Relationship Between Voice Analysis and Functional Status in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
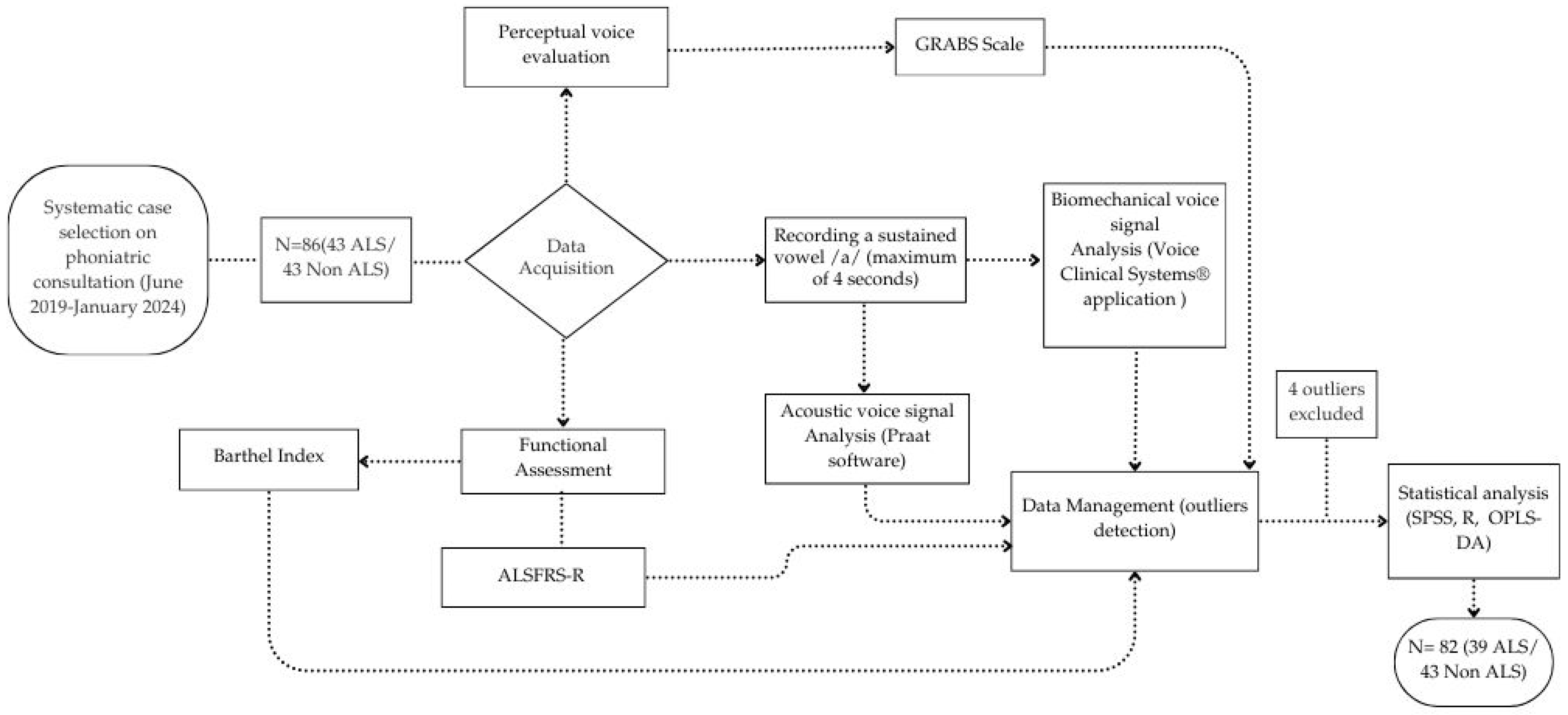
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Testing Procedures
2.3.1. Data Acquisition
2.3.2. Biomechanical Voice Measures
2.3.3. Acoustic Voice Measures
2.3.4. Perceptual Voice Evaluation
2.3.5. Functional and Dependency Measure
2.4. Possible Confounding Variables in Voice Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Vocal Parameters Analysis
3.2.1. Differences in Vocal Parameters Between ALS and Non-ALS Individuals
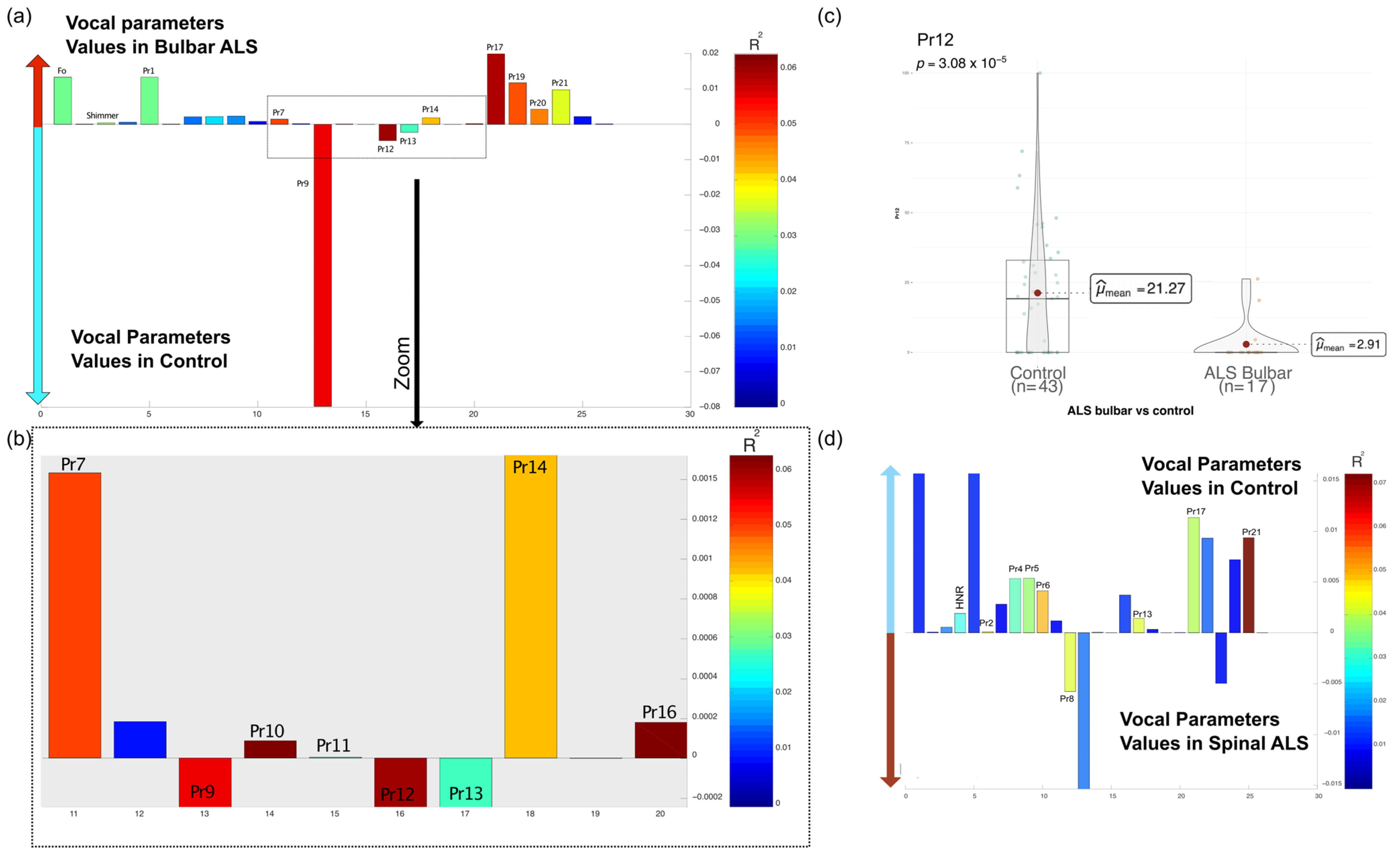
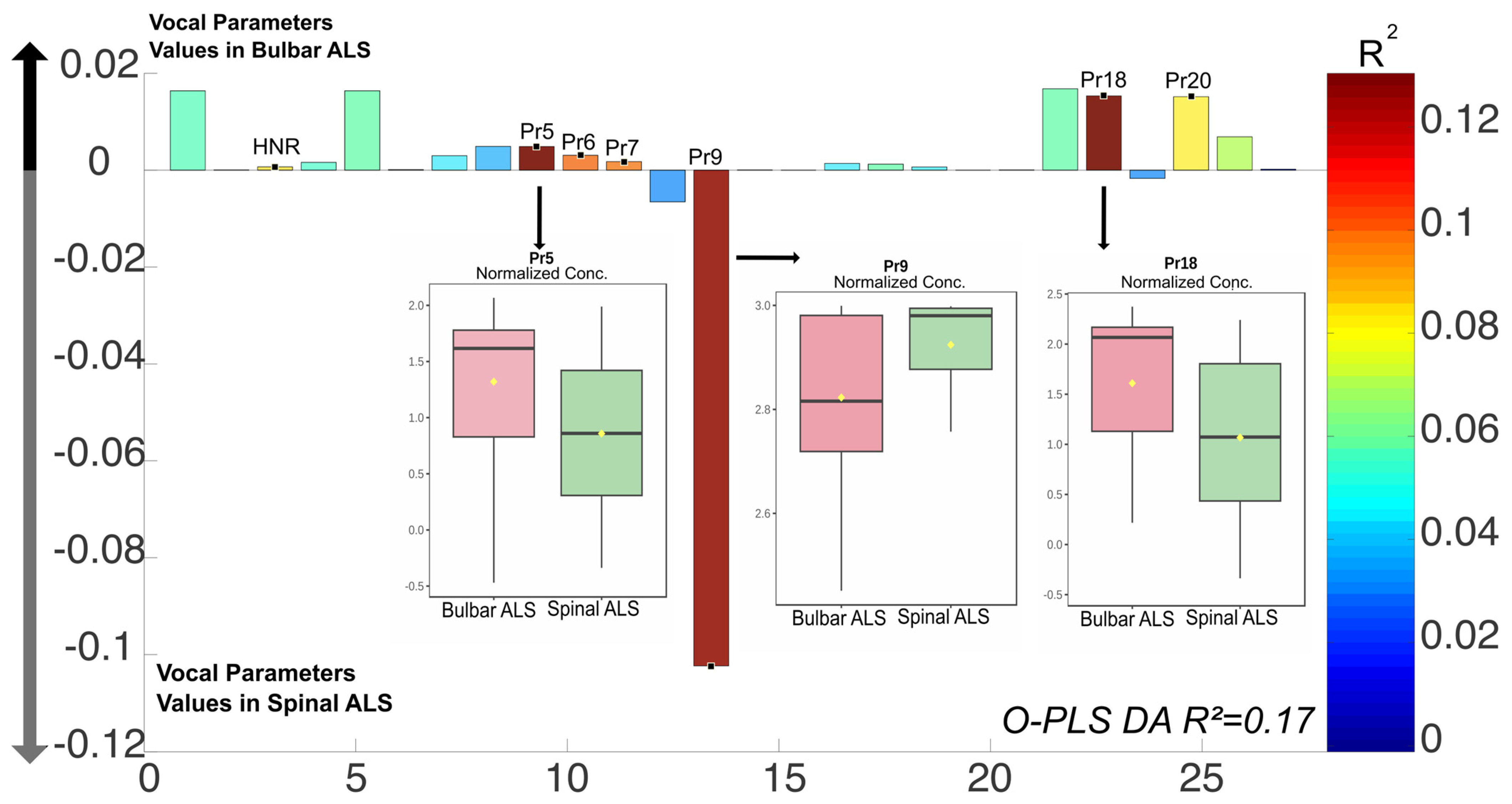
3.2.2. Vocal Parameters and ALS Phenotypes (Bulbar vs. Spinal)
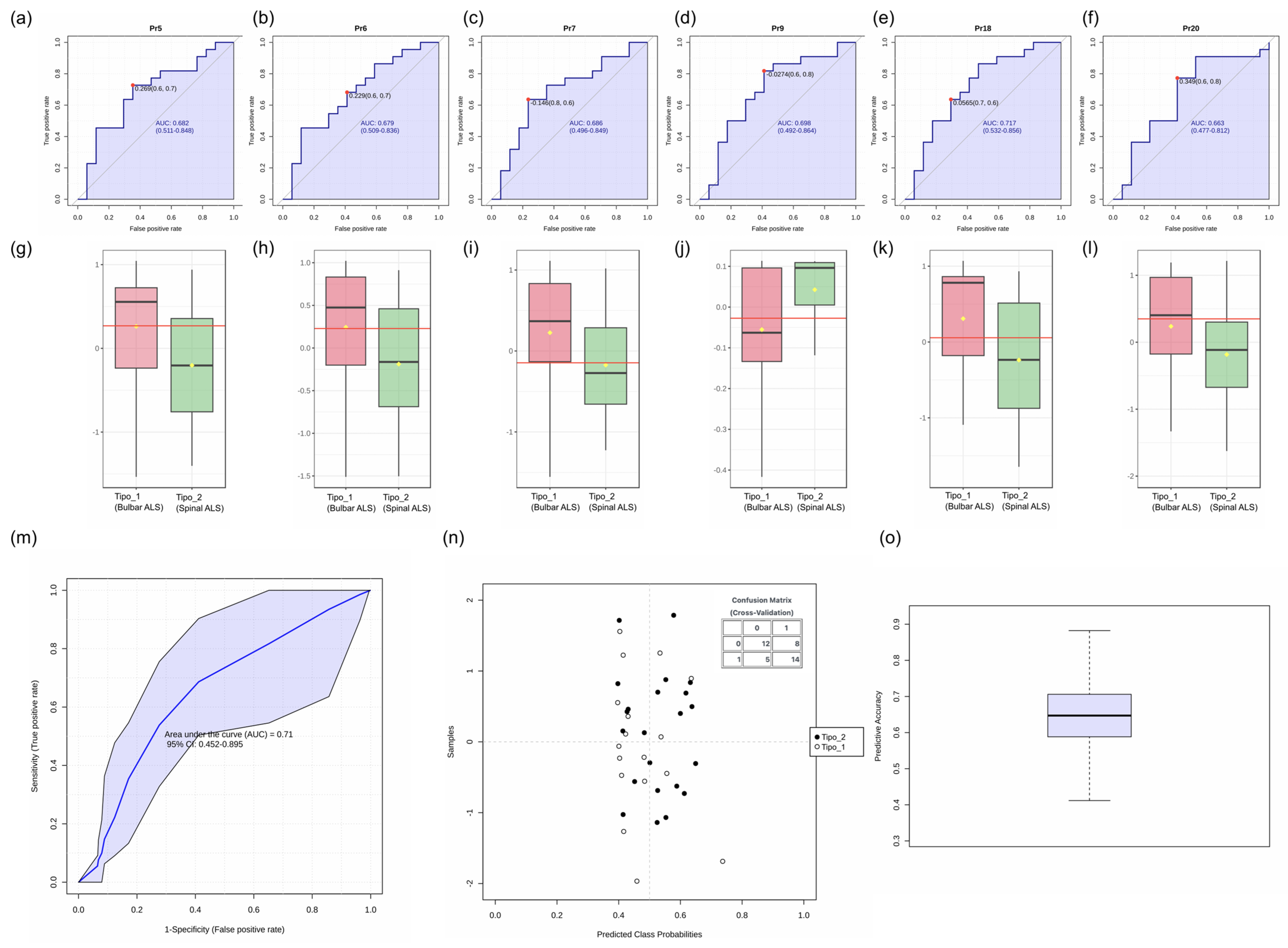
3.2.3. Evaluation of Voice Parameters as Biomarkers for ALS Subtype Differentiation
3.3. Clinical Evaluation and Vocal Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALS | Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis |
| ALSFRS-R | ALS Functional Rating Scale-Revised |
| VC | Vocal Cords |
| GRABS | Global Rating of Acoustic-Perceptual Speech |
| HNR | Harmonics to Noise Ratio |
| O-PLS DA | Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| Pr1–Pr22 | Biomechanical parameters used in voice analysis |
| F0 | Fundamental Frequency |
| NUHSA | Andalusian Unique Health Record Number |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
References
- Camacho, A.; Esteban, J.; Paradas, C. Informe de la Fundación Del Cerebro sobre el impacto social de la esclerosis lateral amiotrófica y las enfermedades neuromusculares. Neurología 2018, 33, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fávero, F.M.; Voos, M.C.; Castro, I.D.; Caromano, F.A.; Oliveira, A.S.B. Epidemiological and clinical factors impact on the benefit of riluzole in the survival rates of patients with ALS. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2017, 75, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomik, B.; Guiloff, R.J. Dysarthria in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A review. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2010, 11, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbergleit, A.K.; Johnson, A.F.; Jacobson, B.H. Acoustic Analysis of Voice in Individuals with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Perceptually Normal Vocal Quality. J. Voice 1997, 11, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaramonte, R.; Bonfiglio, M. Acoustic analysis of voice in bulbar amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies. Logop. Phoniatr. Vocology 2020, 45, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtró Ayats, M.P.; Carmona Lalueza, N. Trastornos de la voz; 1a.; Oberta UOC Publishing, SL: Barcelona, Spain, 2019; ISBN 978-84-9180-547-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lyberg-Åhlander, V.; Rydell, R.; Fredlund, P.; Magnusson, C.; Wilén, S. Prevalence of Voice Disorders in the General Population, Based on the Stockholm Public Health Cohort. J. Voice 2019, 33, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sociedad Española de Otorrinolaringología y Cirugía de Cabeza y Cuello (SEORL-CCC). Una de cada 13 Personas Sufre Trastornos de la voz pero la Mayoría no se Tratan Adecuadamente. SEORL-CCC; 2017. Available online: https://seorl.net/profesiones-de-riesgo-para-la-voz/ (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Brooks, B.R.; Miller, R.G.; Swash, M.; Munsat, T.L. El Escorial revisited: Revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Mot. Neuron Disord. 2000, 1, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Vilda, P.; Fernández-Baillo, R.; Nieto, A.; Díaz, F.; Fernández-Camacho, F.J.; Rodellar, V.; Álvarez, A.; Martínez, R. Evaluation of Voice Pathology Based on the Estimation of Vocal Fold Biomechanical Parameters. J. Voice 2007, 21, 450–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, P.; Weenink, D. Praat: Doing Phonetics by Computer [Computer Program]. 2022. (1999–2022). Available online: https://www.fon.hum.uva.nl/praat/ (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Núñez-Batalla, F.; Díaz-Molina, J.P.; García-López, I.; Moreno-Méndez, A.; Costales-Marcos, M.; Moreno-Galindo, C.; Martínez-Camblor, P. The Effect of Anchor Voices and Visible Speech in Training in the GRABS Scale of Perceptual Evaluation of Dysphonia. Acta Otorrinolaringol. 2012, 63, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedarbaum, J.M.; Stambler, N.; Malta, E.; Fuller, C.; Hilt, D.; Thurmond, B.; Nakanishi, A. The ALSFRS-R: A revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 169, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid-Ruzafa, J.; Damián-Moreno, J. Valoración de la discapacidad física: El indice de Barthel. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 1997, 71, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Matlab Versión R2015b. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Dieterle, F.; Ross, A.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Senn, H. Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bylesjö, M.; Rantalainen, M.; Cloarec, O.; Holmes, E.; Trygg, J. OPLS discriminant analysis: Combining the strengths of PLS-DA and SIMCA classification. J. Metr 2006, 20, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloarec, O.; Dumas, M.-E.; Craig, A.; Barton, R.H.; Trygg, J.; Hudson, J. Statistical total correlation spectroscopy: An exploratory approach for latent biomarker identification from metabolic 1H NMR data sets. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühnlein, P.; Gdynia, H.-J.; Sperfeld, A.-D.; Lindner-Pfleghar, B.; Ludolph, A.C.; Prosiegel, M.; Riecker, A. Diagnosis and treatment of bulbar symptoms in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2008, 4, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkonen, T.; Ruottinen, H.; Puhto, R.; Helminen, M.; Palmio, J. Speech deterioration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) after manifestation of bulbar symptoms. Intl. J. Lang. Comm. Disor 2018, 53, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milella, G.; Sciancalepore, D.; Cavallaro, G.; Piccirilli, G.; Nanni, A.G.; Fraddosio, A.; D’Errico, E.; Paolicelli, D.; Fiorella, M.L.; Simone, I.L. Acoustic Voice Analysis as a Useful Tool to Discriminate Different ALS Phenotypes. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, D.L.; Pouget, J.; Giovanni, A.; Azulay, J.-P.; Triglia, J.-M. Quantitative Voice Analysis in the Assessment of Bulbar Involvement in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Acta Otorrinolaringol. 1999, 119, 724–731. [Google Scholar]
- Ramig, L.O.; Scherer, R.C.; Klasner, E.R.; Titze, I.R.; Horii, Y. Acoustic Analysis of Voice in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Longitudinal Case Study. J. Speech Hear. Disord. 1990, 55, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomik, J.; Tomik, B.; Wiatr, M.; Składzień, J.; Stręk, P.; Szczudlik, A. The Evaluation of Abnormal Voice Qualities in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurodegener. Dis. 2015, 15, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Liesa, R.; Damborenea Tajada, D.; Rueda Gomerdino, P.; García y García, E.; Leache Pueyo, J.; Campos del Álamo, M.; Llorente Arenas, E.; Naya Gálvez, M.J. Análisis acústico de la voz normal en adultos no fumadores. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1999, 50, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Phukan, J.; Pender, N.; Hardiman, O. Cognitive impairment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 11, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pender, N.; Pinto-Grau, M.; Hardiman, O. Cognitive and behavioural impairment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2020, 33, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameter | Description | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Pr1 | Fundamental frequency. Normal range: 180–240 Hz (females)/105–139 Hz (males) | Indicator of pitch control and vocal fold vibration stability |
| Pr2 | Ratio of cycles in the closing phase between free edges | Indicates regularity in vocal fold closure |
| Pr3 | Increased open phase and asymmetry in free edge vibration | May be linked to vocal fold asymmetry and phonatory instability |
| Pr4 | Percentage of time spent in the approximation phase for glottal closure | Affects vocal efficiency and closure coordination |
| Pr5 | Percentage of time vocal folds remain separated | May indicate hypofunctional phonation |
| Pr6 | Duration of the opening phase (vocal fold separation) | Associated with airflow dynamics during phonation |
| Pr7 | Duration of the opening phase (vocal fold approximation) | Reflects closure speed and coordination |
| Pr8 | Tension associated with glottal closure (hyperfunctional glottis) | Suggests excessive muscular tension affecting phonation |
| Pr9 | Glottal closure force | May indicate compensatory mechanisms or phonatory inefficiency |
| Pr10 | Index of optimal energy use during voice production | Evaluates phonatory efficiency and voice sustainability |
| Pr11 | Incomplete glottal closure (gap between edges) | May contribute to breathy voice quality or phonatory inefficiency |
| Pr12 | Alteration in the proportion of the closing phase (GAP size) | Can reflect structural or functional glottal insufficiency |
| Pr13 | Instability in maintaining vibratory tension within a single vocal cycle | Linked to phonatory instability and tremor |
| Pr14 | Instability in maintaining vibratory tension within a single vocal cycle | Similar to Pr13, related to vocal fatigue and tremor |
| Pr15 | Degree of vibratory blockages throughout the voice sample | May indicate phonatory spasms or irregular vocal fold movement |
| Pr16 | Separation between the edges of the vocal folds | Reflects glottal configuration and closure patterns |
| Pr17 | Mucosal wave correlate observed during the closing phase | Related to vocal fold pliability and phonatory function |
| Pr18 | Mucosal wave correlate observed during the opening phase | Provides insight into vibratory mechanics |
| Pr19 | Edema correlate observed during the closing phase | Suggests possible inflammation or structural changes |
| Pr20 | Edema correlate observed during the opening phase | Related to phonatory effort and tissue properties |
| Pr21 | Structural imbalance index | Indicates potential vocal fold asymmetry or stiffness |
| Pr22 | Correlates with potential structural alterations in the free edge mass or supraglottic structures | May indicate vocal fold lesions or supraglottic hyperfunction |
| Parameter | Description | Normal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamental frequency | Fundamental frequency (acoustic analysis, Praat). Same normative values as Pr1 but may slightly differ due to measurement method | 180–240 Hz (females)/105–139 Hz (males) |
| Shimmer | Amplitude perturbation | 0–3% |
| Jitter | Fundamental frequency variation between cycles | ~1% |
| Harmonics to Noise Ratio (HNR) | Signal to noise measure | Values < 20 indicate dysphonia |
| Parameter | Description | Scoring (0 = Normal, 3 = Severe) |
|---|---|---|
| Global | Global voice impairment | 0 to 3 |
| Roughness | Irregular glottic mobility | 0 to 3 |
| Asthenia | Phonatory weakness | 0 to 3 |
| Breathiness | Turbulence due to glottic insufficiency | 0 to 3 |
| Strain | Excessive effort with hyperkinesia | 0 to 3 |
| Domain | Description | Scoring (0 = Complete Impairment, 4 = Normal Function) |
|---|---|---|
| Bulbar | Speech, salivation and swallowing | 0 to 4 |
| Fine motor skills | Writing, utensil use and hygiene/dress | 0 to 4 |
| Gross motor skills | Turning in bed, walking and stair climbing | 0 to 4 |
| Respiratory functions | Dyspnea, orthopnea and ventilatory support | 0 to 4 |
| Sociodemographic | Clinical Score ALS | Clinical Score Non-ALS |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 63.31 ± 9.45 | 64.02 ± 7.47 |
| N (men/women) | 39 (24/15) | 43 (27/16) |
| Smoking (No/Yes) | 20 (24.4%)/19 (23.2%) | 35 (81.4%)/8 (18.6%) |
| Time to diagnosis ALS (months) | 20.56 ± 24.15 | Not applicable |
| Type of ALS: Bulbar/Spinal | 17 (20.7%)/22 (26.8%) | Not applicable |
| ALSFRS-R | 35.38 ± 6.98 | 48 ± 0 |
| Barthel | 67.85 ± 20.95 | 100 ± 0 |
| GRABS | 3.92 ± 4.15 | 5.7 ± 2.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Bonilla, M.; Díaz Borrego, P.; Mora-Ortiz, M.; Fernández-Baillo, R.; Muñoz-Alcaraz, M.N.; Mayordomo-Riera, F.J.; Girela López, E. Relationship Between Voice Analysis and Functional Status in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030053
Pérez-Bonilla M, Díaz Borrego P, Mora-Ortiz M, Fernández-Baillo R, Muñoz-Alcaraz MN, Mayordomo-Riera FJ, Girela López E. Relationship Between Voice Analysis and Functional Status in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(3):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030053
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Bonilla, Margarita, Paola Díaz Borrego, Marina Mora-Ortiz, Roberto Fernández-Baillo, María Nieves Muñoz-Alcaraz, Fernando J. Mayordomo-Riera, and Eloy Girela López. 2025. "Relationship Between Voice Analysis and Functional Status in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis" Audiology Research 15, no. 3: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030053
APA StylePérez-Bonilla, M., Díaz Borrego, P., Mora-Ortiz, M., Fernández-Baillo, R., Muñoz-Alcaraz, M. N., Mayordomo-Riera, F. J., & Girela López, E. (2025). Relationship Between Voice Analysis and Functional Status in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Audiology Research, 15(3), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030053









