Optimizing Tinnitus Management: The Important Role of Hearing Aids with Sound Generators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Information
3.2. Improvement in Tinnitus
3.2.1. Group-Wise Comparisons among the CNT, HA, SG HA, and SG Groups
3.2.2. Group-Wise Comparisons among the CNT, HA, Various Models of SG HA (ZEN and TTHA/TTC), and SG (TT/TTSG and TCI) Groups
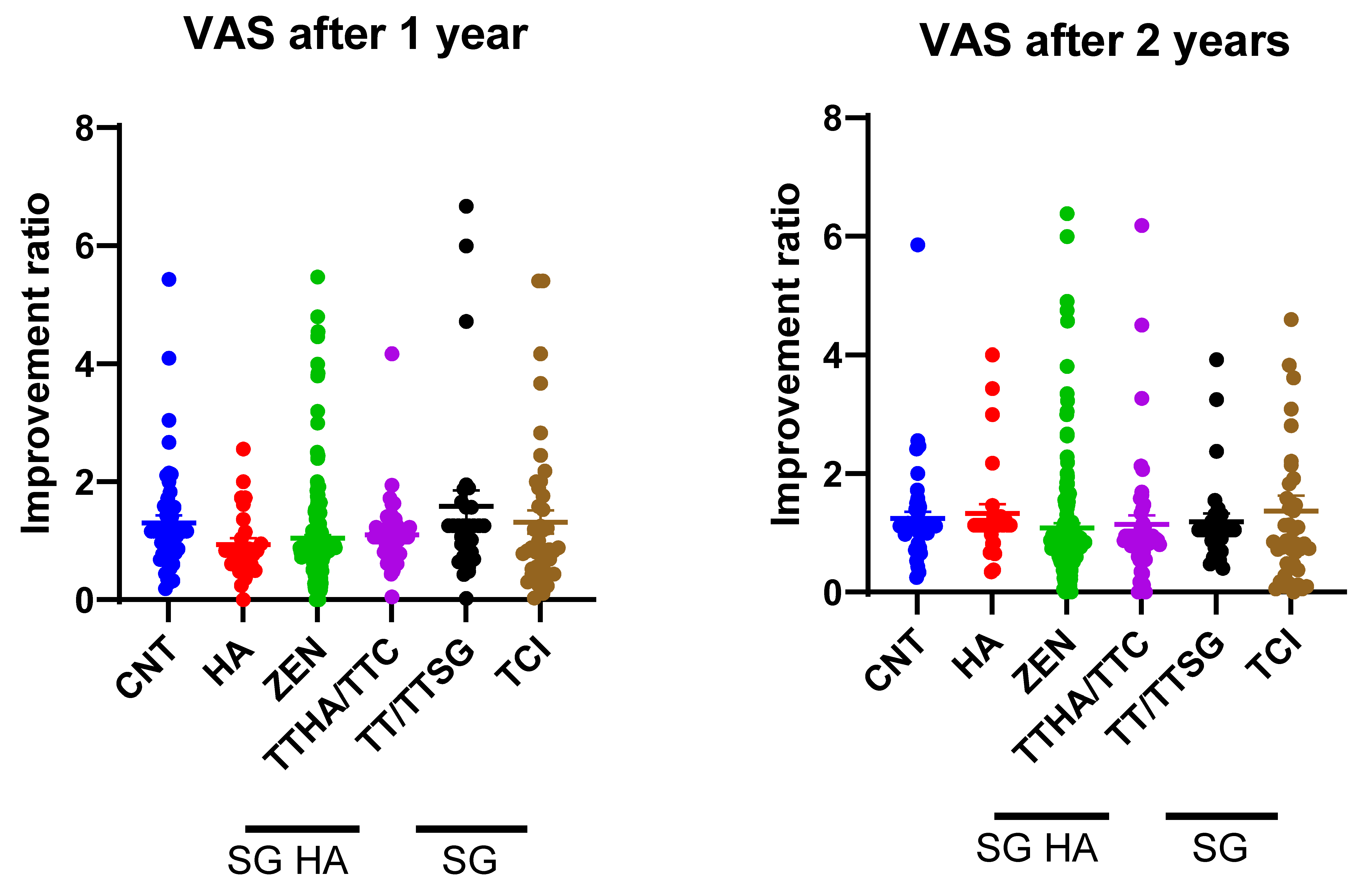
3.3. Improvement in VAS Score
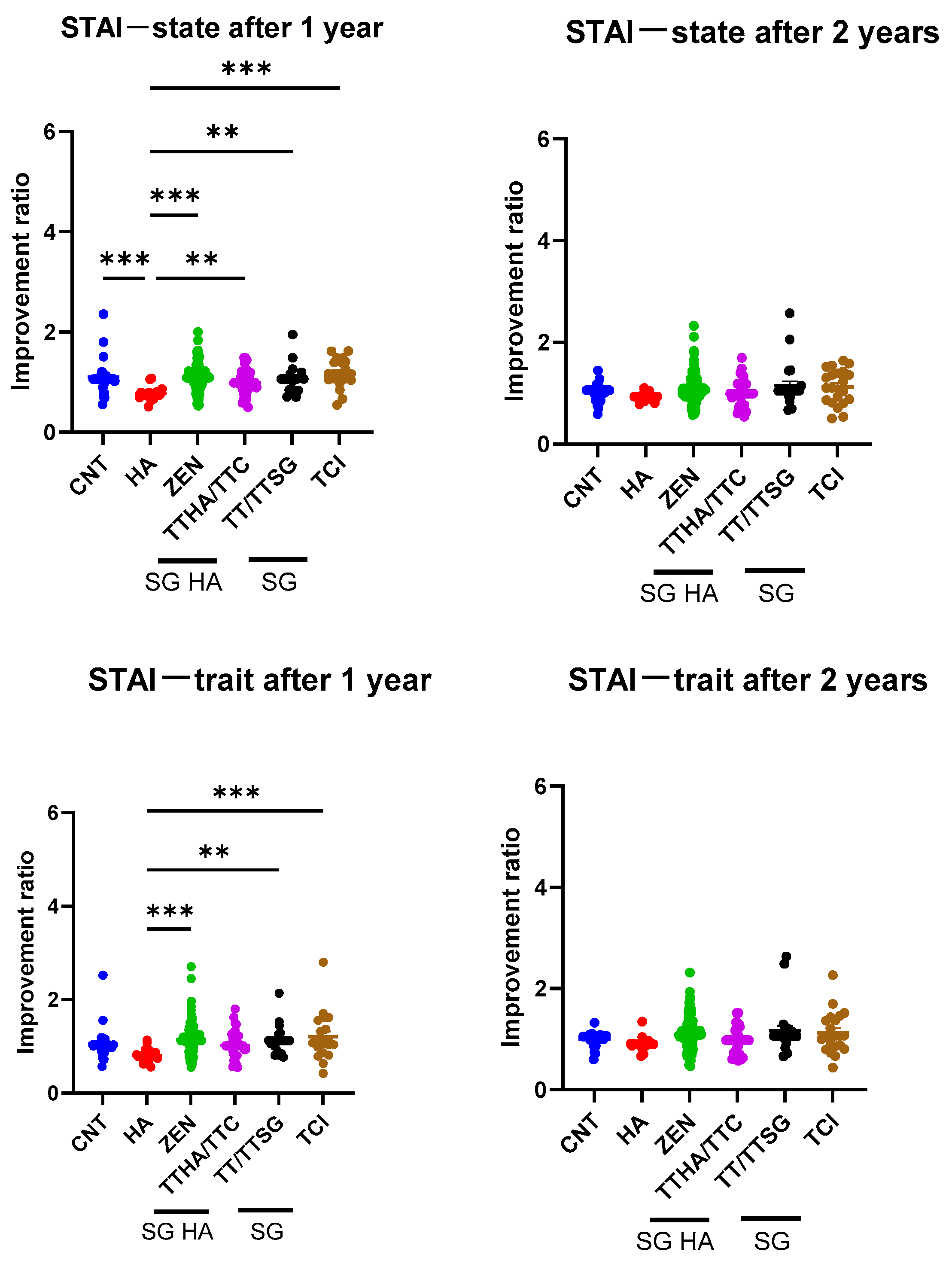
3.4. STAI Improvement Rate
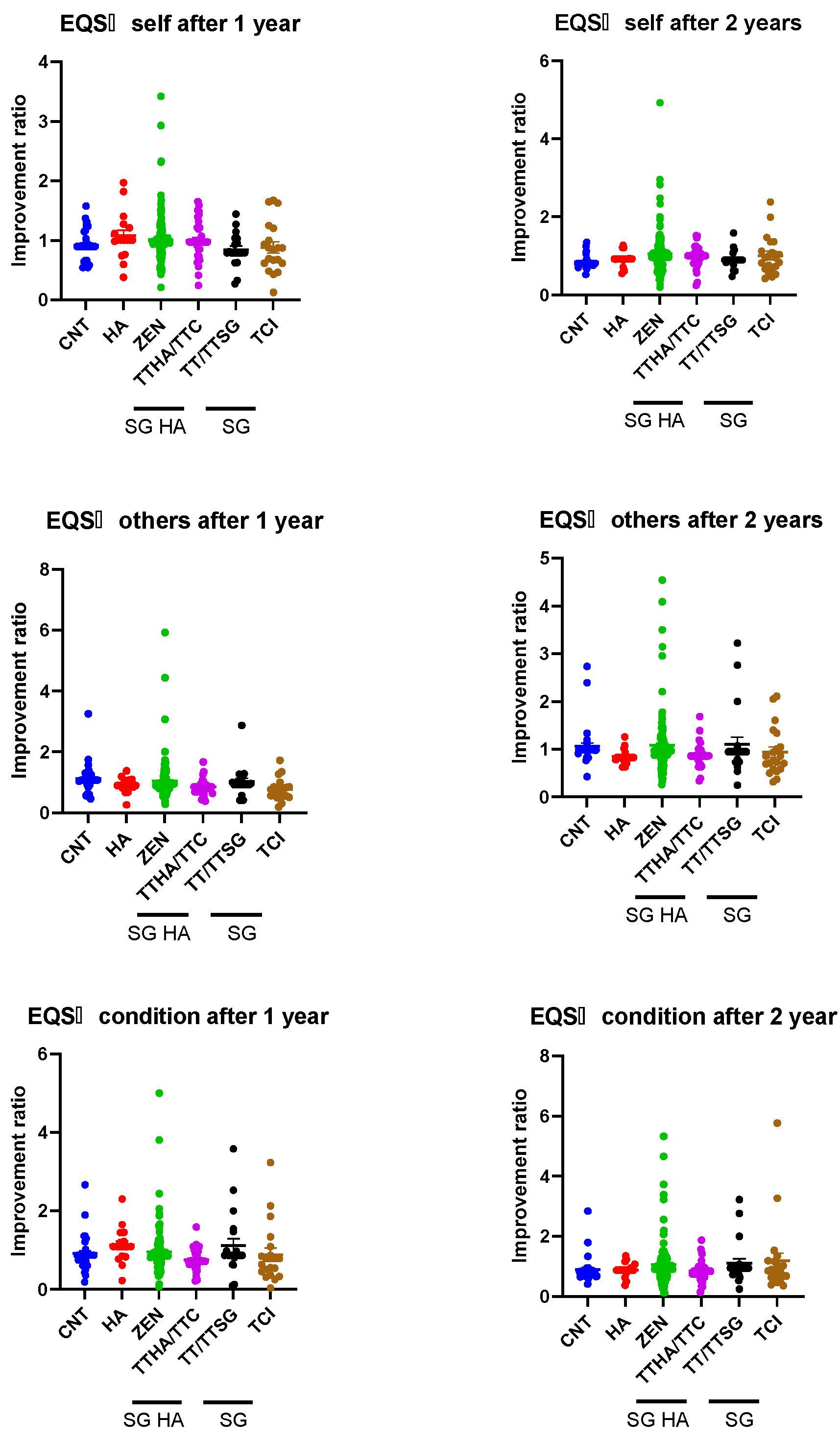
3.5. Improvement in EQS Scores
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Axelsson, A.; Ringdahl, A. Tinnitus—A study of its prevalence and characteristics. Br. J. Audiol. 1989, 23, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Sato, H.; Takahashi, M.; Wada, T.; Naito, Y.; Kawase, T.; Murakami, S.; Hara, A.; Kanzaki, S. Clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of chronic tinnitus in Japan. Auris Nasus Larynx 2020, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, P.J.; Jastreboff, M.M. Tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT) as a method for treatment of tinnitus and hyperacusis patients. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2000, 11, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereda, M.; Xia, J.; El Refaie, A.; Hall, D.A.; Hoare, D.J. Sound therapy (using amplification devices and/or sound generators) for tinnitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, CD013094. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shinden, S.; Suzuki, N.; Oishi, N.; Suzuki, D.; Minami, S.; Ogawa, K. Effective sound therapy using a hearing aid and educational counseling in patients with chronic tinnitus. Auris Nasus Larynx 2021, 48, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Koyama, S.; Kitano, K.; Otsuka, S.; Kitahara, T. Retrospective evaluation of secondary effects of hearing aids for tinnitus therapy in patients with hearing loss. Auris Nasus Larynx 2020, 47, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemin, L.; Gilles, A.; Shekhawat, G.S. Hearing more to hear less: A scoping review of hearing aids for tinnitus relief. Int. J. Audiol. 2022, 61, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunkel, D.E.; Bauer, C.A.; Sun, G.H.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Cunningham, E.R., Jr.; Archer, S.M.; Blakley, B.W.; Carter, J.M.; Granieri, E.C.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Tinnitus. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2014, 151, S1–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenner, H.P.; Delb, W.; Kröner-Herwig, B.; Jäger, B.; Peroz, I.; Hesse, G.; Mazurek, B.; Goebel, G.; Gerloff, C.; Trollmann, R.; et al. On the interdisciplinary S3 guidelines for the treatment of chronic idiopathic tinnitus. HNO 2015, 63, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.A.; Roberts, L.E.; Caspary, D.M.; Theodoroff, S.M.; Salvi, R.J. Underlying mechanisms of tinnitus: Review and clinical implications. J. Am. Acad.Audiol. 2014, 25, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, P.J. Phantom auditory perception (tinnitus): Mechanisms of generation and perception. Neurosci. Res. 1990, 8, 221–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenner, H.P.; Zalaman, I.M. Cognitive tinnitus sensitization: Behavioral and neurophysiological aspects of tinnitus centralization. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2004, 124, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenner, H.P.; Pfister, M.; Birbaumer, N. Tinnitus sensitization: Sensory and psychophysiological aspects of a new pathway of acquired centralization of chronic tinnitus. Otol. Neurotol. 2006, 27, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, L.; Handscomb, L.; Hoare, D.J.; Hall, D.A. A scientific cognitive-behavioral model of tinnitus: Novel conceptualizations of tinnitus distress. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodratitoostani, I.; Zana, Y.; Delbem, A.C.; Sani, S.S.; Ekhtiari, H.; Sanchez, T.G. Theoretical Tinnitus Framework: A Neurofunctional Model. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodratitoostani, I.; Vaziri, Z.; Miranda Neto, M.; de Giacomo Carneiro Barros, C.; Delbem, A.C.B.; Hyppolito, M.A.; Jalilvand, H.; Louzada, F.; Leite, J.P. Conceptual framework for tinnitus: A cognitive model in practice. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.A.; Frederick, M.; Sell, S.; Griest, S.; Abrams, H. Validation of a novel combination hearing aid and tinnitus therapy device. Ear Hear. 2015, 36, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formby, C.; Yang, X.; Scherer, R.W. Contributions of Counseling and Sound Generator Use in Tinnitus Retraining Therapy: Treatment Response Dynamics Assessed in a Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Trial. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2022, 65, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweetow, R.W.; Sabes, J.H. Effects of acoustical stimuli delivered through hearing aids on tinnitus. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2010, 21, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetow, R. The use of fractal tones in tinnitus patient management. Noise Health 2013, 15, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilvand, H.; Pourbakht, A.; Haghani, H. Hearing aid or tinnitus masker: Which one is the best treatment for blast-induced tinnitus? The results of a long-term study on 974 patients. Audiol. Neurotol. 2015, 20, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, C.W.; Jacobson, G.P.; Spitzer, J.B. Development of the tinnitus handicap inventory. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 1996, 122, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielberger, C.D.; Gorsuch, R.L.; Lushene, R.E. STAI Manual for the Stait-Trait Anxiety Inventory (‘Self-Evaluation Questionnaire’); (Libro, 1970) [WorldCat.org]; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, K.; Joshi, S.; Raichaudhuri, A.; Ryali, V.; Bhat, P.S.; Shashikumar, R.; Prakash, J.; Basannar, D. Emotional intelligence scale for medical students. Ind. Psychiatry J. 2011, 20, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouga, T.; Kouda, Y.; Miwa, T.; Sunami, K. Characteristics of Vestibular Migraine Assessed Using the Emotional Intelligence Scale (EQS): A Pilot Study. Equilib. Res. 2023, 82, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, P.; Tziridis, K.; Metzner, C.; Schilling, A.; Hoppe, U.; Schulze, H. Stochastic resonance controlled upregulation of internal noise after hearing loss as a putative cause of tinnitus-related neuronal hyperactivity. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auerbach, B.D.; Rodrigues, P.V.; Salvi, R.J. Central Gain Control in Tinnitus and Hyperacusis. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoare, D.J.; Adjamian, P.; Sereda, M.; Hall, D.A. Recent technological advances in sound-based approaches to tinnitus treatment: A review of efficacy considered against putative physiological mechanisms. Noise Health 2013, 15, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, R.S.; Deshpande, A.K.; Lau, C.C.; Kuk, F. The effectiveness of the progression of widex zen tinnitus therapy: A pilot study. Am. J. Audiol. 2017, 26, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, M.W.; Park, M.K.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.H. The Treatment Outcome of Smart Device–Based Tinnitus Retraining Therapy: Prospective Cohort Study. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2023, 11, e38986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, R.R.; Azevedo, A.A.; Oliveira, P.d.M. Correlation analysis of the visual-analogue scale and the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory in tinnitus patients. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 75, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meikle, M.B.; Stewart, B.J.; Griest, S.E.; Henry, J.A. Tinnitus Outcomes Assessment. Trends Amplif. 2008, 12, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, T.E.; Haider, H.F.; Kikidis, D.; Lapira, A.; Mazurek, B.; Norena, A.; Rabau, S.; Lardinois, R.; Cederroth, C.R.; Edvall, N.K.; et al. Different teams, same conclusions? A systematic review of existing clinical guidelines for the assessment and treatment of tinnitus in adults. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, J.M.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Lin, H.W. Relationships Between Tinnitus And The Prevalence Of Anxiety And Depression. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Ahsan, A.; Kumar, V. Impact of Hearing Aid Usage on Emotional and Social Skills in Persons With Severe to Profound Hearing Loss. J. Audiol. Otol. 2023, 27, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kang, D.W.; Yeo, S.G.; Kim, S.H. Hearing Aid Effects and Satisfaction in Patients with Tinnitus. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, T.; Cima, R.; Langguth, B.; Mazurek, B.; Vlaeyen, J.W.; Hoare, D.J. Cognitive behavioural therapy for tinnitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, CD012614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilar-Corbi, R.; Pozo-Rico, T.; Sánchez, B.; Castejón, J.L. Can emotional intelligence be improved? A randomized experimental study of a business-oriented EI training program for senior managers. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerson, C.; Sherman, R.A.; Kozlowski, G.P. Alpha suppression and symmetry training for generalized anxiety symptoms. J. Neurother. 2009, 13, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
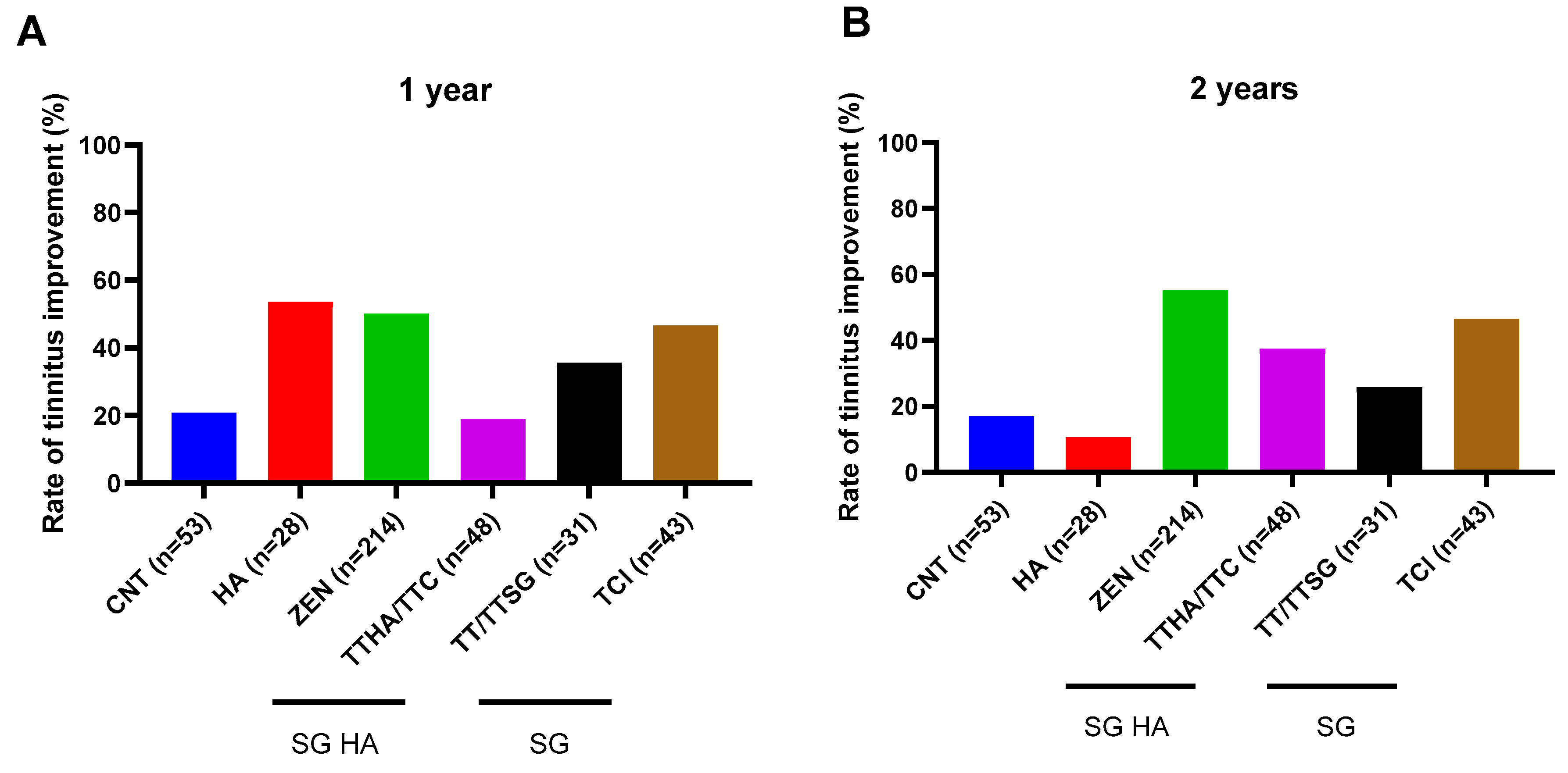
| Group | CNT | HA | SG HA | SG | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgroup | CNT | HA | ZEN | TTHA/TTC | TT/TTSG | TCI | p-Value |
| Manufacturer | - | Various | Widex | Makitie | Makitie | Sivantos | |
| Characteristics for SG | ZEN Tone | White Noise, etc. | |||||
| N | 53 | 28 | 214 | 48 | 31 | 43 | |
| Age (years) (mean ± SD) | 56.8 ± 13.4 | 65.9 ± 10.4 | 63.2 ± 13.0 | 62.4 ± 12.4 | 60.0 ± 12.8 | 60.2 ± 11.4 | ns a |
| Sex (male/female) | 22:31 | 14:14 | 91:123 | 25:23 | 19:12 | 26:17 | ns b |
| Group | CNT | HA | SG HA | SG | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgroup | CNT | HA | ZEN | TTHA/TTC | TT/TTSG | TCI | |
| Manufacturer | - | Various | Widex | Makitie | Makitie | Sivantos | |
| Characteristics for SG | ZEN Tone | White Noise, etc. | |||||
| THI | First visit | 30.7 ±19.4 | 55.4 ± 21.6 | 45.6 ± 29.0 | 46.7 ± 27.5 | 41.0 ± 27.3 | 38.1 ± 23.5 |
| 1 year | 41.1 ± 28.3 | 36.7 ± 21.3 | 37.3 ± 24.3 | 45.4 ± 23.9 | 41.7 ± 26.8 | 33.1 ± 23.3 | |
| 2 years | 35.9 ± 20.9 | 51.3 ± 19.2 | 32.3 ± 24.6 | 43.0 ± 24.2 | 40.4 ± 25.4 | 31.8 ± 26.2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosugi, Y.; Miwa, T.; Haruta, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Kato, S. Optimizing Tinnitus Management: The Important Role of Hearing Aids with Sound Generators. Audiol. Res. 2024, 14, 674-683. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14040057
Kosugi Y, Miwa T, Haruta Y, Hashimoto K, Kato S. Optimizing Tinnitus Management: The Important Role of Hearing Aids with Sound Generators. Audiology Research. 2024; 14(4):674-683. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14040057
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosugi, Yuki, Toru Miwa, Yuka Haruta, Kosuke Hashimoto, and Shoko Kato. 2024. "Optimizing Tinnitus Management: The Important Role of Hearing Aids with Sound Generators" Audiology Research 14, no. 4: 674-683. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14040057
APA StyleKosugi, Y., Miwa, T., Haruta, Y., Hashimoto, K., & Kato, S. (2024). Optimizing Tinnitus Management: The Important Role of Hearing Aids with Sound Generators. Audiology Research, 14(4), 674-683. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14040057






