Assessment of Patient, Physician, Caregiver, and Healthcare Provider-Related Factors Influencing “Glycemic Happiness” of Persons with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Observational Survey
Abstract
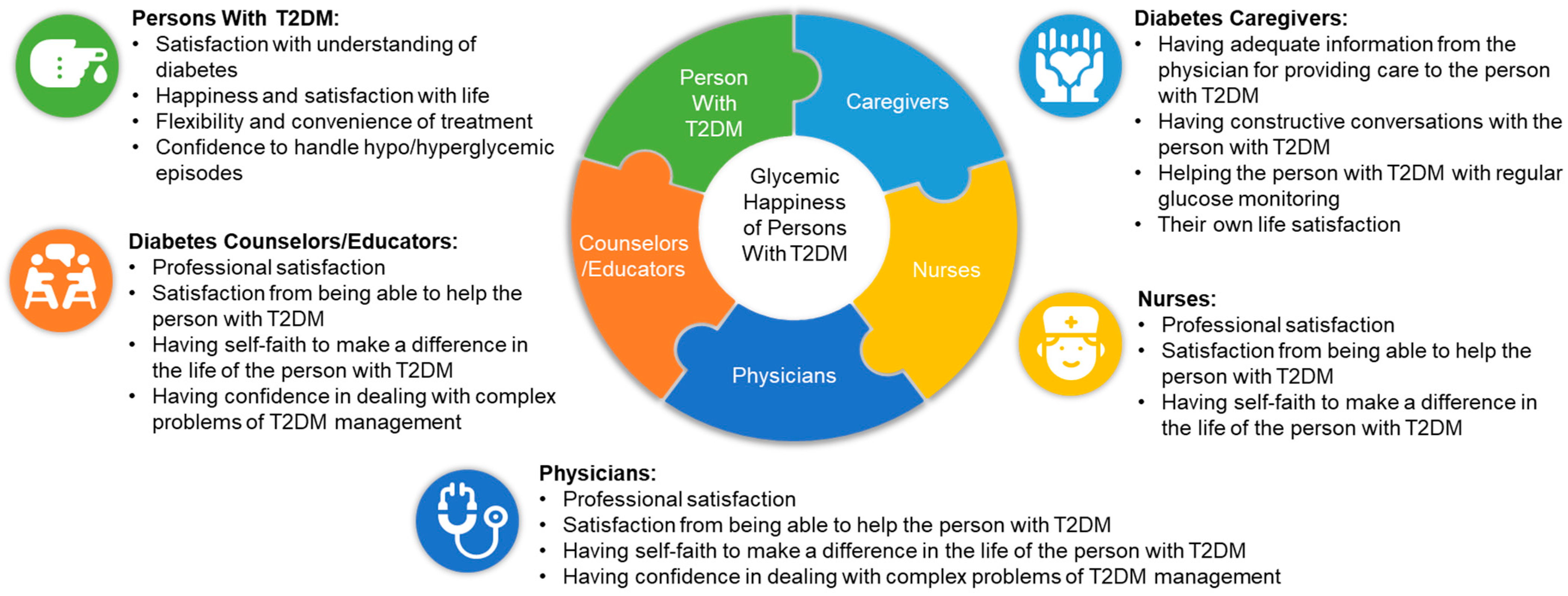
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Setting and Participants
2.2. Questionnaires Used for the Survey
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Ethics
2.5. Statistics and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics of the Survey Participants
3.2. Patient Component of the Survey
3.3. Caregiver Component of the Survey
3.4. Physician, Nurse, and Diabetes Counselor/Educator Components of the Survey
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Five-Component Questionnaire of the “Glycemic Happiness” Scale
| I Glycemic Happiness Scale for Patient Component |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| II Glycemic Happiness Scale for Physician Component |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| III Glycemic Happiness Scale for Caregiver Component |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| IV Glycemic Happiness Scale for Nurse Component |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| V Glycemic Happiness Scale for Counselor/Educator Component |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus. |
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th ed.; 2019; Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/upload/resources/material/20200302_133351_IDFATLAS9e-final-web.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Young-Hyman, D.; de Groot, M.; Hill-Briggs, F.; Gonzalez, J.S.; Hood, K.; Peyrot, M. Psychosocial Care for People with Diabetes: A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2126–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.; Jena, B.N.; Yeravdekar, R. Emotional and Psychological Needs of People with Diabetes. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 22, 696–704. [Google Scholar]
- Kalra, S.; Verma, K.; Singh Balhara, Y.P. Management of diabetes distress. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2017, 67, 1625–1627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nicolucci, A.; Kovacs Burns, K.; Holt, R.I.; Comaschi, M.; Hermanns, N.; Ishii, H.; Kokoszka, A.; Pouwer, F.; Skovlund, S.E.; Stuckey, H.; et al. Diabetes Attitudes, Wishes and Needs second study (DAWN2™): Cross-national benchmarking of diabetes-related psychosocial outcomes for people with diabetes. Diabetes Med. 2013, 30, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemavathi, P.; Satyavani, K.; Smina, T.P.; Vijay, V. Assessment of diabetes related distress among subjects with type 2 diabetes in South India. Int. J. Psychol. Couns. 2019, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlan, D.; Rajput, R.; Gehlawat, P.; Gupta, R. Prevalence and determinants of diabetes distress in patients of diabetes mellitus in a tertiary care centre. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, P.; Prasad, R.; Subhashchandra, B.J. Assessment of depression and diabetes distress in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of South India. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 3880–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hussain, S.; Habib, A.; Singh, A.; Akhtar, M.; Najmi, A.K. Prevalence of Depression among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in India: A Meta-Analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 270, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Thapar, R.; Mithra, P.; Kulkarni, V.; Holla, R.; Bhagawan, D.; Kumar, A.; Aithal, S. Distress and Its Effect on Adherence to Antidiabetic Medications Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Coastal South India. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2017, 8, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, P.; Sasikumar, P.; Medayil, R.; Jacob, R.; Sasidharan, S. High Prevalence of Distress among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (T2DM)—A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study from South India. Diabetes 2018, 67 (Suppl. S1), 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendhilkumar, M.; Tripathy, J.P.; Harries, A.D.; Dongre, A.R.; Deepa, M.; Vidyulatha, A.; Poongothai, S.; Venkatesan, U.; Anjana, R.M.; Mohan, V. Factors associated with high stress levels in adults with diabetes mellitus attending a tertiary diabetes care center, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 21, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S. DAWN2—Results from India. Diabetes Voice 2013, 58, 44. Available online: https://www.idf.org/component/attachments/attachments.html?id=470&task=download (accessed on 22 July 2021).
- Kalra, S.; Das, A.K.; Priya, G.; Joshi, A.; Punyani, H.; Krishna, N.; Gaurav, K. An Expert Opinion on “glycemic happiness”: Delineating the Concept and Determinant Factors for Persons with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Y.; Huang, J.; Dong, Q.L.; Li, B.; Zhao, X.; Xu, R.; Yin, H.F. Diabetes distress, happiness, and its associated factors among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with different therapies. Medicine 2020, 99, e18831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarifsanaiey, N.; Jamalian, K.; Bazrafcan, L.; Keshavarzy, F.; Shahraki, H.R. The effects of mindfulness training on the level of happiness and blood sugar in diabetes patients. J. Diabetes Metabol. Disord. 2020, 19, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Chow, A.; Piatt, J.A. Different Levels of Physical Activity, Physical Health, Happiness, and Depression among Older Adults with Diabetes. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2021, 7, 2333721421995623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, J.; Kumar, A.; Kakar, S.; Bhartia, A. The development of ’Quality of Life Instrument for Indian Diabetes patients (QOLID): A validation and reliability study in middle and higher income groups. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2010, 58, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Priya, T.; Jayaseelan, V.; Krishnamoorthy, Y.; Sakthivel, M.; Majella, M.G. Patient’s Experiences and Satisfaction in Diabetes Care and Out-of-Pocket Expenditure for Follow-Up Care Among Diabetes Patients in Urban Puducherry, South India. J. Patient Exp. 2020, 7, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Chakrawarti, A.; Singh, H.; Guruprasad, P.; Gupta, Y.K. Evaluation of treatment satisfaction, efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in geriatric patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional comparative study. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2018, 7, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Khdour, M.R.; Awadallah, H.B.; Al-Hamed, D.H. Treatment Satisfaction and Quality of Life among Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study in West Bank, Palestine. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 1834534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trockel, M.; Bohman, B.; Lesure, E.; Hamidi, M.S.; Welle, D.; Roberts, L.; Shanafelt, T. A Brief Instrument to Assess Both Burnout and Professional Fulfillment in Physicians: Reliability and Validity, Including Correlation with Self-Reported Medical Errors, in a Sample of Resident and Practicing Physicians. Acad. Psychiatry 2018, 42, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorwal, P.; Verma, R.; Balhara, Y.S. Psychological health of caregivers of individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional comparative study. J. Soc. Health Diabetes 2015, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonsky, W.H.; Fisher, L.; Earles, J.; Dudl, R.J.; Lees, J.; Mullan, J.; Jackson, R.A. Assessing psychosocial distress in diabetes: Development of the diabetes distress scale. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, B.; Kalra, S.; Balhara, Y.P.S.; Verma, K.C.; Azam, A.; Shaikh, F.A. The GlucoCoper-An Exploratory Study to Assess Coping Mechanisms of Women Diagnosed with Diabetes Mellitus. Eur. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonsky, W.H.; Fisher, L.; Hessler, D.; Edelman, S.V. Investigating Hypoglycemic Confidence in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2017, 19, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataraman, K.; Tan, L.S.M.; Bautista, D.C.T.; Griva, K.; Zuniga, Y.L.M.; Amir, M.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Tai, E.S.; Khoo, E.Y.H.; et al. Psychometric Properties of the Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID) Instrument in Singapore. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonsky, W.H.; Fisher, L.; Hessler, D.; Edelman, S.V. Identifying the worries and concerns about hypoglycemia in adults with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, U. Study of life satisfaction and happiness among male patients of diabetes: Insulin vs. non insulin. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 2015, 6, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, M. Anju. A study on life satisfaction level among persons with diabetes. IOSR-J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2017, 3, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Tirumalesh, M.; Chandraiah, K. Psychological wellbeing among diabetes mellitus patients. Int. J. Manag. Appl. Sci. 2017, 3, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- John, R.; Pise, S.; Chaudhari, L.; Deshpande, P.R. Evaluation of quality of life in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients using quality of life instrument for Indian diabetic patients: A cross-sectional study. J. Mid-Life Health 2019, 10, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitara, M.; Constantinou, C.S.; Andreou, E.; Diomidous, M. The Role of Nurses and the Facilitators and Barriers in Diabetes Care: A Mixed Methods Systematic Literature Review. Behav. Sci. 2019, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, C.; Chapman, A.; Yang, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T.; Enticott, J.; Thomas, S. Management of type 2 diabetes in China: The Happy Life Club, a pragmatic cluster randomised controlled trial using health coaches. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e009319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capistrant, B.D.; Friedemann-Sánchez, G.; Novak, L.K.; Zuijdwijk, C.; Ogle, G.D.; Pendsey, S. Mental health and well-being among type 1 diabetes caregivers in India: Evidence from the IDREAM study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 134, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.; Punyani, H.; Dhawan, M. Creating happiness in the diabetes care clinic. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2020, 70, 1099–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Saatci, E.; Tahmiscioglu, G.; Bozdemir, N.; Akpinar, E.; Ozcan, S.; Kurdak, H. The well-being and treatment satisfaction of diabetic patients in primary care. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2010, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, E. Integrated care: Evaluation of patient satisfaction with education provided by the diabetes specialist nurse. J. Diabetes Nurs. 2018, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Al Shahrani, A.; Baraja, M. Patient Satisfaction and its Relation to Diabetic Control in a Primary Care Setting. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2014, 3, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 90 (53.9) |
| Female | 77 (46.1) |
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 55.4 ± 12.0 |
| Height, cm, mean ± SD | 161.3 ± 9.0 |
| Weight, kg, mean ± SD | 70.8 ± 11.8 |
| SBP, mmHg, mean ± SD | 131 ± 19.5 |
| DBP, mmHg, mean ± SD | 81.5 ± 7.5 |
| RBG, mg/dL, mean ± SD (N = 152) | 183.7 ± 63.7 |
| HbA1c, %, mean ± SD (N = 143) | 8.1 ± 1.9 |
| Diabetes duration, months, mean ± SD | 106.6 ± 86.8 |
| Participants | Males, n (%) | Females, n (%) | Age, Years, Mean ± SD | Experience Years, Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caregivers (N = 167) | 77 (46.1) | 90 (53.9) | 44.8 ± 13.3 | NA |
| Physicians (N = 34) | 29 (85.3) | 5 (14.7) | 47.2 ± 8.7 | 18.4 ± 7.2 |
| Nurses (N = 34) | 4 (11.8) | 30 (88.2) | 31.6 ± 8.5 | 6.7 ± 4.6 |
| Diabetes counselors/educators (N = 34) | 9 (26.5) | 25 (73.5) | 32.6 ± 8.3 | 6.4 ± 4.2 |
| Parameters from the Patient Component of the “Glycemic Happiness Survey” | Mean Score | SD |
|---|---|---|
| How satisfied are you with your understanding of your diabetes? | 4.2 | 0.9 |
| Do you feel that friends or family don’t appreciate how difficult living with diabetes can be? | 3.1 | 1.4 |
| How happy and satisfied are you with your life presently? | 4.1 | 0.8 |
| How flexible have you been finding your treatment to be recently? | 4.2 | 0.8 |
| How convenient have you been finding your treatment to be recently? | 4.2 | 0.7 |
| How confident do you feel that you know what to do when your blood glucose level goes higher or lower than it should be? | 4.0 | 0.9 |
| Do you feel your private and social leisure activities are impaired due to diabetes? | 2.9 | 1.2 |
| Do you feel that diabetes is taking up too much of your mental and physical energy every day? | 2.9 | 1.3 |
| Do you get angry, scared, and/or depressed when you think about living with diabetes? | 2.7 | 1.3 |
| Do you feel overwhelmed by the demands of living with diabetes? | 2.9 | 1.1 |
| Parameters from the “Caregiver” Component of the “Glycemic Happiness Survey” | Mean Score | SD |
|---|---|---|
| Do you get adequate information from your doctor for providing care to your relative who has T2DM? | 4.5 | 0.6 |
| As a caregiver, do you have constructive conversations with the person with T2DM, when he or she experiences anxiety? | 4.2 | 0.8 |
| Being a caregiver, do you help the person with T2DM in regular blood glucose monitoring? | 4.2 | 0.9 |
| Do you accompany the person with T2DM during exercise/sports/other physical activity? | 3.5 | 1.0 |
| Do you feel dealing with hypoglycemia is one of the biggest challenges you face when it comes to being a caregiver of a person with T2DM? | 3.6 | 1.1 |
| As a caregiver, do you feel your personal physical and mental health is getting affected? | 2.7 | 1.2 |
| Do you feel you have to give up vacations, hobbies, or other social activities being a caregiver? | 2.5 | 1.2 |
| Do you feel you can keep your energy levels up while caring for the person with T2DM? | 3.6 | 1.0 |
| Do you get time to relax while caring for the person with T2DM? | 3.9 | 0.8 |
| How happy and satisfied are you with your life presently? | 4.2 | 0.8 |
| Parameters | Physicians (N = 34) | Nurses (N = 34) | Diabetes Counselors/Educators (N = 34) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | |
| Do you feel happy and satisfied that you chose to be a diabetes care professional? | 4.9 ± 0.4 | 4.4 ± 0.6 | 4.7 ± 0.4 |
| Do you get satisfaction from being able to help T2DM patients? | 4.9 ± 0.3 | 4.6 ± 0.5 | 4.6 ± 0.5 |
| Do you feel you can make a difference in life of T2DM patients through your work? | 4.8 ± 0.4 | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 4.5 ± 0.5 |
| Do you get physically and emotionally exhausted at work? | 2.6 ± 1.1 | 2.4 ± 1.0 | 2.2 ± 1.0 |
| Do you feel you are losing enthusiasm at work? | 2.0 ± 1.0 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 1.9 ± 0.7 |
| Do you feel you are in control dealing with complex problems of T2DM management? | 4.5 ± 0.6 | 3.6 ± 0.8 | 4.1 ± 0.7 |
| Do you feel worn out by your job as a care provider? | 2.4 ± 1.3 | 2.3 ± 1.0 | 2.2 ± 0.9 |
| Do you feel overwhelmed because diabetic patient load seems endless? | 2.8 ± 1.2 | 2.4 ± 1.2 | 2.5 ± 1.0 |
| Do you feel depressed by the traumatic stress of T2DM patients whom you try to help? | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 2.4 ± 1.1 | 2.3 ± 1.1 |
| Do you feel less empathetic and connected with your colleagues and friends? | 2.4 ± 1.2 | 2.3 ± 0.9 | 2.1 ± 0.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalra, S.; Sagili, V.B.R.; Sanyal, D.; Talwalkar, P.G.; Polavarapu, N.K.; Gaurav, K.; Mane, A.; Pinto, C.S. Assessment of Patient, Physician, Caregiver, and Healthcare Provider-Related Factors Influencing “Glycemic Happiness” of Persons with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Observational Survey. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, 715-727. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040087
Kalra S, Sagili VBR, Sanyal D, Talwalkar PG, Polavarapu NK, Gaurav K, Mane A, Pinto CS. Assessment of Patient, Physician, Caregiver, and Healthcare Provider-Related Factors Influencing “Glycemic Happiness” of Persons with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Observational Survey. Clinics and Practice. 2021; 11(4):715-727. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040087
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalra, Sanjay, Vijaya Bhaskar Reddy Sagili, Debmalya Sanyal, Pradeep G. Talwalkar, Nareen Krishna Polavarapu, Kumar Gaurav, Amey Mane, and Colette Stephen Pinto. 2021. "Assessment of Patient, Physician, Caregiver, and Healthcare Provider-Related Factors Influencing “Glycemic Happiness” of Persons with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Observational Survey" Clinics and Practice 11, no. 4: 715-727. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040087
APA StyleKalra, S., Sagili, V. B. R., Sanyal, D., Talwalkar, P. G., Polavarapu, N. K., Gaurav, K., Mane, A., & Pinto, C. S. (2021). Assessment of Patient, Physician, Caregiver, and Healthcare Provider-Related Factors Influencing “Glycemic Happiness” of Persons with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Observational Survey. Clinics and Practice, 11(4), 715-727. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040087





