Use of Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Strategies by Community-Dwelling Adults to Manage Migraine: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Search Procedure
2.3. Primary Variables of Interest
2.4. Screening Procedure
2.5. Data Extraction Tool
2.6. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
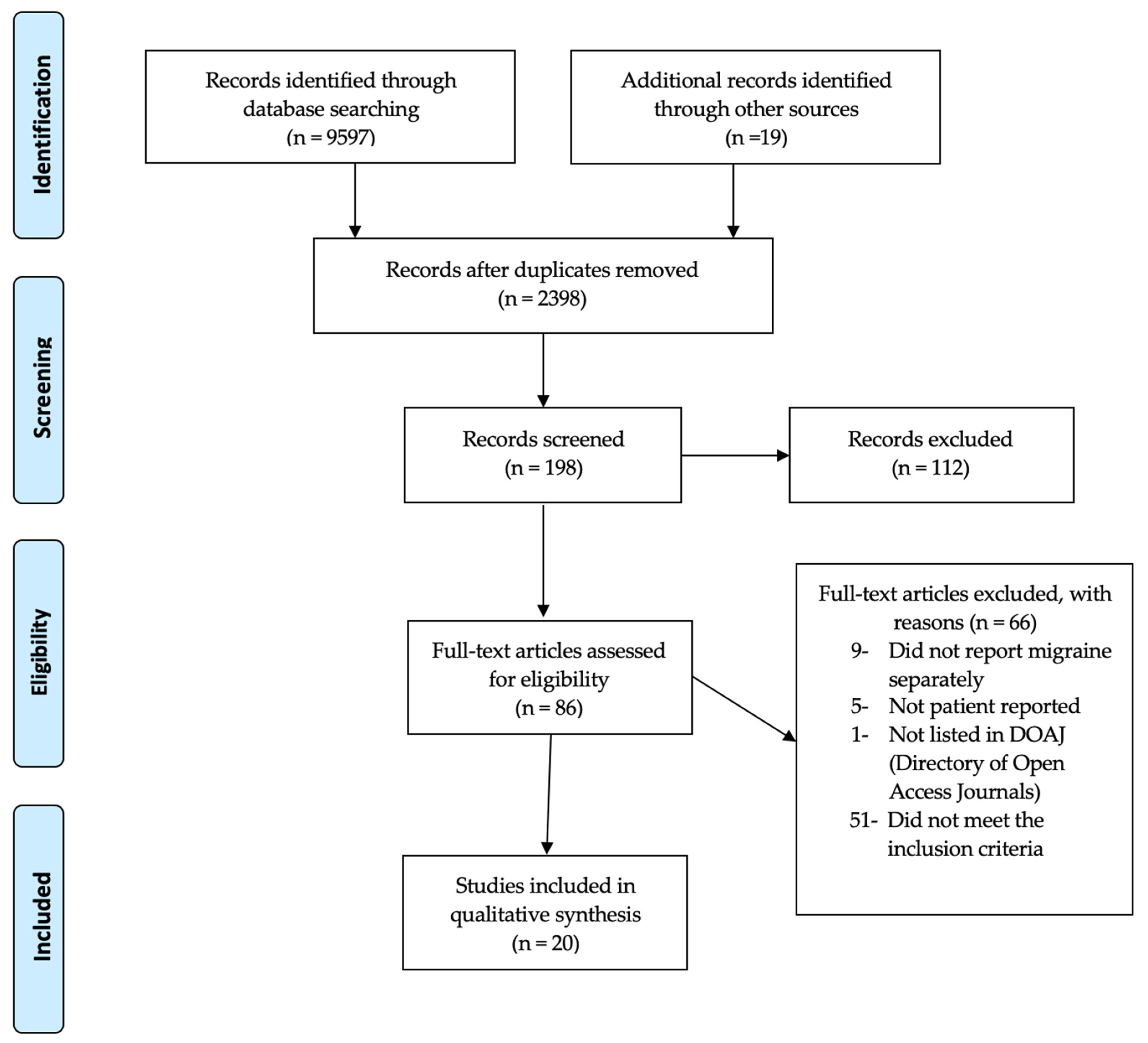
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Types of Pharmacological Strategies Reported
3.4. Types of Non-Pharmacological Strategies Reported
3.5. Satisfaction with Management and Outcomes
3.6. Risk of Bias in Included Studies
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Key Findings
4.2. Comparison to Clinical Guidelines
4.3. Implications for Patient Management
4.4. Implications for Research
4.5. Implications Due to COVID-19
4.6. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Chronic Pain. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/series/chronic-pain (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Lipton, R.B.; Bigal, M.E. Migraine: Epidemiology, impact, and risk factors for progression. Headache 2005, 45, S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 629–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, K. What is migraine? JAMA 2022, 327, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burch, R.C.; Buse, D.C.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine epidemiology, burden, and comorbidity. Neurol. Clin. 2019, 37, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Manack, A.N.; Fanning, K.M.; Serrano, D.; Reed, M.L.; Turkel, C.C.; Lipton, R.B. Chronic migraine prevalence, disability, and sociodemographic factors: Results from the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention Study. Headache 2012, 52, 1456–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stovner, L.J.; Nichols, E.; Steiner, T.J.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Al-Raddadi, R.M.; Ansha, M.G.; Barac, A.; Bensenor, I.M.; Doan, L.P.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 954–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, E.; Banfi, R.; Vaiani, M.; Panconesi, A. Patterns of triptans use: A study based on the records of a community pharmaceutical department. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A 10-Year Report Card Shows Migraine Remains Underdiagnosed and Undertreated. Available online: https://headaches.org/ (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Begasse de Dhaem, O.; Burch, R.; Rosen, N.; Shubin Stein, K.; Loder, E.; Shapiro, R.E. Workforce gap analysis in the field of headache medicine in the United States. Headache 2020, 60, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penzien, D.B.; Irby, M.B.; Smitherman, T.A.; Rains, J.C.; Houle, T.T. Well-established and empirically supported behavioral treatments for migraine. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2015, 19, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Migraine Study I. Available online: https://headaches.org/ (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Axon, D.R.; Patel, M.J.; Martin, J.R.; Slack, M.K. Use of multidomain management strategies by community dwelling adults with chronic pain: Evidence from a systematic review. Scand J. Pain 2019, 19, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelman, J.U.; von Seggern, R.L.; Mannix, L.K. Migraine headaches: Implications for management from a nationwide patient survey. Headache Q. Curr. Treat. Res. 2000, 11, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Brusa, P.; Allais, G.; Bussone, G.; Rolando, S.; Giaccone, M.; Aguggia, M.; Benedetto, C. Migraine attacks in the pharmacy: A survey in Piedmont, Italy. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 35, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusa, P.; Allais, G.; Scarinzi, C.; Baratta, F.; Parente, M.; Rolando, S.; Gnavi, R.; Spadea, T.; Costa, G.; Benedetto, C.; et al. Self-Medication for Migraine: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Italy. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.Y.; Yang, C.C.; Jensen, M.P.; Lai, Y.H. The frequency and perceived effectiveness of pain self-management strategies used by individuals with migraine. J. Nurs. Res. 2021, 29, e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, L.J.; Becker, W.J. Migraine prevalence, treatment and impact: The Canadian women and migraine study. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 37, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnet, A.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; Aucoin, F.; Allaf, B. Use and overuse of antimigraine drugs by pharmacy personnel in France: COTA Survey. Headache 2009, 49, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnet, A.; Becker, H.; Allaf, B.; Lantéri-Minet, M. Migraine and migraines of specialists: Perceptions and management. Headache 2010, 50, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducros, A.; Romatet, S.; Saint Marc, T.; Allaf, B. Use of antimigraine treatments by general practitioners. Headache 2011, 51, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmeads, J.; Findlay, H.; Tugwell, P.; Pryse-Phillips, W.; Nelson, R.F.; Murray, T.J. Impact of migraine and tension-type headache on life-style, consulting behaviour, and medication use: A Canadian population survey. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1993, 20, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertem, D.H. The association between chronicity of migraine and complementary and alternative medication use: The Turkish perspective. Eur. Neurol. 2019, 81, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, K.; Ueda, K.; Komori, M.; Zagar, A.J.; Selzler, K.J.; Nelson, A.M.; Han, Y.; Jaffe, D.H.; Matsumori, Y.; Takeshima, T. Comprehensive population-based survey of migraine in Japan: Results of the ObserVational Survey of the Epidemiology, tReatment, and Care of MigrainE (OVERCOME [Japan]) study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2021, 37, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Al-Hashel, J. Use of traditional medicine in treatment of migraine during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic-an online survey. J. Neurolo. Sci. 2021, 429, 119337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinski, S.E.; Becker, W.J.; Christie, S.N.; Giammarco, R.; Mackie, G.F.; Gawel, M.J.; Eloff, A.G.; Magnusson, J.E. Clinical features and pharmacological treatment of migraine patients referred to headache specialists in Canada. Cephalalgia 2006, 26, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landy, S.H.; Runken, M.C.; Bell, C.F.; Higbie, R.L.; Haskins, L.S. Examining the interrelationship of migraine onset, duration, and time to treatment. Headache 2012, 52, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebedeva, E.R.; Kobzeva, N.R.; Gilev, D.V.; Olesen, J. The quality of diagnosis and management of migraine and tension-type headache in three social groups in Russia. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Munjal, S.; Alam, A.; Buse, D.C.; Fanning, K.M.; Reed, M.L.; Schwedt, T.J.; Dodick, D.W. Migraine in America Symptoms and Treatment (MAST) study: Baseline study methods, treatment patterns, and gender differences. Headache 2018, 58, 1408–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, C.; Géraud, G.; Valade, D.; Chautard, M.; Lantéri-Minet, M. Recognition and therapeutic management of migraine in 2004, in France: Results of FRAMIG 3, a French nationwide population-based survey. Headache 2006, 46, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Abu-Saad, H.H.; Robbins, I.; Vydelingum, V.; Dowson, A.; Murphy, M. Patients’ management of migraine and chronic daily headache: A study of the members of the migraine action association (United Kingdom). Headache 2005, 45, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viticchi, G.; Falsetti, L.; Bartolini, M.; Buratti, L.; Ulissi, A.; Baldassarri, M.; Provinciali, L.; Silvestrini, M. Migraine: Incorrect self-management for a disabling disease. Neurol. Int. 2018, 10, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuković, V.; Plavec, D.; Huzjan, A.L.; Budišić, M.; Demarin, V. Treatment of migraine and tension-type headache in Croatia. J. Headache Pain 2010, 11, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, A.K.; Shah, N.; Poon, J.L.; Shaffer, S.; Sapra, S.; Wilcox, T.K.; Shah, S.; Tepper, S.J.; Dodick, D.W.; Lipton, R.B. Understanding the migraine treatment landscape prior to the introduction of calcitonin gene-related peptide inhibitors: Results from the Assessment of TolerabiliTy and effectiveness in migrAINe patients using preventive treatment (ATTAIN) study. Headache 2021, 61, 438–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonaci, F.; Ghiotto, N.; Wu, S.; Pucci, E.; Costa, A. Recent advances in migraine therapy. Springerplus 2016, 5, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.E.; Bertisch, S.M.; Buettner, C.; Phillips, R.S.; McCarthy, E.P. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults with migraines/severe headaches. Headache 2011, 51, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailani, J.; Burch, R.C.; Robbins, M.S. The American Headache Society Consensus Statement: Update on integrating new migraine treatments into clinical practice. Headache 2021, 61, 1021–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, R.A.; Buse, D.C.; Andrasik, F.; Lipton, R.B. Nonpharmacologic treatments for migraine and tension-type headache: How to choose and when to use. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2011, 13, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.K.; Penzien, D.B.; Wall, E.M. Evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache: Behavioral and physical treatments. US Headache Consort. 2000, 1, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lay, C.L.; Broner, S.W. Migraine in women. Neurol. Clin. 2009, 27, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafata, J.E.; Tunceli, O.; Cerghet, M.; Sharma, K.P.; Lipton, R.B. The use of migraine preventive medications among patients with and without migraine headaches. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccone, M.; Baratta, F.; Allais, G.; Brusa, P. Prevention, education and information: The role of the community pharmacist in the management of headaches. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 35, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehuys, E.; Paemeleire, K.; van Hees, T.; Christiaens, T.; van Bortel, L.M.; van Tongelen, I.; de Bolle, L.; Remon, J.P.; Boussery, K. Self-medication of regular headache: A community pharmacy-based survey. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietary Supplements: Report Adverse Events to FDA. What Is an Adverse Event? Available online: www.safetyreporting.hhs.gov (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Benotsch, E.G.; Koester, S.; Martin, A.M.; Cejka, A.; Luckman, D.; Jeffers, A.J. Intentional misuse of over-the-counter medications, mental health, and polysubstance use in young adults. J. Community Health 2014, 39, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straburzyński, M.; Kuca-Warnawin, E.; Waliszewska-Prosół, M. COVID-19-related headache and innate immune response—A narrative review. Neurol. Neurochi. Pol. 2023, 57, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waliszewska-Prosół, M.; Budrewicz, S. The unusual course of a migraine attack during COVID-19 infection—Case studies of three patients. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 903–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, M.; Waliszewska-Prosół, M.; Koutsokera, M.; Robotti, M.; Straburzyński, M.; Apostolakopoulou, L.; Capizzi, M.; Çibuku, O.; Ambat, F.D.F.; Frattale, I.; et al. Headache onset after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J. Headache Pain 2022, 23, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chodosh, J.; Morton, S.C.; Mojica, W.; Maglione, M.; Suttorp, M.J.; Hilton, L.; Rhodes, S.; Shekelle, P. Meta-analysis: Chronic disease self-management programs for older adults. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 143, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, M.E. Dis-integration of communication in healthcare education: Workplace learning challenges and opportunities. Patient Educ. Couns. 2017, 100, 2054–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author, Year | Country | Purpose | Total N | Female % | Mean (SD) Age | Source Population | Survey Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adelman, 2000 [14] | USA | Experiences and current treatment practices | 801 | N/A | N/A | General population with severe headache | Tel |
| Brusa, 2014 [15] | Italy | Recommendations by pharmacist to manage patient’s migraine and common analgesics medications used | 1042 | 82 | 44.1 (13.5) | Pharmacy customers with headache | SAQ |
| Brusa, 2019 [16] | Italy | Distribution of migraine headaches and overuse of medicines among people seeking medication in pharmacies | 4424 | 45 | 45.1 | Pharmacy customers seeking headache medications | PQ |
| Chang, 2021 [17] | Taiwan | Effectiveness of pain management strategies; relationship between number of strategies and effectiveness | 174 | N/A | 38.5 (11.8) | Adults age 20–65 | FFI |
| Cooke, 2010 [18] | Canada | Prevalence of migraine in Canadian women and treatment practices and psychological burden | 300 | 100 | N/A | Adults age > 18 | Tel |
| Donnet, 2009 [19] | France | Migraine management among pharmacy personnel who were migraineurs | 2094 | 90 | N/A | Pharmacy personnel | SAQ |
| Donnet, 2010 [20] | France | Perceptions of migraine among neurologists and treatments used for their own migraines | 179 | 37 | 47.7 (9.8) | Community neurologists | SAQ |
| Ducros, 2011 [21] | France | Headache treatment patterns in general practitioners who suffered from migraine themselves | 277 | 23 | 50.1 (7.1) | General practitioners | SAQ |
| Edmeads, 1993 [22] | Canada | Prevalence and effects of migraine on lifestyles, consulting behavior and medication use | 138 | N/A | N/A | Adults age > 15 | Tel |
| Ertem, 2019 [23] | Turkey | Association between complementary and alternative usage and chronicity of migraine | 100 | 82 | 42.8 (11.4) | Adults age > 18 | PQ |
| Hirata, 2021 [24] | Japan | Provide up-to-date assessment of migraine epidemiology in Japan | 17,071 | 66.5 | 40.7 (13.0) | Adults age > 18 | OS |
| Ismail, 2021 [25] | Kuwait | Assess traditional medicine in migraine treatment during COVID-19 | 1018 | 86.9 | 34 (9.5) | Headache clinic patients | OS |
| Jelinski, 2006 [26] | Canada | Clinical features and pharmacological treatment of migraine patients | 606 | 83 | 39.7 (12.9) | Headache outpatient database | RD |
| Landy, 2012 [27] | USA | Interrelationship of migraine onset, duration and time to treatment | 509 | 75 | 41.0 (10.0) | Chronic illness panel | SAQ |
| Lebedeva, 2017 [28] | Russia | Evidence-based diagnosis and treatment of headache disorders | 484 | 43 | 31.7 | Adults age 18–65 | FFI |
| Lipton, 2018 [29] | USA | Assess gender difference in sociodemographic and headache features, consultation and diagnosis patterns, and treatment patterns | 15,133 | 73 | 43.1 (13.6) | Adults age > 18 | OS |
| Lucas, 2006 [30] | France | Proportion of migraineurs who are self-aware of their disease | 1652 | 68 | 41.2 (14.5) | Adults age > 18 | SAQ |
| Peters, 2005 [31] | UK | Headache management over the last 12 months | 356 | 90 | 49.1 (9.3) | Adults age 18–65 | SAQ |
| Viticchi, 2018 [32] | Italy | Disease awareness, general approach, and impact on working activity | 294 | 80 | 42.1 (10.6) | Adults age > 18 | SAQ |
| Vukovic, 2010 [33] | Croatia | Treatment patterns of migraine | 289 | 70 | 41.0 (14.0) | Adults age > 18 | SAQ |
| Study | Trip | Ergo | Opioid | NSAID | Para | Asp | Analg | An-caf | Sed | Ste | A/nau | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Adelman [14] | 4 | 37 | 21 | |||||||||
| Brusa [15] | 43 | 10 | 45 | OTC: 0.6 | ||||||||
| Brusa [16] | 57 | 51 | 48 | 39 | ||||||||
| Chang [17] | 13 | 21 | 13 | 5 | ||||||||
| Cooke [18] | 8 | 1 | 23 | OTC: 38 | ||||||||
| Donnet [19] | 32 | 11 | 37 | 10 | 7 | |||||||
| Donnet [20] | 50 | 3 | 4 | 57 | 27 | 32 | 2 | |||||
| Ducros [21] | 73 | 9 | 85 | 16 | 4 | |||||||
| Edmeads [22] | OTC: 91 Rx: 41 | |||||||||||
| Hirata [24] | 20 | OTC: 80 | ||||||||||
| Jelinski [26] | 49 | 3 | 1 | 59 | 24 | 0.5 | 8 | |||||
| Landy [27] | 59 | 41 | ||||||||||
| Lebedeva [28] | 6 | 2 | 44 | 45 | ||||||||
| Lipton [29] | 17 | 1 | 11 | 69 | 36 | 13 | 31 | 4 | ||||
| Lucas [30] | 23 | 7 | 49 | 15 | ||||||||
| Peters [31] | 58 | 8 | 3 | |||||||||
| Viticchi [32] | 9 | 0.3 | 17 | 4 | 6 | |||||||
| Vukovic [33] | 36 | 22 | ||||||||||
| Range | 9–73 | 0.3–51 | 1–37 | 13–85 | 4–49 | 7–32 | 6–45 | 5–31 | 4 | 0.5 | 8 | OTC: 0.6–91 |
| Medical | Physical | Psychological | Self-Initiated | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cons. Med | Mas | Acu | Col | Hot | Exe | Rel | Yog | Rest | Psy | No | Her | H/N | Diet | DS | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Adelman [14] | GP:56 | 11 | |||||||||||||
| Brusa [15] | GP:40, SP:22 | 0.2 | 2 | 0.6 | |||||||||||
| Chang [17] | 11 | 7 | 6 | 11 | |||||||||||
| Cooke [18] | GP:62, SP:50 | 2 | 1 | 10 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Donnet [19] | GP:38 | ||||||||||||||
| Edmeads [22] | ED:14 | ||||||||||||||
| Ertem [23] | 48 | 28 | 12 | 14 | 24 | 60 | |||||||||
| Ismail [25] | 52 | 0.2 | 23 | 8 | 13 | 17 | 0.4 | 15 | 46 | 20 | 22 | ||||
| Lebedeva [28] | GP:40, SP:60 | 3 | 44 | ||||||||||||
| Lucas [30] | GP/SP:60 | ||||||||||||||
| Peters [31] | GP:79 | 47 | 46 | 36 | 68 | 31 | 19 | ||||||||
| Viticchi [32] | GP/SP:51 | ||||||||||||||
| Vukovic [33] | GP:64 | 9 | 4 | 7 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Ranges | 14–79 | 2–52 | 0.2–28 | 23–46 | 8–36 | 12–13 | 4–68 | 0.4–7 | 3–15 | 14 | 10–44 | 0.2–46 | 1–31 | 20 | 0.6–60 |
| Study | Purpose | Survey Reliability and Validity | Data Collection Method | Sample Size | Categories Used to Identify Strategies | Conflict of Interest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adelman [14] | High | Unclear | Unclear | Low | High | High |
| Brusa [15] | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | High | Unclear |
| Brusa [16] | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Chang [17] | Low | Low | low | Low | Low | Low |
| Cooke [18] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| Donnet [19] | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | High | High |
| Donnet [20] | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | High |
| Ducros [21] | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | High | High |
| Edmeads [22] | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Unclear | High |
| Ertem [23] | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Hirata [24] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Ismail [25] | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Moderate | Low |
| Jelinski [26] | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | High |
| Landy [27] | High | Unclear | Low | Low | High | High |
| Lebedeva [28] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Lipton [29] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Lucas [30] | High | Low | Low | Low | Unclear | High |
| Peters [31] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| Viticchi [32] | Unclear | Unclear | Low | Low | High | Low |
| Vukovic [33] | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Unclear |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marupuru, S.; Almatruk, Z.; Slack, M.K.; Axon, D.R. Use of Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Strategies by Community-Dwelling Adults to Manage Migraine: A Systematic Review. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, 553-568. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract13030051
Marupuru S, Almatruk Z, Slack MK, Axon DR. Use of Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Strategies by Community-Dwelling Adults to Manage Migraine: A Systematic Review. Clinics and Practice. 2023; 13(3):553-568. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract13030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarupuru, Srujitha, Ziyad Almatruk, Marion K. Slack, and David R. Axon. 2023. "Use of Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Strategies by Community-Dwelling Adults to Manage Migraine: A Systematic Review" Clinics and Practice 13, no. 3: 553-568. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract13030051
APA StyleMarupuru, S., Almatruk, Z., Slack, M. K., & Axon, D. R. (2023). Use of Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Strategies by Community-Dwelling Adults to Manage Migraine: A Systematic Review. Clinics and Practice, 13(3), 553-568. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract13030051







