Abstract
Common bean production is crucial in Western Kenya due to its economic, nutritional, environmental, and cultural importance. However, challenges such as diseases, especially viral diseases, cause significant crop losses. This study sought to identify potential biomarkers for BCMV and BCMNV viral diseases by analyzing small molecule metabolites in diseased common bean systems and gain an understanding of related metabolic pathways. Virus-free Rosecoco bean cultivars were planted and exposed to BCMV and BCMNV in specific regions, with healthy plants serving as controls. Diseased and healthy leaves were collected for metabolite extraction and analyzed using liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. A total of 354 metabolites were identified across seven pathways, with 51 upregulated metabolites, primarily from fatty acids, terpenoids, and alkaloids. Ten metabolites were differentially expressed, with the molecular structures of two successfully determined. These metabolites serve as potential biomarkers for viral disease detection, monitoring, and resistance in common beans. The findings highlight the role of fatty acids and terpenoids, as well as the importance of regional variability in plant hormone regulation in response to stress, suggesting that further research into these pathways will be essential for understanding plant defense mechanisms.
1. Introduction
Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) production is vital in Western Kenya due to its economic, nutritional, environmental, and cultural significance [1]. It provides an important source of income for smallholder farmers, supports regional trade, and contributes to food security by offering inexpensive, protein-rich food [2]. However, bean production in this region faces numerous constraints, including pests and diseases, climate change, poor soil fertility, limited access to quality seeds, inadequate market access, post-harvest losses, inadequate agricultural knowledge, and high input costs [3,4]. Viral diseases, particularly the Bean Common Mosaic Virus (BCMV), Bean Common Necrotic Virus (BCMNV) [5], and Bean Yellow Mosaic Virus (BYMV) among others, are known to cause substantial yield and quality losses of this crop. Many methods have been used to mitigate these diseases, such as integrated pest management (IPM), using resistant bean varieties, crop rotation, and proper spacing. Nonetheless, resource-limited farmers struggle to afford and implement these interventions.
Metabolomic profiling is emerging as an indispensable tool for understanding the biochemical responses of plants to various stressors [6], including viral infections. In Western Kenya, where smallholder farmers depend heavily on common beans for nutrition and income, viral diseases present a major threat to food security, particularly in areas with limited access to diagnostic tools, pest control, and agricultural extension services. There are two approaches in metabolomics. Targeted metabolomics is critical in understanding plant defense mechanisms and nutrition by comprehensively analyzing specific metabolites [7]. In addition, targeted metabolomics allows for the identification and quantification of key compounds such as phytohormones, secondary metabolites, and defense-related chemicals, which are produced by plants in response to biotic and abiotic stresses [8,9]. This approach has been used to identify metabolic pathways activated during stress responses, enabling the documentation of possible biomarkers for disease resistance [6,10] and improving our understanding of how plants defend themselves in the face of pathogens, pests, or environmental stressors [11]. In addition, targeted metabolomics offers insights into the composition of essential nutrients, including vitamins, amino acids, and minerals, present in plants [12,13]. By analyzing these metabolites, we can assess the nutritional value of crops [14], identify variations in nutrient levels across different plant varieties or growth conditions [15], and optimize agricultural practices to enhance crop yields and nutritional content [16]. Furthermore, developing crops with improved nutrient profiles or increased resistance to stress can contribute to food security and human health [17].
Untargeted metabolome profiling is important in understanding the biochemical intricacies linked with viral infections in common beans, particularly in resource-limited settings of Western Kenya. This approach encompasses a comprehensive analysis of a wide array of metabolites without prior specification of which molecules to target [18], consequently, providing an all-inclusive view of the metabolic alterations occurring post-infection [19]. By using cutting-edge techniques such as liquid chromatography mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance, various metabolic pathways that may be interrupted by viral pathogens can be identified and quantified [20,21]. Investigating the untargeted metabolome profiles of common beans affected by viral diseases can enhance our understanding of the plant’s stress response mechanisms and overall plant health. Such comprehensive profiling will not only improve our understanding of plant–pathogen interactions but also help in developing management approaches to improve crop resilience [22] in the affected regions.
Viral infections have been shown to disrupt plant growth and reproduction, resulting in significant modifications to plant metabolism [23,24]. These changes are thought to reflect the plant’s defense mechanisms, nutrient allocation, and overall physiological state [17,25]. However, many studies have pointed out that the full extent of these metabolic alterations and their implications for plant health and resistance mechanisms remain poorly understood, especially in the context of resource-poor farming systems. Furthermore, the lack of reliable and accessible diagnostic approaches makes it difficult for farmers to detect viral infections early, hindering timely intervention.
This study aimed to identify potential biomarkers for BCMV and BCMNV viral diseases by analyzing small molecule metabolites in diseased common bean systems and exploring the associated metabolic pathways. Targeted metabolomics focuses on specific metabolites, and enables the identification of metabolic markers related to disease presence and progression [26]. In contrast, untargeted metabolomics shall provide a broader view of the complete metabolome, revealing biochemical pathways and possible novel biomarkers [11]. By the integration of these approaches, the objective was to encompass a comprehensive range of metabolites, particularly emphasizing the identification of novel entities. Identifying specific biomarkers will enhance early detection and disease monitoring, while also contributing to breeding programs aimed at developing viral-resistant bean varieties, thereby improving crop resilience in resource-limited settings.
2. Methodology
Four study sites were selected within the Western Region of Kenya: Musasa (Vihiga 34°39′59.99″ E), Sichilayi (Kakamega 34°45′8.24″ E), Butula (Busia34°06′42.08″ E), and Tuti (Bungoma (0°34′ N, 34°32′ E). Temperatures in Western Kenya range from 14 °C to 18 °C minimum to 30 °C to 36 °C maximum year-round, with the heaviest rainfall in April and lowest in January, averaging between 1740 mm and 1940 mm annually, while the soils, mainly acrisols (utisols) and ferralsols (oxisols), are highly weathered and suffer from widespread nitrogen and phosphorus deficiencies. The study adopted a randomized complete block design (RCBD) methodology with three replications. The blocks were the two viruses under study. At these sites, the Rosecoco bean cultivar was planted, and subjected to mechanical inoculation [27] with BCMV and BCMNV viruses at the three-leaf stage. Control plots were established using virus-free Rosecoco seeds obtained from the Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO), Kenya, planted under similar conditions to serve as a baseline comparison (Figure 1). The inoculum for the mechanical transmission experiments was prepared from fresh or lyophilized leaves of common bean plants collected from the field and serologically ascertained to be infected with BCMV and BCMNV. The infected plant material was homogenized in potassium phosphate buffer (0.01 M, pH 7.0) at 1:5 (w/v). The homogenate was then filtered through muslin cloth to remove large debris, yielding a clarified inoculum. This inoculum was used immediately for vascular puncture inoculation. The leaves of the target plants were dusted with 400-mesh carborundum to facilitate virus entry by creating micro-abrasions on the leaf surface. Control plants were similarly dusted with carborundum but inoculated with phosphate buffer alone to ensure the validity of the experimental setup. For the control experiment, all plants were maintained in a greenhouse under controlled environmental conditions, with temperatures ranging from 25 to 30 °C, for 30 days. The plants were monitored daily for symptom development, and serological validation of virus acquisition was performed using ELISA tests with the relevant antisera.


Figure 1.
Common bean (Rosecoco cultivar) plants infected with BCMV and BCMNV viruses, growing in ex-perimental fields at different sites: (A) Sirende (Bungoma), (B) Musasa (Vihiga), (C) Sichilayi (Ka-kamega), and (D) Butula (Busia). (E) Control plants of Rosecoco beans not infected with BCMV or BCMNV. Scale 1:100.
Samples were collected at the near-flowering stage, consisting of 50 leaf samples (at least 10 from each of the 4 study sites) and 10 samples from virus-free controls. The samples were quickly snap-frozen with liquid nitrogen, stored at −80 °C, freeze-dried, and sent to the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena, Germany, for metabolome analysis.
2.1. Phytohormone and Untargeted Metabolome
The leaf samples collected were ground using a HG-600 Geno/Grinder® 2010 (Cole-Parmer, Metuchen, NJ, USA) for 60 s at 1150 strokes/min and extracted in 1 mL of extraction buffer (200 mL Milli-Q water and 800 mL HPLC grade MeOH) with standards (12.5 ng phytohormone IS) for 24 h, then centrifuged at 19,000× g for 20 min at 4 °C. About 600–700 µL of the supernatant was transferred into 1.8 mL autosampler vials and stored at −20 °C until analyzed. The filtrate obtained was analyzed using liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (LCMS-9030 qTOF, Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) to quantify metabolites at various intervals. Chromatographic separation was performed on a Shim-pack Velox C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm, 2.7 µm particle size) maintained at 55 °C (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan). A 3 µL injection volume was used for all samples, which were analyzed with a binary mobile phase: solvent A consisted of 0.1% formic acid in Milli-Q HPLC grade water (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), and solvent B was UHPLC grade methanol with 0.1% formic acid (Romil Ltd., Cambridge, UK). The analysis was conducted on a qTOF high-definition mass spectrometer operating in negative electrospray ionization mode. The instrument parameters included a nebulizer voltage of 4.0 kV, interface temperature of 300 °C, dry gas flow of 3 L/min, detector voltage of 1.8 kV, heat block temperature of 400 °C, DL temperature of 280 °C, and flight tube temperature of 42 °C. Ion fragmentation was induced using argon gas with collision energies of 30 eV and a 5 eV spread [28].
Data pre-processing was performed using XCMS, with HPLC/UHD qTOF parameters employing the centWave feature detection method. A maximum threshold of 15 ppm, a signal-to-noise ratio of 6, and prefilters for intensity and noise set to 100 and 3, respectively, were applied. Retention time correction was done using the Obiwarp method with profStep, while alignment required a minimum sample fraction of 0.5 and an m/z width of 0.015. The data were initially analyzed by visualizing the mass spectra and generating a feature table using MZmine v4.4.0, with parameters adjusted to optimize data processing. Feature quantification was normalized based on the original masses of the samples using custom Python scripts developed with pandas v2.2.3. Principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted using the PCA module from sklearn. decomposition. The differential expression of metabolites was assessed with the edgeR v4.0 package, and the results were visualized through volcano plots and heatmaps, generated using Python scripts built with matplotlib.pyplot.
The mascot generic format (mfg) files and metadata for the respective treatments were processed on the GNPS2 online platform for networking and Sirius v6 for spectral annotation. Spectral searches utilized libraries such as GNPS, Biocyc, CHEBI, COCONUT, DSSTox, Blood Exposome, FooDB, HMBD, HSDB, KEGG, KNApSAck, LOTUS, LipidMaps, Maconda, MeSH, MiMeDB, NORMAN, Plantcyc, PubChem, PubMed, SuperNatural, TeroMOL, and YMDB embedded in Sirius [29,30]. Metabolites were matched to GNPS2-linked databases and were putatively annotated or verified through searches in compound databases using their peak mass and isomeric SMILES. Further confirmation of annotations was carried out through literature searches of relevant studies. Metabolite concentrations were then analyzed to identify enriched metabolomic pathways. Pathway overrepresentation was assessed using a hypergeometric test.
2.2. Phytohormone Analysis
Phytohormone analysis was carried out by LC-MS/MS, following the method of [31] using an Agilent 1260 series HPLC system (Agilent Technologies), with modifications. A tandem mass spectrometer, QTRAP 6500 (SCIEX, Darmstadt, Germany), was used, and the chromatographic gradient was adjusted. Chromatographic separation was performed on a Zorbax Eclipse XDB-C18 column (50 × 4.6 mm, 1.8 µm, Agilent Technologies). The mobile phases were water with 0.05% formic acid (A) and acetonitrile (B). The elution profile was as follows: 0–0.5 min, 5% B; 0.5–9.5 min, 5–58% B; 9.5–9.51 min, 58–100% B; 9.52–11.0 min, 100% B; and 11.01–14.0 min, 5% B. The flow rate was maintained at 1.1 mL/min, and the column temperature was set to 25 °C. The mass spectrometer operated in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode in negative ionization mode.
The Mann–Whitney statistical test was conducted to evaluate whether the distributions of the two groups, sample and control, were different, focusing on the ranks of the values rather than their actual magnitudes.
3. Results
After analysis, a total of 354 metabolites were identified, although some could not be assigned to specific categories. These metabolites were mapped to seven metabolic pathways, with the highest number found in fatty acids (81), followed by shikimates and phenylpropanoids (77), while the carbohydrate pathway contained the least metabolites, totaling just 21. A significant number of metabolites were annotated to the terpenoid pathway (58) (Table 1).

Table 1.
The metabolic pathways and total metabolites upregulated and downregulated.
A total of 51 metabolites were upregulated, with the majority originating from the fatty acid pathway (16), followed by terpenoids and alkaloids, each containing 11 metabolites. Notably, no metabolites from the carbohydrate pathway were upregulated.
A total of 131 metabolites were downregulated, with the majority coming from the fatty acid pathway (53), followed by terpenoids (28). The least downregulated metabolites were from the carbohydrate pathway, with only one. The number of downregulated metabolites was greater than the number of upregulated metabolites, as shown in (Table 1 and Figure 2). Notably, a significant portion of metabolites remained unidentified, possibly due to a lack of characterization.
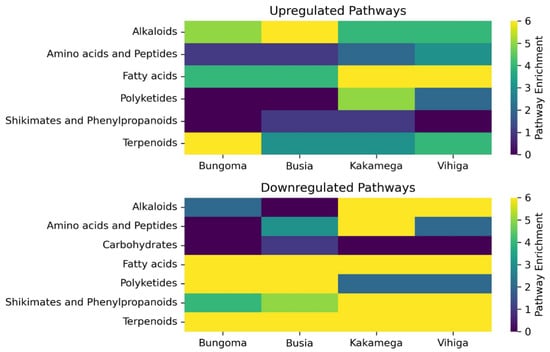
Figure 2.
The upregulated and downregulated pathways, along with the number of metabolites per pathway, are shown on the Y-axis, with the four counties studied represented on the X-axis.
The metabolite with the highest upregulation was monoterpenes (Mapping ID 11308) in Busia, Bungoma, and Vihiga counties (Figure 3A). The following metabolites were significantly downregulated in high concentrations in samples from Kakamega County: pseudoalkaloids (ID 11135), guanidine alkaloids (ID 8613), flavonoids (ID 4437), coumarins (ID 4371), and small peptides (ID 1659) (Figure 3A). In Bungoma County, the downregulated metabolites included triterpenoids (ID 11139), linear polyketides (ID 10826), flavonoids (ID 6843), and naphthalenes (ID 2022). In Busia County, flavonoids (ID 5823) and naphthalene (ID 2022) were the metabolites most downregulated in high concentrations. In Vihiga County, the metabolites showing high downregulation included triterpenoids (ID 11139), pseudoalkaloids (transamidation) (ID 11135), linear polyketides (IDs 11091 and 11089), coumarins (ID 4371), small peptides (ID 3165), phenylpropanoids (C-6-C3), and small peptides (ID 1659), as shown in Figure 3B.
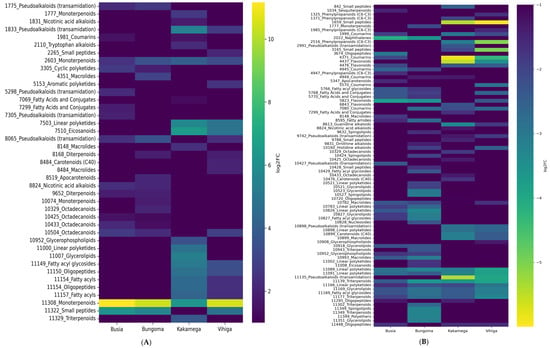
Figure 3.
(A) Upregulated metabolites on the Y-axis, with the corresponding concentrations and sample localities on the X-axis. (B) Downregulated metabolites on the Y-axis, along with their concentrations and sample localities on the X-axis.
In Kakamega County, the compound with the highest fold change was long-chain fatty acid (Mapping ID 10337), followed by Mapping ID 11148 (saccharo lipids), while the least significant metabolites were alpha-amino acid (Mapping ID 5776) and benzenoids (Mapping ID 8480) (Figure 4A). In Bungoma County, the metabolite with the highest fold change was thioesters (Mapping ID 11306), followed by phenolic glycosides (Mapping ID 3767), while the metabolites with the least fold change were Mapping ID 11030 (diterpenoids) and azocyclic compounds (Mapping ID 927) (Figure 4B). In Busia County, the metabolites with the highest fold change were monoterpenes (Mapping ID 11308) and phenolic glycosides (Mapping ID 3767), while the least significant metabolites were Mapping ID 10625 (amino acids and derivatives) and halogenated fatty acids (Mapping ID 11008) (Figure 4C). In Vihiga County, the metabolites with the highest fold change were monoternes (Mapping ID 11308) and toluene (Mapping ID 6331), while the metabolites with the least fold change were azolines (Mapping ID 4254) and tri-acylglycerols (Mapping ID 10918) (Figure 4D).
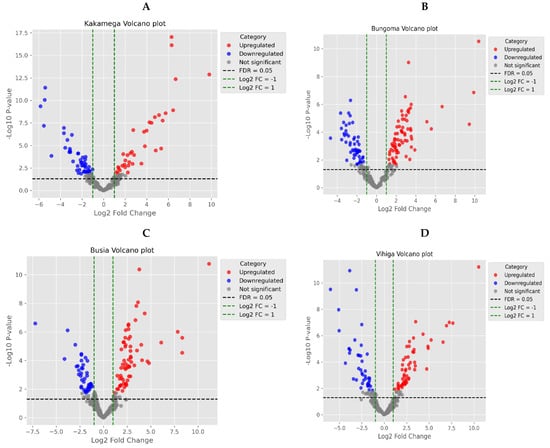
Figure 4.
Volcano plots displaying the following: (A) upregulated metabolites in red and downregulated metabolites in blue for Kakamega samples, (B) upregulated metabolites in red and downregulated metabolites in blue for Bungoma samples, (C) upregulated metabolites in red and downregulated metabolites in blue for Busia samples, and (D) upregulated metabolites in red and downregulated metabolites in blue for Vihiga samples.
3.1. Differentially Expressed Metabolites (DEMs)
Unique metabolites for Kakamega, Bungoma, Busia, and Vihiga are annotated as 13.10, 6, and 3, respectively, in Figure 5A. A comparison of two counties at a time showed that a combination of Busia and Bungoma had the highest number (21) of commonly expressed metabolites. In contrast, a combination of Busia and Kakamega had the lowest (one). Considering three counties at a time, the combination with the highest number of differentially expressed metabolites was a combination of Busia, Bungoma, and Vihiga. Across the four sites, ten metabolites were commonly upregulated, including those with the following mapping IDs: 2603, 2843, 3767, 3773, 6251, 8793, 8796, 9995, 10337, and 11308. The MS2 peak spectrum and databases were used to identify metabolites with Mapping ID 11308 and Mapping ID 2603. Their molecular structures are shown in (Figure 6A,B)
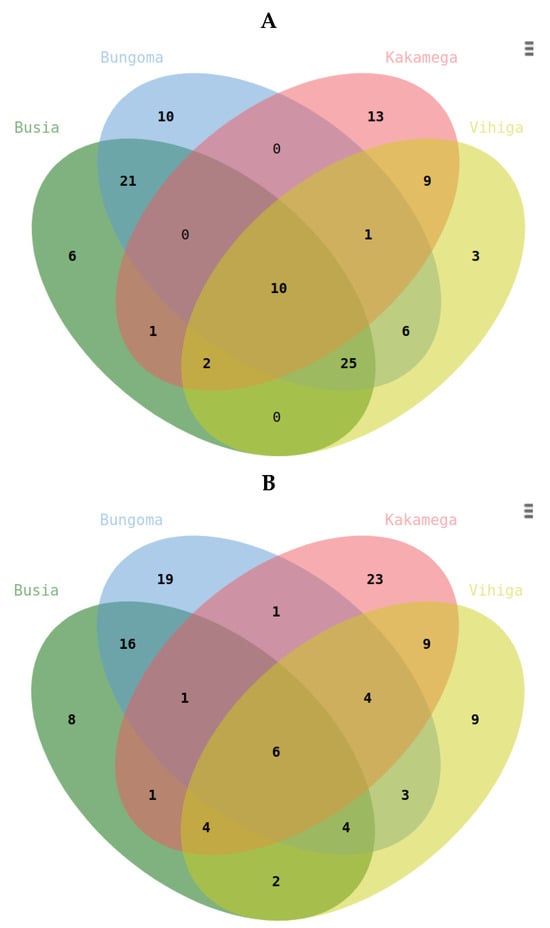
Figure 5.
Venn diagrams illustrating (A) upregulated differentially expressed metabolites across samples from different counties, and (B) downregulated differentially expressed metabolites from various coun-ties within the Western region of Kenya.
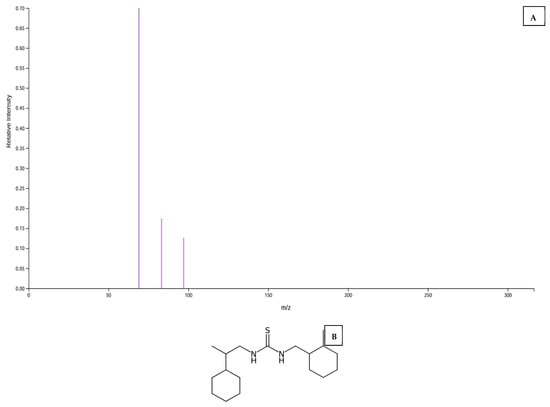
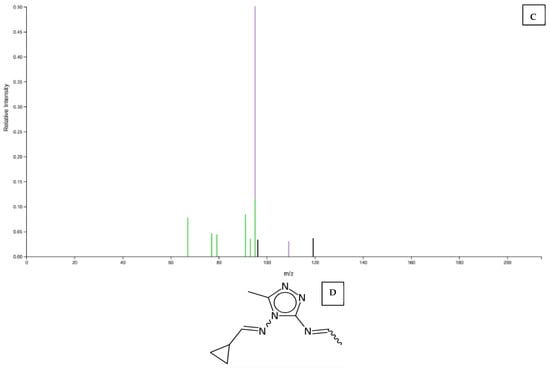
Figure 6.
(A) Graph showing peak spectrum for MS2 of metabolite (Mapping ID 11308), (B) predicted molecular structure of metabolite 11308, (C) graph showing peak spectrum for MS2 metabolite (Mapping ID N0 2603), and (D) predicted molecular structure of metabolite (Mapping ID N0 2603).
Unique downregulated metabolites were identified for Kakamega (23), Bungoma (19), Vihiga (9), and Busia (8). Notably, six metabolites were commonly differentiated across all regions: terpene glycoside (ID 11089), fatty acyls (ID 11091), triterpenoids (ID 1139), terpene glycosides (ID 11166), glycosylglycerols (ID 11169), and alkyl glycosides (ID 11177).
3.2. Phytohormone Analysis
Jasmonic acid-phenylalanine (JA-Phe), JA-Trp, OPDA, and JA-Ile were highly expressed in common bean samples from Kakamega, while SA and ABA exhibited the lowest expression levels (Figure 6). In Bungoma, elevated expression levels of ABA, JA-Trp, and OPDA were observed. Vihiga County samples showed relatively high expression levels of JA-Trp, JA, and OH-JA. Busia County, on the other hand, had high expression levels of OPDA and JA-Trp metabolites (Figure 7).
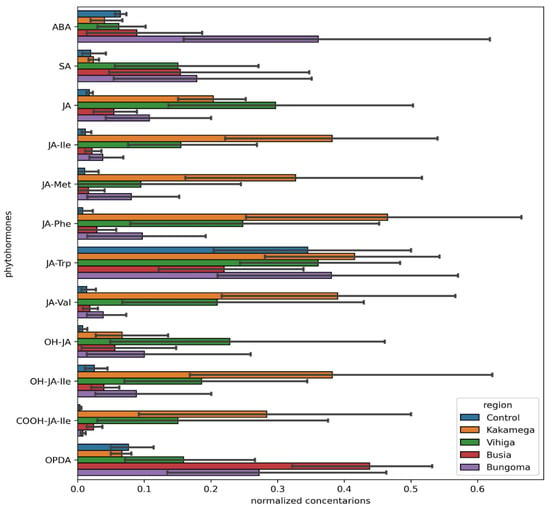
Figure 7.
Phytohormones extracted from diseased common beans in the Western region of Kenya (Kakamega, Bungoma, Vihiga, and Busia), involved in the plant defense mechanism, are shown on the Y-axis, with their concentrations normalized using the MinMaxScaler function from the sklearn.preprocessing module in Python represented on the X-axis.
The phytohormone SA was significantly expressed in all counties within the region. jasmonic acid (JA) was significantly expressed in all counties except Busia. (Table 2)

Table 2.
The p-values for the targeted phytohormones compared to the control across counties in the Western region of Kenya.
4. Discussion
This study identified 354 metabolites within seven metabolic pathways where a complex interaction of biochemical processes was observed. The alkaloid pathway had the same number of upregulated and downregulated metabolites, signifying dynamic regulation in response to biotic stress under study. Upregulation in alkaloid production may indicate an adaptive response to the biotic stress the common bean was subjected to, while the downregulation of 11 metabolites shows a reduction in some alkaloid production since they were not required at this time. Nevertheless, in these findings, the alkaloid pathway has been linked with improving the nutritional value of a healthy diet and enhancing the adaptability of Vicia faba L. [31]. In addition, another study identified 29 differential metabolites and 19 genes (fourteen structural and five regulatory) in Chenopodium quinoa (wild.), illuminating that consistent variations in flavonoid, phenolic acid, and alkaloid metabolites across different quinoa types [32] were linked to mechanisms shaping taste and quality.
The pathway linked with amino acids and peptides presented a significant number of downregulated metabolites (eight downregulated, four upregulated), which may imply a decrease in the synthesis of amino acids. Amino acids are recognized as fundamental units of proteins [33] and as gaseous signaling units, including ethylene, nitric oxide, and hydrogen sulfide [34]. The observed downregulation may imply a metabolic transition towards other pathways, including energy storage and or the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites.
Carbohydrate metabolism is a basic component of the processes through which plants develop stress tolerance and adjust to ecological hardships, including responses to thermal stress [35] and vigor in the face of drought scenarios [36]. In the current investigation, the carbohydrate metabolic pathway exhibited neither the presence of considerably upregulated metabolites nor widespread downregulation, signifying a level of stability and a controlled role in the metabolic remodeling that was observed. This occurrence may be attributed to the potential predominance of other energy sources, such as fatty acids, which could have assumed a more prominent role under this biotic stress.
Flavonoids are a group of secondary metabolites found in various plant parts that play an important role in plant health and interactions with the environment. They are recognized for their many roles including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and signaling properties, which have a role in plant resilience against biotic and abiotic stresses. A diversity of bioactive flavonoids, including chalcones, flavones, flavanones, flavanols, isoflavonoids, and proanthocyanidins, are spread throughout various plant organs such as leaves, roots, bark, stems, flowers, weeds, and fruits. The production of these metabolites occurs in vascular plants via the shikimate, phenylpropanoid, and polyketide metabolic pathways [37]. The polyketide metabolic pathway displayed a complex response, shown by the downregulation of fourteen metabolites and the upregulation of eight metabolites. This implies that though certain metabolites within this pathway may be upregulated to accomplish defensive or specialized functions, the overall activity of the pathway may be impaired, thereby reflecting changes in metabolic priorities toward other biological operations and systems. Similarly, the shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways showed a reduction in metabolite biosynthesis, with sixteen metabolites and one metabolite upregulated and downregulated, respectively. This observation indicates a potential change from the biosynthesis of aromatic and secondary metabolites, perhaps in favor of addressing more immediate metabolic demands. Conversely, in the terpenoid pathway, it was observed that 11 metabolites and 28 metabolites were upregulated and downregulated, respectively. This may imply the selective synthesis of definite terpenoids, likely in reaction to the environmental stimulation or as part of the plant’s defense machinery, while other components of the pathway were inhibited. These outcomes show the dynamic regulation of metabolic pathways in reaction to shifting environmental and physiological stress.
Very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs), are fatty acids containing more than 18 carbon atoms, vital for various physiological and structural roles in plants. These fatty acids are crucial components of membrane lipids and help to maintain membrane homeostasis. In addition, they accumulate selectively in the sphingolipids of the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane, where they play an important role in intercellular communication [38]. Furthermore, VLCFAs are present in phospholipids like phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine, where they influence the organization of membrane domains and the connection between membrane leaflets. In epidermal cells, they act as precursors for cuticular waxes that make up the plant cuticle, which plays a crucial role in regulating interactions with the external environment. [38]. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), produced by colonic bacteria and derived from dietary sources, contribute to human health through their metabolic and signaling properties. The physiological functions of VLCFAs are influenced by the length of their aliphatic tails and are mediated through the activation of specific membrane receptors [39].
One hundred and thirty-one (131) metabolites were found to be downregulated across the seven (seven) pathways, with the fatty acid pathway having the largest reduction (53 metabolites) in this study. This may illustrate a substantial change in lipid metabolism, possibly linked to energy requirements, biotic stress responses, and regulatory feedback machinery. Terpenoid metabolism equally showed substantial downregulation in metabolite assembly (28), illustrating changes in secondary metabolite production. Conversely, carbohydrate metabolism illustrated reduced downregulation, showing it was not a primary target of metabolic remodeling.
The upregulation of definite fatty acid and terpenoid metabolites, together with the downregulation of others, point to a complex metabolic change likely driven by biotic stress and resource distribution. Fatty acids and secondary metabolites such as terpenoids seem to play significant roles in plant adaptation to abiotic and biotic stressors, whereas carbohydrate metabolism remains relatively stable, perhaps indicating reliance on fatty acids for energy. Notably, these results show coordinated metabolic reprogramming, prioritizing lipid and secondary metabolite production, while carbohydrate breakdown remains largely unaltered.
This study similarly disclosed separate regional models in secondary metabolite presence, illustrating the impact of ecological and topographical factors. Kakamega had the highest number of differentially expressed metabolites (twenty-three), followed by Bungoma (nineteen), Vihiga (nine), and Busia (eight). This regional variation indicates that factors such as soil composition, climate, and biotic elements may influence the metabolic profiles of common beans. Notwithstanding these regional differences, six metabolites were commonly downregulated across all four regions. These included terpene glycosides, fatty acyls, triterpenoids, glycosylglycerols, and alkyl glycosides. The downregulation of these metabolites indicates their possible role in biotic stress. In addition, these metabolites could serve as biomarkers for viral disease monitoring and detection.
In Busia, Bungoma, and Vihiga counties, monoterpenes (Mapping ID 11308) were the most upregulated metabolites, indicating an elevated defense reaction to viral diseases. Monoterpenes are known to play roles in plant defense [40], including insect repellence [41] and UV protection [42]. In Kakamega County, eicosanoids (Mapping ID 7510), pseudoalkaloids (Mapping ID 1833), and monoterpenoids (Mapping ID 11308) were upregulated, possibly signifying a specific response to stress or inflammatory processes exclusive to this region.
The enhanced levels of monoterpenes, nicotinic acid alkaloids, and pseudoalkaloid metabolites may provide an opportunity for the manipulation of the botanical systems against detriments caused by viral agents such as BCMV and BCMNV. These phytochemicals also feature prominently in the realm of plant immunity, fulfilling both direct and indirect roles in the protection of plants from viral adversities. Monoterpenes exhibit pronounced efficacy attributable to their antiviral characteristics, which may impede the replication and dissemination of viruses within the plant organism. Empirical investigations have evidenced that monoterpenes can markedly diminish viral activity [43]. Furthermore, these compounds are implicated in the activation of the plant’s defense signaling cascades, culminating in the synthesis of defensive proteins and phytoalexins. Such substances strengthen the plant’s resistance to viral attacks, thus establishing the paramount significance of monoterpenes in the plant’s armamentarium of defense mechanisms [26]. Nicotinic acid alkaloids, including nicotinic acid derivatives, contribute to increasing plant resistance due to their toxicity to pathogens. These alkaloids have the ability to repel herbivorous organisms and prevent pathogen attacks, which reduces the chance of infection [44]. They also participate in the regulation of defense mechanisms through the induction of signal transduction pathways. These modulations generate reactive oxygen species and other metabolites that further protect the plant against viral threats [26]. By contrast, pseudoalkaloids offer a wider range of defense. Such compounds make possible the elaboration of secondary metabolism resistant to a wide range of pathogens, including viruses. Pseudoalkaloids sharply enhance a plant’s general defense mechanism, hence making it more resistant to various environmental stresses [45]. Furthermore, with genetic engineering, which increases pseudoalkaloid levels, it is feasible to produce “pathogen-resistant” varieties that give plants more effective protection against crops [26]. However, while the amplification of these phytochemicals may strengthen the plant’s defense, potential trade-offs associated with enhancement should not be overlooked. These metabolites require increased biosynthesis which involves higher energy costs from the plant, which may adversely affect the plant’s overall growth and productivity. Changes in the concentrations of such chemicals can, on the other hand, have some unexpected ecological implications, including disrupting local ecosystems or harming beneficial organisms. Due to the significant potential of these phytochemical methods in enhancing crop resistance, it is important to carefully consider their potential impact on general ecology.
The downregulation of metabolites across counties is indicative of a prioritization of primary metabolism over secondary metabolite biosynthesis under biotic stress. In Kakamega, the downregulation of pseudoalkaloids, guanidine alkaloids, flavonoids, coumarins, and small peptides may show a possible reduction in metabolic resources assigned to defense and antioxidant synthesis. In contrast, Bungoma and Busia counties showed a downregulation of metabolites related to defense, such as triterpenoids, flavonoids, and naphthalenes. Vihiga County illustrated the widest range of downregulated metabolites, indicating widespread changes in metabolic pathways. This includes the downregulation of triterpenoids, pseudoalkaloids, linear polyketides, coumarins, small peptides, and phenylpropanoids, highlighting intricate responses to viral disease stress.
The results across the counties indicate regional differences in affected metabolites, which may shed light on the physiological response of common beans to viral disease. In Kakamega County, the largest fold change compound was Mapping ID 10337 (long-chain fatty acid), which may suggest that the metabolism of fatty acids is a determining factor for the disease reaction of the plant [38]. This was followed by Mapping ID 11148 (saccharo lipids), which also indicated the fact that lipid-associated pathways may have a central function in plant defense mechanisms in this region. Conversely, Mapping ID 5776 (alpha-amino acid) and Mapping ID 8480 (benzenoids) were least impacted, and this may show that amino acid metabolism and benzenoid-associated pathways have less to contribute to the biotic stress response in Kakamega. In Bungoma County, the metabolite with the highest fold change was Mapping ID 11306 (thioesters), which is involved in several biochemical processes including lipid metabolism and stress responses. This was followed by Mapping ID 3767 (phenolic glycosides), which are also involved in plant defense. The lowest fold change metabolites were Mapping ID 11030 (diterpenoids) and Mapping ID 927 (azacyclic compounds), suggesting these pathways may not be as severely impacted by the disease in Bungoma. In Busia County, the highest fold change metabolites were Mapping ID 11308 (monoterpenes) and Mapping ID 3767 (phenolic glycosides). Monoterpenes are associated with plant stress response and plant defense, and phenolic glycosides have also been implicated in plant defense, which is an indication that both classes of metabolites have important functions to play in this region’s stress response. On the other hand, Mapping ID 10625 (amino acids and derivatives) and Mapping ID 11008 (halogenated fatty acids) had the fewest variations, which may mean these pathways are less significant in the disease response in Busia. In Vihiga County, the most notable fold changes were noted in Mapping ID 11308 (monoterpenes) and Mapping ID 6331 (toluenes). Toluenes, being stress- and signaling-related aromatic hydrocarbons and monoterpenes, suggest the activation of heightened defense in the area. Mapping ID 4254 (azolines) and Mapping ID 10918 (tri-acylglycerols) were the least notable metabolites and indicated that those specific pathways were less impacted in Vihiga.
The findings of phytohormone analysis reveal significant regional variability in the regulation of key phytohormones, particularly abscisic acid (ABA), salicylic acid (SA), and jasmonic acid (JA) derivatives, which are crucial for plant defense and stress adaptation [46]. Abscisic acid (ABA), a hormone primarily linked to stress responses, particularly under drought or water-deficit conditions [47], was significantly upregulated in Bungoma and Kakamega (p-values of 0.0312* and 0.0257*, respectively). This indicates that the common bean plants in these regions likely responded to biotic (viral) stressors, which activated ABA signaling. In contrast, ABA showed no significant change in Busia and Vihiga (p-values of 0.0792 and 0.0890, respectively), which may indicate more stable environmental conditions or a reduced need for ABA-mediated stress responses in these areas. Salicylic acid (SA), known for its role in plant immune responses and defense mechanisms [48,49], was commonly upregulated across all four counties, with p-values ranging from 0.0022* to 0.0113*. This broad upregulation suggests that plants in these regions are facing biotic stressors (e.g., pathogen attack) that activate the plant’s immune system. The steady rise in SA is crucial for plant responses to stress in various environments [24]. Jasmonic acid (JA), a hormone involved in defense responses and stress adaptation [50], displayed a different pattern across the counties. It was significantly upregulated in Kakamega and Vihiga (p = 0* and p = 0.0003*, respectively), cementing its active role in stress and defense pathways in these regions. In Bungoma, JA was also upregulated (p = 0.001), further implying an increase in defense machinery. In Busia, however, no significant changes in JA were observed (p = 0.1041), suggesting that either JA is not essential in the region’s regulatory processes or its regulation remained unchanged. The conjugated form of JA, jasmonic acid-isoleucine (JA-Ile), which is integral to defense signaling [51], was significantly upregulated in Kakamega (p = 0.0022*) and Vihiga (p = 0.0003*), strengthening the hormone’s role in stress or defense responses in these regions. Although JA-Ile also showed upregulation in Bungoma (p = 0.0257*), no significant change was observed in Busia (p = 0.1212), indicating a regional inconsistency in its importance for plant metabolism and stress adaptation [52]. Other JA derivatives, such as JA-Met (a methylated form of jasmonic acid) and JA-Phe (a conjugate with phenylalanine) [53], showed substantial upregulation in some regions but not in others. JA-Met was notably upregulated in Bungoma (p = 0.0019*), while no significant changes were found in Kakamega, Busia, and Vihiga. In contrast, JA-Phe showed important upregulation in Kakamega (p = 0.0005*) and Vihiga (p = 0.026*), signifying its involvement in secondary metabolism and stress responses. These differences further point to the region-specific role of JA derivatives in plant defense [24]. The hydroxyjasmonic acid (OH-JA) and its derivative OH-JA-Ile were also significantly upregulated in Bungoma and Vihiga (p-values ranging from 0.0008* to 0.02*), indicating that biotic stress and defense mechanisms were prevalent in these regions. However, Kakamega and Busia did not exhibit significant changes, signifying that OH-JA and OH-JA-Ile may have played a less critical role in these areas’ stress responses [38]. Further analysis revealed significant changes in carboxylated JA forms, such as 12-JA (COOH-JA), and oxylipins like OPDA [24], which were notably upregulated in Kakamega and Vihiga (p-values ranging from 0.0032* to 0.0007* for COOH-JA, and 0.0173* to 0.0003* for OPDA). These metabolites may likely play a role in stress adaptation and metabolic regulation in these regions. Conversely, Bungoma and Busia did not show significant changes, strengthening the idea that these regions may have experienced less metabolic remodeling in response to the biotic stress.
These outcomes demonstrate the importance of regional variability in the regulation of these plant defense hormones, particularly jasmonic acid (JA) and its derivatives, SA, and ABA. The increase in the expression of these plant hormones in the counties studied, perhaps, emphasizes their key role in stress and plant defense responses in common beans. Kakamega and Vihiga demonstrated more regular upregulation of defense-related hormones, showing enhanced stress levels and or a greater need for vigorous defense mechanisms. Equally, Busia and Bungoma showed more selective responses, possibly due to stable environmental conditions and or different regulatory frameworks.
The observed upregulation and downregulation of common bean metabolites across the regions demonstrate plant flexibility in response to viral disease challenges. For instance, the upregulation of monoterpenes may reveal increased defense mechanisms caused by viral pathogen presence. The downregulation of secondary metabolites like flavonoids and alkaloids may hint at a change away from energy-costly practices in favor of more efficient metabolic pathways.
Future studies should focus on examining the regulation of fatty acid and terpenoid pathways to fully comprehend their adaptation to specific biotic stress while exploring the relationship between their biosynthesis to uncover possible shared regulatory mechanisms or precursor molecules involved in their upregulation and downregulation. Additionally, research into the environmental and ecological factors driving these hormonal changes may enhance agricultural practices, especially in developing region-specific strategies to boost plant resilience to biotic stress.
5. Conclusions
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of the metabolome and phytohormonal responses of common beans under viral disease attack and stress, emphasizing the complexity of metabolomic networks and regional variations in the plant defense reactions. Three hundred and fifty-four (354) metabolites were observed to occur across seven metabolic pathways, uncovering significant changes in plant metabolomic processes, with notable regional differences in the regulation of the metabolites and plant hormones. In addition, ten potential markers were profiled that may be applied in the management of BCMV and BCMNV.
Moreover, the outcome of this investigation underscores the importance of regional variability in plant hormone regulation and the importance of lipid, phenolic, and monoterpene pathways in plant defense, particularly in response to viral disease. Kakamega and Vihiga demonstrated a more consistent and robust defense response, likely due to heightened stress or a greater need for defense mechanisms, while Bungoma and Busia showed more selective and less consistent responses, perhaps due to different regulatory factors.
Author Contributions
A.K.O. and P.O. conceived, performed, and designed the research analyzed data, and wrote the paper; F.N.M. and H.K.W. supervised and edited the manuscript, C.W. performed and designed research, analyzed data and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data can be shared on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Ojiem, J.O. Improving cultivation practices for common beans. In Achieving Sustainable Cultivation of Grain Legumes Volume 2; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 41–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lisciani, S.; Marconi, S.; Le Donne, C.; Camilli, E.; Aguzzi, A.; Gabrielli, P.; Gambelli, L.; Kunert, K.; Marais, D.; Vorster, B.J. Legumes and common beans in sustainable diets: Nutritional quality, environmental benefits, spread and use in food preparations. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1385232. [Google Scholar]
- Farrow, A.; Muthoni Andriatsitohaina, R. Atlas of common bean production in Africa. CIAT Publication. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Rachel-Andriatsitohaina/publication/348860193_Bean_Research_and_Development_in_Sub_Saharan_Africa/links/60136f38a6fdcc071b9d13d0/Bean-Research-and-Development-in-Sub-Saharan-Africa.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Abobatta, W.F.; El-Hashash, E.F.; Hegab, R.H. Challenges and opportunities for the global cultivation and adaption of legumes. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 8, 160–172. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.S.; Lamani, K. Chapter-14 Bean Common Mosaic Necrosis Virus. Viral Dis. Veg. Fruit Crops 2024, 33, 191. [Google Scholar]
- Satrio, R.D.; Fendiyanto, M.H.; Miftahudin, M. Tools and Techniques Used at Global Scale Through Genomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics, and Metabolomics to Investigate Plant Stress Responses at the Molecular Level. In Molecular Dynamics of Plant Stress and Its Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 555–607. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.; Gupta, P.; Kagolla, P.; Hangargi, B.; Veershetty, A.; Ramrao, D.P.; Suresh, S.; Narasanna, R.; Naik, G.R.; Kumar, A. Metabolomics intervention towards better understanding of plant traits. Cells 2021, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Moretti, F.R.; Gentzel, I.N.; Mackey, D.; Alonso, A.P. Metabolomics as an emerging tool for the study of plant–pathogen interactions. Metabolites 2020, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, K.T.X.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Trinh, K.T.T.; Kim, S.T.; Jeon, J.-S. Proteomics and metabolomics studies on the biotic stress responses of rice: An update. Rice 2021, 14, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, M.; Ferreira, A.E.; Nascimento, R.; Monteiro, F.; Traquete, F.; Marques, A.P.; Cunha, J.; Eiras-Dias, J.E.; Cordeiro, C.; Figueiredo, A. Integrating metabolomics and targeted gene expression to uncover potential biomarkers of fungal/oomycetes-associated disease susceptibility in grapevine. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwood, J.W.; Williams, A.; Uthe, H.; van Dam, N.M.; Mur, L.A.; Grant, M.R.; Pétriacq, P. Unravelling plant responses to stress—The importance of targeted and untargeted metabolomics. Metabolites 2021, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Bohra, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Pandey, M.K.; Kumar, A. Metabolomics for plant improvement: Status and prospects. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1302. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.P.; Bisen, M.S.; Shukla, R.; Prabha, R.; Maurya, S.; Reddy, Y.S.; Singh, P.M.; Rai, N.; Chaubey, T.; Chaturvedi, K.K. Metabolomics-driven mining of metabolite resources: Applications and prospects for improving vegetable crops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Luo, J.; Wang, S. The diversity of nutritional metabolites: Origin, dissection, and application in crop breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Zhu, S.; Schultze-Kraft, R.; Liu, G.; Chen, Z. Dissection of crop metabolome responses to nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and other nutrient deficiencies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenda, T.; Liu, S.; Dong, A.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Duan, H. Omics-facilitated crop improvement for climate resilience and superior nutritive value. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 774994. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Chen, Z.; Hong, J.; Shi, J. Promoting human nutrition and health through plant metabolomics: Current status and challenges. Biology 2020, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthubharathi, B.C.; Gowripriya, T.; Balamurugan, K. Metabolomics: Small molecules that matter more. Mol. Omics 2021, 17, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, K.; Maghraby, A.S.; Abd-Elshafy, D.N.; Bahgat, M.M. Carbohydrates Metabolic Signatures in Immune Cells: Response to Infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 912899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchester, M.; Anand, A. Metabolomics: Strategies to define the role of metabolism in virus infection and pathogenesis. Adv. Virus Res. 2017, 98, 57–81. [Google Scholar]
- Purdy, J.G. Pathways to understanding virus-host metabolism interactions. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 6, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K. Metabolomics: Insights into Plant-Pathogen, Symbiont, and Endophyte Interactions Unveiling Chemical Communications. Metabolomics 2024, 9, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, S.P.; Dipankar, P.; Burange, P.S.; Rouse, B.T.; Sarangi, P.P. Climate change: How it impacts the emergence, transmission, resistance and consequences of viral infections in animals and plants. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 47, 307–322. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Li, Y. Current understanding of the interplays between host hormones and plant viral infections. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Carli, M.; Benvenuto, E.; Donini, M. Recent insights into plant–virus interactions through proteomic analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 4765–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Samota, M.K.; Choudhary, M.; Choudhary, M.; Pandey, A.K.; Sharma, A.; Thakur, J. How do plants defend themselves against pathogens-Biochemical mechanisms and genetic interventions. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2022, 28, 485–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.I.; Rao, G.P.; Bhat, A.I.; Rao, G.P. Mechanical Sap Transmission; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; ISBN 1-07-160333-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ramabulana, A.-T.; Petras, D.; Madala, N.E.; Tugizimana, F. Metabolomics and molecular networking to characterize the chemical space of four Momordica plant species. Metabolites 2021, 11, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böcker, S.; Letzel, M.C.; Lipták, Z.; Pervukhin, A. SIRIUS: Decomposing isotope patterns for metabolite identification. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, M.; Fleischauer, M.; Dührkop, K.; Hoffmann, M.A.; Böcker, S. De novo molecular formula annotation and structure elucidation using SIRIUS 4. Comput. Methods Data Anal. Metabolomics 2020, 2104, 185–207. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Zhu, Y.-M.; Jin, Z.-Q.; Wu, F.-B.; Qiu, C.-W. Comparative Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Key Secondary Metabolites Associated with High Quality and Nutritional Value in Broad Bean (Vicia faba L.). Molecules 2022, 27, 8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Xie, H.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Cheng, S.; Qin, P. Elucidating the Differentiation Synthesis Mechanisms of Differently Colored Resistance Quinoa Seedings Using Metabolite Profiling and Transcriptome Analysis. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battezzati, A.; Riso, P. Amino Acids:: Fuel, Building Blocks for Proteins, and Signals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 18, pp. 773–774. ISBN 0899-9007. [Google Scholar]
- Brosnan, J.; Rooyackers, O. The importance of amino acids as independent metabolites, signalling molecules and as building blocks for protein. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2012, 15, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H. Bacterial and viral diseases affecting soybean production Glen L. Hartman, USDA-ARS and University of Illinois, USA. In Achieving Sustainable Cultivation of Soybeans Volume 2; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 43–62. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, A.K.; Singh, V.; Anwar, K.; Pareek, A.; Jain, M. Integrated transcriptome, proteome and metabolome analyses revealed secondary metabolites and auxiliary carbohydrate metabolism augmenting drought tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 201, 107849. [Google Scholar]
- Rehan, M. Biosynthesis of diverse class flavonoids via shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathway. In Bioactive Compounds-Biosynthesis, Characterization and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; Volume 75392. [Google Scholar]
- Batsale, M.; Bahammou, D.; Fouillen, L.; Mongrand, S.; Joubès, J.; Domergue, F. Biosynthesis and functions of very-long-chain fatty acids in the responses of plants to abiotic and biotic stresses. Cells 2021, 10, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Bosch, C.; Boorman, E.; Zunszain, P.A.; Mann, G.E. Short-chain fatty acids as modulators of redox signaling in health and disease. Redox Biol. 2021, 47, 102165. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zha, W.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; You, A. Advances in the biosynthesis of terpenoids and their ecological functions in plant resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelgaleil, S.A.M.; Gad, H.A.; Ramadan, G.R.; El-Bakry, A.M.; El-Sabrout, A.M. Monoterpenes: Chemistry, insecticidal activity against stored product insects and modes of action—A review. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2024, 70, 267–289. [Google Scholar]
- Qasim, M.; Islam, W.; Rizwan, M.; Hussain, D.; Noman, A.; Khan, K.A.; Ghramh, H.A.; Han, X. Impact of plant monoterpenes on insect pest management and insect-associated microbes. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, T.; Sharma, V.; Khan, M.U.; Gupta, K. Terpenoids in Essential Oils: Chemistry, classification, and potential impact on human health and industry. Phytomed. Plus 2024, 4, 100549. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, R.; Saini, R.; Shukla, P.K.; Tiwari, K.N. Role of secondary metabolites in plant defense mechanisms: A molecular and biotechnological insights. Phytochem. Rev. 2024, 24, 953–983. [Google Scholar]
- Shiade, S.R.G.; Zand-Silakhoor, A.; Fathi, A.; Rahimi, R.; Minkina, T.; Rajput, V.D.; Zulfiqar, U.; Chaudhary, T. Plant metabolites and signaling pathways in response to biotic and abiotic stresses: Exploring bio stimulant applications. Plant Stress 2024, 12, 100454. [Google Scholar]
- Pigolev, A.V.; Degtyaryov, E.A.; Miroshnichenko, D.N.; Savchenko, T.V. Prospects for the application of jasmonates, salicylates, and abscisic acid in agriculture to increase plant stress resistance. Sel’skokhozyaistvennaya Biol. 2023, 58, 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad Aslam, M.; Waseem, M.; Jakada, B.H.; Okal, E.J.; Lei, Z.; Saqib, H.S.A.; Yuan, W.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q. Mechanisms of abscisic acid-mediated drought stress responses in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Mou, Z. Salicylic acid and its function in plant immunity F. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Irkitbay, A.; Madenova, A.K.; Sapakhova, Z.B. The role of salicylic acid in the plant defense mechanism. Bull. Gumilyov Eurasian Natl. Univ. Biosci. Ser. 2022, 140, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Mostafa, S.; Zeng, W.; Jin, B. Function and mechanism of jasmonic acid in plant responses to abiotic and biotic stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquis, V.; Smirnova, E.; Poirier, L.; Zumsteg, J.; Schweizer, F.; Reymond, P.; Heitz, T. Stress- and pathway-specific impacts of impaired jasmonoyl-isoleucine (JA-Ile) catabolism on defense signalling and biotic stress resistance. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yu, X.; Cui, G.; Guo, Z.; Lang, D.; Zhang, X. Methyl jasmonate mitigates osmotic stress by regulating carbon and nitrogen metabolism of Glycyrrhiza uralensis seedlings subjected to salt stress. Acta Physiol. Plant 2023, 45, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Per, T.S.; Khan, M.I.R.; Anjum, N.A.; Masood, A.; Hussain, S.J.; Khan, N.A. Jasmonates in plants under abiotic stresses: Crosstalk with other phytohormones matters. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 145, 104–120. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).