Illness Perception and Medication Adherence among Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
Importance of the Review
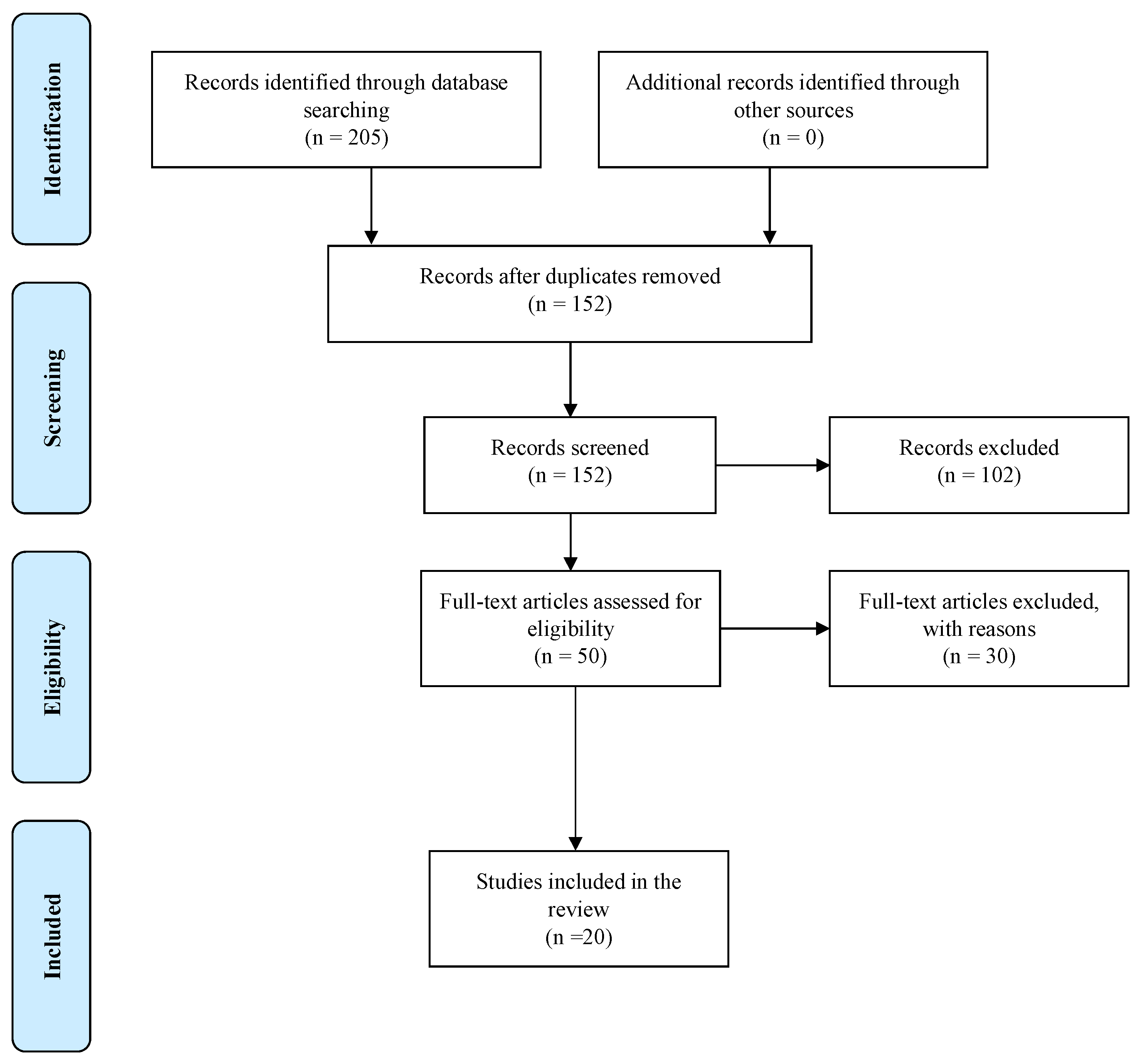
2. Methods
2.1. Research Question
2.2. Search Strategy
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
- Records that focused on illness perceptions and medication adherence in adults with T2DM;
- Studies with adult patients aged at least 18 years;
- Full-text papers;
- Journal articles published within the last 5 years, between 2016 and 2021;
- Studies published in the English language;
- Primary sources with qualitative or quantitative research designs.
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Studies with pregnant participants;
- Studies with participants under treatment for psychiatric disease;
- Studies written in languages other than English;
- Secondary sources, opinion editions, government periodicals, case reports, or lab reports.
2.3. Study Selection Process
2.4. Data Extraction
3. Findings/Results
3.1. Description of the Studies
3.2. Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Themes from the Chosen Studies
4.2. Theme 1: Illness Perception towards T2DM
4.3. Theme 2: Medication Adherence towards T2DM
4.4. Theme 3: Association between Illness Perceptions and Medication Adherence
5. Limitation
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Diabetes [Internet]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Aschner, P.; Muñoz, O.M.; Giron, D.; Garcia, O.M.; Fernández-Ávila, D.; Casas, L.A.; Bohórquez, L.F.; Arango, T.C.M.; Carvajal, L.; Ramirez, D.; et al. Clinical practice guideline for the prevention, early detection, diagnosis, management and follow up of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults. Colomb. Medica 2016, 47, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes–Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Slamah, T.; Nicholl, B.I.; Alslail, F.Y.; Harris, L.; Kinnear, D.; Melville, C.A. Correlates of type 2 diabetes and glycaemic control in adults in Saudi Arabia a secondary data analysis of the Saudi health interview survey. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, A.; Perry, L.; Gholizadeh, L.; Al-Ganmi, A. Incidence and prevalence rates of diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia: An overview. J. Epidemiology Glob. Health 2017, 7, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qiu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, E.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Cao, D. Relationship between Illness Perception and Depressive Symptoms among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in China: A Mediating Role of Coping Style. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 3142495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloudah, N.M.; Scott, N.W.; Aljadhey, H.S.; Araujo-Soares, V.; Alrubeaan, K.A.; Watson, M.C. Medication adherence among patients with Type 2 diabetes: A mixed methods study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiyanbola, O.O.; Unni, E.; Huang, Y.-M.; Lanier, C. The association of health literacy with illness perceptions, medication beliefs, and medication adherence among individuals with type 2 diabetes. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2018, 14, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Shin, S.-J.; Wang, R.-H.; Lin, K.-D.; Lee, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-H. Pathways of empowerment perceptions, health literacy, self-efficacy, and self-care behaviors to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Patient Educ. Couns. 2016, 99, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugbey, N.; Asante, K.O.; Adulai, K. Illness perception, diabetes knowledge and self-care practices among type-2 diabetes patients: A cross-sectional study. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilondi, S.S.; Noghabi, A.D.; Aalami, H. The relationship between illness perception and medication adherence in patients with diabetes mellitus type II: Illness perception and medication adherence. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2021, 62, E966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koponen, A.M.; Simonsen, N.; Suominen, S. Determinants of physical activity among patients with type 2 diabetes: The role of perceived autonomy support, autonomous motivation and self-care competence. Psychol. Health Med. 2017, 22, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Urata, K.; Yoshida, A.; Horiuchi, R.; Yamaaki, N.; Yagi, K.; Arai, K. The relationship between patients’ perception of type 2 diabetes and medication adherence: A cross-sectional study in Japan. J. Pharm. Health Care Sci. 2019, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albargawi, M.; Snethen, J.; Gannass, A.A.; Kelber, S. Perception of persons with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2016, 3, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, R.; Assaf, J.; Jabbour, H.; Licha, H.; Hajj, A.; Hallit, S.; Khabbaz, L.R. Adherence to oral glucose lowering drugs, quality of life, treatment satisfaction and illness perception: A cross-sectional study in patients with type 2 diabetes. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatawi, Y.M.; Kavookjian, J.; Ekong, G.; Alrayees, M.M. The association between health beliefs and medication adherence among patients with type 2 diabetes. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2016, 12, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, K.; Wu, H.; Wu, J. Insulin adherence and persistence among Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective database analysis. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2017, 11, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannoo, Z.; Khan, N.M. Medication Adherence and Diabetes Self-Care Activities Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Value Health Reg. Issues 2019, 18, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.; Ali, A.M.; Bakry, M.M.; Mustafa, N. Impact of a pharmacist led diabetes mellitus intervention on HbA1c, medication adherence and quality of life: A randomised controlled study. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.S.; Islam, T.; Uddin, R.; Tansi, T.; Talukder, S.; Sarker, F.; Al Mamun, K.A.; Adibi, S.; Rawal, L.B. Factors associated with low medication adherence in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus attending a tertiary hospital in Bangladesh. Lifestyle Med. 2021, 2, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Tan, J.H.M.; Sankari, U.; Koh, Y.L.E.; Tan, N.C. Assessing oral medication adherence among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with polytherapy in a developed Asian community: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlQarni, K.; AlQarni, E.A.; Naqvi, A.A.; AlShayban, D.M.; Ghori, S.A.; Haseeb, A.; Raafat, M.; Jamshed, S. Assessment of Medication Adherence in Saudi Patients with Type II Diabetes Mellitus in Khobar City, Saudi Arabia. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, S.U.R.; Hassali, M.A.; Saleem, F.; Bashir, S.; Aljadhey, H. Disease related knowledge, medication adherence and glycaemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Pakistan. Prim. Care Diabetes 2016, 10, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretchy, I.A.; Koduah, A.; Ohene-Agyei, T.; Boima, V.; Appiah, B. The Association between Diabetes-Related Distress and Medication Adherence in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, M.; Serlachius, A.; Mokhtar, I.; Broadbent, E. Illness Perceptions, HbA1c, And Adherence In Type 2 Diabetes In Saudi Arabia. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2019, 13, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matza, L.S.; Boye, K.S.; Currie, B.M.; Paczkowski, R.; Lando, L.F.; Mody, R.; Jordan, J. Patient perceptions of injection devices used with dulaglutide and liraglutide for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2018, 34, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.; Han, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, Q.; Mao, J. Illness perception, risk perception and health promotion self-care behaviors among Chinese patient with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional survey. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2018, 39, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawker, S.; Payne, S.; Kerr, C.; Hardey, M.; Powell, J. Appraising the Evidence: Reviewing Disparate Data Systematically. Qual. Health Res. 2002, 12, 1284–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, B.F.; Flemming, K.; Shulman, C.; Candy, B. Challenges to access and provision of palliative care for people who are homeless: A systematic review of qualitative research. BMC Palliat. Care 2016, 15, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PICOT | SEARCH TERMS | PICOT QUESTION |
|---|---|---|
| Population | Adult patients | How do adult patients diagnosed with T2DM perceive their illness and adhere to their medication? |
| Intervention | Diagnosed with T2DM | |
| Comparison | Nonapplicable | |
| Outcome | Perceive their illness and adhere to their medication | |
| Time | Nonapplicable |
| Keywords | Boolean Operators | Electronic Databases (Via SDL) | Records Found |
|---|---|---|---|
| “Illness perception”, “medication adherence”, “treatment”, “management”, “glycaemic control”, “adults”, “type 2 diabetes mellitus” | “AND” “OR” | PubMed | 104 |
| ScienceDirect | 40 | ||
| MEDLINE | 25 | ||
| CINAHL | 36 |
| Level of Evidence | Research Design | Studies |
|---|---|---|
| I | RCTs; systematic reviews; meta-analysis | Butt et al. (2016) [21] |
| II | Quasi-experimental studies | - |
| III | Nonexperimental studies | Alatawi et al. (2016) [18] Matza et al. (2018) [28] Albargawi et al. (2016) [16] Koponen et al. (2016) [14] Shiyanbola et al. (2018) [10] Nie et al. (2018) [29] Lee et al. (2016) [11] Kugbey et al. (2017) [12] Hashimoto et al. (2019) [15] Farhat et al. (2019) [17] Lee et al. (2017) [23] Nazir et al. (2016) [25] Jannoo & Khan (2019) [20] He et al. (2017) [19] Alqarni et al. (2019) [24] Alyami et al. (2019) [27] Kretchy et al. (2020) [26] Islam et al. (2021) [22] Bilondi et al. (2021) [13] |
| IV | Expert opinions based on scientific evidence | - |
| V | Case reports | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharbi, S.; Alhofaian, A.; Alaamri, M.M. Illness Perception and Medication Adherence among Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Scoping Review. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, 71-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract13010007
Alharbi S, Alhofaian A, Alaamri MM. Illness Perception and Medication Adherence among Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Scoping Review. Clinics and Practice. 2023; 13(1):71-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract13010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharbi, Samaher, Aisha Alhofaian, and Marym M. Alaamri. 2023. "Illness Perception and Medication Adherence among Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Scoping Review" Clinics and Practice 13, no. 1: 71-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract13010007
APA StyleAlharbi, S., Alhofaian, A., & Alaamri, M. M. (2023). Illness Perception and Medication Adherence among Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Scoping Review. Clinics and Practice, 13(1), 71-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract13010007






