Role of NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Disorders of Children’s Digestive Systems: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Inflammasomes
2. Materials and Methods
3. Discussion
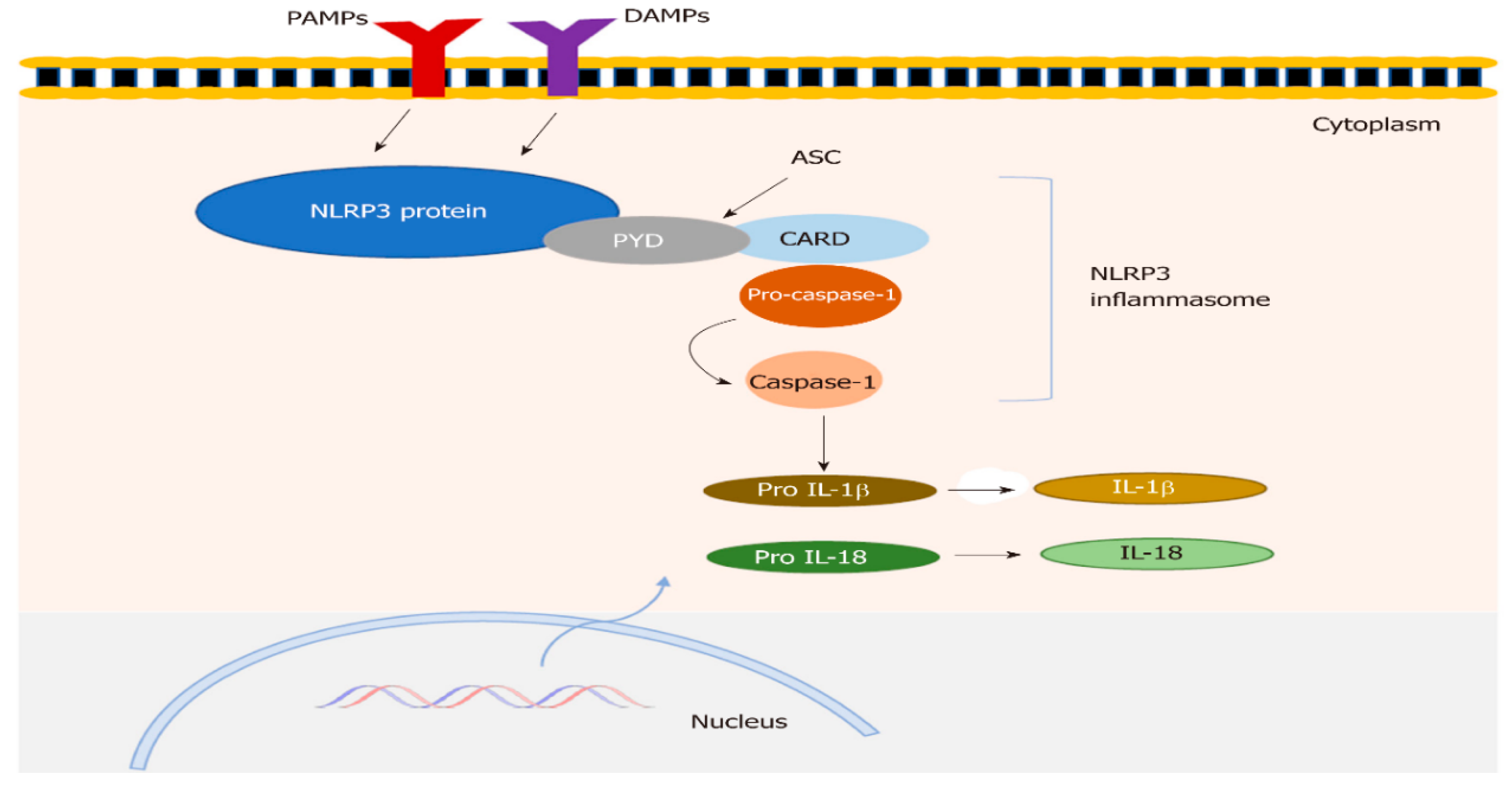
3.1. Structure of NLRP3 Inflammasomes
3.2. NLRP3 Inflammasome in Neonates
3.3. NLRP3 Inflammasome Role in Intestinal Mucosal Immunity
3.4. Pathogenic Roles of the NLRP3 Inflammasome
3.5. Protective Roles of the NLRP3 Inflammasome
3.6. The Causes of Contradictory Results for the Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome
4. NLRP3 Inflammasome in Gastrointestinal Diseases Concerning the Pediatric Age Group
4.1. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
4.2. NLRP3 Inflammasome in Gut–Lung Interaction
4.3. Celiac Disease
5. NLRP3 Inflammasome and Gastrointestinal Tract Infection
5.1. Infectious Enteritis and Colitis
5.2. Helicobacter Pylori
5.3. Protozoan Infections
5.4. Viral
6. Inflammasome and Neonatal Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Necrotizing enterocolitis
7. Inflammasome and Hepatic Disorders
Viral Hepatitis
8. Pharmacological Inhibitors for NLRP3 Inflammasome
9. Quality, Strengths, and Limitations of the Studies
10. The Future Direction
11. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, D.; Guo, Y.; Kamada, N. Interaction between the inflammasome and commensal microorganisms in gastrointestinal health and disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, A.; Li, B.; Kombe, A.J.K.; Jin, T.; Tao, J. Pharmacological Inhibitors of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, J.K.; Günther, S.; Sundberg, E.J. Structural Basis of IL-1 Family Cytokine Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner-Bratkovič, I.; Sušjan, P.; Lainšček, D.; Tapia-Abellán, A.; Cerović, K.; Kadunc, L.; Angosto-Bazarra, D.; Pelegrin, P.; Jerala, R. NLRP3 lacking the leucine-rich repeat domain can be fully activated via the canonical inflammasome pathway. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Rong, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, N. Biological functions of NLRP3 inflammasome: A therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 60, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hara, H.; Núñez, G. Mechanism and Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 4, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Shao, F. Snap Shot: The Noncanonical Inflammasome. Cell 2017, 168, 544–544.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filardy, A.A.; He, J.; Bennink, J.; Yewdell, J.; Kelsall, B.L. Posttranscriptional control of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in colonic macrophages. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, H.M.; Wanderer, A.A. Inflammasome and IL-1beta-mediated disorders. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2010, 10, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.I.; ELMeneza, S.A.; El-Bagoury, I.M.S. The role of nod-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in the diagnosis of late-onset neonatal sepsis. J. Neonatal Perinat. Med. 2022, 15, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaei, S.; Sadr, M.; Rezaei, A.; Shahkarami, S.; Ebrahimi Daryani, N.; Bidoki, A.Z.; Rezaei, N. Association of NLRP3 single nucleotide polymorphisms with ulcerative colitis: A case-control study. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2018, 42, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourkochristou, E.; Aggeletopoulou, I.; Konstantakis, C.; Triantos, C. Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4796–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.A.; Jen, R.; Kan, B.; Sharma, A.; Marchant, E.; Tang, A.; Gadawski, I.; Senger, C.; Skoll, A.; Turvey, S.E.; et al. Impaired NLRP3 inflammasome activity during fetal development regulates IL-1β production in human monocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motomura, K.; Romero, R.; Galaz, G.; Tao, L.; Flores, V.G.; Xu, Y.; Done, B.; Hernandez, M.A.; Miller, D.; Contreras, P.G.; et al. Fetal and maternal NLRP3 signaling is required for preterm labor and birth. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e158238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerbarth, L.M.; Seifert, S.B.; Napoli, M.; Rohwedder, I.; Vogl, T.; Scheiermann, C.; Kolben, T.; Nussbaum, C.; Pruenster, M.; Immler, R.; et al. Neonatal neutrophils exhibit reduced NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2025, 117, qiae206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiser, C.; Ercan, I.; Engur, D.; Genc, S. NLRP3 inflammasome: A key player in neonatal brain injury. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2025, 68, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarakcioglu, E.; Genc, B.; Tufekci, K.U.; Genc, S. Neonatal NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Leads to Perineuronal Net Deficits in Early Adulthood. Dev. Neurobiol. 2025, 85, e22986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Lyu, C.J.; Le, Z.K.; Ji, H.S.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Huang, S.J.; Yu, L.J.; Shu, Q.; Tou, J.F.; et al. NLRP3 activation in macrophages promotes acute intestinal injury in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. World J. Pediatr. 2024, 20, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra-Torres, J.S.; Pinzón-Fernández, M.V.; Ocampo-Posada, M.; Nati-Castillo, H.A.; Jiménez Hincapie, L.A.; Cadrazo-Gil, E.J.; Arias-Intriago, M.; Rojas-Cadena, M.; Tello-De-la-Torre, A.; Osejos, W.; et al. Inflammasomes and Signaling Pathways: Key Mechanisms in the Pathophysiology of Sepsis. Cells 2025, 14, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ELMeneza, S.A.; Bagoury, I.M.; Mohamed, K.E.S. Role of Serum Apelin in the Diagnosis of Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2021, 56, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, W. NLRP3 Inflammasome—A Key Player in Antiviral Responses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierantonelli, I.; Rychlicki, C.; Agostinelli, L.; Giordano, D.M.; Gaggini, M.; Fraumene, C.; Saponaro, C.; Manghina, V.; Sartini, L.; Mingarelli, E.; et al. Lack of NLRP3-inflammasome leads to gut-liver axis derangement, gut dysbiosis and a worsened phenotype in a mouse model of NAFLD. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; She, Y.; Sun, Q.; Shi, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, D.C.; Shao, F. Pore-forming activity and structural autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature 2016, 535, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, H.Y.; Lu, H.H.; Sudhakar, J.N.; Chen, Y.W.; Shih, N.S.; Weng, Y.T.; Shui, J.W. IL-22 initiates an IL-18-dependent epithelial response circuit to enforce intestinal host defence. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Dong, Y.; Ye, M.; Jin, S.; Yang, J.; Joosse, E.M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lazarev, M.; Brant, S.R.; et al. The Pathogenic Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases of Both Mice and Humans. J. Crohns Colitis. 2017, 11, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, W.K.E.; Hoshi, N.; Shouval, D.S.; Snapper, S.; Medzhitov, R. Anti-inflammatory effect of IL-10 mediated by metabolic reprogramming of macrophages. Science 2017, 356, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, M.H.; Boyd, K.L.; Vogel, P.; Kastan, M.B.; Lamkanfi, M.; Kanneganti, T.D. The NLRP3 inflammasome protects against loss of epithelial integrity and mortality during experimental colitis. Immunity 2010, 32, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, M.H.; Lamkanfi, M.; Kanneganti, T.D. The Nlrp3 inflammasome: Contributions to intestinal homeostasis. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, R.; Li, Y.; Dai, X.; Lv, W. NLRP3 inflammasome in digestive diseases: From mechanism to therapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 978190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, O.; Durant, M.; Mow, W.; Finley, A.; Kodali, P.; Wong, A.; Tavares, V.; McCroskey, E.; Liu, L.; Lewis, J.D.; et al. Incidence, prevalence, and time trends of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Northern California, 1996 to 2006. J Pediatr. 2010, 157, 233–239.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirtas Guner, D.; Bildik, H.N.; Demir, H.; Cagdas, D.; Saltik Temizel, I.N.; Ozgul, R.K.; Hizarcioglu Gulsen, H.; Tan, C.; Cicek, B.; Ozen, H.; et al. Genetic Variants in Early-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Monogenic Causes and Clinical Implications. Children 2025, 12, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambu, R.; Warner, N.; Mulder, D.J.; Kotlarz, D.; McGovern, D.P.B.; Cho, J.; Klein, C.; Snapper, S.B.; Griffiths, A.M.; Iwama, I.; et al. A Systematic Review of Monogenic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e653–e663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuijk, S.A.; Camman, A.E.; de Ridder, L. Considerations in Paediatric and Adolescent Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2024, 18 (Suppl. S2), ii31–ii45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.J.; Dhawan, A.; Saeed, S.A. Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children and Adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruel, J.; Ruane, D.; Mehandru, S.; Gower-Rousseau, C.; Colombel, J.F. IBD across the age spectrum: Is it the same disease? Nature reviews. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwassief, A.; Abbas, Q.L.; Al Busafi, S.; Al Lawati, T.T.; Al Shmusi, K. Transitioning Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Key Considerations for Adult Gastroenterologists. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2025, 28, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granot, M.; Kopylov, U.; Loberman-Nachum, N.; Krauthammer, A.; Abitbol, C.M.; Ben-Horin, S.; Weiss, B.; Haberman, Y. Differences in disease characteristics and treatment exposures between paediatric and adult-onset inflammatory bowel disease using a registry-based cohort. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 60, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranson, N.; Veldhuis, M.; Mitchell, B.; Fanning, S.; Cook, A.L.; Kunde, D.; Eri, R. NLRP3-Dependent and -Independent Processing of Interleukin (IL)-1β in Active Ulcerative Colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Han, L.; Chen, S.; Xue, R. Activation of platelet NLRP3 inflammasome in crohn’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 705325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorreja, F.; Caer, C.; Rush, S.T.A.; Forsskal, S.K.; Hartlova, A.; Magnusson, M.K.; Lindskog, E.B.; Börjesson, L.G.; Mattias Block, M.; Jo Wick, M. MEFV and NLRP3 inflammasome expression is attributed to immature macrophages and correlates with serum inflammatory proteins in Crohns disease patients. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1631–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Xing, Y.; Liu, J.; Dong, D.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, L. Lonicerin targets EZH2 to alleviate ulcerative colitis by autophagy-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome inactivation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2880–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 44-Allen, I.C.; TeKippe, E.M.; Woodford, R.M.; Uronis, J.M.; Holl, E.K.; Rogers, A.B.; Herfarth, H.H.; Jobin, C.; Ting, J.P.Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome functions as a negative regulator of tumorigenesis during colitis-associated cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Fan, L.; Qi, Y.; Xu, C.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Si, J. Akkermansia muciniphila alleviates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced acute colitis by NLRP3 activation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0073021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, Y.C. Role of NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathways in the immune mechanism of inflammatory bowel disease in children. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2020, 22, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Kitani, A.; Similuk, M.; Fuss, I.J.; Strober, W. Loss-of-function CARD8 mutation causes NLRP3 inflammasome activation and Crohn’s disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1793–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fuhrer, M.; Bahrami, E.; Socha, P.; Klaudel-Dreszler, M.; Bouzidi, A.; Liu, Y.; Lehle, A.S.; Magg, T.; Hollizeck, S.; et al. Human RIPK1 deficiency causes combined immunodeficiency and inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansi, A.; Cucchiara, S.; Greco, L.; Sarnelli, P.; Pisanti, C.; Franco, M.T. Bronchial hyperresponsiveness in children and adolescents with Crohn’s disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Assaf, A.I.S.; Ali, H.M.; Ad’hiah, A.H. Gene Expression of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Celiac Disease of Iraqi Children. Ibn AL-Haitham J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2021, 2021, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.; Atherton, J.C. The Spectrum of Helicobacter-Mediated Diseases. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2021, 16, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Niu, J.; Guo, Q.; Leng, Q.; Huang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Meng, G. Interleukin-18 protects mice from enterovirus 71 infection. Cytokine 2017, 96, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Aziz, A.I. Molecular study and determining the levels of some interleukins in children with Entamoeba histolytica. Cytokine 2025, 188, 156890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Dong, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, S.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome recognizes alpha-2 and alpha-7.3 giardins and decreases the pathogenicity of Giardia duodenalis in mice. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolovska, A.; Becker, C.E.; Ip, W.K.; Rathinam, V.A.K.; Brudner, M.; Paquette, N.; Tanne, A.; Vanaja, S.K.; Moore, K.J.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Activation of caspase-1 by the NLRP3 inflammasome regulates the NADPH oxidase NOX2 to control phagosome function. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowarski, R.; Jackson, R.; Gagliani, N.; de Zoete, M.; Palm, N.; Bailis, W.; Low, J.; Harman, C.; Graham, M.; Elinav, E.; et al. Epithelial IL-18 Equilibrium Controls Barrier Function in Colitis. Cell 2015, 163, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.U.; Kamada, N.; Muñoz-Planillo, R.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, D.; Koizumi, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Himpsl, S.D.; Browne, H.P.; Lawley, T.D.; et al. Distinct commensals induce interleukin-1b via NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory monocytes to promote intestinal inflammation in response to injury. Immunity 2015, 42, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.; Hirota, S.A.; Gross, O.; Li, Y.; Ulke-Lemee, A.; Potentier, M.S.; Schenck, L.P.; Vilaysane, A.; Seamone, M.E.; Feng, H.; et al. Clostridium difficile toxin-induced inflammation and intestinal injury are mediated by the inflammasome. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 542–552.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thinwa, J.; Segovia, J.A.; Bose, S.; Dube, P.H. Integrin-mediated first signal for inflammasome activation in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.M. Inflammasomes in the gastrointestinal tract: Infection, cancer and gut microbiota homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 721–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Batra, S.; Jeyaseelan, S. Deletion of Nlrp3 Augments survival during polymicrobial sepsis by decreasing autophagy and enhancing phagocytosis. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, H.K.; Koh, G.C.; van Lieshout, M.H.; Roelofs, J.J.; van Dissel, J.T.; van der Poll, T.; Wiersinga, W.J. Limited role for ASC and NLRP3 during in vivo Salmonella Typhimurium infection. BMC Immunol. 2014, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamoto, S.; Nagao-Kitamoto, H.; Jiao, Y.; Gillilland, M.G.; Hayashi, A.; Imai, J.; Sugihara, K.; Miyoshi, M.; Brazil, J.C.; Kuffa, P.; et al. The Intermucosal Connection between the Mouth and Gut in Commensal Pathobiont-Driven Colitis. Cell 2020, 182, 447–462.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Kotilea, K.; Bontems, P.; Miendje Deyi, V.Y. Helicobacter pylori Infections in Children. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachathundikandi, S.K.; Backert, S. Helicobacter pylori controls NLRP3 expression by regulating hsa-miR-223-3p and IL-10 in cultured and primary human immune cells. Innate Immun. 2018, 24, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachathundikandi, S.K.; Blaser, N.; Bruns, H.; Backert, S. Helicobacter pylori avoids the critical activation of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated production of oncogenic mature IL-1beta in human immune cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinaei, R.; Hosseininasab, A.; Abbaslou, P.; Zeinali, M.; Iranmanesh, E.; Sinaei, R.; Rahmanian, K. Gastrointestinal and hepatic manifestations among hospitalized COVID-19 children. BMC Pediatr. 2025, 25, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Lv, P.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Xin, H.; Reilly, S.; Zhang, X. SARS-CoV-2 E protein: Pathogenesis and potential therapeutic development. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 159, 114242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.E.; Hiatt, J.; Bouhaddou, M.; Rezelj, V.V.; Ulferts, S.; Braberg, H.; Jureka, A.S.; Obernier, K.; Guo, J.Z.; Batra, J.; et al. Comparative host-coronavirus protein interaction networks reveal pan-viral disease mechanisms. Science 2020, 370, eabe9403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakra, N.A.; Blumberg, D.A.; Herrera-Guerra, A.; Lakshminrusimha, S. Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Review of Clinical Presentation, Hypothetical Pathogenesis, and Proposed Management. Children 2020, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ELMeneza, S.A.; Arafat, N.M.; El-Bagoury, I.M.; Gaber, A. Inter-Alpha Inhibitor Proteins as a Predictor of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Newborn Infants. Gen. Reanimatol. 2023, 19, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wu, X.; Zou, H.; Qin, Z.; Cao, J. Overexpressed FOXO3 improves inflammatory status in mice by affecting NLRP3-mediated cell coronation in necrotizing colitis mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, L.; Gong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Cai, W.; Wu, J. Blockage of NLRP3 inflammasome activation ameliorates acute inflammatory injury and long-term cognitive impairment induced by necrotizing enterocolitis in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryka-Marton, M.; Grabowska, A.D.; Szukiewicz, D. Breaking the Barrier: The Role of Proinflammatory Cytokines in BBB Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Zhong, X.; Ji, H.; Yang, S.; Jin, J.; Lyu, C.; Ren, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, S.; et al. Macrophage α7nAChR alleviates the inflammation of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis through mTOR/NLRP3/IL-1β pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 139, 112590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 76. Chen, X.; Long, R.; Xu, F.; Ye., W.; Li, N. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, X.; Sheng, Q.; Lv, Z. MiR-146a-5p Mimic Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Downstream Inflammatory Factors and CLIC4 in Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 594143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Kao, J.H. Hepatitis B: Immunization and Impact on Natural History and Cancer Incidence. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 49, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Lei, Q.; Li, T.; Li, L.; Qin, B. Hepatitis b core antigen can regulate NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in HepG2 cells. J. Med. Virol. 2019, 91, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daussy, C.F.; Monard, S.C.; Guy, C.; Muñoz-González, S.; Chazal, M.; Anthonsen, M.W.; Jouvenet, N.; Henry, T.; Dreux, M.; Meurs, E.F.; et al. The inflammasome components NLRP3 and ASC act in concert with IRGM to rearrange the golgi apparatus during hepatitis c virus infection. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e00826-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Kessler, A.L.; Shu, J.; Liu, X.; Liang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; et al. Hepatitis e virus infection activates NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome antagonizing interferon response but therapeutically targetable. Hepatology 2022, 75, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Tang, Y.; Jin, T.; Tao, J. Inflammasomes cross-talk with lymphocytes to connect the innate and adaptive immune response. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 54, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Su, W.; Liu, Y.; Xie, N.; Liu, J. NLRP3 inflammasome in health and disease (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2025, 55, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasti, A.; Katsas, K.; Nikolaki, M.D.; Triantafyllou, K. The Role and the Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, E.M.; Diago-Navarro, E.; Ozog, L.S.; Raheel, M.; Levy, O.; Fries, B.C. A Neonatal Murine Escherichia coli Sepsis Model Demonstrates That Adjunctive Pentoxifylline Enhances the Ratio of Anti- vs. Pro-inflammatory Cytokines in Blood and Organ Tissues. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 577878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon, J.C.; Hawkins, R.B.; Hollen, M.; Nacionales, D.C.; Ungaro, R.; Efron, P.A.; Moldawer, L.L.; Larson, S.D. Aluminum Adjuvant Improves Survival Via NLRP3 Inflammasome and Myeloid Non-Granulocytic Cells in a Murine Model of Neonatal Sepsis. Shock 2021, 55, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luo, R.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, F.; Ma, J.; Mei, L. Nanobody-as versatile tool emerging in autoimmune diseases. Smart Mater. Med. 2024, 5, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, M.; Di Matteo, G.; Ingallina, C.; Ambroselli, D.; Carradori, S.; Gallorini, M.; Giusti, A.M.; Salvo, A.; Grosso, M.; Mannina, L. Modulatory Properties of Food and Nutraceutical Components Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, T.; Shi, X.; Du, H.; Cai, C.; Yang, D.; Qu, L.; Dou, H.; Jiao, B.; Jiao, B. Mechanisms and therapeutic potential of pharmacological agents targeting inflammasomes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 189, 118164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Inflammasome activation and regulation: Toward a better understanding of complex mechanisms. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disease | Protective Role of NLRP3 | Pathogenic Role of NLRP3 | Therapeutic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis | It serves to eradicate infectious agents while triggering a repair response through the action of IL-1β and IL-18. | Uncontrolled and excessive activation leads to epithelial injury and the development of systemic inflammation. | Treatment strategies could include using IL-1 receptor antagonists (like anakinra) and administering probiotics to adjust the gut microbiota. Neonatal-specific dosing and safety data are currently unavailable. |
| Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Crohn’s Disease | It plays a role in both mucosal protection and microbial homeostasis. | Overactivation causes chronic inflammation and barrier dysfunction. | MCC950, which is an NLRP3 inhibitor. Dietary interventions. |
| Viral Hepatitis and Autoimmune Hepatitis | It may facilitate the elimination of infected or compromised hepatocytes. | Sustained activation leads to immune dysregulation and liver injury. | NLRP3 inhibitors and IL-1 β blockade. |
| Gut–Liver Axis Disorders | It maintains the gut barrier and prevents microbial translocation. | Interruption of the gut barrier predisposes to generalized inflammation and liver damage. | Probiotics; bile acid modulators; NLRP3 inhibitors. |
| Giardia duodenalis | It boosts the immune response driven by IL-1β and simultaneously decreases the number of parasites as well as the damage to the intestines. | Excessive activation may contribute to inflammation and epithelial damage. | Targeting extracellular vesicles or modulating NLRP3 may reduce pathogenicity; probiotics and IL-1 blockers could be explored. |
| Entamoeba histolytica | Acts as a sensor for invasive contact; it initiates rapid host defense. | Drives excessive inflammation and tissue destruction in amebic colitis. | Blocking integrin-NLRP3 signaling may reduce tissue damage; anti-inflammatory agents could be beneficial. |
| Helicobacter pylori | Controlled activation may help contain infection and prevent excessive inflammation. | Suppression of NLRP3 allows immune evasion and promotes gastric pathology. | Inhibiting mitophagy or regulating NLRP3 activity may enhance immune clearance; IL-1β modulation is a potential strategy. |
| Item | Identified Evidence | Gaps in the NLRP3 Role in Pediatrics |
|---|---|---|
| Diseases | NLRP3s contribute to mucosal injury in IBD. NLRP3 activation is linked to IL-1β/IL-18 release and immune dysregulation. NLRP3’s role is recognized in MIS–C and NEC. Perinatal complications; preclinical studies, in mouse models, have shown the NLRP3 inflammasome is linked to preterm labor/birth and adverse neonatal outcomes. Evidence from children, adults, and animal models. | The information regarding the activation of NLRP3 in neonatal and pediatric-specific conditions, including biliary atresia, neonatal cholestasis, and pediatric autoimmune hepatitis, is limited. The mechanism related to NLRP3 in neonatal cholestasis is not known. The modulation role of neonatal NEC is not clear. The exact triggers for IBD, regulatory procedures, and progression patterns are unclear. Lack of studies related to the mechanism of injury of pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Underexplored role of autoimmune hepatitis in pediatrics. Pediatric models for liver diseases are deficient. No adequate, precise biomarkers for liver diseases. Lack of clinical studies for the role of NLPR3 in perinatal complications. Genetic susceptibility of NLRP3 inflammasome-associated genes and the molecular regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. |
| Immune System Response | NLRP3 activation mechanisms are characterized in animals and adults. | An immature immune system is primed to incomplete recognition of how neonates’ and children’s immune systems adjust and react to NLRP3 activation. |
| Activation Mechanisms | Both canonical and non-canonical pathways are outlined, with potassium efflux, mitochondrial dysfunction, and lysosomal damage identified as primary activating factors. NLRP3 contributes to hepatocyte death by inducing pyroptosis and promoting the release of inflammatory cytokines. | -Pediatric-specific triggers and regulatory checkpoints remain inadequately characterized, highlighting the need for further research into age-dependent mechanisms of inflammasome activation. |
| Inflammasome Interaction with Intestinal Microbiota | Dysbiosis activates the NLRP3 inflammasome, contributing to both gastrointestinal and hepatic inflammation. | -Intestinal microbiota is different in neonates and children and can affect the response to the inflammasome and vulnerability to diseases. -Scarcity of longitudinal pediatric studies exploring microbiota development and its influence on NLRP3 activation. -Underscoring the need for age-targeted research, especially for inflammasome–microbiota interactions in IBD. |
| Protective vs. Pathogenic Role | NLRP3 can be both protective and abolish pathogens and suppress infection. It is also pathogenic and increases the inflammatory response. | -Few pediatric studies have investigated the dual roles of NLRP3, whether protective or pathological, in gastrointestinal and liver diseases. -Currently, no reliable biomarkers exist to distinguish the protective from injurious role of NLRP3 or to guide precise therapeutic strategies. |
| Diagnosis/monitoring Biomarkers | IL-1β, IL-18, and gasdermin D are known markers of NLRP3 activation in adults and animal studies. | There are no age-specific biomarkers available for early diagnosis or monitoring of NLRP3-related responses. The proven pediatric-specific studies on biomarker responses to NLRP3 remain scarce. |
| Therapeutic Targeting | Several direct and indirect inhibitors of NLRP3 and IL-1 blockers (e.g., anakinra) show promising results; MCC950 and other small molecules are under investigation in animal and early adult studies. | Pediatric susceptibility and inflammasome response to drugs are poorly defined due to inadequate drug safety, dosing, and efficacy. Data are deficient; no approved NLRP3-targeted drugs for children yet. A few preclinical studies in pediatrics have been conducted in relation to targeting activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the related endpoints (IL-1β, IL-18, pyroptosis). Pediatric trials focusing on pharmacogenomic and pharmacokinetic aspects of targeted therapies in children and neonates are lagging, limiting progress toward personalized treatment approaches. Use of food bioactive compounds. |
| Experimental Models | Mouse models have clarified NLRP3’s role in adult GI/liver diseases. | Few neonatal or pediatric animal models (mice, rabbits) exist to study NLRP3 behavior 0000in early gut/liver life diseases. Lack of age-appropriate pediatric models to study the inhibitory drugs. |
| Inflammasome Crosstalk | NLRP3 interacts with other inflammasomes (e.g., NLRP1, AIM2). | Crosstalk in pediatric GI/liver diseases is poorly understood. The relation to the brain axis and the respiratory system needs more investigation. |
| N | Author | Topic | Study Design | Published Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Zahid, et al. [3] | Pharmacological Inhibitors of the NLRP3 Inflammasome | Review—all age groups | 2019 |
| 2. | Song, et al. [6] | Biological functions of NLRP3 inflammasome: A therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel disease. | Review—all age groups | 2021 |
| 3. | Hoffman H.M. [11] | Inflammasome and IL-1beta-mediated disorders. | Review—all age groups | 2010 |
| 4. | Mohamed, et al. [12] | The role of nod-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in the diagnosis of late-onset neonatal sepsis | Original article | 2022 |
| 5. | Hanaei, et al. [13] | Association of NLRP3 single nucleotide polymorphisms with ulcerative colitis: A case-control study | Original article—all age groups | 2018 |
| 6. | Sharma, et al. [15] | Impaired NLRP3 inflammasome activity during fetal development regulates IL-1β production in human monocytes. | Original article | 2015 |
| 7. | Kenichiro Motomura, et al. [16] | Fetal and maternal NLRP3 signaling is required for preterm labor and birth. | Original article | 2022 |
| 8. | Wackerbarth, et al. [17] | Neonatal neutrophils exhibit reduced NLRP3 inflammasome activation | Original article | 2025 |
| 9. | Kiser, et al. [18] | NLRP3 inflammasome: a key player in neonatal brain injury | Original article | 2025 |
| 10. | Shi, et al. [20] | NLRP3 activation in macrophages promotes acute intestinal injury in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis | Original article | 2024 |
| 11. | Zaki, et al. [30] | The Nlrp3 inflammasome: contributions to intestinal homeostasis. | Review—all ages | 2011 |
| 12. | Qiang, et al. [31] | NLRP3 inflammasome in digestive diseases: From mechanism to therapy | Review—all age groups | 2022 |
| 13. | Abramson, et al. [32] | Incidence, prevalence, and time trends of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Northern California, 1996 to 2006 | Original article | 2010 |
| 14. | Guner, et al. [33] | Genetic Variants in Early-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Monogenic Causes and Clinical Implications. | Original article | 2025 |
| 15. | Nambu, et al. [34] | A Systematic Review of Monogenic Inflammatory Bowel Disease | Systematic review | 2022 |
| 16. | Vuijk, et al. [35] | Considerations in Paediatric and Adolescent Inflammatory Bowel Disease | Review | 2024 |
| 17. | Rosen et al. [36] | Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children and Adolescents | Review | 2015 |
| 18. | Ruel, et al. [37] | IBD across the age spectrum: is it the same disease? | Review—all age groups | 2014 |
| 19. | Alwassief, et al. [38] | Transitioning Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Key Considerations for Adult Gastroenterologists. | Review | 2025 |
| 20. | Granot, et al. [39] | Differences in disease characteristics and treatment exposures between paediatric and adult-onset inflammatory bowel disease using a registry-based cohort. | Original article | 2024 |
| 21. | Wang, et al. [46] | Role of NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathways in the immune mechanism of inflammatory bowel disease in children. | Original article | 2020 |
| 22. | Mao, et al. [47] | Loss-of-function CARD8 mutation causes NLRP3 inflammasome activation and Crohn’s disease. | Original article—all age groups | 2018 |
| 23. | Li, et al. [48] | Human RIPK1 deficiency causes combined immunodeficiency and inflammatory bowel disease. | Original article | 2019 |
| 24. | Mansi, et al. [49] | Bronchial hyperresponsiveness in children and adolescents with Crohn’s disease. | Original article | 2000 |
| 25. | Al-Assaf, et al. [50] | Gene Expression of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Celiac Disease of Iraqi Children. | Original article | 2021 |
| 26. | Abdul-Aziz [53] | Molecular study and determining the levels of some interleukins in children with Entamoeba histolytica. | Original article | 2025 |
| 27. | Nguyen et al. [64] | Helicobacter pylori Infections in Children. | Review | 2023 |
| 28. | Sinaei et al. [67] | Gastrointestinal and hepatic manifestations among hospitalized COVID-19 children. | Original article | 2025 |
| 29. | Nakra, et al. [70] | Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Review of Clinical Presentation, Hypothetical Pathogenesis, and Proposed Management | Review | 2020 |
| 30. | ELMeneza, et al. [71] | Inter-Alpha Inhibitor Proteins as a Predictor of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Newborn Infants. | Original article | 2023 |
| 31. | Shen, et al. [75] | Macrophage α7nAChR alleviates the inflammation of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis through mTOR/NLRP3/IL-1β pathway. | Original article | 2024 |
| 32. | Lin, et al. [78] | Hepatitis B: Immunization and Impact on Natural History and Cancer Incidence | Review | 2020 |
| 33. | Chen, et al. [76] | The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in necrotizing enterocolitis. | Original article | 2025 |
| 34. | Chen, et al. [77] | MiR-146a-5p Mimic Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Downstream Inflammatory Factors and CLIC4 in Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis. | Original article | 2021 |
| 35. | Speer, et al. [87] | Neonatal Murine Escherichia Coli Sepsis Model Demonstrates That Adjunctive Pentoxifylline Enhances the Ratio of Anti- vs. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Blood and Organ Tissues | Original article | 2020 |
| 36. | Rincon et al. [88] | Aluminum Adjuvant Improves Survival via NLRP3 Inflammasome and Myeloid Non-Granulocytic Cells in a Murine Model of Neonatal Sepsis. | Original article | 2021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
ELMeneza, S. Role of NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Disorders of Children’s Digestive Systems: A Narrative Review. Pediatr. Rep. 2025, 17, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050103
ELMeneza S. Role of NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Disorders of Children’s Digestive Systems: A Narrative Review. Pediatric Reports. 2025; 17(5):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050103
Chicago/Turabian StyleELMeneza, Safaa. 2025. "Role of NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Disorders of Children’s Digestive Systems: A Narrative Review" Pediatric Reports 17, no. 5: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050103
APA StyleELMeneza, S. (2025). Role of NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Disorders of Children’s Digestive Systems: A Narrative Review. Pediatric Reports, 17(5), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050103






