Transcriptomic Analysis of the CM-334/P. capsici/N. aberrans Pathosystem to Identify Components in Plant Resistance and Resistance-Breaking Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design
2.2. RNA Extraction
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
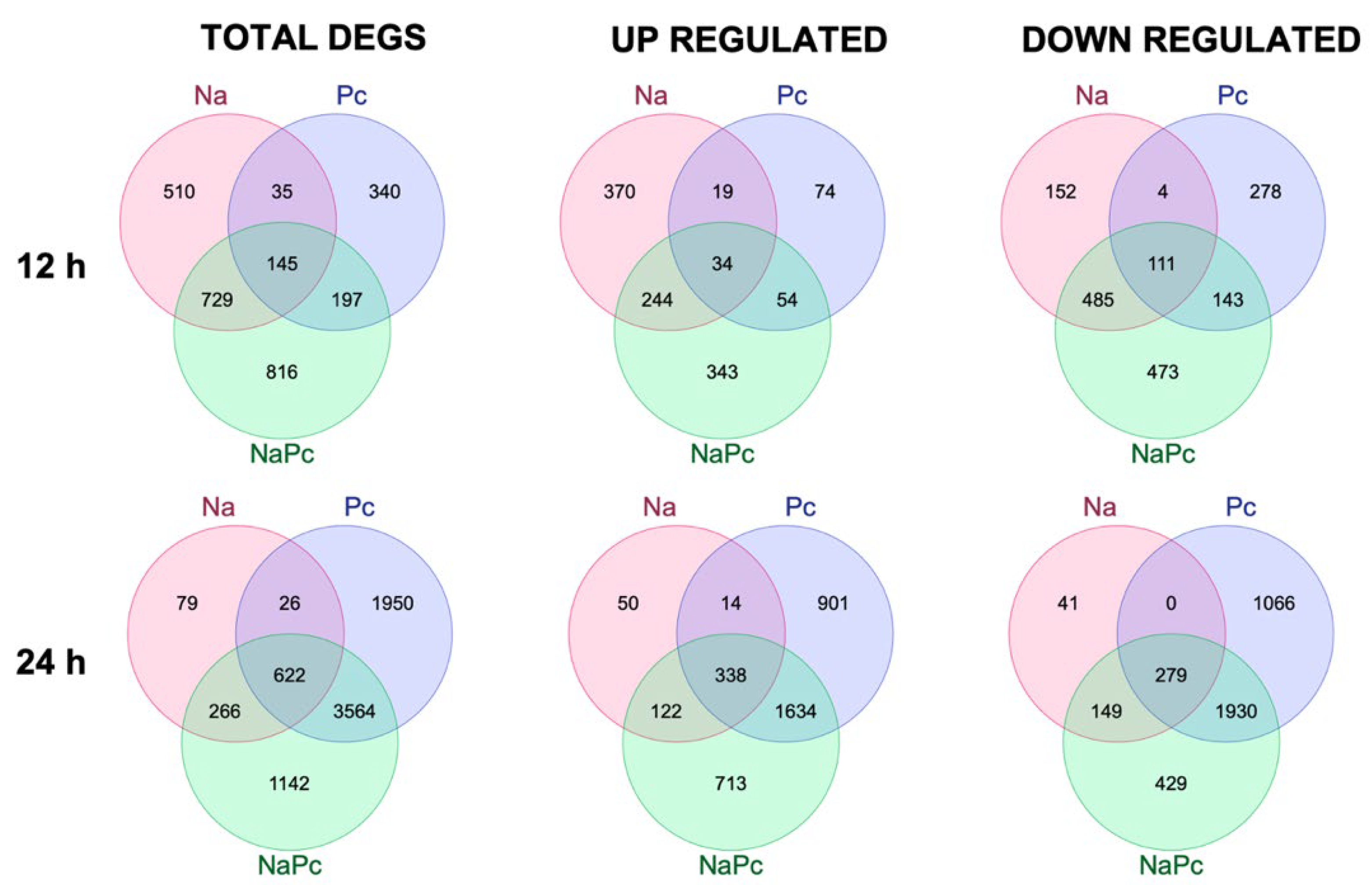
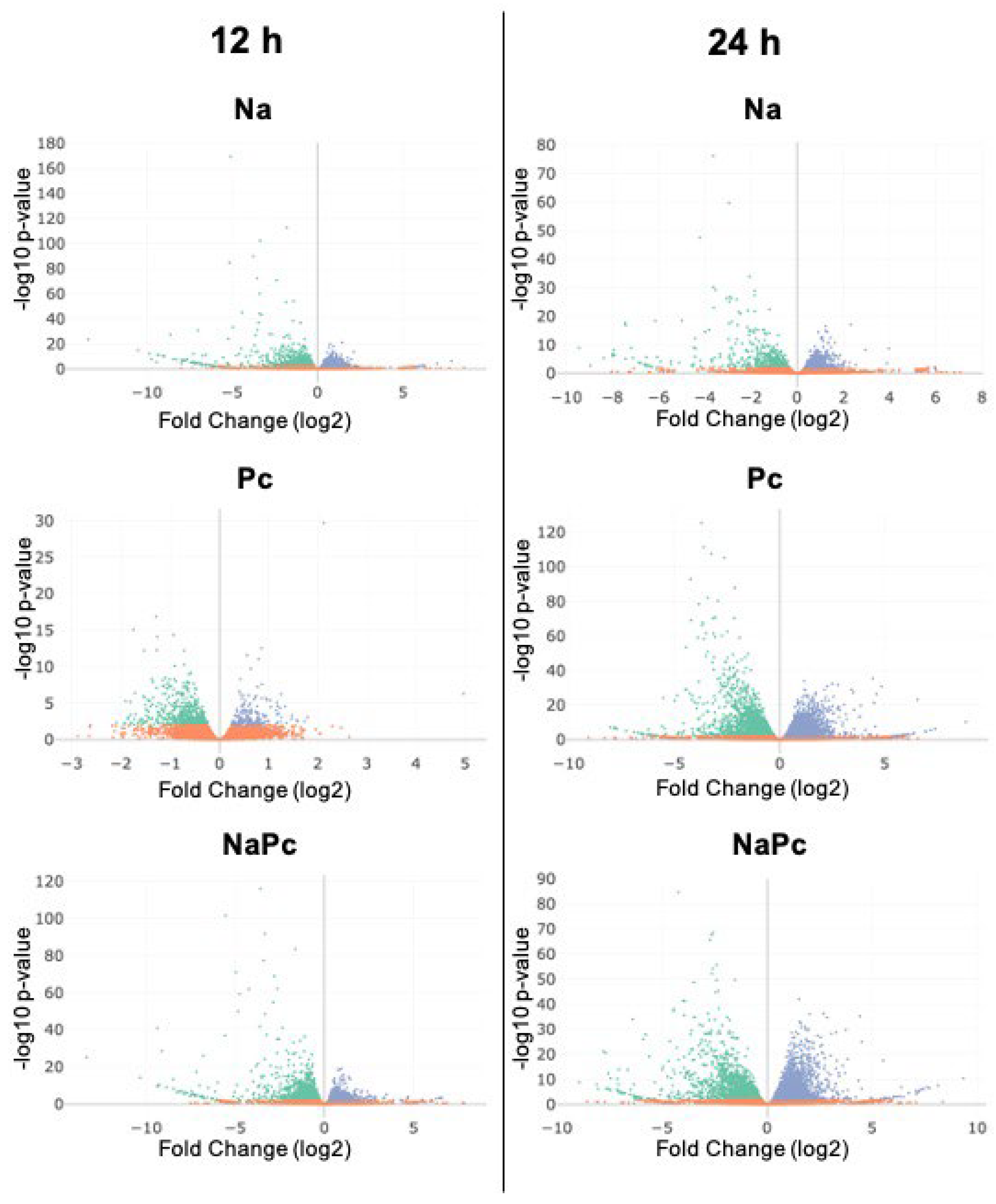
3.1. Differentially Expressed Genes of CM-334 Pepper to P. capsici and N. aberrans
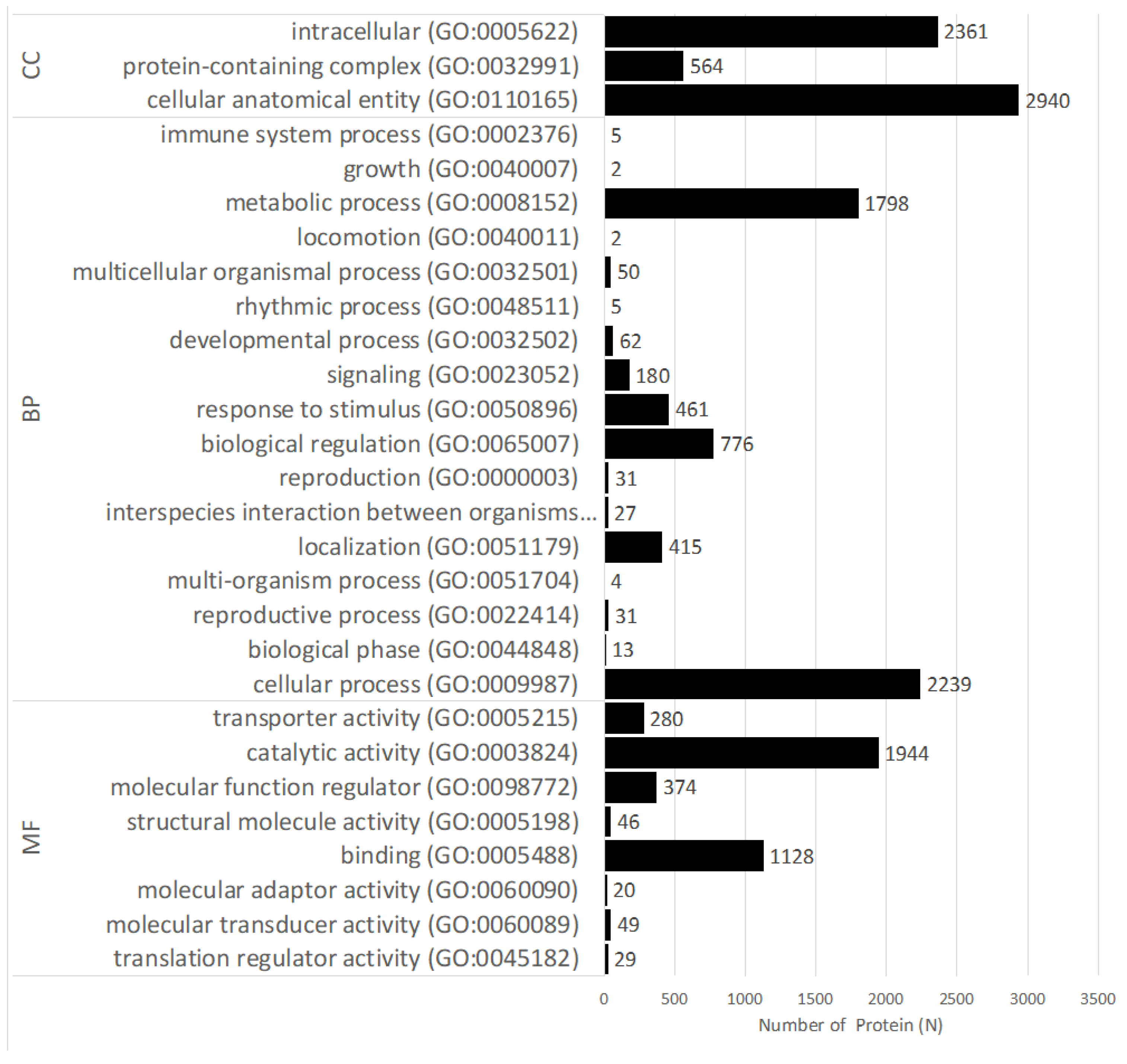
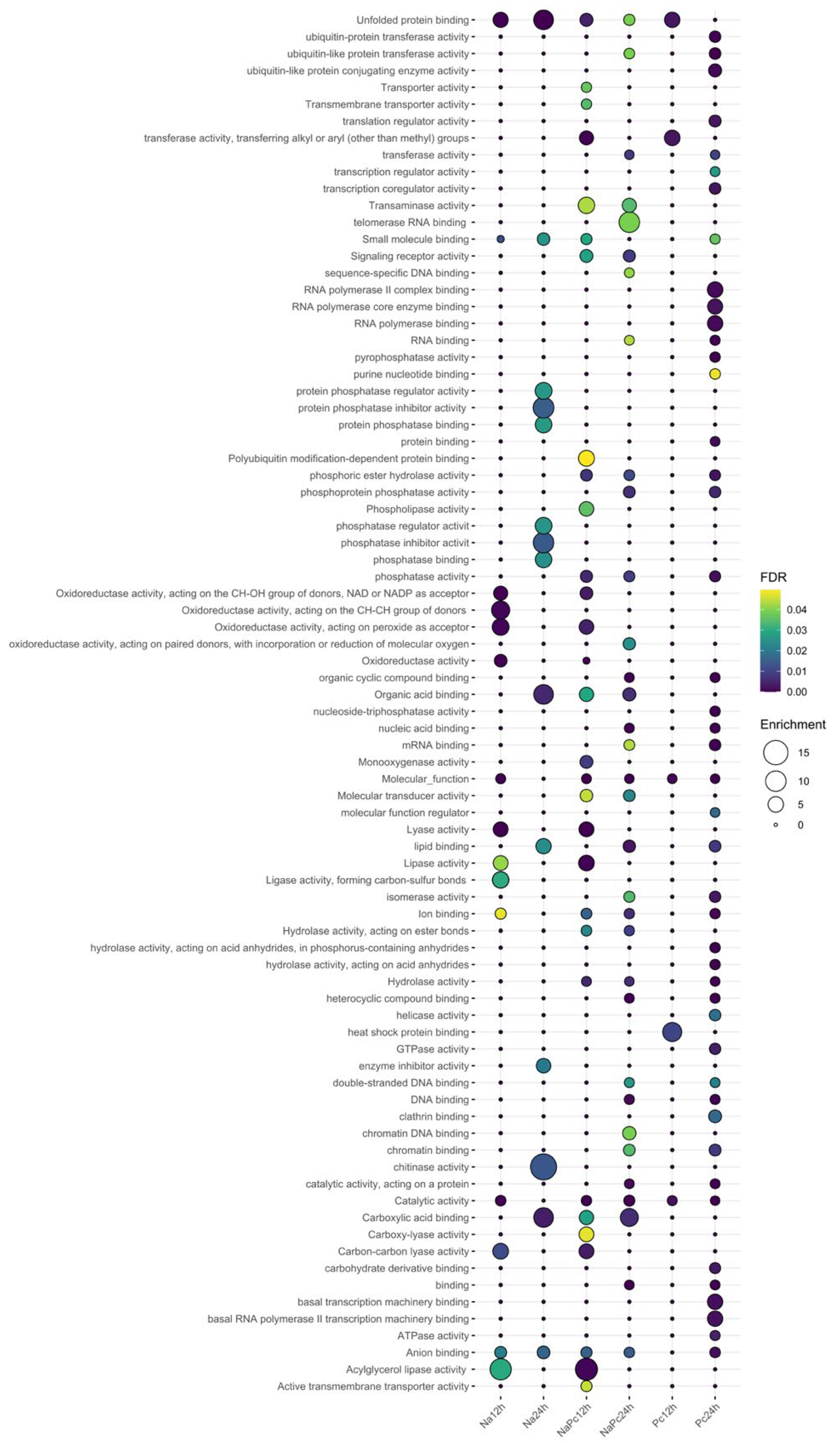
3.2. Functional Annotation of Genes Expressed Differentially
3.3. Resistance Genes Expressed Differentially
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palloix, A.; Daubeze, A.M.; Pochard, E. Phytophthora Root Rot of Pepper Influence of Host Genotype and Pathogen Strain on the Inoculum Density-Disease Severity Relationships. J. Phytopathol. 1988, 123, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarath Babu, B.; Pandravada, S.R.; Prasada Rao, R.D.V.J.; Anitha, K.; Chakrabarty, S.K.; Varaprasad, K.S. Global Sources of Pepper Genetic Resources against Arthropods, Nematodes and Pathogens. Crop Prot. 2011, 30, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Pavia, S.P. Host-Pathogen Interactions in the Root Rot Phytophthora capsici/Capsicum annuum Resistant CM-334 Pathosystem; New Mexico State University: Las Cruces, NM, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Herrera, E.; Rojas-Martínez, R.I.; Gómez-Rodríguez, O.; Guevara-Olvera, L.; Rivas-Dávila, M.E.; Valadez-Moctezuma, E.; Zavaleta-Mejía, E. Defense Genes, Enzymatic Activity and Capsidiol Content in CM-334 Chilli Pepper inoculated with Phytophthora capsici. Interciencia 2012, 37, 370–376. [Google Scholar]
- Villar-Luna, H.; Reyes-Trejo, B.; Gómez-Rodríguez, O.; Villar-Luna, E.; Zavaleta-Mejía, E. Expression of Defense Genes and Accumulation of Capsidiol in the Compatible Interaction CM334/Nacobbus aberrans and Incompatible CM334/Meloidogyne incognita. Nematropica 2015, 45, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Egea, C.; Dickinson, M.J.; Candela, M.; Candela, M.E. β-1,3-Glucanase Isoenzymes and Genes in Resistant and Susceptible Pepper (Capsicum annuum) Cultivars Infected with Phytophthora capsici. Physiol. Plant. 1999, 107, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.I.; Lee, H.Y.; Ro, N.Y.; Han, K.; Venkatesh, J.; Solomon, A.M.; Patil, A.S.; Changkwian, A.; Kwon, J.K.; Kang, B.C. Identifying Candidate Genes for Phytophthora capsici Resistance in Pepper (Capsicum annuum) via Genotyping-by-Sequencing-Based QTL Mapping and Genome-Wide Association Study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richins, R.D.; Micheletto, S.; O’Connell, M.A. Gene Expression Profiles Unique to Chile (Capsicum annuum L.) Resistant to Phytophthora Root Rot. Plant Sci. 2010, 178, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabor-Romero, O. Análisis del Transcriptoma de Chile CM-334 en el Rompimiento de Resistencia A Phytophthora capsici por Nacobbus aberrans; Colegio de Postgraduados: Texcoco, Mexico, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo-Viramontes, F.; Zavaleta-Mejía, E.; Rojas-Martínez, R.I.; Lara, J. Tiempo de Inoculación y Nivel de Inóculo, Factores Determinantes Para el Rompimiento de Resistencia a Phytophthora capsici Inducido Por Nacobbus aberrans en Chile (Capsicum annuum). Nematropica 2005, 35, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Hisat2. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamour, K.H.; Stam, R.; Jupe, J.; Huitema, E. The Oomycete Broad-Host-Range Pathogen Phytophthora capsici. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, T.; Wu, T.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Du, H.; Xu, X.; Xie, D.; Xu, X.M. The Dynamic Transcriptome of Pepper (Capsicum annuum) Whole Roots Reveals an Important Role for the Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis Pathway in Root Resistance to Phytophthora capsici. Gene 2020, 728, 144288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.X.; Ali, M.; Feng, X.H.; Jin, J.H.; Huang, L.J.; Khan, A.; Lv, J.G.; Gao, S.Y.; Luo, D.X.; Gong, Z.H. A Novel Transcription Factor CaSBP12 Gene Negatively Regulates the Defense Response against Phytophthora capsici in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.E.; Liu, K.K.; Li, D.W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhao, Q.; He, Y.M.; Gong, Z.H. A Novel Peroxidase CanPOD Gene of Pepper Is Involved in Defense Responses to Phytophthora capsici Infection as well as Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3158–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcázar, M.D.; Egea, C.; Espín, A.; Candela, M.E. Peroxidase Isoenzymes in the Defense Response of Capsicum annuum to Phytophthora capsici. Physiol. Plant. 1995, 94, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.H.; Zhang, H.X.; Tan, J.Y.; Ming-Jia, Y.; Li, D.W.; Khan, A.; Gong, Z.H. A New Ethylene-Responsive Factor CaPTI1 Gene of Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Involved in the Regulation of Defense Response to Phytophthora capsici. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.C.; Chang, H.S.; Gupta, R.; Wang, X.; Zhu, T.; Luan, S. Transcriptional Profiling Reveals Novel Interactions between Wounding, Pathogen, Abiotic Stress, and Hormonal Responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazan, K.; Manners, J.M. MYC2: The Master in Action. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 686–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Calvo, P.; Chini, A.; Fernández-Barbero, G.; Chico, J.M.; Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Geerinck, J.; Eeckhout, D.; Schweizer, F.; Godoy, M.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; et al. The Arabidopsis BHLH Transcription Factors MYC3 and MYC4 Are Targets of JAZ Repressors and Act Additively with MYC2 in the Activation of Jasmonate Responses. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wasternack, C. Jasmonates in Plant Growth and Stress Responses. In Phytohormones: A Window to Metabolism, Signaling and Biotechnological Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; ISBN 9781493904914. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Memelink, J. Regulation of Secondary Metabolism by Jasmonate Hormones. In Plant-Derived Natural Products: Synthesis, Function, and Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels, L.; Barbero, G.F.; Geerinck, J.; Tilleman, S.; Grunewald, W.; Pérez, A.C.; Chico, J.M.; Bossche, R.V.; Sewell, J.; Gil, E.; et al. NINJA Connects the Co-Repressor TOPLESS to Jasmonate Signalling. Nature 2010, 464, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Gene ID | Product | 12 h | 24 h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NA | Pc | NaPc | Na | Pc | NaPc | ||
| T459_00160 | Putative WRKY transcription factor 46 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | −1.07 |
| T459_00863 | Transcription factor MYC2 | −0.42 | |||||
| T459_01614 | Lignin-forming anionic peroxidase | −1.62 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| T459_04029 | Transcription factor MYC2 | 0.78 | |||||
| T459_05301 | Putative WRKY transcription factor 71 | ― | ― | −1.34 | ― | ― | −1.08 |
| T459_05748 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase RKS1 | ― | ― | ― | ― | 2.83 | ― |
| T459_05984 | Peroxidase 7 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | 1.36 |
| T459_06293 | Homeobox-leucine zipper protein ATHB-21 | 0.78 | ― | 0.72 | ― | −0.55 | ― |
| T459_06371 | Galactinol synthase 2 | −5.17 | ― | −4.85 | −2.53 | 1.63 | −2.81 |
| T459_10498 | Late embryogenesis abundant protein Dc3 | −7.82 | −7.95 | −7.12 | |||
| T459_10725 | Pathogenesis-related protein PR-5 | 1.08 | ― | 0.88 | ― | ― | 1.19 |
| T459_11521 | Caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase | ― | ― | ― | ― | 0.49 | ― |
| T459_14119 | SAR8.2 precursor | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | −1.02 |
| T459_14236 | Inactive leucine-rich repeat receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | 0.84 |
| T459_14243 | Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase | ― | −0.44 | ― | ― | −1.54 | −1.23 |
| T459_14321 | Trypsin and protease inhibitor | ― | ― | 1.51 | ― | 1.69 | 2.12 |
| T459_20142 | Protochlorophyllide reductase | 1.01 | 0.00 | ||||
| T459_21467 | Putative WRKY transcription factor 13 | ― | ― | −3.69 | ― | ― | ― |
| T459_22169 | Pathogenesis-related protein PR-4B | ― | ― | ― | −3.70 | ― | −4.63 |
| T459_22749 | Pathogenesis-related protein 1B | ― | ― | −3.29 | −3.03 | ― | −3.95 |
| T459_25133 | Transcription factor MYC2 | −3.69 | ― | −3.34 | −1.67 | 1.69 | ― |
| T459_25133 | Transcription factor MYC3 | −3.69 | −3.34 | −1.67 | 1.69 | ||
| T459_30069 | Putative WRKY transcription factor 56 | −2.98 | ― | −3.24 | ― | ― | ― |
| T459_31175 | Pathogenesis-related protein STH-21 | ― | ― | −2.25 | ― | ― | −2.19 |
| T459_31889 | Pathogenesis-related protein 1B | ― | ― | 1.12 | ― | ― | ― |
| T459_33283 | 1,4-Dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-CoA synthase | 1.80 | 0.00 | ||||
| T459_33509 | Putative cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase 1 | ― | ― | 0.30 | ― | ― | 0.80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nabor-Romero, O.; Rojas-Martínez, R.I.; Zavaleta-Mejía, E.; Vega-Arreguin, J.; Ochoa-Martínez, D.; Sánchez-Flores, A.; Romo-Castillo, M. Transcriptomic Analysis of the CM-334/P. capsici/N. aberrans Pathosystem to Identify Components in Plant Resistance and Resistance-Breaking Responses. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2022, 13, 151-162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb13020015
Nabor-Romero O, Rojas-Martínez RI, Zavaleta-Mejía E, Vega-Arreguin J, Ochoa-Martínez D, Sánchez-Flores A, Romo-Castillo M. Transcriptomic Analysis of the CM-334/P. capsici/N. aberrans Pathosystem to Identify Components in Plant Resistance and Resistance-Breaking Responses. International Journal of Plant Biology. 2022; 13(2):151-162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb13020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleNabor-Romero, Olivia, Reyna Isabel Rojas-Martínez, Emma Zavaleta-Mejía, Julio Vega-Arreguin, Daniel Ochoa-Martínez, Alejandro Sánchez-Flores, and Mariana Romo-Castillo. 2022. "Transcriptomic Analysis of the CM-334/P. capsici/N. aberrans Pathosystem to Identify Components in Plant Resistance and Resistance-Breaking Responses" International Journal of Plant Biology 13, no. 2: 151-162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb13020015
APA StyleNabor-Romero, O., Rojas-Martínez, R. I., Zavaleta-Mejía, E., Vega-Arreguin, J., Ochoa-Martínez, D., Sánchez-Flores, A., & Romo-Castillo, M. (2022). Transcriptomic Analysis of the CM-334/P. capsici/N. aberrans Pathosystem to Identify Components in Plant Resistance and Resistance-Breaking Responses. International Journal of Plant Biology, 13(2), 151-162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb13020015






