Abstract
Background/Objectives: In recent years, the use of gamification has been growing in health education. In undergraduate nursing programs, it aims to enhance motivation, engagement, knowledge retention, and professional competencies. However, the evidence often combining nursing students with other disciplines or focusing on specific tools rather than the broader concept. This systematic review will synthesize the impact of gamification strategies on educational outcomes in undergraduate nursing education. Methods: This protocol was written according to PRISMA-P guidelines and is registered in PROSPERO (CRD420251117719). Eligible studies will include randomized controlled trials, quasi-experimental, and observational designs involving undergraduate nursing students exposed to gamification interventions in classroom, online, or clinical training settings. Comparators may include traditional lecture-based instruction or other non-gamified methods. We will search the PubMed, CINAHL, PsycINFO, Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases, covering January 2010 to July 2025, without language restrictions. Two reviewers will independently screen studies, extract data, and assess risk of bias using Cochrane RoB-2, ROBINS-I, and JBI Critical Appraisal Tools. Where possible, a meta-analysis will be conducted; otherwise, findings will be synthesized narratively. Results: Not applicable; this is a protocol. Findings will be synthesized as specified in the Methods. Conclusions: This review will provide a comprehensive synthesis of gamification’s effectiveness in undergraduate nursing education, identifying the most effective strategies and the contexts in which they perform best.
1. Introduction
In recent years, there has been a growth of game-based learning in nursing and higher education [1]. Usually summarized as “gamification”, this trend connects to a sizeable body of existing concepts and research in human–computer interaction and game studies, such as serious games, pervasive games, alternate reality games, or playful design [2]. More recent systematic reviews have examined gamification in health professions education, confirming its growing adoption and highlighting heterogeneous effects across contexts [3,4]. Nursing education requires active student engagement as an alternative to traditional knowledge transfer models. Theoretical and procedural content, as well as the development of competencies and skills, must be dynamically integrated, resulting in a complex process that challenges both educators and students [5]. In nursing education, the incorporation of gamification elements can reduce student monotony and passivity, foster active engagement and accelerate the development of professional competencies [6]. The use of gamification has different effects on nursing education, such as control of their learning (autonomy), perceived growth in their skills (competence), and experience collaborative learning (relatedness) [7]. López-Jiménez et al. demonstrated that gamifying an audience response system enhanced both learners’ educational performance and their engagement in anatomy education [8]. Dabbous et al. investigated the use of game-based learning during pharmacy practice experiences, reporting significant improvements in post-test scores and showing that student motivation, measured with the ALMAS scale, predicted learning outcomes [9]. Although game-based learning and gamification are distinct approaches, this study illustrates the potential of playful educational strategies in health professions, reinforcing the need for a review specifically focused on gamification in undergraduate nursing education. In another study involving nursing students, participants were first assessed for their baseline ability to interpret electrocardiograms (ECGs). Each group then received four structured training sessions, and variables of interest were re-evaluated two weeks after the intervention, revealing improved diagnostic accuracy and retention of skills [10]. However, Sanz-Martos et al. [11] evaluated a gamification session within nursing education and found that both student satisfaction and knowledge scores improved significantly (p < 0.001) following gamified lab-based activities.
In recent years, several systematic reviews have investigated the use of gamification in education, but many have included heterogeneous populations, including students from non-healthcare disciplines or education levels other than undergraduate [3,4,12,13]. This approach has produced results that are difficult to generalize to nursing education, where the training needs and required skills are specific and highly professionalizing. Furthermore, the available reviews have not always clearly distinguished between the different types of gamified strategies, nor have they analyzed motivational and affective outcomes in addition to cognitive ones. A preliminary search conducted in JBI, OSF, and PROSPERO databases did not identify any existing systematic reviews on this topic, which supports the rationale for the present protocol. This systematic review aims to fill these gaps by providing a targeted synthesis of the available evidence and a critical analysis of the barriers and facilitators to implementing such interventions in nursing degree programs.
The objective of this systematic review is to assess the impact of gamification strategies on educational outcomes in undergraduate nursing education. Specifically, the review will examine how gamification affects student learning, engagement, motivation, and knowledge retention, and will identify any reported challenges or barriers related to its implementation in academic settings.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
This systematic review protocol will be developed in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) guidelines [14]. The protocol has been registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; ID: CRD420251117719, available online at: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD420251117719) on 10 August 2025 [15].
Any protocol amendments will be updated in PROSPERO with a date-stamped record prior to data extraction and analysis.
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.2.1. Population
Studies will be eligible if they involve undergraduate nursing students enrolled in formal nursing education programs (e.g., bachelor’s or three-year degree courses) participating in educational interventions that incorporate gamification strategies, regardless of the setting (classroom-based, online, or clinical training). Studies involving non-nursing students (e.g., medical, pharmacy, or allied health) or conducted in unrelated educational contexts (e.g., secondary education, non-healthcare disciplines) will be excluded.
2.2.2. Intervention(s) or Exposure(s)
Eligible interventions will be educational strategies explicitly integrating gamification elements—such as points, badges, leaderboards, narratives, and challenges—into undergraduate nursing programs. We define gamification as the integration of game design elements (e.g., points, badges, leaderboards, narrative/quests, levels, feedback loops, cooperative/competitive mechanics) into non-game educational activities. Serious games will be included only if nursing-specific data are reported and will be analyzed separately. Stand-alone serious games without gamification elements will be excluded. Gamification may be implemented in classroom teaching, online modules, or clinical simulations. Studies will be excluded if they do not incorporate gamification elements or if the approach is unrelated to nursing education.
2.2.3. Comparator(s) or Control(s)
When present, comparators may include traditional, non-gamified educational approaches (e.g., lecture-based instruction, standard classroom teaching). Studies comparing two gamified interventions will be excluded.
2.2.4. Study Design
Eligible study designs include randomized controlled trials (RCTs), quasi-experimental studies, nonrandomized controlled studies, and observational designs (cross-sectional and cohort studies). Editorials, opinion papers, reviews, protocols, and conference abstracts without full text will be excluded.
2.2.5. Context
Eligible studies must be conducted in academic or formal educational settings involving undergraduate nursing students (e.g., universities, nursing schools).
2.3. Information Sources and Search Strategy
The main databases to be searched will include CINAHL (via EBSCOhost), PsycINFO (via EBSCOhost), PubMed (MEDLINE), Web of Science Core Collection, and Scopus. Google Scholar will also be consulted, and only the first 200 results sorted by relevance will be screened to ensure feasibility. Search strategies have been harmonized across databases to ensure consistency; Boolean operators (AND, OR) were used systematically, while restrictive operators such as NOT were avoided unless clearly justified.
No language restrictions will be applied. Non-English studies will be translated using professional translation services or validated translation software, with verification by bilingual reviewers to ensure accuracy. The search will cover the period from 1 January 2010 to 31 July 2025. The time frame is to 15 years to capture the emergence and development of gamification in nursing education, because the concept gained relevance in higher education literature after 2010. Search strategies will be adapted for each database. Combinations of keywords and MeSH terms related to “nursing students”, “gamification”, “educational games”, “motivation”, “engagement”, and “knowledge retention” will be used. Search strings were harmonized across databases to reduce redundancy while ensuring sensitivity. Related terms (e.g., ‘nursing student,’ ‘undergraduate nursing,’ ‘bachelor nursing’) were included to account for variations in indexing.
The study selection process will be documented using the PRISMA 2020 flow diagram (Figure 1). At present, the diagram reports the number of records retrieved in preliminary searches (Table 1). The diagram will be completed with counts of screened, excluded, and included studies during the full review process.
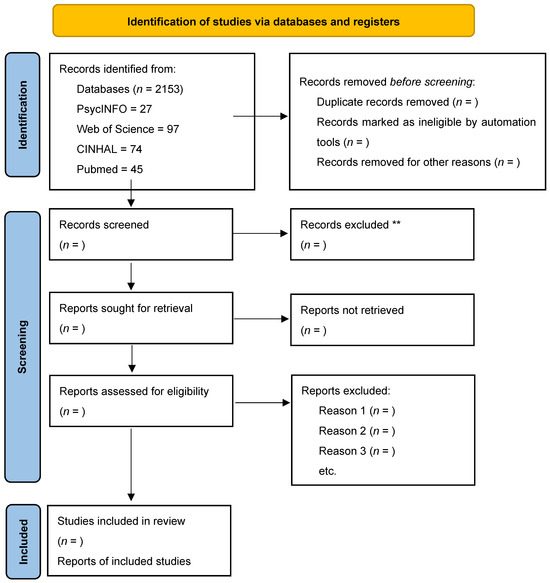
Figure 1.
PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for new systematic reviews which included searches of databases (n values will be added once the screening and selection process has been completed). ** Indicates that further details (such as exclusion reasons) will be added during the full review process.

Table 1.
Presents the search strings and the number of results retrieved from each database. The asterisk (“*”) is used as a truncation symbol to retrieve all possible word variants (e.g., “student *” = “student” OR “students”).
The search strategy was developed and refined with the support of an experienced medical librarian to optimize both sensitivity and specificity [16].
2.4. Study Selection
Search results will be imported into Zotero for reference management and duplicate removal [17]. Two reviewers (R.A.E. and M.C.) will independently screen titles and abstracts, followed by full-text assessments of potentially eligible studies. Disagreements will be resolved by consensus or by consulting a third reviewer (V.C.).
Inter-rater reliability between the two independent reviewers will be assessed using Cohen’s Kappa statistic, with disagreements resolved through discussion or adjudication by a third reviewer.
2.5. Data Extraction
A standardized data extraction form, developed a priori, will be used to collect information on study characteristics (e.g., authors, year, country, setting, design), participant demographics, intervention characteristics (type of gamification, game elements, duration, frequency), comparators, outcomes assessed, measurement instruments, and key findings. The form will be piloted on a sample of studies and refined as necessary. Data will be extracted independently by at least two reviewers (or a person/machine combination) with a process to resolve any discrepancies.
2.6. Risk of Bias Assessment
Risk of bias will be assessed using the following:
- Cochrane RoB-2 for RCTs [18];
- ROBINS-I for nonrandomized studies [19];
- JBI Critical Appraisal Tools for cross-sectional and descriptive studies [20];
- GRADE approach for certainty of evidence for each outcome [21];
- GRADE-CERQual framework for qualitative evidence [22].
Two reviewers will perform assessments independently.
2.7. Outcomes
Primary outcome:
The primary outcome will be academic performance/knowledge retention. Retention will be categorized according to time windows: immediate (≤1 week), short-term (1–4 weeks), medium-term (1–3 months), and long-term (>3 months). Academic performance will be assessed through validated or standardized tests and examinations, with effect sizes extracted as mean difference or standardized mean difference.
Secondary outcomes:
- Motivation and satisfaction, measured through validated questionnaires such as the Gameful Experience Scale (GAMEX) or Likert-style items.
- Engagement and critical thinking, assessed through GAMEX subscales (e.g., Absorption, Creative Thinking) or validated instruments such as the SEGiNAS scale.
- Implementation challenges, defined as barriers and facilitators reported during the design, delivery, or evaluation of gamification strategies. These qualitative findings will be analyzed through thematic synthesis, and their confidence will be appraised using the GRADE-CERQual approach.
2.8. Data Synthesis
Where studies are sufficiently homogeneous in terms of design, population, and outcome measures, a meta-analysis will be conducted, using the Review Manager (RevMan, Version 5.4.1, Cochrane Collaboration, Copenhagen, Denmark). The primary meta-analyses will include randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and controlled quasi-experimental studies. For continuous outcomes, mean differences or standardized mean differences with 95% confidence intervals will be calculated using a random-effects model to account for expected heterogeneity. Observational designs (cross-sectional, cohort, descriptive studies) will be narratively synthesized, and, if feasible, analyzed separately. Studies that directly compare two gamified interventions (e.g., gamified quiz vs. gamified simulation) will be synthesized narratively as a distinct comparison set. When meta-analysis is not feasible, a structured narrative synthesis will be provided. Qualitative findings regarding implementation challenges will be analyzed using a thematic synthesis approach. The methodological quality of qualitative studies will be appraised using the JBI Critical Appraisal Tools (2020 version), and the confidence in the evidence will be assessed using the GRADE-CERQual (2018 guidance) approach.
2.9. Certainty of Evidence
The certainty of evidence will be evaluated using the GRADE approach for each primary outcome, considering risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, and publication bias.
2.10. Ethics and Dissemination
As this review is based solely on published studies, ethical approval is not required. The results will be disseminated via a peer-reviewed publication and conference presentations.
3. Results
It is anticipated that the systematic review will identify a range of gamification strategies implemented in undergraduate nursing education, such as gamified flipped classrooms, laboratory-based simulations, interactive digital quizzes, and serious games. Based on the existing literature, these interventions are likely to be associated with improvements in learning motivation, preparedness, theoretical knowledge, and self-confidence [23]. However, it is also anticipated that some studies will report limited or no effects on practical skill performance, suggesting that the benefits of gamification may be more pronounced for cognitive and motivational outcomes than for psychomotor skills.
The review will likely find that gamified laboratory sessions can increase both student satisfaction and knowledge scores, while also fostering critical thinking and facilitating the transfer of theory into practice. Qualitative evidence is expected to highlight additional benefits in affective learning domains, such as the development of empathy, reflective capacity, and professional identity [9]. For example, gamified activities in mental health nursing may be reported to enhance students’ competencies, confidence, and engagement with complex patient care scenarios [24].
Moreover, this review will assess whether evidence from related health education fields can be synthesized to estimate the impact of gamification on academic achievement and knowledge retention [11]. The review will also explore how the magnitude of effects may differ according to the type of gamification design, the learning context, and the assessment methods used.
4. Discussion
The current literature on gamification in nursing education is characterized by heterogeneity, with differences in populations, designs, outcomes, and measurement instruments, thus making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the effectiveness of gamification, specifically in undergraduate nursing education.
This systematic review aims to fill this gap by providing a targeted and structured synthesis of the available evidence, including cognitive, motivational, and affective outcomes, as well as the challenges associated with the implementation of gamification strategies. Differences in the effectiveness of interventions will be explored according to type (e.g., quizzes with leaderboards, simulation-based gamification, virtual reality, and board games). If sufficient homogeneous data are available, pooled effect sizes will be calculated using a random-effects model to estimate the magnitude of gamification effects. For outcomes not amenable to statistical pooling, a structured narrative synthesis will be conducted, integrating both quantitative and qualitative findings.
5. Conclusions
This review will synthesize the available evidence on the efficacy of gamification in nursing education, highlighting its potential to improve motivation, involvement, knowledge retention, and the development of professional competencies. The expected results will help to identify the most effective strategies and the contexts in which they work better, offering educators useful tools to design innovative, student-centered educational approaches, and to orient future research in this field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A.E. and M.C.; methodology, V.C.; software, not applicable; validation, V.C., D.P. and V.A.; formal analysis, V.C.; investigation, V.C.; resources, V.C.; data curation, V.C.; writing—original draft preparation, V.C.; writing—review and editing, V.C., D.P., and V.A.; visualization, V.C.; supervision, R.A.E.; project administration, R.A.E.; funding acquisition, not applicable. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable. This study is a systematic review protocol and does not involve human or animal participants.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Public Involvement Statement
There was no public involvement in any aspect of this research.
Guidelines and Standards Statement
This manuscript was drafted against the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement for systematic review protocols.
Use of Artificial Intelligence
AI or AI-assisted tools were not used in drafting any aspect of this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all colleagues who provided valuable feedback during the development of the review protocol.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Abbreviation | Full term |
| PRISMA-P | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols |
| CINAHL | Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature |
| WOS | Web of Science |
| GAMEX | Gameful Experience Scale |
| JBI | Joanna Briggs Institute |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| ROBINS-I | Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies—of Interventions |
| GRADE | Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations |
References
- Traister, T. Interleaving Foundational Nursing Concepts for Accelerated Nursing Students Through Gamification. Nurs. Educ. Perspect. 2025, 46, 262–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deterding, S.; Dixon, D.; Khaled, R.; Nacke, L. From game design elements to gamefulness: Defining “gamification”. In Proceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments, Tampere, Finland, 28–30 September 2011; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gaalen, A.E.J.; Brouwer, J.; Schönrock-Adema, J.; Bouwkamp-Timmer, T.; Jaarsma, A.D.C.; Georgiadis, J.R. Gamification of health professions education: A systematic review. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. Theory Pract. 2021, 26, 683–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gentry, S.V.; Gauthier, A.; L’Estrade Ehrstrom, B.; Wortley, D.; Lilienthal, A.; Tudor Car, L.; Dauwels-Okutsu, S.; Nikolaou, C.K.; Zary, N.; Campbell, J.; et al. Serious gaming and gamification education in health professions: Systematic review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mohammadi, A.; Aazami, S.; Azizifar, A. Nursing Students Learn Vaccination Using Kahoot! Gamification: An Intervention Study of Knowledge, Satisfaction, Interest, and Collaboration. Nurs. Res. Pract. 2025, 2025, 3518943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Simin, D.; Dolinaj, V.; Brkić-Jovanović, N.; Brestovački-Svitlica, B.; Milutinović, D. Undergraduate nursing students’ experiences in a face-to-face, hybrid, and online escape room model: A comparative analysis in Serbian context. Med. Educ. Online 2025, 30, 2464204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bellotti, F.; Kapralos, B.; Lee, K.; Moreno-Ger, P.; Berta, R. Assessment in and of Serious Games: An Overview. Adv. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2013, 2013, 136864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Jiménez, J.J.; Fernández-Alemán, J.L.; García-Berná, J.A.; López González, L.; González Sequeros, O.; Nicolás Ros, J.; Carrillo de Gea, J.M.; Idri, A.; Toval, A. Effects of Gamification on the Benefits of Student Response Systems in Learning of Human Anatomy: Three Experimental Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabbous, M.; Kawtharani, A.; Fahs, I.; Hallal, Z.; Shouman, D.; Akel, M.; Rahal, M.; Sakr, F. The Role of Game-Based Learning in Experiential Education: Tool Validation, Motivation Assessment, and Outcomes Evaluation among a Sample of Pharmacy Students. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghinejad, H.; Mozafari, M.; Bazhdan, A.; Vasiee, A. Investigating the Effect of Online Gamification on Electrocardiogram Interpretation and Self-Directed Learning in Nursing Students. J. Adv. Med. Educ. Prof. 2024, 12, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sanz-Martos, S.; Álvarez-García, C.; Álvarez-Nieto, C.; López-Medina, I.M.; López-Franco, M.D.; Fernandez-Martinez, M.E.; Ortega-Donaire, L. Effectiveness of gamification in nursing degree education. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nylén-Eriksen, M.; Stojiljkovic, M.; Lillekroken, D.; Lindeflaten, K.; Hessevaagbakke, E.; Flølo, T.N.; Hovland, O.J.; Solberg, A.M.S.; Hansen, S.; Bjørnnes, A.K.; et al. Game-thinking; utilizing serious games and gamification in nursing education—A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. Educ. 2025, 25, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pangandaman, H.K.; Datumanong, N.T.; Diamla, M.R.L.; Raki-in, R.M.; Hayudini, M.A.A.; Amil, J.H.; Alih, S.-A.J.; Iskandal, I.I.; Abduhadi, A.-R.A.; Tan, A.R.A.; et al. Gamification in nursing education: A systematic review of its impact on knowledge retention and skills development among novice nursing students. Cuest. Fisioter. 2025, 54, 275–293. [Google Scholar]
- Shamseer, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration explanation. BMJ 2016, 354, i4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, R.A.; Colangelo, M.; Cerrone, V.; Pace, D.; Andretta, V. Gamification Strategies in Undergraduate Nursing Education: A Systematic Review Protocol. PROSPERO 2025 CRD420251117719. Available online: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD420251117719 (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kirtley, S.; Waffenschmidt, S.; Ayala, A.P.; Moher, D.; Page, M.J.; Koffel, J.B.; PRISMA-S Group. PRISMA-S: An extension to the PRISMA Statement for reporting literature searches in systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roy Rosenzweig Center for History and New Media. Zotero [Computer Software]. 2016. Available online: www.zotero.org/download (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aromataris, E.; Lockwood, C.; Porritt, K.; Pilla, B.; Jordan, Z. (Eds.) JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2024; Available online: https://sumari.jbi.global/ (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J.; GRADE Working Group. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, S.; Booth, A.; Glenton, C.; Munthe-Kaas, H.; Rashidian, A.; Wainwright, M.; Bohren, M.A.; Tunçalp, Ö.; Colvin, C.J.; Garside, R.; et al. Applying GRADE-CERQual to qualitative evidence synthesis findings: Introduction to the series. Implement. Sci. 2018, 13 (Suppl. 1), 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzeky, M.E.H.; Elhabashy, H.M.M.; Ali, W.G.M.; Allam, S.M.E. Effect of gamified flipped classroom on improving nursing students’ skills competency and learning motivation: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Nurs. 2022, 21, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pozo-Herce, P.; Tovar-Reinoso, A.; García Carpintero-Blas, E.; Casaux Huertas, A.; Ruiz de Viñaspre-Hernández, R.; Martínez-Sabater, A.; Chover-Sierra, E.; Rodríguez-García, M.; Juarez-Vela, R. Gamification as a Tool for Understanding Mental Disorders in Nursing Students: Qualitative Study. JMIR Nurs. 2025, 8, e71921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).