Can Intentional Weight Loss Ameliorate Sarcopenia in Individuals with Obesity? A Longitudinal Interventional Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Demographics and Clinical Status
2.2. Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barazzoni, R.; Bischoff, S.C.; Boirie, Y.; Busetto, L.; Cederholm, T.; Dicker, D.; Toplak, H.; Van Gossum, A.; Yumuk, V.; Vettor, R. Sarcopenic obesity: Time to meet the challenge. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.N. Body Composition in Healthy Aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 904, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamboni, M.; Mazzali, G.; Fantin, F.; Rossi, A.; Di Francesco, V. Sarcopenic obesity: A new category of obesity in the elderly. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 18, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsis, J.A.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: Aetiology, epidemiology and treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malafarina, V.; Úriz-Otano, F.; Iniesta, R.; Gil-Guerrero, L. Sarcopenia in the elderly: Diagnosis, physiopathology and treatment. Maturitas 2012, 71, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadra, D.; Itani, L.; Tannir, H.; Kreidieh, D.; El Masri, D.; El Ghoch, M. Association between sarcopenic obesity and higher risk of type 2 diabetes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Diabetes 2019, 10, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazem, S.; Itani, L.; Kreidieh, D.; El Masri, D.; Tannir, H.; Citarella, R.; El Ghoch, M. Reduced Lean Body Mass and Cardiometabolic Diseases in Adult Males with Overweight and Obesity: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farmer, R.E.; Mathur, R.; Schmidt, A.F.; Bhaskaran, K.; Fatemifar, G.; Eastwood, S.; Finan, C.; Denaxas, S.; Smeeth, L.; Chaturvedi, N. Associations Between Measures of Sarcopenic Obesity and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality: A Cohort Study and Mendelian Randomization Analysis Using the UK Biobank. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2019, 8, e011638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, J.L.; Wannamethee, S.G. The effect of sarcopenic obesity on cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in older people. Rev. Clin. Gerontol. 2015, 25, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, E.; Choi, K.M. Health Consequences of Sarcopenic Obesity: A Narrative Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsis, J.A.; Mackenzie, T.A.; Barre, L.K.; LopezJimenez, F.; Bartels, S.J. Sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity and mortality in older adults: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-H.; Choi, K.M. Sarcopenic Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Their Implications in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Consequences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishii, S.; Chang, C.; Tanaka, T.; Kuroda, A.; Tsuji, T.; Akishita, M.; Iijima, K. The Association between Sarcopenic Obesity and Depressive Symptoms in Older Japanese Adults. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tannir, H.; Kreidieh, D.; Itani, L.; El Masri, D.; El Ghoch, M. Reduction of Resting Energy Expenditure and Sarcopenic Obesity in Adults with Overweight and Obesity: A Brief Report. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreidieh, D.; Itani, L.; El Masri, D.; Tannir, H.; El Ghoch, M. Association between Reduced Daily Steps and Sarcopenic Obesity in Treatment-Seeking Adults With Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Masri, D.; Itani, L.; Tannir, H.; Kreidieh, D.; El Ghoch, M. The Relationship between Sarcopenic Obesity, Weight-Loss and Maintenance Outcomes during Obesity Management: Are Additional Strategies Required? Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreidieh, D.; Itani, L.; Tannir, H.; El Masri, D.; El Ghoch, M. Sarcopenic Obesity Predicts Early Attrition in Treatment-Seeking Patients with Obesity: A Longitudinal Pilot Study. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2020, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poggiogalle, E.; Migliaccio, S.; Lenzi, A.; Donini, L.M. Treatment of body composition changes in obese and overweight older adults: Insight into the phenotype of sarcopenic obesity. Endocrine 2014, 47, 699–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroni, M.L.; Caletti, M.T.; Grave, R.D.; Bazzocchi, A.; Gómez, M.P.A.; Marchesini, G. Prevention and Treatment of Sarcopenic Obesity in Women. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poggiogalle, E.; Parrinello, E.; Barazzoni, R.; Busetto, L.; Donini, L.M. Therapeutic strategies for sarcopenic obesity: A systematic review. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2021, 24, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreidieh, D.; Fakhoury, R.; El Ghoch, M. Exploring the effectiveness of a 1.5-Year weight management intervention for adults with obesity. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 42, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Metcalfe, J. Validity and Reliability of Body Composition Analysis Using the Tanita BC418-MA. J. Exerc. Physiol. 2012, 15, 74–86. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.-C.; Hsieh, K.-C.; Wu, C.-S.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chiang, J.; Chen, Y.-Y. Validity of Standing Posture Eight-electrode Bioelectrical Impedance to Estimate Body Composition in Taiwanese Elderly. Int. J. Gerontol. 2014, 8, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, C.; Jho, S.; No, J.-K.; Kim, H.-S. Body composition changes were related to nutrient intakes in elderly men but elderly women had a higher prevalence of sarcopenic obesity in a population of Korean adults. Nutr. Res. 2015, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.; Xiao, L.; Imayama, I.; Duggan, C.; Foster-Schubert, K.E.; Kong, A.; Campbell, K.L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Villasenor, A.; Neuhouser, M.L.; et al. Influence of Diet, Exercise, and Serum Vitamin D on Sarcopenia in Postmenopausal Women. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villareal, D.T.; Chode, S.; Parimi, N.; Sinacore, D.R.; Hilton, T.; Armamento-Villareal, R.; Napoli, N.; Qualls, C.; Shah, K. Weight Loss, Exercise, or Both and Physical Function in Obese Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Kojima, N.; Fujino, K.; Hosoi, E.; Kobayashi, H.; Somekawa, S.; Niki, Y.; Yamashiro, Y.; Yoshida, H. Exercise and Nutritional Supplementation on Community-Dwelling Elderly Japanese Women With Sarcopenic Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Med Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmler, W.; Teschler, M.; Weissenfels, A.; Bebenek, M.; Von Stengel, S.; Kohl, M.; Freiberger, E.; Goisser, S.; Jakob, F.; Sieber, C.C.; et al. Whole-body electromyostimulation to fight sarcopenic obesity in community-dwelling older women at risk. Resultsof the randomized controlled FORMOsA-sarcopenic obesity study. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 3261–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouwborst, I.; Verreijen, A.; Memelink, R.; Massanet, P.; Boirie, Y.; Weijs, P.; Tieland, M. Exercise and Nutrition Strategies to Counteract Sarcopenic Obesity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heber, D.; Ingles, S.; Ashley, J.M.; Maxwell, M.H.; Lyons, R.F.; Elashoff, R.M. Clinical detection of sarcopenic obesity by bioelectrical impedance analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 472S–477S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | SO at Baseline | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non SO N = 24 | SO N = 17 | Total N = 41 | ||
| Age | 43.9 (14.0) | 43.2 (15.9) | 43.6 (14.6) | p = 0.881 |
| Sex | X2 = 0.397, p = 0.529 | |||
| Male | 5 (20.8) | 5 (29.4) | 10 (24.4) | |
| Female | 19 (79.2) | 12 (70.6) | 31 (75.6) | |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 33.60 (3.51) | 39.44 (5.26) | 36.20 (5.16) | p < 0.001 |
| Education | X2 = 0.897, p = 0.344 | |||
| Lower | 15 (62.5) | 13 (76.5) | 28 (68.3) | |
| Higher | 9 (69.2) | 4 (23.5) | 13 (31.7) | |
| Employment | X2 = 0.897, p = 0.344 | |||
| Not employed | 15 (62.5) | 13 (76.5) | 28 (68.3) | |
| Employed | 9 (37.5) | 4 (23.5) | 13 (31.7) | |
| Variables | Baseline N = 41 | At 6 Months N = 41 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 92.6 (14.8) | 84.1 (15.1) | <0.0001 |
| BF | 39.0 (12.5) | 30.8 (11.0) | <0.0001 |
| BF% | 40.1 (6.7) | 34.2 (10.2) | <0.0001 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 36.0 (5.2) | 32.8 (5.3) | <0.0001 |
| ASM*100/Weight | 24.5 (3.5) | 26.2 (3.6) | <0.0001 |
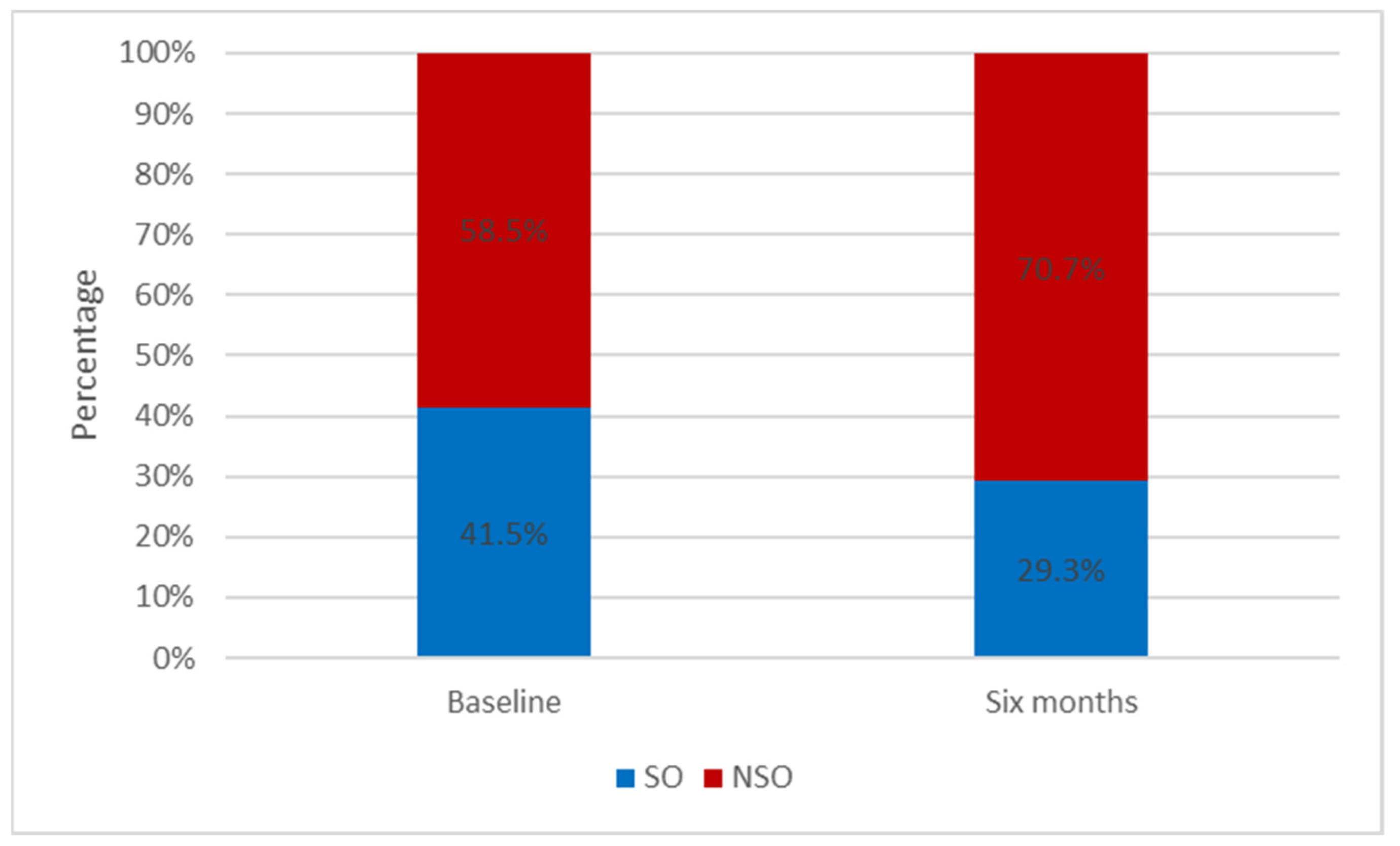
| Non SO | 24 (58.2) | 29 (70.7) | |
| SO | 17 (41.5) | 12 (29.3) |
| Variables | Multivariate Model | |
|---|---|---|
| Odd ratio | 95% CI | |
| Age | 0.99 | 0.93–1.05 |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 1.00 | |
| Female | 0.43 | 0.07–2.50 |
| Walking and Weight loss at 6 months | ||
| Walk < 8000 steps and lost below 5% | 1.00 | |
| Walk ≥ 8000 steps and lost ≥ 5% | 0.09 | 0.02–0.56 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tannir, H.; Itani, L.; Kreidieh, D.; El Masri, D.; El Ghoch, M. Can Intentional Weight Loss Ameliorate Sarcopenia in Individuals with Obesity? A Longitudinal Interventional Study. Clin. Pract. 2022, 12, 106-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12010014
Tannir H, Itani L, Kreidieh D, El Masri D, El Ghoch M. Can Intentional Weight Loss Ameliorate Sarcopenia in Individuals with Obesity? A Longitudinal Interventional Study. Clinics and Practice. 2022; 12(1):106-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleTannir, Hana, Leila Itani, Dima Kreidieh, Dana El Masri, and Marwan El Ghoch. 2022. "Can Intentional Weight Loss Ameliorate Sarcopenia in Individuals with Obesity? A Longitudinal Interventional Study" Clinics and Practice 12, no. 1: 106-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12010014
APA StyleTannir, H., Itani, L., Kreidieh, D., El Masri, D., & El Ghoch, M. (2022). Can Intentional Weight Loss Ameliorate Sarcopenia in Individuals with Obesity? A Longitudinal Interventional Study. Clinics and Practice, 12(1), 106-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12010014







