Padua Prediction Score and Hospital-Acquired Proximal and Isolated Distal Deep Vein Thrombosis in Symptomatic Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting
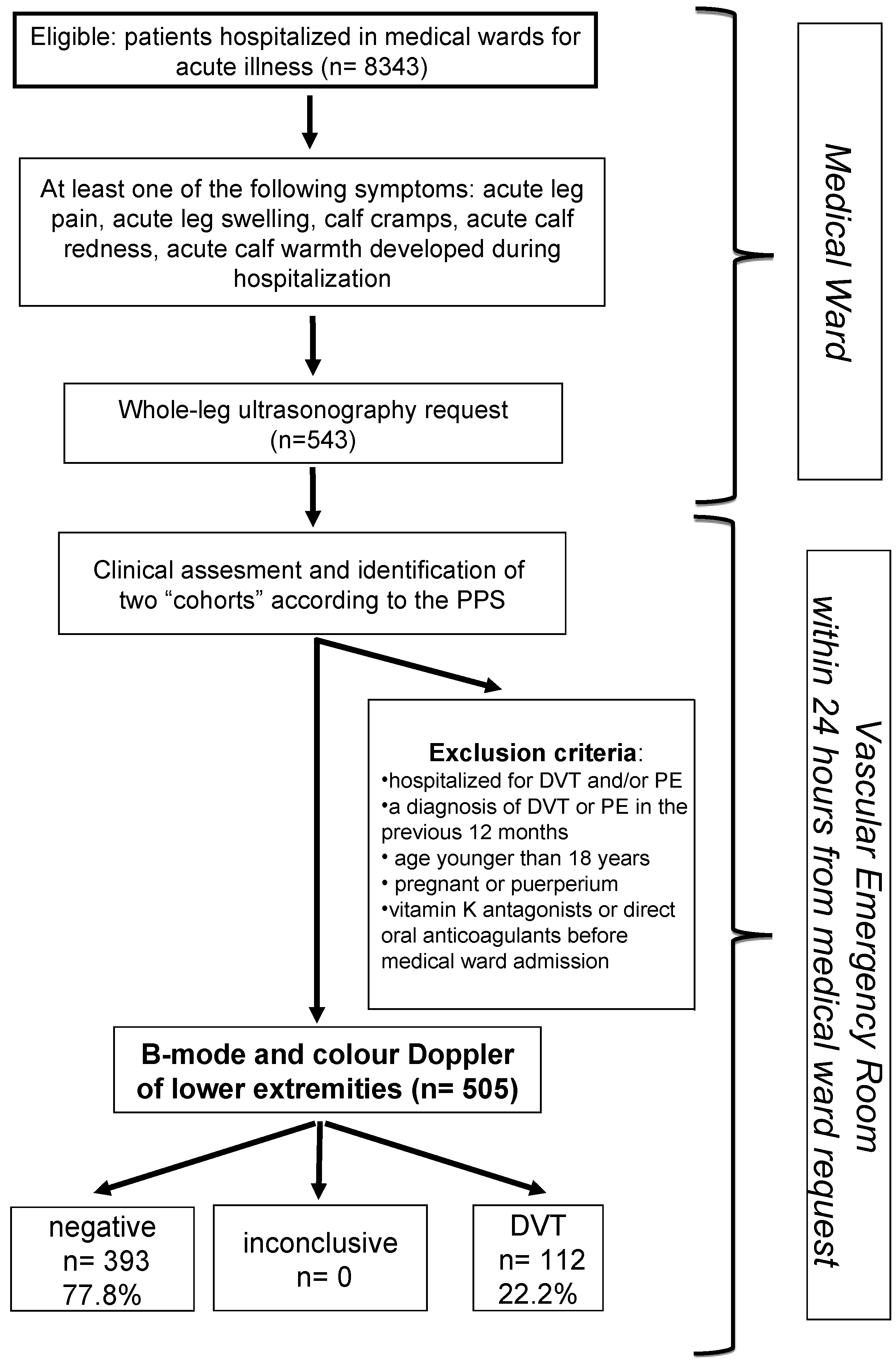
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Padua Prediction Score
2.5. Whole-Leg Ultrasonography Investigation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
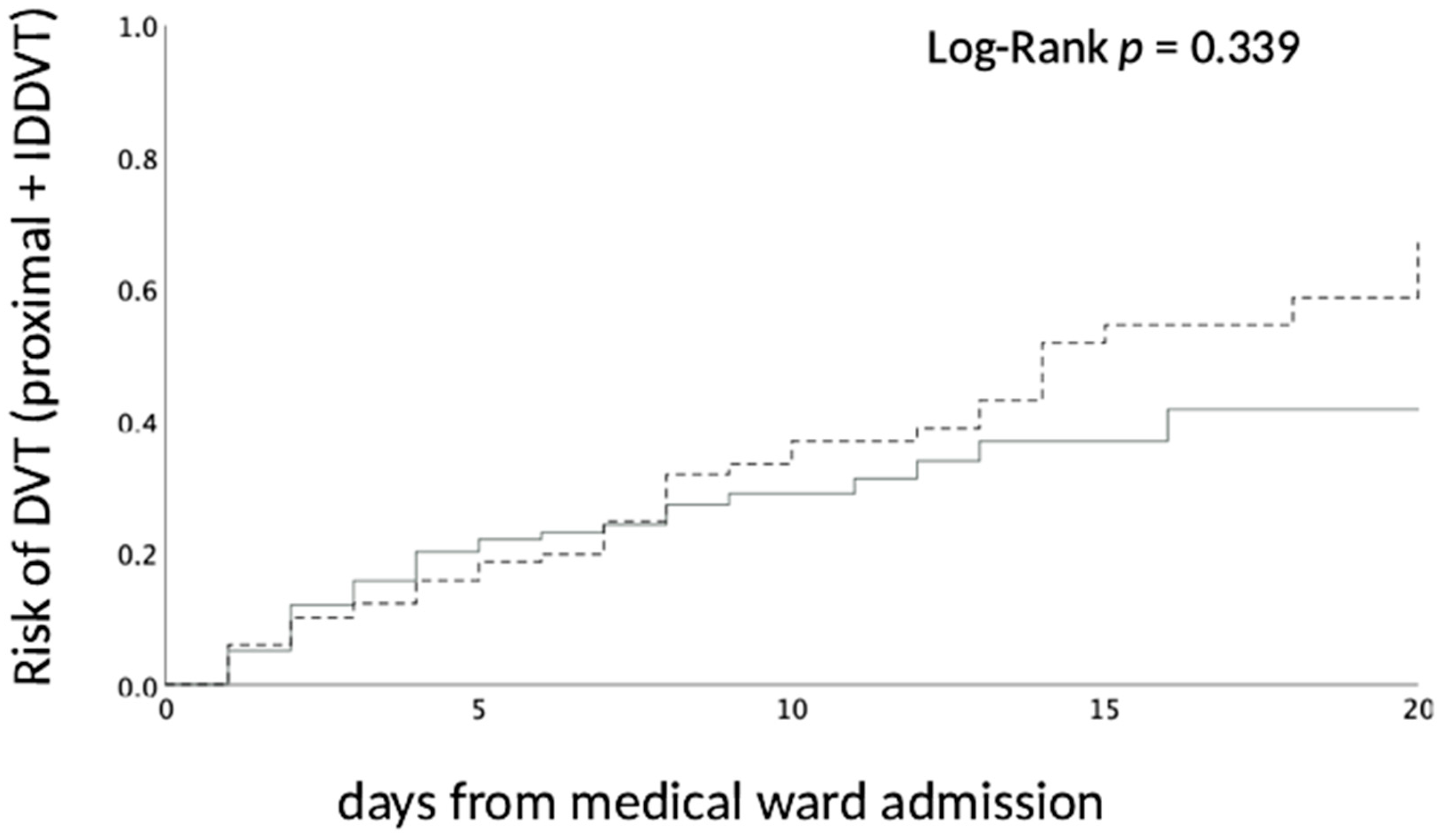
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobesh, P.P. Economic burden of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients. Pharmacotherapy 2009, 29, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, M.; Gabrielli, F.; Favaretto, E.; Filippini, M.; Migliaccio, L.; Cosmi, B. Proximal and isolated distal deep vein thrombosis and Wells score accuracy in hospitalized patients. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2019, 14, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.; Giustozzi, M.; Agnelli, G.; Becattini, C. Anticoagulation in patients with isolated distal deep vein thrombosis: A meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2017, 15, 1142–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.R.; Lim, W.; Dunn, A.S.; Cushman, M.; Dentali, F.; Akl, E.A.; Cook, D.J.; Balekian, A.A.; Klein, R.C.; Le, H.; et al. Prevention of VTE in nonsurgical patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012, 141 (Suppl. S2), e195S–e226S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbar, S.; Noventa, F.; Rossetto, V.; Ferrari, A.; Brandolin, B.; Perlati, M.; De Bon, E.; Tormene, D.; Pagnan, A.; Prandoni, P. A risk assessment model for the identification of hospitalized medical patients at risk for venous thromboembolism: The Padua Prediction Score. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2010, 8, 2450–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moumneh, T.; Riou, J.; Douillet, D.; Henni, S.; Mottier, D.; Tritschler, T.; Le Gal, G.; Roy, P.M. Validation of risk assessment models predicting venous thromboembolism in acutely ill medical inpatients: A cohort study. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2020, 18, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depietri, L.; Marietta, M.; Scarlini, S.; Marcacci, M.; Corradini, E.; Pietrangelo, A.; Ventura, P. Clinical impact of application of risk assessment models (Padua Prediction Score and Improve Bleeding Score) on venous thromboembolism, major hemorrhage and health expenditure associated with pharmacologic VTE prophylaxis: A “real life” prospective and retrospective observational study on patients hospitalized in a Single Internal Medicine Unit (the STIME study). Intern. Emerg. Med. 2018, 13, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schünemann, H.J.; Cushman, M.; Burnett, A.E.; Kahn, S.R.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Spencer, F.A.; Rezende, S.M.; Zakai, N.A.; Bauer, K.A.; Dentali, F.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Prophylaxis for hospitalized and nonhospitalized medical patients. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 3198–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, M.; Lessiani, G.; Favaretto, E.; Migliaccio, L.; Iotti, M.; Giusto, L.; Ghirarduzzi, A.; Palareti, G.; Cosmi, B. Ultrasound Characteristics of Calf Deep Vein Thrombosis and Residual Vein Obstruction After Low Molecular Weight Heparin Treatment. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 52, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, J.A.; Silverstein, M.D.; Mohr, D.N.; Petterson, T.M.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Melton, L.J., 3rd. Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: A population-based case-control study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, J.A.; Melton, L.J., 3rd; Lohse, C.M.; Petterson, T.M.; Silverstein, M.D.; Mohr, D.N.; O’Fallon, W.M. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients vs community residents. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2001, 76, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffredo, L.; Vidili, G.; Sciacqua, A.; Cogliati, C.; Di Giulio, R.; Bernardini, S.; Ciacci, P.; Pietrangelo, A.; Orlando, F.; Paraninfi, A.; et al. AURELIO Study Group. Asymptomatic and symptomatic deep venous thrombosis in hospitalized acutely ill medical patients: Risk factors and therapeutic implications. Thromb. J. 2022, 30, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandor, A.; Tonkins, M.; Goodacre, S.; Sworn, K.; Clowes, M.; Griffin, X.L.; Holland, M.; Hunt, B.J.; de Wit, K.; Horner, D. Risk assessment models for venous thromboembolism in hospitalised adult patients: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardi, M.; Ghanem-Zoubi, N.O.; Zidan, R.; Yurin, V.; Bitterman, H. Venous thromboembolism and the utility of the Padua Prediction Score in patients with sepsis admitted to internal medicine departments. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2013, 11, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nendaz, M.; Spirk, D.; Kucher, N.; Aujesky, D.; Hayoz, D.; Beer, J.H.; Husmann, M.; Frauchiger, B.; Korte, W.; Wuillemin, W.A.; et al. Multicentre validation of the Geneva Risk Score for hospitalised medical patients at risk of venous thromboembolism. Explicit ASsessment of Thromboembolic RIsk and Prophylaxis for Medical PATients in SwitzErland (ESTIMATE). Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 111, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Tang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Yan, Y.; Liang, B.; Wang, K.; Ou, X.; et al. Validation of a venous thromboembolism risk assessment model in hospitalized chinese patients: A case-control study. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2014, 21, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, W.; Lu, G. Comparison between Caprini and Padua risk assessment models for hospitalized medical patients at risk for venous thromboembolism: A retrospective study. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 23, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, P.; Khanna, R.; Dudley, A.; Davies, J.; Jacolbia, R.; McArthur, K.; Auerbach, A.D. Automating Venous Thromboembolism Risk Calculation Using Electronic Health Record Data upon Hospital Admission: The Automated Padua Prediction Score. J. Hosp. Med. 2017, 12, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincentelli, G.M.; Timpone, S.; Murdolo, G.; Fusco Moffa, I.; L’angiocola, P.D.; Borgognoni, F.; Monti, M. A new risk assessment model for the stratification of the thromboembolism risk in medical patients: The TEVere Score. Minerva Medica 2018, 109, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.Q.; Liu, S.H.; Hong, X.Y.; Sun, X.F.; Shi, J.H. Comparing different venous thromboembolism risk assessment machine learning models in Chinese patients. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2020, 26, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayssen, H.; Sahoo, S.; Nguyen, P.; Mayorga-Carlin, M.; Siddiqui, T.; Englum, B.; Slejko, J.F.; Mullins, C.D.; Yesha, Y.; Sorkin, J.D.; et al. Ability of Caprini and Padua risk-assessment models to predict venous thromboembolism in a nationwide Veterans Affairs study. Journal of vascular surgery. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2024, 12, 101693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, M.; Borgese, L.; Favaretto, E.; Lasala, E.; Bortolotti, R.; Cosmi, B. Age-adjusted D-dimer, clinical pre-test probability-adjusted D-dimer, and whole leg ultrasound in ruling out suspected proximal and calf deep venous thrombosis. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 1772–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanaud, J.P.; Quenet, S.; Rivron-Guillot, K.; Quere, I.; Sanchez Muñoz-Torrero, J.F.; Tolosa, C.; Monreal, M.; Riete Investigators. Comparison of the clinical history of symptomatic isolated distal deep-vein thrombosis vs. proximal deep vein thrombosis in 11 086 patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2009, 7, 2028–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forgo, G.; Micieli, E.; Ageno, W.; Castellucci, L.A.; Cesarman-Maus, G.; Ddungu, H.; De Paula, E.V.; Dumantepe, M.; Guillermo Esposito, M.C.; Konstantinides, S.V.; et al. An update on the global use of risk assessment models and thromboprophylaxis in hospitalized patients with medical illnesses from the World Thrombosis Day steering committee: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2022, 20, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Goodacre, S.; Horner, D.; Pandor, A.; Holland, M.; de Wit, K.; Hunt, B.J.; Griffin, X.L. Effectiveness and cost effectiveness of pharmacological thromboprophylaxis for medical inpatients: Decision analysis modelling study. BMJ Med. 2024, 3, e000408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.A.; Stevens, S.M.; Woller, S.C.; Lake, E.; Donadini, M.; Cheng, J.; Labarère, J.; Douketis, J.D. Risk of deep vein thrombosis following a single negative whole-leg compression ultrasound: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2010, 303, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevestre, M.A.; Labarère, J.; Casez, P.; Bressollette, L.; Haddouche, M.; Pernod, G.; Quéré, I.; Bosson, J.L. Outcomes for inpatients with normal findings on whole-leg ultrasonography: A prospective study. Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age, mean (SD), year | 78.0 (13.3) |
| Female sex | 300 (59.2) |
| BMI mean (SD), kg/m2 | 25.4 (4.8) |
| Reduced mobility | 258 (50.9) |
| Active cancer | 113 (22.3) |
| Previous VTE | 70 (13.8) |
| Acute infection/rheumatologic disorder | 242 (47.7) |
| COPD | 98 (19.3) |
| Heart Failure | 78 (15.4) |
| Recent Trauma | 73 (14.4) |
| Stroke | 59 (11.4) |
| Myocardial infarction | 15 (3.0) |
| Hormonal treatment | 13 (2.6) |
| Thrombophilia | 7 (1.4) |
| ICU stay | 0 (0) |
| Hospitalization days at the time of LEUS, mean (SD), d | 5.2 (6.2) |
| Pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis used $ | 282 (55.6) |
| PPS | Low Risk VTE (<4) | High Risk VTE (≥4) | p vs. Low Risk VTE | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 301 (59.2) | 204 (40.2) | 505 (100) | |
| DVT, n (%) | 56 (18.6) | 56 (27.5) | 0.019 | 112 (22.2) |
| proximal DVT, n (%) | 21 (7.0) | 26 (12.7) | 0.029 | 47 (9.3) |
| IDDVT, n (%) | 35 (11.6) | 30 (14.7) | 0.311 | 65 (12.9) |
| Prophylaxix, n (%) | 163 (54.2) | 118 (57.8) | 0.413 | 281 (55.6) |
| PPS | <4 (Low Risk VTE) | ≥4 (High Risk VTE) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prophylaxis − | Prophylaxis + | Prophylaxis − | Prophylaxis + | |
| DUS Negative | 11 (80.4) | 134 (82.2) | 60 (69.8) | 88 (74.6) |
| IDDVT | 16 (11.6) | 19 (11.7) | 16 (18.6) | 14 (11.9) |
| DVT | 11 (8.0) | 10 (6.1) | 10 (11.6) | 16 (13.6) |
| Total DVT | 27 (19.6) | 29 (17.8) | 26 (30.2) | 30 (25.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sartori, M.; Fiocca, M.; Soldati, M.; Borgese, L.; Favaretto, E.; Cosmi, B. Padua Prediction Score and Hospital-Acquired Proximal and Isolated Distal Deep Vein Thrombosis in Symptomatic Patients. Hematol. Rep. 2024, 16, 568-578. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep16040055
Sartori M, Fiocca M, Soldati M, Borgese L, Favaretto E, Cosmi B. Padua Prediction Score and Hospital-Acquired Proximal and Isolated Distal Deep Vein Thrombosis in Symptomatic Patients. Hematology Reports. 2024; 16(4):568-578. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep16040055
Chicago/Turabian StyleSartori, Michelangelo, Miriam Fiocca, Mario Soldati, Laura Borgese, Elisabetta Favaretto, and Benilde Cosmi. 2024. "Padua Prediction Score and Hospital-Acquired Proximal and Isolated Distal Deep Vein Thrombosis in Symptomatic Patients" Hematology Reports 16, no. 4: 568-578. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep16040055
APA StyleSartori, M., Fiocca, M., Soldati, M., Borgese, L., Favaretto, E., & Cosmi, B. (2024). Padua Prediction Score and Hospital-Acquired Proximal and Isolated Distal Deep Vein Thrombosis in Symptomatic Patients. Hematology Reports, 16(4), 568-578. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep16040055







