Sleep Assessment in Patients with Inner Ear Functional Disorders: A Prospective Cohort Study Investigating Sleep Quality Through Polygraphy Recordings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
2.2. Participants
2.3. Sleep Recording Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Studied Groups
3.2. Findings of Measured Parameters
3.2.1. Sleep Time
3.2.2. Apnea-Hypopnea Indicators
3.2.3. Sleep Fragmentation and Autonomous Arousals Indicators
3.2.4. Snoring Intensity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea |
| CSA | Central sleep apnea |
| VNN | Vestibular nuclei |
| SSNHL | Sudden sensorineural hearing loss |
| SVA | Sudden vertigo attack |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| HSAT | Home sleep apnea testing |
| Sn | Snoring |
| TGF | Time with good flow signal quality |
| AHI | Apnea-hypopnea index |
| cAHI | Central apnea-hypopnea index |
| oAHI | Obstructive apnea-hypopnea index |
| AAI | Autonomic arousal index |
| AAIre | AAI caused by respiratory events |
| RERA | AAI caused by increased respiratory effort |
| ENT | Ear, nose and throat |
| BVL | Bilateral vestibular loss |
References
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C.G. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 479–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, D.J.; Jordan, A.S.; Merchia, P.; Malhotra, A. Central Sleep Apnea: Pathophysiology and Treatment. Chest 2007, 131, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, S.; Arnaldi, D.; Nobili, L. The Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2019, 20, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, S.; Giannoni, A.; Somers, V.K.; Malhotra, A.; Emdin, M.; Costanzo, M.R. Central Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease State-of-the-Art. Sleep 2025, 48, zsae307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csipor Fodor, A.; Huțanu, D.; Budin, C.E.; Ianoși, M.B.; Rachiș, D.L.; Sárközi, H.-K.; Vultur, M.A.; Jimborean, G. Central Sleep Apnea in Adults: An Interdisciplinary Approach to Diagnosis and Management—A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola-Saltzman, M.; Watson, N.F. Traumatic Brain Injury and Sleep Disorders. Neurol. Clin. 2012, 30, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urfy, M.Z.; Suarez, J.I. Breathing and the Nervous System. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 119, pp. 241–250. ISBN 978-0-7020-4086-3. [Google Scholar]
- Yates, B.J.; Jakuš, J.; Miller, A.D. Vestibular Effects on Respiratory Outflow in the Decerebrate Cat. Brain Res. 1993, 629, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holstein, G.R.; Friedrich, V.L.; Martinelli, G.P. Projection Neurons of the Vestibulo-Sympathetic Reflex Pathway: Vestibulo-Sympathetic Projections Neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 2053–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, B.J. Autonomic Reaction to Vestibular Damage. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 1998, 119, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniaia, M.S.; Miller, A.D. Vestibular Effects on Upper Airway Musculature. Brain Res. 1996, 736, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, L.A.; Arendt, H.E.; Cass, S.P.; Jian, B.J.; Mays, D.F.; Olsheski, C.J.; Wilkinson, K.A.; Yates, B.J. Effects of Postural Changes and Vestibular Lesions on Genioglossal Muscle Activity in Conscious Cats. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 96, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossiter, C.D.; Yates, B.J. Vestibular Influences on Hypoglossal Nerve Activity in the Cat. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 211, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, B.J.; Bronstein, A.M. The Effects of Vestibular System Lesions on Autonomic Regulation: Observations, Mechanisms, and Clinical Implications. J. Vestib. Res. 2005, 15, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnard, S.; Tighilet, B.; Chabbert, C.; Hitier, M.; Toulouse, J.; Le Gall, A.; Machado, M.-L.; Smith, P.F. The Balance of Sleep: Role of the Vestibular Sensory System. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 42, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Tsai Do, B.S.; Schwartz, S.R.; Bontempo, L.J.; Faucett, E.A.; Finestone, S.A.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Kelley, D.M.; Kmucha, S.T.; Moonis, G.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update). Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161, S1–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvich, C.; Maller, J.J.; Lithgow, B.; Haghgooie, S.; Kulkarni, J. Vestibular Insights into Cognition and Psychiatry. Brain Res. 2013, 1537, 244–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M.; Lee, H.; Lee, B.; Park, S.; Hong, S.K.; Park, I.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, H. Influence of Vestibular Disease on Psychological Distress: A Multicenter Study. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2013, 148, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.-J. Association Between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Sudden Sensorineural Hearing LossA Population-Based Case-Control Study. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 138, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.; Salapatas, A.M.; Bonzelaar, L.B. Updated Friedman Staging System for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Adv. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2017, 80, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putcha, L.; Berens, K.L.; Marshburn, T.H.; Ortega, H.J.; Billica, R.D. Pharmaceutical Use by U.S. Astronauts on Space Shuttle Missions. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1999, 70, 705–708. [Google Scholar]
- Santy, P.A.; Kapanka, H.; Davis, J.R.; Stewart, D.F. Analysis of Sleep on Shuttle Missions. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1988, 59, 1094–1097. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, D.; Xu, D.; Wang, F. On-Orbit Sleep Problems of Astronauts and Countermeasures. Mil. Med. Res. 2018, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albathi, M.; Agrawal, Y. Vestibular Vertigo Is Associated with Abnormal Sleep Duration. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2017, 27, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshian, M.; Holtje, R.J.; Cotter, L.A.; Rice, C.D.; Cass, S.P.; Yates, B.J. Consequences of Postural Changes and Removal of Vestibular Inputs on the Movement of Air in and out of the Lungs of Conscious Felines. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 103, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ris, L.; Godaux, E. Neuronal Activity in the Vestibular Nuclei After Contralateral or Bilateral Labyrinthectomy in the Alert Guinea Pig. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 80, 2352–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jáuregui-Renaud, K.; Villanueva, P.L.; del Castillo, M.S. Influence of Acute Unilateral Vestibular Lesions on the Respiratory Rhythm after Active Change of Posture in Human Subjects. J. Vestib. Res. 2005, 15, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jáuregui-Renaud, K.; Gresty, M.A.; Reynolds, R.; Bronstein, A.M. Respiratory Responses of Normal and Vestibular Defective Human Subjects to Rotation in the Yaw and Pitch Planes. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 298, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregui-Renaud, K.; Yarrow, K.; Oliver, R.; Gresty, M.A.; Bronstein, A.M. Effects of Caloric Stimulation on Respiratory Frequency and Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Variability. Brain Res. Bull. 2000, 53, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowerby, L.J.; Rotenberg, B.; Brine, M.; George, C.F.P.; Parnes, L.S. Sleep Apnea, Daytime Somnolence, and Idiopathic Dizziness-A Novel Association: Sleep Disturbance with Dizziness. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Moussay, S.; Bulla, I.; Bulla, J.; Toupet, M.; Etard, O.; Denise, P.; Davenne, D.; Coquerel, A.; Quarck, G. Exploration of Circadian Rhythms in Patients with Bilateral Vestibular Loss. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancoli-Israel, S.; Cole, R.; Alessi, C.; Chambers, M.; Moorcroft, W.; Pollak, C.P. The Role of Actigraphy in the Study of Sleep and Circadian Rhythms. Sleep 2003, 26, 342–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Jung, M.; Kaplan, R.C.; Appel, D.W.; Dinces, E.A.; Dhar, S.; Zee, P.C.; Gonzalez, F.; Lee, D.J.; Ramos, A.R.; et al. Sleep Apnea Is Associated with Hearing Impairment: The Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.K.; Chen, R. Breathing and the Nervous System. In Aminoff’s Neurology and General Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 3–23. ISBN 978-0-12-407710-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sakellari, V. The Effects of Hyperventilation on Postural Control Mechanisms. Brain 1997, 120, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, S.S.; Blanchard, J.; Morin, L.P. Medial Vestibular Connections with the Hypocretin (Orexin) System. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 487, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Xu, Y.; Wu, H. Research Progress on the First-night Effect in Polysomnography Studies. Sleep Res. 2024, 1, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmyd, B.; Rogut, M.; Białasiewicz, P.; Gabryelska, A. The Impact of Glucocorticoids and Statins on Sleep Quality. Sleep Med. Rev. 2021, 55, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, N.J.; Phillips, B.A.; Guthrie, G.; Barnett, G. Effects of Dexamethasone on Sleep. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1996, 79, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, G.; Hardak, E.; Shaham, B.; Avitan, E.; Yigla, M. Preliminary Prospective Explanatory Observation on the Impact of 3-Month Steroid Therapy on the Objective Measures of Sleep-Disordered Breathing. Sleep Breath 2012, 16, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambon-Barbara, C.; Revol, B.; Hlavaty, A.; Joyeux-Faure, M.; Borel, J.C.; Cracowski, J.L.; Pepin, J.L.; Khouri, C. Signal Detection of Drugs Associated with Obstructive and Central Sleep Apnoea. Sleep Med. 2024, 124, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, A.; Golestan, N.; Tehrani, M.; Diamandis, C. Investigation of the Effect of Piracetam on Patients with Secondary Narcolepsy: A Small Randomized Controlled Trial. 2023. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/8013773 (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Mah, J.; Pitre, T. Oral Magnesium Supplementation for Insomnia in Older Adults: A Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouloukaki, I.; Lampou, M.; Raouzaiou, K.M.; Lambraki, E.; Schiza, S.; Tsiligianni, I. Association of Vitamin B12 Levels with Sleep Quality, Insomnia, and Sleepiness in Adult Primary Healthcare Users in Greece. Healthcare 2023, 11, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Lin, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, N.; Shangguan, W. The Effect of Lidocaine Intraoperative Infusion on Quality of Postoperative Sleep in Patients Undergoing Thyroidectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Anesth. 2023, 23, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Criterion | Exclusion |
|---|---|
| Age | <18 years old |
| Obesity | BMI 1 > 30 kg/m2 |
| Sleep disordered breathing | diagnosed or suspected AHI 2 ≥ 15/h in any previous sleep study ESS 3 score > 15 |
| Comorbidities | mental disorders cardiovascular disorders, e.g., atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, arteriosclerosis neurologic disorders, e.g., CVA 4, SM 5 cranial traumatism (recent or past) pulmonary disorders, e.g., asthma, COPD 6 |
| Blood test abnormalities | electrolytes: potassium, natrium complete blood count lipid panel glucose C-reactive protein coagulation screen |
| Upper airway | nasal septum deviation retrognathia vasomotor or hypertrophic rhinitis enlarged tonsils: 3 or 4 stage Friedman * tongue base or soft palate hypertrophy: III or IV stage Friedman * |
| Exogenous substances | drugs targeting the central or peripheral nervous system drugs targeting muscles system addiction to psychoactive substances alcohol |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| TGF 1 | Time when the diagnostic nasal cannula provided good signal quality for this length of time. |
| AHI | Number of apneas and hypopneas per hour within the artefact-free analysis time of the flow signal. |
| cAHI 2 | Number of central apneas and hypopneas per hour within the artifact-free evaluation time of the flow signal. |
| oAHI 3 | Number of obstructive apneas and hypopneas per hour within the artifact-free evaluation time of the flow signal. |
| AAI 4 | Number of autonomous arousals per hour within the artefact-free analysis time of the pulsoximetry signal. This parameter was not displayed in the event of an arrhythmia warning. |
| AAIre 5 | Number of autonomous arousals per hour within the artefact-free analysis time of the pulsoximetry signals caused by a respiratory event. This parameter was not displayed in the event of an arrhythmia warning. |
| RERA 6 | Number of autonomous arousals per hour within the artefact-free analysis time of the pulsoximetry signals caused by increased respiratory effort. This parameter was not displayed in the event of an arrhythmia warning. |
| Low risk of sleep fragmentation | AHI: <10 and AAI: <30 |
| Moderate risk of sleep fragmentation | AHI: 10–15 and AAI: 30–40 |
| High risk of sleep fragmentation | AHI: >15 and AAI: >40 |
| Sn 7 | Proportion of snoring time within the artifact-free evaluation time of the flow signal, measured in % |
| Group Size | Group A | Group B | Group C |
|---|---|---|---|
| number | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Sex | Group A | Group B | Group C |
| M:F * | 50%:50% | 50%:50% | 50%:50% |
| Age | Group A | Group B | Group C |
| mean ± SD | 55.1 ± 17.4 | 52.9 ± 18 | 43.9 ± 13.4 |
| median | 64.5 | 48 | 40 |
| range | 58 | 54 | 43 |
| p-value | 0.08 | ||
| BMI [kg/m2] | Group A | Group B | Group C |
| mean ± SD | 26.4 ± 3.4 | 25.4 ± 2.8 | 26.2 ± 3.3 |
| median | 27.1 | 24.8 | 27.2 |
| range | 10.8 | 8.37 | 11.9 |
| p-value | 0.58 | ||
| ESS | Group A | Group B | Group C |
| mean ± SD | 6.4 ± 4.1 | 8.5 ± 4.2 | 8 ± 4.2 |
| median | 6.5 | 8 | 8 |
| range | 15 | 13 | 13 |
| p-value | 0.27 | ||
| Interval Between Sleep Studies [Number of Days] | Group A | Group B | Group C |
| mean ± SD 1 | 4.4 ± 2.9 | 3.1 ± 1.9 | 3 ± 2.3 |
| median | 3.5 | 3 | 2 |
| range | 12 | 5 | 7 |
| p-value | 0.13 | ||
| TGF [Minutes] | TGF1A | TGF2A | TGF1B | TGF2B | TGF1C | TGF2C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n 1 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| mean | 388.3 | 400.7 | 416.2 | 418.3 | 430.8 | 418.3 |
| SD | 108.5 | 117.7 | 91.1 | 95.4 | 42.6 | 69.2 |
| difference of the means | 13 | 2 | −13 | |||
| median | 460.5 | 459 | 462.5 | 455.5 | 449.5 | 455 |
| range | 302 | 403 | 324 | 406 | 159 | 243 |
| variance | 11768.1 | 13846.8 | 8299.3 | 9104 | 1817.5 | 4783.8 |
| p-value | 0.761 (ns 2) | 0.609 (ns) | 0.629 (ns) | |||
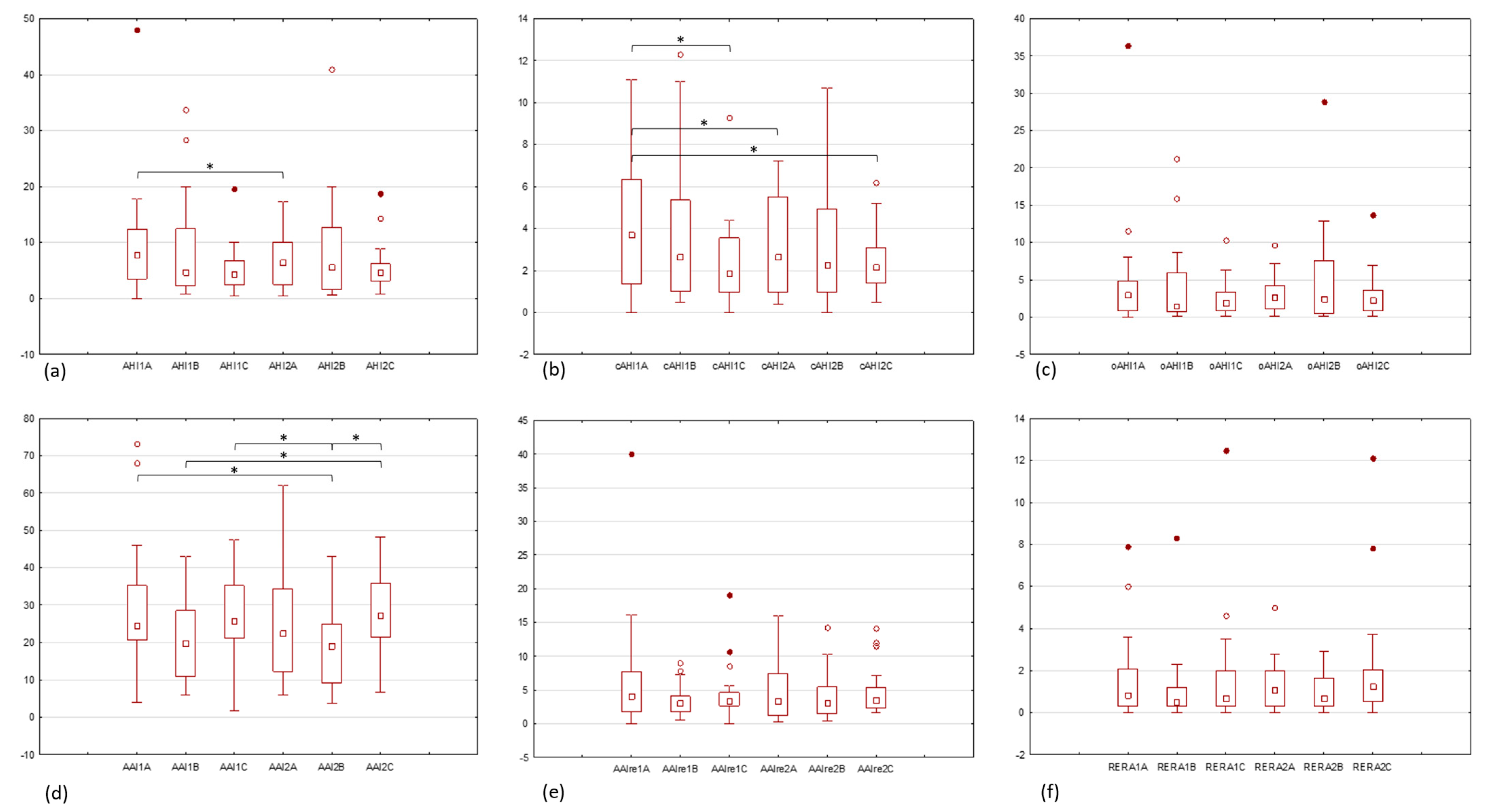
| AHI | AHI1A | AHI2A | AHI1B | AHI2B | AHI1C | AHI2C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| mean | 9.9 | 6.8 | 8.8 | 9.1 | 5.2 | 5.7 |
| SD | 10.3 | 4.4 | 9.3 | 9.7 | 4.3 | 4.3 |
| difference of the means | −3.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | |||
| median | 7.9 | 6.5 | 4.8 | 5.6 | 4.3 | 4.7 |
| range | 48 | 16.8 | 33 | 40.4 | 19.2 | 18 |
| variance | 106.5 | 19.2 | 85.6 | 95.1 | 18.6 | 18.2 |
| p-value | 0.027 | 0.955 (ns) | 0.409 (ns) | |||
| cAHI | cAHI1A | cAHI2A | cAHI1B | cAHI2B | cAHI1C | cAHI2C |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| mean | 4.1 | 3 | 3.9 | 3.5 | 2.3 | 2.4 |
| SD | 3.2 | 2.3 | 3.7 | 3.1 | 2.1 | 1.4 |
| difference of the means | −1.1 | −0.4 | 0.1 | |||
| median | 3.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 1.9 | 2.2 |
| range | 11.1 | 6.8 | 11.8 | 10.7 | 9.3 | 5.7 |
| variance | 10.5 | 5.2 | 13.7 | 9.7 | 4.4 | 2 |
| p-value | 0.011 | 0.765 (ns) | 0.601 (ns) | |||
| oAHI | oAHI1A | oAHI2A | oAHI1B | oAHI2B | oAHI1C | oAHI2C |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| mean | 5 | 3.1 | 4.1 | 5 | 2.5 | 2.9 |
| SD | 7.9 | 2.5 | 5.6 | 6.8 | 2.4 | 3.1 |
| difference of the means | −1.9 | 0.9 | 0.3 | |||
| median | 3 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 2 | 2.2 |
| range | 36.4 | 9.6 | 21.1 | 28.8 | 10.2 | 13.6 |
| variance | 63.1 | 6.4 | 31.6 | 46.8 | 5.8 | 9.5 |
| p-value | 0.204 (ns) | 0.240 (ns) | 0.260 (ns) | |||
| AAI | AAI1A | AAI2A | AAI1B | AAI2B | AAI1C | AAI2C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 18 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| mean | 29.9 | 25.5 | 21 | 18.8 | 27.3 | 28.5 |
| SD | 17.9 | 15.4 | 11.3 | 9.9 | 11.3 | 10.5 |
| difference of the means | −4.4 | −2.2 | 1.2 | |||
| median | 24.4 | 22.5 | 19.8 | 19.1 | 25.7 | 27.3 |
| range | 69.3 | 56.3 | 37.1 | 39.4 | 45.6 | 41.5 |
| variance | 319.3 | 235.7 | 126.9 | 97.5 | 128.6 | 110 |
| p-value | 0.134 (ns) | 0.099 (ns) | 0.36 (ns) | |||
| AAIre | AAIre1A | AAIre2A | AAIre1B | AAIre2B | AAIre1C | AAIre2C |
| n | 18 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| mean | 7 | 4.8 | 3.5 | 4 | 4.5 | 4.9 |
| SD | 9.4 | 4.4 | 2.4 | 3.4 | 4.2 | 3.6 |
| difference of the means | −2.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |||
| median | 4.1 | 3.4 | 3 | 3.2 | 3.4 | 3.5 |
| range | 40 | 15.7 | 8.5 | 13.8 | 19.1 | 12.5 |
| variance | 88.2 | 19 | 5.6 | 11.6 | 18 | 13.3 |
| p-value | 0.266 (ns) | 0.763 (ns) | 0.277 (ns) | |||
| RERA | RERA1A | RERA2A | RERA1B | RERA2B | RERA1C | RERA2C |
| n | 18 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 19 | 20 |
| mean | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1 | 1.7 | 2.1 |
| SD | 2.2 | 1.3 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 2.9 |
| difference of the means | −0.4 | −0.1 | 0.4 | |||
| median | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 1.3 |
| range | 7.9 | 5 | 8.3 | 2.9 | 12.5 | 12.1 |
| variance | 4.8 | 1.6 | 3.4 | 0.8 | 8.5 | 8.6 |
| p-value | 0.955 (ns) | 0.234 (ns) | 0.22 (ns) | |||
| Sn [%TGF] | Sn1A | Sn2A | Sn1B | Sn2B | Sn1C | Sn2C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 15 | 17 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 18 |
| mean | 5 | 3.2 | 4.2 | 5.4 | 7.4 | 6.3 |
| SD | 8.4 | 6.4 | 9.7 | 8.1 | 8.4 | 7.6 |
| difference of the means | −1.8 | 1.3 | −1.1 | |||
| median | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 3 |
| range | 30 | 21 | 40 | 28 | 35 | 27 |
| variance | 70.6 | 40.6 | 93.5 | 65 | 70.1 | 58.1 |
| p-value | 0.028 | 0.410 (ns) | 0.394 (ns) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuryga, D.; Niedzielski, A. Sleep Assessment in Patients with Inner Ear Functional Disorders: A Prospective Cohort Study Investigating Sleep Quality Through Polygraphy Recordings. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15040076
Kuryga D, Niedzielski A. Sleep Assessment in Patients with Inner Ear Functional Disorders: A Prospective Cohort Study Investigating Sleep Quality Through Polygraphy Recordings. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(4):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15040076
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuryga, Dorota, and Artur Niedzielski. 2025. "Sleep Assessment in Patients with Inner Ear Functional Disorders: A Prospective Cohort Study Investigating Sleep Quality Through Polygraphy Recordings" Audiology Research 15, no. 4: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15040076
APA StyleKuryga, D., & Niedzielski, A. (2025). Sleep Assessment in Patients with Inner Ear Functional Disorders: A Prospective Cohort Study Investigating Sleep Quality Through Polygraphy Recordings. Audiology Research, 15(4), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15040076







