Pharmaceutical Compounds in Drinking Water
Abstract
:Introduction
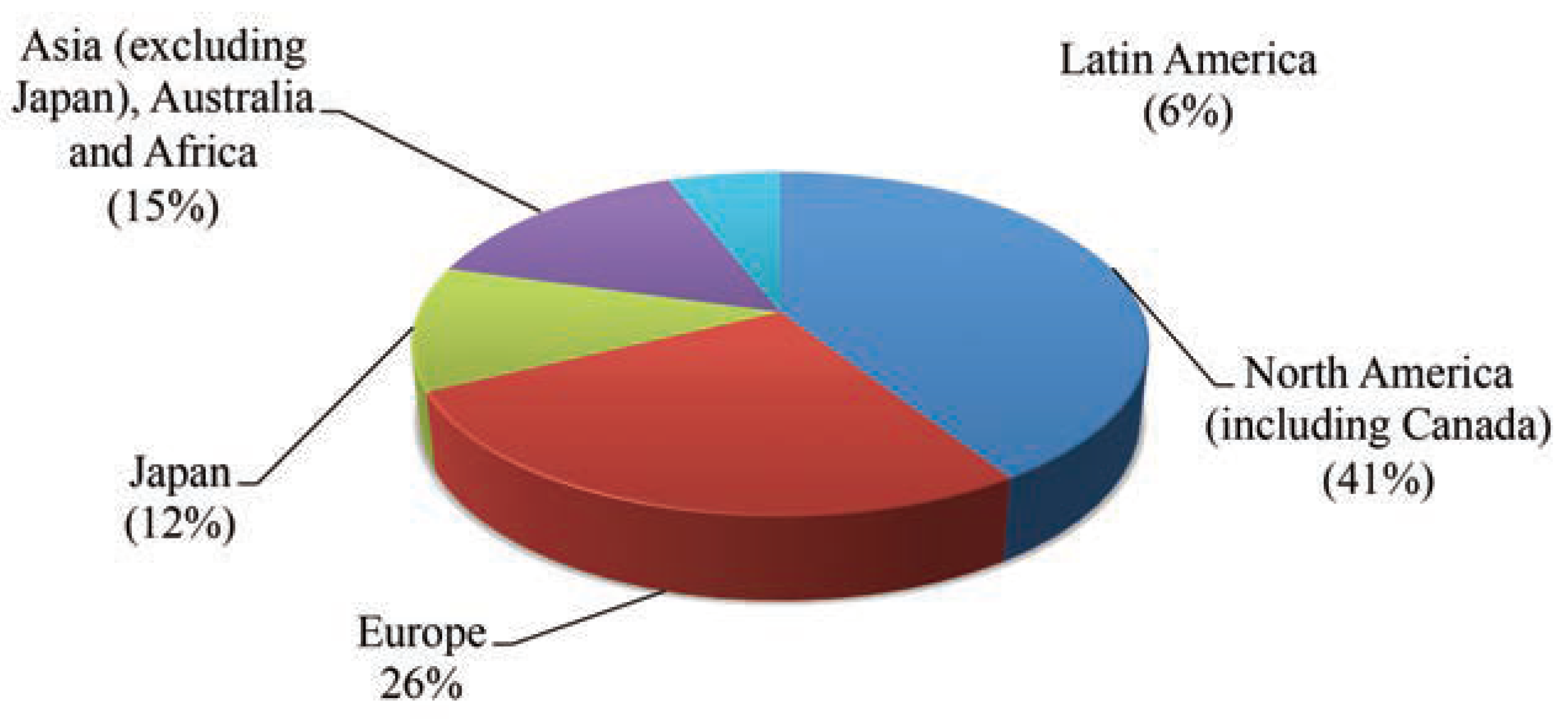
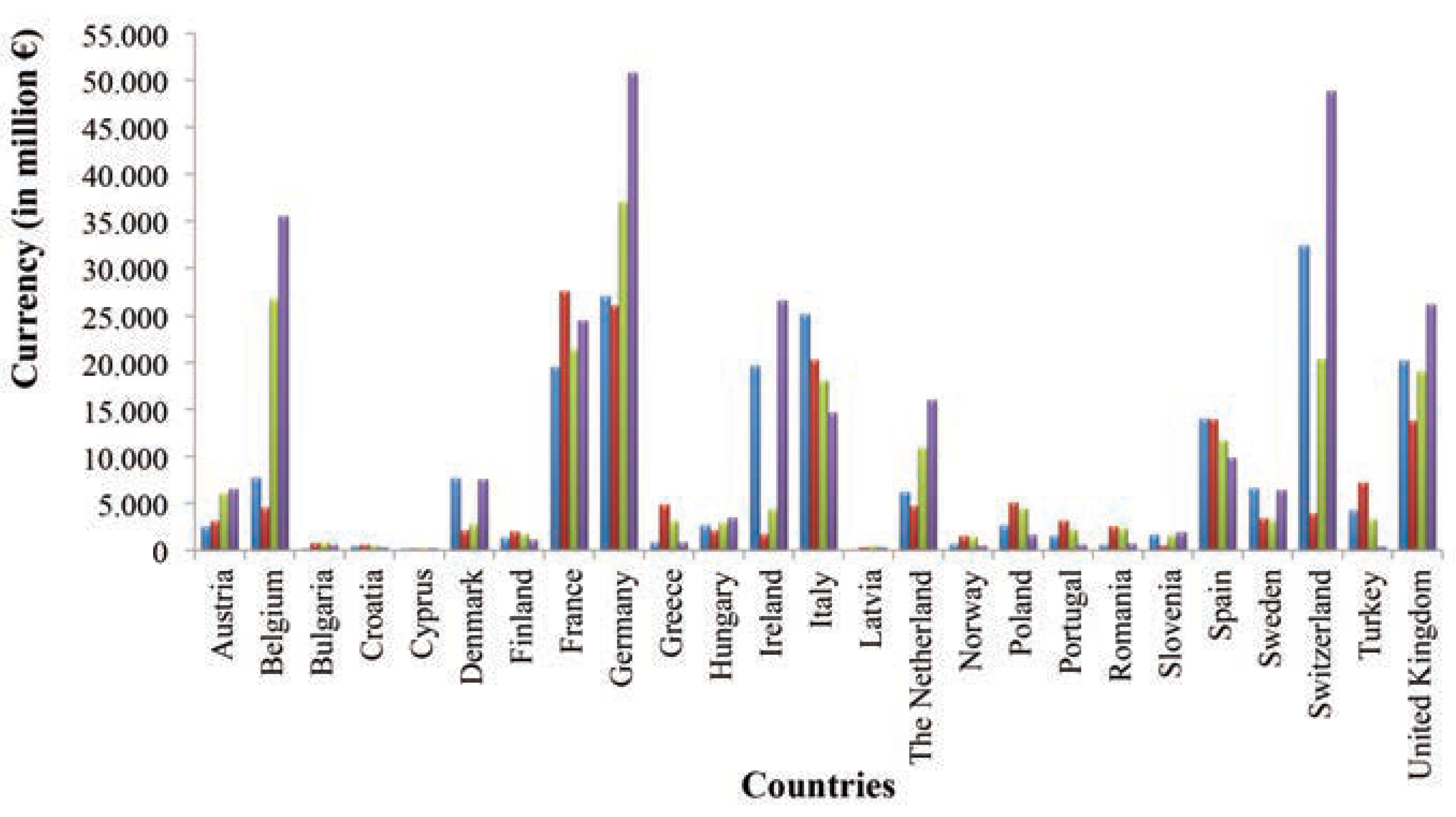
Global pharmaceuticals market status
Route of entry of pharmaceutical compounds into water system
Regulations for monitoring the presence of drugs in environment
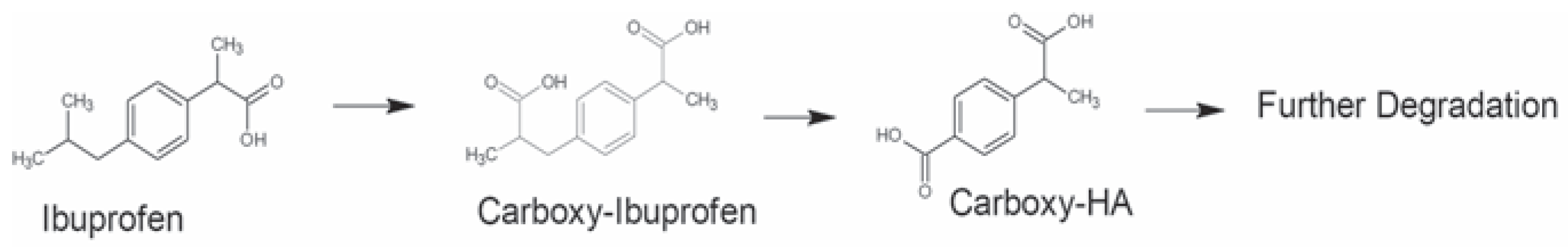
Fate and occurrence of pharmaceuticals in environment
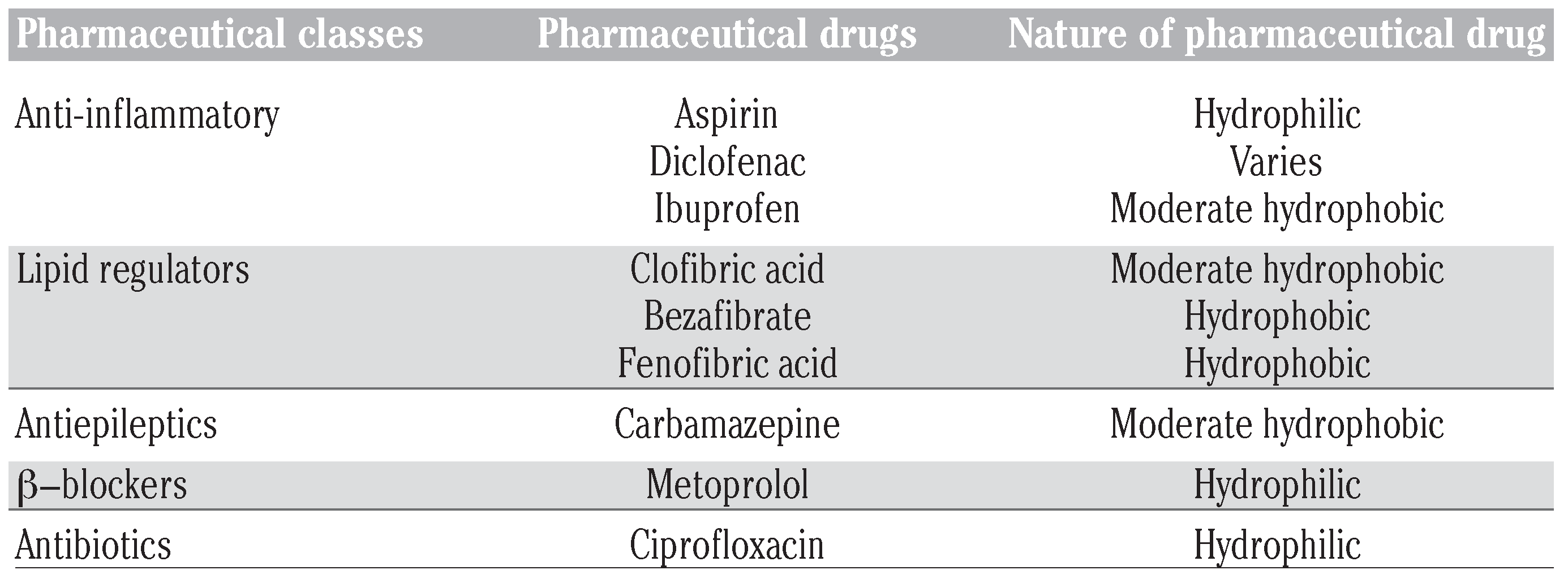
Characteristics of pharmaceutical drugs
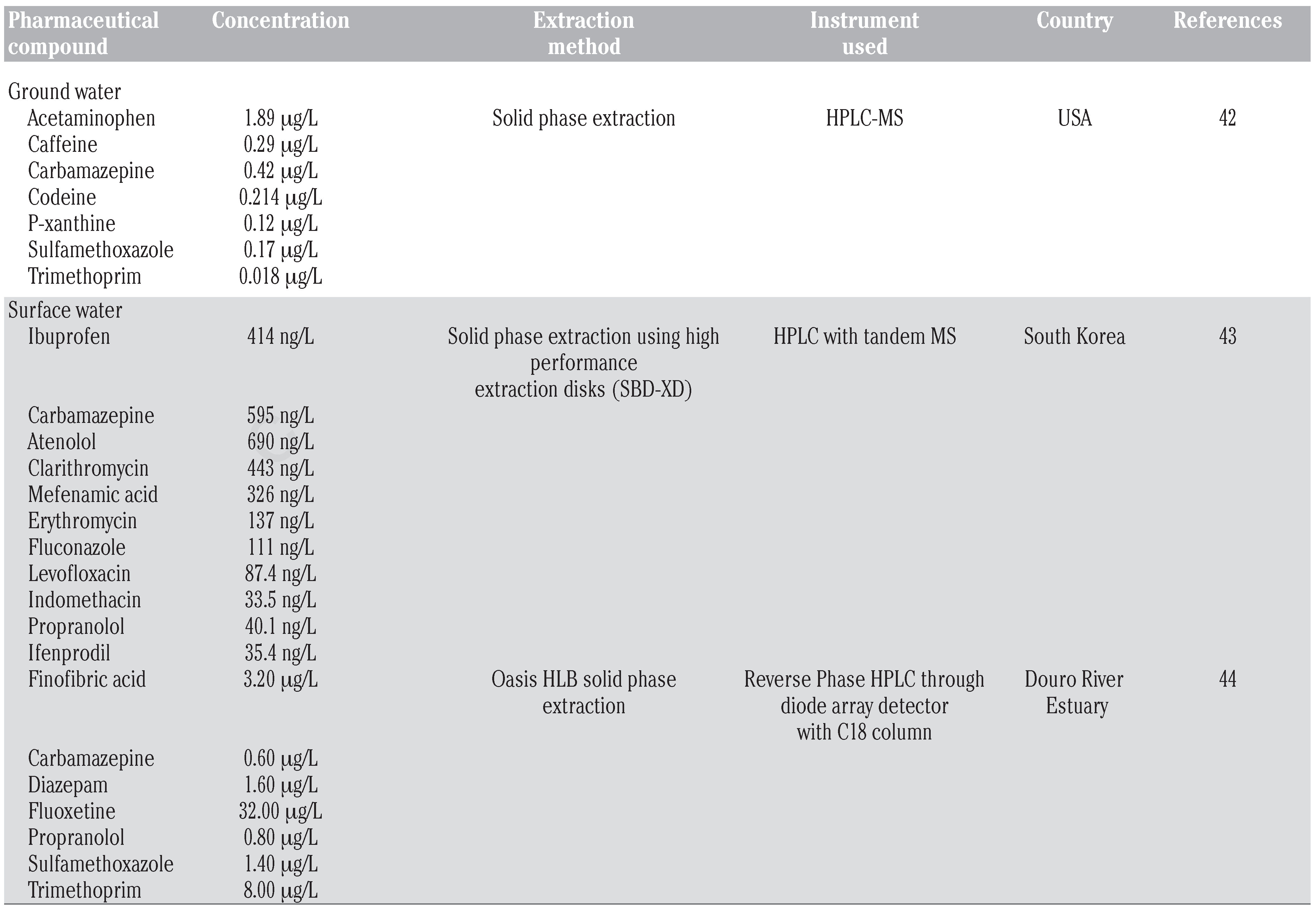
Detection of pharmaceutical compounds in fresh water and wastewater samples
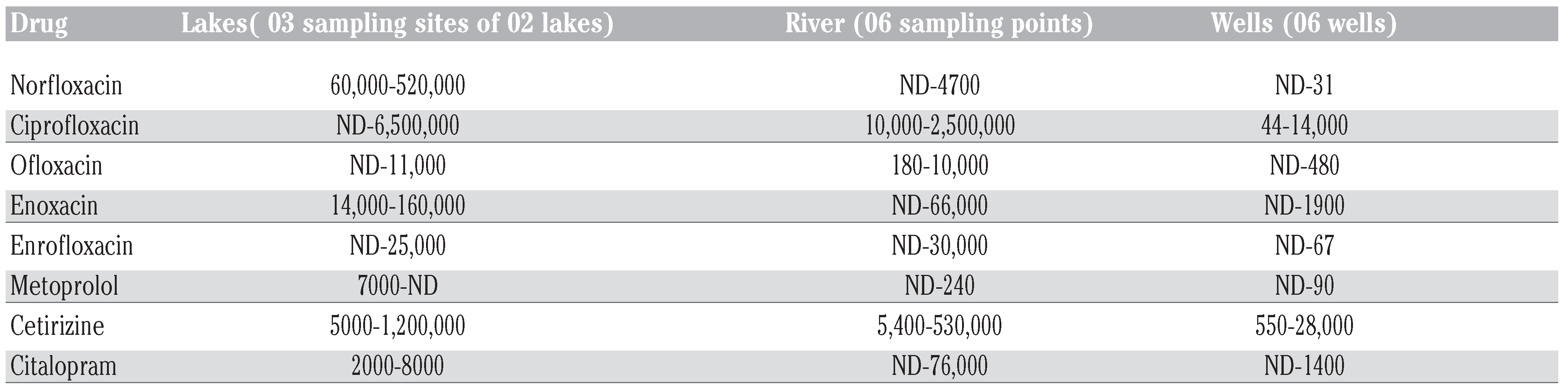
Pharmaceuticals in Indian drinking water
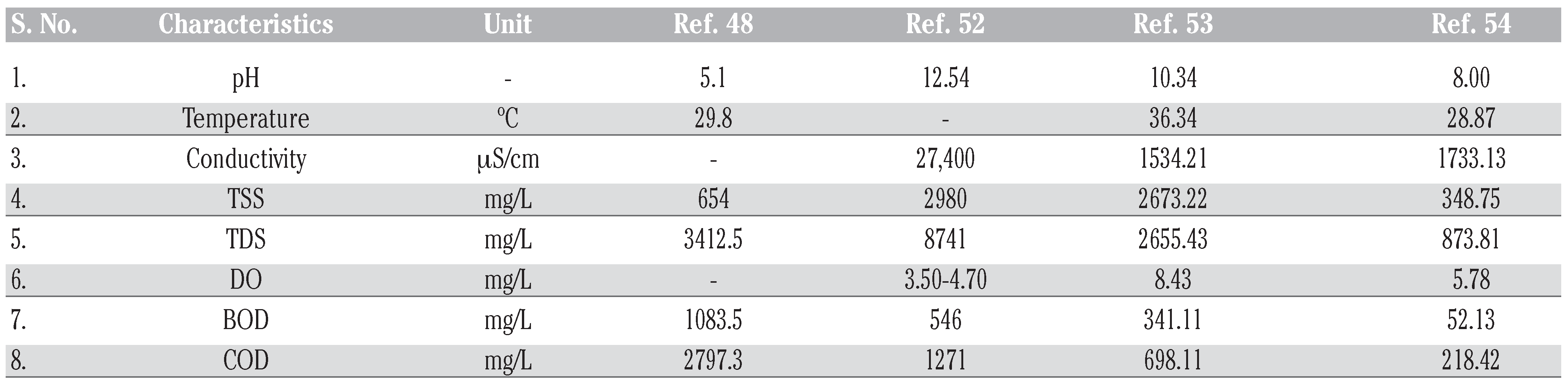
Impact of pharmaceutical pollutants on water quality
Health impacts due to pharmaceutical drugs present in fresh water and waste water
Conclusions
References
- Ternes, T.A.; Joss, A. Human pharmaceuticals, hormones and fragrances-The challenge of micropollutants in urban water management; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kummerer, K. Pharmaceuticals in the environment: sources, fate, effects and risks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Derksen, J.G.M.; Rijs, G.B.J.; Jongbloed, R.H. Diffuse pollution of surface water by pharmaceutical products. Wat Sci Technol 2004, 49, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, G. Systemic failure of regulation: the political economy of pharmaceutical and bulk drug manufacturing. In The politics of the pharmaceutical industry and access to medicines: world pharmacy and India; Lofgren, H., Ed.; Social Science Press: Hyderabad, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- KPMG International. The Indian pharmaceutical industry: collaboration for growth. 2006. Available online: http://www.in.kpmg.com/pdf/Indian%20pharma%20outlook.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2014).
- Mason, M. World’s highest drug pollution levels found in Indian stream. 2009. Available online: http://usatoday30.usato-day.com/tech/science/environment/200901-26-drug-india-stream_n.htm (accessed on 11 May 2016).
- Kumar, A.; Bisht, B.S.; Joshi, V.D.; Singh, A.K.; Talwar, A. Physical, chemical and bacteriological study of water from rivers of Uttarakhand. J Hum Ecol 2010, 32, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SWITCH, Biodegradability and fate of pharmaceutical impact compounds in different treatment processes. Katarzyna Kujawa-Roeleveld, Els Schuman WU, Environmental Technology, Wageningen, The Netherlands. Sustainable water management in the city of the future 2014. Available online: http://www.switchurbanwater.eu/outputs/pdfs/W41_GEN_RPT_D4.1.3_Biodegradability_and_fate_of_phamarceutical_compounds.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2016).
- Reddy, A.G.S.; Boraa, S.; Ganji, S. Hydrogeochemical characterization of contaminated groundwater in Patancheru industrial area, Southern India. Environ. Monit. Assess 2012, 184, 3557–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, G.; Unnikrishnan, M.K. The emerging environmental burden from pharmaceuticals. Econ Polit Week 2012, 47, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mike, A. India’s waterways: a toxic stew of pharmaceutical chemicals dumped from big pharma factories. Natural News. Available online:. 2009. (accessed on 15 June 2014).
- Schertow, J.A. India’s waterways used as dumping grounds for big Pharma. 2009. Available online: http://intercontinentalcry.org/indias-waterways-used-as-dumpinggrounds-for-big-pharma/ (accessed on 20 June 2014).
- CBS Investigates. Indian stream a cocktail of drugs. CBS News. 2009. Available online: http://www.cbsnews.com/2100-202_162-4752641.html (accessed on 31 May 2014).
- Ryu, A. Pharmaceutical pollution of water in India: international market failure. Harv Heal Pol Rev 2013, 14, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The world medicine situation report. 2004. Available online: http://www.who.int/medicines/areas/policy/world_medicines_situation/en/ (accessed on 5 June 2014).
- Corporate Catalyst (India) PVT Ltd. A brief report pharmaceutical industry in India; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Corporate Catalyst (India) PVT Ltd. A brief report on pharmaceutical industry in India; July 2015. Available online: http://www.cci.in/pdfs/surveysreports/pharmaceutical-industry-in-india.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2016).
- European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA). The pharmaceutical industry in figures. 2014. Available online: http://www.efpia.eu/uploads/Figures_2014_Final.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2016).
- Mazumdar, M. Performance of pharmaceutical companies in india, contributions to economics; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaou, A.; Meric, S.; Fatta, D. Occurrence patterns of pharmaceuticals in water and wastewater environments. Anal Bioanal Chem 2007, 387, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fent, K.; Weston, A.A.; Caminada, D. Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquat Toxicol 2006, 76, 122–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, V.; Singh, P.; Sharma, B.; Upadhyay, K.; Singh, R. Environmental and health hazards due to pharmaceutical effluents. Int J Phar Rev Res 2014, 4, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Glassmeyer, S.T.; Furlong, E.T.; Kolpin, D.W.; et al. Transport of chemical and microbial compounds from known wastewater discharge: potential for use as indicators of human feacal contamination. Environ Sci Techno 2005, 39, 5157–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Atchley, D.; Greer, L.; et al. Dosed without prescription: preventing pharmaceutical contamination of our nation’s drinking water. Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) White Paper. December 2009. Available online: https://www.nrdc.org/sites/default/files/hea_10012001a.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2024).
- World HealthOrganization. Pharmaceuticals in drinking-water. 2011. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/201 1/pharmaceuticals/en/ (accessed on 5 June 2014).
- Beachey, M. A pharmaceutical hazard. Pharmaceutical Technology. 2008. Available online: http://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/features/feature45434 (accessed on 20 June 2014).
- Vijayalakshmi, M.S.R.; Deepa, B.S. Impact of Industrial effluent treatment on profitability of small and medium enterprises: a case study of Hyderabad bulk drug industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs: Building Competencies; Macmillan Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Maria, A. The costs of water pollution in India; CERNA: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB). Minimal National standards: pharmaceutical manufacturing and formulation industry; CPCB: New Delhi, India, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Bendz, D.; Paxéus, N.A.; Ginn, T.R.; Loge, F.J. Occurrence and fate of pharmaceutically active compounds in the environment, a case study: Hoje River in Sweden. J Hazard Mat 2005, 122, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.H.; Thomas, K.V. The occurrence of selected pharmaceuticals in wastewater effluent and surface waters of the lower Tyne catchment. Sci Tot Environ 2006, 356, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, C.; Johansson, A.K.; Alvan, G.; Bergman, K.; Kuhler, T. Are pharmaceuticals potent environmental pollutants? Part I: Environmental risk assessments of selected active pharmaceutical ingredients. Sci Tot Environ 2006, 364, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwiener, C.; Seeger, S.; Glauner, T.; Frimmel, F.H. Metabolites from the biodegradation of pharmaceutical residues of ibuprofen in biofilm reactors and batch experiments. Anal Bioanal Chem 2002, 372, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buser, H.R.; Poiger, T.; Muller, M.D. Occurrence and environmental behavior of the chiral pharmaceutical drug ibuprofen in surface waters and in wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 1999, 33, 2529–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Singh, P.; Aboul, E.; Hassan, Y.; Sharma, B. Chiral analysis of ibuprofen residues in water and sediment. Anal Lett 2009, 42, 1747–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevre, N. Pharmaceuticals in surface waters: sources, behavior, ecological risk, and possible solutions. Case study of Lake Geneva, Switzerland. Wiley Interdisciplin Rev Water 2014, 1, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerer, K. The presence of pharmaceuticals in the environment due to human use-Present knowledge and future challenges. J Environ Manage 2009, 90, 2354–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.W.; Huggett, D.B.; Boxall, A.B.A. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products: Research needs for the next decad. Environ Toxicol Chem 2009, 28, 2469–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlicchi, P.; Al Aukidy, M.; Zambello, E. Occurrence of pharmaceutical compounds in urban wastewater: removal, mass load and environmental risk after a secondary treatment—A review. Sci Tot Environ 2012, 429, 123–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce G Pleus, R.; Snyder, S.A. Toxicological relevance of pharmaceuticals in drinking water. Environ Sci Tech 2010, 44, 5619–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, J.; Söderström, H.; Lindberg, R.H.; Phan, C.; Tysklind, M.; Larsson, D.G. Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ Toxicol Chem 2009, 28, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fram, M.S.; Belitz, K. Occurrence and concentrations of pharmaceutical compounds in groundwater used for public drinking-water supply in California. Sci Tot Environ 2011, 409, 3409–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Jang, H.S.; Kim, J.G.; Ishibashi, H.; Hirano, M.; Nasu, K. Occurrence of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) in surface water from Mankyung river, South Korea. J Health Sci 2009, 55, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, T.V.; Rocha, M.J.; Cass, Q.B.; Tiritan, M.E. Development and optimization of a HPLC–DAD method for the determination of diverse, pharmaceuticals in estuarine surface waters. J Chromato Sci 2010, 48, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, L.; Callejon, M. Occurrence of pharmaceutically active compounds during 1-year period in waste-waters from four wastewater treatment plants in Seville (Spain). J Hazard Mat 2009, 164, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; Pedro, C.; Paxeus, N. Effluent from drug manufactures contains extremely high levels of pharmaceuticals. J Hazard Mater 2007, 53, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaider, L.A.; Rudel, R.A.; Ackerman, J.M.; Dunagan, S.C.; Brody, J.C. Pharmaceuticals, perfluorosurfactants, and other organic wastewater compounds in public drinking water wells in a shallow sand and gravel aquifer. Sci Tot Environ 2014, 468, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, R.S.; Singare, P.U.; Pimple, D.S. Study on physicochemical parameters of waste water effluents from Taloja industrial area of Mumbai, India. Int J Eco 2011, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lokhande, R.S.; Singare, P.U.; Pimple, D.S. Toxicity study of heavy metals pollutants in waste water effluent samples collected from Taloja industrial estate of Mumbai, India. Res Environ 2011, 1, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Shivkumar, K.; Biksham, G. Statistical approach for the assessment of water pollution around industrial areas: a case study from Patancheru, Medak district, India. Environ Mon Assess 1995, 36, 229–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, R.V.; Krishna, M.V.; Makam, R.; Asith, K.A. Physicochemical analysis of effluents from pharmaceutical industry and its efficiency study. Int J Eng Res Appl 2012, 2, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Singare, P.U.; Dhabarde, S.S. Studies on pollution due to discharge of effluent from pharmaceutical industries of Dombivali industrial belt of Mumbai, India. Int Lett Chem Phys Astrol 2014, 3, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.N.; Srivastava, G.; Bhatt, A. Physicochemical determination of pollution in wastewater in Dehradun. Curr World Environ 2012, 7, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodhar, U.; Reddy, M.V. Impact of pharmaceutical industry treated effluents on the water quality of river Uppanar, South east coast of India: a case study. Appl Water Sci 2013, 3, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankpal, S.T.; Naikwade, P.V. Heavy metal concentration in effluent discharge of pharmaceutical industries. Sci Res Rep 2012, 2, 88–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ramola, B.; Singh, A. Heavy metal concentrations in pharmaceutical effluents of industrial area of Dehradun (Uttarakhand), India. Int J Environ Sci Res 2013, 1, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, T.; Cherukupalli, A. The cost of cheap medicines: antibiotic pollution in Patancheru. 2010. Available online: http://anilcherukupalli.com/the-cost-of-cheap-medicines-antibiotic-pollution-inpatancheru/ (accessed on 15 October 2012).
- Greenpeace. State of community health at Medak district. 2004. Available online: http://www.greenpeace.org/india/Global/india/report/2004/10/state-of-community-health-at-m.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2012).
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Separation of aluminum and plastic by metallurgy method for recycling waste pharmaceutical blisters. J Clean Prod 2015, 102, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Water sanitation health. Information Sheet: Pharmaceuticals in drinking-water. 2013. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/emerging/info_sheet_pharmaceuticals/en/index.html (accessed on 5 June 2014).
- Buerge, I.J.; Buser, H.R.; Poiger, T.; Müller, M.D. Occurrence and fate of cytostatic drugs cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide in wastewater and surface water. Environ Sci Tech 2006, 40, 7242–7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.C.; Jürgens, M.D.; Williams, R.; Kümmerer, K.; Kortenkamp, A.; Sumpter, J.P. Do cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs discharged into rivers pose a risk to the environment and human health? An overview and UK case study. J Hydrol 2008, 348, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B. Nature of chiral drugs and their occurrence in environment. J Xenobiotics 2014, 4, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Gupta, V.K.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Singh, P.; Sharma, B. Role of racemization in optically active drugs development. Chirality 2007, 19, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
© Copyright V. Chander et al., 2016 Licensee PAGEPress, Italy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 License (CC BY-NC 4.0).
Share and Cite
Chander, V.; Sharma, B.; Negi, V.; Aswal, R.S.; Singh, P.; Singh, R.; Dobhal, R. Pharmaceutical Compounds in Drinking Water. J. Xenobiot. 2016, 6, 5774. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2016.5774
Chander V, Sharma B, Negi V, Aswal RS, Singh P, Singh R, Dobhal R. Pharmaceutical Compounds in Drinking Water. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2016; 6(1):5774. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2016.5774
Chicago/Turabian StyleChander, Vikas, Bhavtosh Sharma, Vipul Negi, Ravinder Singh Aswal, Prashant Singh, Rakesh Singh, and Rajendra Dobhal. 2016. "Pharmaceutical Compounds in Drinking Water" Journal of Xenobiotics 6, no. 1: 5774. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2016.5774
APA StyleChander, V., Sharma, B., Negi, V., Aswal, R. S., Singh, P., Singh, R., & Dobhal, R. (2016). Pharmaceutical Compounds in Drinking Water. Journal of Xenobiotics, 6(1), 5774. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2016.5774




