Association between Anemia and New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Critically Ill Patients in the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
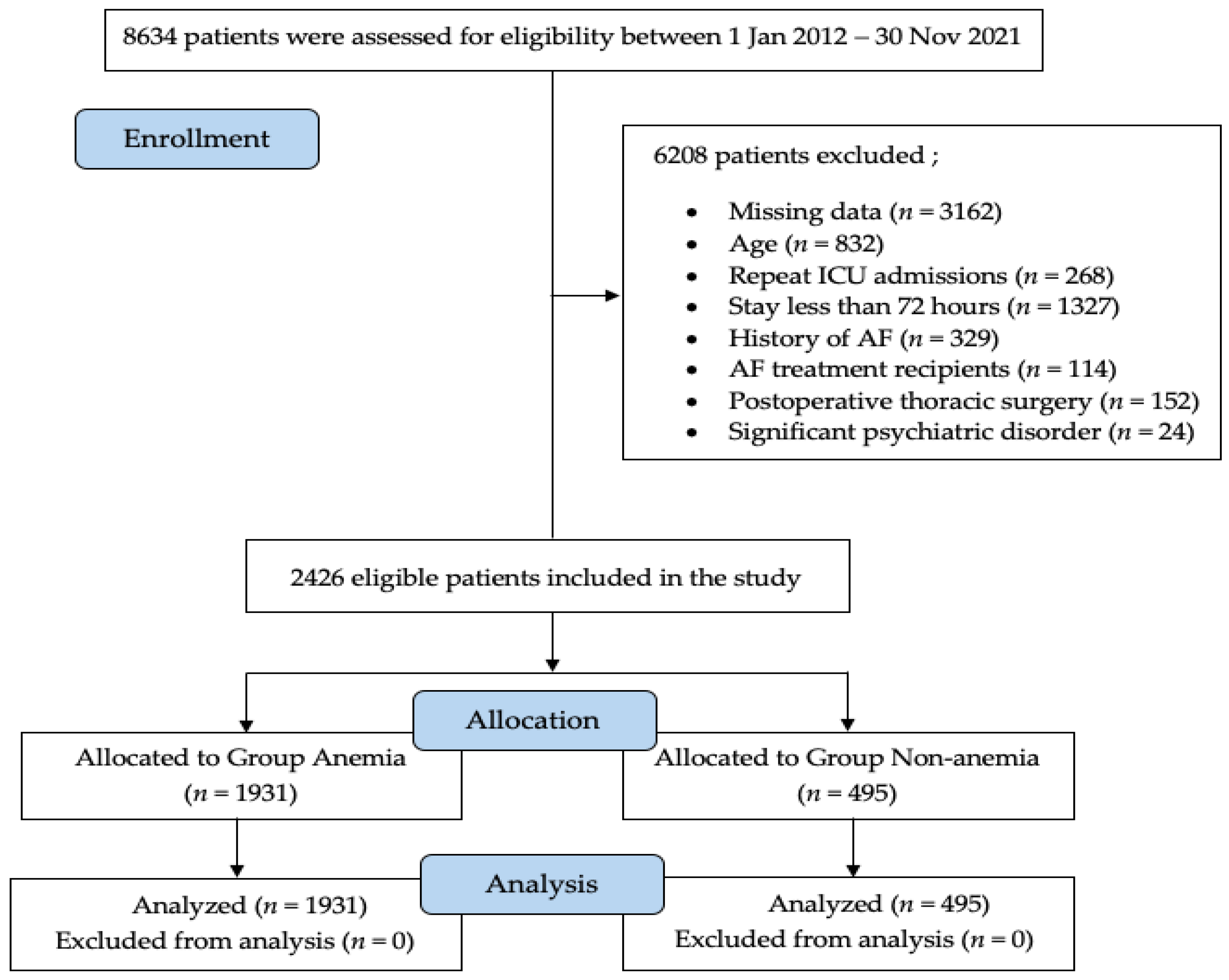
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Red Blood Cell Transfusion Protocol
2.3. Outcome Measurements
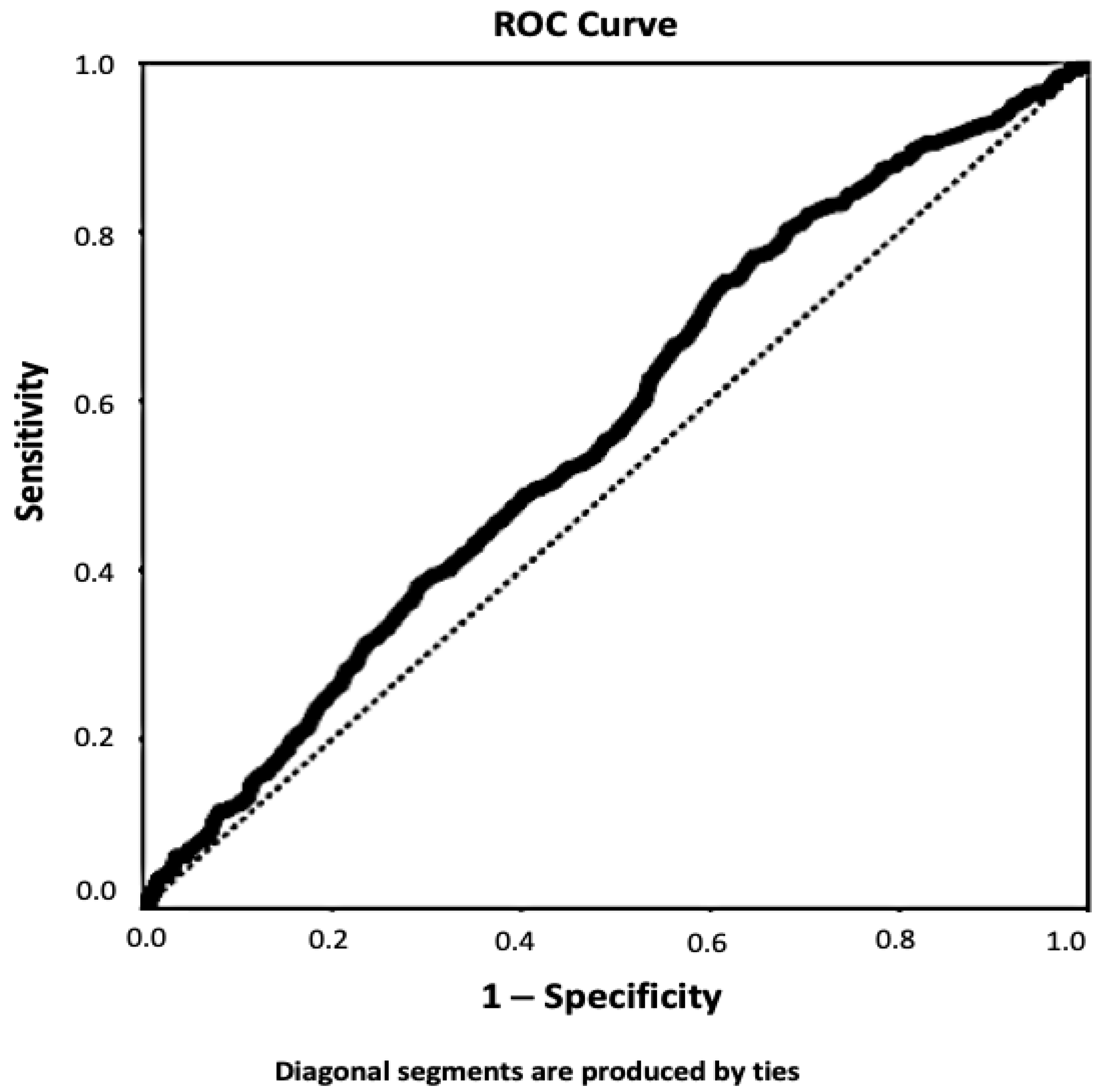
2.4. Statistical Analysis
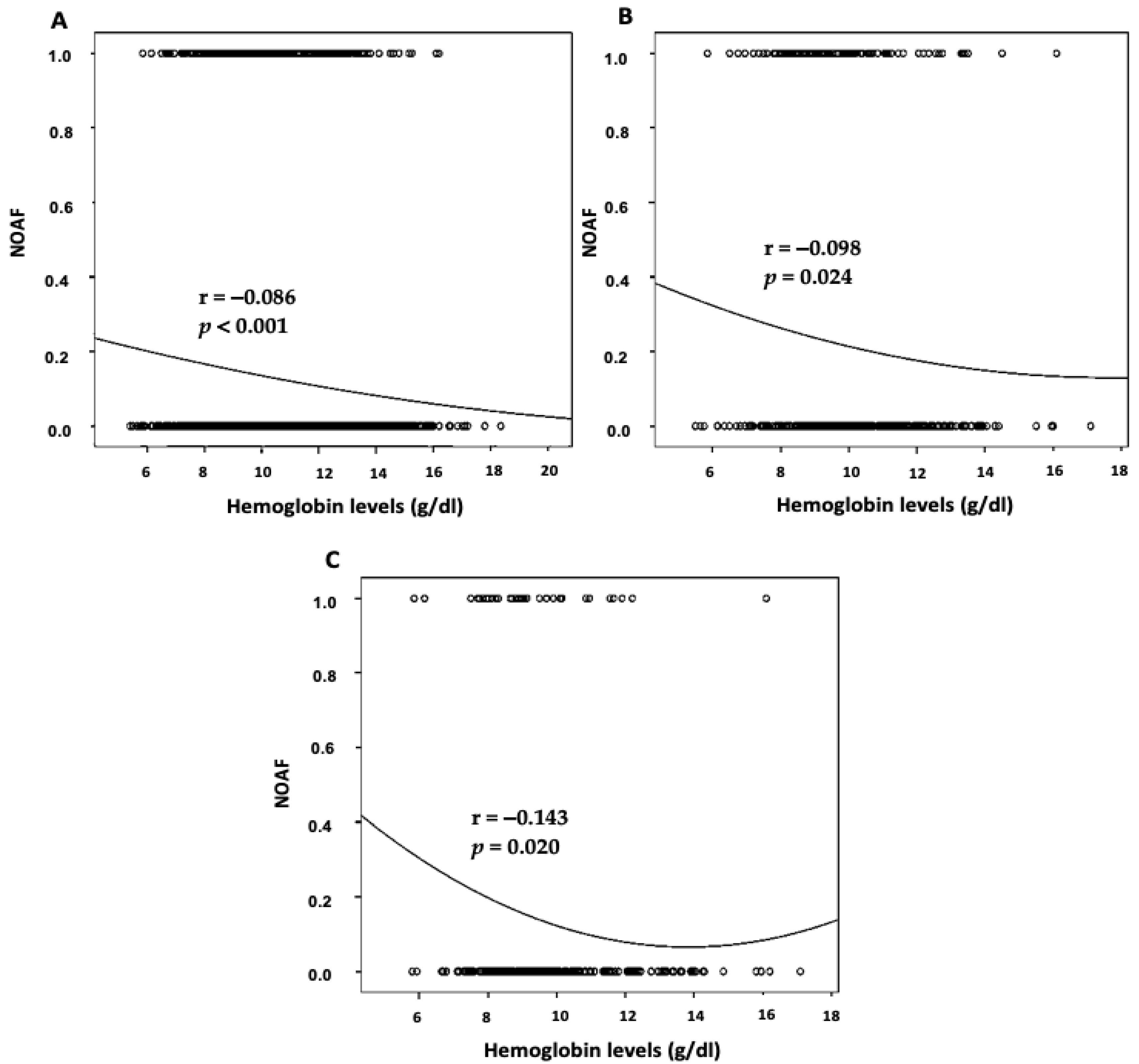
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications for the Pathophysiology of Anemia and AF
4.2. Blood Transfusion to Prevent the Development of AF in Patients with Anemia
4.3. Clinical Results of NOAF
4.4. Strengths and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Artucio, H.; Pereira, M. Cardiac arrhythmias in critically ill patients: Epidemiologic study. Crit. Care Med. 1990, 18, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; He, W.; Li, C.; Xiang, T.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Q. A systematic review and meta-analysis of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 10542–10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Kuang, L.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Che, L. Prognosis and management of new-onset atrial fibrillation in critically ill patients. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, B.W.; Hill, R.; Duarte, R.; Chean, C.S.; McAuley, D.; Blackwood, B.; Pace, N.; Welters, I. Protocol for a systematic review and network meta-analysis of the management of new onset atrial fibrillation in critically unwell adult patients. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klouwenberg, P.M.C.K.; Frencken, J.F.; Kuipers, S.; Ong, D.S.Y.; Peelen, L.M.; Van Vught, L.A.; Schultz, M.J.; Van Der Poll, T.; Bonten, M.J.; Cremer, O.L. Incidence, Predictors, and Outcomes of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis. A Cohort Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Tao, T.; Ma, Z.; Wang, M.; Lu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Z. Predictive value of red blood cell distribution width in critically ill patients with atrial fibrillation: A retrospective cohort study. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 2469–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotten, U.; Verheule, S.; Kirchhof, P.; Goette, A. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Atrial Fibrillation: A Translational Appraisal. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 265–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Male, S.; Scherlag, B.J. Role of neural modulation in the pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation. Indian J. Med Res. 2014, 139, 512–522. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, C. A narrative review of non-coding RNAs in atrial fibrillation: Potential therapeutic targets and molecular mechanisms. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Jensen, L.; Nahirniak, S.; Noel Gibney, R.T. Anemia and blood transfusion practices in the critically ill: A prospective cohort review. Heart Lung 2010, 39, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.S.; Saleh, E.-E.; Lee, R.J.; McClelland, D.B. The prevalence and characteristics of anaemia at discharge home after intensive care. Intensiv. Care Med. 2006, 32, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. The Global Prevalence of Anemia in 2011. 2015. Available online: www.who.int (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Achkasov, E.; Bondarev, S.; Smirnov, V.; Waśkiewicz, Z.; Rosemann, T.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Knechtle, B. Atrial Fibrillation in Athletes—Features of Development, Current Approaches to the Treatment, and Prevention of Complications. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steensma, D.P.; Tefferi, A. Anemia in the Elderly: How Should We Define It, When Does It Matter, and What Can Be Done? Mayo Clin. Proc. 2007, 82, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://akademi.tard.org.tr/?p=kilavuz-detay&bID=16&session=15366555u46099665s76832776 (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Yoshida, T.; Fujii, T.; Uchino, S.; Takinami, M. Epidemiology, prevention, and treatment of new-onset atrial fibrillation in critically ill: A systematic review. J. Intensiv. Care 2015, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-J.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-A. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, E.; Rivera, S.; Gabayan, V.; Keller, C.; Taudorf, S.; Pedersen, B.K.; Ganz, T. IL-6 mediates hypoferremia of in-flammation by inducing the synthesis of the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrighting, D.M.; Andrews, N.C. Interleukin-6 induces hepcidin expression through STAT3. Blood 2006, 108, 3204–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.; Goodnough, L.T. Anemia of chronic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markousis-Mavrogenis, G.; Tromp, J.; Ouwerkerk, W.; Devalaraja, M.; Anker, S.D.; Cleland, J.G.; Dickstein, K.; Filippatos, G.S.; Van Der Harst, P.; Lang, C.C.; et al. The clinical significance of interleukin-6 in heart failure: Results from the BIOSTAT-CHF study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, J.D.; Wilkins, R.G. Atrial fibrillation precipitated by acute hypovolaemia. Br. Med. J. 1987, 294, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shippy, C.R.; Appel, P.L.; Shoemaker, W.C. Reliability of clinical monitoring to assess blood volume in critically ill patients. Crit. Care Med. 1984, 12, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glance, L.G.; Dick, A.W.; Mukamel, D.B.; Fleming, F.J.; Zollo, R.A.; Wissler, R.; Salloum, R.; Meredith, U.W.; Osler, T.M. Association between Intraoperative Blood Transfusion and Mortality and Morbidity in Patients Undergoing Noncardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology 2011, 114, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carson, J.L.; Stanworth, S.J.; Roubinian, N.; Fergusson, D.A.; Triulzi, D.; Doree, C.; Hebert, P.C. Transfusion thresholds and other strategies for guiding allogeneic red blood cell transfusion. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 10, CD002042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, G.; Chacko, J. Red Blood Cell Transfusion Thresholds in Critically Ill Patients. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 23, S181–S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasne, R.W.; Kulkarni, P.A. Landmark Papers on Blood and Component Transfusion Therapy in the Critically Ill: A Critical Analysis. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 23, S207–S211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovaguimian, F.; Myles, P.S. Restrictive versus Liberal Transfusion Strategy in the Perioperative and Acute Care Settings: A context-specific systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Almeida, J.P.; Vincent, J.-L.; Galas, F.R.B.G.; de Almeida, E.P.M.; Fukushima, J.T.; Osawa, E.A.; Bergamin, F.; Park, C.L.; Nakamura, R.E.; Fonseca, S.M.R.; et al. Transfusion Requirements in Surgical Oncology Patients: A prospective, randomized controlled trial. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahecic, T.T.; Dünser, M.; Meier, J. RBC Transfusion Triggers: Is There Anything New? Transfus. Med. Hemotherapy 2020, 47, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, J.L.; Stanworth, S.J.; Dennis, J.A.; Trivella, M.; Roubinian, N.; Fergusson, D.A.; Triulzi, D.; Dorée, C.; Hébert, P.C. Transfusion thresholds for guiding red blood cell transfusion. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 12, CD002042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alameddine, A.K.; Visintainer, P.; Alimov, V.K.; Rousou, J.A. Blood Transfusion and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation after Cardiac Surgery. J. Card. Surg. 2014, 29, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, B.; Wu, Y.; Peng, L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Su, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Chong, Y. Atrial fibrillation increases inpatient and 4-year all-cause mortality in critically ill patients with liver cirrhosis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sensi, F.; De Potter, T.; Cresti, A.; Severi, S.; Breithardt, G. Atrial fibrillation in patients with diabetes: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2015, 5, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, M.; Rothenbacher, D.; Iacoviello, L.; Costanzo, S.; Tunstall-Pedoe, H.; Fitton, C.A.; Söderberg, S.; Hultdin, J.; Salomaa, V.; Jousilahti, P.; et al. Chronic kidney disease and risk of atrial fibrillation and heart failure in general population-based cohorts: The BiomarCaRE project. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 9, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, S.; Klouwenberg, P.M.K.; Cremer, O.L. Incidence, risk factors and outcomes of new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with sepsis: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walkey, A.J.; Wiener, R.; Ghobrial, J.M.; Curtis, L.H.; Benjamin, E. Incident Stroke and Mortality Associated with New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Patients Hospitalized with Severe Sepsis. JAMA 2011, 306, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Anemia Group (n = 1931) | Non-Anemia Group (n = 495) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yr | 75.54 ± 6.98 | 74.95 ± 7.61 | 0.11 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 1042 (54%) | 273 (55.2%) | 0.635 |
| Female | 889 (46%) | 222 (44,8%) | |
| BMI | 27.3 ± 5.53 | 27.5 ± 5.42 | 0.363 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Hypertension | 722 (37.4%) | 180 (36.4%) | 0.673 |
| Cardiac disease | 607 (31.4%) | 130 (26.3%) | 0.026 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 442 (22.9%) | 82 (16.6%) | 0.002 |
| Pulmonary disease | 173 (9%) | 54 (10.9%) | 0.184 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 164 (8.5%) | 23 (4.6%) | 0.004 |
| CKD | 181 (9.4%) | 21 (4.2%) | <0.001 |
| Metastatic cancer | 228 (11.8%) | 41 (8.3%) | 0.026 |
| Liver disease | 71 (3.7%) | 14 (2.8%) | 0.360 |
| Other | 48 (2.5%) | 11 (2.2%) | 0.734 |
| Admission diagnosis | |||
| Sepsis | 483 (25%) | 50 (10.1%) | <0.001 |
| Pulmonary disease | 561 (29.1%) | 160 (32.3%) | 0.155 |
| Cardiac disease | 158 (8.2%) | 63 (12.7%) | 0.002 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 200 (10.4%) | 75 (15.2%) | 0.003 |
| Postoperative care | 446 (23.1%) | 173 (34.9%) | <0.001 |
| Trauma | 42 (2.2%) | 9 (1.8%) | 0.621 |
| Renal failure | 228 (11.8%) | 36 (7.3%) | 0.004 |
| Metastatic cancer | 179 (9.3%) | 79 (16%) | <0.001 |
| Other | 136 (7%) | 17 (3.4%) | 0.003 |
| NOAF diagnosis | 262 (13.6%) | 49 (9.9%) | 0.029 |
| ICU risk scores | |||
| APACHE II | 20.03 ± 7.83 | 18.27 ± 7.02 | <0.001 |
| SAPS III | 52.69 ± 14.91 | 49.31 ± 13.04 | <0.001 |
| SOFA | 6.99 ± 4.02 | 5.87 ± 3.44 | <0.001 |
| Mechanic ventilation | 1458 (75.5%) | 298 (60.2%) | <0.001 |
| CRRT | 578 (29.9%) | 147 (29.7%) | 0.919 |
| Use of vasoactive agents | 1203 (62.3%) | 311 (62.8%) | 0.743 |
| RBC transfusion (mL) | 428.41 ± 276.28 | 164.25 ± 126.67 | <0.001 |
| LOS in ICU (h) | 205.26 ± 276.53 | 90.86 ± 145.33 | <0.001 |
| ICU mortality | 613 (31.7%) | 124 (25.1%) | 0.004 |
| Anemia Group (n = 1931) | Non-Anemia Group (n = 495) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 9.79 ± 1.43 | 13.57 ± 1.08 | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 30.61 ± 4.58 | 41.63 ± 3.79 | <0.001 |
| Platelet (×109/L) | 228.19 ± 105.64 | 218.25 ± 84.62 | 0.094 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 14.18 ± 10.14 | 13.78 ± 6.72 | 0.940 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 84.38 ± 80.85 | 61.22 ± 78.75 | <0.001 |
| Procalcitonin (mcg/L) | 7.91 ± 25.75 | 6.52 ± 15.41 | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 151.04 ± 65.71 | 155.98 ± 62.48 | 0.086 |
| ALT (U/L) | 122.23 ± 335.33 | 149.70 ± 513.95 | 0.404 |
| AST (U/L) | 256.03 ± 742.51 | 240.77 ± 782.88 | 0.006 |
| BUN | 85.12 ± 52.26 | 64.87 ± 42.66 | <0.001 |
| Blood creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.64 ± 1.29 | 1.28 ± 0.90 | <0.001 |
| Albumin (mg/dL) | 18.76 ± 9.20 | 26.18 ± 6.40 | <0.001 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 138.82 ± 6.13 | 138.28 ± 10.19 | 0.475 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.24 ± 0.72 | 4.31 ± 0.70 | 0.017 |
| Magnesium (mg/dL) | 2.02 ± 0.40 | 2.07 ± 0.42 | 0.056 |
| Chlorine (mmol/L) | 107.59 ± 5.92 | 107.69 ± 5.93 | 0.678 |
| Blood gas analysis | |||
| PH | 7.36 ± 1.20 | 7.33 ± 0.19 | 0.532 |
| PO2 (mmHg) | 88.56 ± 38.34 | 88.04 ± 36.20 | 0.966 |
| PCO2 (mmHg) | 43.28 ± 12.36 | 44.64 ± 12.28 | 0.010 |
| HCO3 (mEq/L) | 22.49 ± 4.98 | 23.66 ± 4.62 | <0.001 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 3.18 ± 3.31 | 2.72 ± 2.65 | 0.096 |
| BE | −2.46 ± 6.76 | −2.08 ± 7.30 | 0.007 |
| Patients with NOAF (n = 311) | Patients without NOAF (n = 2115) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Admission diagnosis | |||
| Sepsis | 118 (37.9%) | 415 (19.6%) | <0.001 |
| Renal failure | 37 (11.9%) | 227 (10.7%) | 0.538 |
| Postoperative care | 53 (17%) | 566 (26.8%) | <0.001 |
| Metastatic cancer | 31 (10%) | 227 (10.7%) | 0.683 |
| Other diagnosis | 128 (41.2%) | 850 (40.2%) | 0.745 |
| Baseline characteristics | |||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.10 ± 1.91 | 10.63 ± 2.05 | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 31.49 ± 5.95 | 33.06 ± 6.29 | <0.001 |
| Platelet (×109/L) | 209.85 ± 109.16 | 228.56 ± 100.44 | <0.001 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 15.56 ± 18.60 | 13.89 ± 7.28 | 0.739 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 102.00 ± 90.66 | 76.37 ± 78.91 | <0.001 |
| Procalcitonin (mcg/L) | 9.97 ± 20.79 | 7.28 ± 24.43 | <0.001 |
| Mechanic ventilation | 234 (75.24%) | 1522 (71.96%) | 0.227 |
| PEEP (cmH2O) | 5.1 (4.8–5.6) | 5.3 (5.1–5.8) | 0.443 |
| Tidal volume | 482 (435–528) | 476 (427–534) | 0.622 |
| Tidal volume (mL/kg) | 6.51 (5.86–7.44) | 6.49 (5.74–7.21) | 0.289 |
| Cardiac ultrasound data | |||
| LAD (mm) | 38.3 ± 5.8 | 40.1 ± 6.4 | 0.339 |
| LVEDD (mm) | 46.5 ± 5.4 | 45.9 ± 6.1 | 0.069 |
| LVEDV (mL) | 55.8 ± 7.2 | 58.6 ± 9.8 | 0.075 |
| LVEF (%) | 51.4 ± 12.0 | 52.8 ± 11.2 | 0.042 |
| ICU risk scores | |||
| APACHE II | 20.87 ± 7.81 | 19.49 ± 7.68 | 0.002 |
| SOFA | 7.72 ± 3.88 | 6.62 ± 3.93 | <0.001 |
| SAPS III | 55.12 ± 15.64 | 51.54 ± 14.39 | <0.001 |
| Use of vasoactive agents | 192 (61.8%) | 1315 (62.2%) | 0.639 |
| RBC transfusion (mL) | 386.40 ± 285.12 | 378.32 ± 290.26 | 0.259 |
| LOS in ICU (h) | 202.96 ± 231.00 | 178.82 ± 263.23 | <0.001 |
| ICU mortality | 107 (34.4%) | 610 (28.8%) | 0.045 |
| Covariations | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p adj | OR adj | 95% CI adj |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.772 | 1.002 | 0.986–1.019 | 0.971 | 1.000 | 0.983–1.018 |
| Gender | <0.001 | 0.518 | 0.402–0.666 | 0.142 | 0.779 | 0.557–1.087 |
| BMI | 0.082 | 0.979 | 0.957–1.003 | 0.834 | 0.997 | 0.973–1.022 |
| Sepsis | <0.001 | 2.463 | 1.912–3.173 | 0.151 | 1.457 | 0.872–2.436 |
| Anemia | 0.030 | 1.429 | 1.035–1.973 | 0.001 | 2.865 | 1.511–5.197 |
| Pulmonary disease | <0.001 | 2.263 | 1.776–2.885 | 0.280 | 1.309 | 0.803–2.133 |
| Cardiac disease | <0.001 | 1.986 | 1.404–2.809 | 0.388 | 0.783 | 0.450–1.364 |
| Renal failure | <0.001 | 2.358 | 1.723–3.227 | 0.258 | 1.378 | 0.790–2.405 |
| APACHE II | 0.003 | 1.023 | 1.008–1.038 | 0.319 | 0.988 | 0.966–1.012 |
| SAPS III | 0.000 | 1.016 | 1.008–1.023 | 0.176 | 1.008 | 0.996–1.021 |
| SOFA | <0.001 | 1.070 | 1.039–1.101 | 0.034 | 1.049 | 1.004–1.097 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sertcakacilar, G.; Yildiz, G.O. Association between Anemia and New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Critically Ill Patients in the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. Clin. Pract. 2022, 12, 533-544. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12040057
Sertcakacilar G, Yildiz GO. Association between Anemia and New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Critically Ill Patients in the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. Clinics and Practice. 2022; 12(4):533-544. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12040057
Chicago/Turabian StyleSertcakacilar, Gokhan, and Gunes Ozlem Yildiz. 2022. "Association between Anemia and New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Critically Ill Patients in the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis" Clinics and Practice 12, no. 4: 533-544. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12040057
APA StyleSertcakacilar, G., & Yildiz, G. O. (2022). Association between Anemia and New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Critically Ill Patients in the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. Clinics and Practice, 12(4), 533-544. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12040057






