Abstract
Over the past decade, quetiapine has become one of the most commonly used psychotropic drugs in acute intoxication events worldwide. A structured literature review and analysis were conducted to assess the relationship between the kinetic and dynamic profiles in acute quetiapine intoxication. The correlation between dose and peak serum concentration (cmax) was determined using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Binary logistic regression was used to evaluate dose and cmax as predictors of the most common clinical events, signs and symptoms. One hundred and thirty-four cases of acute quetiapine ingestion were included in the analysis, with a median ingested dose of 10 g and a median cmax of 4 mg/L. The typical half-life was estimated to be 16.5 h, significantly longer than at therapeutic doses. For the immediate-release formulation, a biphasic disposition could not be excluded. Dose and cmax demonstrated a weak but significant correlation (r = 0.256; N = 63; p = 0.043). Central nervous system depression and tachycardia were the most common clinical signs. Higher doses and concentrations increased the risk of severe intoxication and were good predictors of intubation, tachycardia, hypotension, QTc prolongation and seizures, but not QRS prolongation, arrhythmia, heart block, hypokalaemia or acidosis. The thresholds for dose and cmax that increased the risk for individual signs and symptoms varied widely. However, doses > 3 g or cmax > 2 mg/L can be considered as alert levels that represent a high risk for severe clinical course of acute quetiapine intoxication.
1. Introduction
Quetiapine (QTP) is a dibenzothiazepine antipsychotic drug approved for the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder [1,2,3]. However, estimates from several Western countries have shown that 60–70% of patients receiving QTP use it for indications outside the registration [4,5,6,7,8,9]. In particular, low-dose QTP has demonstrated efficacy and tolerability in a broader range of psychiatric disorders and has become a common substitute for benzodiazepines in the treatment of anxiety and insomnia [3,5,7,8,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. As patients treated with QTP frequently suffer from debilitating and chronic psychiatric conditions, intoxication events, including suicide attempts with QTP, are not uncommon [23]. Over the past decade, QTP has become one of the psychotropic drugs most commonly implicated in acute intoxication events worldwide [17,18,24,25].
The severity of QTP intoxication may be difficult to predict [12]. Reported toxicity varies widely across the dose range. Peak serum concentration may be a good predictor of QTP toxicity [2] but is infrequently measured [26]. The existing data from individual case reports and studies in this regard have been confounding [2,12,27,28,29,30]. With the lack of clinical trials related to a toxicological setting [31], determining the relationship between dose, concentration and clinical picture can provide essential information in the management of intoxications.
This review article focuses on the relationship between the kinetic and dynamic profiles in acute intoxication with QTP. In the first part, the existing knowledge is described. In the second part, previously published cases are collected from the literature, and the joint data are statistically analysed to determine the relationship between the ingested QTP dose, serum concentrations and individual toxicodynamic parameters.
2. Review of the Existing Literature
2.1. Quetiapine in Therapeutic Use
2.1.1. Pharmacokinetic Profile and Dose–Concentration Correlation in Therapeutic Use
QTP is therapeutically administered in single or multiple oral doses, ranging from 25 to 800 mg daily. It is available in immediate-release (IR) and extended-release (XR) oral dosage forms [32]. In the therapeutic dose range, QTP exhibits linear pharmacokinetics [2,33,34,35,36,37,38]. Table 1 presents the kinetic parameters for the IR and XR formulations in therapeutic and toxic dose ranges.

Table 1.
Pharmacokinetic and toxicokinetic parameters of quetiapine [2,10,19,27,28,32,33,34,35,36,37,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58].
At therapeutic doses, the time to peak concentration (tmax) with XR form is delayed by approximately 3 h, and serum concentration peak (cmax) is attenuated [19]. Release occurs over 20 h [51]. A similar relative exposure is achieved with both forms in the therapeutic range [41,51]. The steady-state cmax and area under curve (AUC) of 300 mg XR once daily and 150 mg IR twice daily are considered equivalent [51]. QTP population pharmacokinetic models were one compartmental with first-order absorption [42,45,46]. Interindividual variability of pharmacokinetic parameters was estimated to be 78% to 140% [42].
QTP is a CYP3A4 substrate and may interact with analgesic, anticonvulsant, antiarrhythmic and antiparkinsonian drugs [17]. Coadministration of ketoconazole, a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor, results in a 3–4-fold increase in QTP cmax, whereas phenytoin and carbamazepine as CYP3A4 inducers cause a 5-fold increase in QTP metabolism and a similar decrease in steady-state cmax [34,57,59].
In the «Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Neuropsychopharmakologie und Pharmakopsychiatrie» (AGNP) consensus guidelines, the reference range for QTP serum/plasma concentrations are set at 0.1–0.5 mg/L [33,51,60,61,62]. However, the required concentrations vary for different mental conditions. QTP trough levels of 0.02–0.3 mg/L have been associated with efficacy [28], while concentrations of up to 1 mg/L have been described as therapeutic [23,33,62,63].
The relationship between QTP dose and concentration demonstrates large interindividual variability. In 62 patients treated with 37.5–1200 mg QTP daily, the concentration/dose (C/D) ratio varied 238-fold [64]. In a therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) analysis of adult patients treated with 12.5–2600 mg QTP daily, C/D ratios ranged from 0.01 to 6.9 nmol/L/mg [65]. In certain subpopulations, the C/D correlation may be stronger. A linear relationship between QTP plasma levels and dose per kg body weight was found in 41 patients with schizophrenia, drug-induced psychosis or borderline personality disorder [66]. C/D correlation was strong in 12 elderly patients with selected psychotic disorders [67]. A weak positive linear C/D relationship was found in 180 children and adolescents with psychotic and mood disorders [68].
2.1.2. Clinical and Adverse Effects of Quetiapine
QTP acts via several pathways in the central nervous system (CNS). The desired effects and the adverse drug reaction (ADR) profile follow receptor binding affinity, which is largely dose-dependent [14]. Sedative effects at low doses are mainly mediated by histaminergic (H1) and adrenergic receptors [1,2,28,37,69]. H1 antagonism is associated with increased appetite and weight gain [70]. α1 blockade can cause orthostasis, hypotension and reflex tachycardia [70]. At higher doses (>300 mg), the mood-stabilising and antipsychotic effects increase due to antagonistic effects on serotonin (5-HT2A, 5-HT1A, 5-HT2C) and dopamine (D1, D2) receptors [14]. Extrapyramidal symptoms do not normally occur at therapeutic doses due to lower affinity for D2 receptors [1,61]. Antimuscarinic ADRs, e.g., dry mouth or constipation, can be observed at higher doses [2]. Less common ADRs include dyspepsia, hyperprolactinaemia and sexual dysfunction [39,62,68,71,72,73,74,75]. As with other antipsychotics, QTc prolongation is likely to be dose-related [76,77,78,79]. Other rare but serious ADRs include neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS), hepatotoxicity, myocarditis and blood dyscrasia [80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88]. The XR form is generally better tolerated and causes less drowsiness in the initial hours post-ingestion. However, its effects may last longer [26,39].
Certain ADRs, e.g., anticholinergic delirium, urinary retention, sinus tachycardia and increased intraocular pressure, can be partly attributed to one of the two active metabolites, norquetiapine (N-desalkylquetiapine, norQTP) [70,89,90,91].
2.1.3. Relationship Between Dose or Concentration and Clinical Response
Data on the relationship between QTP dose or plasma concentration and clinical response are limited [61]. Most studies have failed to demonstrate a significant correlation [46,51,68,73,92,93,94,95,96]. In Chinese patients with bipolar disorder, QTP serum concentrations but not daily doses were strongly correlated with clinical outcomes [62]. In 41 patients with schizophrenia, drug-induced psychosis or borderline personality disorder, patient improvement correlated with plasma levels and dose/kg body weight within each diagnostic category but not between categories [66].
2.2. Quetiapine in Acute Intoxication
2.2.1. Acute Toxicity Dose and Concentration Range
A single dose of QTP that presents an acute intoxication is not defined, and there is a large overlap with therapeutic doses. For atypical antipsychotics, an expert consensus panel suggested that ingestion of <5 times the initial adult single dose (i.e., <125 mg for QTP) presented a relatively low risk of severe intoxication in naïve patients ≥ 12 years old. For patients receiving chronic therapy with QTP, the suggested threshold was five times their personal single dose [97]. In a retrospective analysis, QTP intoxication was defined as “a one-time ingestion of more than 400 mg of QTP” [10]. On the other hand, in studies assessing the correlation between QTP plasma concentration and therapeutic response, daily doses of up to 1800 mg were used [51,98]. In a small open-label study, doses of up to 1600 mg daily were well tolerated during a four-week acute phase, and doses up to 1000 mg were used and tolerated in the maintenance phase [99].
In the AGNP guidelines, QTP plasma concentration > 1.0 mg/L is considered toxic. This threshold was calculated by doubling the upper limit of therapeutic concentration [21], which frequently defines the laboratory alert level for antipsychotics [100]. Based on case reports, a higher toxicity threshold of 1.8 mg/L has been proposed. Concentrations ≥ 1.9 mg/L have been reported as potentially comatose-fatal [101]. In postmortem analyses, blood levels > 1 mg/L generally indicated QTP as a contributing factor to death [69].
2.2.2. Toxicokinetic Profile
The available toxicokinetic data for QTP are based on cohort studies and case reports (Table 1). The bioavailability in acute intoxication is lower than at therapeutic doses [40]. In part, this may be due to the anticholinergic effects of QTP [40]. The use of decontamination procedures, e.g., activated charcoal, when administered promptly, may significantly reduce the amount absorbed [35,40]. Gastric emptying may be prolonged due to acute stress associated with severe poisoning and coingested drugs [28,35,100,102]. In several cases of QTP IR ingestion, the tmax was >12 h [27,54]. The reported half-life (t1/2) has a wide range. Both linear and non-linear elimination have been suggested [35,40,54]. Clinical studies conducted during product registration in which therapeutic doses were analysed may underestimate t1/2 at toxic doses [33,40].
Pharmacobezoars may contribute to delayed absorption and tmax, particularly with XR formulations, but have also been found in rare cases with IR formulations at doses > 2.5 g [54,100,103,104,105,106]. In an in vitro study of QTP XR, the bezoars remained stable for more than 4 h, and the drug release was reduced by 53% [107]. In addition to the delayed serum concentration increase, bezoars pose a risk of additional complications, e.g., gastric or intestinal obstruction [107].
2.2.3. Toxicodynamic Profile
QTP demonstrates a variable range of toxicity [23,58]. Intoxication causes symptoms such as CNS depression, lethargy, confusion, drowsiness, tachycardia, hypotension, respiratory depression, anticholinergic symptoms and ataxia [1,2,10,12,26,33,58,97,108,109,110,111,112,113]. Orthostatic hypotension, miosis, agitation and delirium are commonly encountered [2,29,108,114]. Hyperglycaemia and hypokalaemia occur less frequently [52]. Severe toxicity may be more common than with other atypical antipsychotics, occurring in about one-sixth of patients [1,111,115]. Clinical signs include seizures, status epilepticus, rhabdomyolysis, respiratory depression, hypotension, coma and death [1,2,29,116,117,118,119]. In a review of 945 cases of QTP overdose, 388 cases (41.1%) required admission to the intensive care unit (ICU) [1]. Coma was reported in 10% of QTP intoxication cases [60]. Fatal outcomes are rare, and there are known cases of patients surviving a very high overdose [26,58]. On the other hand, deaths have been reported even after therapeutic doses [29]. The mortality risk is higher than with other atypical antipsychotics [120,121]. In acute poisoning, complications such as aspiration pneumonia can contribute to death [60]. An Australian analysis estimated a 1.2% death rate directly attributable to QTP overdose in cases with QTP detected in postmortem blood [115,122].
Sinus tachycardia occurs in the majority of patients after severe intoxication [106,123]. It results from antimuscarinic activity and may also be a reflex to α1-induced vasodilation and hypotension [2,52,58,103,124]. Hypotension is more common than with most other antipsychotics and occurs in up to 40% of patients [28,106,115,123]. In most cases, it can be resolved with intravenous fluid replacement. Profound hypotension resistant to volume resuscitation is rare [125]. CNS and respiratory depression are related to the antagonistic action on 5-HT and dopamine receptors [126,127]. The antimuscarinic effects can cause transient sedation [128]. Histaminergic sedation is predominant in lower dose ranges [14].
There are several published reports of QTc interval prolongation [33,52,128], but its clinical significance remains controversial [1,129,130]. In a US multicentre cohort study, QTP caused severe QT prolongation, defined as QTc ≥ 500 ms using Bazett’s correction, in 96 of 471 intoxication cases [131]. In a case series of QTP poisoning published by Balit et al., the uncorrected QT interval was not altered despite the QTc increase. The authors argued that the prolonged QTc interval resulted from overcorrection by Bazett’s formula due to tachycardia rather than from intrinsic cardiac toxicity [2]. Cardiac arrhythmias are very rare [107,132,133]. Ngo et al. reported two cases of ventricular tachycardia without torsade de pointes [1]. A single case report describes Brugada syndrome following QTP intoxication [134]. Widened QRS complexes can be a sign of immediate circulatory collapse [135]. They have been associated with an increased risk of seizures and ventricular dysrhythmia [136]. Heart block, possibly related to hypokalaemia, is not uncommon [27,137].
Seizures can be induced by antagonism on dopamine (D2), histamine or adrenergic receptors, as well as hypoxia [138]. They occur infrequently, typically within 4–8 h post-ingestion, and are self-limiting in the majority of cases [2,106,138]. In a retrospective 5-year case series, the incidence of seizures in acute QTP intoxication events was 2% [1]. Late-onset seizures (≥24 h post-ingestion) have been described after ingestion of QTP at doses of 4 g to 30 g [58,139,140]. The relationship between severity and QTP serum concentration has not been clarified, and seizures have been reported at therapeutic doses [141,142,143,144]. Similarly, myoclonus has been reported as a leading symptom of QTP intoxication [145] but may also occur at higher therapeutic doses administered therapeutically [146,147].
Agitation has been reported at higher therapeutic doses [148]. In acute intoxication, it may follow initial drowsiness and lethargy after several hours [149]. Anticholinergic delirium may also occur at a late stage after a period of decreased consciousness and persist for several days, possibly due to delayed QTP absorption and/or elimination [2,55,91]. Coingested drugs, clinical interventions (e.g., intubation), somatic complications and underlying psychiatric disorders may contribute to delirium [91,150,151].
Rhabdomyolysis has been described after a period of immobility of at least 14 h [152,153,154]. However, in the case of a 48-year-old man ingesting 12 g of QTP, rhabdomyolysis may have occurred due to a direct toxic effect of QTP, as no muscle wasting or pain was present [152]. NMS has been rarely reported and is considered idiosyncratic. It has occurred even at therapeutic doses as low as 12.5 mg daily [155,156,157,158,159,160,161]. It is characterised by fever, rigidity, autonomic instability and altered mental status. Elevated creatine kinase levels and leucocytosis are common. Without early recognition, it can lead to rhabdomyolysis, respiratory failure, acute kidney injury, seizures and death [162]. Following intoxication with the XR form, delayed toxicity with prolonged coma, rhabdomyolysis and aspiration pneumonia are more likely [26,32,40].
Treatment of acute QTP intoxication is symptomatic, and patients should be monitored [26,33]. There is no specific antidote. The use of activated charcoal within 6 h post-ingestion reduces the absorption of QTP by 35% and shortens the apparent t1/2 [33,35,163]. Gastric lavage may be considered for severe intoxications, ideally within 1 h post-ingestion [33]. Whole bowel irrigation has also been used [149]. During gastric lavage, a temporary increase in serum concentrations may occur [164]. QTP is not dialysable [85,165].
All patients experiencing symptoms beyond mild drowsiness should be referred to the Emergency Department, regardless of the ingested dose [97]. With an ingested dose < 3 g and a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of 15 for 4 h post-ingestion, patients may be discharged to a psychiatric unit [2]. The expected time of onset and peak of toxicity symptoms is within 6 h post-ingestion for the IR formulation [97]. For the XR formulation, the initial assessment of vital signs and mental status may not predict the severity of intoxication as the peak toxicity takes longer to develop [10]. If no sedation or tachycardia occurs within 12 h after an overdose with the XR formulation, severe intoxication can be excluded [10].
2.2.4. Relationship Between Dose or Concentration and Clinical Presentation in Quetiapine Intoxication
While the clinical signs and symptoms vary across the QTP dose range, cmax may be a good predictor of toxicity [2]. However, despite its therapeutic implications, plasma concentration is not commonly measured in toxicology, and obtaining a measurement at tmax is challenging [26]. An unreliable medical history, coingested drugs and the use of decontamination procedures can complicate the correlation assessment [28]. Therefore, dose, serum concentration and clinical presentation generally demonstrated a poor correlation [12,27,28,29,30]. However, in a retrospective analysis of 18 cases, QTP dose correlated with both cmax and the severity of the outcome [2]. In a cohort study of 286 QTP intoxication events, there was a modest correlation between dose and minimum blood pressure, and dose influenced the probability of intubation [111].
In postmortem analyses, whole blood concentrations may be more informative than serum concentrations [166]. The concentration ratio between whole blood and serum exceeded 1 at concentrations > 2.5 mg/L [166], in contrast to therapeutic doses with a ratio of ~0.7 [167,168]. QTP is likely to undergo a significant postmortem redistribution from striated muscle, connective and adipose tissue [21]. Drug diffusion from bezoars in the gastrointestinal tract to adjacent tissues may occur following ingestion of large quantities [21]. In fatal QTP monointoxications, postmortem whole blood concentrations were above 7.2 mg/L [47,166,169]. In a study of 21 fatal cases, the authors reported the (central and peripheral) blood concentrations < 1 mg/L as “therapeutic”, i.e., not related to death, and concentrations > 1 mg/L as “above therapeutic” and death-related [53]. Higher postmortem blood concentrations, reaching up to 170 mg/L, were found in heart or central body cavity blood samples, probably due to a higher susceptibility for postmortem redistribution [21,47,169,170,171,172].
3. Analysis of Published Cases of Acute Quetiapine Intoxication
The aim of the analysis was to investigate the relationship between the ingested QTP dose, serum concentrations and individual toxicodynamic parameters with the joint data of published cases from the literature. While the clinical signs and symptoms of QTP intoxication have been well described, it remains unclear how specific parameters correlate with the ingested dose and concentration. Therefore, dose and concentration ranges for each dynamic parameter were investigated. Potential thresholds that represent an increased risk for the occurrence of individual signs and symptoms were determined.
3.1. Methods
3.1.1. Literature Search and Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
A literature search was conducted for relevant sources on QTP poisoning in the PubMed® and EBSCO databases (including the Science Citation Index expanded). The search string was any combination of the words “quetiapine” or “Seroquel” and “poisoning”, “overdose” or “intoxication”. In the second phase, the references and the citing literature (if available on the website) were analysed. Book chapters, preclinical studies and in vitro studies were not analysed.
Cases of QTP intoxication in patients ≥ 12 years old were included if the ingested dose and/or serum/plasma concentration of QTP were reported, along with a description of the clinical presentation. Cases with coingested agents were included if QTP was described as relevant to the clinical course. Cases of ADRs and drug interactions with therapeutic doses of QTP were excluded. Doses representing acute intoxication were the ingestions of >5 times the initial adult single dose of QTP in naïve patients [97] or doses exceeding the approved therapeutic range, i.e., >800 mg, in patients with regularly prescribed QTP [173].
Postmortem cases were included if any information on the clinical picture before death was available, together with the postmortem QTP concentration or the ingested dose. Only concentrations from peripheral blood samples were captured. Heart or cavity blood concentrations were not included as values may have been exaggerated due to postmortem redistribution [69,171,174].
3.1.2. Data Gathering and Statistical Analysis
The following data were extracted from the references: patient demographics (age, sex), details of QTP ingestion (amount ingested [mg], IR/XR form), QTP serum/plasma concentrations [mg/L], time from QTP ingestion and/or time from hospital admission to sampling [h], use of clinically relevant coingestants, treatment strategies and interventions (decontamination procedures, intubation, use of vasopressors, specific therapies), length of hospital stay [days], ICU admission, length of ICU stay [days], clinical events, signs and symptoms (lowest GCS score, tachycardia [heart rate ≥ 100 beats per minute], hypotension [blood pressure < 90/60 mm Hg, or <100/50 mm Hg, or explicitly stated], QTc prolongation [QTc > 480 ms, or >55 ms above baseline, or explicitly stated QT or QTc prolongation], QRS prolongation [QRS > 100 ms], arrhythmia, heart block, seizures, agitation, delirium, acidosis [serum pH < 7.34], rhabdomyolysis [creatine kinase levels > 1000 U/L], hypokalaemia [serum potassium level < 3.5 mmol/L, or explicitly stated], hyperglycaemia [serum glucose level ≥ 9 mmol/L]. Based on the lowest GCS score, cases were categorised into four grades according to the severity of intoxication: Grade 1: death; Grade 2: GCS = 3–8; Grade 3: GCS = 9–14; Grade 4: GCS = 15. If the GCS score was not explicitly stated, a three-member panel reviewed the case to determine whether the GCS grade (1–4) could be estimated from the clinical description.
Coingestants, considered clinically relevant, were all drugs taken in the context of acute intoxication affecting CNS, i.e., drugs of abuse, ethanol, drugs of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification Group N (nervous system drugs), baclofen or diphenhydramine. Other clinically relevant coingestants were drugs with suspected clinically relevant kinetic interaction with QTP, e.g., potent CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Cases with reported ingested QTP dose and concentration, together with the estimated time from ingestion to sampling, were included in the concentration–time analysis. All concentration time points were dose normalised to 10 g of QTP. Time points < 5 h post-ingestion for the XR QTP formulation were excluded from the t1/2 estimation.
Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to determine the correlation between QTP dose and cmax. Binary logistic regression was used to evaluate QTP dose and cmax as continuous predictor variables for individual toxicodynamic parameters (clinical events, signs and symptoms, and treatment strategies). For each parameter, cases were divided into two separate groups, the “event” group and the “no event” group. Logistic regression was performed for the parameters with at least 15 cases in the “event” group with reported QTP dose or concentration. The case distribution for each dynamic parameter was reviewed. Based on the distribution figures, additional logistic regression models with dose or concentration as categorical variables were created where appropriate. Pearson’s chi-square test was used to test the association between tachycardia and QTc prolongation, and Fisher’s exact test was used to test the association between QTc prolongation and arrhythmia. For all tests, a p-value < 0.05 was the threshold for statistical significance.
Data analyses were performed in Microsoft Excel 2016 (descriptive statistics, dose-normalised concentration–time figures) and IBM SPSS Statistics 25 (distribution figures, logistic regression and other statistical tests).
3.2. Results and Discussion
The literature search, conducted on 11 March 2024, yielded 5437 results in the EBSCO database and 508 results in PubMed. Relevant case reports, case series, clinical studies, review articles, conference abstracts or annual Poison Control Centre reports were extracted. A total of 444 QTP intoxication cases were closely reviewed. Finally, 63 cases were included in the dose–concentration correlation assessment, 58 cases in the dose-normalised concentration–time figures, and 134 cases in the toxicokinetic–toxicodynamic correlation analysis, which were collected from 68 case reports, 16 case series, two cohort studies and six annual Poison Control Centre reports [1,2,12,27,28,29,33,40,49,52,54,55,56,58,71,72,85,103,104,106,111,114,116,125,126,128,137,138,139,141,144,150,152,153,154,157,163,164,175,176,177,178,179,180,181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189,190,191,192,193,194,195,196,197,198,199,200,201,202,203,204,205,206,207,208,209,210,211,212,213,214,215,216,217,218,219,220,221,222,223,224,225,226,227,228]. For 20 cases from an original cohort study, additional primary data were provided by the authors [27].
3.2.1. Dose–Concentration Correlation
The ingested QTP dose and the measured cmax demonstrated a weak but significant correlation using Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r = 0.256; N = 63; p = 0.043). Since large discrepancies were observed in several cases, it is questionable whether the measured concentrations in these cases really corresponded to the cmax. In addition, the information on QTP dose and the time of ingestion may have been inaccurate. If only the cases with a reliable medical history were analysed, the correlation would probably be stronger. Uncertainties related to dose and the time of ingestion have previously been used to improve the stability of a predictive model [35]. However, a relatively weak correlation between dose and exposure appears to be inherent to QTP, as evidenced by population pharmacokinetic analyses, demonstrating large interindividual variability even at therapeutic doses [42]. Therefore, the measurement of QTP concentration is advised to predict the toxicodynamic profile.
Of the 58 cases with an estimated time between ingestion and concentration measurements, 32 had multiple concentration measurements performed. One hundred and sixty-three concentration points are included in the dose-normalised concentration–time analysis (Figure 1).
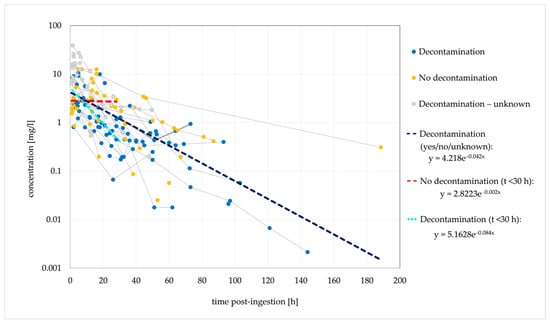
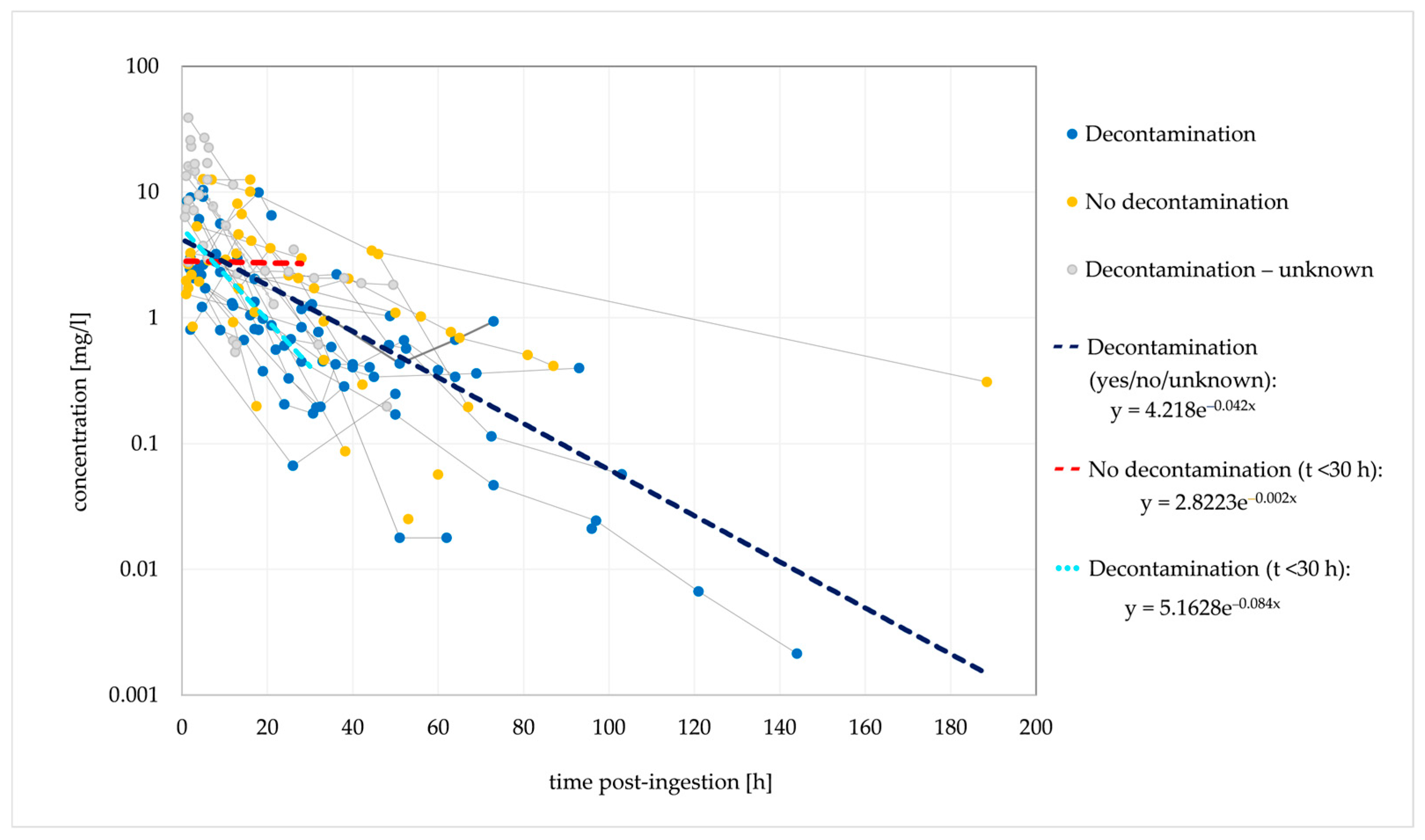
Figure 1.
Observed dose-normalised quetiapine concentration vs. time (decontamination/no decontamination). Dashed lines are fitted monoexponential curves.
Based on the elimination rate constant (ke) of 0.042/h, the typical t1/2 was 16.5 h. In the cases where no decontamination was performed, a stagnant concentration trend line was observed for 30 h post-ingestion, suggesting that the absence of decontamination causes a delayed tmax and a delayed (or extended) concentration peak. Figure 2 shows the ingestions of IR and XR formulations separately; cases with unknown formulations are not included.
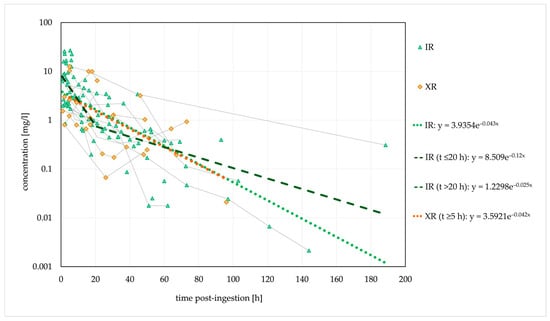
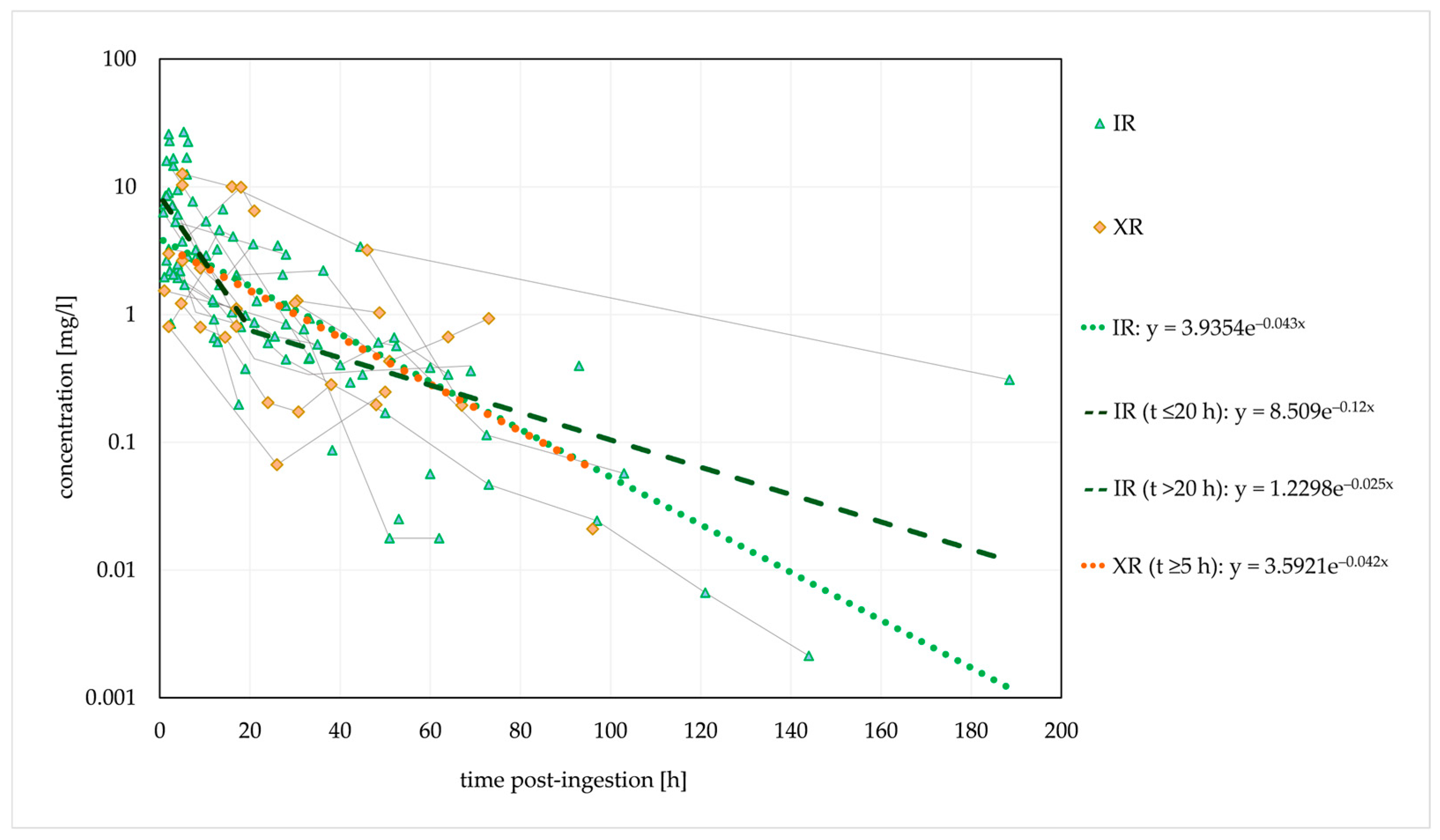
Figure 2.
Observed dose-normalised quetiapine concentration versus time (immediate-release/extended-release formulation). Dashed lines are fitted monoexponential curves.
The estimated t1/2 was similar for both formulations. However, a biphasic disposition cannot be excluded for the IR form, with an initial t1/2 of 5.8 h (within 20 h post-ingestion, probably with a significant influence of the distribution) and a longer terminal t1/2 of 27.7 h (>20 h post-ingestion). Thus, the estimated initial t1/2 corresponded to the therapeutic t1/2.
A median t1/2 of 6.6 h was previously reported in a clinical evaluation of the effect of activated charcoal in 54 intoxication events [35]. The authors developed a one-compartment model with first-order absorption and first-order elimination that described the observed data. However, other studies and case reports demonstrated conflicting findings, and biphasic elimination was suggested in several cases [27,40,54,106]. This could indicate the presence of a third compartment, bezoar formation or hepatic redistribution [33,85,106]. Saturated hepatic metabolism is not very likely. The reported cmax values are several times lower than the previously estimated in vitro Km values for the formation of QTP metabolites [57,106]. QTP was detected in plasma for a maximum of 7 days post-ingestion [47]. In the terminal phase, the rate of decline in QTP concentrations may be significantly reduced due to redistribution from a third compartment or the release of QTP from bezoars in the gastrointestinal tract. A slower elimination rate in the terminal phase could explain the longer duration of clinical symptoms in several described cases [54,106].
A second concentration peak was noted in 12 cases, five of which were intoxications with the XR form; in an additional four cases, the formulation was not explicitly stated. Activated charcoal was used in three cases, and gastric lavage was performed in five cases. Pharmacobezoar formation was recognised in three cases [164,204]. One case was a probable drug interaction with antiretroviral therapy [56]. The second concentration peak occurred between 20 and 56 h post-ingestion.
In the case of a 39-year-old female patient who had ingested 30 g of QTP (formulation unknown), norQTP concentrations were measured. The cmax of 10.2 µmol/L was reached 62 h post-admission, and the concentrations were still elevated after 80 h. The possibility of pharmacobezoar formation was not discussed [54,228]. Vignali et al. found norQTP in significant concentrations in 13 postmortem cases. The femoral blood concentrations of norQTP exceeded those of QTP in four cases. The correlation between QTP and norQTP may be useful in determining the time and route of ingestion [60].
3.2.2. Relationship Between Dose or Concentration and Clinical Presentation
Table 2 shows the characteristics of the 134 patients with QTP intoxication. The median ingested QTP dose for 118 cases was 10 g (IQR 4.25–17.50 g, range 0.25–48 g), and the median cmax measured in 65 cases was 4.04 mg/L (IQR 1.83–7.45 mg/L, range 0.03–38.35 mg/L).

Table 2.
Patient demographics, clinical presentation and treatment strategies.
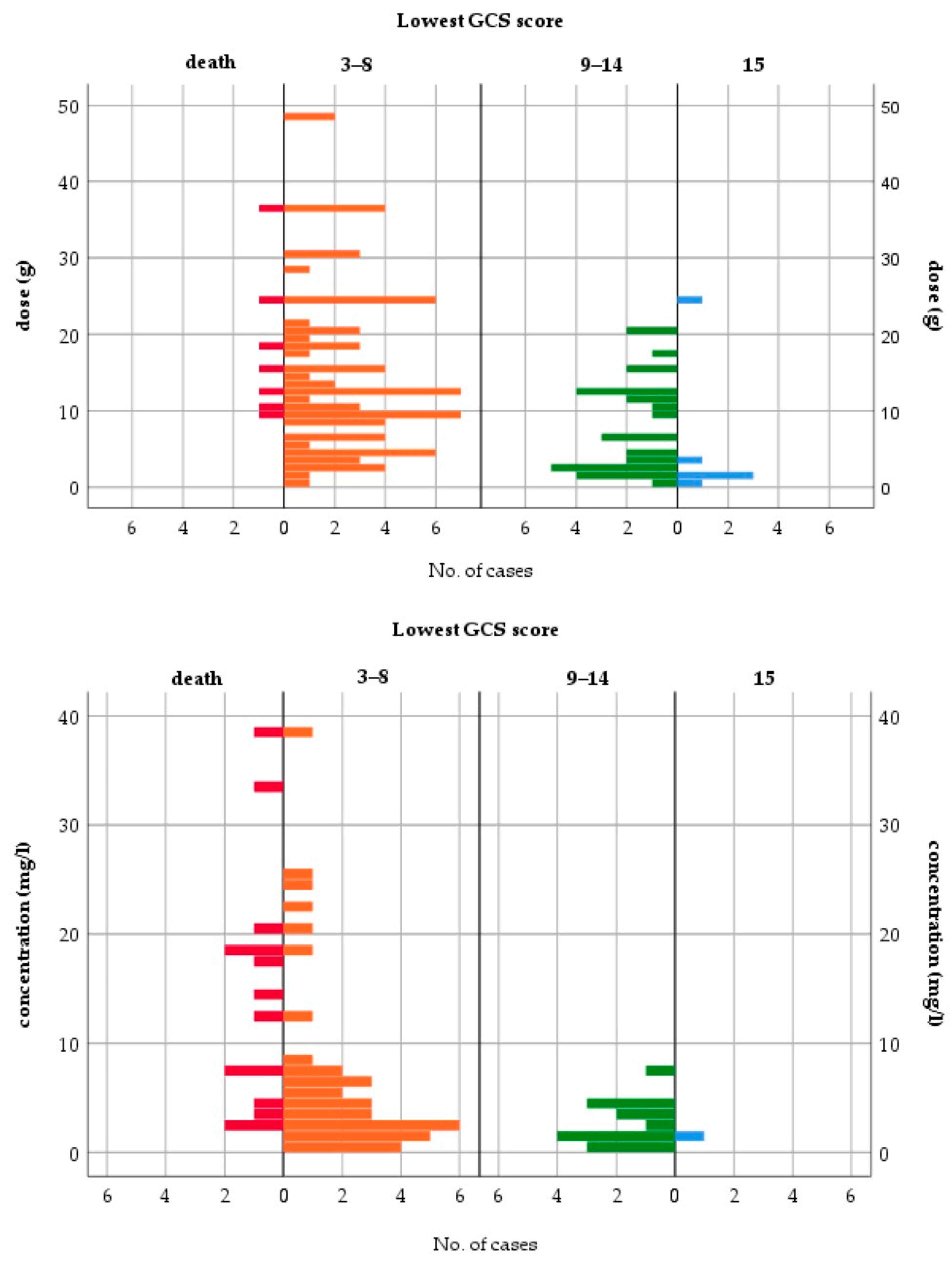
All fatalities occurred either with QTP doses ≥ 9 g or cmax > 2 mg/L (Figure 3). The median ingested dose and median cmax in fatal cases were 15 g and 13.39 mg/L, respectively. CNS depression (GCS < 15) occurred in 95.5% of patients. The case distributions by dose and cmax for other toxicodynamic parameters are presented in Supplementary Figures S1 and S2. To assess the relationship between dose or cmax and the severity of intoxication, patients with mild to moderate symptoms (GCS ≥ 9) were compared to patients with severe symptoms, including fatal outcomes (GCS ≤ 8). Table 3 shows the results of the logistic regression models for the severity of intoxication.
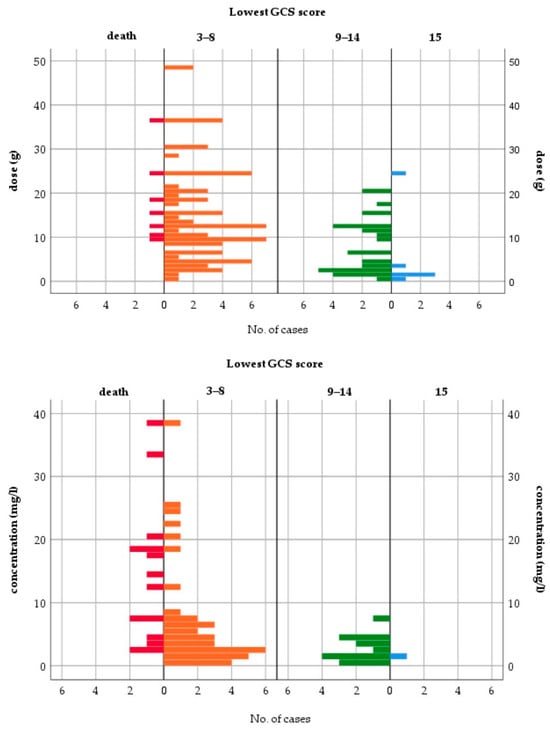
Figure 3.
Lowest Glasgow Coma Scale score—case distribution by dose and peak concentration.

Table 3.
Lowest Glasgow Coma Scale (≤8 or ≥9) vs. quetiapine dose and peak concentration—logistic regression results.
Dose and cmax were good predictors of severe intoxication. Doses > 3 g and cmax > 5 mg/L were associated with a higher risk for the lowest GCS score ≤ 8. The previously reported dose thresholds for increasing severity of symptoms were comparable and ranged from 2.5 to 5.4 g [2,97,114,229]. However, individual cases of only mild toxicity at a 20 g dose and survival after a dose of 36 g have been reported [52,220]. For the XR formulation, a dose > 1.5 g and two or more coingested agents were associated with greater severity of poisoning in a retrospective study of 372 cases [26]. Another retrospective analysis of QTP intoxications without sedative coingestants revealed a poor correlation between the ingested dose and the lowest GCS for both formulations. While the signs of peak toxicity were similar for the IR and XR forms, the time to peak toxicity was significantly longer for the XR form: 7 h vs. 3.8 h for the lowest GCS score and 9 h vs. 2.5 h for the maximum heart rate. The median time to recovery from sedation was longer for the XR form (20 h vs. 12 h after IR) [10].
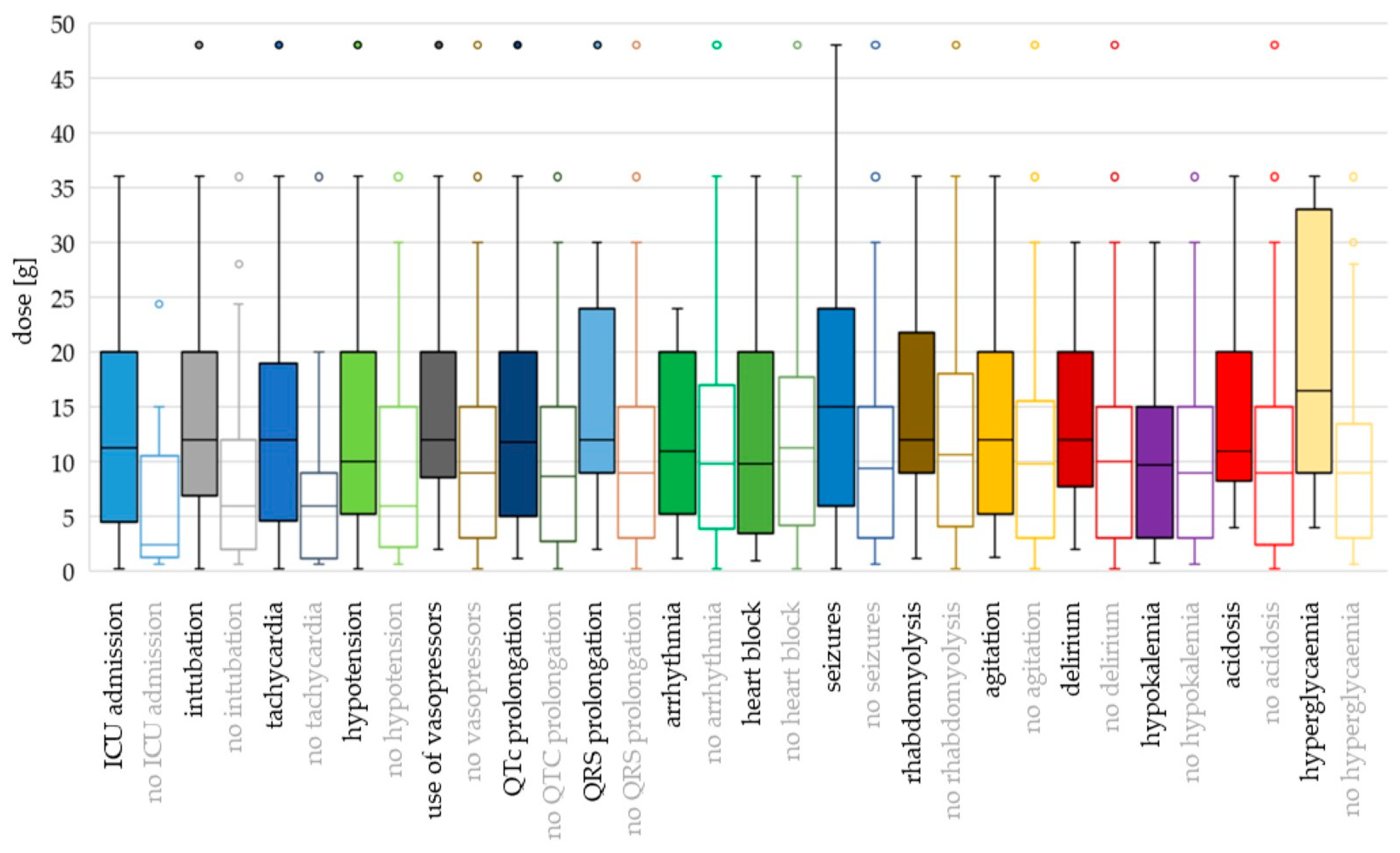
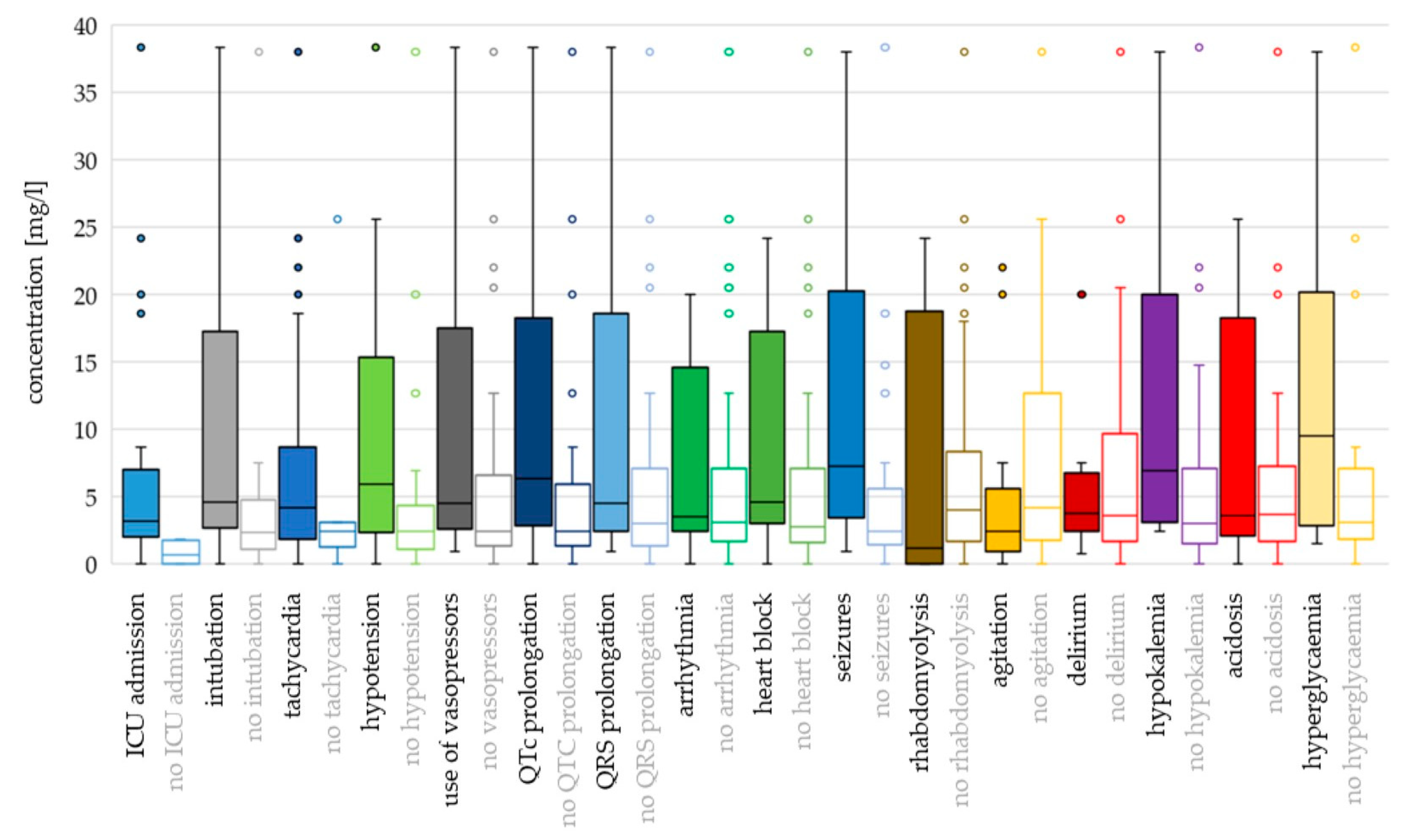
For most toxicodynamic parameters, the ingested QTP dose and cmax were higher in the “event” groups compared to the “no event” groups (Figure 4 and Figure 5; Supplementary Table S1). Patients without heart block ingested a higher median dose than patients with heart block, and patients without rhabdomyolysis, agitation and acidosis had higher median cmax values compared to the “event” groups. However, none of these differences were found to be significant in the logistic regression analyses (Supplementary Table S2).
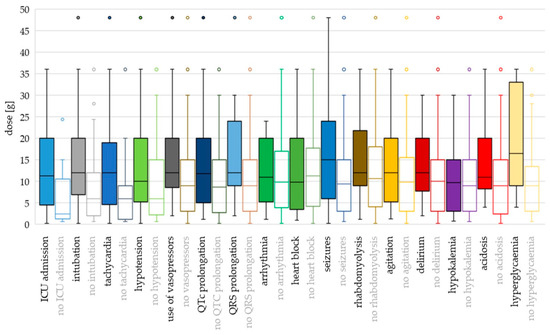
Figure 4.
Toxicodynamic parameters vs. ingested quetiapine dose boxplot. Circles denote outlyers by Tukey’s test.
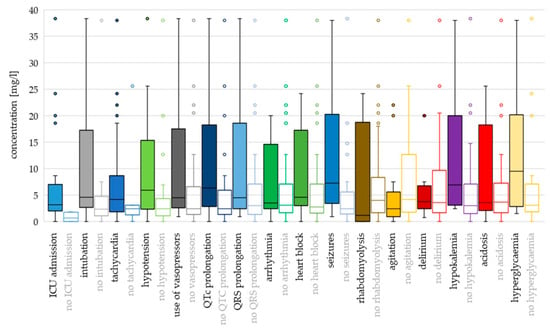
Figure 5.
Toxicodynamic parameters vs. quetiapine peak serum concentration boxplot. Circles denote outlyers by Tukey’s test.
Hyperglycaemia and seizures occurred at the highest ingested doses and cmax values (median dose 16.5 g and 15 g; median cmax 9.54 mg/L and 7.30 mg/L, respectively). Median doses were >12 g also for intubation, tachycardia, use of vasopressors, QRS prolongation, rhabdomyolysis, agitation and delirium, while median cmax values were >5 mg/L for QTc prolongation, hypotension and hypokalaemia.
Using binary logistic regression with dose as a continuous variable, the differences were significant for ICU admission (OR 1.142; p = 0.005), intubation (OR 1.082; p = 0.001), tachycardia (OR 1.079; p = 0.040), use of vasopressors (OR 1.042; p = 0.043), QTc prolongation (OR 1.043; p = 0.041) and seizures (OR 1.051; p = 0.016). With dose categorisation, the risk of hypotension was higher for doses >8 g compared to doses ≤ 3 g (OR 3.070; p = 0.028) (Supplementary Table S2).
Cmax as a continuous variable was associated with ICU admission (OR 4.263; p = 0.023), intubation (OR 1.100; p = 0.001) and seizures (OR 1.110; p = 0.009). In addition, cmax values > 7 mg/L presented greater odds for the use of vasopressors (OR 14.545; p = 0.013), values > 4 mg/L were associated with QTc prolongation (OR 4.889; p = 0.009) and values >5 mg/L presented greater odds for hypotension, compared to cmax ≤ 2 mg/L (OR 7.500; p = 0.008).
The odds for ICU admission increased by 14% for every 1 g of QTP ingested and were 6-fold greater for doses between 3 and 8 g and >9-fold greater for doses > 8 g than for doses ≤ 3 g. QTP concentration was a strong predictor of ICU treatment. All patients with a cmax > 2 mg/L were admitted to the ICU. In a published case series of 18 patients with QTP poisoning, a dose < 3 g generally did not require ICU admission or hospitalisation for >24 h [2].
The risk of intubation was related to both increasing dose and concentration; the odds were 9.5-fold higher for doses > 4 g QTP (compared to ≤ 2 g), 3.5-fold higher for cmax 3-8 mg/L, and 22-fold higher for cmax > 8 mg/L (compared to cmax < 3 mg/L). In a cohort study of 286 QTP intoxication events, the risk of intubation was dose-dependent, increasing from 10% at a dose of 2 g, 22% at 5 g, 37% at 10 g, and 55% at 20 g [48,106]. The median dose in intubated patients was 5 g (IQR 2.52–11.85 g) [111]. Taylor and Graudins found a higher ingested dose (median 5.8 g) in patients requiring intubation (median 2 g in non-intubated patients). The duration of intubation was significantly longer after ingestion of the XR form compared to the IR form (47 h and 17 h, respectively). However, the ingested doses of the XR form in the study were significantly higher (5.7 g vs. 1.75 g for the IR form) [10].
Apart from CNS depression, tachycardia was the most common sign of QTP intoxication and occurred in >80% of cases. The odds were 12-fold greater for doses 1–10 g and 44-fold greater for doses > 10 g than for doses < 1 g. We also observed a trend of increased risk of tachycardia for cmax > 4 mg/L (OR 8.348; p = 0.054). There was only one case with cmax > 5 mg/L and without tachycardia (compared to 20 cases with tachycardia at cmax > 5 mg/L—Supplementary Figure S2).
The risk for hypotension was significantly associated with doses > 8 g (compared to doses ≤ 3 g) and with cmax > 5 mg/L (compared to cmax ≤ 2 mg/L). Similarly, doses > 7 g demonstrated 4-fold greater odds for the use of vasopressors than doses ≤ 7 g. In a retrospective analysis of 286 QTP intoxication events, a modest correlation was found between the ingested dose and the lowest systolic blood pressure [111].
The lowest dose associated with QTc prolongation was 1.2 g. Increasing dose was significantly correlated with QTc prolongation, confirming previous findings on QTc dose-dependence [76,77,78,79]. The odds for QTc prolongation were 5-fold greater for cmax > 4 mg/L. Berling and Isbister analysed the relationship between QTP dose and the risk of uncorrected QT prolongation in 202 patients and found no correlation [230]. Most QT prolongations occurred in patients with tachycardia (rates > 105 bpm) [230]. In our dataset, there was no association between QTc prolongation and tachycardia (Pearson χ2(1, N = 103) = 1.88, p = 0.170). Uncorrected QT prolongation was not analysed. Several other risk factors for QTc interval prolongation are known, e.g., electrolyte imbalances, female sex, older age, pre-existing cardiac disease and drug–drug interactions [129,132], which were not assessed in this analysis.
The following arrhythmia patterns were described: ventricular tachycardia, ventricular extrasystoles, ventricular fibrillation, self-limiting ventricular bursts, (paroxysmal) supraventricular tachycardia, ectopic atrial rhythm, palpitations, atrioventricular nodal re-entry tachycardia and wide complex rhythm. Arrhythmia was rarely reported, and the number of cases included in analysis was low (seven cases with prolonged QTc interval, four cases without prolonged QTc interval, and three cases with no QT or QTc reported). The association between arrhythmia and QTc prolongation failed to reach statistical significance using Fisher’s exact test (p = 0.098). In published studies, acute intoxication with QTP as a single agent did not increase the risk of torsade de pointes [9,111].
There was a small but statistically significant increase of 5% in the odds of seizures for every 1 g of QTP ingested (OR 1.051, p = 0.016) and an increase of 10% in the odds for every 1 mg/L increase in cmax value (OR 1.110, p = 0.009). The odds were 5-fold greater with doses > 20 g (compared to doses ≤ 10 g) and 7.5-fold greater with cmax > 4 mg/L. In a cohort study of 286 QTP intoxication events, all five patients who experienced seizures had ingested high doses (6–24 g) of QTP and concurrent drugs, including high doses of citalopram in two cases [111]. In our dataset, seizures occurred at higher dose and concentration ranges than other signs and symptoms, with the exception of hyperglycaemia (median 15 g and 7.3 mg/L, respectively). Half of these patients (17/34) had coingested clinically relevant agents.
There was no association between QTP dose or cmax and the risk of QRS prolongation, arrhythmia, heart block, agitation, hypokalaemia or acidosis. There was a trend towards an increased risk of heart block at a cmax > 3 mg/L (OR 4.033; p = 0.053) and for acidosis at doses > 7 g (OR 3.667; p = 0.057). In line with these findings, the occurrence of arrhythmias, AV block, QTc prolongation, hypokalaemia and acidosis in QTP intoxications is not as consistently described as in intoxications with several other antipsychotics [136,231,232]. A recent study by Tang et al. showed no significant increase in QRS prolongation (>120 ms) in QTP poisoning in a large cohort of 11,945 patients with pharmaceutical overdoses [233].
Logistic regression analyses were not performed for rhabdomyolysis, delirium and hyperglycaemia as the number of cases in the “event” group with reported ingested dose or cmax was low.
Fourteen cases with confirmed pharmacobezoar formation were included. All involved ingestion of the XR formulation with doses ranging from 3 g to 48 g. None of the cases were fatal. In a series of nine cases of bezoar formation after an overdose of XR QTP, eight patients had coingested other drugs. A gradual or rapid deterioration after several hours was typical in these cases. However, after endoscopic removal of the pharmacobezoars, none of the patients experienced significant toxicity, and all recovered within 3 days [104].
IR and XR forms can differ in their toxicodynamic profile. The IR form may be more likely to cause severe signs, e.g., coma and respiratory depression, in the first hours post-ingestion due to higher cmax [29]. On the other hand, symptoms may be prolonged with the XR form, especially if no decontamination has been performed. Fifty-eight of the included patients ingested other clinically relevant agents, most commonly ethanol, benzodiazepines, antidepressants and other antipsychotics, similar to previous reports [26]. Information on the ingested formulation was frequently missing from the reports. It was not feasible to include the QTP formulation, coingested agents or decontamination procedures as covariates in the statistical models with the collected dataset.
In summary, higher QTP dose and concentration were significantly associated with the lowest GCS score, ICU admission, intubation, hypotension, use of vasopressors, QTc prolongation and seizures. Dose, but not concentration, was also associated with tachycardia. The thresholds for increased risk of these events were variable, between 3 g and 20 g for QTP dose and between 2 mg/L and 7 mg/L for QTP concentration. Therefore, doses > 3 g and concentrations > 2 mg/L presented a higher risk of a severe clinical presentation. The probabilities for the parameters, significantly associated with QTP dose and concentration, below and above the 3 g dose and 2 mg/L concentration thresholds are presented in Supplementary Figures S3 and S4.
4. Limitations
The reliability of data in the context of intoxication may be questionable. In the existing studies, obtaining accurate information on the dose and time of ingestion presented a challenge, and it was often not documented [1]. In addition, reviewing cases from the literature presents a limitation, as publications may contain different amounts and types of data, and gaining additional information is not possible. Therefore, not all parameters of interest can be captured for every included case. Due to the heterogeneity of data from published reports and studies on acute QTP intoxication, a systematic review was not conducted. However, the literature search, data collection and analysis were clearly structured and described.
With the collected dataset, it was not possible to perform statistical analyses with multiple covariates, as data for different parameters were frequently missing from the references. Imputation, maximum likelihood or a similar method to include missing values was not attempted. Coingestion of other agents was one of the factors that undoubtedly had an impact on the clinical presentation in several cases but was not evaluated.
The frequencies for clinical events, signs and symptoms in the analysis do not represent true incidences, as they are based on published case reports and series and not on population data. The inclusion of published cases has inevitably led to a bias towards more severe cases, as asymptomatic and mild intoxications are not usually published.
The lack of a significant correlation between QTP dose or cmax and several toxicodynamic parameters does not mean that these signs and symptoms do not occur in acute QTP intoxication. Rather, it indicates that they may occur regardless of the dose taken or the concentration measured when the QTP dose exceeds the upper therapeutic limit of 800 mg. None of the dynamic parameters were analysed as continuous variables. Therefore, the exact pattern of this relationship cannot be assessed using the data collected from the literature.
5. Conclusions
In this structured literature review and analysis of acute QTP intoxication cases, the typical t1/2 (16.5 h) was longer than for therapeutic doses. Decontamination procedures may have significantly reduced tmax, cmax and estimated t1/2. The ingested QTP dose and cmax were significantly correlated. CNS depression (GCS < 15) and tachycardia were the most common signs of QTP intoxication. Dose as a continuous variable was generally a better predictor of clinical events than cmax. However, with dose and cmax categorisation, both were significantly correlated with the same clinical events. Higher doses and cmax values increased the risk of ICU admission, intubation, hypotension, use of vasopressors, QTc prolongation and seizures, but not QRS prolongation, arrhythmia, heart block, agitation, hypokalaemia or acidosis. Tachycardia was associated with increasing doses and was short of a significant correlation with cmax. The dose thresholds for an increased risk of “event” for individual toxicodynamic parameters were typically between 3 g and 7 g (20 g for seizures and QTc prolongation), and the cmax thresholds were between 2 mg/L and 4 mg/L (7 mg/L for the use of vasopressors). Therefore, doses > 3 g and cmax > 2 mg/L may be considered alert levels for high risk of severe complications in acute QTP intoxication.
Patients ingesting >3 g of QTP should be observed at the Emergency Department and may be transferred to a psychiatric unit no sooner than after 6 h if no severe signs and symptoms are present. The type of formulation (IR or XR) should be specified together with the dose. If ingestion of XR QTP is suspected, patients may require longer, e.g., 12 h observation. Prompt decontamination (e.g., use of activated charcoal within 6 h post-ingestion) is likely to improve the clinical course of intoxication. If a serum QTP concentration measurement is available on site, sampling upon admission, but not earlier than 2 h post-ingestion, is recommended to confirm or exclude the intoxication with QTP. A concentration > 2 mg/L indicates a severe, potentially lethal intoxication. However, lower concentrations may still anticipate a severe clinical course, depending on the time from ingestion to sampling, so caution is required when interpreting concentration results.
6. Future Directions
Future studies may investigate closely the duration of common signs and symptoms, particularly when evaluating treatment strategies. The reports on QTP intoxication should state the formulation (IR or XR) that may influence the clinical course and is relevant for clinical decision-making. Determining the concentration–time relationship for two analytes, QTP and its active metabolite norQTP, could be informative. The measurement of both analytes in clinical practice might improve the estimation of the time from ingestion to sampling.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jox14040085/s1, Figure S1: Toxicodynamic parameters—case distribution by dose; Figure S2: Toxicodynamic parameters—case distribution by peak concentration; Figure S3: Toxicodynamic parameters—probabilities with quetiapine dose below and above 3 g; Figure S4: Toxicodynamic parameters—probabilities with quetiapine concentration below and above 2 mg/l; Table S1: Dose and peak concentration data for toxicodynamic parameters; Table S2: Toxicodynamic parameters—logistic regression results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, M.D.V., I.G. and M.B.; methodology, M.D.V. and I.G.; literature search, M.D.V. and F.E.; data analysis, M.D.V., F.E. and I.G.; resources, M.B.; data curation, M.D.V.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D.V.; writing—review and editing, M.D.V., I.G., F.E. and M.B.; visualisation, M.D.V.; supervision, M.B.; project administration, M.B.; funding acquisition, M.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Slovenian Research and Innovation Agency grant No. P3-0019 to M.B.; I.G acknowledges the financial support from the Slovenian Research and Innovation Agency (grant No. P1-0189).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created in this study. Statistical analyses are provided as Supplementary Materials. A data spreadsheet with collected information on the cases included in the analysis is available upon request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ngo, A.; Ciranni, M.; Olson, K.R. Acute Quetiapine Overdose in Adults: A 5-Year Retrospective Case Series. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2008, 52, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balit, C.R.; Isbister, G.K.; Hackett, L.P.; Whyte, I.M. Quetiapine Poisoning: A Case Series. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2003, 42, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vento, A.E.; Kotzalidis, G.D.; Cacciotti, M.; Papanti, G.D.; Orsolini, L.; Rapinesi, C.; Savoja, V.; Calabrò, G.; Del Casale, A.; Piacentino, D.; et al. Quetiapine Abuse Fourteen Years Later: Where Are We Now? A Systematic Review. Subst. Use Misuse 2020, 55, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, N.S.; Mello, K.; Carpenter, L.L.; Tyrka, A.R.; Price, L.H. Patterns of quetiapine use in psychiatric inpatients: An examination of off-label use. Ann. Clin. Psychiatry 2008, 20, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, D.L. Off-label prescription of quetiapine in psychiatric disorders. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2007, 7, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piróg-Balcerzak, A.; Habrat, B.; Mierzejewski, P. Misuse and abuse of quetiapine. Psychiatr. Pol. 2015, 49, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huthwaite, M.; Cleghorn, M.; MacDonald, J. “Out of the frying pan”: The challenges of prescribing for insomnia in psychiatric patients. Australas. Psychiatry 2014, 22, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, J. Concerns about quetiapine. Aust. Prescr. 2015, 38, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montebello, M.E.; Brett, J. Misuse and Associated Harms of Quetiapine and Other Atypical Antipsychotics. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 34, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.; Graudins, A. Extended-release quetiapine overdose is associated with delayed onset of toxicity compared to immediate-release quetiapine overdose. EMA Emerg. Med. Australas. 2019, 31, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Charreteur, R.; Peries, M.; Kheloufi, F.; Eiden, C.; Nagot, N.; Donnadieu-Rigole, H.; Micallef, J.; Peyrière, H. Abuse and misuse of second-generation antipsychotics: An analysis using VigiBase, the World Health Organisation pharmacovigilance database. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 4646–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, M.; Brigadeiro, D.; Luís, F.; Nunes, J. Acute quetiapine overdose is associated with risk of ectopic atrial rhythm. Actas Españolas Psiquiatr. 2023, 51, 216–219. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, C.P.; Karanges, E.; McGregor, I.S. Trends in the utilisation of psychotropic medications in Australia from 2000 to 2011. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2013, 47, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesto-Lowe, V.; Harabasz, A.K.; Walker, S.A. Quetiapine for primary insomnia: Consider the risks. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2021, 88, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenqvist, T.W.; Osler, M.; Wium-Andersen, M.K.; Wium-Andersen, I.K. Sedative drug-use in Denmark, 2000 to 2019: A nationwide drug utilization study. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2023, 58, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha Krishnan, R.P.; Harrison, C.; Buckley, N.; Raubenheimer, J.E. On- and off-label utilisation of antipsychotics in Australia (2000–2021): Retrospective analysis of two medication datasets. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2024, 58, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, A.Y.; Theodoros, T.; Harris, K.; Isoardi, K.Z. Overdose and off-label psychotropic prescribing in patients with borderline personality disorder: A retrospective series. Australas. Psychiatry 2023, 31, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.E.; Albright, V.A.; Yoon, J.; Council, C.L. Emergency department visits involving misuse and abuse of the antipsychotic quetiapine: Results from the drug abuse warning network (DAWN). Subst. Abus. Res. Treat. 2015, 9, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappini, S.; Schifano, F. Is There a Potential of Misuse for Quetiapine?: Literature Review and Analysis of the European Medicines Agency/European Medicines Agency Adverse Drug Reactions’ Database. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 38, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.; Jayathilake, R.; Peacock, A.; Dietze, P.; Bruno, R.; Reddel, S.; Gisev, N. Trends and characteristics of extra-medical use of quetiapine among people who regularly inject drugs in Australia, 2011–2018. Drug Alcohol Depend 2021, 221, 108636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breivik, H.; Frost, J.; Løkken, T.N.; Slørdal, L. Post mortem tissue distribution of quetiapine in forensic autopsies. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 315, 110413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indave, B.I.; Minozzi, S.; Pani, P.P.; Amato, L. Antipsychotic medications for cocaine dependence. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 3, CD006306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.; Sweeney, R. Overdose and Treatment of Quetiapine Ingestions. J. Emerg. Nurs. 2007, 33, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobravc Verbič, M.; Grabnar, I.; Brvar, M. Association between Prescribing and Intoxication Rates for Selected Psychotropic Drugs: A Longitudinal Observational Study. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Methling, M.; Krumbiegel, F.; Hartwig, S.; Parr, M.K.; Tsokos, M. Toxicological findings in suicides—Frequency of antidepressant and antipsychotic substances. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2019, 15, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peridy, E.; Hamel, J.F.; Rolland, A.L.; Gohier, B.; Boels, D. Quetiapine poisoning and factors influencing severity. J. Clin. sychopharmacol 2019, 39, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyer, F.; Pfab, R.; Felgenhauer, N.; Strubel, T.; Saugel, B.; Zilker, T. Clinical and analytical features of severe suicidal quetiapine overdoses—A retrospective cohort study. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunfeld, N.G.M.; Westerman, E.M.; Boswijk, D.J.; De Haas, J.A.M.; Van Putten, M.J.A.M.; Touw, D.J. Quetiapine in overdosage: A clinical and pharmacokinetic analysis of 14 cases. Ther. Drug Monit. 2006, 28, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, A.; Ruggiero, S.; Vestini, F.; Ianniello, B.; Rafaniello, C.; Rossi, F.; Mucci, A. Survival from coma induced by an intentional 36-g overdose of extended-release quetiapine. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 34, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenafi, S.; Jaffal, K.; Soichot, M.; Labat, L.; Megarbane, B. Acute quetiapine poisoning admitted in the intensive care unit: Features, complications and usefulness of plasma concentration measurement. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 571. [Google Scholar]
- Mégarbane, B.; Oberlin, M.; Alvarez, J.C.; Balen, F.; Beaune, S.; Bédry, R.; Chauvin, A.; Claudet, I.; Danel, V.; Debaty, G.; et al. Management of pharmaceutical and recreational drug poisoning. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, M.; Musil, R.; Spellmann, I.; Seemüller, F.; Möller, H.-J. Quetiapine XR—A new retard formulation in the treatment of schizophrenia. Eur. Psychiatr. Rev. 2008, 1, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Bertol, E.; Vaiano, F.; Argo, A.; Zerbo, S.; Trignano, C.; Protani, S.; Favretto, D. Overdose of quetiapine—A case report with QT prolongation. Toxics 2021, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devane, C.L.; Nemeroff, C.B. Clinical pharmacokinetics of quetiapine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2001, 40, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbister, G.K.; Friberg, L.E.; Hackett, L.P.; Duffull, S.B. Pharmacokinetics of quetiapine in overdose and the effect of activated charcoal. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 81, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, H.R.; Earley, W.R.; Hamer-Maansson, J.E.; Davis, P.C.; Smith, M.A. Steady-State Pharmacokinetic, Safety, and Tolerability Profiles of Quetiapine, Norquetiapine, and Other Quetiapine Metabolites in Pediatric and Adult Patients with Psychotic Disorders. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2008, 18, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, M.C.; Volonteri, L.S.; Colasanti, A.; Fiorentini, A.; De Gaspari, I.F.; Bareggi, S.R. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Atypical Antipsychotics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2007, 46, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.C.; Wong, J.; Gefvert, O. Analysis and pharmacokinetics of quetiapine and two metabolites in human plasma using reversed-phase HPLC with ultraviolet and electrochemical detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 20, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, K.; Earley, W.; Nyberg, S. Pharmacokinetic profile of the extended-release formulation of quetiapine fumarate (quetiapine XR): Clinical implications. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2013, 29, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, P.T.; Zbuk, K. Quetiapine fumarate overdose: Clinical and pharmacokinetic lessons from extreme conditions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 68, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.N.; Zhou, D.; Bui, K.H. Development of physiologically based pharmacokinetic model to evaluate the relative systemic exposure to quetiapine after administration of IR and XR formulations to adults, children and adolescents. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2014, 35, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigos, K.L.; Bies, R.R.; Marder, S.R.; Pollock, B.G. Population pharmacokinetics of antipsychotics. In Antipsychotic Trials in Schizophrenia: The CATIE Project; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, V.; Bies, R.R.; Mo, G.; Dolton, M.J.; Carr, V.J.; McLachlan, A.J.; Day, R.O.; Polasek, T.M.; Forrest, A. Optimal sampling of antipsychotic medicines: A pharmacometric approach for clinical practice. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 78, 800–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimko, H.C.; Reele, S.S.B.; Holford, N.H.G.; Peck, C.C. Prediction of the outcome of a phase 3 clinical trial of an antischizophrenic agent (quetiapine fumarate) by simulation with a population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic model. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 68, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Bui, K.H.; Li, J.; Al-Huniti, N. Population pharmacokinetic modeling of quetiapine after administration of seroquel and seroquel XR formulations to Western and Chinese patients with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, or bipolar disorder. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 55, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushi, R.; Nomura, Y.; Katashima, M.; Komatsu, K.; Sato, Y.; Takada, A. Population Pharmacokinetics Analysis of Quetiapine Extended-release Formulation in Japanese Patients with Bipolar Depression. Clin. Ther. 2020, 42, 1067–1076.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langman, L.J.; Kaliciak, H.A.; Carlyle, S. Fatal overdoses associated with quetiapine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2004, 28, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopenwasser, J.; Mozayani, A.; Danielson, T.J.; Harbin, J.; Narula, H.S.; Posey, D.H.; Shrode, P.W.; Wilson, S.K.; Li, R.; Sanchez, L.A. Postmortem Distribution of the Novel Antipsychotic Drug Quetiapine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2004, 28, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, R.G.; Morocco, A.P. Quetiapine cross-reactivity among three tricyclic antidepressant immunoassays. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datto, C.; Berggren, L.; Patel, J.B.; Eriksson, H. Self-reported sedation profile of immediate-release quetiapine fumarate compared with extended-release quetiapine fumarate during dose initiation: A randomized, double-blind, crossover study in healthy adult subjects. Clin. Ther. 2009, 31, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, M.C.; Paletta, S.; Di Pace, C.; Reggiori, A.; Cirnigliaro, G.; Valli, I.; Altamura, A.C. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Atypical Antipsychotics: An Update. Clin. Pharmacokit 2018, 57, 1493–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Reuter, H.; Dohmen, C. Intoxication after Extreme Oral Overdose of Quetiapine to Attempt Suicide: Pharmacological Concerns of Side Effects. Case Rep. Med. 2009, 2009, 371698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, D.R.; McIntyre, I.M. Case studies of postmortem quetiapine: Therapeutic or toxic concentrations? J. Anal. Toxicol. 2005, 29, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Langberg, C.; Hadley, C.L.; Midtrevold, M.; Edvardsen, H.M.E.; Molden, E.; Shafiei, M.; Jacobsen, D. Quetiapine Poisoning—Epidemiology, Toxicokinetics and Review of the Literature. LOJ Med. Sci. 2021, 5, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptist, E.; de Graaf, I.; Bannink, M. Delier als late complicatie van intoxicatie met quetiapine. Tijdschr. Psychiatr. 2018, 60, 548–551. [Google Scholar]
- Hantson, P.; Fazio, V.; Wallemacq, P. Toxicokinetic Interaction Between Quetiapine and Antiretroviral Therapy Following Quetiapine Overdose. Drug Metab. Lett. 2010, 4, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, S.W.; Richtand, N.M.; Winter, H.R.; Stams, K.R.; Reele, S.B. Effects of cytochrome P450 3A modulators ketoconazole and carbamazepine on quetiapine pharmacokinetics. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 61, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, M.F.C.; Kiew, C.F.; Chong, C.P. Hyperglycemia and late onset seizures associated with quetiapine overdose. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2013, 25, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.W.J.; Yeh, C.; Thyrum, P.T. The effects of concomitant phenytoin administration on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of quetiapine. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2001, 21, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignali, C.; Freni, F.; Magnani, C.; Moretti, M.; Siodambro, C.; Groppi, A.; Osculati, A.M.M.; Morini, L. Distribution of quetiapine and metabolites in biological fluids and tissues. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 307, 110108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhan, R.K.S.; Macfarlane, H. Quetiapine dose optimisation during gestation: A pharmacokinetic modelling study. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.F.; Lu, S.J.; Ye, Z.Q.; Lai, J.B.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.D.; Zhang, P.F.; Wu, L.L.; Huang, H.M.; et al. Relationship between serum concentration and clinical response of quetiapine in adolescents and adults with bipolar disorders in acute stage: A prospective observational study. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 324, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; O’Donnell, J.; Gladden, R.M.; McGlone, L.; Chowdhury, F. Trends in Nonfatal and Fatal Overdoses Involving Benzodiazepines—38 States and the District of Columbia, 2019–2020. Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasselstrøm, J.; Linnet, K. Quetiapine serum concentrations in psychiatric patients: The influence of comedication. Ther. Drug Monit. 2004, 26, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castberg, I.; Skogvoll, E.; Spigset, O. Pharmacokinetics of quetiapine: Evidence from a routine therapeutic drug monitoring service. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006, 16, S444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, M.C.; Volonteri, L.S.; Fiorentini, A.; Pirola, R.; Bareggi, S.R. Two weeks’ quetiapine treatment for schizophrenia, drug-induced psychosis and borderline personality disorder: A naturalistic study with drug plasma levels. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2007, 8, 2207–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskiw, G.E.; Thyrum, P.T.; Fuller, M.A.; Arvanitis, L.A.; Yeh, C. Pharmacokinetics of quetiapine in elderly patients with selected psychotic disorders. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 43, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albantakis, L.; Egberts, K.; Burger, R.; Mehler-Wex, C.; Taurines, R.; Unterecker, S.; Wevetzer, C.; Romanos, M.; Gerlach, M. Relationship between Daily Dose, Serum Concentration, and Clinical Response to Quetiapine in Children and Adolescents with Psychotic and Mood Disorders. Pharmacopsychiatry 2017, 50, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammia, D.D.; Valouch, T.; Venuti, S. Tissue distribution of quetiapine in 20 cases in Virginia. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2006, 30, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Muñoz, F.; Álamo, C. Active metabolites as antidepressant drugs: The role of norquetiapine in the mechanism of action of quetiapine in the treatment of mood disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2013, 4, 48288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beelen, A.P.; Yeo, K.T.J.; Lewis, L.D. Asymptomatic QTc prolongation associated with quetiapine fumarate overdose in a patient being treated with risperidone. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2001, 20, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, G.; Catalano, M.C.; Agustines, R.E.; Dolan, E.M.; Paperwalla, K.N. Pediatric Quetiapine Overdose: A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2002, 12, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConville, B.J.; Arvanitis, L.A.; Thyrum, P.T.; Yeh, C.; Wilkinson, L.A.; Chaney, R.O.; Foster, K.D.; Sorter, M.T.; Friedman, L.M.; Brown, K.L.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, Tolerability, and Clinical Effectiveness of Quetiapine Fumarate: An Open-Label Trial in Adolescents With Psychotic Disorders. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2000, 61, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.A.; Lewis, J.E.; Pascal, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Rodriguez, R.A.; Guillen, R.; Pupo-Guillen, M. A Study of Quetiapine: Efficacy and Tolerability in Psychotic Adolescents. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2004, 11, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twaites, B.R.; Wilton, L.V.; Shakir, S.A.W. The safety of quetiapine: Results of a post-marketing surveillance study on 1728 patients in England. J. Psychopharmacol. 2007, 21, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, B.A.; Champion, K.M.; Pierre, J.M.; Wirshing, D.A.; Wirshing, W.C. Possible association of QTc interval prolongation with co-administration of quetiapine and lovastatin. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 51, 264–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Lim, K.S.; Lee, H.; Chung, H.; Yoon, S.H.; Yu, K.S.; Cho, J.Y.; Jang, I.J.; Chung, J.Y. A thorough QT study to evaluate the QTc prolongation potential of two neuropsychiatric drugs, quetiapine and escitalopram, in healthy volunteers. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 31, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.G.; Ayis, S.A.; Ferrier, I.N.; Jones, S.J.; Thomas, S.H.L. QTc-interval abnormalities and psychotropic drug therapy in psychiatric patients. Lancet 2000, 355, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, P.M.; Anderson, I.M. Antipsychotic-related QTc prolongation, torsade de pointes and sudden death. Drugs 2002, 62, 1649–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gaaly, S.; St John, P.; Dunsmore, S.; Bolton, J.M. Atypical Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome With Quetiapine: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2009, 29, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belvederi Murri, M.; Guaglianone, A.; Bugliani, M.; Calcagno, P.; Respino, M.; Serafini, G.; Innamorati, M.; Pompili, M.; Amore, M. Second-Generation Antipsychotics and Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: Systematic Review and Case Report Analysis. Drugs R. D 2015, 15, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detweiler, M.B.; Sullivan, K.; Sharma, T.R.; Kim, K.Y.; Detweiler, J.G. Case reports of neuroleptic malignant syndrome in context of quetiapine use. Psychiatr. Q 2013, 84, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, Y.J.; Lee, Y.; Lin, C.C.; Huang, T.L. A Case Report of Catatonia and Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome With Multiple Treatment Modalities: Short Communication and Literature Review. Medicine 2015, 94, e1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, M.V.; Demir, T.O.; Yaylaci, S.; Yildiz, H.; Tayci, I.; Baydar, M. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome induced by concomitant use of risperidone and quetiapine. Chrismed J. Heal. Res. 2016, 3, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuntoli, L.; Dalmastri, V.; Cilloni, N.; Orsi, C.; Stalteri, L.; Demelas, V.; Giuliani, G.; Gordini, G.; De Ponti, F.; La Manna, G. Severe quetiapine voluntary overdose successfully treated with a new hemoperfusion sorbent. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2019, 42, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.; Lippmann, S. Blood Dyscrasia With Quetiapine and Ziprasidone. Psychosomatics 2005, 46, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpaner, A.; Li, W.; Ankoma-Sey, V.; Botero, R.C. Drug-induced liver injury: Hepatotoxicity of quetiapine revisited. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 20, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naharci, M.I.; Karadurmus, N.; Demir, O.; Bozoglu, E.; Ak, M.; Doruk, H. Fatal hepatotoxicity in an elderly patient receiving low-dose quetiapine. Am. J. Psychiatry 2011, 168, 212–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.; Albuquerque, E.; Murta, I. Delirium induced by quetiapine and the potential role of norquetiapine. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, N.H.; Rodriguiz, R.M.; Caron, M.G.; Wetsel, W.C.; Rothman, R.B.; Roth, B.L. N-Desalkylquetiapine, a Potent Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor and Partial 5-HT1A Agonist, as a Putative Mediator of Quetiapine’s Antidepressant Activity. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 33, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crombez, S.; Van Den Wijngaert, V.; Demyttenaere, K.; De Fruyt, J. Delier ten gevolge van intoxicatie met quetiapine: Een systematisch literatuuronderzoek. Tijdschr. Psychiatr. 2020, 62, 358–367. [Google Scholar]
- Fabre, L.F.; Arvanitis, L.; Pultz, J.; Jones, V.M.; Malick, J.B.; Slotnick, V.B. ICI 204,636, a novel, atypical antipsychotic: Early indication of safety and efficacy in patients with chronic and subchronic schizophrenia. Clin. Ther. 1995, 17, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragicevic, A.; Sachse, J.; Härtter, S.; Hiemke, C.; Müller, M.J. Serum Concentrations of Quetiapine and Clinical Effects. Pharmacopsychiatry 2005, 38, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragicevic, A.; Trotzauer, D.; Hiemke, C.; Müller, M.J. Gender and age effects on quetiapine serum concentrations in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorders. Pharmacopsychiatry 2005, 38, A044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragicevic, A.; Müller, M.J.; Sachse, J.; Härtter, S.; Hiemke, C. Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of quetiapine. Pharmacopsychiatry 2003, 36, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, M.; Hünnerkopf, R.; Rothenhöfer, S.; Libal, G.; Burger, R.; Clement, H.W.; Fegert, J.M.; Wewetzer, C.; Mehler-Wex, C. Therapeutic drug monitoring of quetiapine in adolescents with psychotic disorders. Pharmacopsychiatry 2007, 40, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobaugh, D.J.; Erdman, A.R.; Booze, L.L.; Scharman, E.J.; Christianson, G.; Manoguerra, A.S.; Caravati, E.M.; Chyka, P.A.; Woolf, A.D.; Nelson, L.S.; et al. Atypical antipsychotic medication poisoning: An evidence-based consensus guideline for out-of-hospital management. Clin. Toxicol. 2008, 45, 918–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichhorn, W.; Marksteiner, J.; Walch, T.; Zernig, G.; Saria, A.; Kemmler, G. Influence of age, gender, body weight and valproate comedication on quetiapine plasma concentrations. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 21, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, J. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of quetiapine: Short-term high doses with long-term follow-up. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2005, 9, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, E.; Sotiriou, A.; Graham, G.G.; Wilhelm, K.; Snowden, L.; Day, R.O. Restarting antidepressant and antipsychotic medication after intentional overdoses: Need for evidence-based guidance. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 9, 2045125319836889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.; Iwersen-Bergmann, S.; Andresen, H.; Schmoldt, A. Therapeutic and toxic blood concentrations of nearly 1000 drugs and other xenobiotics. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.K.; Mann, M.D.; Aboo, A.; Isaacs, S.; Evans, A. Prolonged gastric emptying half-time and gastric hypomotility after drug overdose. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2004, 22, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartos, M.; Knudsen, K. Use of intravenous lipid emulsion in the resuscitation of a patient with cardiovascular collapse after a severe overdose of quetiapine. Clin. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauber-Lüthy, C.; Hofer, K.E.; Bodmer, M.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Kupferschmidt, H.; Ceschi, A. Gastric pharmacobezoars in quetiapine extended-release overdose: A case series. Clin. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceschi, A.; Rauber-Luthy, C.; Bodmer, M.; Kupferschmidt, H.; Hofer, K.E. Gastric pharmacobezoars in quetiapine overdose: A case series. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 533–534. [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer, M.; Burkard, T.; Kummer, O.; Beyrau, R.; Krähenbühl, S.; Haschke, M. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of quetiapine in a patient with a massive overdose. Ther. Drug Monit. 2008, 30, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegberg, L.C.G.; Refsgaard, F.; Pedersen, S.H.; Personne, M.; Ullah, S.; Panagiotidis, G.; Studsgaard Petersen, T.; Annas, A. Potential pharmacobezoar formation of large size extended-release tablets and their dissolution–an in vitro study. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.; Ruha, A.M. Overdose of atypical antipsychotics: Clinical presentation, mechanisms of toxicity and management. CNS Drugs 2012, 26, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minns, A.B.; Clark, R.F. Toxicology and overdose of atypical antipsychotics. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 43, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.J. The pharmacology and toxicology of atypical antipsychotic agents. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2001, 39, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbister, G.K.; Duffull, S.B. Quetiapine overdose: Predicting intubation, duration of ventilation, cardiac monitoring and the effect of activated charcoal. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2009, 24, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenton, A.F.; Currier, G.W.; Zwemer, F.L. Fatalities associated with therapeutic use and overdose of atypical antipsychotics. CNS Drugs 2003, 17, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowry, J.; Sanftleben, J.; Smith, J. Eighteen month retrospective evaluation of Seroquel(R) exposures. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 631. [Google Scholar]
- Backman, E.; Luhr, K.M.; Sjöberg, G. Acute Quetiapine Overdose in Adults—Experience in Sweden. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 267–268. [Google Scholar]
- Pillay-Fuentes Lorente, V.; van Rensburg, R.; Cloete, D.A.; Lahri, S.; Decloedt, E.H. Vasopressor therapy in atypical antipsychotic overdose. S. Afr. Med. J. 2020, 110, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.B.; Stellpflug, S.J.; Ellsworth, H.; Harris, C.R. Reversal of quetiapine-induced altered mental status with physostigmine: A case series. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 30, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, C.; Reichert, P.; Monnet-Tschudi, F.; Kupferschmidt, H.; Ceschi, A.; Rauber-Lüthy, C. Seizures after single-agent overdose with pharmaceutical drugs: Analysis of cases reported to a poison center. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainio, A.; Kuusisto, L.; Hakko, H.; Riipinen, P. Antipsychotics as a method of suicide: Population based follow-up study of suicide in Northern Finland. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2021, 75, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.C.; Spyker, D.A. Morbidity and mortality associated with medications used in the treatment of depression: An analysis of cases reported to U.S. poison control centers, 2000-2014. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiihonen, J.; Lönnqvist, J.; Wahlbeck, K.; Klaukka, T.; Niskanen, L.; Tanskanen, A.; Haukka, J. Articles 11-year follow-up of mortality in patients with schizophrenia: A population-based cohort study (FIN11 study). Lancet 2009, 374, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.; Flanagan, R.J. Fatal poisoning with antipsychotic drugs, England and Wales 1993-2002. J. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 19, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Pilgrim, J.; Gerostamoulos, D.; Robinson, J.; Wong, A. Increasing rates of quetiapine overdose, misuse, and mortality in Victoria, Australia. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2018, 187, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.H.; Hoppe, J.; Heard, K. A systematic review of cardiovascular effects following atypical antipsychotic medication overdose. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2009, 27, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, G.; Kim, E.; Jung, H.; Chang, J. Quetiapine misuse and abuse: Is it an atypical paradigm of drug seeking behavior? J. Res. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, D.J.; Unwin, P. Paradoxical and severe hypotension in response to adrenaline infusions in massive quetiapine overdose. Crit. Care Resusc. 2008, 10, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibiino, S.; Trappoli, A.; Balzarro, B.; Atti, A.R.; de Ronchi, D. Coma after quetiapine fumarate intentional overdose in a 71-year-old man: A case report. Drug Saf. Case Rep. 2015, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, M.T.; Tsai, C.L.; Lin, C.W.; Yeh, C.B.; Wang, Y.H.; Lin, H.L. Association Between Antipsychotic Agents and Risk of Acute Respiratory Failure in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gomaa, H.; Cortez-Resendiz, A.; Martin, C.; Francis, A.; Bellon, A. Quetiapine and Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2020, 2020, 6633385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, F.D.; Simonsen, U.; Andersen, C.U. Quetiapine and other antipsychotics combined with opioids in legal autopsy cases: A random finding or cause of fatal outcome? Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 128, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderone, V.; Testai, L.; Martinotti, E.; Del Tacca, M.; Breschi, M.C. Drug-induced block of cardiac HERG potassium channels and development of torsade de pointes arrhythmias: The case of antipsychotics. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 57, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campleman, S.L.; Brent, J.; Pizon, A.F.; Shulman, J.; Wax, P.; Manini, A.F. Drug-specific risk of severe QT prolongation following acute drug overdose. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, M.; Vieweg, W.V.R.; Howland, R.H.; Kogut, C.; Breden Crouse, E.L.; Koneru, J.N.; Hancox, J.C.; Digby, G.C.; Baranchuk, A.; Deshmukh, A.; et al. Quetiapine, QTc interval prolongation, and torsade de pointes: A review of case reports. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 4, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K.; Jenkins, S. Quetiapine overdose, good or bad, or just more of the same? Clin. Toxicol. 2023, 61, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Khaire, S.S.; Nagarajarao, H.; Quin, E.M.; Borganelli, S.M.; Marshall, R.C. Electrocardiographic brugada pattern induced by quetiapine overdose. J. Investig. Med. 2012, 60, 322–323. [Google Scholar]
- Lannemyr, L.; Knudsen, K. Severe overdose of quetiapine treated successfully with extracorporeal life support. Clin. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Kaplan, S.; Muschler, K.; Hoyte, C.; Brent, J. The role of QRS complex prolongation in predicting severe toxicity in single-xenobiotic overdose. Clin. Toxicol. 2024, 62, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.P.; Marcil, W.A. Death associated with quetiapine overdose. Am. J. Psychiatry 2002, 159, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.A.; Unverferth, K.M.; Cheung, E.H. Delayed-Onset Seizure in a Mild Quetiapine Overdose: Report of a Case and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2018, 2018, 7623051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.C.; Kleinschmidt, K.C.; Wax, P.M. Late-onset seizures associated with quetiapine poisoning. J. Med. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelo, B.; Yates, C.; Castanyer, B.; Puiguriguer, J. Delayed seizures after topiramate, venlafaxine and quetiapine overdose. Med. Clin. 2010, 135, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachan, P.M.; Benoff, B.A. Mental status change, myoclonus, electrocardiographic changes, and acute respiratory distress syndrome induced by quetiapine overdose. Pharmacotherapy 2006, 26, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogu, O.; Sevim, S.; Kaleagasi, H.S. Seizures associated with quetiapine treatment. Ann. Pharmacother. 2003, 37, 1224–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedges, D.W.; Jeppson, K.G. New-Onset Seizure Associated with Quetiapine and Olanzapine. Ann. Pharmacother. 2002, 36, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, F.; Iga, K.; Maeda, K.; Sera, S.; Fujisaki, N.; Okazaki, Y.; Ichiba, T.; Chiba, T.; Namera, A. Refractory seizures due to severe quetiapine poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 2023, 61, 620–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioravanti, V.; Cavallieri, F.; Rossi, J.; Macaluso, M.C.; Valzania, F. Subcortical generalized myoclonus as a presenting symptom of quetiapine overdose. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayudhan, L.; Kirchner, V. Quetiapine-induced myoclonus. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 20, 119–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.; Jiloha, R. Quetiapine induced myoclonus. Indian. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 62, 422–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fond, G.; MacGregor, A.; Ducasse, D.; Brittner, M. Paradoxical severe agitation induced by add-on high-doses quetiapine in schizo-affective disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 216, 286–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antia, S.X.; Sholevar, E.H.; Baron, D.A. Overdoses and ingestions of second-generation antipsychotics in children and adolescents. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 15, 970–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhyee, S.H.; Pedapati, E.V.; Thompson, J. Prolonged delirium after quetiapine overdose. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2010, 26, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miodownik, C.; Alkatnany, A.; Frolova, K.; Lerner, V. Delirium associated with lithium-quetiapine combination. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2008, 31, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liolios, A.; Sentissi, O. Rhabdomyolysis following Acute Extended-Release Quetiapine Poisoning: A Case Report. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2012, 2012, 347421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickmann, J.R.M.; Dickmann, L.M. An uncommonly recognized cause of rhabdomyolysis after quetiapine intoxication. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 28, 1060.e1–1060.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.P.; Puckett, B.N.; Crawford, J.; Elliott, R.L. Quetiapine overdose and severe rhabdomyolysis. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2004, 24, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, S.D.; Marotta, D.A.; Goteti, R. Atypical Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome in the Setting of Quetiapine Overdose: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Cureus 2021, 13, e12602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Précourt, A.; Dunewicz, M.; Grégoire, G.; Williamson, D.R. Multiple Complications and Withdrawal Syndrome Associated with Quetiapine/Venlafaxine Intoxication. Ann. Pharmacother. 2005, 39, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninčević, Ž.; Lasić, D.; Glavina, T.; Mikačić, M.; Carev, M.; Podrug, K. Quetiapine poisoning associated with neuroleptic malignant syndrome, rhabdomyolysis and renal failure: A case report. Psychiatr. Danub. 2017, 29, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özçelık Eroğlu, E.; Yildiz, M.İ.; Yazici, M.K. Atypical neuroleptic malignant syndrome induced by low dose quetiapine in a patient treated with donepezil. Noropsikiyatri Ars. 2021, 58, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schattner, A.; Kitroser, E.; Cohen, J.D. Fatal Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome Associated With Quetiapine. Am. J. Ther. 2016, 23, e1209–e1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, C.; O’Brien, D.; Dwyer, R. Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome Secondary to Quetiapine in Critical Care: A Case Report. A&A Pract. 2020, 14, e01318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.J.; Ramaekers, G.M.G.I.; Van Harten, P.N. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome and quetiapine. Am. J. Psychiatry 2002, 159, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, D.C.L.; Wong, H.K.; Tan, S.N. Atypical neuroleptic malignant syndrome precipitated by clozapine and quetiapine overdose: A diagnostic challenge. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 15, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Filkins, P.; Walsh, C.; Kiernan, E. An atypical use of MDAC: Enhanced elimination of quetiapine in a massive overdose. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 1057. [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel, J.; Ruhnau, L.; Einwaechter, H.; Felgenhauer, N.; Romaneck, K.; Stich, R.; Pfab, R.; Eyer, F. Gastroscopic bezoar removal in acute quetiapine poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 317–318. [Google Scholar]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Schmidt, J.J.; Ghannoum, M. Letter to the editor concerning the case report “Successful treatment of severe quetiapine intoxication with CytoSorb hemoadsorption”. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2022, 47, 1493–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Tsuji, T.; Namera, A.; Morita, S.; Nakagawa, Y. Comparison of serum and whole blood concentrations in quetiapine overdose cases. Forensic Toxicol. 2022, 40, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breivik, H.; Tunset, M.E.; Schou, M.B.; Frost, J. Distribution of quetiapine between serum and whole blood in therapeutic drug-monitoring specimens. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2024, 48, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.S.; Van Schalkwyk, G.I.; Seedat, S.; Curran, S.R.; Flanagan, R.J. Plasma, oral fluid, and whole-blood distribution of antipsychotics and metabolites in clinical samples. Ther. Drug Monit. 2013, 35, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, L.; Johansen, S.S.; Linnet, K. Postmortem quetiapine reference concentrations in brain and blood. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 39, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, I.M. Analytical data supporting the “theoretical” postmortem redistribution factor (Ft): A new model to evaluate postmortem redistribution. Forensic Sci. Res. 2016, 1, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anderson, D.T.; Fritz, K.L. Quetiapine (Seroquel®) concentrations in seven postmortem cases. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2000, 24, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, G.M.M.; Hegazy, N.I.; Etewa, R.L.; Elmesallamy, G.E.A. Postmortem redistribution of drugs: A literature review. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maan, J.S.; Ershadi, M.; Khan, I.; Saadabadi, A. Quetiapine. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459145/ (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Skov, L.; Johansen, S.S.; Linnet, K. Postmortem femoral blood reference concentrations of aripiprazole, chlorprothixene, and quetiapine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 39, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hieger, M.A.; Peters, N.E. Lipid Emulsion Therapy for Quetiapine Overdose. Am. J. Ther. 2020, 27, E518–E519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, T.J.; Benitez, J.G.; Krenzelok, E.P.; Cortes-Belen, E. Loss of consciousness from acute quetiapine overdosage. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Farah, N. Quetiapine overdose. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2010, 44, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.; Wax, P. Physostigmine administration for quetiapine toxicity. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 646–647. [Google Scholar]
- Watt, P.; Malik, P.; Dyson, L. Gift of the glob—Is it foolproof? Anaesthesia 2009, 64, 1031–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowry, J.B.; Spyker, D.A.; Brooks, D.E.; Zimmerman, A.; Schauben, J.L. 2015 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 33rd Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 924–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummin, D.D.; Mowry, J.B.; Beuhler, M.C.; Spyker, D.A.; Bronstein, A.C.; Rivers, L.J.; Pham, N.P.T.; Weber, J. 2020 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 38th Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 1282–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek, S. No QT interval prolongation associated with quetiapine overdose. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2004, 22, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.; Loftus, R.; Dewhirst, W.; Surgenor, S.; Koff, M. A Unique Presentation of Massive Quetiapine Overdose: Prolonged Anticholinergic Delirium and Acute Reversal with Physostigmine. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, U277. [Google Scholar]
- Galdós Barroso, M.; Ulla Anés, M.; Martínez Vicente, S.; Arozemena Baquerizo, J. Intoxicación por quetiapina. Med. Clin. 2001, 117, 638–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, A.M.; House, L.M.; Lee, J.M. Low-dose lipid emulsion for pediatric vasoplegic shock due to quetiapine and fluvoxamine overdose: A case report. J. Emerg. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuchsel, C.; Gonnert, F.A. Successful treatment of severe quetiapine intoxication with CytoSorb hemoadsorption. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2022, 47, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulzen, M.; Grunder, G.; Orlikowsky, T.; Hoeltzenbein, M.; Graf, C.M.; Veselinovic, T. Suicide attempt during late pregnancy with quetiapine: Nonfatal outcome despite severe intoxication. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 35, 343–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seewoogoolam, G.; Miller, G.; Tan, B. Compartment syndrome of the deltoid and pectoralis major in a young man following quetiapine use. ANZ J. Surg. 2019, 89, E335–E336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, M.; Azzoni, A. Valproate and quetiapine overdose with benign outcome: A case report. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2002, 6, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purg, D.; Markota, A.; Grenc, D.; Sinkovič, A. Low-dose intravenous lipid emulsion for the treatment of severe quetiapine and citalopram poisoning. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2016, 67, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesnicar, B.K.; Lasic, J.K.; Plesnicar, A. Quetiapine and elevated creatine phosphokinase (CK). Pharmacopsychiatry 2007, 40, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais, V.M.; Ayvazian, P.J. Priapism from quetiapine overdose: First report and proposal of mechanism. Urology 2001, 58, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudelman, E.; Vinuela, L.M.; Cohen, C.I. Safety in overdose of quetiapine: A case report. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1998, 59, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahieu, B.; Martens, F.; Vanlerberghe, G.; Croes, K. Persisting Tachycardia and Late Onset Seizures in two Non Fatal Cases of Quetiapine Intoxication. Clin. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 366. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, A.R.; Wolf, P.K.; Ravasia, S. Hypokalemia from risperidone and quetiapine overdose. Can. J. Psychiatry 2005, 50, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobilinschi, C.; Mirea, L.; Andrei, C.A.; Ungureanu, R.; Cotae, A.M.; Avram, O.; Isac, S.; Grințescu, I.M.; Țincu, R. Biodetoxification Using Intravenous Lipid Emulsion, a Rescue Therapy in Life-Threatening Quetiapine and Venlafaxine Poisoning: A Case Report. Toxics 2023, 11, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomruk, N.B.; SaatçIoǧlu, Ö.; DelIce, M.; Alpay, N. Is quetiapine safe in overdose?: A case report and literature review. Noropsikiyatri. Ars. 2012, 49, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuerzebecher, A.; Groeneveld, A.; Lehmann, T.; Prasa, D. Different courses of quetiapine poisoning in two patients with gastric decontamination. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 620–621. [Google Scholar]
- Otte, S.; Fischer, B.; Sayk, F. Successful lipid rescue therapy in a case of severe amitriptyline/quetiapine intoxication. Med. Klin. Intensivmed. Notfmed 2018, 113, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajwani, P.; Pozuelo, L.; Tesar, G.E. Qt interval prolongation associated with quetiapine (Seroquel) overdose. Psychosomatics 2000, 41, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinci, E.; Koylu, R.; Akilli, N.B.; Cander, B. Rhabdomyolysis Secondary to Quetiapine and Olanzapine Intoxication Olanzapin ve Ketiapin intoksikasyonuna İkincil Rabdomiyoliz. J. Acad. Emerg. Med. Case Reports 2014, 5, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, S.D.H.; Uncles, D.R.; Willers, J.; Sable, N. Early treatment of a quetiapine and sertraline overdose with Intralipid®. Anaesthesia 2009, 64, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.; Taori, G.; Braitberg, G.; Graudins, A. Methylene blue used in the treatment of refractory shock resulting from drug poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonati, D.; Bernabe, L.; Cirronis, M.; Potalivo, A.; Giovanardi, M.; Schicchi, A.; Crevani, M.; Scaravaggi, G.; Petrolini, V.M.; Locatelli, C.A. Pharmacobezoar and gastric perforation in severe quetiapine intoxication: A case report. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 630. [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo, S.K.; Shah, R.; Rajagopal, R.; Biswas, P.S.; Singh, S.M. Quetiapine: Relatively safe in overdose? Indian. J. Psychiatry 2009, 51, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J. Delirium as a symptom of quetiapine poisoning. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2009, 43, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silversides, J.A.; Scott, K.C. Diabetes Insipidus following Overdose of Baclofen and Quetiapine. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2009, 37, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurth, J.; Maguire, G. Pediatric case report of quetiapine overdose and QTc prolongation. Ann. Clin. Psychiatry 2004, 16, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.J.; Hast, H.A.; Erickson, T.B. Dramatic QTc Narrowing after Intralipid Administration in Quetiapine Overdose. Clin. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 740. [Google Scholar]
- Presley, J.D.; Chyka, P.A. Intravenous Lipid Emulsion to Reverse Acute Drug Toxicity in Pediatric Patients. Ann. Pharmacother. 2013, 47, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anomelechi, E.; Hirst, R. Adrenaline-induced hypotension in the context of significant quetiapine overdose. Clin. Case Reports 2023, 11, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veli, S.B.; Atanasov, V.N.; Angelov, J.S.; Kanev, K.P. Simultaneous application of intravenous fat emulsion and charcoal hemoperfusion in quetiapine overdose case. Cent. Eur. J. Med. 2014, 9, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, S.E.; Tasyurek, T.; Guneysel, O. Intralipid emulsion treatment as an antidote in lipophilic drug intoxications. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 32, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, K.; Beppu, S.; Nishiyama, K.; Shimizu, M.; Yamazaki, H. Pharmacokinetics of duloxetine self-administered in overdose with quetiapine and other antipsychotic drugs in a Japanese patient admitted to hospital. J. Pharm. Health Care Sci. 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, E.D.; Demir, A.; Yilmaz, F.; Kavalci, C.; Karakilic, E.; Çelikel, E. Treatment of Quetiapine Overdose with Intravenous Lipid Emulsion. Keio J. Med. 2013, 62, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, M.J.; Benitez, J.G.; Ternullo, S.; Juhl, G.A. Acute oxcarbazepine and atomoxetine overdose with quetiapine. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 2004, 46, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.; Bakhit, A.; Dufresne, A.; Sapkota, D.; Altekreti, A. LBBB Induced by Quetiapine Overdose: A Case Report and Literature Review. Am. J. Ther. 2017, 24, e618–e620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulec, H.; Babayigit, M.; Kurtay, A.; Sahap, M.; Ulus, F.; Tutal, Z.; Horasanli, E. Seizure due to multiple drugs intoxication: A case report. Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2016, 66, 651–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klučka, J.; Juřenčák, T.; Kosinová, M.; Štourač, P.; Kratochvíl, M.; Sedláčková, Y.; Tomáš, N.; Pelclová, D.; Jabandžiev, P. Intralipid infusion in paediatric patient with quetiapine and lamotrigine intoxication. Monatshefte Fur Chem. 2019, 150, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanns Clausen, M.; Stedtler, U.; Reinhardt, M. Quetiapine Overdose-A Case Series. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 443–444. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, R.L. Fatal combination of mitragynine and quetiapine—A case report with discussion of a potential herb-drug interaction. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2019, 15, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzog, T.; Cetran, L.; Labadie, M.; Braganca, C.; Goncalves, R. Delayed cardiotoxicity in venlafaxine and quetiapine overdose. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 1279–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstein, A.C.; Spyker, D.A.; Cantilena, L.R.; Green, J.L.; Rumack, B.H.; Giffin, S.L. 2008 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 26th Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 911–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronstein, A.C.; Spyker, D.A.; Cantilena, L.R.; Green, J.L.; Rumack, B.H.; Heard, S.E. 2007 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 25th Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 927–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronstein, A.C.; Spyker, D.A.; Cantilena, L.R.; Green, J.; Rumack, B.H.; Heard, S.E. 2006 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS). Clin. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 815–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronstein, A.C.; Spyker, D.A.; Cantilena, L.R.; Green, J.L.; Rumack, B.H.; Giffin, S.L. 2009 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 27th Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 979–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampschulte, B.; Klauwer, D.; Faas, D.; Heckmann, M. Therapierefraktäre arterielle Hypotension infolge Intoxikation mit Quetiapin und Escitalopram—Therapie mit Terlipressin und Vasopressin. Klin. Pädiatrie 2010, 222, GNPI_FV_64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, C.; Shafiei, M.; Molden, E.; Jacobsen, D. Toxicokinetics of Quetiapine and its Active Metabolite N-desalkylquetiapine During Acute Poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 267. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, I.; Rauber-Luthy, C.; Kupferschmidt, H. Acute Intoxication with Quetiapine: A Cohort Study. Clin. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berling, I.; Isbister, G.K. Prolonged QT Risk Assessment in Antipsychotic Overdose Using the QT Nomogram. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2015, 66, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, H.K.; Mansour, N.M.; Elmansy, A. Predictors for prolonged qt intervals in acute antipsychotic poisoned patients. Toxicol. Res. 2024, 13, tfae038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, N.A.; Whyte, I.M.; Dawson, A.H. Cardiotoxicity more common in thioridazine overdose than with other neuroleptics. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1995, 33, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.B.; Simpson, M.D.; Burns, M.M. Toxicology Investigators Consortium (ToxIC). Evolving trends of pharmaceutical poisonings associated with QRS complex prolongation. Clin. Toxicol. 2024, 62, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).