrition Periodontitis (PD > 3 mm) or recessions Medicinal treatment with a known effect on periodontal soft tissues, pregnant/lactating women, bone disease Smoking (>10 cigarettes/day) | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness, papillary height Gum height Crown length/width ratio Protocol: A single calibrated examiner (97% reliability) UNC-15 periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, Il, USA)Transparent probe technique |
| Shah et al. 2015 [18] | Primary: To assess the prevalence of gingival biotypes. Secondary: Evaluate the relationship between the gender, the recessions, and the gum height. | 400 subjects (200 M, 200 F) 50% F/50% M (mean age 28.82 years) Max central and lateral incisors, canines Recruitment: not specified (India) | Inclusion criteria: Good general health, no dental crowding Exclusion criteria: Removable prosthesis, orthodontic device Absence of one of the six max anterior teeth Periodontal recessions (class III/IV Miller) History of smoking or mouth breathing | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness, gingival height (with iodine solution) PD, gingival recession Protocol: Single blind calibrated examiner (kappa not quoted) UNC-15 periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, Il, USA) Transgingival probing (endodontic file) |
| Peixoto et al. 2015 [19] | Primary: Determine the relationship between the gingival thickness, the papillary height, and the height of the gum Secondary: Assess the relationship with the gender, the shape, and the location of the crown | 50 subjects (20 M, 30 F) 60% F/40% M (average age not given) Max central incisors Place and method of recruitment not cited (Portugal) | Inclusion criteria: Good general health, max anterior teeth present Exclusion criteria: Dental malposition, restorations/crowns History of orthodontic treatment, periodontal surgery Periodontitis Medicinal treatment known to have an effect on periodontal soft tissues, pregnant/breastfeeding women | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness, gingival height Papillary height Crown length/width ratio Gingival angle, gingival asymmetry Protocol: No information about the examiner OMS periodontal probe (Henry Schein®, Melville, NY, USA) Probe transparency technique + analysis based on the intraoral photographs |
| Frost et al. 2015 [20] | Primary: To determine the objective measurement of the gingival thickness in relation to a gold standard (transparency of the probe). Secondary: To correlate with the thickness of the alveolar bone. | 56 subjects (33 F, 23 M) 58.9% F/41% M (mean age 53) Max incisors, canines, premolars Inclusion in UTHSCSA Dental School (Texas, USA) unspecified | Inclusion criteria: Age > 18 years No gum disease Presence of at least one maxillary anterior tooth (incisors), one canine, one first PM Exclusion criteria: Restoration, dental malposition, gingival hypertrophy History of orthodontic treatment or surgery Periodontitis (PD ≥ 4 mm) Uncontrolled systemic disease Drug treatment with a known effect on periodontal soft tissues, pregnant women | Parameters recorded: Gingival biotype, gingival thickness Thickness of the bone table Protocol: UNC-15 periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) Probe transparency technique (gold standard) + intra-oral photographs (three examiners) Transgingival probing (endodontic file) + intraoral photographs (one examiner) CBCT |
| Fischer et al. 2015 [21] | Primary: Assess the association between the gingival biotype and the gingival thickness. Secondary: Compare and analyze the extreme biotypes (very thin, very thick). | 36 subjects (19 F, 17 M) 53% F/47% M (average age 24.9) Max central incisors Inclusion in the Julius-Maximilians University in Wuerzburg (Germany) without further details | Inclusion criteria: Presence of teeth, 13 to 23 Exclusion criteria: Restoration/crown, crowding/dental malposition Periodontitis (PD > 3 mm) or recessions Drug treatment with a known effect on the periodontal soft tissues, pregnant/lactating women Smoking (>10 cigarettes/day) | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness, gingival height Papillary height PD Protocol: A single calibrated examiner (kappa not quoted) UNC-15 periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) + digital caliper Probe transparency technique |
| Singh et al. 2016 [22] | Primary: Assess the correlation between the gingival thickness, the gingival height, PP, and the papillary height. | 363 subjects, sex distribution not given (mean age not given) Max central, lateral, and canine incisors Inclusion in the Navi Mumbai Dental College (India) without further details | Inclusion criteria: Over 18 years of age Presence of maxillary anterior teeth Exclusion criteria: Low lip-brake attachment, restorations/crowns Orthodontic treatment or history of periodontal surgery Medicinal treatment with a known effect on periodontal soft tissues, self-mutilation | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness, gingival height PD, papillary filling Protocol: One single calibrated examiner (kappa not quoted) UNC-15 periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) Transparent probe technique |
| Joshi et al. 2017 [32] | Primary: Assess and compare the gingival biotype by gender. Secondary: Evaluate the relationship between the gingival thickness and the alveolar bone thickness according to gender. | 800 subjects (400 M, 400 F) 50% F, 50% M (average age 22/21 years) Max central incisors Inclusion in the Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Sciences (India), unspecified | Inclusion criteria: Presence of teeth, from 13 to 23 Exclusion criteria: Restoration/crown, cervical attrition Periodontitis (PD ≥ 4 mm) or recessions Drug treatment with known effect on periodontal soft tissues, pregnant/lactating women Systemic disease (gingival or bone manifestation) | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness (clinical and radiographic), gingival height Papillary height (photographic measurement) Crown width/length ratio (photographic measurement) Alveolar bone thickness (radiographic) Protocol: A single calibrated examiner (kappa not quoted) UNC-15 periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) Transparent probe technique |
| Lee et al. 2018 [23] | Primary: Determine the gingival biotype of the teeth and the association with age, ethnicity, gender, the type of teeth, the presence of plaque, and the recessions. Secondary: Evaluate the concordance of the gingival thickness assessment methods (probe transparency/transgingival probing). | 51 subjects (24 M, 27 F) 53% F/47 M (average age 30.3 years) Max and mandibular incisors, canines, first and second premolars, first molars Inclusion in the Singapore National Dental Centre without further details | Inclusion criteria: 21 years or older Healthy or reduced periodontium Bleeding scores ≤ 15% Exclusion criteria: Orthodontic treatment, restoration less than 1 mm from the marginal gingiva, dental crowding, dystopia/ectopia Previous periodontal surgery Uncontrolled systemic disease, allergy to iodine solution Drug treatment with a known effect on periodontal soft tissues, pregnant/lactating women | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness, gingival height Gingival recession Bleeding on probing Protocol: A single calibrated examiner (kappa not quoted) UNC-15 periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) Transparent probe technique Transgingival probing (endodontic file) Use of an iodine solution |
| Shao et al. 2018 [31] | Primary: Assess the distribution of the periodontal biotype. Secondary: Evaluate the different techniques for assessing gingival thickness (probe transparency/transgingival/CBCT). | 31 subjects (15 M, 16 F) 51% F/49% M (mean age 22.2 years) Max and mandibular incisors and canines Inclusion in the College of Stomatology at Nanjing University (China), unspecified | Inclusion criteria: Age between 18 and 30 years No gingival index ≤ 1, PD ≤ 3 mm, no loss of attachment ≥ 1 mm No radiological signs of alveolar lysis, no malocclusion, no crowding, no supernumerary teeth Presence of anterior teeth Exclusion criteria: Restoration/crown, orthodontic appliance Previous periodontal surgery Uncontrolled systemic disease Medicinal treatment with a known effect on periodontal soft tissues, pregnant or breastfeeding women Smoking, bruxism | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness, gingival height, and AG Height of papillae Crown length/width ratio PD Protocol: A single calibrated examiner (kappa not quoted) Williams periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) Probe transparency technique Transgingival probing (endodontic file) CBCT |
| Alhajj 2020 [24] | Primary: Assess the prevalence of gingival phenotypes. Secondary: Assess the correlation between age, gender, and tobacco and khat consumption. | 456 subjects (215 M, 241 F) 53% F/47% M (mean age 29.9 years) Max and mandibular central and lateral incisors and first molars Inclusion in the private clinic in the city of Sanaa (Yemen) without further details | Inclusion criteria: Good general health No dental crowding Exclusion criteria: Oral ventilation, restoration/crown Removable appliance (partial prosthesis or orthodontic) Absence of one of the six max anterior teeth Recessions (Miller class III/IV) Drug treatment with a known effect on periodontal soft tissues, pregnant/lactating women | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness, gingival height Height of papillae Crown width/length ratio Protocol: A single calibrated examiner (kappa not quoted) UNC-12 periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) Transgingival probing (endodontic file) |
| Yin et al. 2020 [33] | Primary: Correlate the periodontal biotype and the clinical parameters of the gingiva and the crown. | 56 subjects (13 M, 43 F) 77% F/23% M (average age 23.6) Max right central incisor Inclusion in the campus of the School of Stomatology at Shandong University (China) without further details | Inclusion criteria: Age between 18 and 40 years Plaque index < 1, gingival index < 1 No dental malposition or anomaly of shape Presence of all max anterior teeth Exclusion criteria: Dental restoration/cavity Drug treatment with a known effect on periodontal soft tissues Periodontitis (PD ≥ 4 mm) or recession Gingival pigmentation | Parameters recorded: - Gingival thickness, gingival height Gingival angle, width, and height of the papilla Crown length and width Bucco-lingual width of the crown Width and height of contact surface Protocol: Two calibrated examiners (kappa: 0.733) William periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) Transparent probe technique + intraoral photographs |
| Collins et al. 2021 [25] | Primary: Assess the prevalence of gingival phenotypes. Secondary: Assess the association with the other clinical and demographic variables. | 107 subjects (63 M, 44 F) 41% F/59% M (mean age 30.7 years) Max central incisors Recruitment: voluntary work in eight districts of Santo Domingo (Dominican Republic) with no further details available | Inclusion criteria: 18 years and over Good general health Presence of at least the max central incisors Exclusion criteria: Restoration/veneer, crowding > 3 mm Periodontitis and/or gum recession History of periodontal surgery Fixed or removable orthodontic appliance Attrition of more than a third of the crown Medicinal treatment with a known effect on periodontal tissues, pregnant or breast-feeding women | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness, gingival height, and AG PD Dental morphology (Gobbato classification) Protocol: A single calibrated examiner (98% agreement) UNC-15 periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) Transparent probe technique |
| Fischer et al. 2022 [26] | Primary: Screening for gingival biotype on different teeth. Secondary: Evaluate the association with gender. | 56 subjects (20 M, 36 F) 64% F/36% M (average age 23) Teeth: 16, 21, 24, 36, 41, 44 Inclusion in the University of Witten/Herdecke (Germany) without further details | Inclusion criteria: Not indicated Exclusion criteria: Restoration/crown Crowding or malposition Periodontitis (PD ≥ 3 mm) or recessions Drug treatment with a known effect on periodontal soft tissues, pregnant women Smoking (>10 cigarettes/day) | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness + gingival height PD Protocol: A single calibrated examiner (kappa not quoted) PCP12 periodontal probe (Deppeler SA®, Rolle, Switzerland) Transparent probe technique |
| Rodrigues et al. 2022 [27] | Primary: Assess the correlation between the smile type and the periodontal phenotype. | 164 subjects (48 M, 116 F) 30% M/70% F (average age 23) Maxillary central incisors (328 teeth) Inclusion in the dental school of the Federal University of Fluminense (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil), unspecified | Inclusion criteria: 18 years and over Presence of intact maxillary anterior teeth (central and lateral incisors, canines) Exclusion criteria: History of periodontal surgery in the anterior maxilla Periodontitis or recessions History of orthodontic treatment Drug treatment with a known effect on periodontal soft tissues, pregnant or breastfeeding women Systemic disease Tobacco consumption Gingival smile (greater than 3–4 mm) Symptoms of facial paralysis Cosmetic procedure on the upper lip | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness, gingival height Gingival architecture Crown length and width Width and height of contact surface Protocol: Photographs: two calibrated examiners (kappa: 0.955). Gingival phenotype: a single examiner (kappa: 0.967). Tomography: a single examiner (kappa > 0.895) UNC-15 periodontal probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) Transparent probe technique + intraoral photographs + tomographic measurements |
| Nik-Azis et al. 2023 [28] | Primary: Compare the probe visibility method with the direct caliper measurement for measuring gingival thickness. Secondary: Compare the gingival measurements in subjects with different levels of gingival pigmentation. | 171 subjects (45 M, 126 F) 26% M/74% F (average age 25) Max right central incisor (171 teeth)Recruitment of students, staff, and patients from the UKM Faculty of Dentistry (Malaysia) without further details | Inclusion criteria: 18 years and over Good general health Presence of upper central incisors Healthy periodontium Exclusion criteria: Restoration/crown on max central incisors Periodontitis or recessions Medicinal treatment with a known effect on periodontal soft tissues, pregnant or breastfeeding women Smoking | Parameters recorded: Gingival thickness Gingival pigmentation Protocol: Two calibrated examiners (kappa = 0.694 and 0.667) UNC-15 periodontal probe and colored plastic probe (Hu-Friedy®, Chicago, IL, USA) Transparent probe technique + transgingival technique (endodontic file) + direct measurement with a caliper |
| Authors Year of Publication | Prevalence | Other Results |
|---|---|---|
| Zawawi et al. 2012 [16] | Thick biotype (F and H groups): 111 teeth (55.5%) (probe not visible) Thin biotype (F and H groups): 89 teeth (44.5%) (visible probe) Thick biotype (group H): n = 75 (75%) Thick biotype (group F): n = 36 (36%) | Gums significantly thinner in women. No difference between gingival biotype and malocclusions. No difference between gingival biotype and smoking status. |
| Shetty and Bhat 2013 [17] | Thick biotype (F and H groups): 108 teeth (54.75%) probe not visible Thin biotype (F and H groups): 92 teeth (45.25%) visible probe Thick biotype (group H): n = 79 (63%) Thick biotype (group F): n = 30 (41%) | Participants with short, wide teeth: 56% have a thick gingival biotype. Participants with long, narrow teeth: 39% have a thick gingival biotype. |
| Fischer et al. 2014 [30] | Thick biotype (F and H groups): 42 teeth (53%) probe not visible Thin biotype (H and F groups): 38 teeth (47%) visible probe Thick biotype (group H): n = 20 (47%) Thick biotype (group F): n = 22 (52%) | 24 F out of 38 have a fine gingival biotype. No correlation between gingival biotype and crown width/length ratio (p > 0.05). |
| Shah et al. 2015 [18] | Thick biotype (H and F groups): 227 teeth (56.75%) greater than 1 mm Thin biotype (H and F groups): 173 teeth (43.25%) less than or equal to 1 mm | Average gingival thickness greater than 1 mm. No correlation between gingival biotype and gender (p > 0.05). |
| Peixoto et al. 2015 [19] | Thick biotype (H and F groups): 28 teeth (56%) probe not visible Intermediate biotype (H and F groups): seven teeth (14%) probe visible on a CI Thin biotype (H and F groups): 15 teeth (30%) probe visible on both ICs Thick biotype (group H): n = 14 (70%) Thick biotype (group F): n = 14 (47%) Intermediate biotype (group H): n = 3 (15%) Intermediate biotype (group F): n = 4 (13%) Thin biotype (group H): n = 3 (15%) Thin biotype (group F): n = 12 (40%) | No correlation between gingival biotype and gender. |
| Frost et al. 2015 [20] | Thick biotype (H and F groups): 254 teeth (83%) probe not visible Thin biotype (H and F groups): 52 teeth (17%) visible probe Thin premolar biotype: seven teeth/62 (11%) Thin canine biotype: 20 teeth/83 (24%) Thin lateral incisor biotype: 20 teeth/86 (23%) Thin central incisor biotype: five teeth/75 (7%) | Mean gingival thickness significantly smaller for the thin biotype (p < 0.001). |
| Fischer et al. 2015 [21] | Thick biotype (H and F groups): 18 teeth probe not visible Thin biotype (H and F groups): 18 visible probe teeth Thin biotype (group H): n = 7 (39%) Thin Biotype (group F): n = 11 (61%) Thick biotype (group H): n = 10 (56%) Thick biotype (group F): n = 8 (44%) | Significant difference between groups in terms of gingival thickness (p < 0.0001), keratinized tissue height (p = 0.0371), and papillary height (p = 0.0247). |
| Singh et al. 2016 [22] | Thick biotype (H and F groups): 819 teeth (37.6%) probe not visible Thin biotype (H and F groups): 1359 teeth (62.4%) visible probe | Positive correlation between gingival thickness and height of keratinized tissue. |
| Joshi et al. 2017 [32] | Thick biotype (H and F groups): 367 teeth probe not visible Thin biotype (H and F groups): 433 teeth visible probe Thin biotype (group H): n = 97 (24.2%) Thin biotype (group F): n = 336 (84%) Thick biotype (group H): n = 303 (75.8%) Thick biotype (group F): n = 64 (16%) | Significant positive correlation between gingival thickness and bone thickness in men and women (p < 0.01). |
| Lee et al. 2018 [23] | Thick maxillary biotype: 134 teeth (36.2%) greater than or equal to 1.5 mm Thin maxillary biotype: 236 teeth (63.8%) smaller than 1.5 mm Thin mandibular biotype: 355 teeth (92.4%) Thick mandibular biotype: 29 teeth (7.6%) | Out of 51 patients: 90% of probes visible on maxillary central incisors, 85% on maxillary lateral incisors, 84% on maxillary first premolars, 75% on mandibular central incisors, 85% on mandibular lateral incisors. No significant differences for gender, age, ethnicity, or type of periodontium. Significant difference in gingival thickness between posterior and anterior teeth. Significant difference in HTK between maxillary anterior and posterior teeth. HTK significantly higher for mandibular incisors. |
| Shao et al. 2018 [31] | Thick biotype: 222/372 teeth (59.68%) probe transparency Thick biotype: 266/372 teeth (71.51%) endodontic file Thick biotype: 303/372 teeth (81.45%) CBCT Thin biotype: 150/372 teeth (40.32%) probe transparency Thin biotype: 106/372 teeth (28.49%) endodontic file Thin biotype: 69/372 teeth (18.55%) CBCT | Kappa value for transgingival technique: 0.24. No consistency between probe transparency technique and CBCT. |
| Alhaij 2020 [24] | Thick biotype: 69 teeth (15.1%) thicker than 2 mm Thin biotype: 83 teeth (18.2%) less than 1.5 mm thick Uncategorized biotype: 304 teeth (66.7%) between 1.5 and 2 mm thick | HTK lower in men than in women (p = 0.006). Correlation between thin gums and HTK between 4.1 and 8 mm. The rectangular shape of the teeth is preferably associated with thin gums. |
| Yin et al. 2020 [33] | Thick biotype (H and F groups): 39 teeth (69.6%) probe not visible Thin biotype (H and F groups): 17 teeth (30.4%) visible probe Thick biotype (group H): n = 12 (92.3%) Thick biotype (group F): n = 27 (62.7%) | Significant differences in gingival biotypes between H and F (p < 0.2). Significant differences in periodontal biotypes between H and F (p = 0.043). |
| Collins et al. 2021 [25] | Thick biotype (H and F groups): 43 teeth (40.2%) probe not visible Thin biotype (H and F groups): 64 teeth (59.8%) visible probe Thick biotype (group H): n = 24 (37.5%) Thick biotype (group F): n = 19 (44.2%) | No significant difference in the gingival biotype according to gender and age. Significantly finer biotype in individuals with square teeth. HTK significantly greater in patients with thin gums (p = 0.011). |
| Fischer et al. 2022 [26] | Thick maxillary biotype: 59% of teeth probe not visible Thin maxillary biotype: 41% of teeth probe visible Thick mandibular biotype: 49.4% of teeth probe not visible Thin mandibular biotype: 50.6% of teeth probe visible Thick molar biotype: 94.6% of teeth probe not visible Thin molar biotype: 5.4% of teeth probe visible Thick incisor biotype: 29.5% of teeth probe not visible Thin incisor biotype: 70.5% of teeth probe visible | Statistically significant distribution between gingival phenotypes in the maxilla and mandible (p = 0.001). Thicker gingivae for molars than for other teeth (p = 0.006). No correlation between gingival biotype and gender (p = 0.722). |
| Rodrigues et al. 2022 [27] | Thick biotype (H and F groups): 170 teeth (51.8%) probe not visible Thin biotype (H and F groups): 158 teeth (48.2%) visible probe | Significant association between the gingival smile (high, medium, low) and gingival phenotype assessed by transparency of the periodontal probe (p = 0.021). |
| Nik-Azis et al. 2023 [28] | Thick biotype (H and F groups): 138 teeth (80.7%) probe not visible Thin biotype (H and F groups): 33 teeth (19.3%) visible probe Thick biotype (H and F groups): 143 teeth (83.6%) endo file (>1 mm) Thin biotype (H and F groups): 28 teeth (16.4%) endo file (≤1 mm) Thin biotype (H and F groups): 17 teeth (51.1%) with visible white tips Medium biotype (H and F groups): 13 teeth (39.4%) with visible green tip Thick biotype (H and F groups): 3 teeth (9.1%) visible blue tip Very thick biotype (H and F groups): 0 teeth (0%) no visible tips | Significant correlation between gingival measurements with the caliper and the transgingival method (p = 0.003). Subjects with a high level of gingival pigmentation were more likely to have thickened gums. |
| Authors Country | Number of Subjects (F, M), Number of Teeth | Number and Percentage of Teeth with a Thick Gingiva (F, M) |
|---|---|---|
| Maxillary arch | ||
| Periodontal probe transparency test | ||
| Singh et al., 2016 India [22] | n = 363, 2178 teeth | 819 teeth, 37.6% (ND) |
| Joshi et al., 2017 India [32] | n = 800 (400 F, 400 M), 800 teeth | 367 teeth, 45.9% (17.5%, 82.5%) |
| Collins et al., 2021 Dominican Republic [25] | n = 107 (44 F, 83 M), 107 teeth | 43 teeth, 40.2% (44%, 56%) |
| Fischer et al., 2015 Germany [21] | n = 36 (19 F, 17 M), 36 teeth | 18 teeth, 50% (44.4%, 55.6%) |
| Zawawi et al., 2012 Saudi Arabia [16] | n = 200 (100 F, 100 M), 200 teeth | 111 teeth, 55.5% (32.4%, 67.6%) |
| Shetty and Bhat, 2013 India [17] | n = 200 (75 F, 125 M), 200 teeth | 108 teeth, 54% (27.8%, 73.2%) |
| Fischer et al., 2014 Germany [30] | n = 80 (46 F, 34 M), 80 teeth | 42 teeth, 52.5% (52.4%, 47.6%) |
| Yin et al., 2020 China [33] | n = 56 (43 F, 13 M), 56 teeth | 39 teeth, 69.6% (69.2%, 30.8%) |
| Peixoto et al., 2015 Portugal [19] | n = 50 (30 F, 20 M), 50 teeth | 28 teeth, 56% (50%, 50%) |
| Fischer et al., 2022 Germany [26] | n = 56 (36 F, 20 M), 168 teeth | 99 teeth, 58.9% (ND) |
| Frost et al., 2015USA [20] | n = 56 (33 F, 33 M), 306 teeth | 254 teeth, 83%’ND) |
| Rodrigues et al., 2022 Brazil [27] | n = 164 (116 F, 48 M), 328 teeth | 170 teeth, 51.8% (ND) |
| Nik-Azis et al., 2023 Malaysia [28] | n = 171 (126 F, 45 M), 171 teeth | 138 teeth, 80.7% (ND) |
| Transgingival probing | ||
| Lee et al., 2018 Singapore [23] | n = 51 (27 F, 24 M), 548 teeth | 256 teeth, 46.7% (ND) |
| Shah et al., 2015 India [18] | n = 400 (200 F, 200 M), 1200 teeth | 681 teeth, 56.7% (ND) |
| Mandibular arch | ||
| Periodontal probe transparency test | ||
| Fischer et al., 2022 Germany [26] | n = 56 (36 F, 20 M), 168 teeth | 83 teeth, 49.4%(ND) |
| Authors, Countries | Percentage of CI with a TG/All the CI | Percentage of IL with a TG/All the IL | Percentage of C with a TG/All the C | Percentage of PM with a TG/All the PM | Percentage of 1st M with a TG/All the 1st M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxillary arch | |||||
| Periodontal probe transparency test | |||||
| Joshi et al., 2017, India [32] | 45.8% | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Lee et al., 2018, Singapore [23] | 10% | 15% | 15% | 20% | 83% |
| Fischer et al., 2022, Germany [26] | 38.9% | ND | ND | 48.3% | 94.6% |
| Collins et al., 2021, Dominican Republic [25] | 40.2% | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Fischer et al., 2015, Germany [21] | 50% | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Zawawi et al., 2012, Saudi Arabia [16] | 55.5% | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Shetty and Bhat, 2013, India [17] | 54.7% | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Fischer et al., 2014, Germany [30] | 53% | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Peixoto et al., 2015, Portugal [19] | 56% | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Yin et al., 2020, China [33] | 69.6% | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Rodrigues et al., 2022, Brazil [27] | 51.8% | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Nik-Azis et al., 2023, Malaysia [28] | 80.7% | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Transgingival probing | |||||
| Lee et al., 2018, Singapore [23] | 56.2% | 31.2% | 21.2% | 45.9% | 86% |
| Mandibular arch | |||||
| Periodontal probe transparency test | |||||
| Fischer et al., 2022, Germany [26] | 23.2% | ND | ND | 32.5% | 94.6% |
| Transgingival probing | |||||
| Lee et al., 2018, Singapore [23] | 7% | 5% | 5% | 22% | 96.4% |
| Authors | Q 1 | Q 2 | Q 3 | Q 4 | Q 5 | Scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zawawi et al. 2012 [16] | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | 60% |
| Shetty and Bhat 2013 [17] | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO | 0% |
| Fischer et al. 2014 [30] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Shah et al. 2015 [18] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Peixoto et al. 2015 [19] | NO | NO | NO | NO | YES | 20% |
| Frost et al. 2015 [20] | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Fischer et al. 2015 [21] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Singh et al. 2016 [22] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Lee et al. 2018 [23] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Joshi et al. 2017 [32] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Shao et al. 2018 [31] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Alhajj 2020 [24] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Yin et al. 2020 [33] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Collins et al. 2021 [25] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Fischer et al. 2022 [26] | NO | NO | NO | NO | YES | 20% |
| Rodrigues et al. 2022 [27] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
| Nik-Azis et al.2023 [28] | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | 40% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dridi, S.-M.; Ameline, C.; Heurtebise, J.M.; Vincent-Bugnas, S.; Charavet, C. Prevalence of the Gingival Phenotype in Adults and Associated Risk Factors: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 801-833. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14030064
Dridi S-M, Ameline C, Heurtebise JM, Vincent-Bugnas S, Charavet C. Prevalence of the Gingival Phenotype in Adults and Associated Risk Factors: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clinics and Practice. 2024; 14(3):801-833. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14030064
Chicago/Turabian StyleDridi, Sophie-Myriam, Clément Ameline, Jean Michel Heurtebise, Séverine Vincent-Bugnas, and Carole Charavet. 2024. "Prevalence of the Gingival Phenotype in Adults and Associated Risk Factors: A Systematic Review of the Literature" Clinics and Practice 14, no. 3: 801-833. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14030064
APA StyleDridi, S.-M., Ameline, C., Heurtebise, J. M., Vincent-Bugnas, S., & Charavet, C. (2024). Prevalence of the Gingival Phenotype in Adults and Associated Risk Factors: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clinics and Practice, 14(3), 801-833. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14030064






