Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms in Modifier Genes in Determining Fetal Hemoglobin Levels in Beta-Thalassemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hematological Investigation
2.2. Molecular Analysis
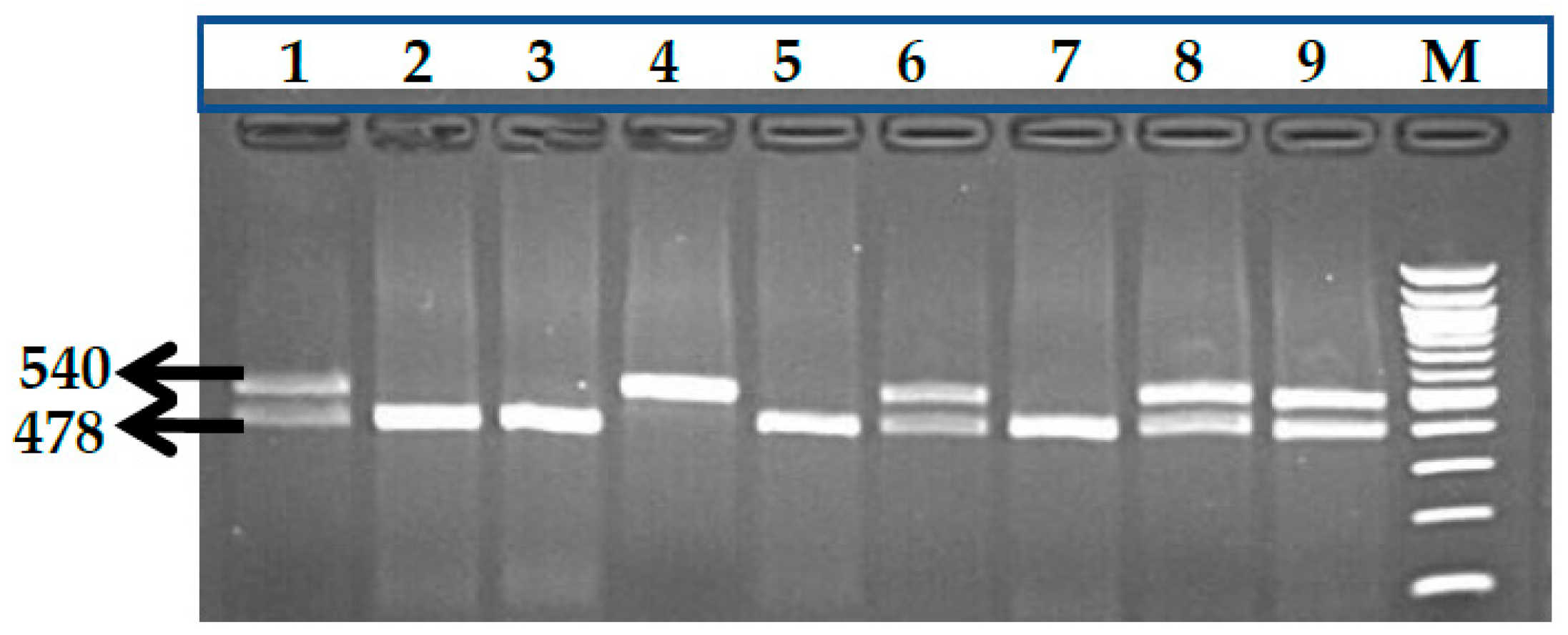
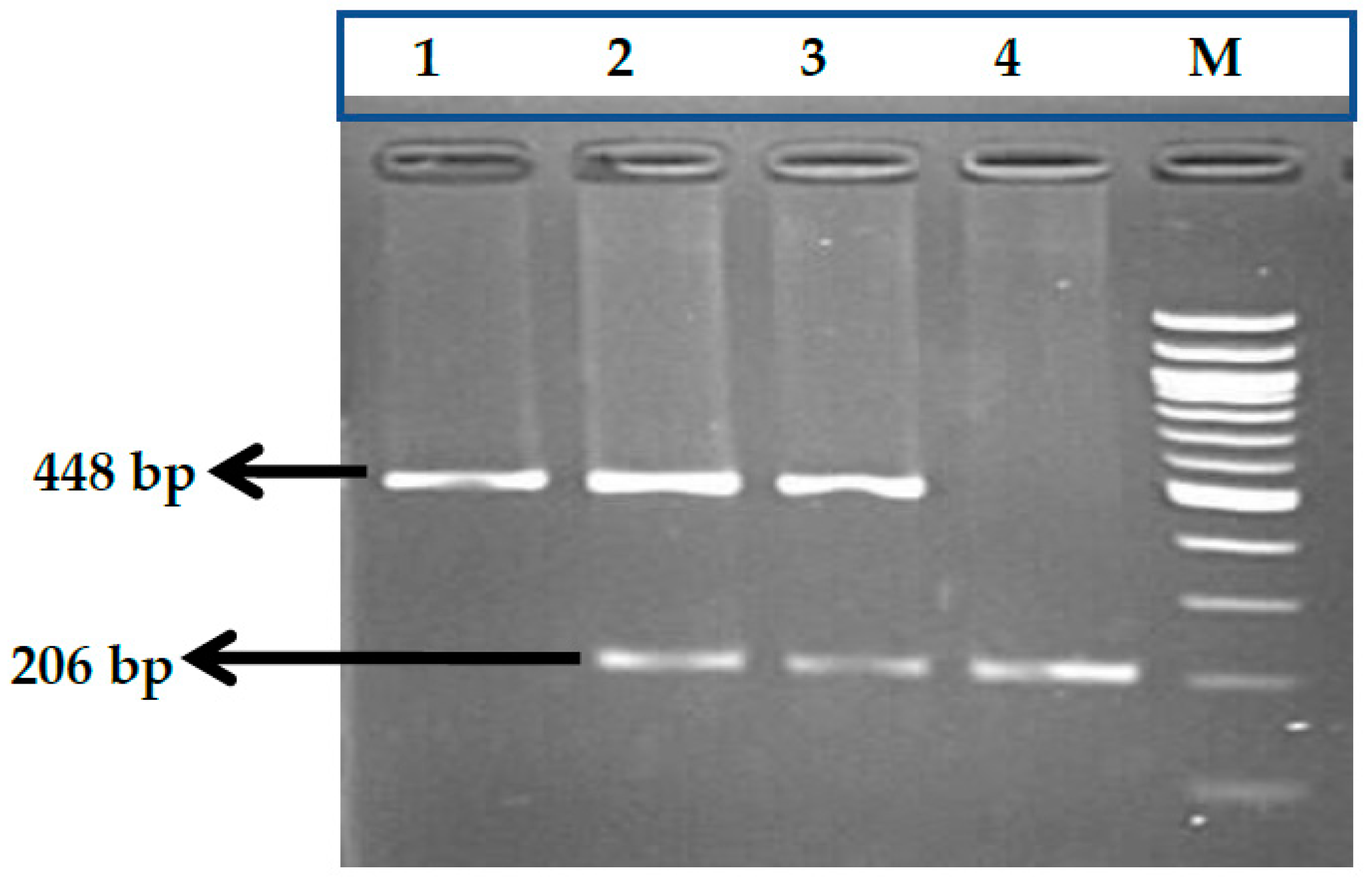
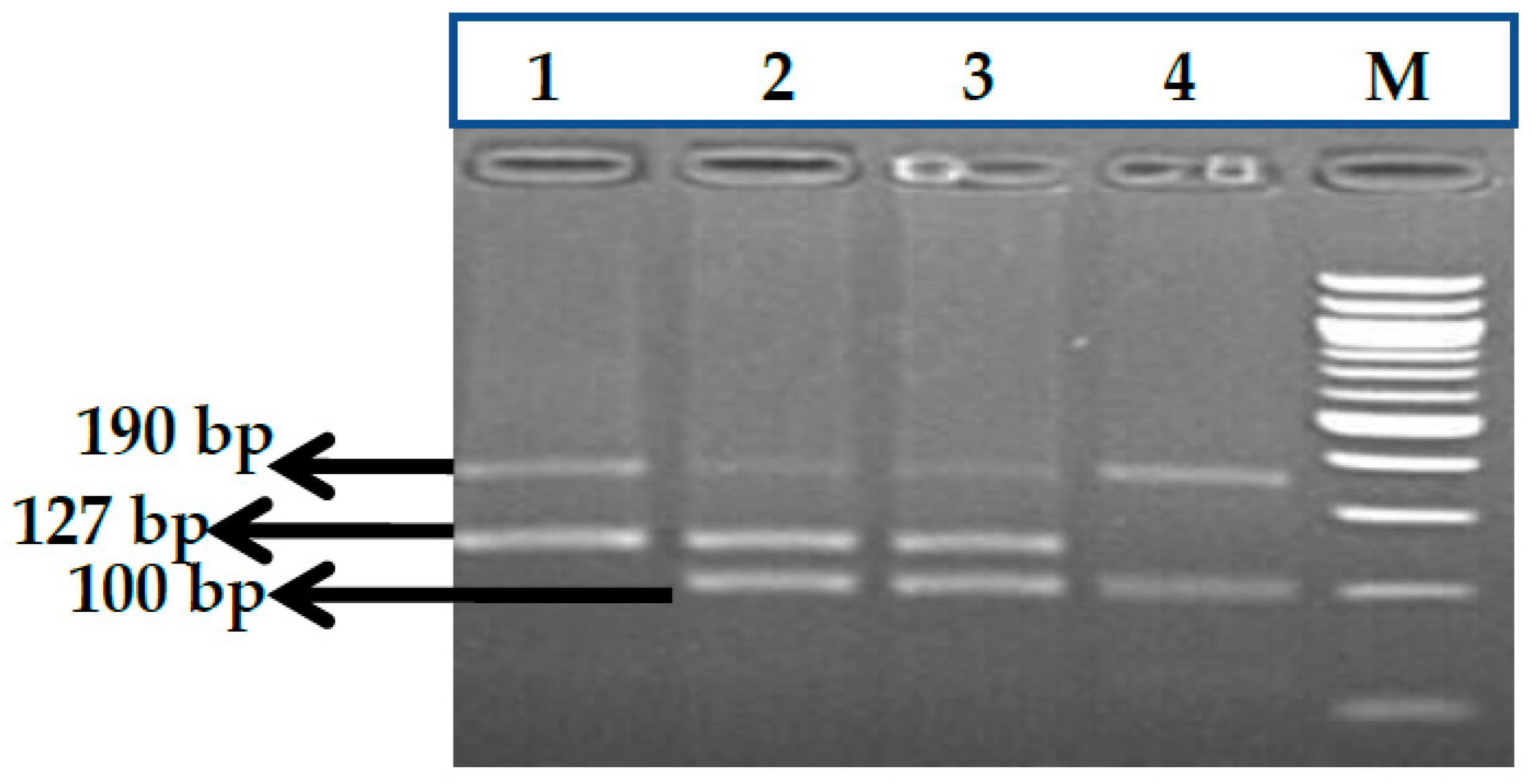
2.2.1. Genotype Analysis of Genetic Markers
2.2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.2.3. In Silico Analysis
3. Results
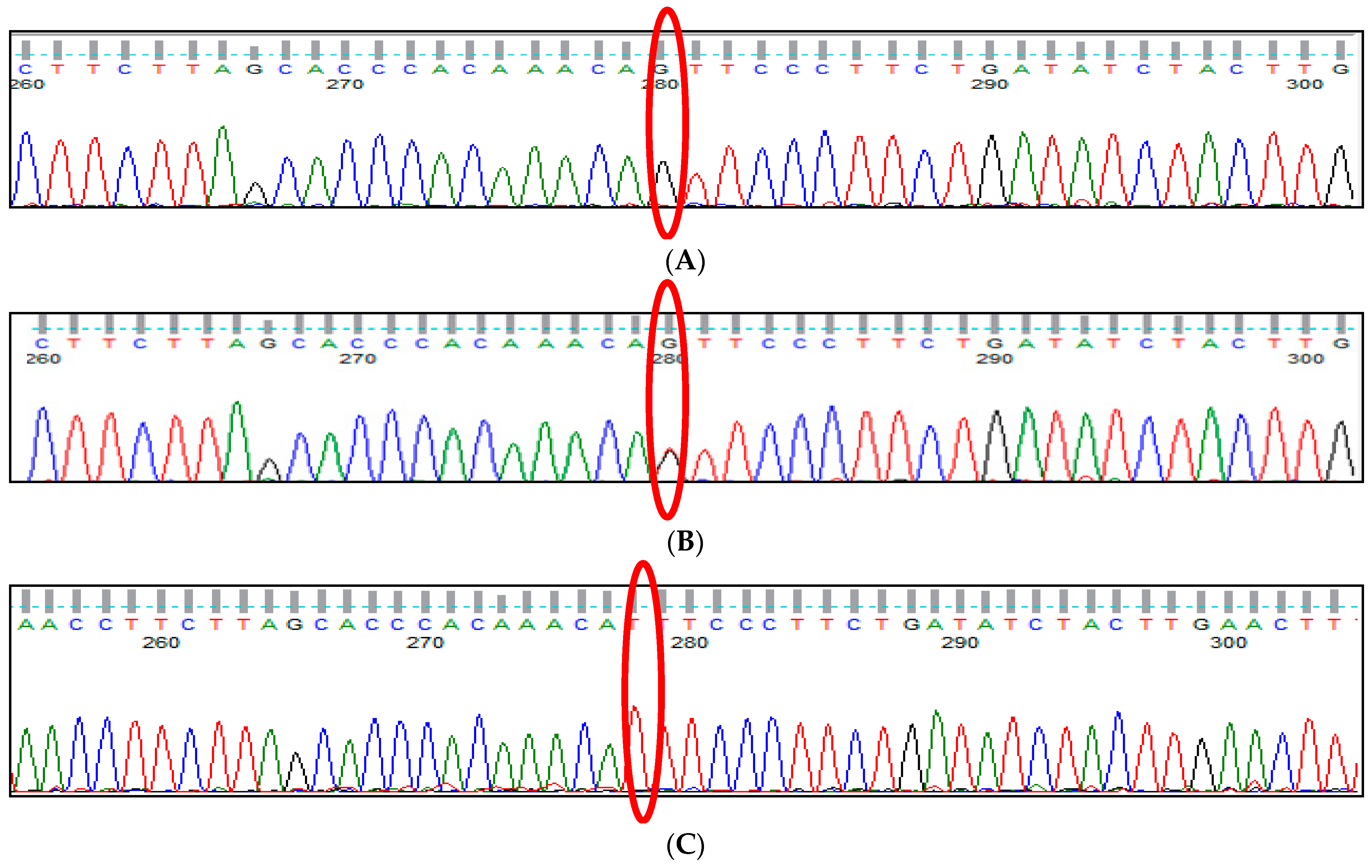
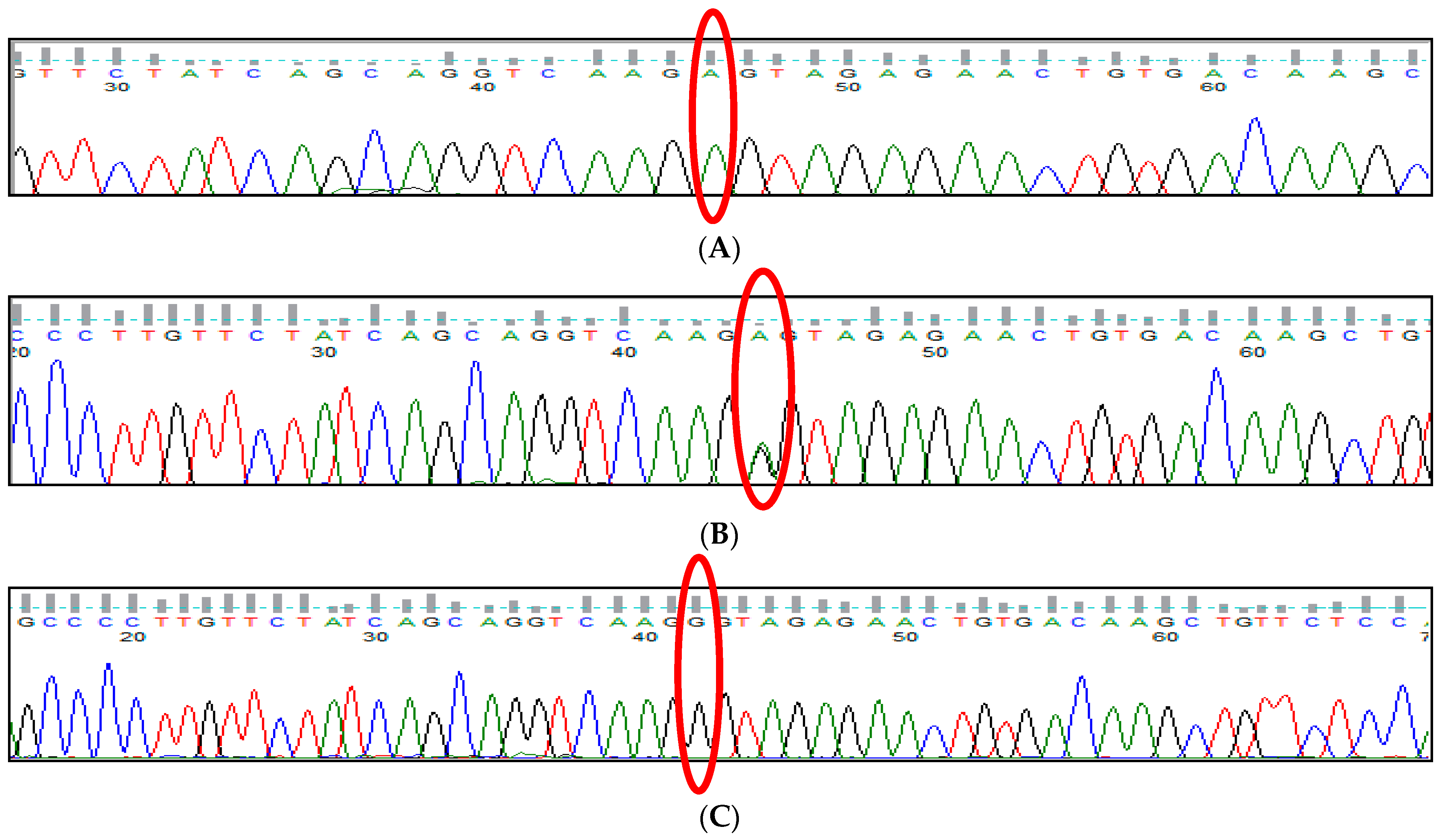
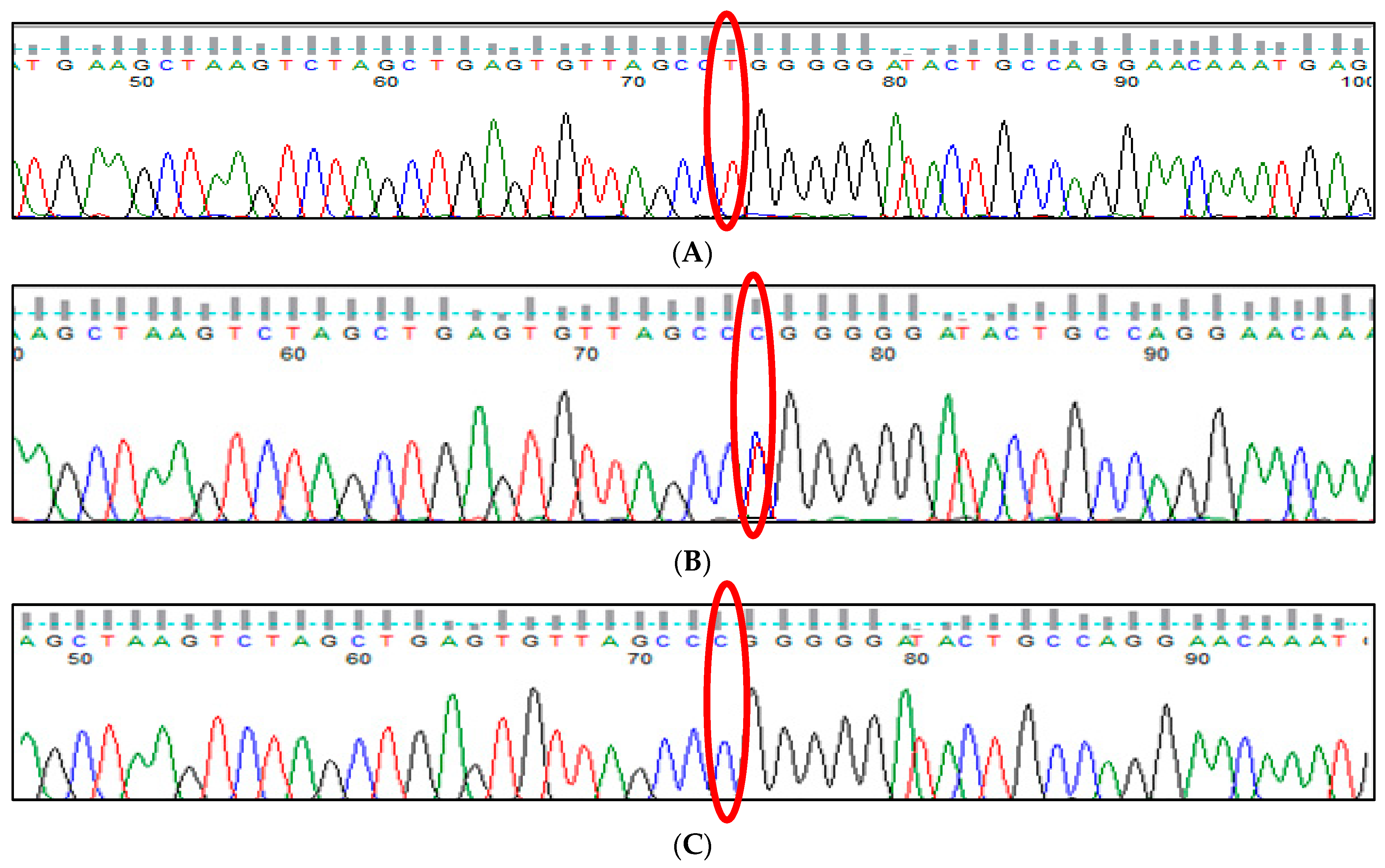
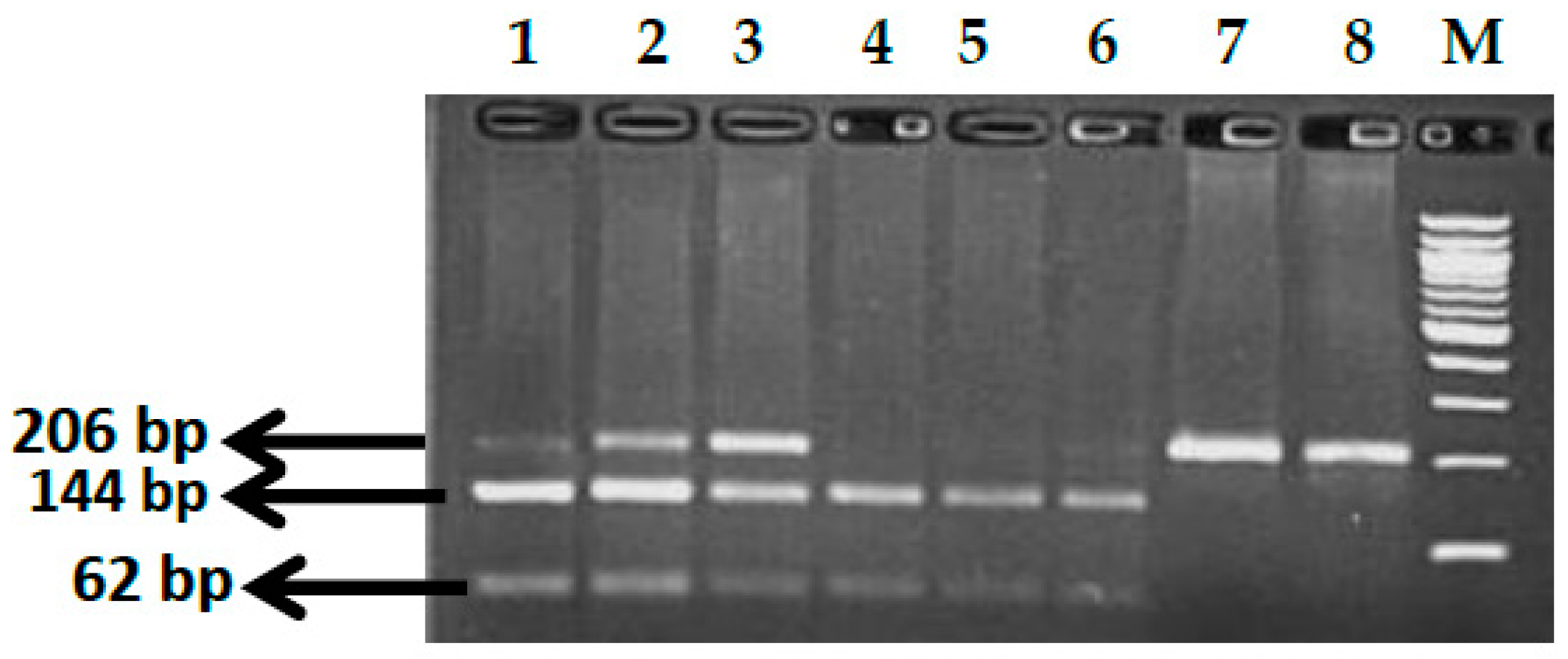
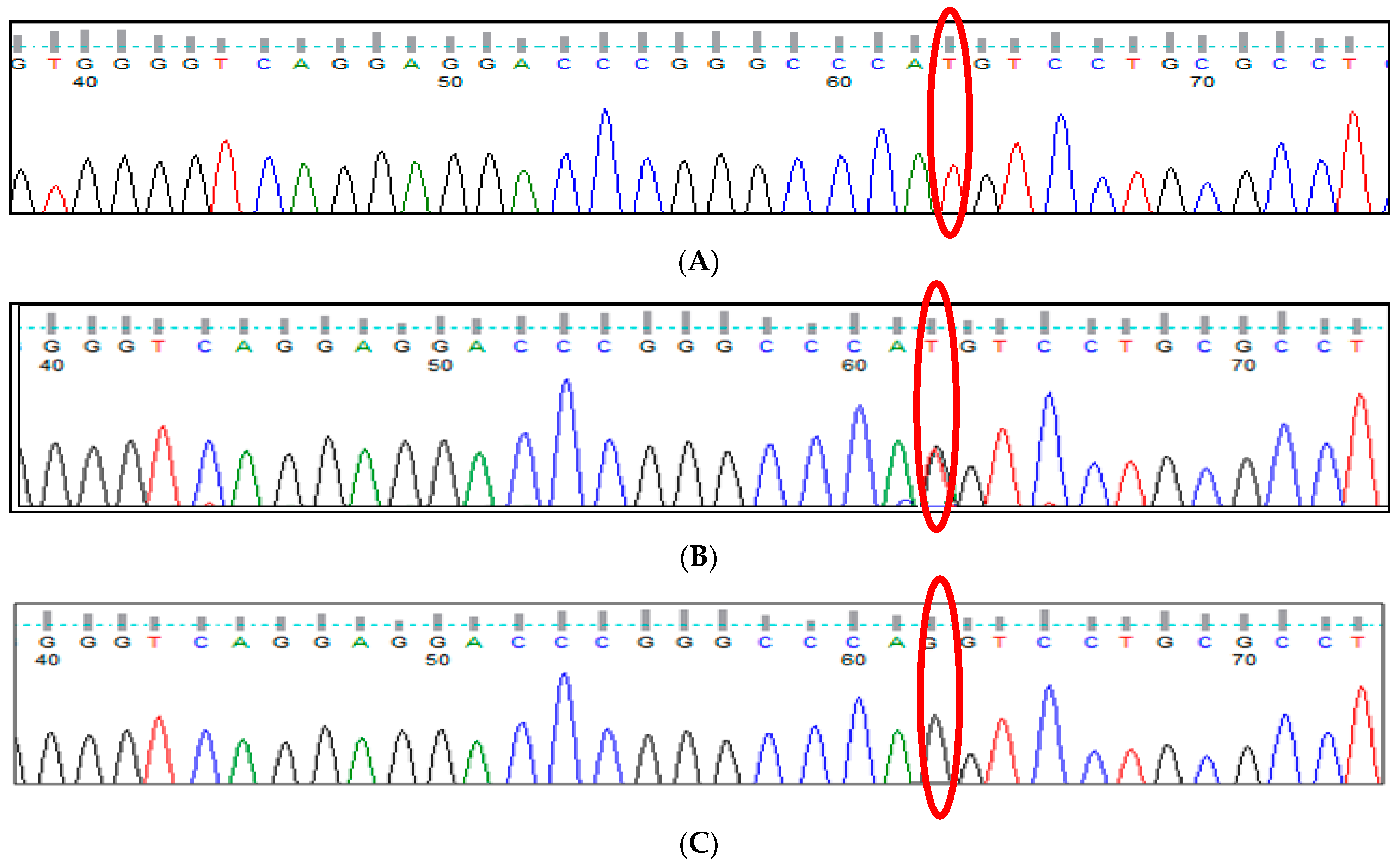
3.1. BCL11A rs1427407 (G>T) Polymorphism
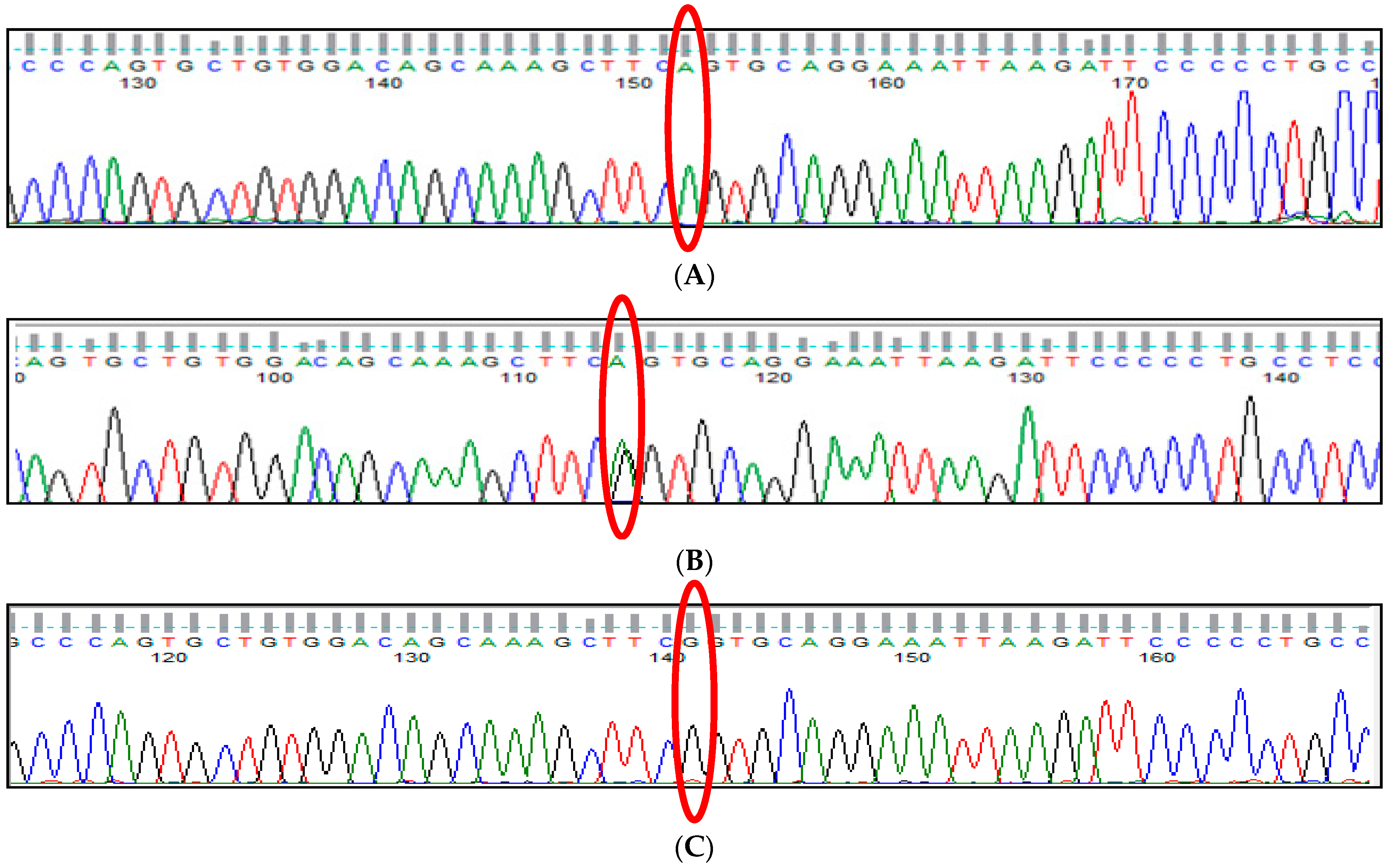
3.2. BCL11A rs766432 (A>C) Polymorphism
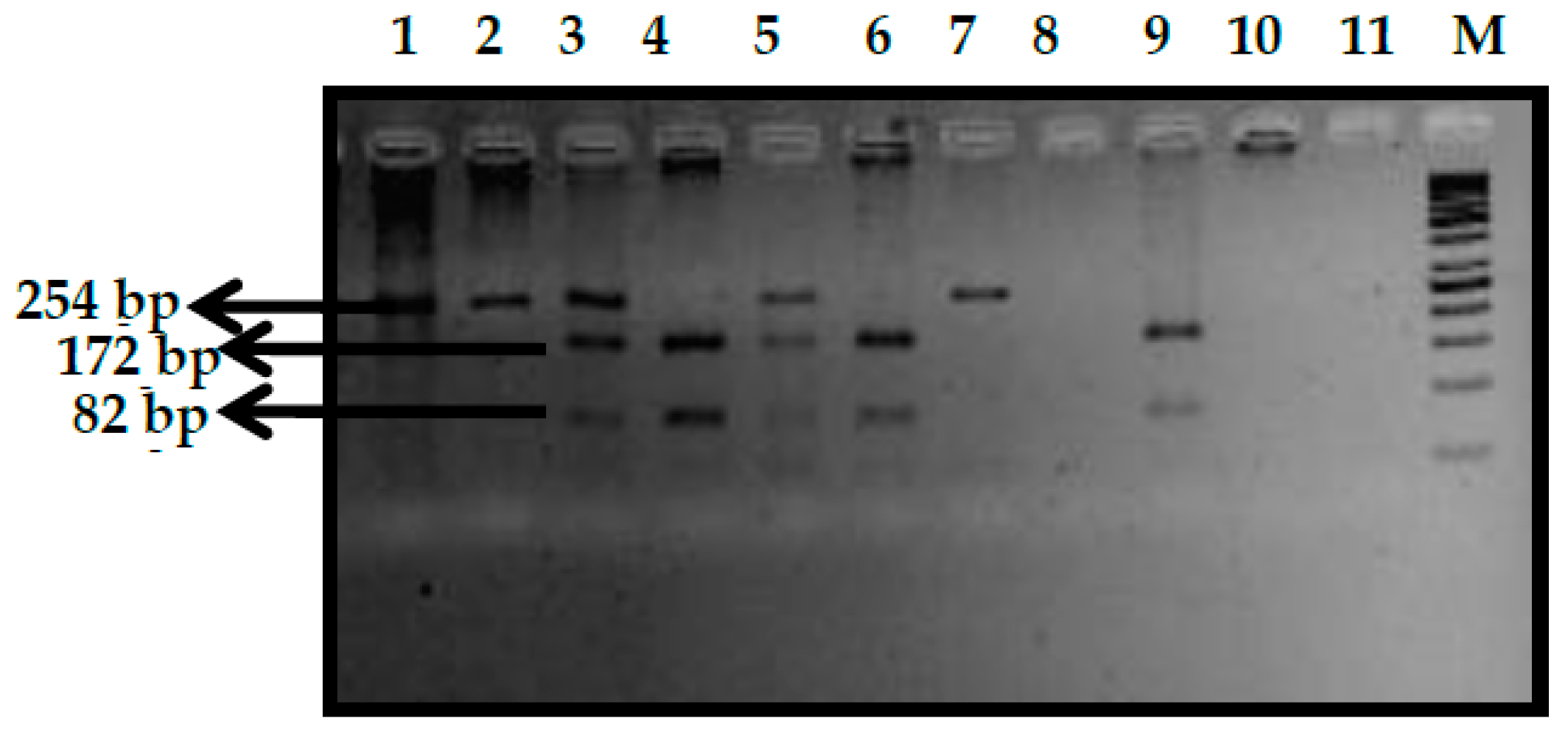
3.3. BCL11A rs11886868 (C>T) Polymorphism
3.4. BCL11A rs4671393 (A>G) Polymorphism
3.5. BCL11A rs10189857 (A>G) Polymorphism
3.6. BCL11A rs7557939 (G>A) Polymorphism
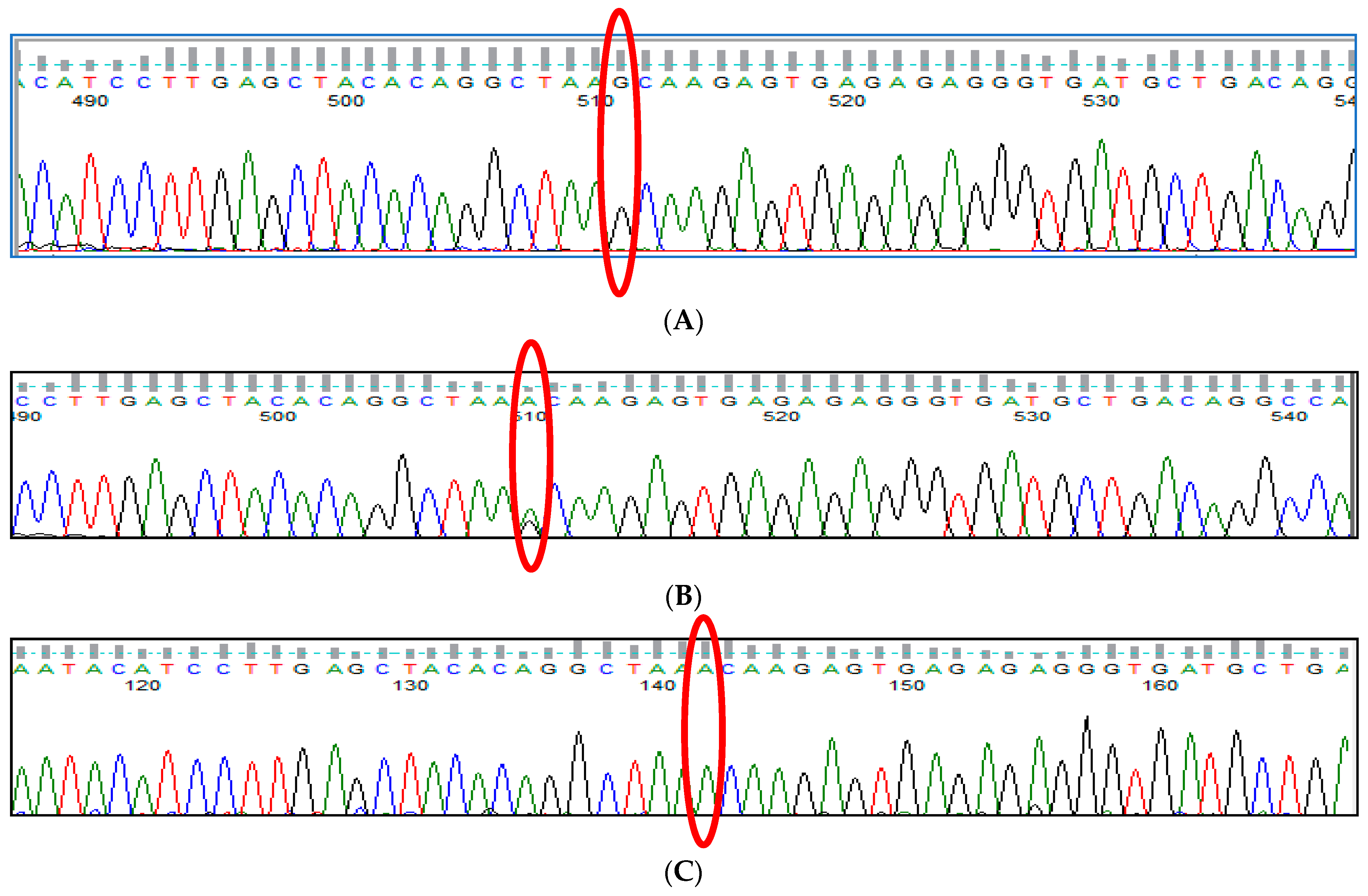
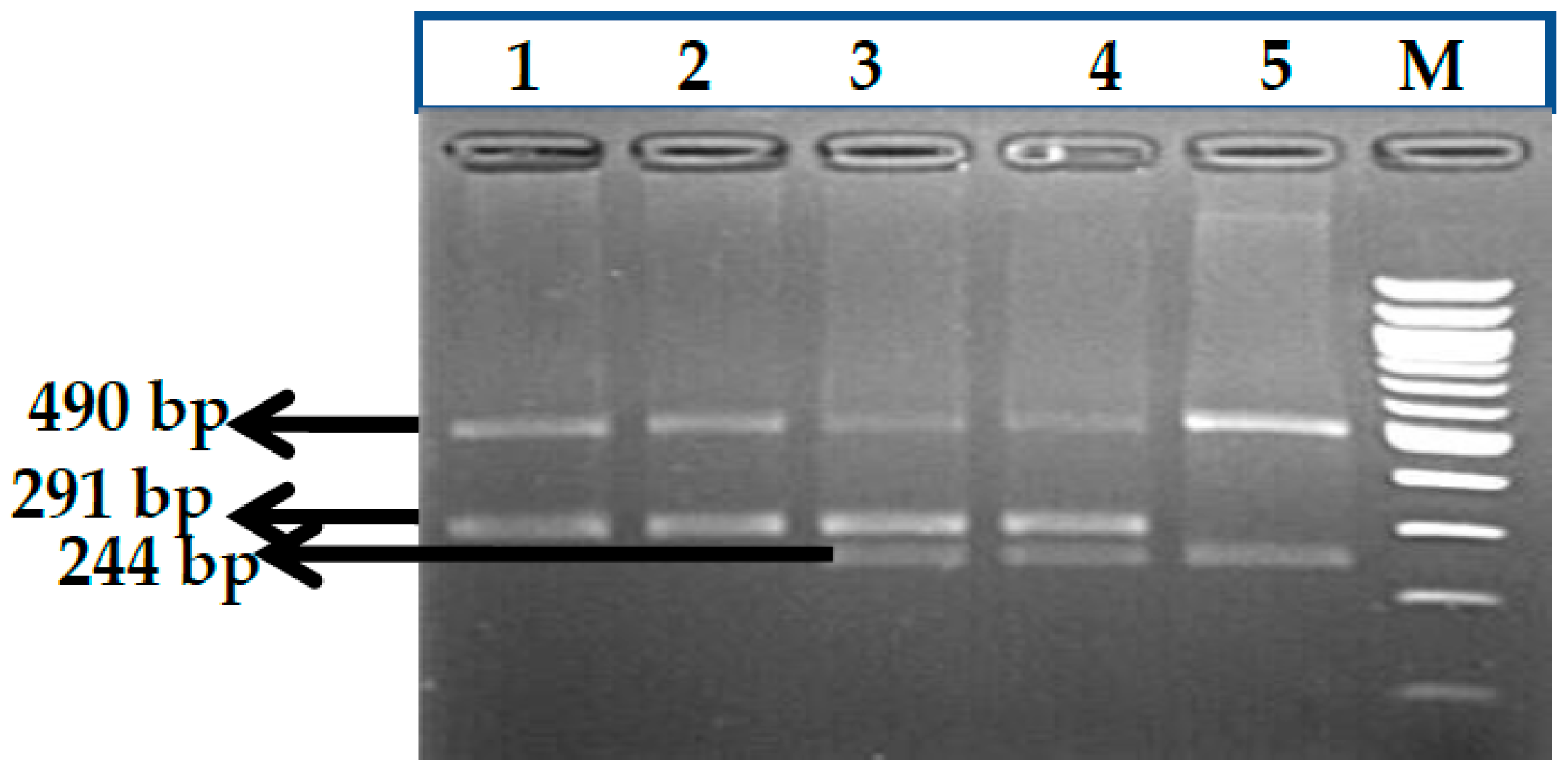
3.7. HBS1L-MYB rs9399137 (T>C) Polymorphism
3.8. HBS1L-MYB rs9376090 (T>C) Polymorphism
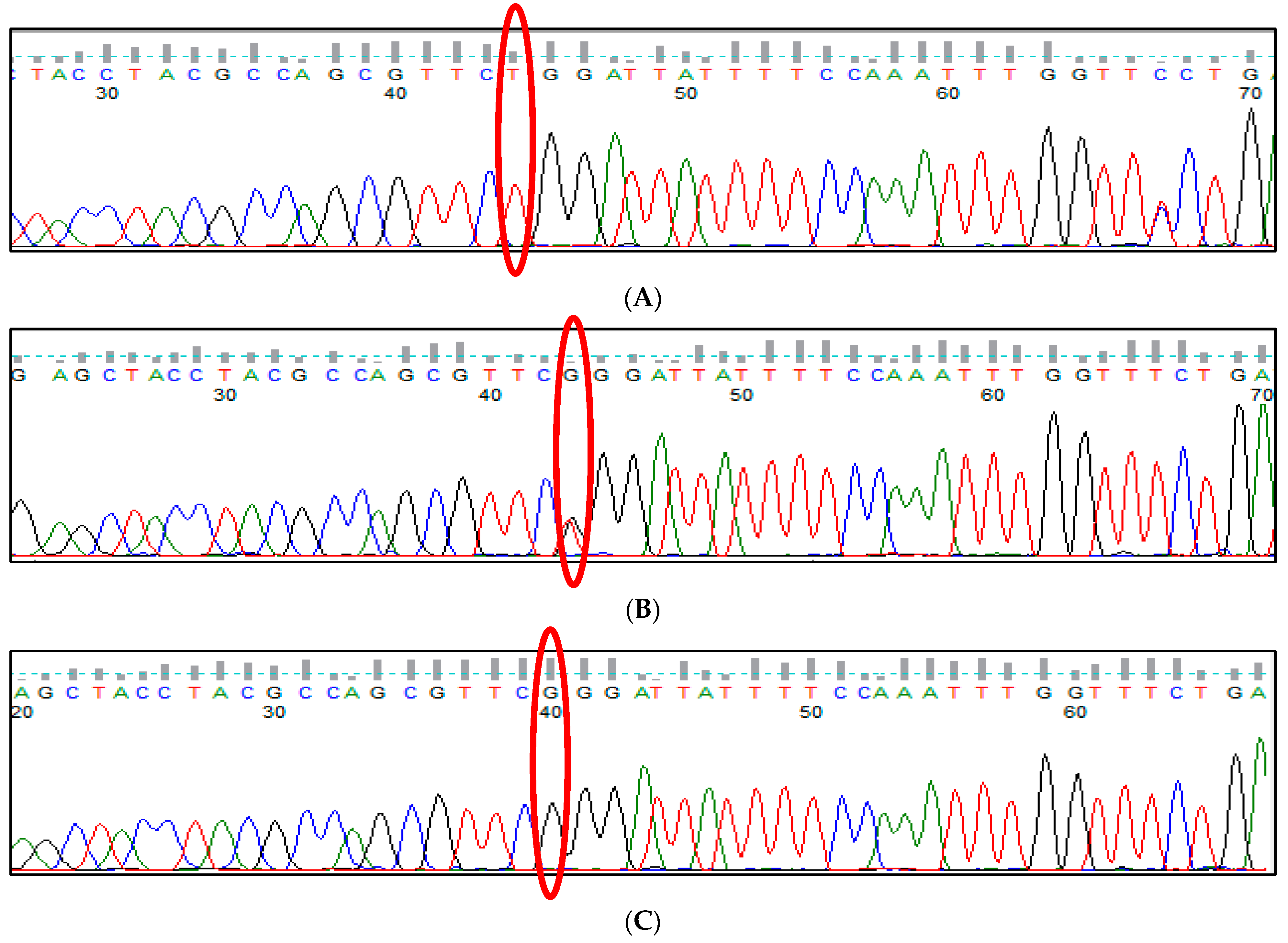
3.9. HBS1L-MYB rs28384513 (A>C) Polymorphism
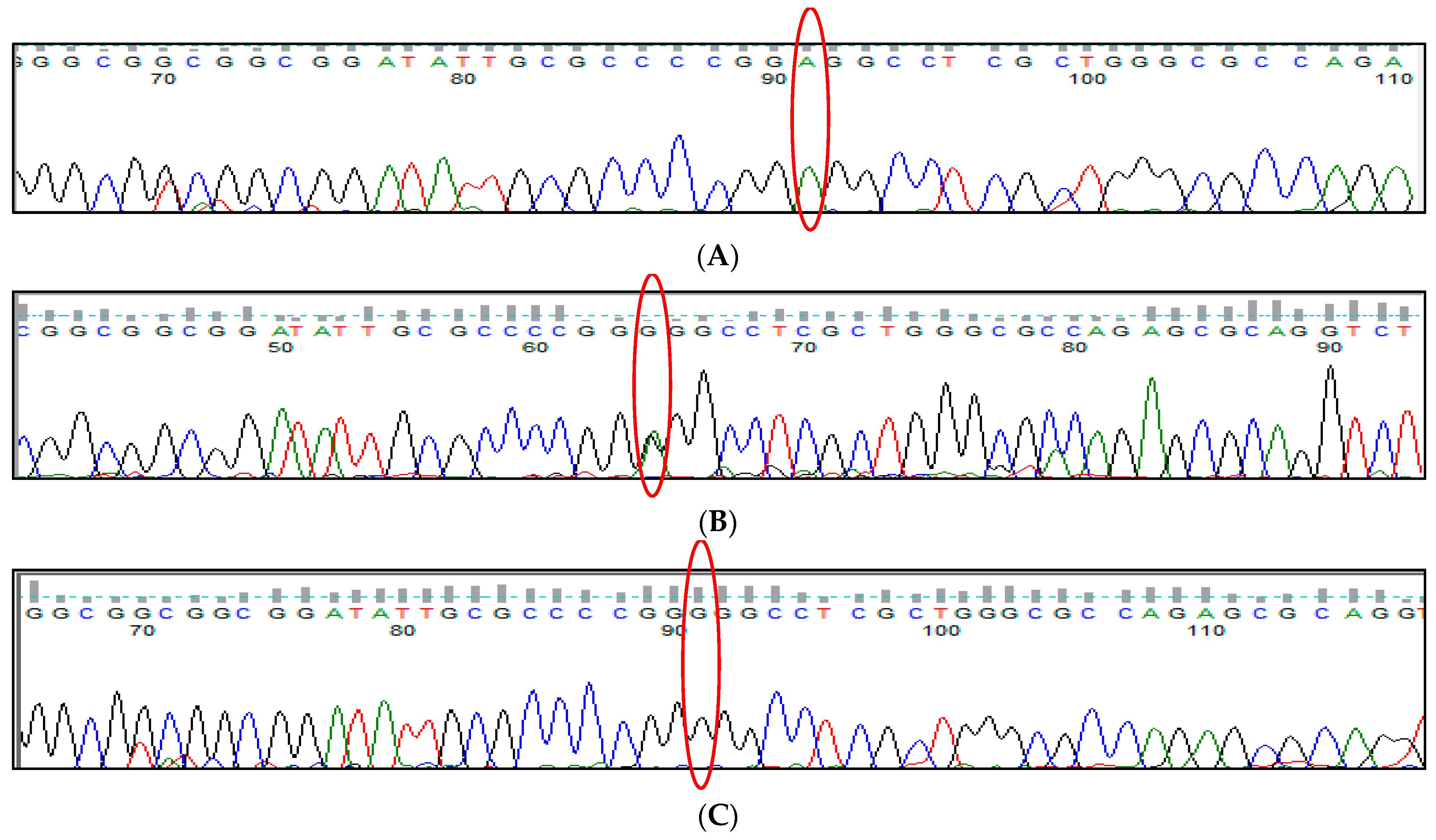
3.10. KLF1 rs2072597 (A>G) Polymorphism
3.11. KLF1 rs112631212 (T>G) Polymorphism
3.12. Comparison of Clinical Parameter between Two Groups of TM Patients
3.13. Influence of Genetic Modifier Variants on HbF and on Hematological Parameters
3.14. Age of Onset of the Disease and Age at First Blood Transfusion among TM Patients with Low and High HbF Levels
3.15. In Silico Analysis for All Variants of Modifier Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weatherall, D. 2003 William Allan Award address. The Thalassemias: The role of molecular genetics in an evolving global health problem. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 74, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.; Moi, P.; Galanello, R. Recent Advances in β-Thalassemias. Pediatr. Rep. 2011, 3, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienhuis, A.W.; Nathan, D.G. Pathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations of the β- Thalassemias. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012, 2, 011726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, S.; Garner, C.; Gut, I.; Matsuda, F.; Yamaguchi, M.; Heath, S.; Foglio, M.; Zelenika, D.; Boland, A.; Rooks, H.; et al. A QTL influencing F cell production maps to a gene encoding a zinc-finger protein on chromosome 2p15. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1197–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, M.; Amendolara, M.; Rescigno, G.; Danise, P.; Todisco, N.; Izzo, P.; Amendola, G. Delayed decline of γ-globin expression in infant age associated with the presence of Gγ-158 (C→T) polymorphism. Int. J. Lab Hem. 2008, 30, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thein, S.L.; Menzel, S.; Lathrop, M.; Garner, C. Control of fetal hemoglobin: New insights emerging from genomics and clinical implications. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, R216–R223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.S.; Hong, X.; Wang, G. Induction of endogenous γ-globin gene expression with decoy oligonucleotide targeting Oct-1 transcription factor consensus sequence. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funnell, A.P.; Mak, K.S.; Twine, N.A.; Pelka, G.J.; Norton, L.J.; Radziewic, T.; Crossley, M. Generation of mice deficient in both KLF3/BKLF and KLF8 reveals a genetic interaction and a role for these factors in embryonic globin gene silencing. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 2976–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, V.G.; Menne, T.F.; Xu, J.; Akie, T.E.; Lettre, G.; Van Handel, B.; Mikkola, H.K.A.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Cantor, A.B.; Orkin, S.H. Human Fetal Hemoglobin Expression Is Regulated by the Developmental Stage-Specific Repressor BCL11A. Science 2008, 322, 1839–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoch, C.; Hargreaves, D.C.; Hodges, C.; Elias, L.; Ho, L.; Ranish, J.; Crabtree, G.R. Proteomic and bioinformatic analysis of mammalian SWI/SNF complexes identifies extensive roles in human malignancy. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettre, G.; Sankaran, V.G.; Bezerra, M.A.; Araújo, A.S.; Uda, M.; Sanna, S.; Cao, A.; Schlessinger, D.; Costa, F.F.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; et al. DNA polymorphisms at the BCL11A, HBS1L-MYB, and beta-globin loci associate with fetal hemoglobin levels and pain crises in sickle cell disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11869–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherry, S.T.; Ward, M.-H.; Kholodov, M.; Baker, J.; Phan, L.; Smigielski, E.M.; Sirotkin, K. dbSNP: The NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.E.; Kamran, S.C.; Lessard, S.; Xu, J.; Fujiwara, Y.; Lin, C.; Shao, Z.; Canver, M.C.; Smith, E.C.; Pinello, L.; et al. An Erythroid Enhancer of BCL11A Subject to Genetic Variation Determines Fetal Hemoglobin Level. Science 2013, 342, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dijk, T.B.; Gillemans, N.; Pourfarzad, F.; van Lom, K.; von Lindern, M.; Grosveld, F.; Philipsen, S. Fetal globin expression is regulated by Friend of Prmt1. Blood 2010, 116, 4349–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, J.E.; Rochette, J.; Fisher, C.A.; Weatherall, D.J.; Marc, S.; Lathrop, G.M.; Demenais, F.; Thein, S. Dissecting the loci controlling fetal haemoglobin production on chromosomes 11p and 6q by the regressive approach. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlberg, K.; Jiang, J.; Rooks, H.; Jawaid, K.; Matsuda, F.; Yamaguchi, M.; Lathrop, M.; Thein, S.L.; Best, S. The HBS1L-MYB intergenic interval associated with elevated HbF levels shows characteristics of a distal regulatory region in erythroid cells. Blood 2009, 114, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, M.H. Management of sickle cell disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.K.T.; Joly, P.; Bardel, C.; Moulsma, M.; Bonello-Palot, N.; Francina, A. The XmnI Gγ polymorphism influences hemoglobin F synthesis contrary to BCL11A and HBS1L-MYB SNPs in a cohort of 57 β-thalassemia intermedia patients. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2010, 45, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, C.; Silver, N.; Best, S.; Menzel, S.; Martin, C.; Spector, T.D.; Thein, S.L. Quantitative trait locus on chromosome 8q influences the switch from fetal to adult hemoglobin. Blood 2004, 104, 2184–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, C.P.; Tatu, T.; Best, S.; Creary, L.; Thein, S.L. Evidence of genetic interaction between the beta-globin complex and chromosome 8q in the expression of fetal hemoglobin. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labie, D.; Dunda-Belkhodja, O.; Rouabhi, F.; Pagnier, J.; Ragusa, A.; Nagel, R.L. The -158 site 5’ to the G gamma gene and G gamma expression. Blood 1985, 66, 1463–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasing, W.; Mekki, C.; Traisathit, P.; Pissard, S.; Pornprasert, S. Genotyping of BCL11A and HBS1L-MYB Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in β-thalassemia/HbE and Homozygous HbE Subjects with Low and High Levels of HbFWalailak. J. Sci. Tech 2018, 15, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, I.J.; Bieker, J.J. A novel, erythroid cell-specific murine transcription factor that binds to the CACCC element and is related to the Kr¨uppel family of nuclear proteins. Mol. Cell Biol. 1993, 13, 2776–2786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drissen, R.; von Lindern, M.; Kolbus, A.; Driegen, S.; Steinlein, P.; Beug, H.; Grosveld, F.; Philipsen, S. The Erythroid Phenotype of EKLF-Null Mice: Defects in Hemoglobin Metabolism and Membrane Stability. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 5205–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilon, A.M.; Ajay, S.S.; Kumar, S.A.; Steiner, L.A.; Cherukuri, P.F.; Wincovitch, S.; Bodine, D.M. NISC Comparative Sequencing Center. Genome-wide ChIP-Seq reveals a dramatic shift in the binding of the transcription factor erythroid Kruppel-like factor during erythrocyte differentiation. Blood 2011, 118, e139–e148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, J.; Papadopoulos, P.; Georgitsi, M.; Gutierrez, L.; Grech, G.; Fanis, P.; Phylactides, M.; Verkerk, A.J.; van derSpek, P.J.; Scerri, C.A.; et al. Haploinsufficiency for the erythroid transcription factor KLF1 causes hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, K.; Sun, C.W.; Pawlik, K.M.; Townes, T.M. KLF1 regulates BCL11A expression and gamma- to beta-globin gene switching. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 742–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, D.; Coghill, E.; Keys, J.; Maguire, T.; Hartmann, B.; McDowall, A.; Weiss, M.; Grimmond, S.; Perkins, A. A global role for EKLF in definitive and primitive erythropoiesis. Blood 2006, 107, 3359–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funnell, A.P.; Maloney, C.A.; Thompson, L.J.; Keys, J.; Tallack, M.; Perkins, A.C.; Crossley, M. Erythroid Kruppel-like factor directly activates the basic Kr¨ uppel-like factor gene in erythroid cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 2777–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satta, S.; Perseu, L.; Maccioni, L.; Giagu, N.; Galanello, R. Delayed fetal hemoglobin switching in subjects with KLF1 gene mutation. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2012, 48, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadhouders, R.; Aktuna, S.; Thongjuea, S.; Aghajanirefah, A.; Pourfarzad, F.; van Ijcken, W.; Lenhard, B.; Rooks, H.; Best, S.; Menzel, S.; et al. HBS1L-MYB intergenic variants modulate fetal hemoglobin via long-range MYB enhancers. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weatherall, D. Anaemia: Pathophysiology, classification, and clinical features. In Oxford Textbook of Medicine, 3rd ed.; Weatherall, D.J., Ledingham, J.G.G., Warrell, D.A., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 3457–3462. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall, D. Single gene disorders or complex traits: Lessons from the thalassaemias and other monogenic diseases. Br. Med. J. 2000, 321, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weatherall, D.J.; Clegg, J.B. The Thalassaemia Syndromes, 4th ed.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall, D.J. Phenotype—Genotype relationships in monogenic disease: Lessons from the thalassaemias. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouch, L.; Moumni, I.; Ouragini, H.; Darragi, I.; Kalai, M.; Chaouachi, D.; Boudrigua, I.; Hafsia, R.; Abbes, S. rs11886868 and rs4671393 ofBCL11Aassociated with HbF level variation and modulate clinical events among sickle cell anemia patients. Hematology 2016, 21, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadheech, S.; Madhulatha, D.; Jain, S.; Joseph, J.; Jyothy, A.; Munshi, A. Association of BCL11A Genetic Variant (rs11886868) with severity in β-Thalassemia Major and Sickle Cell Anemia. Ind. J. Med. Res. 2016, 143, 449. [Google Scholar]
- Sales, R.R.; Belisário, A.R.; Faria, G.; Mendes, F.; Luizon, M.R.; Viana, M.B. Functional polymorphisms of BCL11A and HBS1L-MYB genes affect both fetal hemoglobin level and clinical outcomes in a cohort of children with sickle cell anemia. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszlak, M.; Pissard, S.; Badens, C.; Chamouine, A.; Maillard, O.; Thuret, I. Genetic Modifiers of Sickle Cell Disease: A Genotype-Phenotype Relationship Study in a Cohort of 82 Children on Mayotte Island. Hemoglobin 2015, 39, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanushali, A.A.; Patra, P.K.; Pradhan, S.; Khanka, S.S.; Singh, S.; Das, B.R. Genetics of fetal hemoglobin in tribal Indian patients with sickle cell anemia. Transl. Res. 2015, 165, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, A.; El Rassi, F.; Isma’eel, H.; Koussa, S.; Inati, A.; Cappellini, M.D. Letter to the Editor: Correlation of liver iron concentration determined by R2 MRI with serum ferritin in patients with thalassemia intermedia. Haematologica 2008, 93, 1584–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarneau, G.; Palmer, C.D.; Sankaran, V.G.; Orkin, S.H.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Lettre, G. Fine-mapping at three loci known to affect fetal hemoglobin levels explains additional genetic variation. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 1049–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winichagoon, P.; Fucharoen, S.; Chen, P.; Wasi, P. Genetic Factors Affecting Clinical Severity in β-Thalassemia Syndromes. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2000, 22, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labie, D.; Pagnier, J.; Lapoumeroulie, C.; Rouabhi, F.; Dunda-Belkhodja, O.; Chardin, P.; Beldjord, C.; Wajcman, H.; E Fabry, M.; Nagel, R.L. Common haplotype dependency of high G gamma-globin gene expression and high Hb F levels in beta-thalassemia and sickle cell anemia patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 2111–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rujito, L.; Basalamah, M.; Siswandari, W.; Setyono, J.; Wulandari, G.; Mulatsih, S.; Sofro, A.S.M.; Sadewa, A.H.; Sutaryo, S. Modifying effect of XmnI, BCL11A, and HBS1L-MYB on clinical appearances: A study on β-thalassemia and hemoglobin E/β-thalassemia patients in Indonesia. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2016, 9, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Yadav, R.; Mishra, S.; Singh, M.P.S.S.; Gwal, A.; Bharti, P.K.; Rajasubramaniam, S. Krüppel-like factor 1 (KLF1) gene single nucleotide polymorphisms in sickle cell disease and its association with disease-related morbidities. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Allawi, N.; Qadir, S.M.A.; Puehringer, H.; Chui, D.H.K.; Farrell, J.J. The association of HBG2, BCL11A, and HMIP polymorphisms with fetal hemoglobin and clinical phenotype in Iraqi Kurds with sickle cell disease. Int. J. Lab Hematol. 2019, 41, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadah, T.; Noorwali, A.; Alzahrani, F.; Banjar, A.; Filimban, N.; Felimban, R. Detection of BCL11A and HBS1L-MYB Genotypes in Sickle Cell Anemia. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2020, 36, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, P.; Colah, R.; Ghosh, K.; Nadkarni, A. Differential role of Kruppel like factor 1 (KLF1) gene in red blood cell disorders. Genomics 2019, 111, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionel, A.; Carole, S.; Virginie, H.; Nicole, L.; Dominique, S. A Dominant Mutation in the Gene Encoding the Erythroid Transcription Factor KLF1 Causes a Congenital Dyserythropoietic Anemia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 87, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Gene | Polymorphism | Primer Sequences | Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCL11A | rs766432 | (A)F: TTGTTTCGCTTTAGCTTTATTAAGGTACAA | ARMS-PCR |
| 432(A)R: GACGTGTTCTGTATCTTGATTTTGGT | |||
| 432(C)F: CCAAACAGTTTAAAGGTTACAGACAGACT | |||
| 432(C)R: AAAATGAATGACTTTTGTTGTATGTAGAG | |||
| rs4671393 | F-GAGATAACTTAAGTGTGGTGTT | ARMS-PCR | |
| R-GCTGTGGACAGCAAAGCTTCA | |||
| F-ATCCTCATCAGCTTGGCCATG | |||
| R-GGAAGACGTGGGCTGGGAGCTGGGAGTT | |||
| rs11886868 | F-TTTGGTGCTACCCTGAAAGAC | RFLP | |
| R-ACTCAACAGTAGCAGAATGAAAGAG | |||
| rs7557939 | F-AGACAACAATGCAAGGGGGA | RFLP | |
| R-TGAGAAGCCAAACTCCCAGC | |||
| rs1427407 | F-CACTCATCCCATGCACCACTC | RFLP | |
| R-CCACGTAGTTGGGCTTCACA | |||
| rs10189857 | Forward inner primer (A-allele)—TGCCCCTTGTGAACTACG Reverse inner primer(A-allele)- TTCTATCAGCAGGTCAAGA | ARMS-PCR | |
| Forward outer primer (G-allele)- GGATTTCAGGGTCCTTG Reverse outer primer (G-allele)- GGTAGAGAACTGTGACA | |||
| HBS1L-MYB | rs9399137 | 137(C)F: AATGTAATTAACTGAACATATGGTTAGTC | ARMS-PCR |
| 137(C)R: TTTATTGTTACAAGGTTAATTCACTGCC | |||
| 137(T)F: GAAATACCATCACTGAGAAAAGCATAAG | |||
| 137(T)R: CAGCAGGGTTGCTTGTGAAAAAACTTTA | |||
| rs9376090 | Forward inner primer (C allele) GCTAAGTCTAGCTGAGTGTTAGACC | ARMS-PCR | |
| Reverse inner primer (T allele) GTTCCTGGCAGTATCCCACA | |||
| Forward outer primer TCACAACTTTCATGCAAACATAA | |||
| Reverse outer primer TGCTTCAGTCTTGTGCCTATTAT | |||
| rs28384513 | Forward inner primer (Tallele) TGAGCTACCTACGCCAGCGTCCT | ARMS-PCR | |
| Reverse inner primer (C allele) TATCAGGAACCAAATTTGGAAAATAATACG | |||
| Reverse inner primer (g allele) TCAGGAACCAAATTTGGAAAATAATTCC | |||
| Forward outer primer CCGCCTAGAATTGACTGGTTTG | |||
| Reverse outer primer TTTGTTGAATGCCCACTGTGTGC | |||
| KLF1 | rs2072597 | F-ATCCTCCGAACCCAAAAGCC | RFLP |
| R-ACCTGGATCTCCTCCTCACC | |||
| rs112631212 | F-GGCTGGTCCTCAGACTTCAC | RFLP | |
| R-GACAGGCAAACAAGACCCCT |
| BCL11A Gene Polymorphism | HBF (%) <40 (n = 38) | HBF (%) >40 (n = 62) | OR | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs No | Genotype | ||||
| rs1427407 | GG | 19 (50.0) | 16 (25.8) | Ref | Ref |
| GT | 10 (26.3) | 23 (37.1) | 0.321 (0.113 to 0.916) | 0.034 | |
| TT | 9 (23.7) | 23 (37.1) | 0.329 (0.114 to 0.944) | 0.039 | |
| Allele Frequency | |||||
| G | 48 (63.2) | 55 (44.4) | Ref | Ref | |
| T | 28 (36.8) | 69 (55.6) | 2.1506 (1.1976 to 3.8621) | 0.0104 | |
| rs766432 | AA | 14 (42.4) | 10 (18.9) | Ref | Ref |
| AC | 11 (21.2) | 25 (34.5) | 0.307 (0.094 to 1.002) | 0.050 | |
| CC | 13 (36.4) | 27 (46.6) | 0.409 (0.138 to 1.214) | 0.107 | |
| Allele Frequency | |||||
| A | 39 (55.0) | 45 (36.2) | Ref | Ref | |
| C | 37 (46.9) | 79 (63.8) | 1.8505 (1.0361 to 3.3048) | 0.0375 | |
| rs11886868 | CC | 17 (44.7) | 11 (17.7) | Ref | Ref |
| CT | 11 (28.9) | 29 (46.8) | 0.236 (0.081 to 0.690) | 0.008 | |
| TT | 10 (26.4) | 22 (35.5) | 0.338 (0.113 to 1.012) | 0.053 | |
| Allele Frequency | |||||
| C | 45 (59.2) | 51 (41.1) | Ref | Ref | |
| T | 31 (40.8) | 73 (58.9) | 2.0778 (1.1625 to 3.7137) | 0.0136 | |
| rs4671393 | AA | 14 (36.8) | 20 (32.3) | Ref | Ref |
| AG | 16 (42.1) | 22 (35.4) | 0.942 (0.355 to 2.498) | 0.904 | |
| GG | 8 (21.1) | 20 (32.3) | 0.550 (0.176 to 1.720) | 0.304 | |
| Allele Frequency | |||||
| A | 44 (57.9) | 62 (50.0) | Ref | Ref | |
| G | 32 (42.1) | 62 (50.0) | 0.7097 (0.420 to 1.196) | 0.1984 | |
| rs10189857 | AA | 22 (57.9) | 30 (48.4) | Ref | Ref |
| AG | 6 (15.8) | 18 (29.0) | 0.441 (0.144 to 1.348) | 0.151 | |
| GG | 10 (26.3) | 14 (22.6) | 0.936 (0.321 to 2.728) | 0.936 | |
| Allele Frequency | |||||
| A | 50 (65.8) | 78 (62.9) | Ref | Ref | |
| G | 26 (34.2) | 46 (37.1) | 1.1341 (0.623 to 2.061) | 0.6799 | |
| rs7557939 | GG | 15 (39.5) | 26 (41.9) | Ref | Ref |
| GA | 19 (50.0) | 11 (17.7) | 3.789 (1.313 to 10.932) | 0.014 | |
| AA | 4 (10.5) | 25 (40.4) | 0.262 (0.072 to 0.952) | 0.042 | |
| Allele Frequency | |||||
| G | 49 (64.5)) | 63 (50.8) | Ref | Ref | |
| A | 27 (35.5) | 61 (49.2) | 1.7572 (0.9769 to 3.1607) | 0.0598 | |
| rs9399137 | TT | 14 (37.9) | 16 (25.4) | Ref | Ref |
| TC | 14 (35.1) | 13 (22.2) | 1.259 (0.416 to 3.812) | 0.683 | |
| CC | 10 (27.0) | 33 (52.4) | 0.329 (0.114 to 0.956) | 0.041 | |
| Allele Frequency | |||||
| T | 42 (55.3) | 45 (36.3) | Ref | Ref | |
| C | 34 (44.7) | 79 (63.7) | 2.1686 (1.2121 to 3.8801) | 0.0091 | |
| rs9376090 | TT | 22 (59.5) | 31 (47.6) | Ref | Ref |
| TC | 10 (27.0) | 29 (46.0) | 0.532 (0.208 to 1.360) | 0.188 | |
| CC | 6 (13.5) | 2 (6.4) | 4.575 (0.783 to 26.742) | 0.091 | |
| Allele Frequency | |||||
| T | 54 (71.1)) | 91 (73.4) | Ref | Ref | |
| C | 22 (28.9) | 33 (26.6) | 0.8901 (0.4713 to 1.6812) | 0.7197 | |
| rs28384513 | AA | 18 (48.6) | 35 (56.5) | Ref | Ref |
| AC | 12 (32.4) | 22 (38.7) | 1.083 (0.426 to 2.754) | 0.866 | |
| CC | 8 (21.0) | 5 (4.8) | 3.061 (0.819 to 11.436) | 0.096 | |
| Allele Frequency | |||||
| A | 48 (64.9) | 92 (74.2) | Ref | Ref | |
| C | 28 (36.8) | 32 (25.8) | 0.5963 (0.3222 to 1.1036) | 0.0997 | |
| rs2072597 | AA | 18 (47.4) | 39 (64.9) | Ref | Ref |
| AG | 6 (15.8) | 7 (11.3) | 1.628 (0.459 to 5.777) | 0.451 | |
| GG | 14 (36.8) | 16 (25.8) | 1.645 (0.635 to 4.263) | 0.306 | |
| Allele Frequency | |||||
| A | 42 (56.3) | 85 (68.5) | Ref | Ref | |
| G | 34 (44.7) | 39 (31.5) | 0.566 (0.314 to 1.022) | 0.059 | |
| rs112631212 | TT | 25 (65.8) | 39 (62.9) | Ref | Ref |
| TG | 8 (21.0) | 13 (20.9) | 0.956 (0.335 to 2.732) | 0.933 | |
| GG | 5 (13.2) | 10 (16.2) | 0.644 (0.182 to 2.280) | 0.495 | |
| Allele Frequency | |||||
| T | 58 (76.3) | 91 (73.4) | Ref | Ref | |
| G | 18 (23.7) | 33 (26.6) | 1.168 (0.602 to 2.265) | 0.644 | |
| Hematological Parameter | Patients with HbF < 40 | Patients with HbF > 40 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hb (g/dL) | 7.24 ± 1.25 | 6.91 ± 1.26 | 0.550 |
| MCV | 68.02 ± 5.43 | 68.11 ± 4.99 | 0.575 |
| MCH | 23.40 ± 3.84 | 22.70 ± 3.65 | 0.972 |
| MCHC | 28.49 ± 4.09 | 29.0 ± 3.43 | 0.384 |
| HbA (%) | 56.70 ± 30.77 | 14.29 ± 12.79 | 0.000 |
| HbA2 (%) | 3.79 ± 0.86 | 3.53 ± 0.98 | 0.191 |
| HbF (%) | 12.12 ± 6.09 | 65.99 ± 14.56 | 0.000 |
| Clinical Parameters | Patients with HbF < 40 (n = 38) | Patients with HbF > 40 (n = 62) | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatomegaly | ||||
| Present | 5 | 9 | 0.892 | |
| Absent | 33 | 53 | (0.275–2.893) | 0.849 |
| Splenomegaly | ||||
| Mild | 26 | 50 | 0.135 (1.25–1.80) | |
| Moderate | 4 | 6 | 0.081 (1.13–1.45) | |
| Normal | 8 | 6 | 0.072 (1.24–1.52) | 0.113 |
| Transfusion history | ||||
| 4 weeks | 29 | 58 | 0.222 | |
| 3 weeks | 9 | 4 | (0.063–0.783) | 0.013 |
| SNP (rsno) | HB | MCV | MCH | MCHC | HBA | HBA2 | HBF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs766432 | 0.019 (0.853) | −0.136 (0.199) | −0.074 (0.496) | −0.142 (0.194) | 0.009 (0.930) | −0.034 (0.762) | 0.177 (0.058) |
| rs4671393 | 0.247 (0.030) | −0.046 (0.690) | 0.010 (0.930) | 0.014 (0.905) | −0.019 (0.861) | 0.031 (0.793) | 0.147 (0.144) |
| rs11886868 | 0.002 (0.983) | 0.089 (0.415) | 0.0207 (0.065) | 0.015 (0.897) | −0.162 (0.128) | 0.077 (0.501) | 0.200 (0.038) |
| rs7557939 | −0.184 (0.074) | 0.016 (0.875) | −0.031 (0.768) | −0.056 (0.600) | −0.129 (0.202) | 0.002 (0.983) | 0.173 (0.060) |
| rs10189857 | 0.110 (0.323) | −137 (0.228) | −0.070 (0.547) | 0.003 (0.981) | −0.045 (0.684) | 0.007 (0.956) | 0.046 (0.646) |
| rs1427407 | 0.091 (0.397) | 0.134 (0.222) | −0.009 (0.934) | −0.013 (0.908) | −0.115 (0.280) | −0.059 (0.611) | 0.215 (0.028) |
| rs9399137 | 0.037 (0.734) | 0.152 (0.171) | −0.034 (0.762) | 0.039 (0.731) | −0.043 (0.689) | 0.029 (0.802) | 0.146 (0.136) |
| rs9376090 | −0.141 (0.191) | −0.081 (0.457) | 0.005 (0.964) | −0.042 (0.712) | 0.109 (0.308) | 0.072 (0.535) | −0.139 (0.149) |
| rs28384513 | −0.064 (0.552) | −0.103 (0.344) | −0.025 (0.824) | −0.095 (0.399) | 0.025 (0.817) | 0.158 (0.170) | −0.214 (0.057) |
| rs2072597 | −0.027 (0.807) | 0.121 (0.280) | 0.027 (0.810) | −0.010 (0.929) | 0.266 (0.016) | −0.051 (0.667) | −0.132 (0.180) |
| rs112631212 | 0.115 (0.280) | 0.045 (0.673) | 0.001 (0.994) | −0.086 (0.441) | 0.001 (0.994) | 0.162 (0.157) | −0.053 (0.577) |
| Gene/Refrence Sequence No | Genotype | Age of Onset | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1 Year | >1 Year | ||||||
| HbF <40% | HbF >40% | p-Value | HbF <40% | HbF >40% | p-Value | ||
| BCL11A rs766432 | AA | 5 | 4 | 0.191 | 9 | 6 | 0.435 |
| AC | 5 | 15 | 6 | 10 | |||
| CC | 6 | 18 | 7 | 9 | |||
| BCL11A rs4671393 | AA | 5 | 13 | 0.142 | 9 | 7 | 0.534 |
| AG | 8 | 9 | 8 | 13 | |||
| GG | 3 | 15 | 5 | 5 | |||
| BCL11A rs11886868 | CC | 9 | 16 | 0.758 | 8 | 9 | 0.805 |
| CT | 2 | 6 | 8 | 11 | |||
| TT | 5 | 15 | 6 | 5 | |||
| BCL11A rs7557939 | GG | 7 | 16 | 0.407 | 8 | 10 | 0.053 |
| GA | 5 | 9 | 10 | 4 | |||
| AA | 4 | 12 | 4 | 11 | |||
| BCL11A rs10189857 | AA | 9 | 18 | 0.862 | 13 | 12 | 0.150 |
| AG | 4 | 10 | 2 | 8 | |||
| GG | 3 | 9 | 7 | 5 | |||
| BCL11A rs1427407 | GG | 9 | 11 | 0.188 | 10 | 5 | 0.174 |
| GT | 3 | 11 | 7 | 12 | |||
| TT | 4 | 15 | 5 | 8 | |||
| HBS1L- MYB rs9399137 | TT | 7 | 9 | 0.228 | 7 | 7 | 0.512 |
| TC | 4 | 18 | 7 | 5 | |||
| CC | 4 | 10 | 8 | 13 | |||
| HBS1L- MYB rs9376090 | TT | 10 | 16 | 0.055 | 12 | 15 | 0.158 |
| TC | 3 | 19 | 7 | 10 | |||
| CC | 3 | 2 | 3 | 0 | |||
| HBS1L-MYB rs28384513 | AA | 5 | 23 | 0.167 | 13 | 12 | 0.395 |
| AC | 7 | 10 | 2 | 6 | |||
| CC | 3 | 4 | 7 | 7 | |||
| KLF1 rs2072597 | TT | 7 | 26 | 0.182 | 11 | 13 | 0.958 |
| TC | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | |||
| CC | 7 | 9 | 7 | 7 | |||
| KLF1 rs112631212 | AA | 9 | 22 | 0.700 | 16 | 17 | 0.844 |
| AC | 5 | 8 | 3 | 5 | |||
| CC | 2 | 7 | 3 | 3 | |||
| Gene/Reference Sequence No | Genotype | Age of First Transfusion | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1 Year | >1 Year | ||||||
| HbF <40% | HbF >40% | p-Value | HbF <40% | HbF >40% | p-Value | ||
| BCL11A rs766432 | AA | 5 | 4 | 0.236 | 9 | 6 | 0.253 |
| AC | 5 | 12 | 6 | 13 | |||
| CC | 6 | 18 | 7 | 9 | |||
| BCL11A rs4671393 | AA | 5 | 13 | 0.233 | 9 | 7 | 0.488 |
| AG | 8 | 9 | 8 | 13 | |||
| GG | 3 | 12 | 5 | 8 | |||
| BCL11A rs11886868 | CC | 9 | 16 | 0.628 | 8 | 9 | 0.765 |
| CT | 3 | 11 | 8 | 13 | |||
| TT | 4 | 10 | 6 | 6 | |||
| BCL11A rs7557939 | GG | 6 | 14 | 0.969 | 8 | 10 | 0.102 |
| GA | 5 | 10 | 10 | 6 | |||
| AA | 5 | 10 | 4 | 12 | |||
| BCL11A rs10189857 | AA | 9 | 18 | 0.949 | 13 | 12 | 0.220 |
| AG | 4 | 10 | 2 | 8 | |||
| GG | 3 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |||
| BCL11A rs1427407 | GG | 9 | 9 | 0.122 | 10 | 7 | 0.311 |
| GT | 3 | 10 | 7 | 13 | |||
| TT | 4 | 13 | 5 | 8 | |||
| HBS1L-MYB rs9399137 | TT | 8 | 9 | 0.200 | 7 | 9 | 0.667 |
| TC | 4 | 15 | 7 | 6 | |||
| CC | 4 | 12 | 8 | 13 | |||
| HBS1L- MYB rs9376090 | TT | 10 | 14 | 0.053 | 12 | 17 | 0.129 |
| TC | 3 | 18 | 7 | 11 | |||
| CC | 3 | 2 | 3 | 0 | |||
| HBS1L-MYB rs28384513 | AA | 5 | 21 | 0.081 | 13 | 12 | 0.395 |
| AC | 10 | 10 | 2 | 6 | |||
| CC | 1 | 3 | 7 | 7 | |||
| KLF1 rs2072597 | TT | 7 | 25 | 0.098 | 11 | 14 | 0.947 |
| TC | 2 | 1 | 4 | 6 | |||
| CC | 7 | 8 | 7 | 8 | |||
| KLF1 rs112631212 | AA | 9 | 20 | 0.802 | 16 | 19 | 0.913 |
| AC | 5 | 8 | 3 | 5 | |||
| CC | 2 | 6 | 3 | 4 | |||
| Gene | SNP rsID | Chromosome | Position | Reference | Alternate | CADD C-Score | FATHMM Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KLF1 | rs112631212 | chr19 | 12996929 | T | G | 12.95 | 0.59047 |
| BCL11A | rs10189857 | chr2 | 60713235 | A | G | 15.53 | 0.39301 |
| BCL11A | rs1427407 | chr2 | 60718043 | T | G | 16.86 | 0.82499 |
| BCl11A | rs766432 | chr2 | 60719970 | C | A | 3.196 | 0.1122 |
| BCL11A | rs11886868 | chr2 | 60720246 | C | T | 4.324 | 0.10101 |
| BCL11A | rs4671393 | chr2 | 60720951 | A | G | 6.308 | 0.23428 |
| BCL11A | rs7557939 | chr2 | 60721347 | G | A | 4.807 | 0.19352 |
| HBS1L-MYB | rs28384513 | chr6 | 135376209 | T | G | 7.663 | 0.33151 |
| HBS1L-MYB | rs9376090 | chr6 | 135411228 | T | C | 0.687 | 0.1287 |
| HBS1L-MYB | rs9399137 | chr6 | 135419018 | T | C | 12.68 | 0.80652 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tripathi, P.; Agarwal, S.; Mandal, K.; Gupta, A.; Sarangi, A.N. Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms in Modifier Genes in Determining Fetal Hemoglobin Levels in Beta-Thalassemia. Thalass. Rep. 2023, 13, 85-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/thalassrep13010009
Tripathi P, Agarwal S, Mandal K, Gupta A, Sarangi AN. Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms in Modifier Genes in Determining Fetal Hemoglobin Levels in Beta-Thalassemia. Thalassemia Reports. 2023; 13(1):85-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/thalassrep13010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleTripathi, Poonam, Sarita Agarwal, Kausik Mandal, Anshul Gupta, and Aditya Narayan Sarangi. 2023. "Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms in Modifier Genes in Determining Fetal Hemoglobin Levels in Beta-Thalassemia" Thalassemia Reports 13, no. 1: 85-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/thalassrep13010009
APA StyleTripathi, P., Agarwal, S., Mandal, K., Gupta, A., & Sarangi, A. N. (2023). Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms in Modifier Genes in Determining Fetal Hemoglobin Levels in Beta-Thalassemia. Thalassemia Reports, 13(1), 85-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/thalassrep13010009






