Genomic and Phylogenetic Evidence for a Novel Emaravirus Infecting Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) in Amazonas, Peru
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Samples
2.2. Next-Generation Sequencing, Sequence Assembly, and Annotation
2.3. Phylogenetic and Protein Structure Analysis
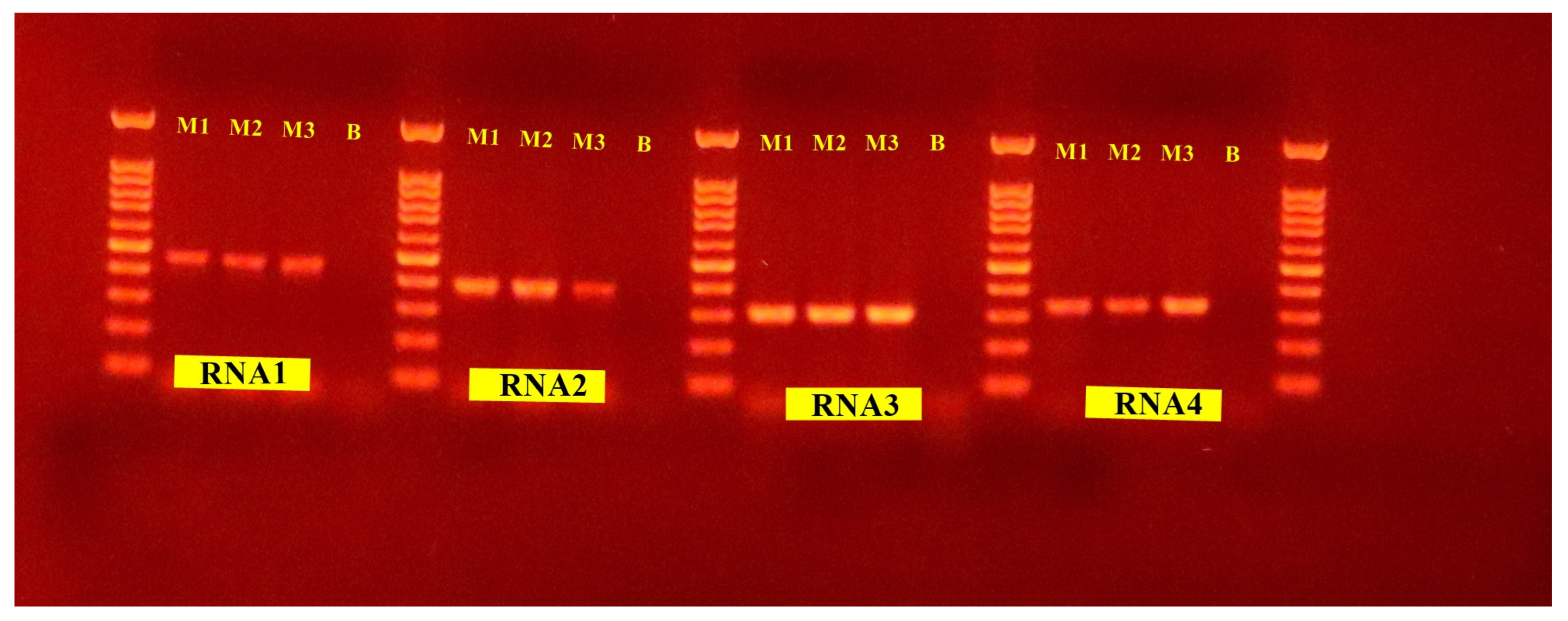
2.4. Occurrence of the Novel Virus in Native Cacao Accessions
3. Results
3.1. Virus Identification by High Throughput Sequencing
3.2. Genome Structure and Encoded Proteins
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of the New Emaravirus
3.4. Validation of the Presence of Novel Virus in Native Accessions of Cacao
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Souza, P.A.; Moreira, L.F.; Sarmento, D.H.A.; Da Costa, F.B. Cacao—Theobroma cacao. Exot. Fruits 2018, 3, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Vega, R.; Nieto-Figueroa, K.H.; Oomah, B.D. Cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) pod husk: Renewable source of bioactive compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 81, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, V.H.; Zambrano, J.L.; Iglesias, C.; Rodríguez, E.; Villalobos, V.; Díaz, F.J.; Carrillo, N.; Gutiérrez, A.; Camacho, A.; Rodríguez, O. La Cadena de Valor del Cacao en América Latina y el Caribe. 2019. Available online: https://repositorio.iniap.gob.ec/bitstream/41000/5382/1/Informe%20CACAO.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2025).
- Díaz-Valderrama, J.R.; Leiva-Espinoza, S.T.; Aime, M.C. The history of cacao and its diseases in the Americas. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 1604–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huaman-Pilco, A.F.; Torres-De la Cruz, M.; Aime, M.C.; Leiva-Espinoza, S.T.; Oliva-Cruz, S.M.; Díaz-Valderrama, J.R. First report of thread blight caused by Marasmius tenuissimus on cacao (Theobroma cacao) in Peru. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaman-Pilco, A.F.; Ramos-Carrasco, T.A.; Franco, M.E.E.; Tineo-Flores, D.; Estrada-Cañari, R.; Romero, P.E.; Aguilar-Rafael, V.; Ramírez-Orrego, L.A.; Tincopa-Marca, R.; Márquez, F.R.; et al. Morphological, phylogenetic, and genomic evidence reveals the causal agent of thread blight disease of cacao in Peru is a new species of Marasmius in the section Neosessiles, Marasmius infestans sp. nov. F1000Research 2024, 12, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, G.K. Cocoa necrosis virus in Ghana. Trop. Agric. 1971, 48, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Brunt, A.A.; Kenten, R.H.; Gibbs, A.J.; Nixon, H.L. Further studies on cocoa yellow mosaic virus. Microbiology 1965, 38, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posnette, A.F. Virus diseases of cacao in Trinidad. Trop. Agric. 1947, 24, 127–130. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/pdf/10.5555/20063049488 (accessed on 11 November 2025).
- Chingandu, N.; Kouakou, K.; Aka, R.; Ameyaw, G.; Gutierrez, O.A.; Herrmann, H.W.; Brown, J.K. The proposed new species, cacao red vein virus, and three previously recognized badnavirus species are associated with cacao swollen shoot disease. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Sobrinho, R.; Ferro, M.M.M.; Nagata, T.; Puig, A.S.; Von Keith, C.; Britto, D.S.; Gutierrez, O.A.; Marelli, J.P.; Brown, J.K. Complete genome sequences of three newly discovered cacao mild mosaic virus isolates from Theobroma cacao L. in Brazil and Puerto Rico, and evidence for recombination. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2027–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandito, A.; Hartono, S.; Trisyono, Y.A.; Somowiyarjo, S. First report of cacao mild mosaic virus associated with cacao mosaic disease in Indonesia. New Dis. Rep. 2022, 45, e12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, E.; Ravel, S.; Agret, C.; Abrokwah, F.; Dzahini-Obiatey, H.; Galyuon, I.; Kouakou, K.; Jeyaseelan, E.C.; Allainguillaumen, J.; Wetten, A. Next-generation sequencing elucidates cacao badnavirus diversity and reveals the existence of more than ten viral species. Virus Res. 2018, 244, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelli, J.P.; Guest, D.I.; Bailey, B.A.; Evans, H.C.; Brown, J.K.; Junaid, M.; Barreto, R.W.; Lisboa, D.O.; Puig, A.S. Chocolate under threat from old and new cacao diseases. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 1331–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmedo-Velarde, A.; Park, A.C.; Sugano, J.; Uchida, J.Y.; Kawate, M.; Borth, W.B.; Hu, J.S.; Melzer, M.J. Characterization of Ti ringspot-associated virus, a novel emaravirus associated with an emerging ringspot disease of Cordyline fruticosa. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digiaro, M.; Elbeaino, T.; Kubota, K.; Ochoa-Corona, F.M.; von Bargen, S. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Fimoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2024, 105, e001943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Hein, G.L.; Graybosch, R.A.; Tatineni, S. Octapartite negative-sense RNA genome of High Plains wheat mosaic virus encodes two suppressors of RNA silencing. Virology 2018, 518, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, N.; Muehlbach, H.P. A novel, multipartite, negative-strand RNA virus is associated with the ringspot disease of European mountain ash (Sorbus aucuparia L.). J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laney, A.G.; Keller, K.E.; Martin, R.R.; Tzanetakis, I.E. A discovery 70 years in the making: Characterization of the rose rosette virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Song, Y.; Cao, M.J.; Cheng, Q.; Wu, J.X.; Hu, T. Identification of a novel emaravirus infecting lilac through next-generation sequencing. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2064–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peracchio, C.; Forgia, M.; Chiapello, M.; Vallino, M.; Turina, M.; Ciuffo, M. A complex virome including two distinct emaraviruses associated with virus-like symptoms in Camellia japonica. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 197964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, K.; Yanagisawa, H.; Chiaki, Y.; Yamasaki, J.; Horikawa, H.; Tsunekawa, K.; Morita, Y.; Kadono, F. Complete nucleotide sequence of chrysanthemum mosaic-associated virus, a novel emaravirus infecting chrysanthemum. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGavin, W.J.; Mitchell, C.; Cock, P.J.A.; Wright, K.M.; MacFarlane, S.A. Raspberry leaf blotch virus, a putative new member of the genus Emaravirus, encodes a novel genomic RNA. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Navarro, B.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhu, C.; Wang, L.; Di Serio, F.; Hong, N. Actinidia chlorotic ringspot-associated virus: A novel emaravirus infecting kiwifruit plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 18, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Di Bello, P.L.; Keller, K.E.; Martin, R.R.; Sabanadzovic, S.; Tzanetakis, I.E. A new, widespread emaravirus discovered in blackberry. Virus Res. 2017, 235, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzkan, N.; Chiumenti, M.; Massart, S.; Sarpkaya, K.; Karadağ, S.; Minafra, A. A new emaravirus discovered in Pistacia from Turkey. Virus Res. 2019, 263, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; Han, T.; Fu, J.; Di Serio, F.; Cao, M. Identification and characterization of a novel emaravirus associated with jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) yellow mottle disease. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Waqas, M.; Hong, N.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; et al. Identification and characterization of a pear chlorotic leaf spot-associated virus, a novel emaravirus causing severe disease in pear trees in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2786–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeaino, T.; Digiaro, M.; Martelli, G.P. Complete nucleotide sequence of four RNA segments of fig mosaic virus. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatineni, S.; Hein, G.L. High Plains wheat mosaic virus: An enigmatic disease of wheat and corn causing the High Plains disease. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeaino, T.; Digiaro, M.; Uppala, M.; Sudini, H. Deep sequencing of pigeonpea sterility mosaic virus discloses five RNA segments related to emaraviruses. Virus Res. 2014, 188, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, M.; Avelar, S.; Schuch, U.K.; Brown, J.K. First report of an emaravirus associated with witches’ broom disease and eriophyid mite infestations of the blue palo verde tree in Arizona. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Bargen, S.; Al Kubrusli, R.; Gaskin, T.; Fürl, S.; Hüttner, F.; Blystad, D.R.; Karlin, D.G.; Jalkanen, R.; Büttner, C. Characterisation of a novel emaravirus identified in mosaic-diseased Eurasian aspen (Populus tremula). Ann. Appl. Biol. 2020, 176, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumbou, A.; Candresse, T.; Von Bargen, S.; Büttner, C. Next-generation sequencing reveals a novel emaravirus in diseased maple trees from a German urban forest. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 621179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehanek, M.; Von Bargen, S.; Bandte, M.; Karlin, D.G.; Büttner, C. A novel emaravirus comprising five RNA segments is associated with ringspot disease in oak. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Yu, M.C.; Cao, M.; Yang, C. A putative new emaravirus isolated from Ailanthus altissima (Mill.) Swingle with severe crinkle symptoms in China. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 2403–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskin, T.R.; Tischendorf, M.; Günther, I.; Rehanek, M.; Büttner, C.; von Bargen, S. Characterization of a novel emaravirus affecting ash species (Fraxinus spp.) in Europe. Forests 2021, 12, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bello, P.L.; Laney, A.G.; Druciarek, T.; Ho, T.; Gergerich, R.C.; Keller, K.E.; Martin, R.R.; Tzanetakis, I.E. A novel emaravirus is associated with redbud yellow ringspot disease. Virus Res. 2016, 222, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, K.; Usugi, T.; Tomitaka, Y.; Shimomoto, Y.; Takeuchi, S.; Kadono, F.; Yanagisawa, H.; Chiaki, Y.; Tsuda, S. Perilla mosaic virus is a highly divergent emaravirus transmitted by Shevtchenkella sp. (Acari: Eriophyidae). Phytopathology 2020, 110, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomoto, Y.; Okada, T.; Ikeda, K.; Tatara, A.; Hasegawa, Y.; Yanagisawa, H.; Takeyama, S.; Hayashi, K.; Yano, K.; Morita, Y.; et al. Japanese star anise ringspot-associated virus is a distinct emaravirus transmitted by the eriophyid mite (family Diptilomiopidae). J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2022, 88, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; An, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Cao, M. Detection and characterization of a putative emaravirus infecting Clematis brevicaudata DC. in China. Arch. Virol. 2024, 169, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidharthan, V.K.; Chaturvedi, K.K.; Baranwal, V.K. Diverse RNA viruses in a parasitic flowering plant (spruce dwarf mistletoe) revealed through RNA-seq data mining. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2022, 88, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaman-Pilco, A.F.; Tineo, D.; Guelac-Santillan, M.; Zamorano, A.; Bustamante, D.E. First report of babaco virus Q infecting babaco (Vasconcellea heilbornii) in Amazonas, Peru. New Dis. Rep. 2025, 52, e70046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Hurtado-Gonzales, O.P.; Adhikari, B.N.; French-Monar, R.D.; Malapi, M.; Foster, J.A.; McFarland, C.D. PhytoPipe: A phytosanitary pipeline for plant pathogen detection and diagnosis using RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Schwartz, T.; Pickett, B.E.; He, S.; Klem, E.B.; Scheuermann, R.H.; Passarotti, M.; Kaufman, S.; O’Leary, M.A. A RESTful API for access to phylogenetic tools via the CIPRES science gateway. Evol. Bioinform. 2015, 11, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S. Next-generation sequencing in clinical virology: Discovery of new viruses. World J. Virol. 2015, 4, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, D.E.; Motilal, L.A.; Calderon, M.S.; Mahabir, A.; Oliva, M. Genetic diversity and population structure of fine aroma cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) from north Peru revealed by single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 895056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, F.; Hu, G.; Shen, H.; Zhang, B.; Dong, Y. Identification and characterization of a novel emaravirus from grapevine showing chlorotic mottling symptoms. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 694601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Ma, L.; Tian, X.; Li, R.; Zhou, C.; Cao, M. Virome of Camellia japonica: Discovery and molecular characterization of new viruses of different taxa in camellias. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke-Ehret, N.; Mühlbach, H.P. Emaravirus: A novel genus of multipartite, negative strand RNA plant viruses. Viruses 2012, 4, 1515–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, A.N.; Navia, D.; De Lillo, E.; Ferragut, F.; Oliveira, A.R. The cacao bud mite, Aceria reyesi (Nuzzaci 1973)—Supplementary description, distribution and comparison with Gymnaceria cupuassu Oliveira, Rodrigues & Flechtmann 2012 (Acari: Eriophyidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 23, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Genomic Segment | Primer | Sequence 5′ to 3′ | Target Gene | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNA1 | ThC-EmRep-F ThC-EmRep-R | TCCAAACTGCTGATCCTGGA CAAGGGATCTGGGTCGTGAG | RNA polymerase | 456 |
| RNA2 | ThC-EmGly-F ThC-EmGly-R | ACATGGAGTTGCGAAGGTATT TGGTCCCCAACATCCATAAGC | Glycoprotein | 390 |
| RNA3 | ThC-EmNuc-F ThC-EmNuc-R | GGCTGAACAAATGGGATGCC AACACTCCTTCCACCAGCTG | Nucleocapsid | 310 |
| RNA4 | ThC-EmMP-F ThC-EmMP-R | TGTTGGTGGTATGGACTTCGA CCCACCATCCTGTAGCTGTT | Movement protein | 390 |
| RNA Genomic Segment | Consensus Length (nt) | Total Read Count | Average Coverage | BlastX | % Identity | Accession GenBank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNA1 | 7142 | 27,993 | 534.27 | AcCRaV | 46.35 | QJD14761 |
| RNA2 | 2225 | 16,074 | 979.44 | PPSMV2 | 33.23 | YP_009268865 |
| RNA3 | 1269 | 55,076 | 5755.23 | PaEV | 34.54 | QJX15716 |
| RNA4 | 1286 | 1578 | 201.82 | ASaV | 30.14 | CAA0079685 |
| Accession/Clone | District | Locality | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| INDES-24 | Cajaruro | La Concordia | yellow-mosaic |
| INDES-53 | Cajaruro | Diamante bajo | asymptomatic |
| INDES-65 | Cajaruro | Naranjos alto | yellow-mosaic |
| INDES-67 | Cajaruro | Naranjos alto | yellow-mottling |
| INIA-13 | La Peca | San Francisco | asymptomatic |
| INIA-20 | Bagua | El Tomaque | yellow-mottling, deformation |
| INIA-23 | Bagua | El Tomaque | yellow-mottling |
| INIA-35 | Copallin | Lluahuana | asymptomatic |
| INIA-107 | Imaza | Shushunga | yellow-mottling |
| TSH-565 (R1) | asymptomatic | ||
| TSH-565 (R2) | yellow-mosaic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huaman-Pilco, A.F.; Fiore, N.; Hurtado-Gonzales, O.P.; Carvalho Costa, L.; Hu, X.; Oliva-Cruz, M.; Díaz-Valderrama, J.R.; Zamorano, A. Genomic and Phylogenetic Evidence for a Novel Emaravirus Infecting Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) in Amazonas, Peru. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2025, 16, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16040142
Huaman-Pilco AF, Fiore N, Hurtado-Gonzales OP, Carvalho Costa L, Hu X, Oliva-Cruz M, Díaz-Valderrama JR, Zamorano A. Genomic and Phylogenetic Evidence for a Novel Emaravirus Infecting Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) in Amazonas, Peru. International Journal of Plant Biology. 2025; 16(4):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16040142
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuaman-Pilco, Angel F., Nicola Fiore, Oscar P. Hurtado-Gonzales, Larissa Carvalho Costa, Xiaojun Hu, Manuel Oliva-Cruz, Jorge R. Díaz-Valderrama, and Alan Zamorano. 2025. "Genomic and Phylogenetic Evidence for a Novel Emaravirus Infecting Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) in Amazonas, Peru" International Journal of Plant Biology 16, no. 4: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16040142
APA StyleHuaman-Pilco, A. F., Fiore, N., Hurtado-Gonzales, O. P., Carvalho Costa, L., Hu, X., Oliva-Cruz, M., Díaz-Valderrama, J. R., & Zamorano, A. (2025). Genomic and Phylogenetic Evidence for a Novel Emaravirus Infecting Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) in Amazonas, Peru. International Journal of Plant Biology, 16(4), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16040142







