PPP2R5D-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder and Multiple Haemangiomas: A Novel Phenotypic Trait?
Abstract
1. Introduction
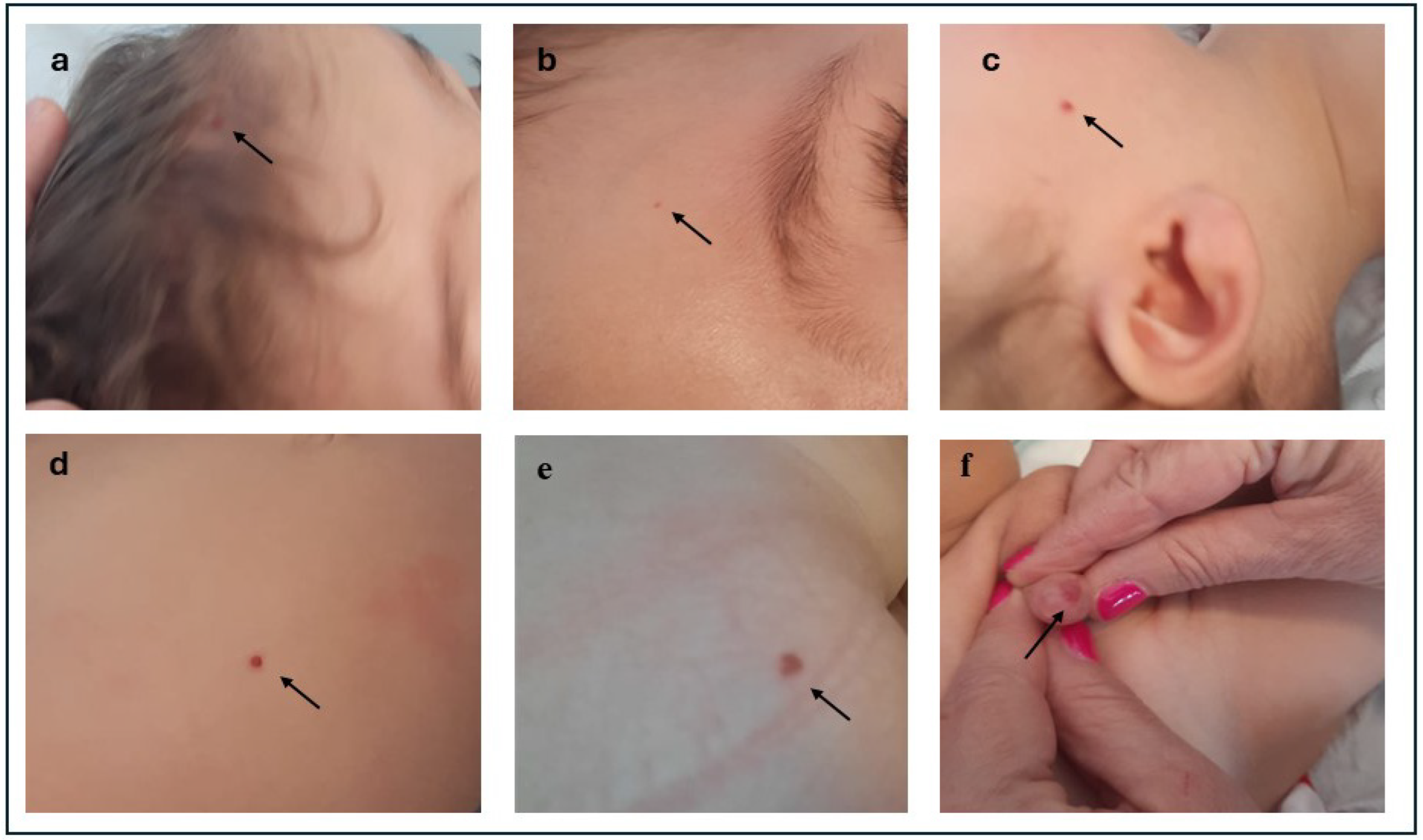
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Houge, G.; Haesen, D.; Vissers, L.E.L.M.; Mehta, S.; Parker, M.J.; Wright, M.; Vogt, J.; McKee, S.; Tolmie, J.L.; Cordeiro, N.; et al. B56δ-Related Protein Phosphatase 2A Dysfunction Identified in Patients with Intellectual Disability. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3051–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.D.; Chung, W.K. Clinical Features of PPP2 Syndrome Type R5D (Jordan’s Syndrome) to Support Standardization of Care. Mol. Case Stud. 2023, 9, a006285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaa, G.; Foss, K.; Nattakom, M.; Chung, W.K. PPP2R5D-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, D.; Cary, W.; Nolta, J.A. PPP2R5D-Related Intellectual Disability and Neurodevelopmental Delay: A Review of the Current Understanding of the Genetics and Biochemical Basis of the Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, K.S.; Tso, W.W.Y.; Ip, J.J.K.; Mak, C.C.Y.; Leung, G.K.C.; Tsang, M.H.Y.; Ying, D.; Pei, S.L.C.; Lee, S.L.; Yang, W.; et al. Identification of Mutations in the PI3K-AKT-mTOR Signalling Pathway in Patients with Macrocephaly and Developmental Delay and/or Autism. Mol. Autism 2017, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Henderson, L.B.; Cho, M.T.; Petrey, D.S.; Fong, C.T.; Haude, K.M.; Shur, N.; Lundberg, J.; Hauser, N.; Carmichael, J.; et al. De Novo Missense Variants in PPP2R5D Are Associated with Intellectual Disability, Macrocephaly, Hypotonia, and Autism. Neurogenetics 2016, 17, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCright, B.; Rivers, A.M.; Audlin, S.; Virshup, D.M. The B56 Family of Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Regulatory Subunits Encodes Differentiation-Induced Phosphoproteins that Target PP2A to Both Nucleus and Cytoplasm. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 22081–22089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, V.; Goris, J.; Van Hoof, C. PP2A: The Expected Tumor Suppressor. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolnierowicz, S. Type 2A Protein Phosphatase, the Complex Regulator of Numerous Signaling Pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechward, K.; Awotunde, O.S.; Swiatek, W.; Muszyńska, G. Protein Phosphatase 2A: Variety of Forms and Diversity of Functions. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2001, 48, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Takimoto, E.; Lu, Q.; Liu, P.; Fukuma, N.; Adachi, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Chou, S.; Baur, W.; Aronovitz, M.J.; et al. Membrane-Initiated Estrogen Receptor Signaling Mediates Metabolic Homeostasis via Central Activation of Protein Phosphatase 2A. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.Y.; Lai, T.Y.; Lin, S.C.; Wu, C.W.; Ni, I.F.; Yang, Y.S.; Hung, L.Y.; Law, B.K.; Chiang, C.W. The B56γ3 Regulatory Subunit of Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Regulates S Phase-Specific Nuclear Accumulation of PP2A and the G1 to S Transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 21567–21580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loveday, C.; Tatton-Brown, K.; Clarke, M.; Westwood, I.; Renwick, A.; Ramsay, E.; Nemeth, A.; Campbell, J.; Joss, S.; Gardner, M.; et al. Mutations in the PP2A Regulatory Subunit B Family Genes PPP2R5B, PPP2R5C and PPP2R5D Cause Human Overgrowth. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 4775–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, A.G.; Kang, S.; Zhao, L.; Vogt, P.K. Oncogenic PI3K Deregulates Transcription and Translation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, J.; Maity, A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Angiogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seshacharyulu, P.; Pandey, P.; Datta, K.; Batra, S.K. Phosphatase: PP2A Structural Importance, Regulation and Its Aberrant Expression in Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamibayashi, C.; Estes, R.; Lickteig, R.L.; Yang, S.I.; Craft, C.; Mumby, M.C. Comparison of Heterotrimeric Protein Phosphatase 2A Containing Different B Subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20139–20148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.H.; Liu, L.Z. PI3K/PTEN Signaling in Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis. Adv. Cancer Res. 2009, 102, 19–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.H.; Zheng, J.Z.; Aoki, M.; Vogt, P.K. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Signaling Mediates Angiogenesis and Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Endothelial Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1749–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Z.; Tschopp, O.; Hemmings-Mieszczak, M.; Feng, J.; Brodbeck, D.; Perentes, E.; Hemmings, B.A. Protein Kinase B α/Akt1 Regulates Placental Development and Fetal Growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 32124–32131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, K.; Li, L.; Xu, C.; Xiang, B. Signaling Pathways in the Development of Infantile Hemangioma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.D.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Sebire, N.J. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase: A New Kid on the Block in Vascular Anomalies. J. Pathol. 2016, 240, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.D.; Baselga, E.; Graupera, M. PIK3CA Mutations in Vascular Malformations. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2019, 26, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaud, G.; Hammill, A.M.; Adams, D.; Vikkula, M.; Keppler-Noreuil, K.M. A Review of Mechanisms of Disease Across PIK3CA-Related Disorders with Vascular Manifestations. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castel, P.; Carmona, F.J.; Grego-Bessa, J.; Berger, M.F.; Viale, A.; Anderson, K.V.; Bague, S.; Scaltriti, M.; Antonescu, C.R.; Baselga, E.; et al. Somatic PIK3CA Mutations as a Driver of Sporadic Venous Malformations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 332ra42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.D.; Tzouanacou, E.; Zaw-Thin, M.; Berenjeno, I.M.; Parker, V.E.; Chivite, I.; Milà-Guasch, M.; Pearce, W.; Solomon, I.; Angulo-Urarte, A.; et al. Somatic Activating Mutations in Pik3ca Cause Sporadic Venous Malformations in Mice and Humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 332ra43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler-Noreuil, K.M.; Rios, J.J.; Parker, V.E.; Semple, R.K.; Lindhurst, M.J.; Sapp, J.C.; Alomari, A.; Ezaki, M.; Dobyns, W.; Biesecker, L.G. PIK3CA-Related Overgrowth Spectrum (PROS): Diagnostic and Testing Eligibility Criteria, Differential Diagnosis, and Evaluation. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2015, 167A, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobialka, P.; Sabata, H.; Vilalta, O.; Gouveia, L.; Angulo-Urarte, A.; Muixí, L.; Zanoncello, J.; Muñoz-Aznar, O.; Olaciregui, N.G.; Fanlo, L.; et al. The Onset of PI3K-related Vascular Malformations Occurs during Angiogenesis and Is Prevented by the AKT Inhibitor Miransertib. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e15619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliazzi, A.; Oranges, T.; Traficante, G.; Trapani, C.; Facchini, F.; Martin, A.; Semeraro, A.; Perrone, A.; Filippeschi, C.; Giglio, S. PIK3CA-Related Overgrowth Spectrum from Diagnosis to Targeted Therapy: A Case of CLOVES Syndrome Treated With Alpelisib. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 732836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Bao, X.; Yu, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Q. Disruption and Inactivation of the PP2A Complex Promotes the Proliferation and Angiogenesis of Hemangioma Endothelial Cells through Activating AKT and ERK. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25660–25676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maines, E.; Franceschi, R.; Martinelli, D.; Soli, F.; Lepri, F.R.; Piccoli, G.; Soffiati, M. Hypoglycemia Due to PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway Defects: Two Novel Cases and Review of the Literature. Hormones 2021, 20, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Our Case | Maines et al. [33] | |
|---|---|---|
| Head Circumference | Macrocephaly with HC 37 cm (2.3 SD) | Macrocephaly with HC 47.5 cm (4.1 SD) |
| Dysmorphic Features | Frontal bossing and telecanthus | Wide forehead |
| Down-slanting palpebral fissures | Epicanthus | |
| Depressed nasal bridge | ||
| Deep philtrum Cupid bow on the upper lip | ||
| Asymmetric jaw with left hypoplasia | ||
| Micrognathia | ||
| Pectus excavatum | ||
| Haemangiomas | Several diffuse, bright red haemangiomas of various sizes and types at 12 months. | Two haemangiomas (lip, back) at 7 months |
| Neurological Findings | Persistent axial hypotonia | Nystagmus |
| Epilepsy | Seizures | |
| Stereotypes | Developmental delay | |
| Diffuse hypotonia | ||
| Hypoglycaemia | Transient hypoglycaemia at birth | Hypoglycaemic episodes in the first days of life |
| MRI Findings | Normal brain MRI | Normal brain MRI |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Comisi, F.; Soddu, C.; Lai, F.; Marica, M.; Lorrai, M.; Mancuso, G.; Giglio, S.; Savasta, S. PPP2R5D-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder and Multiple Haemangiomas: A Novel Phenotypic Trait? Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16, 1200-1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16040101
Comisi F, Soddu C, Lai F, Marica M, Lorrai M, Mancuso G, Giglio S, Savasta S. PPP2R5D-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder and Multiple Haemangiomas: A Novel Phenotypic Trait? Pediatric Reports. 2024; 16(4):1200-1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16040101
Chicago/Turabian StyleComisi, Francesco, Consolata Soddu, Francesco Lai, Monica Marica, Michela Lorrai, Giancarlo Mancuso, Sabrina Giglio, and Salvatore Savasta. 2024. "PPP2R5D-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder and Multiple Haemangiomas: A Novel Phenotypic Trait?" Pediatric Reports 16, no. 4: 1200-1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16040101
APA StyleComisi, F., Soddu, C., Lai, F., Marica, M., Lorrai, M., Mancuso, G., Giglio, S., & Savasta, S. (2024). PPP2R5D-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder and Multiple Haemangiomas: A Novel Phenotypic Trait? Pediatric Reports, 16(4), 1200-1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16040101







