Minimally Invasive Techniques for Large-Volume Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comparative Study Between HoLEP and Robotic Simple Prostatectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surgical Techniques
2.2. Analyzed Variables
- Demographic data: age (years), Charlson comorbidity index [10], history of urological surgery and/or pelvic radiotherapy (RT) (yes/no), permanent catheterization prior to surgery (yes/no).
- Preoperative variables: maximum flow rate on uroflowmetry (Qmax) (mL/s), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), quality of life score (IPSS-QoL), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) (ng/dL), prostate volume (cm3), and preoperative haemoglobin (g/dL).
- Intraoperative variables: surgical time (min), enucleated gland weight (g), and surgical efficiency (g/min).
- Postoperative variables: hospital stay (days), catheterization time (days), haemoglobin at discharge (g/dL), postoperative PSA at 6 months (ng/dL), postoperative Qmax at 6 months (mL/s), and IPSS and IPSS-QoL scores at 6 months. Perioperative complications: categorized according to the Clavien–Dindo classification [8].
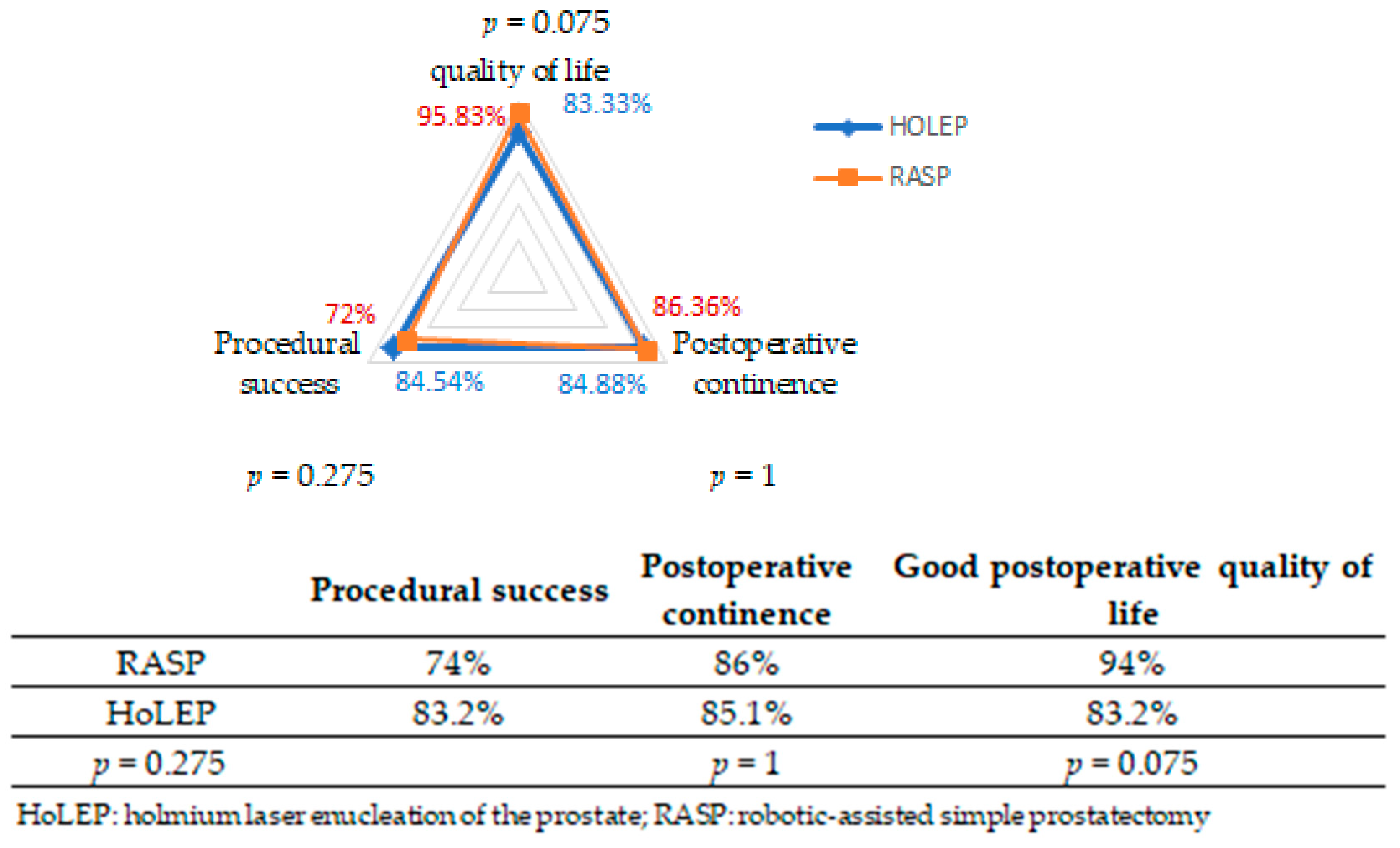
- Procedural success: complete adenoma enucleation (endoscopic or robotic) without complications, technical conversion, blood transfusion, or reintervention.
- Good postoperative quality of life: defined as an IPSS-QoL score between 0 and 2.
- Postoperative continence: defined by the absence of leakage and no need for absorbent pads 6 months after surgery.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RASP | robot-assisted simple prostatectomy |
| HoLEP | holmium laser enucleation of the prostate |
| BHP | benign prostatic hyperplasia |
| IPSS | International Prostate Symptom Score |
| PSA | prostate-specific antigen |
| Q max | maximum flow rate |
| OSP | open simple prostatectomy |
| LUTS | lower urinary tract symptoms |
| IPSS-QoL | International Prostate Symptom quality of life score |
| TRUS | transrectal ultrasound |
| mpMRI | multiparametric prostate magnetic resonance imaging |
| SD | standard deviation |
| UTI | urinary tract infection |
References
- Management of Non-neurogenic Male LUTS. EAU Guidelines. 2024. Available online: https://uroweb.org/guidelines/management-of-non-neurogenic-male-luts (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Gilling, P.J.; Cass, C.B.; Cresswell, M.D.; Fraundorfer, M.R. Holmium laser resection of the prostate: Preliminary results of a new method for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology 1996, 47, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotelo, R.; Clavijo, R.; Carmona, O.; Garcia, A.; Banda, E.; Miranda, M.; Fagin, R. Robotic simple prostatectomy. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autorino, R.; Zargar, H.; Mariano, M.B.; Sanchez-Salas, R.; Sotelo, R.J.; Chlosta, P.L.; Castillo, O.; Matei, D.V.; Celia, A.; Koc, G.; et al. Perioperative Outcomes of Robotic and Laparoscopic Simple Prostatectomy: A European–American Multi-institutional Analysis. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rij, S.; Gilling, P.J. In 2013, holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) may be the new “gold standard”. Curr. Urol. 2012, 13, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinar, U.; Sarrazin, C.; Anract, J.; Chevrot, A.; Fassi-Fehri, H.; Wilisch, J.; Gas, J.; Rouscoff, Y.; Dellanegra, E.; Klein, C.; et al. Benign prostate hyperplasia over 150 cm3: Should we perform an endoscopic enucleation of the prostate or robotic-assisted simple prostatectomy? Fr. J. Urol. 2025, 35, 102877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, J.S.; Bixler, B.R.; Dahm, P.; Goueli, R.; Kirkby, E.; Stoffel, J.T.; Wilt, T.J. Management of lower urinary tract symptoms attributed to benign prostatic hy-perplasia (BPH): AUA Guideline amendment. J. Urol. 2023, 211, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavien, P.A.; Barkun, J.; de Oliveira, M.L.; Michelle, L.; Vauthey, J.N.; Dindo, D.; Schulick, R.; de Santibañes, E.; Pekolj, J.; Slankamenac, K.; et al. The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: Five-year expe-rience. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millin, T. Retropubic prostatectomy. Br. J. Urol. 1946, 18, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roffman, C.E.; Buchanan, J.; Allison, G.T. Charlson Comorbidities Index. J. Physiother. 2016, 62, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, D.A.; Kaouk, J.; Zeinab, M.A.; Ferguson, E.L.; Abramczyk, E.; Wright, H.C.; Pramod, N.; De, S. Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate vs Transvesical Single-port Robotic Simple Prostatectomy for Large Prostatic Glands. Urology 2023, 181, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Alzweri, L.; Rai, B.P.; Somani, B.K.; Bates, C.; Aboumarzouk, O.M. Holmium laser enucleation versus simple prostatectomy for treating large prostates: Results of a systemic review and metaanalysis. Arab. J. Urol. 2016, 14, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assmus, M.A.; Large, T.; Lee, M.S.; Agarwal, D.K.; Rivera, M.E.; Krambeck, A.E. Same-Day Discharge Following Holmium Laser Enucleation in Patients Assessed to Have Large Gland Prostates (≥175 cc). J. Endourol. 2021, 35, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, D.K.; Rivera, M.E.; Nottingham, C.U.; Large, T.; Krambeck, A.E. Catheter Removal on the Same Day of Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate: Outcomes of a Pilot Study. Urology 2020, 146, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauhar, V.; Gilling, P.; Pirola, G.M.; Chan, V.W.-S.; Lim, E.J.; Maggi, M.; Teoh, J.Y.-C.; Krambeck, A.; Castellani, D. Does MOSES Technology Enhance the Efficiency and Outcomes of Standard Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate? Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Comparative Studies. Eur. Urol. Focus 2022, 8, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.W.; El Tayeb, M.M.; Borofsky, M.S.; Dauw, C.A.; Wagner, K.R.; Lowry, P.S.; Bird, E.T.; Hudson, T.C.; Lingeman, J.E. Comparison of Perioperative Outcomes Between Holmium Laser Enu-cleation of the Prostate and Robot-Assisted Simple Prostatectomy. J. Endourol. 2017, 31, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricard, T.; Xia, S.; Xiao, D.; Tong, Z.; Gaillard, V.; Sun, J. Outcomes of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) for very large-sized benign prostatic hyperplasia (over 150 mL): Open simple prostatectomy is dead. World J. Urol. 2023, 41, 2249–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalewski, K.-F.; Hartung, F.O.; von Hardenberg, J.; Haney, C.M.; Kriegmair, M.C.; Nuhn, P.; Patroi, P.; Westhoff, N.; Honeck, P.; Herrmann, T.R.; et al. Robot-Assisted Simple Prostatectomy vs Endoscopic Enucleation of the Prostate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Trials. J. Endourol. 2022, 36, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.C.; Park, J.H.; Jeong, M.S.; Yi, J.; Ku, J.H.; Oh, S.; Kim, S.W.; Paick, J. Predictor of de novo urinary incontinence following holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2011, 30, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Yano, M.; Nakayama, T.; Kitahara, S. Predictive risk factors of postoperative urinary incontinence following holmium laser enucleation of the prostate during the initial learning period. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2016, 42, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, A.M.; Brassetti, A.; Ochoa, M.; Anceschi, U.; D’Annunzio, S.; Ferriero, M.; Tuderti, G.; Misuraca, L.; Mastroianni, R.; Cartolano, S.; et al. Robotic simple prostatectomy vs HOLEP, a “multi single-center” experiences comparison. Cent. European J. Urol. 2023, 76, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, N.; Zargar, H.; Sanchez-Salas, R.; Castillo, O.; Celia, A.; Gallo, G.; Sivaraman, A.; Cathelineau, X.; Autorino, R. Robot-assisted versus standard laparoscopy for simple prostatectomy: Multicenter comparative outcomes. Urology 2016, 91, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umari, P.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Pokorny, M.; De Groote, R.; Geurts, N.; Goossens, M.; Schatterman, P.; De Naeyer, G.; Mottrie, A. Robotic Assisted Simple Prostatectomy versus Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Patients with Large Volume Prostate: A Comparative Analysis from a High Volume Center. J. Urol. 2017, 197, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agreda Castañeda, F.; Buisan Rueda, Ó.; Areal Calama, J.J. The complications of the HoLEP learning curve. A systematic review. Actas Urol. Esp. 2020, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmansy, H.M.; Kotb, A.; Elhilali, M.M. Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate: Long-Term Durability of Clinical Outcomes and Complication Rates During 10 Years of Followup. J. Urol. 2011, 186, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, S.; Abreu, A.L.d.C.; Chopra, S.; Ramos, P.; Park, D.; Berger, A.K.; Desai, M.M.; Gill, I.S.; Aron, M. Transvesical Robotic Simple Prostatectomy: Initial Clinical Experience. Eur. Urol. 2014, 66, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.A.; Krol, B.C.; Crain, N.A.; Hemal, A.K. Robot-Assisted Simple Prostatectomy: A Comparison of Primary Simple Prostatectomy vs Salvage Simple Prostatectomy in Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. J. Endourol. 2023, 37, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagaskar, V.G.; Zaytoun, O.; Kale, P.; Pedraza, A.; Haines, K., 3rd; Tewari, A. Robot-assisted simple prostatectomy for prostates greater than 100 g. World J. Urol. 2023, 41, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestler, S.; Bach, T.; Herrmann, T.; Jutzi, S.; Roos, F.C.; Hampel, C.; Thüroff, J.W.; Thomas, C.; Neisius, A. Surgical treatment of large volume prostates: A matched pair analysis comparing the open, endoscopic (ThuVEP) and robotic approach. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1927–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschovas, M.C.; Timóteo, F.; Lins, L.; Neves, O.d.C.; Bhat, K.R.S.; Patel, V.R. Robotic surgery techniques to approach benign prostatic hyperplasia disease: A comprehensive literature review and the state of art. Asian J. Urol. 2021, 8, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enikeev, D.; Morozov, A.; Taratkin, M.; Misrai, V.; Rijo, E.; Podoinitsin, A.; Gabdullina, S.; Herrmann, T.R.W. Systematic review of the endoscopic enucleation of the prostate learning curve. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 2427–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Assmus, M.A.; Ganesh, M.; Han, J.; Helon, J.; Mai, Q.; Mi, X.; Krambeck, A.E. An outcomes comparison between holmium laser enucleation of the prostate, open simple prostatectomy, and robotic simple prostatectomy for large gland benign prostatic hypertrophy. Urology 2023, 173, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunckhorst, O.; Ahmed, K.; Nehikhare, O.; Marra, G.; Challacombe, B.; Popert, R. Evaluation of the Learning Curve for Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate Using Multiple Outcome Measures. Urology 2015, 86, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, A.; Lima, E. Urethra-sparing minimally invasive simple prostatectomy: An old technique revisited. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2021, 31, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wymer, K.M.; Narang, G.; Slade, A.; Sharma, V.; Thao, V.; Borah, B.J.; Rivera, M.; Cheney, S.; Humphreys, M.R. Evaluation of the Cost-Effectiveness of Surgical Treatment Options for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Urology 2022, 171, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, D.V.; Brescia, A.; Mazzoleni, F.; Spinelli, M.; Musi, G.; Melegari, S.; Galasso, G.; Detti, S.; de Cobelli, O. Robot-assisted simple prostatectomy (RASP): Does it make sense? BJU Int. 2012, 110, E972–E979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, D.E.; Perez, D.S.; Weeks, D.C. Robot-Assisted Simple Prostatectomy for Severe Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Endourol. 2011, 25, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszczak, M.; Schalken, J.A.; Salagierski, M. Prostate Cancer Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers’ Clinical Utility in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HoLEP 1 (95 Patients) | RASP (50 Patients) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age Mean (SD) | 72.36 (8.92) | 72.4 (7.78) | 0.978 |
| Charlson index Mean (SD) | 3.54 (1.09) | 3.46 (1.36) | 0.712 |
| Prior urological surgery and/or pelvic RT (%) | 0 | 10% | 0.004 |
| Prostatic volume (cm3) Mean (SD) | 187.72 (45.91) | 203.38 (98.06) | 0.192 |
| Prior urethral catheter (%) | 42.1% | 20% | 0.013 |
| Qmax (mL/s) Mean (SD) | 10.89 (5.84) | 8.12 (3.46) | 0.002 |
| IPSS score Mean (SD) | 21.66 (4.9) | 21.92 (4.9) | 0.765 |
| PSA Mean (SD) | 8.73 (8) | 7.73 (4.21) | 0.414 |
| Haemoglobin (g/dL) Mean (SD) | 14.41 (1.57) | 14.41 (1.52) | 0.998 |
| HoLEP 1 | RASP | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical time (minutes) Mean (SD) | 97.58 (39.83) | 122.4 (25.13) | <0.01 |
| Enucleated gland weight (g) Mean (SD) | 124.85 (51.1) | 129.6 (102.53) | 0.712 |
| Surgical efficiency (g/min) Mean (SD) | 1.28 | 1.06 | 0.01 |
| HoLEP 1 | RASP | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital stay (days) Mean (SD) | 3.46 (2.67) | 4.22 (1.94) | 0.079 |
| Catheterization time (days) Mean (SD) | 3.6 (2) | 5.9 (0.9) | 0.01 |
| PSA Mean (SD) | 0.96 (1.44) | 0.8 (0.7) | 0.462 |
| Qmax (mL/s) Mean (SD) | 29.91 (11.62) | 23.6 (6.66) | <0.001 |
| IPSS Score Mean (SD) | 6.64 (5.40) | 4 (3.49) | 0.002 |
| Good quality of life (%) | 83.2% | 94% | 0.075 |
| Haemoglobin (g/dL) Mean (SD) | 12.29 (2.24) | 11.71 (1.49) | 0.104 |
| Hospital stay (days) Mean (SD) | 3.46 (2.67) | 4.22 (1.94) | 0.079 |
| Clavien–Dindo System [8] | Type of Complication | n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Grade I | - | 0 |
| UTI 1 | 5 (5.15) | |
| Grade II | Mild Haematuria | 2 (2.1) |
| Significant haematuria + transfusion | 8 (8.2) | |
| Grade III | - | 0 |
| Conversion to an open approach | 3 (3.09) |
| Clavien–Dindo System [8] | Type of Complication | n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Grade I | Wound dehiscence Wound bleeding | 1 (2) 2 (4) |
| Grade II | UTI 1 | 6 (12) |
| Significant haematuria + transfusion | 3 (6) | |
| Grade III | pneumothorax | 1 (2) |
| Conversion to an open approach | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juste-Alvarez, S.; Zaccaro, C.; Gil-Moradillo, J.; Romero-Otero, J.; Moncada, I.; Rodríguez-Antolín, A.; Garcia-Gomez, B. Minimally Invasive Techniques for Large-Volume Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comparative Study Between HoLEP and Robotic Simple Prostatectomy. Surg. Tech. Dev. 2025, 14, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14020017
Juste-Alvarez S, Zaccaro C, Gil-Moradillo J, Romero-Otero J, Moncada I, Rodríguez-Antolín A, Garcia-Gomez B. Minimally Invasive Techniques for Large-Volume Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comparative Study Between HoLEP and Robotic Simple Prostatectomy. Surgical Techniques Development. 2025; 14(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuste-Alvarez, Silvia, Claudia Zaccaro, Javier Gil-Moradillo, Javier Romero-Otero, Ignacio Moncada, Alfredo Rodríguez-Antolín, and Borja Garcia-Gomez. 2025. "Minimally Invasive Techniques for Large-Volume Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comparative Study Between HoLEP and Robotic Simple Prostatectomy" Surgical Techniques Development 14, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14020017
APA StyleJuste-Alvarez, S., Zaccaro, C., Gil-Moradillo, J., Romero-Otero, J., Moncada, I., Rodríguez-Antolín, A., & Garcia-Gomez, B. (2025). Minimally Invasive Techniques for Large-Volume Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comparative Study Between HoLEP and Robotic Simple Prostatectomy. Surgical Techniques Development, 14(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14020017






