Introduction
Bivalves are filter feeders widely used in ecotoxicological monitoring because of their sensitivity to contaminants present in the environment. [1,2] Their immunity depends of their freely open blood cells, which are directly in contact with xenobiotics make them good species to monitor environmental contamination. Decreased immunotoxicity can affect host resistance and result in an increase in disease incidence with potential effects at the population level, reinforcing the ecological relevance of studying this endpoint in bivalves. [3] However, this endpoint can be subjected to natural variability related to environmental abiotic factors. The presence of two species of bivalves in the Saguenay Fjord, the soft-shell clam (Mya arenaria) and the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis), allows us to compare the immunological status of these two species.
The Saguenay Fjord is the main tributary of the St. Lawrence Estuary and has an important variation of salinity. This gradient allows the establishment of a rich biodiversity. However, it also limits the distribution of some species, such as M. edulis, which is absent upstream of Anse St-Étienne (ASE), given that the salinity is under 18 psu. This tributary is also subject to various sources of contamination. [4,5] A complex mixture of urban, industrial and agricultural xenobiotics arising from upstream Saguenay watershed and atmospheric deposition contaminate the Saguenay-St. Lawrence. [6,7,8,9] Because of its industrial past, the sedimentary matrix of Saguenay is contaminated with toxic and potentially bioaccumulative substances like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, heavy metals and tributyltin. [4,5,10] In addition, municipal wastewater from local villages may not be properly treated and flows directly into the watershed. [6,11] It is therefore crucial to assess the toxicity of all these xenobiotics on sentinel species. In this context, we have assessed the immunological response of two bivalves: the soft-shell-clams and the blue mussels and compared their status according to the sampling site.
We first evaluated the impact of the salinity on the immunocompetence of M. edulis and M. arenaria, between two reference stations, [12] ASE (18 psu) and Baie du Moulin à Baude (BMB) at salinity corresponding to the estuary (28 psu). Then, we compared the impact of corresponding harbors in two bivalve species with different habitats in the attempt to examine the cumulative effects of pollution and salinity in these bivalves.
Materials and Methods
Site location of bivalve collection
Bivalves were collected in 2013 at 4 different stations [ASE, BMB, Baie de Tadoussac (BT), Baie Sainte-Catherine (BSC)] in the Saguenay River, Québec, Canada (48° 15’ N, 70° 09’ W) (Figure 1). ASE and BMB were not exposed to any direct contamination (reference sites) but differed in salinity at 18 and 28 part per thousand respectively. The other two stations, BT and BSC were the two polluted stations because of the intensive commercial and recreational boating activities. [4,12] At each site, 15 clams and 15 mussels were sampled and maintained at 4°C in icebox.
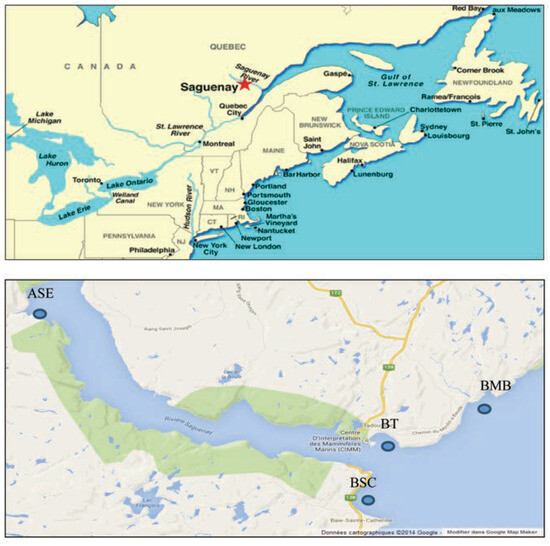
Figure 1.
Map of the study area showing the 4 sites where bivalves were sampled. BT, Baie de Tadoussac; BSC, Baie Sainte-Catherine; BMB, Baie du Moulin-à-Baude; ASE, Anse Saint-Étienne.
Viability and phagocytosis assessments
Hemolymph was extracted from the adductor muscle using 3 mL syringe with 23 G needle. The viability was determined by flow cytometry using a BD Accuri™ C6 (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA, USA) and by propidium iodide (PI) staining. Phagocytosis was evaluated according to the method developed by our laboratory. [13] Briefly, hemocytes were mixed with yellow-green latex FluoSpheres (Molecular Probes Inc., Eugene, OR, USA) at a ratio of 1:100 (hemocytes:beads) in flat-bottom 96 wells plate. The mixtures were incubated at 20°C in the dark. After 18 h, the supernatant was delicately removed. The cells were fixed with 200 µL of 0.5% formalin in sterile water. Phagocytosis was measured by flow cytometry, BD Accuri™ C6 (Becton Dickinson) following the analysis of hemocytes according to their scattering properties of forward and right angle. A total of 3000 events were acquired to analyze fluorescence frequency distribution on FL1 and determined phagocytic activity (one bead and more) and phagocytic efficacy (three beads and more). Data collection and analysis were performed with BD Accuri™ C6 (Becton Dickinson) software.
Statistical analysis
The difference between each station in the Saguenay River was evaluated by analysis if variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s test for pairwise comparisons. Statistical analyses were performed using SigmaStat (version 3.5; Systat Software, Inc., San Jose, CA, USA). Significance was set at P<0.05.
Results
The hemocytes viability of each species was not significantly different for both species between ASE and BMB. However, the phagocytic activities significantly differed for Mya arenaria. No variations were observed for M. edulis in salinity gradient (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Phagocytic activity (1 bead and more) and efficacy (3 beads and more) of Mya arenaria (n=15) and Mytilus edulis (n=15) from two reference stations in the Saguenay River in a salinity gradient (ASE; 18 psu and BMB; 28 psu). *Significant difference between station, P<0.05.
The hemocytes viability and phagocytosis were then evaluated for the polluted stations (BT and BSC) compared with reference stations but only with BMB for M. arenaria because of salinity impact observed in Figure 3. For both species, no variations were observed in the hemocytes viability despite the anthropic activities and known contamination present at BT and BSC. For M. arenaria, no differences were observed in hemocytes phagocytic activity and efficacy, but significant variation occurs for M. edulis. This variation was observed between ASE and only one polluted station (BSC), where the phagocytosis significantly increased. However, no modulation of the phagocytic competence has been observed when BMB was compared with BT and BSC for both species. On the other side, the phagocytosis of mussel hemocytes of the two polluted stations differs significantly and was increased at BSC (Figure 3). The hemocytes viability and phagocytosis of each species were compared to determine the immunological modulation at each station. In the reference stations, ASE and BMB, no significant differences were observed between clams and mussels. In contrast, the hemocytes viability showed no differences in contaminated stations, at BT and BSC, but the immune response was significantly modulated. In BT, the phagocytic competence of soft-shell clams was higher than for mussels. In BSC, mussels’ hemocytes had higher phagocytic capacity (1 bead and more) but no differences other were observed for the phagocytic efficacy (3 beads and more).
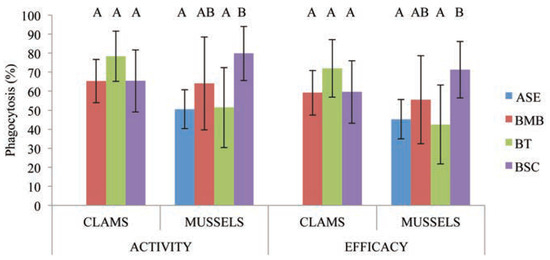
Figure 3.
Phagocytic activity (1 bead and more) and efficacy (3 beads and more) of Mya arenaria (n=15) from three stations and Mytilus edulis (n=15) from four stations in the Saguenay River (ASE is excluded for clams because of the modulation induced by the salinity gradient, see Figure 1). Letters indicate significant difference between sites, P<0.05.
Discussion
The large distribution of bivalves in the intertidal zone and in the Saguenay makes them good species to follow environmental conditions and contamination. However, the impact of xenobiotics must be evaluated for each species because they are not subject to the same types of exposure. [12,14] The analysis of the immune-modulation in field studies is complex due to the multitude of confounding factors in the habitat of these species may influence this reaction. [12,14] In this study, we want to assess the immunomodulation of M. edulis and Mya arenaria in four different stations in Saguenay Fjord including a salinity gradient between two reference stations. By this investigation, we initially evaluated the impact of this confounding factor, then the anthropic pollution impact in BT and BSC and finally, if both species showed the same immunological response.
The reduction of salinity is already known to induce many physiological changes like growth rate, [15] heart rate, [16,17] respiration [18] and energy acquisition. [19,20] Moreover, a reduction of salinity from 32 psu to 16 psu induced a decrease in the immune response of mussels in controlled conditions. [20] However, our results demonstrate no significant difference between ASE (18 psu) and BMB (28 psu) for this species (Figure 2). This may be explained by the natural adaptation of the mussels from ASE. In contrast, the soft-shell clams hemocytes phagocytic efficacy is significantly lower at ASE (Figure 2). Despite this observed modulation in hemocytes, there are no differences between the immune response of these two bivalves at ASE and BMB.
In contaminated stations, it is noteworthy that M. arenaria and M. edulis seem to be affected differently by the xenobiotics present in the environment, principally at BT. This variation may be caused by a difference in sensitivity for each species facing contamination, [21] but also by the difference in the way of exposure to xenobiotics. [1] Indeed, M. arenaria is exposed directly to sediments and water column contaminants, while M. edulis is only exposed to the xenobiotics when filtering water. [1,4,5,22] Furthermore, the properties of some xenobiotics can change with salinity and affect their biodisponibility enable them to be absorbed by the sediments particles and accumulate in the organisms. [23] Because of this chemical variation, all comparisons with ASE, need to be done with a lot of cautiousness despite the absence of immunological variation in the salinity gradient for mussels (Figure 2). Indeed, both species absorb contaminants in their tissues by filtering water, but the clams also accumulate them through direct contact with sediment and porewater [23] resulting in increased transfer. [24] The sediment matrix in the Saguenay Fjord is more heavily polluted than the water column for a given station, thus exposing the clams to a broader range of contaminants with higher concentrations. [10]
Conclusions
In this study, we demonstrated that mussels living in natural environment and exposed to different salinity (18 psu and 28 psu) adapt their immunocompetence and show no difference in basal immunocompetence. However, the clam is slightly affected by this salinity reduction by a decreased in their phagocytic efficacy. Moreover, stations heavily affected by human activities (BT and BSC), reveal a clear different modulation of the phagocytosis between clams and mussels, highlighting their own sensitivity to pollution. This shows the relevance of using multiple sentinel species in field studies to have a better overview and comprehension of the impact of human activities.
References
- Pellerin, J; Amiard, J-C. Comparison of bioaccumulation of metals and induction of metallothioneins in two marine bivalves (Mytilus edulis and Mya arenaria). Comp Biochem Phys C 2009, 150, 186–95. [Google Scholar]
- Blaise, C; Gagné, F; Pellerin, J; Hansen, PD; Trottier, S. Molluscan shellfish biomarker study of the Quebec, Canada, Saguenay Fjord with the soft-shell clam, Mya arenaria. Environ Toxicol 2002, 17, 170–86. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, TS; Depledge, MH. Immunotoxicity in invertebrates: measurement and ecotoxicological relevance. Ecotoxicology 2001, 10, 5–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gagné, F; Blaise, C; Pellerin, J; Pelletier, E; Strand, J. Health status of Mya arenaria bivalves collected from contaminated sites in Canada (Saguenay Fjord) and Denmark (Odense Fjord) during their reproductive period. Ecotox Environ Safe 2006, 64, 348–61. [Google Scholar]
- Pellerin, J; Fournier, M; Gauthier-Clerc, S; Blaise, C; Garnerot, F; Amiard, J-C; et al. Qu’en est-il de l’état de santé des myes au Saguenay? Un bilan d’études sur plus d’une décennie. Rev Sci Eau 2009, 22, 271–89. [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire, N; Pelletier, E. Chemical and microbial contamination baseline in the Saguenay-St. Lawrence Marine Park (Eastern Canada): concentrations and fluxes from land-based sources. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 2013, 65, 421–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gobeil, C; Rondeau, B; Beaudin, L. Contribution of municipal effluents to metal fluxes in the St. Lawrence River. Environ Sci Technol 2005, 39, 456–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lebeuf, M; Nunes, T. PCBs and OCPs in sediment cores from the lower St. Lawrence Estuary, Canada: evidence of fluvial inputs and time lag in delivery to coring sites. Environ Sci Technol 2005, 39, 1470–8. [Google Scholar]
- Viglino, L; Pelletier, E; Lee, L. Butyltin species in benthic and pelagic organisms of the Saguenay Fjord (Canada) and imposex occurrence in common whelk (Buccinum undatum). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 2006, 50, 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier, E; Desbiens, I; Sargian, P; Côté, N; Curtosi, A; St-Louis, R. Présence des hydrocarbures aromatiques polycycliques (HAP) dans les compartiments biotiques et abiotiques de la rivière et du fjord du Saguenay. Rev Sci Eau 2009, 22, 235–51. [Google Scholar]
- Dionne, S. Plan de conservation des écosystèmes du Parc marin du Saguenay-Saint-Laurent. Parcs, Canada; Parc Marin du Saguenay-Saint-Laurent, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gagné, F; Blaise, C; Pellerin, J; Fournier, M; Durand, MJ; Talbot, A. Relationships between intertidal clam population and health status of the soft-shell clam Mya arenaria in the St. Lawrence Estuary and Saguenay Fjord (Québec, Canada). Environ Int 2008, 34, 30–43. [Google Scholar]
- Brousseau, P; Pellerin, J; Morin, Y; Cyr, D; Blakley, B; Boermans, H. Flow cytometry as a tool to monitor the disturbance of phagocytosis in the clam Mya arenaria hemocytes following in vitro exposure to heavy metals. Toxicology 2000, 142, 145–56. [Google Scholar]
- Vasseur, P; Cossu-Leguile, C. Linking molecular interactions to consequent effects of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) upon populations. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1033–42. [Google Scholar]
- Westerbom, M; Kilpi, M; Mustonen, O. Blue mussels, Mytilus edulis, at the edge of the range: population structure, growth and biomass along a salinity gradient in the north-eastern Baltic Sea. Mar Biol 2002, 40, 991–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhmet, IN; Berger, VJ; Khalaman, VV. The effect of salinity change on the heart rate of Mytilus edulis specimens from different ecological zones. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 2005, 318, 121–6. [Google Scholar]
- Braby, CE; Somero, GN. Following the heart: temperature and salinity effects on heart rate in native and invasive species of blue mussels (genus Mytilus). J Exp Biol 2006, 209, 2554–66. [Google Scholar]
- Stickle, WB; Sabourin, TD. Effects of salinity on the respiration and heart rate of the common mussel, Mytilus edulis L., and the black chiton, Katherina tunicata (Wood). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 1979, 41, 257–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, JPA; Thompson, RJ. The effects of coastal and estuarine conditions on the physiology and survivorship of the mussels Mytilus edulis, M. trossulus and their hybrids. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 2001, 265, 119–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bussell, JA; Gidman, EA; Causton, DR; Gwynn-Jones, D; Malham, SK; Jones, MLM; et al. Changes in the immune response and metabolic fingerprint of the mussel, Mytilus edulis (Linnaeus) in response to lowered salinity and physical stress. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 2008, 358, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, M; Pellerin, J; Clermont, Y; Morin, Y; Brousseau, P. Effects of in vivo exposure of Mya arenaria to organic and inorganic mercury on phagocytic activity of hemocytes. Toxicology 2001, 161, 201–11. [Google Scholar]
- White, PA; Blaise, C; Rasmussen, JB. Detection of genotoxic substances in bivalve molluscs from the Saguenay Fjord (Canada), using the SOS chromotest. Mutat Res 1997, 392, 277–300. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, RH. Model of PAH and PCB bioaccumulation in Mya arenaria and application for site assessment in conjunction with sediment quality screening criteria. MIT library, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, M; Pellerin, J; Lebeuf, M; Brousseau, P; Morin, Y; Cyr, D. Effects of exposure of Mya arenaria and Mactromeris polynyma to contaminated marine sediments on phagocytic activity of hemocytes. Aquat Toxicol 2002, 59, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
©Copyright A. Beaudry et al., 2015 Licensee PAGEPress, Italy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 3.0 License (CC BY-NC 3.0).