Sense of Coherence and Adherence to Self-Care in People with Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Quality Assessment of Included Studies
2.6. Certainty Assessment
2.7. Analysis
3. Results
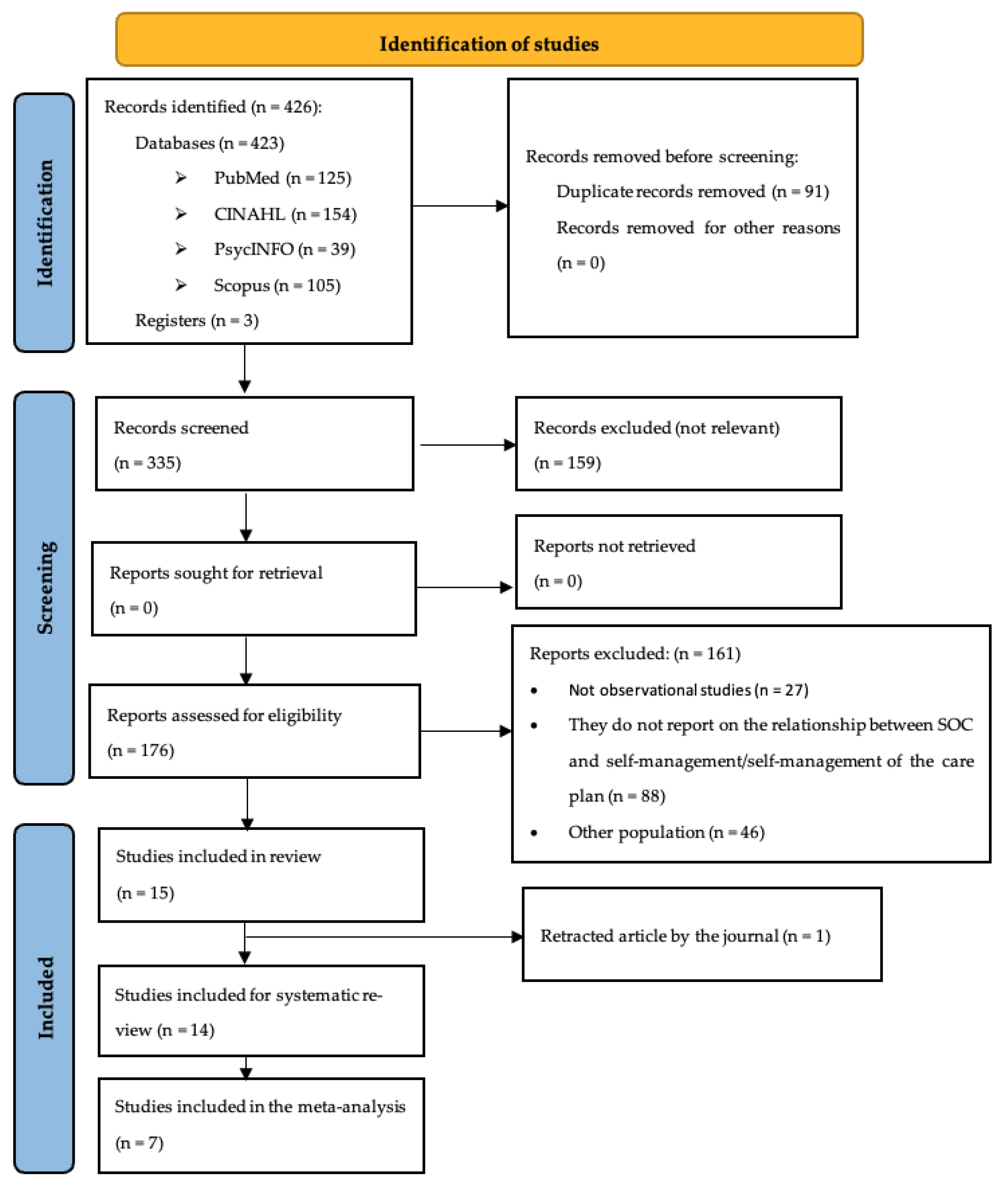
3.1. Description of Search Results
3.2. Description of Included Studies
3.3. Assessment of the Methodological Quality of the Included Studies
3.4. Results of the Review
3.5. Narrative Synthesis
3.5.1. Sense of Coherence and Adherence to Self-Care
3.5.2. Sense of Coherence and Perception of the Self-Care Plan
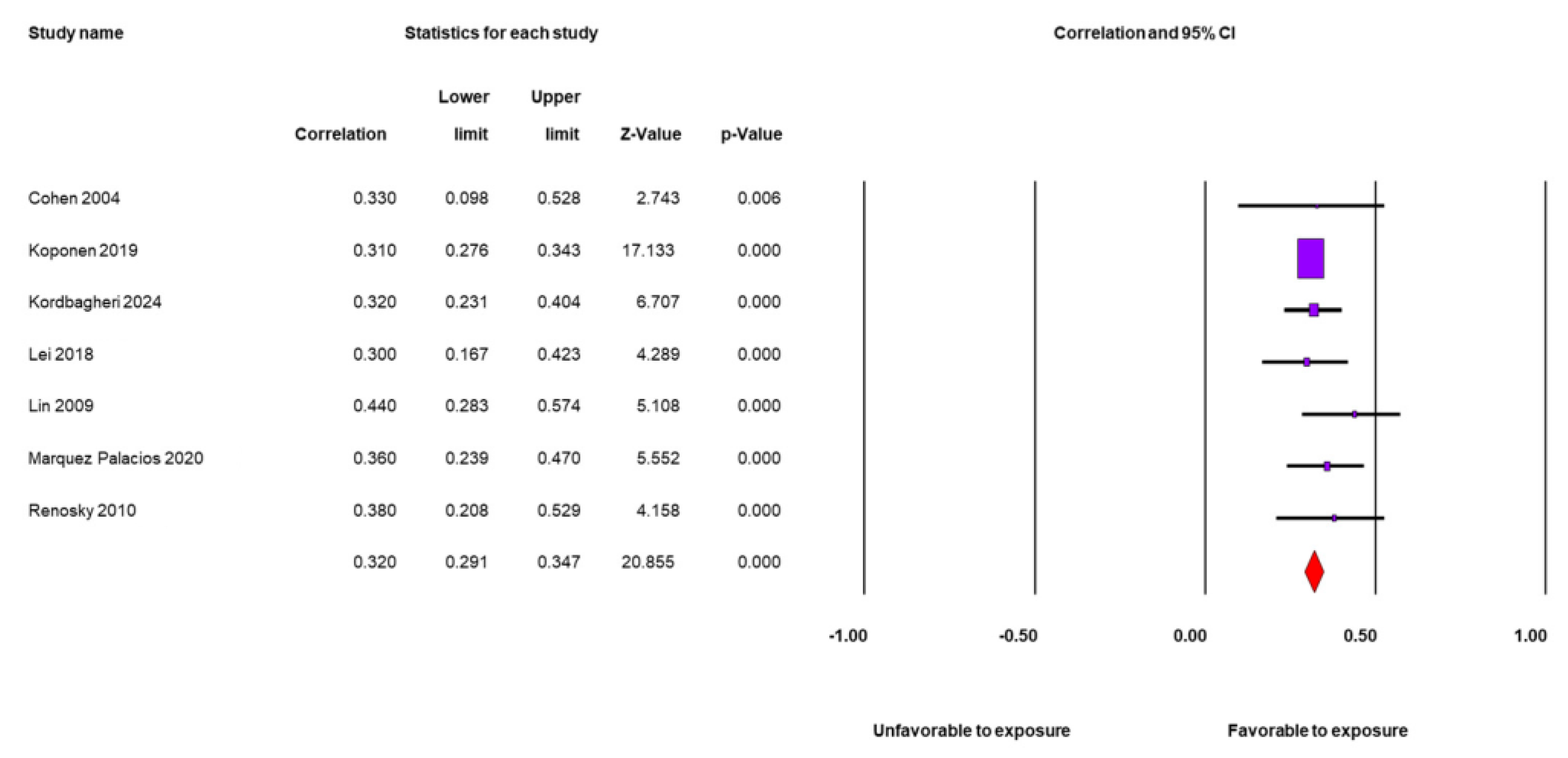
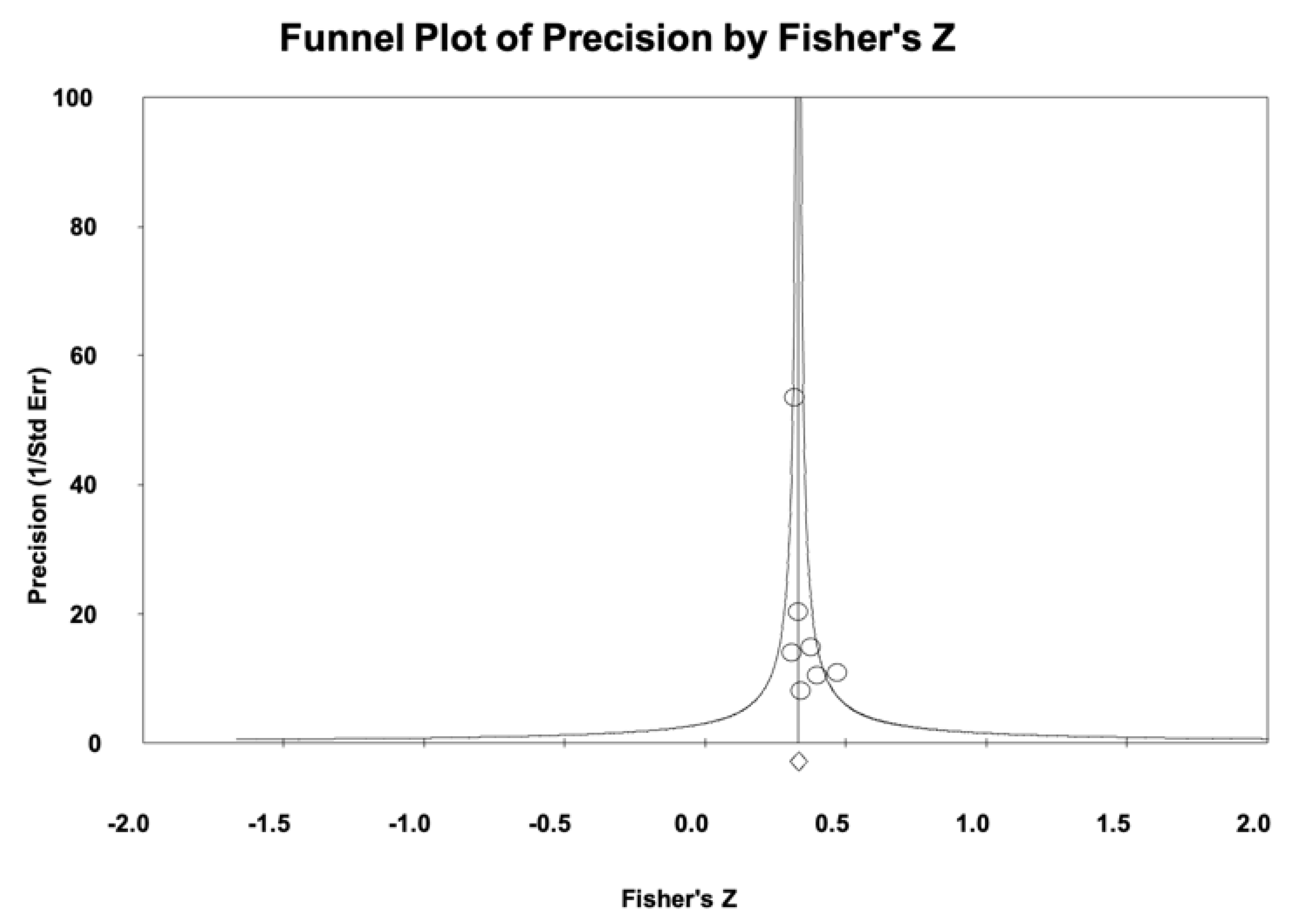
3.6. Meta-Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Strengths and Limitations
4.2. Recommendations for Further Research
4.3. Implications for Policy and Practice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Public Involvement Statement
Guidelines and Standards Statement
Use of Artificial Intelligence
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| WHO | World health organization |
| SOC | Sense of coherence |
| PRISMA | Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews |
| T1D | Diabetes type 1 |
| T2D | Diabetes type 2 |
| GDM | Gestational diabetes mellitus |
| GRADE | Grading of recommendation, assessment, development, and evaluation guidelines |
| CI | Confidence intervals |
Appendix A
- Search String in Each Database
- PUBMED
- Diabet* AND (“sense of coherence” OR Salutogenesis) AND (adherence OR compliance OR diet OR “physical activity” OR exercise OR insulin OR medication OR treatment* OR drug therapy OR self-management OR self care OR self-care OR self-control OR care plan* OR care management)
- CINAHL
- Diabetes mellitus AND (“sense of coherence” OR Salutogenesis) AND AB ((adherence OR compliance OR diet OR “physical activity” OR exercise OR insulin OR medication OR treatment* OR drug therapy OR self care OR self-management OR self control OR care plan* OR care management))
- PSYCINFO
- Diabetes AND (“sense of coherence” OR salutogenesis) AND AB (adherence OR compliance OR diet OR “physical activity” OR exercise OR insulin OR medication OR treatment* OR drug therapy OR self-management OR self care OR self control OR care plan* OR care management)
- SCOPUS
- TITLE-ABS-KEY(diabetes) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(“sense of coherence” OR salutogenesis) AND (TITLE-ABS-KEY(adherence) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (compliance) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (diet) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“physical activity”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (exercise) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (insulin) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (medication) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (treatment) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (drug therapy) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (selfcare) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (self-management) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (self control) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (care plan*) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (care management))
References
- Magliano, D.; Boyko, E. Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Goday, A. Epidemiología de la diabetes y sus complicaciones no coronarias. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2002, 55, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, A.; Whitehead, L. Evolution of the concept of self-care and implications for nurses: A literature review. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2009, 46, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Health Education, S. Health Education in Self-Care: Possibilities and Limitations; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Adherence to Long-Term Therapies: Evidence for Action; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Locke, S.R.; Brawley, L.R. Making one-sided exercise decisions: The influence of exercise-related cognitive errors. J. Health Psychol. 2018, 23, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Healthy Diet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/healthy-diet (accessed on 29 March 2025).
- World Health Organization. Physical Activity. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity (accessed on 29 March 2025).
- Zeballos-Palacios, C.; Morey-Vargas, O.L.; Brito, J.P.; Montori, V.M. Toma de decisiones compartidas y medicina mínimamente impertinente en el manejo de las enfermedades crónicas. Rev. Perú. Med. Exp. Salud Pública 2014, 31, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonsky, W. Understanding and Assessing Diabetes-Specific Quality of Life. Diabetes Spectr. 2000, 13, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Egede, L.E.; Dismuke, C.E. Serious psychological distress and diabetes: A review of the literature. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2012, 14, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonsky, W.H.; Davis, C.L.; Jacobson, A.M.; Anderson, B.J. Correlates of hypoglycemic fear in type I and type II diabetes mellitus. Health Psychol. 1992, 11, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.J.; Irvine, A.; Gonder-Frederick, L.; Nowacek, G.; Butterfield, J. Fear of hypoglycemia: Quantification, validation, and utilization. Diabetes Care 1987, 10, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, S.F.; Anthony, S.; Harrell, R.; Tripp, C.; Bowman, J.; Khan, S.; Naniwadekar, A. Managing atrial fibrillation: The intersection of cardiology, health psychology, and the patient experience. Health Psychol. 2022, 41, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaarsma, T.; Strömberg, A.; Dunbar, S.B.; Fitzsimons, D.; Lee, C.; Middleton, S.; Vellone, E.; Freedland, K.E.; Riegel, B. Self-care research: How to grow the evidence base? Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2020, 105, 103555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonovsky, A. Health, Stress, and Coping, 1st ed.; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Antonovsky, A. The salutogenic model as a theory to guide health promotion. Health Promot. Int. 1996, 11, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.; Mittelmark, M.B. The Sense of Coherence and Its Measurement. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK435830/ (accessed on 9 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.; Lindström, B. Antonovsky’s sense of coherence scale and the relation with health: A systematic review. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2006, 60, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świątoniowska-Lonc, N.; Tański, W.; Polański, J.; Jankowska-Polańska, B.; Mazur, G. Psychosocial determinants of treatment adherence in patients with type 2 diabetes—A review. Diabetes Metabolic. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 2701–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, K.; Sparud-Lundin, C.; Adolfsson, A.; Berg, M. Well-being and diabetes management in early pregnant women with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, A.; Adner, N.; Nordstrom, G. Persons with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Acceptance and coping ability. J. Adv. Nurs. 2001, 33, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Lin, X.; Wan, L. A study on correlation between self-care behavior and psychological concordance and depression of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Chin. Nurs. Res. 2009, 23, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Koponen, A.M.; Simonsen, N.; Suominen, S. How to promote fruits, vegetables and berries intake among patients with type 2 diabetes in primary care? A self-determination theory perspective. Health Psychol. Open 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez Palacios, J.H.; Urzúa Morales, A.; Calderón Carvajal, C.; Salazar Estrada, J.G.; Díaz Reséndiz, F.d.J. El efecto mediador del sentido de coherencia en la relación entre autocuidado y control glucémico de personas diabéticas. Glob. Health Promot. 2021, 28, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odajima, Y.; Sumi, N. Factors related to sense of coherence in adult patients with Type 2 diabetes. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandén-Eriksson, B. Coping with type-2 diabetes: The role of sense of coherence compared with active management. J. Adv. Nurs. 2000, 31, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, A.T. Sense of coherence amongst Hong Kong Chinese adults with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2004, 41, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, N.O.B.; Björk, J.; Cederlund, R.I. Health-related quality of life 5 years after carpal tunnel release among patients with diabetes: A prospective study with matched controls. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2014, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, T.P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del-Pino-Casado, R. Cómo aprender (y enseñar) a realizar búsquedas en CINAHL y PubMed. Evidentia 2017, 14, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, M. Guidelines for evaluating prevalence studies. Evid. Based Ment. Health 1998, 1, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, M.; Berkman, N.D.; Dryden, D.M.; Hartling, L. AHRQ Methods for Effective Health Care. In Assessing Risk of Bias and Confounding in Observational Studies of Interventions or Exposures: Further Development of the RTI Item Bank; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- López Simarro, F.; Brotons, C.; Moral, I.; Aguado Jodar, A.; Cols Sagarra, C.; Miravet Jiménez, S. Concordance between two methods in measuring treatment adherence in patients with type 2 diabetes. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2016, 4, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, D.; Maiorino, M.I.; Bellastella, G.; Esposito, K. Clinical inertia, reverse clinical inertia, and medication non-adherence in type 2 diabetes. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datye, K.A.; Boyle, C.T.; Simmons, J.; Moore, D.J.; Jaser, S.S.; Sheanon, N.; Kittelsrud, J.M.; Woerner, S.E.; Miller, K.M. Timing of Meal Insulin and Its Relation to Adherence to Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2018, 12, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, M.; Berkman, N.D.; Dryden, D.M.; Hartling, L. Assessing Risk of Bias and Confounding in Observational Studies of Interventions or Exposures: Further Development of the RTI Item Bank; Agency for Healthcare Rsearch and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rothman, K.J.; Greenland, S.; Lash, T.L. Modern Epidemiology; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, D.; Best, D.; Briss, P.A.; Eccles, M.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Flottorp, S.; Guyatt, G.H.; Harbour, R.T.; Haugh, M.C.; Henry, D.; et al. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2004, 328, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meader, N.; King, K.; Llewellyn, A.; Norman, G.; Brown, J.; Rodgers, M.; Moe-Byrne, T.; Higgins, J.P.; Sowden, A.; Stewart, G. A checklist designed to aid consistency and reproducibility of GRADE assessments: Development and pilot validation. Syst. Rev. 2014, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.; Hedges, L.; Valentine, J. The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis; Russell Sage Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.; Thompson, S.; Deeks, J.; Altman, D. Statistical heterogeneity in systematic reviews of clinical trials: A critical appraisal of guidelines and practice. J. Health Serv. Res. Policy 2002, 7, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borenstein, M. Avoiding common mistakes in meta-analysis: Understanding the distinct roles of Q, I-squared, tau-squared, and the prediction interval in reporting heterogeneity. Res. Synth. Methods 2024, 15, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Bagheri, S.M.; Jalali Heris, N.; Matbouraftar, P.; Azarian, M.; Kordbagheri, M. Structural equation modeling to estimate treatment adherence based on the light triad of personality and sense of coherence in patients with type-2 diabetes: Examining the mediating role of psychological well-being. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1285808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, A.M.; Simonsen, N.; Suominen, S.B. Success in Weight Management Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Do Perceived Autonomy Support, Autonomous Motivation, and Self-Care Competence Play a Role? J. Behav. Med. 2017, 44, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Y.; Shiu, A.T. Sense of coherence and diabetes-specific stress perceptions of diabetic patients in central Mainland China. J. Clin. Nurs. 2006, 15, 1460–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renosky, J. Psychosocial Adjustment to Diabetes: An Integrative Model for Glycemic Control and Quality of Life. Doctoral Thesis, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, M.; Kanter, Y. Relation between sense of coherence and glycemic control in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J. Behav. Med. 2004, 29, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahola, A.J.; Saraheimo, M.; Forsblom, C.; Hietala, K.; Groop, P.H. The cross-sectional associations between sense of coherence and diabetic microvascular complications, glycaemic control and patients’ conceptions of type 1 diabetes. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2010, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahola, A.J.; Mikkilä, V.; Saraheimo, M.; Wadén, J.; Mäkimattila, S.; Forsblom, C.; Freese, R.; Groop, P.H. Sense of coherence, food selection, and leisure time, physical activity in type 1 diabetes. Scand J. Public Health 2012, 40, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Martínez, M.d.C.; López-Martínez, C.; Del-Pino-Casado, R. Sense of Coherence and Health Self-Care in People with Diabetes. Doctoral Thesis, University of Jaén, Jaén, Spain, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kordbagheri, M.; Bagheri, S.; Heris, N.; Matbouraftar, P.; Azarian, M.; Mousavi, S. The mediating role of psychological well-being in the relationship between the light triad of personality and sense of concordance with treatment adherence in patients with type 2 diabetes: A network analysis and structural equation modeling study. Acta Psychol. 2024, 248, 104361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y. The Effects of a Strengths-Based Intervention Based on Salutogenic Model on Self-Care Behaviors and Sense of Coherence in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Doctoral Thesis, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.5 (Updated August 2024). Cochrane 2024. Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- Olesen, K.; Jensen, T.M.; Diaz, L.J.; Møller, A.C.L.; Willaing, I.; Lyssenko, V. Sense of Coherence is associated with LDL-cholesterol in patients with type 1 diabetes—The PROLONG-Steno study. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya Bravo, M.-C. Sentido de Coherencia y Adhesión Terapéutica Antirretroviral en Personas con VIH SIDA. Doctoral Thesis, Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú, Lima, Perú, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Orihuela, R. Relación entre sentido de coherencia y adhesión al tratamiento en mujeres adultas con cáncer de mama de un hospital nacional de Lima Metropolitana. Rev. Psicol. Hered. 2019, 11, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Mantovani, M.; Miranda, F.; Paes, R.; Paz, V.; de Souza, T. Sentido de coherencia en las enfermedades crónicas: Una revisión integradora. Enferm. Univ. 2021, 18, 525–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera Suquet, J.; Reig-Garcia, G. El sentido de coherencia y las habilidades para la vida como factores protectores en personas con prediabetes. Glob. Health Promot. 2023, 30, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundman, B.; Norberg, A. The significance of a sense of coherence for subjective health in persons with insulin-dependent diabetes. J. Adv. Nurs. 1993, 18, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, V.M.; Araújo, G.L.; Lyra, M.C.A.; Rosenblatt, A.; Heimer, M.V. Sense of coherence and quality of life in adolescents with heart disease. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2022, 40, e2021104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author/Year | N | Study Design | Mean Age (Standard Deviation) and [Range] | % Women | Type of DM | SOC Instrument | Type of Drug Treatment | Outcomes | Measuring Instrument |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ahola 2010 [51] | 1264 | CS | 45 (12) [33–57] | 56 | T1D | SOC-13 | Insulin | Doctor and nurse visits | Ad hoc |
| Ahola 2012 [52] | 1104 | CS | 44 (12) [33–53] | 56.0 | T1D | SOC-13 | Not specified | Diet | Diet questionnaire |
| Exercise | Leisure Time Physical Activity (LTPA) questionnaire | ||||||||
| Cohen 2004 [50] | 67 | CS | 52.6 (13) [36–65] | 37.3 | T1D and T2D | SOC-29 | ADO and insulin | Self-care | Adherence to Self-care Behaviors questionnaire from the Self-care Inventory |
| He 2006 [48] | 202 | CS | 62.0 (9) [53–71] | 43.6 | T2D | C-SOC 13 | ADO and insulin | Diabetes-specific stress | Diabetes-specific Stress Perceptions (DSSP) |
| Kordbagheri 2024 [54] | 412 | CS | 58.2 (6.4) [51.8–64.5] | 34.8 | T2D | SOC-29 | Not specified | Self-care | Adherence questionnaire |
| Koponen 2017 [47] | 2866 | CS | 63.0 [27–75] | 43 | T2D | SOC-13 | ADO, insulin or only self-care | Diet and exercise | Success in Weight Management (SWM) |
| Koponen 2019 [24] | 2860 | CS | 63.0 [27–75] | 44.1 | T2D | SOC-13 | ADO, insulin and only self-care | Self-care | Perceived Competence for Diabetes Scale (PCS) |
| Intake of fruits and vegetables | Fruits, Vegetables and Berries Intake (FVBI) | ||||||||
| Lei 2018 [55] | 195 | CS (RCT Baseline) | 58.0 (13.2) [22–83] | 45.1 | T2D | SOC-13 | ADO, insulin and only self-care | Self-care | Summary of Diabetes Self-Care Activities Measure (SDSCA) |
| Lin 2009 [23] | 120 | CS | 59.0 [18.82] | Not specified | T2D | SOC-13 | Not specified | Self-care | Diabetes Self-care Behavior Scale (DSCS) |
| Marquez-Palacios 2021 [25] | 220 | CS | 56.1 (10.4) [20–69] | 74.5 | T2D | SOC-13 | Not specified | Self-care | Summary of Diabetes Self-Care Activities Measure (SDSCA) |
| Odajima 2018 [26] | 177 | CS | 57.9 (10.9) [20–75] | 39.5 | T2D | SOC-13 | Not specified | Burden by self-care plan | Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID) Survey |
| Renosky 2010 [49] | 111 | CS | 56.0 (14.2) [41.8–70.2] | 60.0 | T1D and T2D | SOC-29 | Not specified | Self-care | Summary of Diabetes Self-Care Activities Measure (SDSCA) |
| Shiu 2004 [28] | 72 | CS | 51.6 (11.7) [39.9–63.3] | 61.1 | T2D | SOC-13 | Insulin | Fear of hypoglycemia | Worry Scale |
| Vega-Martínez, López-Martínez and Del-Pino-Casado [53] | 130 | CS | 65.2 (9.8) [18–82] | 36.2 | T2D | SOC-13 | Not specified | Medication | Morisky-Green test |
| Mediterranean diet | Mediterranean Diet Follow-up Questionnaire (PREDIMED) | ||||||||
| Exercise | International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) |
| Selection Bias | Classification Bias | Confounding Bias | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ahola 2010 [51] | + | + | − |
| Ahola 2012 [52] | + | − | − |
| Cohen 2004 [50] | − | + | − |
| He 2006 [48] | + | + | − |
| Kordbagheri 2024 [54] | − | + | − |
| Koponen 2017 [47] | + | + | − |
| Koponen 2019 [24] | + | + | + |
| Lei 2018 [55] | + | + | − |
| Lin 2009 [23] | ? | + | − |
| Márquez-Palacios 2020 [25] | − | + | − |
| Odajima 2018 [26] | − | + | + |
| Renosky 2010 [49] | + | + | − |
| Shiu 2004 [28] | − | + | − |
| Vega-Martínez, López-Martínez and Del-Pino-Casado [53] | − | + | + |
| SOC | Issue | Subgroup | K | r | CI 95% | |
| Lower limit | Upper limit | |||||
| Type of DM | T1D | 2 | 0.36 | 0.23 | 0.48 | |
| T2D | 5 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.35 | ||
| Sampling | Probabilistic | 3 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.34 | |
| Non-probabilistic | 4 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.41 | ||
| Confounding bias | Control | 1 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.34 | |
| No control | 6 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.39 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vega-Martínez, M.d.C.; López-Martínez, C.; Del-Pino-Casado, R. Sense of Coherence and Adherence to Self-Care in People with Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15070230
Vega-Martínez MdC, López-Martínez C, Del-Pino-Casado R. Sense of Coherence and Adherence to Self-Care in People with Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nursing Reports. 2025; 15(7):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15070230
Chicago/Turabian StyleVega-Martínez, María del Carmen, Catalina López-Martínez, and Rafael Del-Pino-Casado. 2025. "Sense of Coherence and Adherence to Self-Care in People with Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nursing Reports 15, no. 7: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15070230
APA StyleVega-Martínez, M. d. C., López-Martínez, C., & Del-Pino-Casado, R. (2025). Sense of Coherence and Adherence to Self-Care in People with Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nursing Reports, 15(7), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15070230