Combined Effects of Nano-Polystyrene and Heavy Metal Mixture on the Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals and Physiological Changes in Macrobrachium rosenbergii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Acclimation of Shrimps
2.2. Chemicals
2.2.1. Preparation of the Heavy Metal Cocktail
2.2.2. Nano-Polystyrene Particles
2.3. Preparation of Experimental Solutions
2.4. Experimental Design
- I: Control group (no exposure);
- II: Heavy metal cocktails (HMCs) at 0.5 mg/L;
- III: NPs50 + HMC, consisting of 50 µg/L NPs combined with 0.5 mg/L HMC;
- IV: NPs100 + HMC, with 100 µg/L NPs and 0.5 mg/L HMC;
- V: NPs150 + HMC, containing 150 µg/L NPs and 0.5 mg/L HMC;
- VI: NPs200 + HMC, which included 200 µg/L NPs and 0.5 mg/L HMC;
- VII: NPs250 + HMC, with 250 µg/L NPs and 0.5 mg/L HMC.
2.5. Shrimp Sampling
2.6. Biochemical and Antioxidant Biomarkers
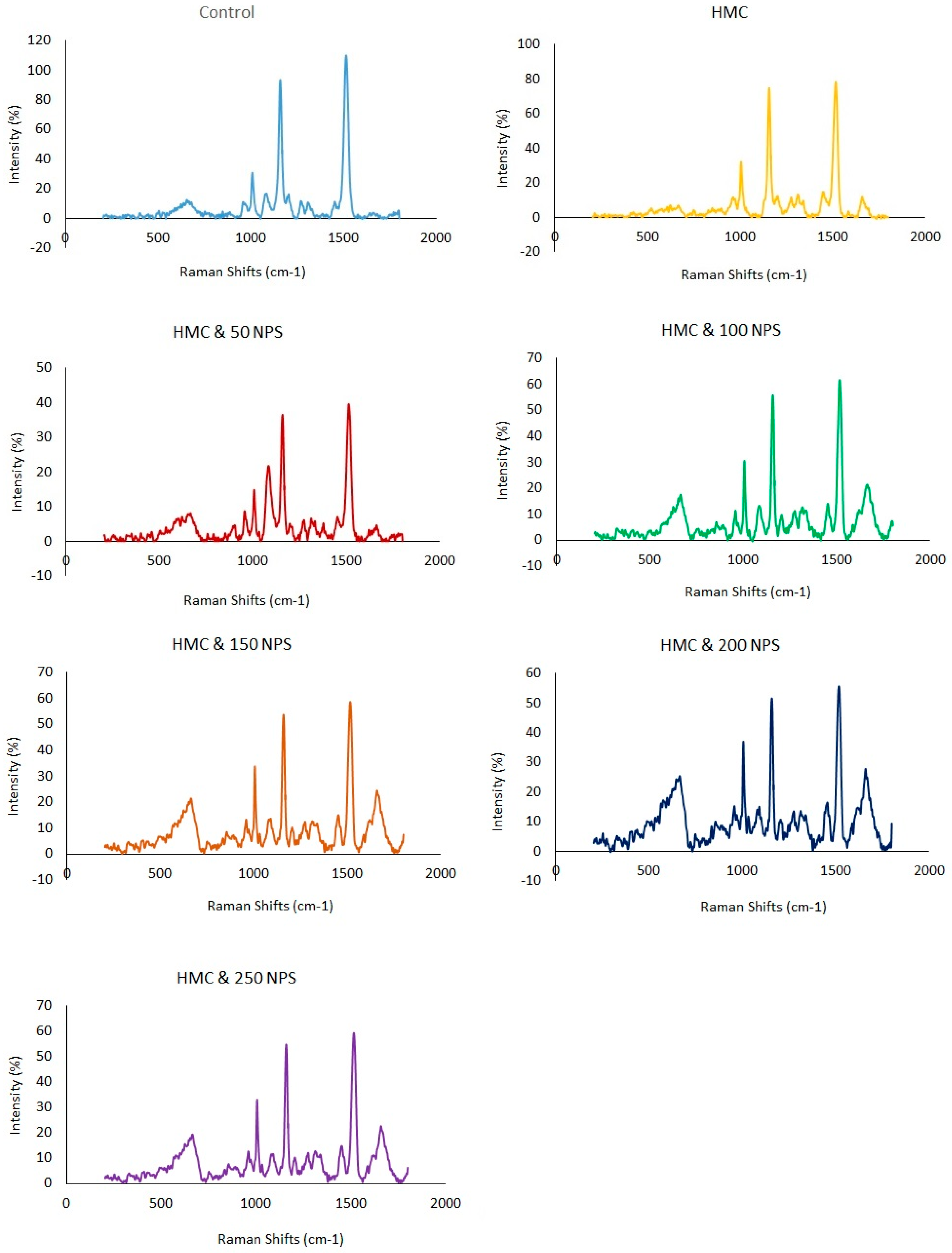
2.7. Metabolic Profile Analysis
2.8. Bio-Concentrations of Heavy Metals Analysis
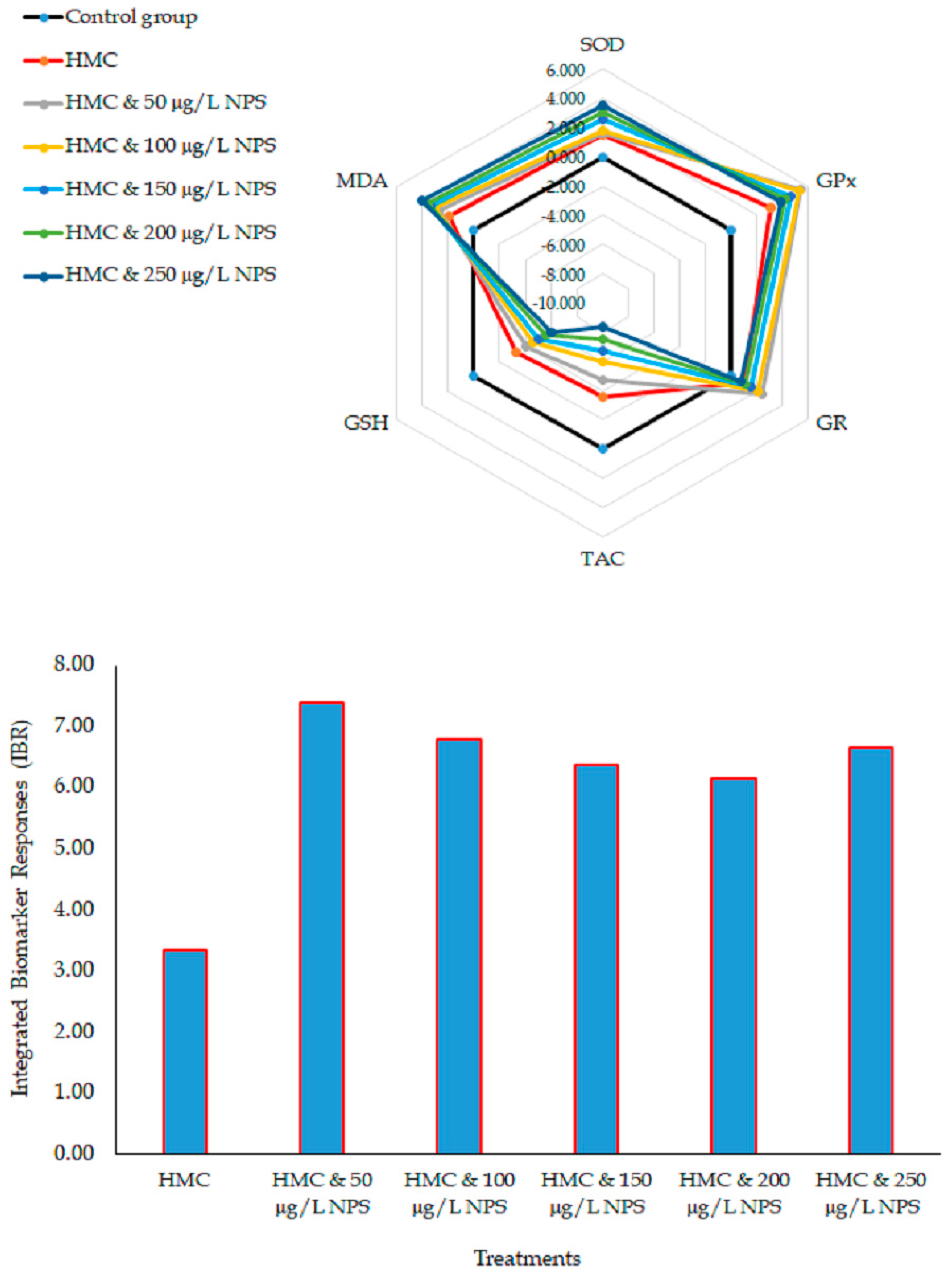
2.9. Integrated Biomarker Response (IBR) Calculation
2.10. Statistical Analysis
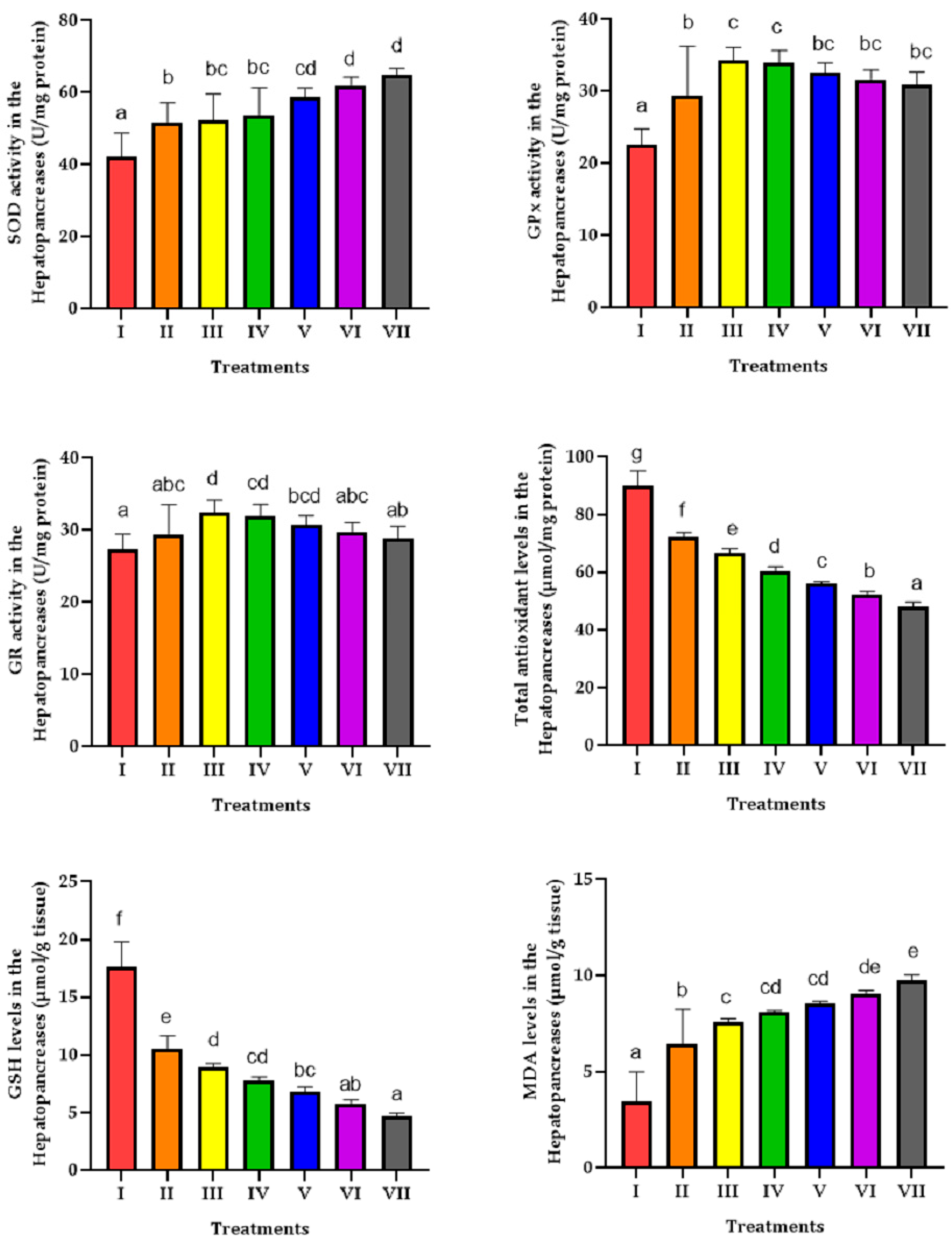
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gangadoo, S.; Owen, S.; Rajapaksha, P.; Plaisted, K.; Cheeseman, S.; Haddara, H.; Truong, V.K.; Ngo, S.T.; Vu, V.V.; Cozzolino, D.; et al. Nano-plastics and their analytical characterisation and fate in the marine environment: From source to sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 138792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Multisanti, C.R.; Ferrara, S.; Piccione, G.; Faggio, C. Plastics and their derivatives are impacting animal ecophysiology: A review. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 291, 110149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, W.; Huang, R.; Lv, X.; Jing, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Y. Role of surface functionalities of nano-plastics on their transport in seawater-saturated sea sand. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113177. [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Herrera, A.; Garcia-Torné, M.; Borrell-Diaz, X.; Abad, E.; Llorca, M.; Villanueva, C.M.; Farré, M. Exposure to micro(nano)plastics polymers in water stored in single-use plastic bottles. Chemosphere 2023, 343, 140106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wong, K.K.; Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, T.; Stanescu, S.; Boult, S.; van Dongen, B.; Mativenga, P.; Li, L. Characteristics of nano-plastics in bottled drinking water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirinzi, G.F.; Llorca, M.; Seró, R.; Moyano, E.; Barceló, D.; Abad, E.; Farré, M. Trace analysis of polystyrene microplastics in natural waters. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gola, D.; Tyagi, P.K.; Arya, A.; Chauhan, N.; Agarwal, M.; Singh, S.; Gola, S. The impact of microplastics on marine environment: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.; Giltrap, M.; Chambers, G. Evaluation of non-invasive toxicological analysis of nano-polystyrene in relative in vivo conditions to D. magna. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 2832–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, Z.; Thomas, J.; Shivashankar, M.; Chandrasekaran, N. The impact of nano-polystyrene on human serum albumin–paracetamol interactions: Understanding the impact on therapeutic development and safety. Environ. Sci. Nano 2024, 11, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, P.; Naagar, M.; Chalia, S.; Dhar, R.; Ravelo, B.; Thakur, P.; Thakur, A. Recent advances in synthesis, characterization, and applications of nanoparticles for contaminated water treatment-A review. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 1526–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Tan, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Tan, X.; Chen, Q. Characteristic of microplastics in the atmospheric fallout from Dongguan city, China: Preliminary research and first evidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24928–24935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, T.; Tanaka, S.; Kohama-Inoue, A.; Watanabe, A. The quantification of the airborne plastic particles of 0.43–11 μm: Procedure development and application to atmospheric environment. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kik, K.; Bukowska, B.; Sicińska, P. Polystyrene nanoparticles: Sources, occurrence in the environment, distribution in tissues, accumulation and toxicity to various organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Deng, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, F.; Luo, T.; Kuang, H.; Kuang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, D. Exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics induces hepatotoxicity involving NRF2-NLRP3 signaling pathway in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, N.A.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Ahmed, Z.S.O.; Galal, M.K.; Rashad, M.M.; Youssef, A.M.; Elleithy, E.M. Exposure to Polystyrene nanoparticles induces liver damage in rat via induction of oxidative stress and hepatocyte apoptosis. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 94, 103911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Fan, S.; Yang, Y.; Long, Y.; Liu, X. Acute exposure to polystyrene nanoparticles promotes liver injury by inducing mitochondrial ROS-dependent necroptosis and augmenting macrophage-hepatocyte crosstalk. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2024, 21, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Huang, Z. Underestimated health risks: Polystyrene micro-and nanoplastics jointly induce intestinal barrier dysfunction by ROS-mediated epithelial cell apoptosis. Part. Fibre toxicol. 2021, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kaur, M.; Sharma, K.; Bunkar, S.K.; John, P.; Bhatnagar, P. Nano polystyrene induced changes in anxiety and learning behaviour are mediated through oxidative stress and gene disturbance in mouse brain regions. NeuroToxicology 2023, 99, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, B.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, W. Polystyrene micro (nano) plastics damage the organelles of RBL-2H3 cells and promote MOAP-1 to induce apoptosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Yang, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Liang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Teng, M.; Hou, G.; Niu, L.; et al. Heteroaggregation and sedimentation of natural goethite and artificial Fe3O4 nanoparticles with polystyrene nanoplastics in water. Carbon Res. 2024, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghinia, H.; Hanachi, P.; Ramezani, R.; Karbalaei, S. Toxic effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer and HFF-2 normal fibroblast cells: Viability, cell death, cell cycle and antioxidant enzyme activity. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2025, 37, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.; Mortimer, M.; Richter, J.; Rani-Borges, B.; Yu, Z.; Heinlaan, M.; Lin, S.; Ivask, A. Hazard of polystyrene micro-and nanospheres to selected aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, P.; Cai, M.; Wu, D.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Polystyrene nanoplastic exposure induces immobilization, reproduction, and stress defense in the freshwater cladoceran Daphnia pulex. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, S.L.; Hsieh, S.; Xu, R.Q.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, C.W.; Singhania, R.R.; Dong, C.D. Toxicological effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on marine organisms. Environ. Technol. Innovation. 2023, 30, 103073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sökmen, T.Ö.; Sulukan, E.; Türkoğlu, M.; Baran, A.; Özkaraca, M.; Ceyhun, S.B. Polystyrene nanoplastics (20 nm) are able to bioaccumulate and cause oxidative DNA damages in the brain tissue of zebrafish embryo (Danio rerio). NeuroToxicology 2020, 77, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehr, S.; Esser, D.; Schlechtriem, C. Invertebrate species for the bioavailability and accumulation assessment of manufactured polymer-based nano-and microplastics. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 961–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Lu, S.; Hu, J.; Cao, C.; He, D. Polystyrene (nano) microplastics cause size-dependent neurotoxicity, oxidative damage and other adverse effects in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousaviyon, Z.; Pourkhabbaz, H.R.; Banaee, M.; Khodadoust, S.; Pourkhabbaz, A.R.; Trivedi, A.; Faggio, C.; Multisanti, C.R. Toxicity of Crude Oil Wastewater Treated with Nano-ZnO as a Photocatalyst on Labeo rohita: A Biochemical and Physiological Investigation. J. Xenobiotics 2025, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, R.; Ramaswamy, S.N. Nanoplastics as Trojan Horses: Deciphering Complex Connections and Environmental Ramifications: A Review. Chem. Afr. 2024, 7, 2265–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.C.; Pham, M.H. Ecotoxicological effects of microplastics on aquatic organisms: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44716–44725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, S.; Huang, M.; Ma, H.; Wan, Z.; Feng, J.; Ding, S.; Li, X. Toxic effects of nanopolystyrene and cadmium on the intestinal tract of the Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 270, 115936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, I.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Khan, F.U.; Tan, K.A.; Waiho, K.; Wang, Y.; Kwan, K.Y.; Hu, M. Combined effects of nanoplastics and heavy metal on antioxidant parameters of juvenile tri-spine horseshoe crabs. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1005820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Mi, Y.; Xiang, J.; Gong, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, T. Chronic toxicity effects of sediment-associated polystyrene nanoplastics alone and in combination with cadmium on a keystone benthic species Bellamya aeruginosa. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliwat, G.C.; Velasquez, S.; Robil, J.L.; Chan, M.; Traifalgar, R.F.; Tayamen, M.; A Ragaza, J. Growth and immune response of giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man) postlarvae fed diets containing Chlorella vulgaris (Beijerinck). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1666–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreescu, S.; Henkel, R.; Khelfi, A. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rifai, N. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics-E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Banaee, M.; Zeidi, A.; Gholamhosseini, A.; Shakeri, R.; Faggio, C.; Multisanti, C.R. Potential synergistic effects of microplastics and zinc oxide nanoparticles: Biochemical and physiological analysis on Astacus leptodactylus. Ecotoxicology 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beliaeff, B.; Burgeot, T. Integrated biomarker response: A useful tool for ecological risk assessment. Environ. Toxicol. chem. 2002, 21, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodkovicova, N.; Hollerova, A.; Svobodova, Z.; Faldyna, M.; Faggio, C. Effects of plastic particles on aquatic invertebrates and fish—A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 96, 104013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multisanti, C.R.; Riolo, K.; Impellitteri, F.; Zicarelli, G.; Vazzana, I.; Cafeo, G.; Russo, M.; Dugo, P.; Faggio, C.; Giannetto, A. Bergamot (Citrus bergamia) as a potential anti-stress agent: Counteracting cellular and physiological changes by Sodium Lauryl Sulphate in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 371, 125939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Ye, B.; Qian, H.; Guo, Z.; Bai, H.; Gong, J.; Feng, J.; Ma, K. Comparative transcriptome analysis of the gills and hepatopancreas from Macrobrachium rosenbergii exposed to the heavy metal Cadmium (Cd2+). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafiz, F.; Islam, M.M.; Saha, B.; Hossain, M.K.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M. Bioaccumulation of trace metals in freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii from farmed and wild sources and human health risk assessment in Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 16426–16438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, N.P.C.; Ha, N.N.; Ikemoto, T.; Tuyen, B.C.; Tanabe, S.; Takeuchi, I. Bioaccumulation and distribution of trace elements in tissues of giant river prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Decapoda: Palaemonidae) from South Vietnam. Fish. Sci. 2008, 74, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shen, Y.-C.; Liang, J.-R.; Liu, H.; Chen, T.-C.; Guo, H. Accumulation and Depuration of Cd and its Effect on the Expressions of Metallothionein and Apoptotic Genes in Litopenaeus vannamei. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, T.; Lin, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Mai, K. The assessment of dietary organic zinc on zinc homeostasis, antioxidant capacity, immune response, glycolysis and intestinal microbiota in white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei Boone, 1931). Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyachandran, S.; Chellapandian, H.; Park, K.; Kwak, I.-S. A review on the involvement of heat shock proteins (extrinsic chaperones) in response to stress conditions in aquatic organisms. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.-M.; Niu, R.-G.; Wang, H.; Li, X.-Y.; Zeng, Q.-F.; Lan, J.-F. Symbiotic hemolymph bacteria reduce hexavalent chromium to protect the host from chromium toxicity in Procambarus clarkii. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bao, Z.; Guo, J.; Su, X.; Zou, Y.; Guo, H. Comparative transcriptome analysis of the hepatopancreas from Macrobrachium rosenbergii exposed to the heavy metal copper. Animals 2024, 14, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliso, M.C.; Billè, B.; Cappello, T.; Maisano, M. Polystyrene micro- and nanoplastics (PS MNPs): A review of recent advances in the use of -omics in PS MNP toxicity studies on aquatic organisms. Fishes 2024, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Feng, G.; Yan, Y. Effects of polystyrene nanoplastics and copper on gill tissue structure, metabolism, and immune function of the Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1538734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yang, P.; Qiao, Y.; Su, M.; Zhang, G. Polystyrene nanoplastics decrease molting and induce oxidative stress in adult Macrobrachium nipponense. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 122, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-W.; Cho, S.; Lee, Y.-M. Combined effects of microplastics and methylmercury on the activity of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter in the brackish water flea Diaphanosoma celebensis. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2024, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zhong, Y.; Wei, W.; Luo, M.; Xu, X. Combined exposure to microplastics and copper elicited size-dependent uptake and toxicity responses in red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkia). J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, A.K.; Srivastava, S.; Srivastav, S.K.; Faggio, C.; Sekiguchi, T.; Suzuki, N. Response of ultimobranchial and parathyroid glands of the Indian skipper frog, Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis to cadmium toxicity. Iran. J. Toxicol. 2019, 13, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Li, F.; Deng, D.-M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C. Cadmium availability in rice paddy fields from a mining area: The effects of soil properties highlighting iron fractions and pH value. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 209, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Xia, S.; Zhao, J. Adsorption behavior of commercial biodegradable plastics towards pollutants during the biodegradation process: Taking starch-based biodegradable microplastics, oxytetracycline and Cu (II) as examples. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 366, 125538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, H.; Kamogashira, T.; Yamasoba, T. Heavy metal exposure: Molecular pathways, clinical implications, and protective strategies. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feola, A.; Madheswaran, M.; Romano, G.; Tewelde, A.G.; Maina, E.W.; D’ABrosca, G.; della Valle, M.; Cocca, M.; Errico, M.E.; Isernia, C.; et al. Polystyrene nanoparticles induce DNA damage and apoptosis in HeLa cells. Heliyon 2024, 11, e41298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.-Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, L.; Ge, Y.-P.; Liu, B.; Li, X.-F. The essentiality of dietary myo-inositol to oriental river prawn (Macrobrachium nipponense): Evidence in growth performance, lipid metabolism and mitochondrial function. Aquaculture 2023, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaee, M.; Beitsayah, A.; Prokić, M.D.; Petrović, T.G.; Zeidi, A.; Faggio, C. Effects of cadmium chloride and biofertilizer (Bacilar) on biochemical parameters of freshwater fish, Alburnus mossulensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 268, 109614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, F.N.; Guimarães, A.T.B.; Silva, F.G.; da Luz, T.M.; Silva, A.M.; Pereira, P.S.; Malafaia, G. Effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on Ctenopharyngodon idella (grass carp) after individual and combined exposure with zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Gao, T.; Liu, G.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, T.; Sun, M.; Li, J.; Ji, F.; Si, Q.; Jiang, Q. The effect of a polystyrene nanoplastic on the intestinal microbes and oxidative stress defense of the freshwater crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z. Combined effects of micro/nanoplastics and ZnO nanoparticles on lactuca sativa seedlings under varied lighting. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 296, 110233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidi, A.; Sayadi, M.H.; Rezaei, M.R.; Banaee, M.; Gholamhosseini, A.; Pastorino, P.; Faggio, C. Single and combined effects of CuSO4 and polyethylene microplastics on biochemical endpoints and physiological impacts on the narrow-clawed crayfish Pontastacus leptodactylus. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaikumar, I.M.; Periyakali, S.B.; Rajendran, U.; Joen-Rong, S.; Thanasekaran, J.; Tsorng-Harn, F. Effects of microplastics, polystyrene, and polyethylene on antioxidants, metabolic enzymes, HSP-70, and myostatin expressions in the giant river prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii: Impact on survival and growth. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varó, I.; Perini, A.; Torreblanca, A.; Garcia, Y.; Bergami, E.; Vannuccini, M.L.; Corsi, I. Time-dependent effects of polystyrene nanoparticles in brine shrimp Artemia franciscana at physiological, biochemical and molecular levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Deng, B.; Kang, Z.; Araujo, P.; Mjøs, S.A.; Liu, R.; Lin, J.; Yang, T.; Qu, Y. Tissue accumulation of polystyrene microplastics causes oxidative stress, hepatopancreatic injury and metabolome alterations in Litopenaeus vannamei. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 256, 114871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moruf, R.O.; Sanni, Z.A.; Lawal-Are, A.O. Hemato-biochemical profiling of a burrowing crab exposed to polystyrene microplastic contaminant. FUDMA J. Sci. 2020, 4, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamhosseini, A.; Banaee, M.; Zeidi, A.; Multisanti, C.R.; Faggio, C. Individual and combined impact of microplastics and lead acetate on the freshwater shrimp (Caridina fossarum): Biochemical effects and physiological responses. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2024, 262, 104325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multisanti, C.R.; Zicarelli, G.; Caferro, A.; Filice, M.; Faggio, C.; Vazzana, I.; Impellitteri, F. From personal care to coastal concerns: Investigating polyethylene glycol impact on mussel’s antioxidant, physiological, and cellular responses. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ye, Y.; Yuan, H.; Rihan, N.; Han, M.; Liu, X.; Che, X. Exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics induces apoptosis, autophagy, histopathological damage, and intestinal microbiota dysbiosis of the Pacific whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramazinia, M.; Sabzghabaei, G.R.; Multisanti, C.R.; Banaee, M.; Piccione, G.; Trivedi, A.; Faggio, C. Individual and combined effects of microplastics and diphenyl phthalate as plastic additives on male goldfish: A biochemical and physiological investigation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 290, 110144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghi, B.N.; Banaee, M. Effects of micro-plastic particles on paraquat toxicity to common carp (Cyprinus carpio): Biochemical changes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J. Toxic effects of cadmium and lead exposure on intestinal histology, oxidative stress response, and microbial community of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals (µg/g Tissue) | Control | 0.5 mg/L HMC | 0.5 mg/L HMC & 50.0 µg/L NPS | 0.5 mg/L HMC & 100 µg/L NPS | 0.5 mg/L HMC & 150 µg/L NPS | 0.5 mg/L HMC & 200 µg/L NPS | 0.5 mg/L HMC & 250 µg/L NPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 6.59 ± 1.28 a | 13.51 ± 1.87 b | 15.33 ± 3.61 bc | 18.33 ± 3.44 c | 25.67 ± 5.32 d | 27.83 ± 4.45 de | 31.83 ± 4.45 e |
| Cu | 2.49 ± 0.98 a | 6.50 ± 2.07 ab | 10.67 ± 5.24 bc | 13.83 ± 2.32 c | 21.83 ± 8.59 d | 34.33 ± 3.67 e | 37.00 ± 2.19 e |
| Zn | 4.85 ± 2.15 a | 11.90 ± 2.65 b | 13.33 ± 3.01 b | 15.17 ± 2.79 b | 22.83 ± 6.55 c | 26.67 ± 5.99 cd | 28.17 ± 4.54 d |
| Mg | 1.00 ± 0.64 a | 2.53 ± 1.23 ab | 4.62 ± 2.63 b | 8.00 ± 1.10 c | 13.00 ± 3.52 d | 16.67 ± 2.88 e | 17.50 ± 2.43 e |
| Co | 0.72 ± 0.46 a | 2.15 ± 0.32 ab | 4.33 ± 2.25 b | 5.50 ± 2.35 b | 7.67 ± 2.25 c | 9.00 ± 0.63 c | 9.50 ± 0.55 c |
| Mn | 1.76 ± 0.50 a | 5.00 ± 0.87 ab | 11.17 ± 4.49 b | 13.33 ± 3.01 c | 21.00 ± 6.99 d | 28.67 ± 5.16 e | 29.50 ± 4.09 e |
| V | 0.40 ± 0.22 a | 1.95 ± 0.32 ab | 3.33 ± 1.03 bc | 4.00 ± 0.63 bc | 5.67 ± 1.86 c | 11.17 ± 2.14 d | 11.33 ± 1.75 d |
| Cd | 0.93 ± 0.51 a | 7.85 ± 0.96 a | 23.83 ± 4.71 b | 29.33 ± 5.28 b | 43.00 ± 12.41 c | 46.00 ± 8.99 cd | 53.50 ± 9.01 d |
| Ni | 0.56 ± 0.42 a | 5.53 ± 1.12 b | 7.50 ± 2.26 b | 7.67 ± 1.75 b | 11.83 ± 4.26 c | 16.50 ± 2.59 d | 18.17 ± 2.23 d |
| Pb | 0.71 ± 0.45 a | 5.05 ± 2.14 b | 8.00 ± 2.90 bc | 9.17 ± 1.72 c | 15.83 ± 6.24 d | 19.00 ± 3.03 de | 21.50 ± 2.95 e |
| Biochemical Parameters | Control | 0.5 mg/L HMC | 0.5 mg/L HMC & 50.0 µg/L NPS | 0.5 mg/L HMC & 100 µg/L NPS | 0.5 mg/L HMC & 150 µg/L NPS | 0.5 mg/L HMC & 200 µg/L NPS | 0.5 mg/L HMC & 250 µg/L NPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (U/g protein) | |||||||
| AST | 8.8 ± 1.4 b | 5.6 ± 2 a | 5.3 ± 1.9 a | 5.1 ± 1.8 a | 4.9 ± 1.6 a | 4.7 ± 1.5 a | 4.4 ± 1.5 a |
| ALT | 5 ± 1.7 a | 3.2 ± 1.4 a | 3.1 ± 1.3 a | 3.0 ± 1.2 a | 2.9 ± 1.1 a | 2.7 ± 1.1 a | 2.6 ± 1.0 a |
| ALP | 12.2 ± 2.4 b | 8.8 ± 2.0 ab | 8.3 ± 2.0 a | 7.9 ± 1.8 a | 7.6 ± 1.7 a | 7.3 ± 1.6 a | 6.9 ± 1.5 a |
| GGT | 3.8 ± 1.2 b | 2.2 ± 0.3 a | 1.9 ± 0.4 a | 1.8 ± 0.5 a | 1.9 ± 0.4 a | 1.7 ± 0.4 a | 1.7 ± 0.4 a |
| LDH | 32.8 ± 1.9 a | 56.3 ± 11.8 ab | 57.7 ± 12.2 b | 56.0 ± 11.8 ab | 59.6 ± 15.0 b | 58.1 ± 14.7 b | 56.8 ± 14.4 b |
| (mg/g tissue) | |||||||
| Glycogen | 31.3 ± 5.2 b | 22.8 ± 4.5 a | 21.7 ± 4.3 a | 20.5 ± 4.1 a | 19.3 ± 3.9 a | 18.3 ± 3.9 a | 17.2 ± 3.7 a |
| Cholesterol | 26.5 ± 9.6 a | 25.2 ± 7.8 a | 20.5 ± 5.2 a | 19.3 ± 5.0 a | 18.2 ± 4.7 a | 17.6 ± 4.7 a | 16.8 ± 4.5 a |
| Triglycerides | 43.2 ± 0.51 b | 38.3 ± 0.96 ab | 32.8 ± 4.71 ab | 31.2 ± 5.28 ab | 29.5 ± 12.41 a | 27.8 ± 8.99 a | 30.3 ± 9.01 a |
| Protein | 4.5 ± 0.6 c | 4.0 ± 0.4 bc | 3.8 ± 0.4 abc | 3.6 ± 0.3 ab | 3.5 ± 0.3 ab | 3.3 ± 0.2 a | 3.2 ± 0.2 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banaee, M.; Zeidi, A.; Beitsayah, A.; Multisanti, C.R.; Faggio, C. Combined Effects of Nano-Polystyrene and Heavy Metal Mixture on the Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals and Physiological Changes in Macrobrachium rosenbergii. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040113
Banaee M, Zeidi A, Beitsayah A, Multisanti CR, Faggio C. Combined Effects of Nano-Polystyrene and Heavy Metal Mixture on the Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals and Physiological Changes in Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2025; 15(4):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040113
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanaee, Mahdi, Amir Zeidi, Amal Beitsayah, Cristiana Roberta Multisanti, and Caterina Faggio. 2025. "Combined Effects of Nano-Polystyrene and Heavy Metal Mixture on the Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals and Physiological Changes in Macrobrachium rosenbergii" Journal of Xenobiotics 15, no. 4: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040113
APA StyleBanaee, M., Zeidi, A., Beitsayah, A., Multisanti, C. R., & Faggio, C. (2025). Combined Effects of Nano-Polystyrene and Heavy Metal Mixture on the Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals and Physiological Changes in Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Journal of Xenobiotics, 15(4), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040113









