Psychological Factors Related to Impotence as a Sexual Dysfunction in Young Men: A Literature Scan for Noteworthy Research Frameworks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Article Selection and Data Extraction
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Source of Articles/Studies
3.3. Type of Articles/Studies
| Review’s Study Design | Authors | Psychological Therapy | Psychological and Relational Causes | Organic Correlations Highlighted |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narrative review | Sooriyamoorthy et al. [14] | Psychotherapy (orientation not specified); Psychosexual counselling | Anxiety; Depression; Relational components | ED is closely linked to CVD (diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidaemia, and hypertension), among other disorders. Men with erectile dysfunction had 44% more cardiovascular events, 62% more myocardial infarctions, 39% more strokes, and a 25% increased risk of death compared with patients without ED. |
| Narrative review | Nguyen et al. [13] | Cognitive–behavioral sexual therapy; Psychosexual counselling | Anxiety; Depression; Relational components | ED is correlated with endocrinological risk factors such as diabetes, thyroid disease, excessive soy consumption, and KS (Klinefelter syndrome). For the treatment of ED in young men, oral PDE5Is remain the first-line oral agents used. In addition, surgical and hormonal treatments have been more widely used in the treatment of ED in young men. |
| Narrative review | Papagiannopoulos et al. [19] | Psychosexual therapy (only regarding possible pre-1970s therapies); | Anxiety (named only for differential with organic causes); Relational components (as a differential between psychogenic and organic ED) | Young men with ED may be at higher risk of future morbidity and mortality: ED may be an indicator of poor general health and CVD. Men with ED should be evaluated for subclinical CVD risk factors. |
| Narrative review | Ho et al. [10] | Behavioral therapy (for ED) | Depression | Modern medicine is complemented by traditional medicine (e.g., acupuncture, acupressure, yoga, herbal medicine, and spiritual healing): in Malaysia, 65% of men felt that traditional medicines were better than conventional ones. |
| Scoping review | Rastrelli et al. [16] | Cognitive–behavioral sexual therapy Psychoanalysis (only regarding possible pre-1970s therapies) | Anxiety; Depression; Relational components | ED in young men, even more so than in older men, can be considered a harbinger of CVD. Young men reporting ED risk being dismissed without a specific medical assessment because of the assumption that ED in young men is a self-limiting condition without clinical consequences. |
| Umbrella review | Allen et al. [15] | Psychosexual therapy; Couple therapy; Group psychotherapy (orientation not specified) | Anxiety (only in relation to the decrease in depression anxiety with alcohol assumption); Depression | Because diabetes, poor diet, obesity, low exercise, and CVD are interconnected, identifying the primary risk factor can be difficult. The most obvious candidate for a primary risk factor is a weakened vascular system. |
3.4. Psychological and Organic Aetiology
3.5. Depression and Anxiety
3.6. Relational Conditions
3.7. Organic Causes
3.8. Diagnosis
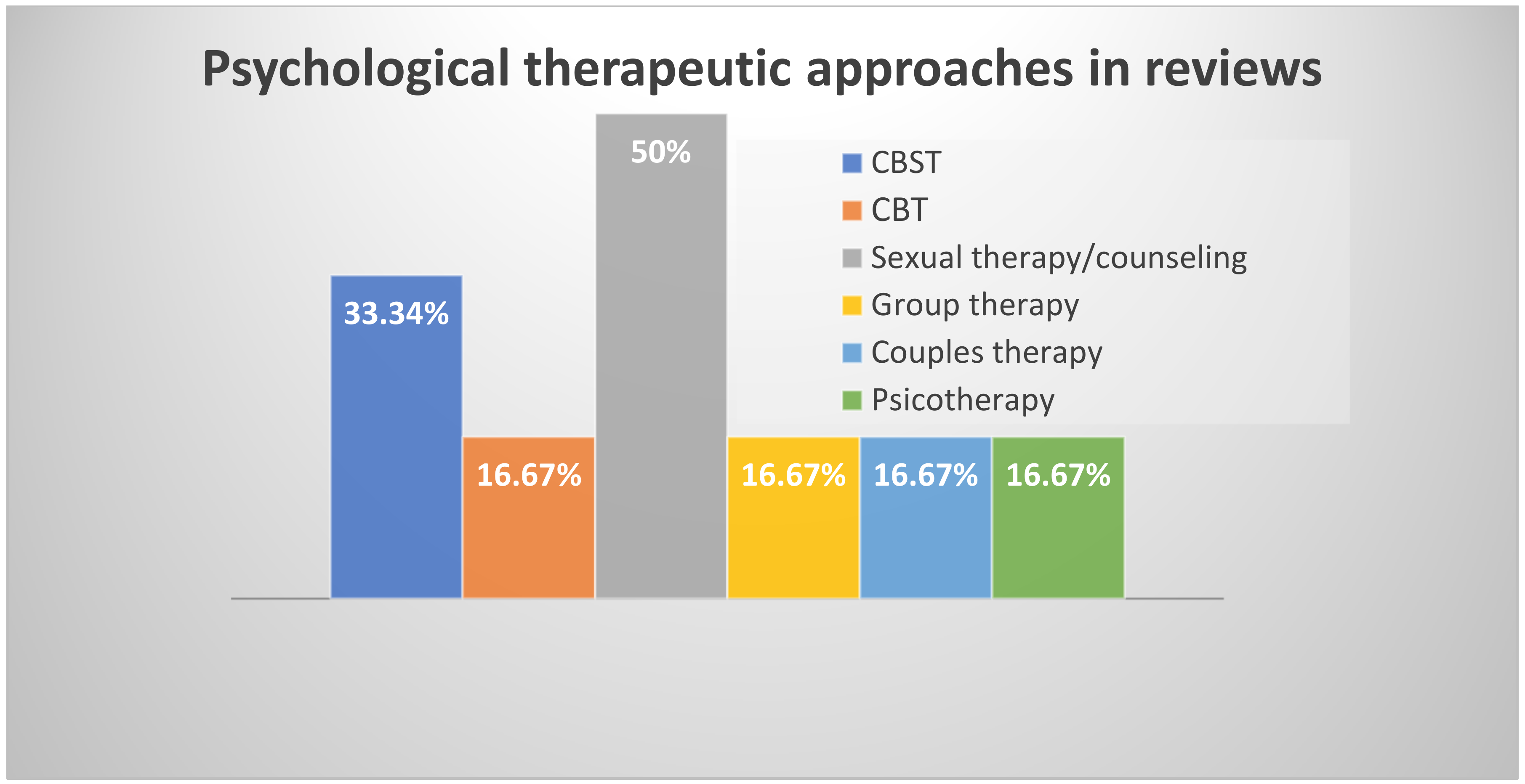
3.9. Efficacy of Psychological Therapy
3.10. Medical Therapy
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aytaç, I.A.; McKinlay, J.B.; Krane, R.J. The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int. 1999, 84, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, J.; Tang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhu, Z. Erectile Dysfunction and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Sex. Med. 2018, 15, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totaro, M.; Dimarakis, S.; Castellini, C.; D’Andrea, S.; Parisi, A.; D’Amato, F.; Tienforti, D.; Palazzi, S.; Baroni, M.G.; Francavilla, S.; et al. Erectile dysfunction in hyperuricemia: A prevalence meta-analysis and meta-regression study. Andrology 2021, 10, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Petrone, L.; Mannucci, E.; Mansani, R.; Balercia, G.; Krausz, C.; Giommi, R.; Forti, G.; Maggi, M. Difficulties in achieving vs maintaining erection: Organic, psychogenic and relational determinants. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2005, 17, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kaplan, H.S. Disorders of Sexual Desire; Brunner/Mazel: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, S.K.; Choudhury, A.; Singh, A.P. Understanding normal development of adolescent sexuality: A bumpy ride. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 8, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akre, C.; Berchtold, A.; Gmel, G.; Suris, J.-C. The Evolution of Sexual Dysfunction in Young Men Aged 18–25 Years. J. Adolesc. Health 2014, 55, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddi, V.; Fanni, E.; Castellini, G.; Fisher, A.D.; Corona, G.; Maggi, M. Conflicts Within the Family and Within the Couple as Contextual Factors in the Determinism of Male Sexual Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2015, 12, 2425–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawton, K.; Catalan, J.; Fagg, J. Sex therapy for erectile dysfunction: Characteristics of couples, treatment outcome, and prognostic factors. Arch. Sex. Behav. 1992, 21, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, C.; Otero, J.R.; Djinovic, R. Penile girth enhancement procedures for aesthetic purposes. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2021, 34, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shi, G.-R.; Huang, D.-D.; Li, Y.; Ma, C.-C.; Shi, M.; Su, B.-X. Male sexual dysfunction: A review of literature on its pathological mechanisms, potential risk factors, and herbal drug intervention. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jern, P.; Gunst, A.; Sandnabba, K.; Santtila, P. Are Early and Current Erectile Problems Associated with Anxiety and Depression in Young Men? A Retrospective Self-Report Study. J. Sex Marital Ther. 2012, 38, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Otero, J.; Manfredi, C.; Ralph, D.; Osmonov, D.; Verze, P.; Castiglione, F.; Serefoglu, E.C.; Bozzini, G.; García-Gómez, B. Non-invasive and surgical penile enhancement interventions for aesthetic or therapeutic purposes: A systematic review. Br. J. Urol. 2020, 127, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, R.; Catania, J.; Lue, T.; Althof, S.; Henne, J.; Hellstrom, W.; Levine, L. Impact of Peyronie’s Disease on Sexual and Psychosocial Functioning: Qualitative Findings in Patients and Controls. J. Sex. Med. 2008, 5, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, W.-Y.; Khoo, E.-M.; Tan, H.-M.; Hew, F.-L.; Teoh, S.-H. Depression, hormonal status and erectile dysfunction in the aging male: Results from a community study in Malaysia. J. Men’s Health Gend. 2006, 3, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. Prisma2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.C.; Singam, P.; Hong, G.E.; Zainuddin, Z.M. Male sexual dysfunction in Asia. Asian J. Androl. 2011, 13, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caskurlu, T.; Tascı, A.I.; Resim, S.; Sahinkanat, T.; Ergenekon, E. The etiology of erectile dysfunction and contributing factors in different age groups in Turkey. Int. J. Urol. 2004, 11, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatucci, C.F.; Lue, T.F. Erectile dysfunction in men under 40: Etiology and treatment choice. Int. J. Impot. Res. 1993, 5, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.M.T.; Gabrielson, A.T.; Hellstrom, W.J. Erectile Dysfunction in Young Men—A Review of the Prevalence and Risk Factors. Sex. Med. Rev. 2017, 5, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooriyamoorthy, T.; Leslie, S. Erectile Dysfunction; StatPearls Publishing: College Station, TX, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562253/ (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Allen, M.S.; Walter, E.E. Erectile Dysfunction: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Risk-Factors, Treatment, and Prevalence Outcomes. J. Sex. Med. 2019, 16, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastrelli, G.; Maggi, M. Erectile dysfunction in fit and healthy young men: Psychological or pathological? Transl. Androl. Urol. 2017, 6, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Ma, H.; Deng, C.; Lin, H.; Liu, D.; Lu, K. Subclinical endothelial dysfunction and low-grade inflammation play roles in the development of erectile dysfunction in young men with low risk of coronary heart disease. Int. J. Androl. 2012, 35, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibium, S.R.; Rosen, R.C. Principi e Pratica di Terapia Sessuale; CIC Edizioni Internazionali: Rome, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Papagiannopoulos, D.; Nehra, A.; Khare, N. Evaluation of young men with organic erectile dysfunction. Asian J. Androl. 2015, 17, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
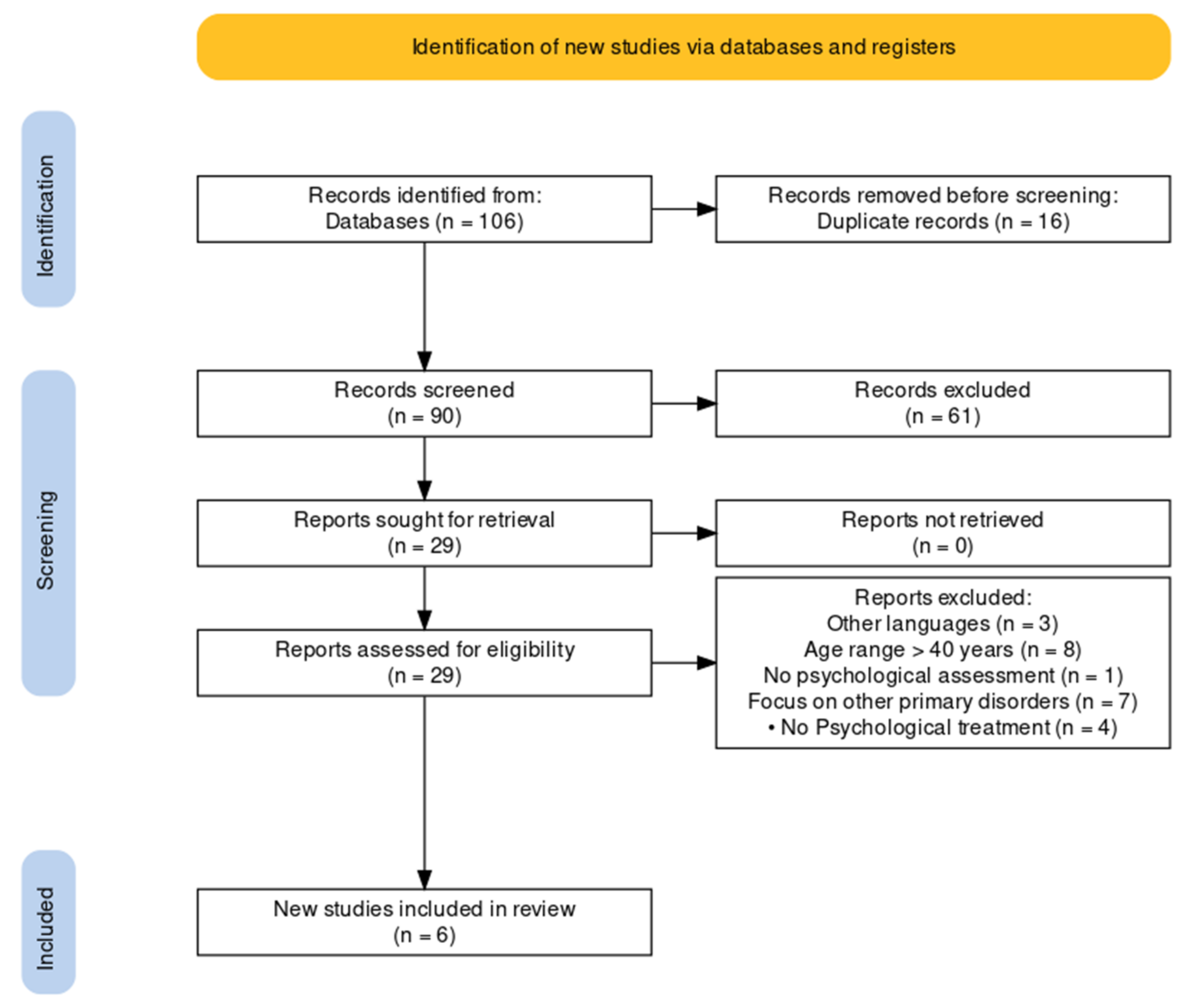
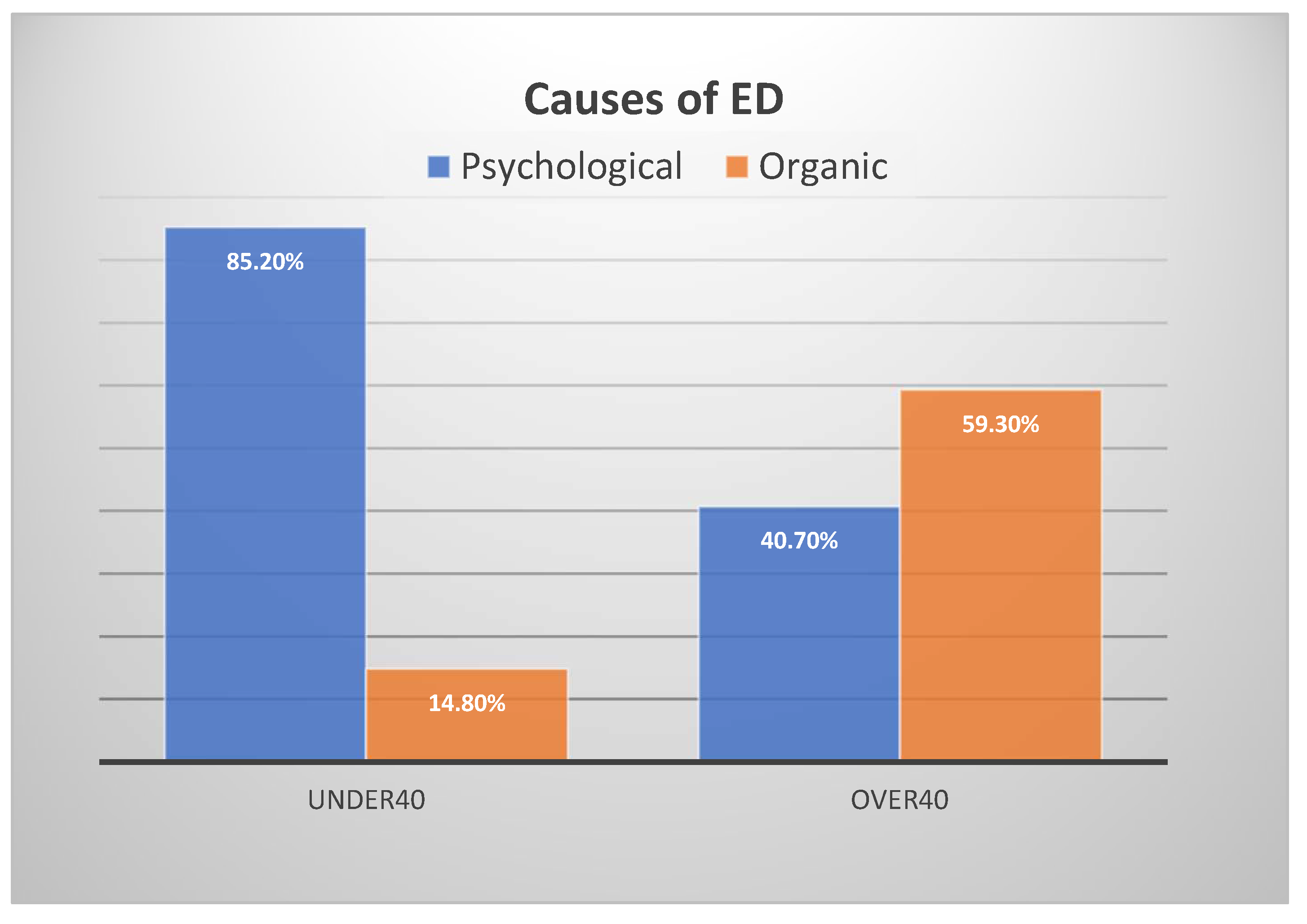
| Characteristics of Articles/Studies | Number | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Platform Publication: Journal (=) | Asian journal of andrology | 2 | 33.33% |
| Sexual medicine reviews | 1 | 16.67% | |
| StatPearls | 1 | 16.67% | |
| The journal of sexual medicine | 1 | 16.67% | |
| Translational andrology and urology | 1 | 16.67% | |
| First Author’ Country | Australia | 1 | 16.67% |
| Italy | 1 | 16.67% | |
| Malaysia | 1 | 16.67% | |
| UK | 1 | 16.67% | |
| USA | 2 | 33.33% | |
| Publication or posted date | 2011 | 1 | 16.67% |
| 2015 | 1 | 16.67% | |
| 2017 | 2 | 33.33% | |
| 2019 | 1 | 16.67% | |
| 2021 | 1 | 16.67% | |
| Type of review | Narrative | 4 | 66.67% |
| Scoping | 1 | 16.67% | |
| Umbrella | 1 | 16.67% | |
| Psychological and Relational conditions | Anxiety | 5 | 83.33% |
| Depression | 5 | 83.33% | |
| Relational conditions | 4 | 66.67% | |
| Presence of psychological tests in the reference articles | Reviews reporting tests both for depression and anxiety | 2 | 33.34% |
| Reviews reporting tests for depression | 2 | 33.34% | |
| Review without psychological testing | 2 | 33.34% | |
| Psychological therapies currently used | Behavioral therapy | 1 | 16.67% |
| Cognitive–behavioral sexual therapy; | 2 | 33.34% | |
| Couple therapy (orientation not specified); | 1 | 16.67% | |
| Group Psychotherapy (orientation not specified); | 1 | 16.67% | |
| Psychosexual counselling and therapy (orientation not specified); | 3 | 50% | |
| Psychotherapy (orientation not specified); | 1 | 16.67% | |
| Description of sex education programs | Yes | 0 | 0% |
| No | 6 | 100% | |
| Hypotheses of multidisciplinary diagnosis protocols. | Yes | 3 | 50% |
| No | 3 | 50% | |
| Hypotheses of multidisciplinary therapy protocols. | Yes | 0 | 0% |
| No | 6 | 100% | |
| Medical treatments reported | Pharmacological and surgical | 5 | 83.33% |
| Traditional oriental medicine (in addition to others) | 1 | 16.67% | |
| Sexual Disorder | Erectile Dysfunction | 5 | 83.33% |
| Sexual Dysfunctions (ED, premature ejaculation, and hypogonadism) | 1 | 16.67% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciaccio, V.; Di Giacomo, D. Psychological Factors Related to Impotence as a Sexual Dysfunction in Young Men: A Literature Scan for Noteworthy Research Frameworks. Clin. Pract. 2022, 12, 501-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12040054
Ciaccio V, Di Giacomo D. Psychological Factors Related to Impotence as a Sexual Dysfunction in Young Men: A Literature Scan for Noteworthy Research Frameworks. Clinics and Practice. 2022; 12(4):501-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12040054
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiaccio, Valentina, and Dina Di Giacomo. 2022. "Psychological Factors Related to Impotence as a Sexual Dysfunction in Young Men: A Literature Scan for Noteworthy Research Frameworks" Clinics and Practice 12, no. 4: 501-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12040054
APA StyleCiaccio, V., & Di Giacomo, D. (2022). Psychological Factors Related to Impotence as a Sexual Dysfunction in Young Men: A Literature Scan for Noteworthy Research Frameworks. Clinics and Practice, 12(4), 501-512. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12040054







