Abstract
Manganese (Mn) is an essential trace element and a cofactor for several key enzymes, such as mitochondrial superoxide dismutase. Consequently, it plays an important defense role against reactive oxygen species. Despite this, Mn chronic overexposure can result in a neurological disorder referred to as manganism, which shares some similarities with Parkinson’s disease. Mn levels seem regulated by many transporters responsible for its uptake and efflux. These transporters play an established role in many inherited disorders of Mn metabolism and neurotoxicity. Some inherited Mn metabolism disorders, caused by mutations of SLC30A10 and SLC39A14, assume crucial importance since earlier treatment results in a better prognosis. Physicians should be familiar with the clinical presentation of these disorders as the underlying cause of dystonia/parkinsonism and look for other accompanying features, such as liver disease and polycythemia, which are typically associated with SLC30A10 mutations. This review aims to highlight the currently known Mn transporters, Mn-related neurotoxicity, and its consequences, and it provides an overview of inherited and acquired disorders of Mn metabolism. Currently available treatments are also discussed, focusing on the most frequently encountered presentations.
1. Introduction
Manganese (Mn) is a trace element in the body that is found in good concentrations in food [1]; for instance, the content of Mn in human milk is 3–10 μg/L, while that of soy formula is 100-fold higher (i.e., 200–300 μg/L) [2]. As a result, acquired Mn deficiency has not been reported in the literature so far [3]. Consequently, Mn deficiency disorders are mainly inherited. Mn plays a critical role in numerous biological systems, such as cell survival, bone formation, metabolism, and the antioxidant system [3]. Mn is a key element for the catalytic function of multiple metalloenzymes and many metabolic processes [4]. Mn supports a variety of biochemical and physiological processes. It also plays a critical role in enzymatic reactions since it acts as a cofactor for many enzymes, such as Mn superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), which is a key element involved in protection from oxidative damage [5]. Moreover, Mn is involved in arginase activity in the urea cycle, facilitating the removal of ammonia from the body [6]. Mn influences brain function in many ways, especially being a crucial component in neurotransmitter synthesis, including dopamine, glutamate, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which are key elements for maintaining neural signaling and survival [7]. Mn homeostasis disruption has been involved in numerous neurological diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease (PD), Alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), prion disease, and Huntington’s disease [8]. Growing evidence suggests increased Mn exposure can negatively affect cognition, behavior, and intellectual functions, particularly in the developing brain [9].
Mn toxicity can result from an impaired or not fully developed excretion system, transporter malfunction, or excessive exposure to high levels of Mn in the air, food, water, or total parenteral nutrition. Mn toxicity and overload in humans have been commonly described as manganism, an acquired condition that shares many similarities with Parkinsonism. This syndrome is characterized by bradykinesia, rigidity, and tremor [10,11] and it results from the basal ganglia being the primary site of accumulation [12]. Mn intoxication is common in people with a history of mining, welding, battery manufacturing, and use of fungicides [13,14,15]. Nonetheless, Mn toxicity and exposure are not limited to miners or welders. Water and foods containing high levels of Mn represent an increasingly recognized source of contamination for the general population, with important implications for the health systems [16]. Levels of Mn in the atmosphere may also be increased due to gasoline additives [17]. Manganism classically requires occupational exposure of 6 months to 2 years. Once developed, symptoms resulting from Mn toxicity usually persist even when the source of Mn exposure is eliminated [18]. Drug abuse has recently become a recognized cause of Mn toxicity since abusers of methcathinone may be exposed to Mn due to the use of potassium permanganate in the synthesis process [19]. Mn accumulation results in oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [20,21], which lead to neuronal apoptosis and neuroinflammation [22,23]. The effect of maternal Mn exposure on perinatal health has been investigated, and a recent systematic review found no significant association between Mn exposure and gestational diabetes mellitus; nonetheless, other pregnancy complications (e.g., risk of preterm birth) still need further investigation [24]. An inverted U-shaped relationship has been observed between Mn levels in maternal whole blood and birth weight, and between Mn levels in umbilical cord blood and birth weight [25]. Other studies have found that low and high maternal Mn levels are associated with adverse health outcomes in newborns [26,27]. Table 1 summarizes adequate Mn intakes for different age groups.

Table 1.
Suggested Mn intakes per age and sex. Measurement units are in milligrams (mg).
Understanding the balance between Mn’s physiological and pathological roles is crucial for developing preventive and therapeutic strategies against Mn-related neurotoxicity. The objective of the present review is to provide pathophysiological evidence of Mn neurotoxicity and the resultant effects of its accumulation in the brain, discussing the influence of genetic and environmental conditions.
2. Methods and Research Output
The articles for the main search were sought from PubMed with a publication date up to 31 January 2025. We limited the research to English-language manuscripts. The following search terms were used: “manganese”, “hypomanganesemia”, “hypermanganesemia”, “manganese neurotoxicity”, “manganese-exposed workers”, “manganism”, “slc39a14”, “slc39a8”, and “slc30a10”. As the main inclusion criterion, the main focus of the articles should have been occupational and genetic Mn neurotoxicity. We mostly used case series and human studies to describe Mn genetic disorders. The relative search string (“slc39a14” OR “slc39a8” OR “slc30a10”) yielded 539 results. For the Mn metabolism section, we used previous reviews. The relative search string (“manganese” OR “hypomanganesemia” OR “hypermanganesemia” OR “manganese neuro-toxicity” OR “manganese exposed workers” OR “manganism”), filtered to include review studies only, yielded 2973 results. Four authors (GM, AT, FT, and VL) examined the outputs of the research. The first screening was based on title only, followed by abstract and full-text screening. We also included relevant cited literature from the retrieved records. The authors were allowed to look for more articles based on their knowledge. All records were screened based on their relevance to the study objective; 131 records were included after careful screening.
3. Mn Transportation to the Brain
Mn transportation usually happens via dedicated transporters [29]. Multiple transporters for Mn have been described, but not all are selective for Mn transportation [9,29]. Several transporters are involved in Mn transport in the brain across the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Among the carrier proteins involved, the most important ones are divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), zinc-interacting protein 8 (ZIP8, encoded by SLC39A8), ZIP10 (SLC30A10), and ZIP14 (SLC39A14), other carriers involved in Mn transport are also transferrin and transferrin receptor (TR), citrate transporter, and calcium channels. Mn can be transported into the brain in different forms, such as Mn2+, Mn-citrate, or Mn3+-transferrin. As of today, all those mechanisms are believed to play a part in Mn transportation into the brain, and Mn transportation cannot be attributed to a single mechanism [30].
3.1. DMT1
DMT1 belongs to the family of natural resistance-associated macrophage proteins (NRAMPs) [31], which is a family of proteins involved in the host defense against several kinds of infections [32,33]. It is highly expressed in the plasma membrane and in the mitochondria, and it plays a role in mitochondrial iron and Mn acquisition [34]. DMT1 gene mutations are associated with severe microcytic anemia and iron overload [35]. DMT1 is ubiquitously expressed, with the highest expression in the basal ganglia, especially in the caudate nucleus, the putamen, and the substantia nigra. This is why these are the preferred manganese accumulation sites in Mn neurotoxicity [36]. Mn exposure induced DMT1 expression in mouse models in the subventricular zone [37]. DMT1 facilitates Mn transport in its divalent state (Mn2+), and it is regulated by iron status: iron deficiency enhances Mn absorption and brain accumulation [1]. Besides ingestion, olfactory absorption also plays a role in Mn uptake in the brain via DMT1 [38].
3.2. ZIP8 and ZIP14
ZIP8 is a transmembrane protein expressed on the surface of brain capillaries; it usually transports various divalent ions, including Mn, and it is encoded by the SLC39A8 [30,39]. ZIP8 is another membrane transporter whose activity has been recognized to be involved in the inhalation route since it is highly expressed in the lungs [40]. Nonetheless, it is also expressed at the apical side of the choroid plexus papilloma cells, and as such, it favors the influx of Mn through the blood–brain barrier [41]. ZIP8 (SLC39A8) is also localized to the apical membrane of hepatocytes, where it seems to reclaim Mn from the bile, suggesting a role for Mn homeostasis [42]. Mn deficiency mediated by ZIP8 impairment has recently been linked to a high degree of intestinal inflammation, leading to inflammatory bowel disease [43].
ZIP14, on the other hand, mediates the cellular transportation of Mn, Zn, and Fe and is encoded by the SLC39A14 gene [44]. ZIP14 seems to downregulate Mn absorption; as such, an animal model lacking ZIP14 accumulated higher Mn levels in the brain compared to the wild type [45]. Its function is due to the location, more specifically concentrated on the basolateral side of the choroid plexus cells, contributing to Mn transport through these cells and the subsequent excretion [41]. These findings are also supported by high Mn CSF levels in patients carrying an SLC39A14 mutation [46]. ZIP14 mutations lead to Mn accumulation in early-onset parkinsonism dystonia patients, thus highlighting an important role of ZIP14 in Mn level regulation [41].
3.3. SLC30A10
SLC30A10 (ZIP10) is one of the 10 solute carrier family 30 transporters. Unlike the majority of the family members of this family, which mediate zinc transport, the SLC30A10 mediates Mn efflux [47]. Its role in Mn-related inherited disorders is well established. Mutation of the SLC30A10 results in Mn accumulation and parkinsonism with dystonia, polycythemia, and liver cirrhosis. This protein is highly expressed in the digestive tract and liver [48].
3.4. Other Transportation Mechanisms
Citrate transporters, such as Mn-citrate, seem to be one of the major forms of Mn transported to the brain [49]. Mn-citrate crosses the blood–brain barrier with a citrate transporter-dependent mechanism [50]. Mn can also enter the brain through ligand-gated and voltage-gated calcium channels, respectively expressed in the brain endothelial cells and dopaminergic neurons of the midbrain. This could explain the selective vulnerability of these neurons to Mn toxicity [51].
Transferrin and transferrin receptor (TR) also help with Mn transportation. Transferrin mediates iron transport, but it can also favor the influx of Mn in the brain [52], in its trivalent state (Mn3+). TR is expressed in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes, and it binds the Mn-transferring complex into the cells [53]. This mechanism seems to play a less important role compared to others.
Another protein involved in Mn transportation is Fpn, a transmembrane protein expressed in the plasma membrane that exports intracellular iron [54]. Fpn plays an important role in regulating Mn levels in the brain, as it also exports intracellular Mn into the extracellular space, thus protecting against Mn toxicity [55].
4. Mechanisms Involved with Mn Toxicity
Mn toxicity can lead to the dysfunction of numerous pathways, such as the alteration and inhibition of mitochondrial respiration, resulting in energy failure, oxidative stress, and excitotoxicity [56,57].
Oxidative stress is one of the most implicated mechanisms of Mn-induced neurotoxicity. Mn accumulation in the brain can lead to damage in the basal ganglia, which are particularly susceptible to oxidative injury due to high oxygen demand and consumption. Mn increased oxidative damage and the activation of caspase-3, DNA fragmentation, and cytochrome c release from the mitochondria, which resulted in DNA fragmentation in dopaminergic cells [58]. Oxidative stress, a crucial mechanism of Mn-induced toxicity, was demonstrated in attenuated Mn neurotoxicity induced by antioxidant compounds, which also ameliorated dopaminergic transmission in experimental settings [59]. Mn also seems to exacerbate dopamine-induced oxidative damage since dopamine (DA) can undergo oxidation, producing free radicals [60]. Impairment of the neuronal antioxidant system may also result from altered striatal concentration of glutathione and glutathione reductase and peroxidase activity [61]. Oxidative stress can also result in nucleic acid damage, higher levels of oxidized DNA products have been observed in the substantia nigra and CSF of PD patients [62].
Another important mechanism of Mn-induced neurotoxicity is neuro-inflammation, which seems to be enhanced by astrocytes since Mn accumulates mainly in these cells in the brain [63]. This is probably the result of the abundant expression of many Mn transporters; among these, DMT1 and mostly TRs expressed on the astrocytic surface bind to Mn-transferrin with a resulting concentration of Mn inside the cell that is up to 50-fold greater than that in neurons [23]. Astrocytes are more susceptible to Mn-induced neurotoxicity; this leads to the release of many cytotoxic substances, such as iNOS, TNF-alfa, IL-1beta, and IL-6, in addition to the activation of numerous pro-inflammatory genes [30,64,65].
Mn seems to interfere with multiple neurotransmission systems. Evidence suggests involvement in DA, glutamate, acetylcholine, and GABA neurotransmitters [30]. Interestingly, Mn toxicity seems to result in decreased levels of DA and its turnover [66], depleted DA stores [67], decreased DA release in the striatum of rats, and concomitantly reduced dopaminergic neurotransmission [68]. Mn induces dopaminergic neuronal injury by decreasing the expression of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) [69], and as a result, Mn leads to aberrant DA neurotransmission [30]. Glutamate neurotransmission is also impaired by Mn excess in the brain due to overstimulation of postsynaptic glutamate receptors and excitotoxic neuronal death [70]. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAr) is dysregulated by an altered phosphorylation mechanism and its subunits’ impairment. Mn exposure reduced glutamate uptake by astrocytes while simultaneously lowering the expression of glutamate aspartate transporter 1 (GLAST) and glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1), ultimately leading to elevated extracellular glutamate levels [71]. Mn induces neuronal injury by disrupting glutamate signaling, partly through the impaired regulation of the glutamate transporters GLT-1/GLAST and the NMDA receptor [30]. Other neurotransmitters have been implicated in Mn neurotoxicity too; among these, the cholinergic system seems to be affected by Mn excess. Mn also reduced the activity of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), thereby lowering ACh production in striatal cholinergic terminals [72]. Mn primarily accumulates in the GABAergic neurons of the globus pallidus within the basal ganglia, although its effects on GABAergic neurotransmission are variable. Some studies have found that Mn disrupts GABA signaling by reducing GABA levels, which in turn increases seizure susceptibility in rats [30].
Protein Aggregation
Protein aggregation is another significant Mn-induced neurotoxicity mechanism, as it contributes to the progression and development of neurodegeneration. Protein misfolding, trafficking, and degradation are all impaired mechanisms resulting from chronic Mn exposure [1,73,74,75]. Mn can directly interact with proteins, causing misfolding and aggregation. This is the case of alpha-synuclein, which is a hallmark of neurodegenerative disorders, such as PD [76,77]. Mn alters the structural conformation of alpha-synuclein, increasing its propensity to form oligomers. These neurotoxic aggregates impair synaptic function and induce mitochondrial dysfunction [78]. Many studies have shown how Mn-induced alpha-synuclein aggregates alter cellular components, disrupt axonal transport, and activate microglial neuroinflammation [79,80]. Many other proteins are altered by Mn excess; among these, tau and TDP-43 are well recognized. Mn seems to promote tau hyperphosphorylation, which is linked to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles observed in tauopathies, such as Alzheimer’s disease [81]. Also, TDP-43, which is implicated in ALS and frontotemporal dementia (FTD), seems to be induced to form aggregates by Mn excess [56,82,83]. The impairment of protein degradation pathways is another leading mechanism of the Mn-induced aggregation process, and autophagy and the proteasome system are involved. Moreover, Mn impairs autophagy by disrupting lysosomal function and inhibiting autophagosome–lysosome fusion, leading to the accumulation of protein aggregates [78,79].
5. Hereditary Disorders of Manganese Metabolism
The first hereditary disorder of Mn metabolism was reported in 2012 [84]. The discovery led to the group of hereditary Mn transporter defects, hypermanganesemia with dystonia (HMNDYT 1 and 2) disorders being described. Usually, genetic forms manifest with developmental delay, childhood onset of “cock-walking” gait, and dystonia with or without parkinsonism. Mutations in SLC30A10 lead to a syndrome of hypermanganesemia with dystonia, polycythemia, and chronic liver disease, referred to as hypermanganesemia with dystonia 1 (HMNDYT1) (OMIM#613280) [85]. In 2016, a comparable hereditary Mn transporter defect known as hypermanganesemia with dystonia 2 (HMNDYT2) (OMIM #617013) was reported, which can be differentiated from SLC30A10 deficiency by the lack of liver involvement and polycythemia. Mutations in SLC39A14 result in swiftly advancing dystonia accompanied by varying degrees of parkinsonism and other neurological symptoms, typically beginning in infancy or early childhood. Both types of inherited Mn transporter defects exhibit distinctive MRI brain characteristics, which are marked by hyperintensity on T1-weighted images in areas such as the globus pallidus and striatum, as well as in the white matter of the cerebrum and cerebellum, midbrain, dorsal pons, and medulla. Notably, the ventral pons is generally unaffected by these changes [45,84,85].
Table 2 highlights the clinical features of genetic and acquired Mn-overload syndromes.

Table 2.
Summary of inherited and acquired causes of manganese (Mn) neurotoxicity. Legend: TPN: total parenteral nutrition.
5.1. HMNDYT1 SLC30A10 Deficiency
Hypermanganesemia with dystonia 1 (HMNDYT1), resulting from bi-allelic mutations in SLC30A10, was the initial inherited defect in Mn transporters identified [84,85]. The accumulation of Mn in the body due to systemic factors results in a unique syndrome characterized by hypermanganesemia, an increase in red blood cell count (polycythemia), movement disorders (dystonia), and chronic liver diseases, which can vary from asymptomatic fat accumulation in the liver (steatosis) to severe liver damage (cirrhosis) accompanied by liver failure, as well as a reduction in iron reserves. Urinary and blood Mn levels are significantly elevated, typically reported to be ten times higher than normal. When examining brain MRI scans, Mn deposition can be observed in the basal ganglia, especially in the globus pallidus and striatum. This is characterized by a marked hyperintensity on T1-weighted images and a corresponding hypointensity on T2-weighted images, indicating the presence of Mn in these areas. The white matter of the cerebrum and cerebellum, midbrain, dorsal pons, and medulla are also affected, while the ventral pons shows a characteristic sparing [84,85,86,87,88,89]. Clinically, most patients exhibit dystonia in early childhood. Dystonia in the lower limbs results in a distinct high-stepping gait, often referred to as the “cock walk gait”. The involvement of white matter may lead to spasticity and signs of pyramidal tract dysfunction [84]. From a histological perspective, significant neuronal loss in the globus pallidus and a vacuolated myelinopathy have been reported [90]. The brain is not the only organ where Mn deposits accumulate; the liver is the second most commonly involved organ that may present damage induced by Mn toxicity. Liver damage can range from mild (steatosis) to more severe (cirrhosis). Polycythemia has been observed in all patients and may occur before clinical symptoms appear. It has been proposed that Mn triggers the expression of the erythropoietin gene. Erythropoietin levels have been elevated in some affected individuals [85]. Given that Mn and iron (Fe) compete for similar transporters, it is not unexpected that individuals with mutations in the SLC30A10 gene exhibit depleted iron stores. These individuals also demonstrate an elevated total iron-binding capacity and a reduced level of ferritin [84,85]. Chelation therapy using EDTA-CaNa2 has proven to be effective for decreasing Mn accumulation, alleviating neurological symptoms, and halting the progression of liver disease. In many instances, the process of Mn chelation results in the resolution of polycythemia, the normalization of iron parameters, and the stabilization of blood Mn levels. Nevertheless, it is important to note that blood Mn levels frequently do not return to normal and may remain elevated [88,91,92]. A successful decrease in Mn levels can be observed through brain MRI, which shows a decrease in T1 hyperintensity. EDTA-CaNa2 is administered intravenously throughout 5 to 8 days every 4 weeks. It is essential to closely monitor calcium and other trace metal levels, including zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and selenium (Se), to prevent any negative side effects [93]. Although chelation using EDTA-CaNa2 is effective, the requirement for intravenous administration renders the treatment less practical. Some case reports indicate that 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid and d-penicillamine offer effective oral alternatives [87,94]. It is unclear whether this alternative treatment can slow disease progression as effectively as EDTA-CaNa2.
5.2. HMNDYT2 SLC39A14 Deficiency
In 2016, bi-allelic mutations in SLC39A14 were identified in individuals with features of Mn neurotoxicity, such as rapidly progressing dystonia, variable parkinsonism, and T1 hyperintensity in the globus pallidus observed on brain MRI [45]. Individuals with HMNDYT2 exhibited hypermanganesemia but lacked systemic features of Mn overload, such as liver disease or polycythemia. Blood levels of Fe, Zn, and cadmium (Cd)—divalent metals transported by SLC39A14—are usually normal. Additionally, liver MRI findings are usually normal, indicating no hepatic Mn accumulation. Neurological symptoms in HMNDYT2 tend to manifest earlier than in HMNDYT1, with some individuals experiencing severe hypotonia and dystonia within their first year of life [45,91]. MRI images show no difference from those of HMNDYT1.
The cornerstone of treatment involves chelation therapy using intravenous disodium calcium edetate (EDTA-CaNa2) and iron supplementation. This treatment algorithm is consolidated and shows greater response in HMNDYT1 [84,85,86,93]. Chelation therapy using EDTA-CaNa2 has been tried with variable degrees of success in HMNDYT2 [45]. Although there is evidence of Mn mobilization, indicated by increased urinary excretion and a reduction in blood Mn levels, the neurological symptoms in these individuals did not show significant improvement [45,46,95]. Two oral chelating agents, 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid and d-penicillamine, were tested in one patient but were ineffective, failing to increase urinary Mn excretion [95].
5.3. Manganese Disorders Associated with Low Levels of Mn
Conversely, mutations in SLC39A8, another transporter for Mn uptake, have been linked to lower Mn levels in the blood. A deficiency in Mn results in reduced activity of Mn-dependent enzymes, such as β-1,4-galactosyltransferase and MnSOD, which can cause dysglycosylation, known as congenital disorder of glycosylation type IIn (CDG2N), along with compromised mitochondrial function [96,97,98]. Individuals affected may show signs from infancy, including developmental delays, short stature, dwarfism, seizures, hypotonia, and dystonia. Oral treatment with Mn and galactose may offer potential strategies for management [99].
6. Acquired Disorders of Manganese Metabolism
Numerous studies have suggested a high brain vulnerability to Mn, especially during developmental phases. Exposure to increased Mn concentrations in drinking water correlates with neurological abnormalities in children and psychological impairment. These neurological abnormalities result in behavior and cognition impairment, as well as motor functions with tremors and coordination difficulties [100]. The most well-known entity of acquired Mn neurotoxicity is the so-called manganism in people who misuse drugs and especially exposed workers (such as miners). Occupational exposure to inhaled Mn compounds in the welding industry accounts for many reported cases [89,101].
Mn toxicity can also result from the misuse of intravenous ephedrone (or methcathinone) due to the potassium permanganate required for the drug’s synthesis, which can deposit in the brain, leading to manganism symptoms [102]. This parkinsonian syndrome was noted in methcathinone users in Russia and the Baltic states [103]. Methcathinone is a stimulant with euphoric effects; it is derived from a process of potassium permanganate oxidation for the intravenous formulation. One of the largest case series of 23 adults in Latvia reported the most frequent symptoms to be gait disturbance, which occurred after a mean of 5.8 years from methcathinone use; difficulty walking backward seemed to be a distinguishing feature. Tremors during rest were not a distinguishing feature, which is commonly observed during PD. Methcathinone patients had a symmetric motor disorder, fell frequently, walked on the balls of their feet (the typical “cock walk gait”), had profoundly soft speech, and did not respond to treatment with levodopa [19,104,105].
Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration patients with advanced cirrhosis present an excess of brain Mn accumulation and associated clinical features of neurotoxicity [106]. Interestingly, in one study, T1 hyperintensity of the globus pallidum was reported in 26 out of 90 cirrhotic patients on the liver transplant waiting list [107].
Another well-known cause of excessive Mn accumulation is total parenteral nutrition, especially in neonates, which can have critical negative consequences since parenteral nutrition bypasses the little-developed homeostatic mechanism of the gut and liver [3,13,102]. Toxicity related to Mn exposure was noted as little as 15 days after parenteral nutrition. The Mn dosage, often influenced by its content in commercially available products, may frequently surpass the limits recommended by clinical guidelines and should be restricted to 55 µg/day [108].
Despite the route, Mn seems to accumulate in the brain regions with dopaminergic pathways (mainly in the basal ganglia and mostly in the globus pallidum), potentially leading to dopaminergic dysfunction. MRI imaging for Mn encephalopathy typically reveals symmetrical hyperintensities on T1-weighted images, predominantly in the basal ganglia. These changes are most evident in the globus pallidus and cerebellum. Changes in the hypothalamus and midbrain are less common [109,110,111]. Symptoms of Mn encephalopathy are often permanent, and symptomatic treatments, such as the use of anti-Parkinson drugs, typically show limited effectiveness [105,112].
Mn role has also been investigated in autism spectrum disorder (ASD): an increasing number of studies suggest an inverse relationship between systemic Mn levels and ASD. Conversely, the majority of findings report elevated systemic Mn levels in individuals with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder [113].
Figure 1 summarizes distinguishing features between acquired and inherited Mn disorders.
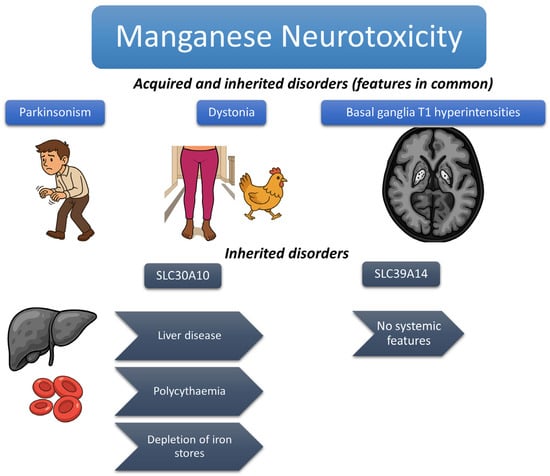
Figure 1.
The figure shows the typical features of acquired and inherited Mn metabolism disorders. Parkinsonism and basal ganglia T1 hyperintensities are shared features, as is the classical “cock-walk” gait (a particular form of dystonic gait in which patients walk on their toes with a high-stepping gait that is more classically reported in inherited forms but described in both). Other distinguishing features of inherited forms, typically associated with SLC30A10 mutations, are highlighted.
7. Distinguishing Features from Parkinson’s Disease
Mn toxicity shares many similarities and clinical features with PD, such as bradykinesia, rigidity, tremors, and postural instability. Nonetheless, many differences exist in the clinical presentation, underlying mechanisms, and treatment responses. Unlike PD, which is usually associated with dopaminergic neuron impairment in the substantia nigra, Mn toxicity usually leads to excessive Mn accumulation in the basal ganglia, especially in the globus pallidus, without the presence of Lewy bodies [114,115]. Magnetic resonance of Mn-exposed individuals typically shows T1 diffuse hyper-intensities, especially in the globus pallidus, which is not seen in PD [10,101,116]. An important clinical distinction is the lack of resting tremors in manganism, usually present in PD. Mn neuro-toxicity is usually more commonly associated with action tremors and dystonia [10,117]. Cognitive symptoms and neuropsychiatric impairment are usually earlier features compared to PD [9,118,119]. Another main difference is the treatment response to levodopa, manganism does not respond to levodopa given the absence of primary involvement of the substantia nigra. Mn seems to primarily disrupt dopaminergic transmission through interference with dopamine release, synthesis, and reuptake [7,12,52,120]. On the other hand, manganism tends to stabilize upon removal from Mn exposure, whilst the progression of the disease is well recognized in PD [19].
8. Therapeutic Options
Chelation therapy remains a cornerstone for treating Mn toxicity to reduce its neurotoxic effects. Among the most used therapeutic agents, chelation therapy with disodium edetate has been administered to patients with hypermanganesemia disorders to reduce Mn levels, but its effectiveness has been inconsistent [45,46,87,88,89]. A motor improvement has been reported in some patients, whilst others do not respond to the therapy at all. Some patients with monogenic inherited causes of hypermanganesemia have shown clinical improvement, including decreased Mn levels, stabilized gait, reduced bradykinesia, and improved dystonia, following chelation therapy [45,84,86,88]. Improvement with chelation therapy in genetic Mn disorders is not always to be expected. Clinical response may depend on many variables, such as age and time of treatment. Acquired causes of Mn do not always respond to chelation treatment, and symptoms may continue even many years after exposure cessation [12]. Moreover, chelation intravenous therapy increases the risk of side effects and requires close monitoring of other essential trace metals for reduced absorption. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and calcium disodium EDTA are the most extensively studied chelators for Mn toxicity, demonstrating effectiveness in reducing blood Mn levels in cases of both occupational and environmental exposure [1]. Recent studies have explored using newer chelating agents, like deferoxamine (DFO) and deferasirox (DFX), which were initially developed for treating iron overload. These agents have shown promise in mobilizing Mn from tissues and reducing neuroinflammatory markers [76,121]. Given the intravenous administration of calcium disodium EDTA and its side effects and low availability, other strategies are being investigated. Among those, penicillamine has reported variable responses for inherited disorders, such as hypermanganesemia with dystonia, polycythemia, and cirrhosis [92,94,122,123]. Interestingly, iron supplementation may lower Mn concentration by competing for the same transport mechanism. Animal studies have demonstrated the neuroprotective effects of DFO, showing its ability to reduce oxidative stress and restore mitochondrial function in cases of Mn-induced neurotoxicity [56,80].
The effectiveness of chelation therapy depends on the duration and severity of Mn exposure. Early intervention is essential, as extended exposure may cause irreversible neurodegeneration, reducing the efficacy of chelating agents. Antioxidants are gaining attention as a potential therapy for manganese-induced neurotoxicity by targeting oxidative stress, a key factor in Mn-related neuronal damage. Recent research showed that antioxidants, like N-acetylcysteine (NAC), can effectively decrease ROS and enhance mitochondrial function in cells and animal models exposed to Mn [1]. Many other antioxidants are being investigated, but at the moment, their use in clinical practice remains controversial. Mn supplementation appears to be an effective treatment for patients with inherited Mn deficiency, as shown in a study that reported significant improvement in motor function and neurological symptoms in two patients with SLC39A8 after Mn supplementation [99].
Dietary approaches include high-iron diets that suppress Mn absorption [124]. Also, adding calcium to human milk significantly decreases Mn absorption; a similar effect is observed with dietary phytate, which can reduce the absorption of many other minerals [125]. Another approach could be avoiding foods rich in Mn, such as grain products, tea, vegetables, and seafood, like mussels [28,126].
As for symptomatic treatment, Levodopa has been administered as a symptomatic treatment to some patients with hypermanganesemia, showing variable effectiveness in alleviating symptoms. Several cases of acquired hepatocerebral degeneration have also reported clinical improvement with levodopa therapy [127]. Welders exposed to Mn do not seem to respond to levodopa treatment, regardless of the dosage [128]. Patients with inherited Mn transport disorders have exhibited a variable clinical response to levodopa treatment [84,86,89].
9. Future Directions
Despite the progress in understanding the pathophysiology of Mn disorders, many questions remain unsolved. Among these, the timing of Mn deposition in the brain remains elusive, such as the fact that different brain regions seem to exhibit different elimination rates of Mn upon cessation of exposure [129]. A comparison is needed between dopamine terminals and dopamine release in individuals with PD and those with manganism. In cases of manganism, both mice and primates exhibit intact dopamine terminals but impaired dopamine release; in contrast, individuals with Parkinson’s disease show impairments in both dopamine terminals and release [114].
No well-established biomarkers exist for Mn-induced damage to the central nervous system yet. Although animal studies have provided valuable insights, these findings still need to be validated in humans [9]. Metabolomics offers promising potential for identifying candidate markers of Mn exposure, uncovering disrupted biological pathways, and detecting early signs of Mn toxicity. However, its application in exposure assessment faces several challenges, mainly due to the natural variability of small-molecule metabolites [130]. It is also essential to understand the role of other metals in diagnosing manganism, especially since low iron levels are often observed in cases of hypermanganesemia. Recent studies have shown that Mn exposure affects the transcriptional regulation of key pathways, including those related to oxidative stress, through Mn-induced modulation of sirtuin and Keap1-Nrf2 signaling. Also, a significant role of autophagy as a protective mechanism against Mn neurotoxicity has been described [131]. Many gaps related to Mn toxicity still remain to be filled in. The present review discussed the pathological implications of Mn transportation disruption in environmental and genetic conditions. The latter provide a good disease model to enhance our comprehension of Mn toxicity.
10. Conclusions
Although progress has been made in understanding Mn neurotoxicity, there are still significant challenges in early diagnosis, effective treatment, and long-term management of these conditions. Further research is needed to identify reliable biomarkers, develop targeted therapies, and conduct longitudinal studies to gain deeper insights into the long-term effects of Mn neurotoxicity.
Author Contributions
G.M. wrote the first draft of the manuscript and was responsible for the first literature search. V.L., F.T., and A.T. helped with the PubMed research and reviewed the manuscript. All authors had full access to all the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
There was no funding source for this study.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Acknowledgments
We all thank our family and loved ones for their continuous support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chen, P.; Bornhorst, J.; Aschner, M. Manganese metabolism in humans. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2018, 23, 1655–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnerdal, B. Nutritional aspects of soy formula. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 1994, 402, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschner, J.L.; Aschner, M. Nutritional aspects of manganese homeostasis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2005, 26, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maret, W. The Metals in the Biological Periodic System of the Elements: Concepts and Conjectures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschner, M.; Guilarte, T.R.; Schneider, J.S.; Zheng, W. Manganese: Recent advances in understanding its transport and neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 221, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, A.B. Manganese exposure, essentiality & toxicity. Indian. J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 484–500. [Google Scholar]
- Erikson, K.M.; Syversen, T.; Aschner, J.L.; Aschner, M. Interactions between excessive manganese exposures and dietary iron-deficiency in neurodegeneration. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 19, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.C., Jr.; Gubert, P.; Villas Boas, G.R.; Meirelles Paes, M.; Santamaría, A.; Lee, E.; Tinkov, A.A.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Manganese-induced neurodegenerative diseases and possible therapeutic approaches. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2020, 20, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, T.V.; Schettinger, M.R.; Chen, P.; Carvalho, F.; Avila, D.S.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. “Manganese-induced neurotoxicity: A review of its behavioral consequences and neuroprotective strategies”. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilarte, T.R. Manganese and Parkinson’s disease: A critical review and new findings. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neal, S.L.; Zheng, W. Manganese Toxicity Upon Overexposure: A Decade in Review. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakye, G.F.; Paoliello, M.M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism and Parkinson’s Disease: Shared and Distinguishable Features. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7519–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschner, M.; Erikson, K.M.; Herrero Hernández, E.; Tjalkens, R. Manganese and its role in Parkinson’s disease: From transport to neuropathology. Neuromolecular Med. 2009, 11, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephs, K.A.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Klos, K.J.; Kumar, N.; Fealey, R.D.; Trenerry, M.R.; Cowl, C.T. Neurologic manifestations in welders with pallidal MRI T1 hyperintensity. Neurology 2005, 64, 2033–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, K.; Lin, G.X.; Jefferson, A.M.; Stone, S.; Afshari, A.; Keane, M.J.; McKinney, W.; Jackson, M.; Chen, B.T.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; et al. Modifying welding process parameters can reduce the neurotoxic potential of manganese-containing welding fumes. Toxicology 2015, 328, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulhote, Y.; Mergler, D.; Barbeau, B.; Bellinger, D.C.; Bouffard, T.; Brodeur, M.; Saint-Amour, D.; Legrand, M.; Sauvé, S.; Bouchard, M.F. Neurobehavioral function in school-age children exposed to manganese in drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulson, B.; Mizon, K.; Taylor, A.; Korsch, M.; Stauber, J.; Davis, J.M.; Louie, H.; Wu, M.; Swan, H. Changes in manganese and lead in the environment and young children associated with the introduction of methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl in gasoline--preliminary results. Environ. Res. 2006, 100, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, M.; Mergler, D.; Baldwin, M.; Panisset, M.; Bowler, R.; Roels, H.A. Neurobehavioral functioning after cessation of manganese exposure: A follow-up after 14 years. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2007, 50, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepens, A.; Logina, I.; Liguts, V.; Aldins, P.; Eksteina, I.; Platkājis, A.; Mārtinsone, I.; Tērauds, E.; Rozentāle, B.; Donaghy, M. A Parkinsonian syndrome in methcathinone users and the role of manganese. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HaMai, D.; Rinderknecht, A.L.; Guo-Sharman, K.; Kleinman, M.T.; Bondy, S.C. Decreased expression of inflammation-related genes following inhalation exposure to manganese. Neurotoxicology 2006, 27, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erikson, K.M.; Dorman, D.C.; Lash, L.H.; Aschner, M. Manganese inhalation by rhesus monkeys is associated with brain regional changes in biomarkers of neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 97, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Yang, Y.; Lang, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Meng, J.; Wu, J.; Zeng, X.; Li, H.; Ma, H.; et al. SIRT1/FOXO3-mediated autophagy signaling involved in manganese-induced neuroinflammation in microglia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 256, 114872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harischandra, D.S.; Ghaisas, S.; Zenitsky, G.; Jin, H.; Kanthasamy, A.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity: New Insights Into the Triad of Protein Misfolding, Mitochondrial Impairment, and Neuroinflammation. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.; Rizwan, A.A.M.; Juweria, A.; Taima, Q.; Mahmoud, A.-D.M.; Inayat, A.; Malik, Z.I. Manganese exposure and perinatal health: A systematic review of literature. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Piao, F.; Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Kitamura, F.; Yokoyama, K. Manganese concentrations in maternal and umbilical cord blood: Related to birth size and environmental factors. Eur. J. Public Health 2013, 24, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ding, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, P.; Shi, R.; Huang, H.; Tian, Y. Manganese concentrations in maternal–infant blood and birth weight. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6170–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng, S.K.; Kulhánek, M.; Balík, J.; Černý, J.; Sedlář, O. Manganese: From Soil to Human Health—A Comprehensive Overview of Its Biological and Environmental Significance. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on Micronutrients. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, A.B.; Kwakye, G.F.; Herrero Hernández, E.; Aschner, M. Role of manganese in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2011, 25, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyarko-Danquah, I.; Pajarillo, E.; Digman, A.; Soliman, K.F.A.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. Manganese Accumulation in the Brain via Various Transporters and Its Neurotoxicity Mechanisms. Molecules 2020, 25, 5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunshin, H.; Mackenzie, B.; Berger, U.V.; Gunshin, Y.; Romero, M.F.; Boron, W.F.; Nussberger, S.; Gollan, J.L.; Hediger, M.A. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian proton-coupled metal-ion transporter. Nature 1997, 388, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruenheid, S.; Cellier, M.; Vidal, S.; Gros, P. Identification and characterization of a second mouse Nramp gene. Genomics 1995, 25, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, S.; Belouchi, A.M.; Cellier, M.; Beatty, B.; Gros, P. Cloning and characterization of a second human NRAMP gene on chromosome 12q13. Mamm. Genome 1995, 6, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff , N.A.; Garrick, M.D.; Zhao, L.; Garrick, L.M.; Ghio, A.J.; Thévenod, F. A role for divalent metal transporter (DMT1) in mitochondrial uptake of iron and manganese. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mims, M.P.; Guan, Y.; Pospisilova, D.; Priwitzerova, M.; Indrak, K.; Ponka, P.; Divoky, V.; Prchal, J.T. Identification of a human mutation of DMT1 in a patient with microcytic anemia and iron overload. Blood 2005, 105, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.; Ong, W.Y.; Connor, J.R. Distribution of divalent metal transporter-1 in the monkey basal ganglia. Neuroscience 2004, 128, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; O’Neal, S.; Hong, L.; Jiang, W.; Zheng, W. Elevated Adult Neurogenesis in Brain Subventricular Zone Following In vivo Manganese Exposure: Roles of Copper and DMT1. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 143, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, K.; Molina, R.M.; Donaghey, T.; Schwob, J.E.; Brain, J.D.; Wessling-Resnick, M. Olfactory uptake of manganese requires DMT1 and is enhanced by anemia. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishiro, H.; Doi, M.; Enomoto, S.; Himeno, S. High sensitivity of RBL-2H3 cells to cadmium and manganese: An implication of the role of ZIP8†. Metallomics 2011, 3, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.E.; Schroten, H.; Ishikawa, H.; Zhao, N. Localization of ZIP14 and ZIP8 in HIBCPP Cells. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Geng, X.; Cai, Y.; Copple, B.; Yoshinaga, M.; Shen, J.; Nebert, D.W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z. Hepatic ZIP8 deficiency is associated with disrupted selenium homeostasis, liver pathology, and tumor formation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G569–G579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.-K.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Soni, T.; Park, J.-H.; Aring, L.; Muraleedharan, C.K.; Garcia-Hernandez, V.; Kamada, N.; Samuelson, L.C.; Nusrat, A.; et al. The manganese transporter SLC39A8 links alkaline ceramidase 1 to inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.M.; Morgan, H.E.; Johnson, A.; Nicholson, R.I. Structure–function analysis of a novel member of the LIV-1 subfamily of zinc transporters, ZIP14. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuschl, K.; Meyer, E.; Valdivia, L.E.; Zhao, N.; Dadswell, C.; Abdul-Sada, A.; Hung, C.Y.; Simpson, M.A.; Chong, W.K.; Jacques, T.S.; et al. Mutations in SLC39A14 disrupt manganese homeostasis and cause childhood-onset parkinsonism–dystonia. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti-Sanchez, L.; Ortigoza-Escobar, J.D.; Darling, A.; Villaronga, M.; Baide, H.; Molero-Luis, M.; Batllori, M.; Vanegas, M.I.; Muchart, J.; Aquino, L.; et al. Hypermanganesemia due to mutations in SLC39A14: Further insights into Mn deposition in the central nervous system. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Illades, D.; Chen, P.; Zogzas, C.E.; Hutchens, S.; Mercado, J.M.; Swaim, C.D.; Morrisett, R.A.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S. SLC30A10 Is a Cell Surface-Localized Manganese Efflux Transporter, and Parkinsonism-Causing Mutations Block Its Intracellular Trafficking and Efflux Activity. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 14079–14095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.A.; Hutchens, S.; Liu, C.; Jursa, T.; Shawlot, W.; Aschner, M.; Smith, D.R.; Mukhopadhyay, S. SLC30A10 transporter in the digestive system regulates brain manganese under basal conditions while brain SLC30A10 protects against neurotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 1860–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalke, B.; Berthele, A.; Mistriotis, P.; Ochsenkühn-Petropoulou, M.; Halbach, S. Manganese species from human serum, cerebrospinal fluid analyzed by size exclusion chromatography-, capillary electrophoresis coupled to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2007, 21, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossgrove, J.S.; Allen, D.D.; Bukaveckas, B.L.; Rhineheimer, S.S.; Yokel, R.A. Manganese Distribution Across the Blood–Brain Barrier: I. Evidence for Carrier-Mediated Influx of Manganese Citrate as Well as Manganese and Manganese Transferrin. NeuroToxicology 2003, 24, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dučić, T.; Barski, E.; Salome, M.; Koch, J.C.; Bähr, M.; Lingor, P. X-ray fluorescence analysis of iron and manganese distribution in primary dopaminergic neurons. J. Neurochem. 2013, 124, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunter, T.E.; Gerstner, B.; Gunter, K.K.; Malecki, J.; Gelein, R.; Valentine, W.M.; Aschner, M.; Yule, D.I. Manganese transport via the transferrin mechanism. NeuroToxicology 2013, 34, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.K.; Lowe, J.E.W.; Aboud, A.A.; Neely, M.D.; Redha, R.; Bauer, J.A.; Odak, M.; Weaver, C.D.; Meiler, J.; Aschner, M.; et al. Cellular manganese content is developmentally regulated in human dopaminergic neurons. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, A.; Lima, C.A.; Pinkus, J.L.; Pinkus, G.S.; Zon, L.I.; Robine, S.; Andrews, N.C. The iron exporter ferroportin/Slc40a1 is essential for iron homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.-K.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Iwase, S.; Seo, Y.A. Ferroportin disease mutations influence manganese accumulation and cytotoxicity. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 2228–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Fu, J. Effect of manganese chloride exposure on liver and brain mitochondria function in rats. Environ. Res. 2003, 93, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centonze, D.; Gubellini, P.; Bernardi, G.; Calabresi, P. Impaired excitatory transmission in the striatum of rats chronically intoxicated with manganese. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 172, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harischandra, D.S.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A.; Kanthasamy, A.G. α-Synuclein protects against manganese neurotoxic insult during the early stages of exposure in a dopaminergic cell model of Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 143, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milatovic, D.; Gupta, R.C.; Yu, Y.; Zaja-Milatovic, S.; Aschner, M. Protective effects of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents against manganese-induced oxidative damage and neuronal injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 256, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roth, J.A.; Li, Z.; Sridhar, S.; Khoshbouei, H. The effect of manganese on dopamine toxicity and dopamine transporter (DAT) in control and DAT transfected HEK cells. NeuroToxicology 2013, 35, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukhande, V.V.; Malthankar-Phatak, G.H.; Hugus, J.J.; Daniels, C.K.; Lai, J.C.K. Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity is Differentially Enhanced by Glutathione Depletion in Astrocytoma and Neuroblastoma Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2006, 31, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, C.; Abe, T.; Terayama, Y. Levels of reduced and oxidized coenzymeQ-10 and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with living Parkinson’s disease demonstrate that mitochondrial oxidative damage and/or oxidative DNA damage contributes to the neurodegenerative process. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 469, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedler, F.C.; Denman, R.B. Glutamine synthetase: The major Mn(II) enzyme in mammalian brain. Curr. Top. Cell Regul. 1984, 24, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.A.; Sullivan, K.A.; Carbone, D.L.; Hanneman, W.H.; Tjalkens, R.B. Manganese potentiates nuclear factor-κB-dependent expression of nitric oxide synthase 2 in astrocytes by activating soluble guanylate cyclase and extracellular responsive kinase signaling pathways. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 2028–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, A.; Mense, S.M.; Lan, C.; Zhou, M.; Mauro, R.E.; Kellerman, L.; Bentsman, G.; Volsky, D.J.; Louis, E.D.; Graziano, J.H.; et al. Gene expression profiling of human primary astrocytes exposed to manganese chloride indicates selective effects on several functions of the cells. NeuroToxicology 2007, 28, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos-Kroohs, R.M.; Davenport, L.L.; Gutierrez, A.; Hufgard, J.R.; Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Developmental manganese exposure in combination with developmental stress and iron deficiency: Effects on behavior and monoamines. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2016, 56, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.; Aoun, R.A.; Mathews, T.A. Altered striatal dopamine release following a sub-acute exposure to manganese. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 202, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezér, T.; Kurunczi, A.; Náray, M.; Papp, A.; Nagymajtényi, L. Behavioral effects of subchronic inorganic manganese exposure in rats. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2007, 50, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajarillo, E.; Rizor, A.; Son, D.-S.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. The transcription factor REST up-regulates tyrosine hydroxylase and antiapoptotic genes and protects dopaminergic neurons against manganese toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 3040–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danbolt, N.C. Glutamate uptake. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 65, 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, P.; Kim, C.; Smith, K.; Son, D.-S.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. Transcriptional Regulation of the Astrocytic Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter 1 (EAAT1) via NF-κB and Yin Yang 1 (YY1) *. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 23725–23737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.C.K.; Leung, T.K.C.; Lim, L. Brain Regional Distribution of Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase, Choline Acetyltransferase, and Acetylcholinesterase in the Rat: Effects of Chronic Manganese Chloride Administration after Two Years. J. Neurochem. 1981, 36, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Totten, M.; Zhang, Z.; Bucinca, H.; Erikson, K.; Santamaría, A.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Iron and manganese-related CNS toxicity: Mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, H.; Qi, X.; Wu, C.; Chang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z. Sex-Specific Differences in Cognitive Abilities Associated with Childhood Cadmium and Manganese Exposures in School-Age Children: A Prospective Cohort Study. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 193, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, S.; Barhydt, T.; Jacobs, R.; Killilea, D.W.; Lithgow, G.J.; Andersen, J.K. Manganese disturbs metal and protein homeostasis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Metallomics 2014, 6, 1816–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Pedersen, J.A.; Gu, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.Q.; et al. Methylmercury Degradation by Trivalent Manganese. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 5988–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzaroba, L.; Alfieri, D.F.; Colado Simão, A.N.; Vissoci Reiche, E.M. The role of zinc, copper, manganese and iron in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurotoxicology 2019, 74, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, L.; Liang, D.; Shi, W.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Ou, C. Manganese induced nervous injury by α-synuclein accumulation via ATP-sensitive K(+) channels and GABA receptors. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 332, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wan, C.; Gu, Y.; Wang, D.; Yu, H. Manganese promotes α-synuclein amyloid aggregation through the induction of protein phase transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Liu, K.; Liu, Z.F.; Cong, L.; Lei, M.Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, J.; Deng, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, B. Manganese-induced alpha-synuclein overexpression aggravates mitochondrial damage by repressing PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Che, H.; Yao, T.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Du, K.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Manganese induces tau hyperphosphorylation through the activation of ERK MAPK pathway in PC12 cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 119, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.N.; Lim, N.K.; Grubman, A.; Li, Q.X.; Volitakis, I.; White, A.R.; Crouch, P.J. Increased metal content in the TDP-43(A315T) transgenic mouse model of frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hester, K.; Kirrane, E.; Anderson, T.; Kulikowski, N.; Simmons, J.E.; Lehmann, D.M. Environmental exposure to metals and the development of tauopathies, synucleinopathies, and TDP-43 proteinopathies: A systematic evidence map protocol. Environ. Int. 2022, 169, 107528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, M.; Federico, A.; Zhao, T.; Breedveld, G.J.; Battisti, C.; Delnooz, C.; Severijnen, L.A.; Di Toro Mammarella, L.; Mignarri, A.; Monti, L.; et al. Mutations in SLC30A10 cause parkinsonism and dystonia with hypermanganesemia, polycythemia, and chronic liver disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuschl, K.; Clayton, P.T.; Gospe, S.M., Jr.; Gulab, S.; Ibrahim, S.; Singhi, P.; Aulakh, R.; Ribeiro, R.T.; Barsottini, O.G.; Zaki, M.S.; et al. Syndrome of hepatic cirrhosis, dystonia, polycythemia, and hypermanganesemia caused by mutations in SLC30A10, a manganese transporter in man. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, M.; Kamate, M.; Sharma, S.; Olgiati, S.; Graafland, J.; Breedveld, G.J.; Kori, I.; Hattiholi, V.; Jain, P.; Aneja, S.; et al. Manganese transport disorder: Novel SLC30A10 mutations and early phenotypes. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, M.S.; Issa, M.Y.; Elbendary, H.M.; El-Karaksy, H.; Hosny, H.; Ghobrial, C.; El Safty, A.; El-Hennawy, A.; Oraby, A.; Selim, L.; et al. Hypermanganesemia with dystonia, polycythemia and cirrhosis in 10 patients: Six novel SLC30A10 mutations and further phenotype delineation. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulab, S.; Kayyali, H.R.; Al-Said, Y. Atypical Neurologic Phenotype and Novel SLC30A10 Mutation in Two Brothers with Hereditary Hypermanganesemia. Neuropediatrics 2018, 49, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budinger, D.; Barral, S.; Soo, A.K.S.; Kurian, M.A. The role of manganese dysregulation in neurological disease: Emerging evidence. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechpammer, M.; Clegg, M.S.; Muzar, Z.; Huebner, P.A.; Jin, L.W.; Gospe, S.M., Jr. Pathology of inherited manganese transporter deficiency. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuschl, K.; Mills, P.B.; Parsons, H.; Malone, M.; Fowler, D.; Bitner-Glindzicz, M.; Clayton, P.T. Hepatic cirrhosis, dystonia, polycythaemia and hypermanganesaemia—A new metabolic disorder. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2008, 31, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamelou, M.; Tuschl, K.; Chong, W.K.; Burroughs, A.K.; Mills, P.B.; Bhatia, K.P.; Clayton, P.T. Dystonia with brain manganese accumulation resulting from SLC30A10 mutations: A new treatable disorder. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagianni, S.; Tuschl, K. Genetic Disorders of Manganese Metabolism. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtiar, K.; Ibrahim, S.; Tuschl, K.; Mills, P. Hypermanganesemia with Dystonia, Polycythemia and Cirrhosis (HMDPC) due to mutation in the SLC30A10 gene. Brain Dev. 2016, 38, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodan, L.H.; Hauptman, M.; D’Gama, A.M.; Qualls, A.E.; Cao, S.; Tuschl, K.; Al-Jasmi, F.; Hertecant, J.; Hayflick, S.J.; Wessling-Resnick, M.; et al. Novel founder intronic variant in SLC39A14 in two families causing Manganism and potential treatment strategies. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 124, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boycott, K.M.; Beaulieu, C.L.; Kernohan, K.D.; Gebril, O.H.; Mhanni, A.; Chudley, A.E.; Redl, D.; Qin, W.; Hampson, S.; Küry, S.; et al. Autosomal-Recessive Intellectual Disability with Cerebellar Atrophy Syndrome Caused by Mutation of the Manganese and Zinc Transporter Gene SLC39A8. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Hogrebe, M.; Grüneberg, M.; DuChesne, I.; von der Heiden, A.L.; Reunert, J.; Schlingmann, K.P.; Boycott, K.M.; Beaulieu, C.L.; Mhanni, A.A.; et al. SLC39A8 Deficiency: A Disorder of Manganese Transport and Glycosylation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, L.G.; Cowley, M.J.; Gayevskiy, V.; Roscioli, T.; Thorburn, D.R.; Prelog, K.; Bahlo, M.; Sue, C.M.; Balasubramaniam, S.; Christodoulou, J. A SLC39A8 variant causes manganese deficiency, and glycosylation and mitochondrial disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2017, 40, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Hogrebe, M.; Fobker, M.; Brackmann, R.; Fiedler, B.; Reunert, J.; Rust, S.; Tsiakas, K.; Santer, R.; Grüneberg, M.; et al. SLC39A8 deficiency: Biochemical correction and major clinical improvement by manganese therapy. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyare, P.U. The effects of manganese exposure from drinking water on school-age children: A systematic review. Neurotoxicology 2019, 73, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criswell, S.R.; Nielsen, S.S.; Warden, M.N.; Flores, H.P.; Lenox-Krug, J.; Racette, S.; Sheppard, L.; Checkoway, H.; Racette, B.A. MRI Signal Intensity and Parkinsonism in Manganese-Exposed Workers. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 61, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschner, J.L.; Anderson, A.; Slaughter, J.C.; Aschner, M.; Steele, S.; Beller, A.; Mouvery, A.; Furlong, H.M.; Maitre, N.L. Neuroimaging identifies increased manganese deposition in infants receiving parenteral nutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, O.S. [“Ephedron” encephalopathy]. Zh Nevrol. Psikhiatr Im. S S Korsakova 2005, 105, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J. Searching for a relationship between manganese and welding and Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 2005, 64, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, W.C.; Lyons, K.E.; Truly, W. Effect of levodopa treatment for parkinsonism in welders: A double-blind study. Neurology 2004, 62, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.W.; Park, H.K. Recent Updates on Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration. Tremor Other Hyperkinet. Mov. 2017, 7, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffeo, E.; Montuschi, A.; Stura, G.; Giordana, M.T. Chronic acquired hepatocerebral degeneration, pallidal T1 MRI hyperintensity and manganese in a series of cirrhotic patients. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 35, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, J.P.; Forbes, L.D. Manganese Toxicity Associated With Total Parenteral Nutrition: A Review. J. Pharm. Technol. 2021, 37, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habrat, B.; Silczuk, A.; Klimkiewicz, A. Manganese Encephalopathy Caused by Homemade Methcathinone (Ephedrone) Prevalence in Poland. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Kim, Y.; Woo, S.T.; Song, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.; Kwon, Y.J.; Ahn, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Chung, I.S.; et al. High signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging is a better predictor of neurobehavioral performances than blood manganese in asymptomatic welders. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poniatowska, R.; Lusawa, M.; Skierczyńska, A.; Makowicz, G.; Habrat, B.; Sienkiewicz-Jarosz, H. MRI brain findings in ephedrone encephalopathy associated with manganese abuse: Single-center perspective. Pol. J. Radiol. 2014, 79, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Mancía, S.; Ríos, C.; Montes, S. Manganese accumulation in the CNS and associated pathologies. Biometals 2011, 24, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschner, M.; Martins, A.C.; Oliveira-Paula, G.H.; Skalny, A.V.; Zaitseva, I.P.; Bowman, A.B.; Kirichuk, A.A.; Santamaria, A.; Tizabi, Y.; Tinkov, A.A. Manganese in autism spectrum disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: The state of the art. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 6, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilarte, T.R.; Gonzales, K.K. Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism Is Not Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease: Environmental and Genetic Evidence. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 146, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racette, B.A.; Nelson, G.; Dlamini, W.W.; Prathibha, P.; Turner, J.R.; Ushe, M.; Checkoway, H.; Sheppard, L.; Nielsen, S.S. Severity of parkinsonism associated with environmental manganese exposure. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, D.C. Chapter Six—Manganese Neurodegeneration. In Advances in Neurotoxicology; Aschner, M., Costa, L.G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 157–183. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Martin, C.J.; Doney, B.C. From manganism to manganese-induced parkinsonism: A conceptual model based on the evolution of exposure. Neuromolecular Med. 2009, 11, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, R.M.; Koller, W.; Schulz, P.E. Parkinsonism due to manganism in a welder: Neurological and neuropsychological sequelae. Neurotoxicology 2006, 27, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergler, D.; Huel, G.; Bowler, R.; Iregren, A.; Bélanger, S.; Baldwin, M.; Tardif, R.; Smargiassi, A.; Martin, L. Nervous system dysfunction among workers with long-term exposure to manganese. Environ. Res. 1994, 64, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitsanakis, V.A.; Au, C.; Erikson, K.M.; Aschner, M. The effects of manganese on glutamate, dopamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid regulation. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 48, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaseth, J.O.; Nurchi, V.M. Chelation Combination-A Strategy to Mitigate the Neurotoxicity of Manganese, Iron, and Copper? Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Majumdar, R.; Dubey, S.; Pandit, A. Penicillamine for Hypermanganesemia With Dystonia, Polycythemia, and Cirrhosis in 2 Sisters. Neurology 2021, 96, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavasoli, A.; Arjmandi Rafsanjani, K.; Hemmati, S.; Mojbafan, M.; Zarei, E.; Hosseini, S. A case of dystonia with polycythemia and hypermanganesemia caused by SLC30A10 mutation: A treatable inborn error of manganese metabolism. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Finley, E.J.; Gavin, C.E.; Aschner, M.; Gunter, T.E. Manganese neurotoxicity and the role of reactive oxygen species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidsson, L.; Cederblad, A.; Lönnerdal, B.; Sandström, B. The effect of individual dietary components on manganese absorption in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 54, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeland-Graves, J.H.; Mousa, T.Y.; Kim, S. International variability in diet and requirements of manganese: Causes and consequences. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 38, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Park, S.H.; Seo, M.; Weon, Y.C.; Kim, Y. (18)F-FP-CIT dopamine transporter PET findings in cirrhotic patients with parkinsonism. Neurotoxicology 2018, 64, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marreilha Dos Santos, A.P.; Andrade, V.; Aschner, M. Neuroprotective and Therapeutic Strategies for Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity. Clin. Pharmacol. Transl. Med. 2017, 1, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, D.A.; Ma, R.E.; Yeh, C.L.; Ward, E.; Snyder, S.; Azizi, E.; Zauber, S.E.; Wells, E.M.; Dydak, U. Reversibility of Neuroimaging Markers Influenced by Lifetime Occupational Manganese Exposure. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 172, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.G.; Simpson, C.D.; Lin, Y.S.; Shireman, L.M.; Seixas, N. The Use of Metabolomics to Identify Biological Signatures of Manganese Exposure. Ann. Work. Expo. Health 2017, 61, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinkov, A.A.; Paoliello, M.M.B.; Mazilina, A.N.; Skalny, A.V.; Martins, A.C.; Voskresenskaya, O.N.; Aaseth, J.; Santamaria, A.; Notova, S.V.; Tsatsakis, A.; et al. Molecular Targets of Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity: A Five-Year Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).