Patterns of Cannabis- and Substance-Related Congenital General Anomalies in Europe: A Geospatiotemporal and Causal Inferential Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
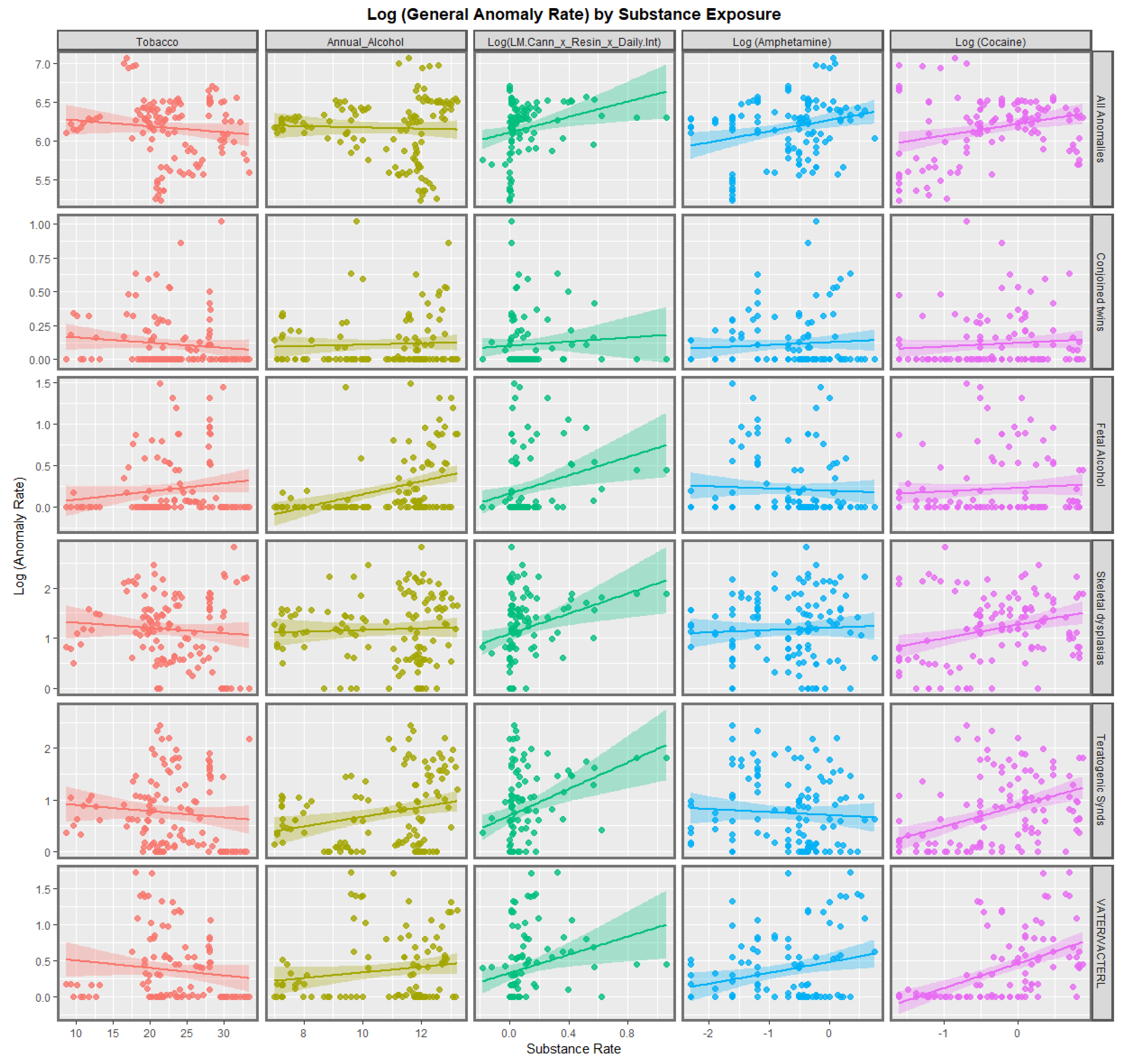
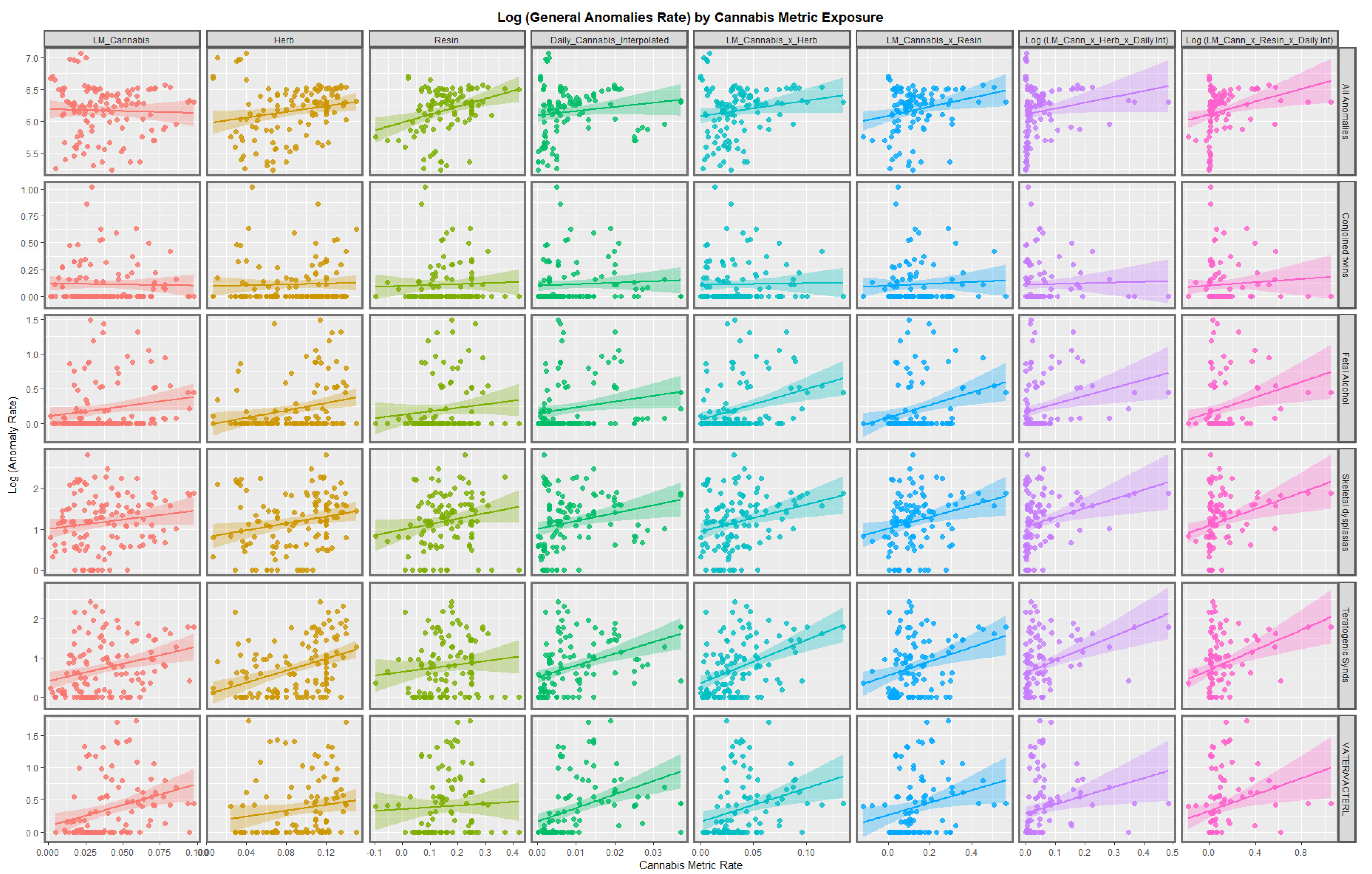
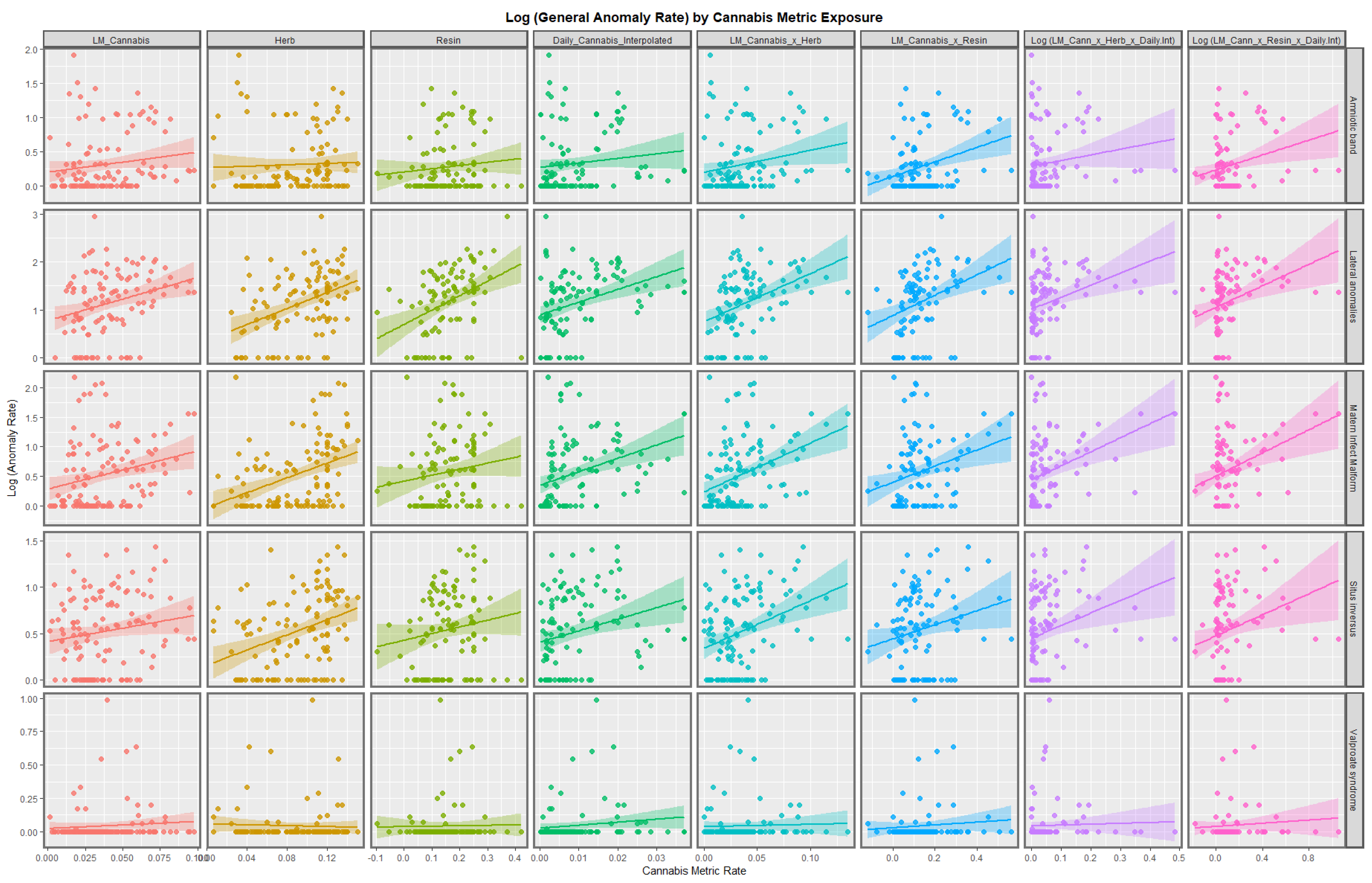
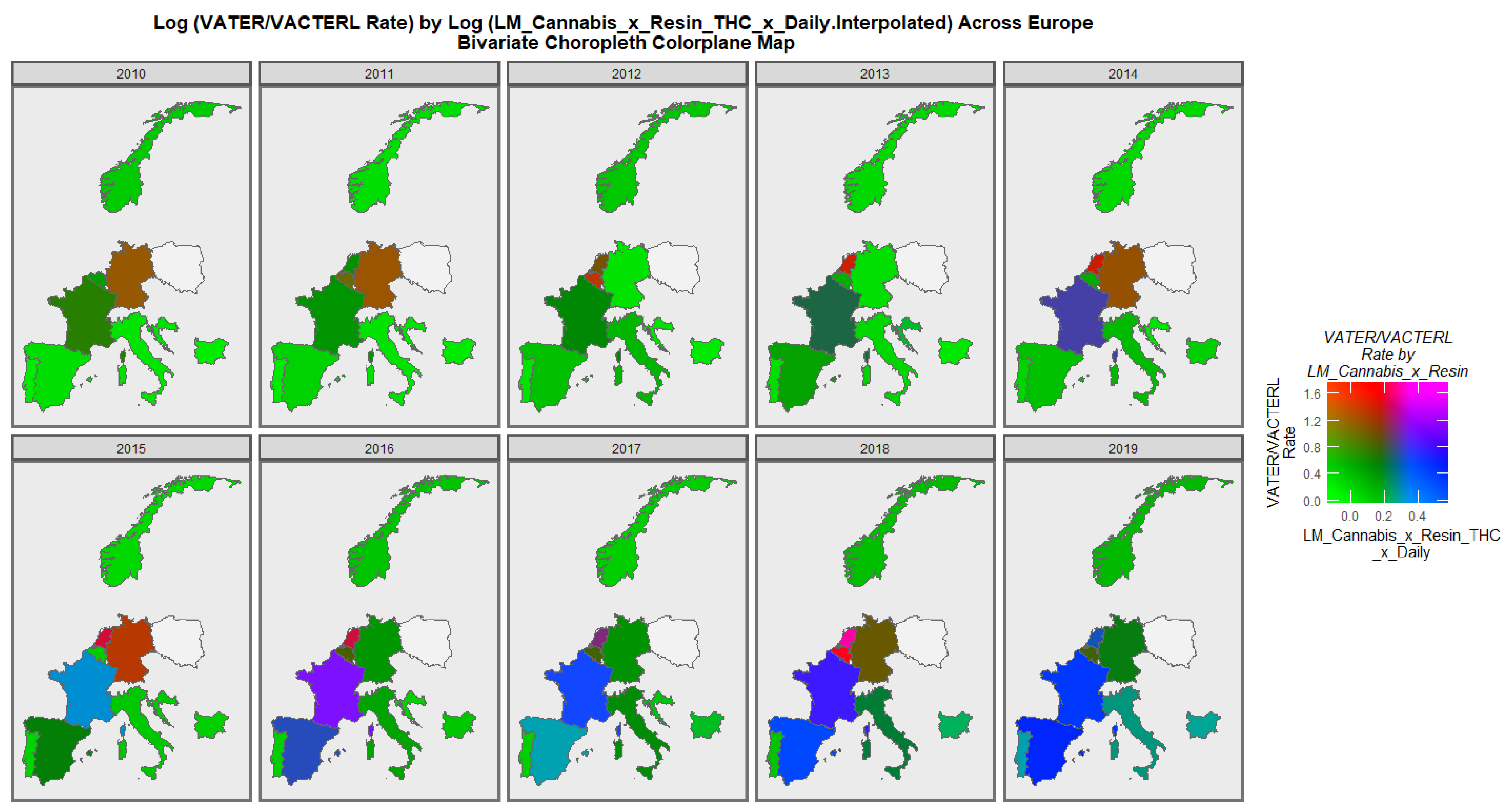
3.1. Data Presentation
3.2. Bivariate Analysis
3.2.1. Continuous Data
3.2.2. Categorical Bivariate Analysis
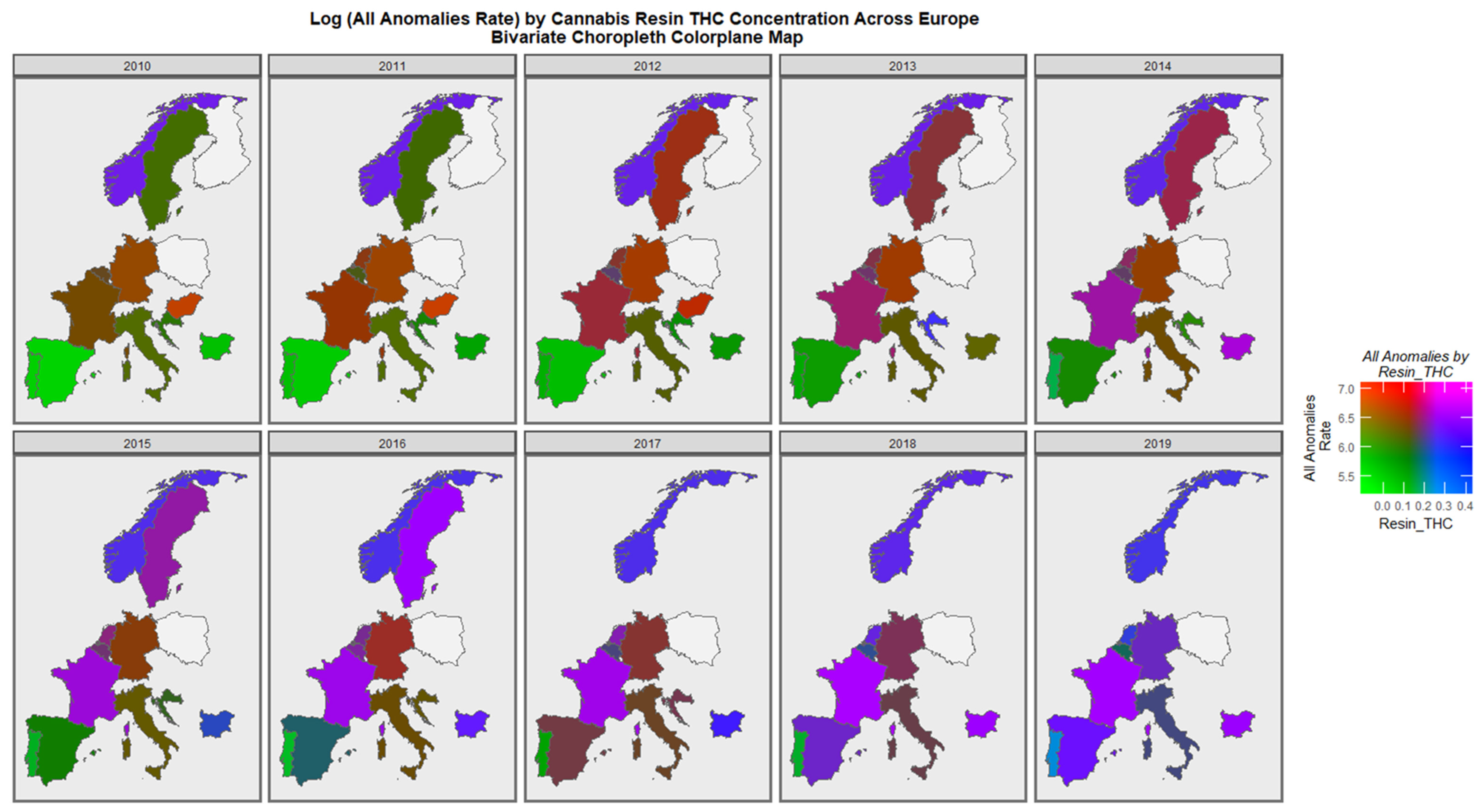
3.3. Multivariate Analysis
3.3.1. Panel Regression
3.3.2. Geospatial Analysis
3.4. Causal Inference
E-Values
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Results
4.2. Choice of Anomalies
4.3. Qualitative Causal Inference
4.4. Quantitative Causal Inference
4.5. Mechanisms
4.6. Epigenomic Controls
4.7. Morphogen Gradients
4.8. Exponential Genotoxic Effects
4.9. Generalizability
4.10. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Epidemiological Overview of Multidimensional Chromosomal and Genome Toxicity of Cannabis Exposure in Congenital Anomalies and Cancer Development. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13892–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Cannabis in Pregnancy—Rejoinder, Exposition and Cautionary Tales; Psychiatric Times: Irvine, CA, USA, 2020; p. 37. Available online: https://www.bing.com/search?q=Cannabis+in+Pregnancy+%E2%80%93+Rejoinder%82C+Exposition+and+Cautionary+Tales&cvid=22538e20124c04711b92017489c92063214a&aqs=edge..92017469i92017457.92017439j92017480j92017481&pglt=92017443&FORM=ANSPA92017481&PC=U92017531 (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Forrester, M.B.; Merz, R.D. Risk of Selected Birth Defects with Prenatal Illicit Drug Use, Hawaii, 1986–2002. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2006, 70, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Canadian Cannabis Consumption and Patterns of Congenital Anomalies: An Ecological Geospatial Analysis. J. Addict. Med. 2020, 14, e195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Cannabis Consumption Patterns Explain the East-West Gradient in Canadian Neural Tube Defect Incidence: An Ecological Study. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2019, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Impacts of cannabinoid epigenetics on human development: Reflections on Murphy et. al. ‘cannabinoid exposure and altered DNA methylation in rat and human sperm’ epigenetics 2018; 13: 1208–1221. Epigenetics 2019, 14, 1041–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Cannabinoid- and Substance-Relationships of European Congenital Anomaly Patterns: A Space-Time Panel Regression and Causal Inferential Study. Environ. Epigenet. 2022, 8, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Effect of Cannabis Legalization on US Autism Incidence and Medium Term Projections. Clin. Pediatr. Open Access 2019, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Epidemiological Associations of Various Substances and Multiple Cannabinoids with Autism in USA. Clin. Pediatr. Open Access 2019, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Cannabis Teratology Explains Current Patterns of Coloradan Congenital Defects: The Contribution of Increased Cannabinoid Exposure to Rising Teratological Trends. Clin. Pediatr. 2019, 58, 1085–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Cannabinoid Genotoxicity and Congenital Anomalies: A Convergent Synthesis of European and USA Datasets. In Cannabis, Cannabinoids and Endocannabinoids; Preedy, V., Patel, V., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2022; Volume 1, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Cannabis Genotoxicity and Cancer Incidence: A Highly Concordant Synthesis of European and USA Datasets. In Cannabis, Cannabinoids and Endocannabinoids; Preedy, V., Patel, V., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2022; Volume 1, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Broad Spectrum epidemiological contribution of cannabis and other substances to the teratological profile of northern New South Wales: Geospatial and causal inference analysis. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 21, 75–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Geotemporospatial and causal inference epidemiological analysis of US survey and overview of cannabis, cannabidiol and cannabinoid genotoxicity in relation to congenital anomalies 2001–2015. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 47–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Contemporary epidemiology of rising atrial septal defect trends across USA 1991–2016: A combined ecological geospatiotemporal and causal inferential study. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. A geospatiotemporal and causal inference epidemiological exploration of substance and cannabinoid exposure as drivers of rising US pediatric cancer rates. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 197–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Cannabinoid exposure as a major driver of pediatric acute lymphoid Leukaemia rates across the USA: Combined geospatial, multiple imputation and causal inference study. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 984–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S. Rapid Response: Cannabinoid Genotoxic Trifecta—Cancerogenesis, Clinical Teratogenesis and Cellular Ageing. Br. Med. J. 2022, 376, n3114. [Google Scholar]
- Reece, A.S. Limblessness: Cannabinoids Inhibit Key Embryonic Morphogens both Directly and Epigenomically. Br. Med. J. 2022, 376, n3114. [Google Scholar]
- Reece, A.S. Rapid Response: Known Cannabis Teratogenicity Needs to be Carefully Considered. BMJ 2018, 362, k3357. [Google Scholar]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Quadruple convergence—Rising cannabis prevalence, intensity, concentration and use disorder treatment. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 10, 100245–100246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthey, J.; Freeman, T.P.; Kilian, C.; Lopez-Pelayo, H.; Rehm, J. Public health monitoring of cannabis use in Europe: Prevalence of use, cannabis potency, and treatment rates. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 10, 100227–200237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United National Office of Drugs and Crime. Drugs and Crime. In World Drug Report 2019; United National World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 1–5, Available online: https://wdr.unodc.org/wdr2019/index.html (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Tahir, S.K.; Trogadis, J.E.; Stevens, J.K.; Zimmerman, A.M. Cytoskeletal organization following cannabinoid treatment in undifferentiated and differentiated PC12 cells. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1992, 70, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, G.; Martin, S.; Garcia-Gil, L.; Crespo, J.A.; Ruiz-Gayo, M.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J.J.; Garcia-Lecumberri, C.; Pelaprat, D.; Fuentes, J.A.; Ramos, J.A.; et al. Maternal exposure to delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol facilitates morphine self-administration behavior and changes regional binding to central mu opioid receptors in adult offspring female rats. Brain Res. 1998, 807, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, F.W.; Seid, D.A.; Wei, E.T. Mutagenic activity of marihuana smoke condensates. Cancer Lett. 1979, 6, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, V.J.; Ferk, F.; Al-Serori, H.; Misik, M.; Nersesyan, A.; Auwarter, V.; Grummt, T.; Knasmuller, S. Genotoxic properties of representatives of alkylindazoles and aminoalkyl-indoles which are consumed as synthetic cannabinoids. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 80, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, S.K.; Zimmerman, A.M. Influence of marihuana on cellular structures and biochemical activities. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 40, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.M.; Raj, A.Y. Influence of cannabinoids on somatic cells in vivo. Pharmacology 1980, 21, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, V.J.; Auwarter, V.; Grummt, T.; Moosmann, B.; Misik, M.; Knasmuller, S. Investigation of the in vitro toxicological properties of the synthetic cannabimimetic drug CP-47,497-C8. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 277, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisar, Z.; Singh, N.; Hroudova, J. Cannabinoid-induced changes in respiration of brain mitochondria. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 231, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Hroudova, J.; Fisar, Z. Cannabinoid-Induced Changes in the Activity of Electron Transport Chain Complexes of Brain Mitochondria. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 56, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, C.; Ferk, F.; Misik, M.; Ropek, N.; Nersesyan, A.; Mejri, D.; Holzmann, K.; Lavorgna, M.; Isidori, M.; Knasmuller, S. Low doses of widely consumed cannabinoids (cannabidiol and cannabidivarin) cause DNA damage and chromosomal aberrations in human-derived cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 93, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fish, E.W.; Murdaugh, L.B.; Zhang, C.; Boschen, K.E.; Boa-Amponsem, O.; Mendoza-Romero, H.N.; Tarpley, M.; Chdid, L.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Cole, G.J.; et al. Cannabinoids Exacerbate Alcohol Teratogenesis by a CB1-Hedgehog Interaction. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16057–16075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölzel, B.N.; Pfannkuche, K.; Allner, B.; Allner, H.T.; Hescheler, J.; Derichsweiler, D.; Hollert, H.; Schiwy, A.; Brendt, J.; Schaffeld, M.; et al. Following the adverse outcome pathway from micronucleus to cancer using H2B-eGFP transgenic healthy stem cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 3265–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VACTERL Association. Available online: https://www.gosh.nhs.uk/conditions-and-treatments/conditions-we-treat/vacterl-association-0/ (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Schrott, R.; Murphy, S.K.; Modliszewski, J.L.; King, D.E.; Hill, B.; Itchon-Ramos, N.; Raburn, D.; Price, T.; Levin, E.D.; Vandrey, R.; et al. Refraining from use diminishes cannabis-associated epigenetic changes in human sperm. Environ. Epigenet. 2021, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fergusson, D.M.; Boden, J.M.; Horwood, L.J. Cannabis use and other illicit drug use: Testing the cannabis gateway hypothesis. Addiction 2006, 101, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiani, A.; Boden, J.M.; De Pirro, S.; Fergusson, D.M.; Horwood, L.J.; Harold, G.T. Tobacco smoking and cannabis use in a longitudinal birth cohort: Evidence of reciprocal causal relationships. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2015, 150, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, E.J.; Miles, J.N.; Tucker, J.S. Gateway to curiosity: Medical marijuana ads and intention and use during middle school. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2015, 29, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergusson, D.M.; Boden, J.M.; Horwood, L.J. Psychosocial sequelae of cannabis use and implications for policy: Findings from the Christchurch Health and Development Study. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2015, 50, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, D.; Kandel, E. The Gateway Hypothesis of substance abuse: Developmental, biological and societal perspectives. Acta. Paediatr. 2015, 104, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabin, R.A.; George, T.P. A review of co-morbid tobacco and cannabis use disorders: Possible mechanisms to explain high rates of co-use. Am. J. Addict. 2015, 24, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secades-Villa, R.; Garcia-Rodriguez, O.; Jin, C.J.; Wang, S.; Blanco, C. Probability and predictors of the cannabis gateway effect: A national study. Int. J. Drug Policy 2015, 26, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkansah-Amankra, S.; Minelli, M. “Gateway hypothesis” and early drug use: Additional findings from tracking a population-based sample of adolescents to adulthood. Prev. Med. Rep. 2016, 4, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.C.; Lopez-Quintero, C.; Alshaarawy, O. Cannabis Epidemiology: A Selective Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 22, 6340–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.D.; Loffredo, C.A.; Correa-Villasenor, A.; Ferencz, C. Attributable fraction for cardiac malformations. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 148, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.F.S.; Nahas, G.G.; Hembree, W.C. Effects of Marijuana Inhalation on Spermatogenesis of the Rat. In Marijuana in Medicine; Nahas, G.G., Sutin, K.M., Harvey, D.J., Agurell, S., Eds.; Human Press: Totowa, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 1, pp. 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, A.M.; Zimmerman, S.; Raj, A.Y. Effects of Cannabinoids on Spermatogensis in Mice. In Marijuana in Medicine; Nahas, G.G., Sutin, K.M., Harvey, D.J., Agurell, S., Eds.; Human Press: Totowa, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 1, pp. 347–358. [Google Scholar]
- Morishima, A. Effects of cannabis and natural cannabinoids on chromosomes and ova. NIDA Res. Monogr. 1984, 44, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stenchever, M.A.; Kunysz, T.J.; Allen, M.A. Chromosome breakage in users of marihuana. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1974, 118, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuchtenberger, C.; Leuchtenberger, R. Morphological and cytochemical effects of marijuana cigarette smoke on epithelioid cells of lung explants from mice. Nature 1971, 234, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishima, A.; Henrich, R.T.; Jayaraman, J.; Nahas, G.G. Hypoploid metaphases in cultured lymphocytes of marihuana smokers. Adv. Biosci. 1978, 22–23, 371–376. [Google Scholar]
- Henrich, R.T.; Nogawa, T.; Morishima, A. In vitro induction of segregational errors of chromosomes by natural cannabinoids in normal human lymphocytes. Environ. Mutagen. 1980, 2, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.; Degenhardt, L. Adverse health effects of non-medical cannabis use. Lancet 2009, 374, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Chromothripsis and epigenomics complete causality criteria for cannabis- and addiction-connected carcinogenicity, congenital toxicity and heritable genotoxicity. Mutat. Res. 2016, 789, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bileck, A.; Ferk, F.; Al-Serori, H.; Koller, V.J.; Muqaku, B.; Haslberger, A.; Auwarter, V.; Gerner, C.; Knasmuller, S. Impact of a synthetic cannabinoid (CP-47,497-C8) on protein expression in human cells: Evidence for induction of inflammation and DNA damage. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferk, F.; Gminski, R.; Al-Serori, H.; Misik, M.; Nersesyan, A.; Koller, V.J.; Angerer, V.; Auwarter, V.; Tang, T.; Arif, A.T.; et al. Genotoxic properties of XLR-11, a widely consumed synthetic cannabinoid, and of the benzoyl indole RCS-4. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 3111–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukudai, Y.; Kondo, S.; Fujita, A.; Yoshihama, Y.; Shirota, T.; Shintani, S. Tumor protein D54 is a negative regulator of extracellular matrix-dependent migration and attachment in oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived cell lines. Cell Oncol. 2013, 36, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, M.; Castiglioni, S.; Magni, S.; Della Torre, C.; Binelli, A. Increase in cannabis use may indirectly affect the health status of a freshwater species. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Went, G.F. Mutagenicity testing of 3 hallucinogens: LSD, psilocybin and delta 9-THC, using the micronucleus test. Experientia 1978, 34, 324–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhoum, S.F.; Ngo, B.; Laughney, A.M.; Cavallo, J.A.; Murphy, C.J.; Ly, P.; Shah, P.; Sriram, R.K.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Taunk, N.K.; et al. Chromosomal instability drives metastasis through a cytosolic DNA response. Nature 2018, 553, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatti, E.; Rizzi, R.; Re, F.; Chiesara, E. Genotoxicity of heroin and cannabinoids in humans. Pharmacol. Res. 1989, 21 (Suppl. S1), 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, M.; Binelli, A. Oxidative and genetic responses induced by Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta-9-THC) to Dreissena polymorpha. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, R.D.; Regan, J.D. Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol: Effect on macromolecular synthesis in human and other mammalian cells. Arch. Toxicol. 1976, 35, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon, M.J.; Haas, A.E.; Stein, J.L.; Stein, G.S. Influence of psychoactive and nonpsychoactive cannabinoids on cell proliferation and macromolecular biosynthesis in human cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1981, 30, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon, M.J.; Jansing, R.L.; Doggett, S.; Stein, J.L.; Stein, G.S. Influence of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on cell proliferation and macromolecular biosynthesis in human cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1978, 27, 1759–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahas, G.G.; Morishima, A.; Desoize, B. Effects of cannabinoids on macromolecular synthesis and replication of cultured lymphocytes. Fed. Proc. 1977, 36, 1748–1752. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McClean, D.K.; Zimmerman, A.M. Action of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol on cell division and macromolecular synthesis in division-synchronized protozoa. Pharmacology 1976, 14, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, N.A.E.M.; El-Toukhy, M.A.E.-F.; Kazem, A.H.; Ali, M.E.-S.; Ahmad, M.A.E.-R.; Ghazy, H.M.R.; El-Din, A.M.G. Protective and therapeutic effects of cannabis plant extract on liver cancer induced by dimethylnitrosamine in mice. Alex. J. Med. 2014, 50, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon, M.J.; Haas, A.E.; Stein, J.L.; Stein, G.S. Influence of psychoactive and nonpsychoactive cannabinoids on chromatin structure and function in human cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1981, 30, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Hegde, V.L.; Rao, R.; Zhang, J.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Histone modifications are associated with Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol-mediated alterations in antigen-specific T cell responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 18707–18718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossato, M.; Ion Popa, F.; Ferigo, M.; Clari, G.; Foresta, C. Human sperm express cannabinoid receptor Cb1, the activation of which inhibits motility, acrosome reaction, and mitochondrial function. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNieri, J.A.; Wang, X.; Szutorisz, H.; Spano, S.M.; Kaur, J.; Casaccia, P.; Dow-Edwards, D.; Hurd, Y.L. Maternal cannabis use alters ventral striatal dopamine D2 gene regulation in the offspring. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.J.; Bara, A.; Vargas, C.A.; Frick, A.L.; Loh, E.; Landry, J.; Uzamere, T.O.; Callens, J.E.; Martin, Q.; Rajarajan, P.; et al. Prenatal Δ(9)-Tetrahydrocannabinol Exposure in Males Leads to Motivational Disturbances Related to Striatal Epigenetic Dysregulation. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szutorisz, H.; Hurd, Y.L. Epigenetic Effects of Cannabis Exposure. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szutorisz, H.; DiNieri, J.A.; Sweet, E.; Egervari, G.; Michaelides, M.; Carter, J.M.; Ren, Y.; Miller, M.L.; Blitzer, R.D.; Hurd, Y.L. Parental THC exposure leads to compulsive heroin-seeking and altered striatal synaptic plasticity in the subsequent generation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.T.; Szutorisz, H.; Garg, P.; Martin, Q.; Landry, J.A.; Sharp, A.J.; Hurd, Y.L. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Profiling Reveals Epigenetic Changes in the Rat Nucleus Accumbens Associated with Cross-Generational Effects of Adolescent THC Exposure. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 2993–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szutorisz, H.; Hurd, Y.L. High times for cannabis: Epigenetic imprint and its legacy on brain and behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 85, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.K.; Itchon-Ramos, N.; Visco, Z.; Huang, Z.; Grenier, C.; Schrott, R.; Acharya, K.; Boudreau, M.H.; Price, T.M.; Raburn, D.J.; et al. Cannabinoid exposure and altered DNA methylation in rat and human sperm. Epigenetics 2018, 13, 1208–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrott, R.; Acharya, K.; Itchon-Ramos, N.; Hawkey, A.B.; Pippen, E.; Mitchell, J.T.; Kollins, S.H.; Levin, E.D.; Murphy, S.K. Cannabis use is associated with potentially heritable widespread changes in autism candidate gene DLGAP2 DNA methylation in sperm. Epigenetics 2019, 15, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafian, T.A.; Habib, N.; Oldham, M.; Seeram, N.; Lee, R.P.; Lin, L.; Tashkin, D.P.; Roth, M.D. Inhaled marijuana smoke disrupts mitochondrial energetics in pulmonary epithelial cells in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. 2006, 290, L1202–L1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafian, T.A.; Kouyoumjian, S.; Khoshaghideh, F.; Tashkin, D.P.; Roth, M.D. Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol disrupts mitochondrial function and cell energetics. Am. J. Physiol. 2003, 284, L298–L306. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, V.; Schlagowski, A.I.; Rouyer, O.; Charles, A.L.; Singh, F.; Auger, C.; Schini-Kerth, V.; Marescaux, C.; Raul, J.S.; Zoll, J.; et al. Tetrahydrocannabinol induces brain mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction and increases oxidative stress: A potential mechanism involved in cannabis-related stroke. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 323706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Colleoni, M. Changes in rat brain energetic metabolism after exposure to anandamide or Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 395, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, Z.S.; Chohan, K.R.; Whyte, D.A.; Penefsky, H.S.; Brown, O.M.; Souid, A.K. Cannabinoids inhibit the respiration of human sperm. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 91, 2471–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Baler, R.D.; Compton, W.M.; Weiss, S.R. Adverse Health Effects of Marijuana Use. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 878–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, V.; Rouyer, O.; Schlagowski, A.; Zoll, J.; Raul, J.S.; Marescaux, C. Étude de l’effet du THC sur la respiration mitochondriale du cerveau de rat. Une piste de réflexion pour expliquer le lien entre la consommation de cannabis et la survenue d’infarctus cérébral chez l’homme. Study of the effect of THC on mitochondrial respiration of the rat brain. One line of thought to explain the link between cannabis use and the occurrence of cerebral infarction in men Revue Neurologique, Neurological Review. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 170 (Supp. 1), A19–A20. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, W.; Li, M.D. Genes and pathways co-associated with the exposure to multiple drugs of abuse, including alcohol, amphetamine/methamphetamine, cocaine, marijuana, morphine, and/or nicotine: A review of proteomics analyses. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 44, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eurocat Data. Prevalence Charts and Tables. Available online: https://eu-rd-platform.jrc.ec.europa.eu/eurocat/eurocat-data/prevalence_en (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Global Health Observatory. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/indicators/indicator-details/GHO/total-(recorded-unrecorded)-alcohol-per-capita-(15-)-consumption (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). Statistical Bulletin 2021—Prevalence of Drug Use. Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/data/stats2021/gps_en (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- The World Bank: Crude Data. Adjusted Net National Income per Capita (Current US$). Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.ADJ.NNTY.PC.CD (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/ (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; Francios, R.; Groelmund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pebesma, E. Simple Features for R: Standardized Support for Spatial Vector Data. R J. 2018, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viridis. Default Color Maps from ‘Matplotlib’. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=viridis (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Colorplaner. ggplot2 Extension to Visualize Two Variables per Color Aesthetic through Colorspace Projection. Available online: https://github.com/wmurphyrd/colorplaner (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; R Core Team. nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R Compr. R Arch. Netw. 2020, 1. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Broom.mixed. Tidying Methods for Mixed Models. Available online: http://github.com/bbolker/broom.mixed (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Broom. Convert Statistical Objects into Tidy Tibbles. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=broom (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Leeper, T.J. Margins: Marginal Effects for Model Objects; R Package Version; Leeper, T.J., Ed.; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, M.N.; Ziegler, A. Ranger: A Fast Implementation of Random Forests for High Dimensional Data in C++ and R. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 77, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwell, B.M.; Boehmke, B.C. Variable Importance Plots—An Introduction to the vip Package. R J. 2021, 12, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Package ‘Plm’. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/plm/plm.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Bivand, R.; Anselin, L.; Berke, O.; Bernat, A.; Carvalho, M.; Chun, Y.; Dormann, C.; Dray, S.; Halbersma, R.; Lewis-Koh, N.; et al. The spdep Package. Compr. R Arch. Netw. 2007, 1, 1–143. [Google Scholar]
- Millo, G.; Piras, G. splm: Spatial Panel Data Models in R. J. Stast. Softw. 2012, 47, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Millo, G.; Piras, G. Package ‘Splm’; CRAN (Central R-Archive Network): Trieste, Italy, 2018; pp. 1–27. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/splm/splm.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Croissant, Y.; Millo, G. Panel Data Econometrics with R; John Wiley and Sons: Oxford, UK, 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wal, W.; Geskus, R. ipw: An R Package for Inverse Probability Weighting. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 43, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderWeele, T.J.; Ding, P. Sensitivity Analysis in Observational Research: Introducing the E-Value. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 167, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderWeele, T.J.; Martin, J.N.; Mathur, M.B. E-values and incidence density sampling. Epidemiology 2020, 31, e51–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderWeele, T.J.; Mathur, M.B. Commentary: Developing best-practice guidelines for the reporting of E-values. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 1495–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderWeele, T.J.; Ding, P.; Mathur, M. Technical Considerations in the Use of the E-Value. J. Causal Inference 2019, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, J.; Mackaenzie, D. The Book of Why: The New Science of Cause and Effect; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1, Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/EValue/EValue.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Subbanna, S.; Nagre, N.N.; Umapathy, N.S.; Pace, B.S.; Basavarajappa, B.S. Ethanol exposure induces neonatal neurodegeneration by enhancing CB1R Exon1 histone H4K8 acetylation and up-regulating CB1R function causing neurobehavioral abnormalities in adult mice. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbanna, S.; Psychoyos, D.; Xie, S.; Basavarajappa, B.S. Postnatal ethanol exposure alters levels of 2-arachidonylglycerol-metabolizing enzymes and pharmacological inhibition of monoacylglycerol lipase does not cause neurodegeneration in neonatal mice. J. Neurochem. 2015, 134, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleverstov, O.; Tobiasz, A.; Jackson, J.S.; Sullivan, R.; Ma, D.; Sullivan, J.P.; Davison, S.; Akkhawattanangkul, Y.; Tate, D.L.; Costello, T.; et al. Maternal alcohol exposure during mid-pregnancy dilates fetal cerebral arteries via endocannabinoid receptors. Alcohol Fayettev. 2017, 61, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbanna, S.; Nagre, N.N.; Shivakumar, M.; Joshi, V.; Psychoyos, D.; Kutlar, A.; Umapathy, N.S.; Basavarajappa, B.S. CB1R-Mediated Activation of Caspase-3 Causes Epigenetic and Neurobehavioral Abnormalities in Postnatal Ethanol-Exposed Mice. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, V.; Subbanna, S.; Shivakumar, M.; Basavarajappa, B.S. CB1R regulates CDK5 signaling and epigenetically controls Rac1 expression contributing to neurobehavioral abnormalities in mice postnatally exposed to ethanol. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakumar, M.; Subbanna, S.; Joshi, V.; Basavarajappa, B.S. Postnatal Ethanol Exposure Activates HDAC-Mediated Histone Deacetylation, Impairs Synaptic Plasticity Gene Expression and Behavior in Mice. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 23, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbanna, S.; Basavarajappa, B.S. Postnatal Ethanol-Induced Neurodegeneration Involves CB1R-Mediated β-Catenin Degradation in Neonatal Mice. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussier, A.A.; Bodnar, T.S.; Moksa, M.; Hirst, M.; Kobor, M.S.; Weinberg, J. Prenatal Adversity Alters the Epigenetic Profile of the Prefrontal Cortex: Sexually Dimorphic Effects of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and Food-Related Stress. Genes 2021, 12, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussier, A.A.; Bodnar, T.S.; Weinberg, J. Intersection of Epigenetic and Immune Alterations: Implications for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder and Mental Health. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 788630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Virdee, M.S.; Eckerle, J.K.; Sandness, K.E.; Georgieff, M.K.; Boys, C.J.; Zeisel, S.H.; Wozniak, J.R. Polymorphisms in SLC44A1 are associated with cognitive improvement in children diagnosed with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: An exploratory study of oral choline supplementation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terracina, S.; Ferraguti, G.; Tarani, L.; Messina, M.P.; Lucarelli, M.; Vitali, M.; De Persis, S.; Greco, A.; Minni, A.; Polimeni, A.; et al. Transgenerational Abnormalities Induced by Paternal Preconceptual Alcohol Drinking. Findings from Humans and Animal Models. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 20, 1158–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.N.; Zimmel, K.N.; Roach, A.N.; Basel, A.; Mehta, N.A.; Bedi, Y.S.; Golding, M.C. Maternal background alters the penetrance of growth phenotypes and sex-specific placental adaptation of offspring sired by alcohol-exposed males. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e22035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallén, E.; Auvinen, P.; Kaminen-Ahola, N. The Effects of Early Prenatal Alcohol Exposure on Epigenome and Embryonic Development. Genes 2021, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbinian, N.; Selzer, M.E. Oligodendrocyte pathology in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Gutherz, O.R.; Deyssenroth, M.; Li, Q.; Hao, K.; Jacobson, J.L.; Chen, J.; Jacobson, S.W.; Carter, R.C. Potential roles of imprinted genes in the teratogenic effects of alcohol on the placenta, somatic growth, and the developing brain. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 347, 113919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernán, M.A. Methods of Public Health Research—Strengthening Causal Inference from Observational Data. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Epidemiological Overview of Cannabis- and Substance-Carcinogenesis in Europe: A Lagged Causal Inferential Panel Regression Modelling and Marginal Effects Study. Mendeley Data 2022. manuscript submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Novel Insights into Potential Cannabis-Related Cancerogenesis from Recent Key Whole Epigenome Screen of Cannabis Dependence and Withdrawal: Epidemiological Comment and Explication of Schrott et al. Genes 2023, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Geotemporospatial and Causal Inferential Epidemiological Overview and Survey of USA Cannabis, Cannabidiol and Cannabinoid Genotoxicity Expressed in Cancer Incidence 2003–2017: Part 1—Continuous Bivariate Analysis. Arch. Public Health 2022, 80, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Geotemporospatial and Causal Inferential Epidemiological Overview and Survey of USA Cannabis, Cannabidiol and Cannabinoid Genotoxicity Expressed in Cancer Incidence 2003–2017: Part 2—Categorical Bivariate Analysis and Attributable Fractions. Arch. Public Health 2022, 80, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Geotemporospatial and Causal Inferential Epidemiological Overview and Survey of USA Cannabis, Cannabidiol and Cannabinoid Genotoxicity Expressed in Cancer Incidence 2003–2017: Part 3—Spatiotemporal, Multivariable and Causal Inferential Pathfinding and Exploratory Analyses of Prostate and Ovarian Cancers. Arch. Public Health 2022, 80, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard, C.; Sarsfield, S.; Merte, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, P.; Beppu, H.; Kolodkin, A.L.; Sucov, H.M.; Ginty, D.D. MEGF8 is a modifier of BMP signaling in trigeminal sensory neurons. eLife 2013, 2, e01160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Han, B.; Compton, W.M.; Blanco, C. Marijuana Use During Stages of Pregnancy in the United States. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 166, 763–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Compton, W.M.; Wargo, E.M. The Risks of Marijuana Use During Pregnancy. JAMA 2017, 317, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldington, S.; Harwood, M.; Cox, B.; Weatherall, M.; Beckert, L.; Hansell, A.; Pritchard, A.; Robinson, G.; Beasley, R. Cannabis use and risk of lung cancer: A case-control study. Eur. Respir J. 2008, 31, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voirin, N.; Berthiller, J.; Benhaim-Luzon, V.; Boniol, M.; Straif, K.; Ayoub, W.B.; Ayed, F.B.; Sasco, A.J. Risk of lung cancer and past use of cannabis in Tunisia. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2006, 1, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthiller, J.; Straif, K.; Boniol, M.; Voirin, N.; Benhaim-Luzon, V.; Ayoub, W.B.; Dari, I.; Laouamri, S.; Hamdi-Cherif, M.; Bartal, M.; et al. Cannabis smoking and risk of lung cancer in men: A pooled analysis of three studies in Maghreb. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 1398–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Morgenstern, H.; Spitz, M.R.; Tashkin, D.P.; Yu, G.P.; Marshall, J.R.; Hsu, T.C.; Schantz, S.P. Marijuana use and increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1999, 8, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Hashibe, M.; Ford, D.E.; Zhang, Z.F. Marijuana smoking and head and neck cancer. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 42 (Suppl. S11), 103S–107S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidney, S.; Quesenberry, C.P., Jr.; Friedman, G.D.; Tekawa, I.S. Marijuana use and cancer incidence (California, United States). Cancer Causes Control. 1997, 8, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daling, J.R.; Doody, D.R.; Sun, X.; Trabert, B.L.; Weiss, N.S.; Chen, C.; Biggs, M.L.; Starr, J.R.; Dey, S.K.; Schwartz, S.M. Association of marijuana use and the incidence of testicular germ cell tumors. Cancer 2009, 115, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efird, J.T.; Friedman, G.D.; Sidney, S.; Klatsky, A.; Habel, L.A.; Udaltsova, N.V.; Van den Eeden, S.; Nelson, L.M. The risk for malignant primary adult-onset glioma in a large, multiethnic, managed-care cohort: Cigarette smoking and other lifestyle behaviors. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2004, 68, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiche Bokobo, P.; Atxa de la Presa, M.A.; Cuesta Angulo, J. Transitional cell carcinoma in a young heavy marihuana smoker. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2001, 54, 165–167. [Google Scholar]
- Chacko, J.A.; Heiner, J.G.; Siu, W.; Macy, M.; Terris, M.K. Association between marijuana use and transitional cell carcinoma. Urology 2006, 67, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieder, A.M.; Lipke, M.C.; Madjar, S. Transitional cell carcinoma associated with marijuana: Case report and review of the literature. Urology 2006, 67, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Causal inference multiple imputation investigation of the impact of cannabinoids and other substances on ethnic differentials in US testicular cancer incidence. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 22, 40–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Geospatiotemporal and Causal Inference Study of Cannabis and Other Drugs as Risk Factors for Female Breast Cancer USA 2003–2017. Environ. Epigenet. 2022, 8, dvac006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Epigenomic and Other Evidence for Cannabis-Induced Aging Contextualized in a Synthetic Epidemiologic Overview of Cannabinoid-Related Teratogenesis and Cannabinoid-Related Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse, G.K.; White, J.; Cape, G. (Eds.) Management of Alcohol and Drug Problems, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Melbourne, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fraher, D.; Ellis, M.K.; Morrison, S.; McGee, S.L.; Ward, A.C.; Walder, K.; Gibert, Y. Lipid Abundance in Zebrafish Embryos Is Regulated by Complementary Actions of the Endocannabinoid System and Retinoic Acid Pathway. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 3596–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kučukalić, S.; Ferić Bojić, E.; Babić, R.; Avdibegović, E.; Babić, D.; Agani, F.; Jakovljević, M.; Kučukalić, A.; Bravo Mehmedbašić, A.; Šabić Džananović, E.; et al. Genetic Susceptibility to Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Analyses of the Oxytocin Receptor, Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor A and Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Genes. Psychiatr. Danub. 2019, 31, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Jeong, W.I. Retinoic acids and hepatic stellate cells in liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27 (Suppl. S2), 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallee, A.; Lecarpentier, Y.; Guillevin, R.; Vallee, J.N. Effects of cannabidiol interactions with Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and PPARgamma on oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallathambi, R.; Mazuz, M.; Namdar, D.; Shik, M.; Namintzer, D.; Vinayaka, A.C.; Ion, A.; Faigenboim, A.; Nasser, A.; Laish, I.; et al. Identification of Synergistic Interaction Between Cannabis-Derived Compounds for Cytotoxic Activity in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines and Colon Polyps That Induces Apoptosis-Related Cell Death and Distinct Gene Expression. Cannabis. Cannabinoid. Res. 2018, 3, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petko, J.; Tranchina, T.; Patel, G.; Levenson, R.; Justice-Bitner, S. Identifying novel members of the Wntless interactome through genetic and candidate gene approaches. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 138, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, X.; Tang, L.; Wu, C.; Huang, L. miR-23b-3p and miR-130a-5p affect cell growth, migration and invasion by targeting CB1R via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in gastric carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 7503–7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, M.G.; Cobbs, L.V.; Dummer, P.D.; Petros, T.J.; Halford, M.M.; Stacker, S.A.; Zou, Y.; Fishell, G.J.; Au, E. Non-canonical Wnt Signaling through Ryk Regulates the Generation of Somatostatin- and Parvalbumin-Expressing Cortical Interneurons. Neuron 2019, 103, 853–864.e854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalli, Y.; Dar, M.S.; Bano, N.; Rasool, J.U.; Sarkar, A.R.; Banday, J.; Bhat, A.Q.; Rafia, B.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Dar, M.J.; et al. Analyzing the role of cannabinoids as modulators of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway for their use in the management of neuropathic pain. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birerdinc, A.; Jarrar, M.; Stotish, T.; Randhawa, M.; Baranova, A. Manipulating molecular switches in brown adipocytes and their precursors: A therapeutic potential. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, D.; Picard, F. Brown fat biology and thermogenesis. Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 1233–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.R.; Yang, Y.; Ward, R.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y. Orexin receptors: Multi-functional therapeutic targets for sleeping disorders, eating disorders, drug addiction, cancers and other physiological disorders. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 2413–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lim, S.; Park, M.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Han, H.; Yoon, K.; Kim, K.; Lim, J.; Park, S. Ubiquitination-dependent CARM1 degradation facilitates Notch1-mediated podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xapelli, S.; Agasse, F.; Sarda-Arroyo, L.; Bernardino, L.; Santos, T.; Ribeiro, F.F.; Valero, J.; Braganca, J.; Schitine, C.; de Melo Reis, R.A.; et al. Activation of type 1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1R) promotes neurogenesis in murine subventricular zone cell cultures. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e635292013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, R.; Gowran, A.; Noonan, J.; Keating, S.E.; Bowie, A.G.; Campbell, V.A. The endocannabinoid, anandamide, augments Notch-1 signaling in cultured cortical neurons exposed to amyloid-beta and in the cortex of aged rats. J. Biol. Chem 2012, 287, 34709–34721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foldy, C.; Malenka, R.C.; Sudhof, T.C. Autism-associated neuroligin-3 mutations commonly disrupt tonic endocannabinoid signaling. Neuron 2013, 78, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, T.; Romero, E.; Monory, K.; Palazuelos, J.; Sendtner, M.; Marsicano, G.; Lutz, B.; Guzmán, M.; Galve-Roperh, I. The CB1 cannabinoid receptor mediates excitotoxicity-induced neural progenitor proliferation and neurogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23892–23898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.J.; Walsh, F.S.; Doherty, P. The FGF receptor uses the endocannabinoid signaling system to couple to an axonal growth response. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willsher, K. Baby Arm Defects Prompt Nationwide Investigation in France. The Guardian. 31 October 2018. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2018/oct/31/baby-arm-defects-prompt-nationwide-investigation-france (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Agence France-Presse in Paris. France to Investigate Cause of Upper Limb Defects in Babies. The Guardian, 31 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gant, J. Scientists are Baffled by Spatter of Babies Born without Hands or Arms in France, as Investigation Fails to Discover a Cause. Daily Mail, 14 July 2019. [Google Scholar]







| Anomaly | Mean ± S.E. Increasing | Mean ± S.E. Decreasing | Relative Rate Incr./Decr. | Student’s t | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VATER/VACTERL | 0.46 (0.42, 0.5) | 0.02 (0.03, 0.07) | 31.820 | 8.3870 | 7.49× 10−13 |
| Teratogenic Synds | 1.07 (0.52, 1.62) | 0.28 (−0.09, 0.23) | 3.830 | 6.1691 | 1.81 × 10−8 |
| Matern Infect Malform | 0.73 (0.44, 1.02) | 0.15 (−0.08, 0.2) | 4.748 | 5.7942 | 1.01 × 10−7 |
| Situs inversus | 0.63 (−0.06, 1.32) | 0.35 (−0.05, 0.15) | 1.789 | 3.6097 | 5.18 × 10−4 |
| Fetal Alcohol | 0.25 (0.01, 0.49) | 0.12 (−0.04, 0.12) | 2.161 | 2.3870 | 0.0186 |
| Lateral anomalies | 1.52 (−0.48, 3.52) | 1.02 (−0.33, 0.45) | 1.497 | 1.5385 | 0.1374 |
| Valproate syndrome | 0.05 (0.01, 0.09) | 0.02 (0, 0.04) | 2.104 | 1.2358 | 0.2190 |
| Conjoined twins | 0.12 (−0.04, 0.28) | 0.08 (−0.02, 0.06) | 1.448 | 1.1442 | 0.2555 |
| Skeletal dysplasias | 1.55 (−0.9, 4) | 1.25 (−0.21, 0.33) | 1.239 | 1.1265 | 0.2656 |
| Amniotic band | 0.34 (−0.19, 0.87) | 0.27 (−0.14, 0.22) | 1.261 | 0.6950 | 0.4902 |
| All Anomalies | 233.39 (−251.87, 718.65) | 247.58 (−0.14, 0.22) | 0.943 | 0.6372 | 0.5271 |
| Anomaly | Substance | Mean Anomaly Rate | Estimate | Std. Error | Sigma | t_Statistic | p_Value | E-Value Estimate | E-Value Lower Bound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VATER/VACTERL | Daily.Interpol. | 0.4377 | 20.8858 | 4.6484 | 0.4252 | 4.4932 | 4.4932 | 1.81 × 10−5 | 5.19 × 1019 |
| Teratogenic Synds | Daily.Interpol. | 1.0683 | 29.9733 | 6.8274 | 0.6408 | 4.3901 | 4.3901 | 2.56 × 10−5 | 6.10 × 1018 |
| Lateral anomalies | Daily.Interpol. | 1.7332 | 26.6028 | 6.7914 | 0.6212 | 3.9172 | 3.9172 | 1.60 × 10−4 | 1.68 × 1017 |
| Matern Infect Malform | Daily.Interpol. | 0.6880 | 22.6665 | 5.8194 | 0.5462 | 3.8950 | 3.8950 | 1.67 × 10−4 | 5.02 × 1016 |
| Teratogenic Synds | LMCannabis_Herb | 1.0683 | 11.1368 | 2.1817 | 0.6263 | 5.1046 | 5.1046 | 1.26 × 10−6 | 2.13 × 107 |
| Situs inversus | Daily.Interpol. | 0.5932 | 12.3967 | 4.2919 | 0.4029 | 2.8884 | 2.8884 | 0.0046 | 2.90 × 1012 |
| Lateral anomalies | LMCannabis_Herb | 1.7332 | 10.0481 | 2.3741 | 0.6147 | 4.2324 | 4.2324 | 4.96 × 10−5 | 5.78 × 106 |
| Matern Infect Malform | LMCannabis_Herb | 0.6880 | 8.2647 | 1.8585 | 0.5335 | 4.4469 | 4.4469 | 1.96 × 10−5 | 2.65 × 106 |
| Skeletal dysplasias | Daily.Interpol. | 1.8050 | 19.3566 | 7.0728 | 0.6639 | 2.7368 | 2.7368 | 0.0072 | 6.67 × 1011 |
| Lateral anomalies | Herb | 1.7332 | 8.3890 | 1.8336 | 0.6072 | 4.5752 | 4.5752 | 1.31 × 10−5 | 5.76 × 105 |
| Teratogenic Synds | Herb | 1.0683 | 7.7193 | 1.6312 | 0.6343 | 4.7322 | 4.7322 | 6.13 × 10−6 | 1.29 × 105 |
| Matern Infect Malform | Herb | 0.6880 | 6.2822 | 1.3652 | 0.5308 | 4.6016 | 4.6016 | 1.05 × 10−5 | 9.51 × 104 |
| Situs inversus | LMCannabis_Herb | 0.5932 | 5.1389 | 1.3379 | 0.3840 | 3.8410 | 3.8410 | 1.97 × 10−4 | 3.88 × 105 |
| Situs inversus | Herb | 0.5932 | 4.0862 | 0.9779 | 0.3802 | 4.1784 | 4.1784 | 5.60 × 10−5 | 3.53 × 104 |
| Fetal Alcohol | LMCannabis_Herb | 0.2458 | 4.3930 | 1.2221 | 0.3508 | 3.5945 | 3.5945 | 4.73 × 10−4 | 1.78 × 105 |
| VATER/VACTERL | LM_Cannabis | 0.4377 | 6.5421 | 2.0669 | 0.4436 | 3.1652 | 3.1652 | 0.0020 | 1.35 × 106 |
| Teratogenic Synds | LM_Cannabis | 1.0683 | 8.8997 | 2.7367 | 0.6624 | 3.2519 | 3.2519 | 0.0015 | 4.09 × 105 |
| Lateral anomalies | LM_Cannabis | 1.7332 | 8.9858 | 2.9721 | 0.6378 | 3.0234 | 3.0234 | 0.0031 | 7.39 × 105 |
| VATER/VACTERL | LMCannabis_Herb | 0.4377 | 5.1942 | 1.7200 | 0.4453 | 3.0199 | 3.0199 | 0.0032 | 8.14 × 104 |
| Matern Infect Malform | LM_Cannabis | 0.6880 | 6.4725 | 2.3045 | 0.5577 | 2.8087 | 2.8087 | 0.0058 | 7.72 × 104 |
| Skeletal dysplasias | LMCannabis_Herb | 1.8050 | 6.5116 | 2.2481 | 0.6453 | 2.8965 | 2.8965 | 0.0045 | 1.94 × 104 |
| Teratogenic Synds | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.0683 | 3.1437 | 0.7564 | 0.6457 | 4.1562 | 4.1562 | 6.32 × 10−5 | 167.39 |
| Lateral anomalies | Resin | 1.7332 | 3.0137 | 0.7391 | 0.6363 | 4.0773 | 4.0773 | 9.46 × 10−5 | 148.33 |
| Fetal Alcohol | Herb | 0.2458 | 2.6533 | 0.9181 | 0.3570 | 2.8898 | 2.8898 | 0.0046 | 1.73 × 103 |
| Matern Infect Malform | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.6880 | 2.3897 | 0.6433 | 0.5492 | 3.7149 | 3.7149 | 3.18 × 10−4 | 104.39 |
| Lateral anomalies | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.7332 | 2.4982 | 0.7511 | 0.6325 | 3.3259 | 3.3259 | 0.0012 | 72.26 |
| All Anomalies | Resin | 255.4744 | 1.2426 | 0.3661 | 0.3291 | 3.3942 | 3.3942 | 9.72 × 10−4 | 61.62 |
| Fetal Alcohol | Daily.Interpol. | 0.2458 | 8.2930 | 3.9391 | 0.3697 | 2.1053 | 2.1053 | 0.0375 | 1.46 × 109 |
| Lateral anomalies | LMCannabis_Resin | 1.7332 | 2.1164 | 0.5631 | 0.6436 | 3.7586 | 3.7586 | 2.95 × 10−4 | 39.37 |
| Skeletal dysplasias | Herb | 1.8050 | 4.2006 | 1.6733 | 0.6506 | 2.5103 | 2.5103 | 0.0134 | 711.51 |
| Amniotic band | LMCannabis_Resin | 0.3730 | 1.0556 | 0.3089 | 0.3699 | 3.4170 | 3.4170 | 9.02 × 10−4 | 26.33 |
| Skeletal dysplasias | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.8050 | 2.2295 | 0.7751 | 0.6617 | 2.8764 | 2.8764 | 0.0048 | 42.40 |
| Situs inversus | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.5932 | 1.3525 | 0.4721 | 0.4031 | 2.8647 | 2.8647 | 0.0050 | 41.87 |
| Teratogenic Synds | LMCannabis_Resin | 1.0683 | 1.8066 | 0.5687 | 0.6810 | 3.1768 | 3.1768 | 0.0020 | 21.85 |
| Fetal Alcohol | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.2458 | 1.1590 | 0.4278 | 0.3653 | 2.7090 | 2.7090 | 0.0078 | 35.39 |
| Teratogenic Synds | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.0683 | 1.2927 | 0.3585 | 0.6708 | 3.6062 | 3.6062 | 4.91 × 10−4 | 11.03 |
| Fetal Alcohol | LMCannabis_Resin | 0.2458 | 0.8989 | 0.3077 | 0.3684 | 2.9213 | 2.9213 | 0.0043 | 17.90 |
| Matern Infect Malform | LMCannabis_Resin | 0.6880 | 1.3658 | 0.4763 | 0.5703 | 2.8674 | 2.8674 | 0.0050 | 17.16 |
| All Anomalies | Herb | 255.4744 | 2.2466 | 1.0012 | 0.3893 | 2.2438 | 2.2438 | 0.0267 | 381.13 |
| Matern Infect Malform | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.6880 | 0.9847 | 0.3031 | 0.5672 | 3.2483 | 3.2483 | 0.0016 | 9.18 |
| VATER/VACTERL | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.4377 | 1.3541 | 0.5352 | 0.4507 | 2.5300 | 2.5300 | 0.0129 | 30.28 |
| Lateral anomalies | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.7332 | 1.1244 | 0.3521 | 0.6555 | 3.1934 | 3.1934 | 0.0019 | 9.00 |
| Amniotic band | LMCannabis_Herb | 0.3730 | 3.2048 | 1.4989 | 0.4302 | 2.1381 | 2.1381 | 0.0345 | 1.76 × 103 |
| VATER/VACTERL | Cocaine | 0.4377 | 0.3393 | 0.0527 | 0.3931 | 6.4369 | 6.4369 | 3.72 × 10−9 | 3.81 |
| Skeletal dysplasias | LMCannabis_Resin | 1.8050 | 1.3870 | 0.5266 | 0.6306 | 2.6337 | 2.6337 | 0.0097 | 14.28 |
| Skeletal dysplasias | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.8050 | 1.0055 | 0.3440 | 0.6436 | 2.9233 | 2.9233 | 0.0043 | 7.75 |
| All Anomalies | LMCannabis_Resin | 255.4744 | 0.7027 | 0.2813 | 0.3368 | 2.4982 | 2.4982 | 0.0140 | 12.83 |
| All Anomalies | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 255.4744 | 0.4992 | 0.1811 | 0.3388 | 2.7572 | 2.7572 | 0.0070 | 7.11 |
| Matern Infect Malform | Cocaine | 0.6880 | 0.3460 | 0.0644 | 0.5169 | 5.3762 | 5.3762 | 3.80 × 10−7 | 3.08 |
| Fetal Alcohol | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.2458 | 0.5533 | 0.2024 | 0.3787 | 2.7344 | 2.7344 | 0.0074 | 7.02 |
| Teratogenic Synds | Cocaine | 1.0683 | 0.3971 | 0.0780 | 0.6266 | 5.0903 | 5.0903 | 1.34 × 10−6 | 2.96 |
| Amniotic band | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.3730 | 0.5439 | 0.2053 | 0.3842 | 2.6491 | 2.6491 | 0.0094 | 6.71 |
| VATER/VACTERL | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.4377 | 0.9512 | 0.4034 | 0.4610 | 2.3582 | 2.3582 | 0.0204 | 12.55 |
| Lateral anomalies | Cocaine | 1.7332 | 0.3713 | 0.0815 | 0.6077 | 4.5565 | 4.5565 | 1.41 × 10−5 | 2.88 |
| VATER/VACTERL | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.4377 | 0.6332 | 0.2464 | 0.4587 | 2.5702 | 2.5702 | 0.0117 | 6.48 |
| Situs inversus | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.5932 | 0.5669 | 0.2250 | 0.4211 | 2.5194 | 2.5194 | 0.0134 | 6.27 |
| Situs inversus | Cocaine | 0.5932 | 0.2054 | 0.0471 | 0.3781 | 4.3619 | 4.3619 | 2.74 × 10−5 | 2.66 |
| Situs inversus | LMCannabis_Resin | 0.5932 | 0.7543 | 0.3444 | 0.4123 | 2.1905 | 2.1905 | 0.0307 | 10.04 |
| Skeletal dysplasias | Cocaine | 1.8050 | 0.2686 | 0.0794 | 0.6378 | 3.3820 | 3.3820 | 9.72 × 10−4 | 2.29 |
| All Anomalies | Cocaine | 255.4744 | 0.1491 | 0.0476 | 0.3821 | 3.1349 | 3.1349 | 0.0022 | 2.21 |
| Fetal Alcohol | Annual_Alcohol | 0.2458 | 0.0793 | 0.0169 | 0.3393 | 4.6992 | 4.6992 | 7.02 × 10−6 | 1.78 |
| All Anomalies | Daily.Interpol. | 255.4744 | 0.1426 | 0.0481 | 0.3836 | 2.9645 | 2.9645 | 0.0037 | 2.15 |
| VATER/VACTERL | Amphetamine | 0.4377 | 0.1506 | 0.0582 | 0.4501 | 2.5891 | 2.5891 | 0.0110 | 2.05 |
| Amniotic band | Annual_Alcohol | 0.3730 | 0.0709 | 0.0208 | 0.4186 | 3.4067 | 3.4067 | 8.95 × 10−4 | 1.61 |
| Teratogenic Synds | Annual_Alcohol | 1.0683 | 0.0942 | 0.0333 | 0.6690 | 2.8296 | 2.8296 | 0.0055 | 1.53 |
| Valproate syndrome | Cocaine | 0.0434 | 0.0362 | 0.0169 | 0.1354 | 2.1472 | 2.1472 | 0.0338 | 1.87 |
| Parameter Values | Model Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate (C.I.) | p-Value | Parameter | Value | Significance |
| Additive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + Alcohol + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income) | |||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 0.94 (0.53, 1.36) | 8.96 × 10−6 | psi | 0.9116 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Cocaine | 0.09 (0.02, 0.17) | 0.0136 | rho | 0.6488 | 2.81 × 10−12 |
| lambda | −0.4147 | 0.00167 | |||
| Interactive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC * Herb + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Herb | 2.02 (1.13, 2.9) | 8.09 × 10−6 | psi | 0.9073 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.05 (0.01, 0.1) | 2.23 × 10−2 | rho | −0.5330 | 1.50 × 10−5 |
| lambda | 0.5605 | 2.34 × 10−7 | |||
| 2 Lags | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC * Herb + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 0.74 (0.24, 1.23) | 0.0037 | psi | 0.9215 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.06 (0.01, 0.1) | 0.0198 | rho | 0.6514 | 1.89 × 10−8 |
| Cocaine | −0.09 (−0.17, −0.01) | 0.0304 | lambda | −0.406 | 0.013 |
| Parameter Values | Model Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate (C.I.) | p-Value | Parameter | Value | Significance |
| Additive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + Alcohol + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income) | |||||
| Alcohol | 0.07 (0, 0.13) | 0.0472 | psi | 0.5261 | 5.52 × 10−12 |
| Daily.Interpol. | 15.4 (2.37, 28.43) | 0.0205 | Log.Lik. | −26.1038 | |
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 0.0011 | |||
| Interactive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco * Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Tobacco | 0.04 (0, 0.07) | 0.0383 | psi | 0.2864 | 0.00512 |
| Daily.Interpol. | 118 (50.77, 185.23) | 0.0006 | |||
| Alcohol | 0.1 (0.05, 0.16) | 0.0002 | |||
| Cocaine | 0.29 (0.06, 0.51) | 0.0121 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 0.0097 | |||
| Tobacco: Daily.Interpol. | −4.97 (−7.56, −2.38) | 0.0002 | |||
| 2 Lags | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco * Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Tobacco | 0.04 (0, 0.07) | 0.029285 | Least Squares | ||
| Daily.Interpol. | 184 (103.84, 264.16) | 6.56 × 10−6 | S.D. | 0.3114 | |
| Alcohol | 0.11 (0.06, 0.16) | 1.90 × 10−5 | Log.Lik. | −22.2103 | |
| Cocaine | 0.33 (0.09, 0.57) | 0.0072 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 0.0291 | |||
| Tobacco: Daily.Interpol. | −7.43 (−10.33, −4.53) | 4.97 × 10−7 | |||
| 4 Lags | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco * Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Tobacco | 0.06 (0.03, 0.09) | 0.0002 | Least Squares | ||
| Daily.Interpol. | 277 (197.82, 356.18) | 6.81 × 10−12 | S.D. | 0.2859 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC | 7.9 (2.84, 12.96) | 0.0022 | |||
| Alcohol | 0.09 (0.04, 0.13) | 0.0001 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 3.26 × 10−5 | |||
| Tobacco: Daily.Interpol. | −10.6 (−13.68, −7.52) | 1.29 × 10−11 | |||
| 6 Lags | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco * Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Tobacco | 0.12 (0.07, 0.16) | 9.80 × 10−7 | Least Squares | ||
| Daily.Interpol. | 375 (255.44, 494.56) | 8.10 × 10−10 | S.D. | 0.2953 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | −0.31 (−0.46, −0.17) | 3.13 × 10−5 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 4.57 × 10−6 | |||
| Tobacco: Daily.Interpol. | −13.8 (−18.43, −9.17) | 4.95 × 10−9 | |||
| Parameter Values | Model Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate (C.I.) | p-Value | Parameter | Value | Significance |
| Additve Model without Cannabis Terms | |||||
| Rate ~ Alcohol + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Alcohol | 0.09 (0.04, 0.15) | 0.0010 | psi | 3.73 × 10−7 | |
| Resin | 0.24 (0.1, 0.38) | 0.0007 | S.D. | 0.3495 | |
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 0.0059 | Log.Lik. | −28.449 | |
| Spatial Hausman Test | |||||
| Chi.Squared | 8.12 | ||||
| Deg.Freedom | 3 | ||||
| p-Value | 0.0436 | ||||
| Models at 2 Lags without Cannabis Terms | |||||
| Alcohol | 0.07 (0.02, 0.11) | 0.0029 | Least Squares | ||
| Cocaine | 0.4 (0.28, 0.52) | 2.90 × 10−11 | S.D. | 0.3796 | |
| Log.Lik. | −39.6349 | ||||
| Spatial Hausman Test | |||||
| Chi.Squared | 82.41 | ||||
| Deg.Freedom | 3 | ||||
| p-Value | <2.2 × 10−16 | ||||
| Parameter Values | Model Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate (C.I.) | p-Value | Parameter | Value | Significance |
| Additive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + Alcohol + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income) | |||||
| Tobacco | 0.05 (0.03, 0.06) | 3.96 × 10−9 | rho | −0.4998 | 7.08 × 10−5 |
| Alcohol | 0.06 (0.03, 0.08) | 1.32 × 10−5 | lambda | 0.4343 | 9.82 × 10−5 |
| Herb | 2.46 (1.1, 3.82) | 0.0004 | |||
| Amphetamines | −0.11 (−0.17, −0.05) | 0.0004 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 5.36 × 10−8 | |||
| Interactive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC * Herb + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Tobacco | 0.05 (0.03, 0.06) | 3.96 × 10−9 | rho | −0.4998 | 7.10 × 10−5 |
| Herb | 2.46 (1.1, 3.82) | 0.0004 | lambda | 0.4343 | 9.79 × 10−5 |
| Alcohol | 0.06 (0.03, 0.08) | 1.32 × 10−5 | |||
| Amphetamines | −0.11 (−0.17, −0.05) | 0.0004 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 5.36 × 10−8 | |||
| 2 Lags | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC * Herb + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Tobacco | 0.05 (0.04, 0.07) | 1.36 × 10−10 | rho | −0.6212 | 3.41 × 10−9 |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.41 (0.47, 2.35) | 0.0034 | lambda | 0.4866 | 1.44 × 10−7 |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | −2.92 (−5.06, −0.78) | 0.0076 | |||
| Alcohol | 0.07 (0.04, 0.1) | 9.45 × 10−6 | |||
| Amphetamines | −0.18 (−0.26, −0.1) | 1.09 × 10−5 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 6.49 × 10−12 | |||
| Parameter Values | Model Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate (C.I.) | p-Value | Parameter | Value | Significance |
| Additive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + Alcohol + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income) | |||||
| Alcohol | 0.04 (0.01, 0.07) | 0.0169 | Least Squares | ||
| Herb | 2.99 (1.11, 4.87) | 0.0019 | S.D. | 0.2519 | |
| Amphetamines | −0.2 (−0.27, −0.12) | 1.74 × 10−7 | |||
| Cocaine | 0.2 (0.11, 0.28) | 9.22 × 10−6 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 4.11 × 10−6 | |||
| Interactive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC * Herb + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Herb | 2.99 (1.11, 4.87) | 0.0019 | Least Squares | ||
| Alcohol | 0.04 (0.01, 0.07) | 0.0169 | S.D. | 0.2519 | |
| Amphetamines | −0.2 (−0.27, −0.12) | 1.74 × 10−7 | |||
| Cocaine | 0.2 (0.11, 0.28) | 9.22 × 10−6 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 4.11 × 10−6 | |||
| 1 Lags | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC * Herb + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Herb | 2.37 (0.23, 4.51) | 0.0299 | Least Squares | ||
| Amphetamines | −0.19 (−0.27, −0.1) | 1.64 × 10−5 | S.D. | 0.3024 | |
| Cocaine | 0.18 (0.08, 0.28) | 0.0003 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 5.31 × 10−5 | |||
| Parameter Values | Model Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate (C.I.) | p-Value | Parameter | Value | Significance |
| Additive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + Alcohol + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income) | |||||
| Alcohol | 0.12 (0.06, 0.18) | 2.50 × 10−5 | rho | 0.4947 | 4.86 × 10−5 |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 3.31 (1.42, 5.2) | 0.0006 | lambda | −0.5897 | 1.68 × 10−8 |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | −1.83 (−3.58, −0.08) | 0.0412 | |||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 2.09 (0.01, 4.17) | 0.0476 | |||
| Amphetamines | −0.15 (−0.28, −0.03) | 0.0182 | |||
| Cocaine | 0.29 (0.14, 0.44) | 0.0001 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 3.88 × 10−7 | |||
| Interactive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC * Herb + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 3.31 (1.42, 5.2) | 0.0006 | rho | 0.4947 | 4.89 × 10−5 |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | −1.83 (−3.58, −0.08) | 0.0412 | lambda | −0.5897 | 1.69 × 10−8 |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 2.09 (0.01, 4.17) | 0.0476 | |||
| Alcohol | 0.12 (0.06, 0.18) | 2.50 × 10−5 | |||
| Amphetamines | −0.15 (−0.28, −0.03) | 0.0182 | |||
| Cocaine | 0.29 (0.14, 0.44) | 0.0001 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 3.88 × 10−7 | |||
| 2 Lags | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC * Herb + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 1.65 (0.34, 2.96) | 0.0134 | rho | 0.4855 | 0.00038 |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | −0.05 (−0.09, −0.01) | 0.0083 | lambda | −0.6324 | 1.91 × 10−8 |
| Alcohol | 0.14 (0.08, 0.21) | 1.01 × 10−5 | |||
| Amphetamines | −0.18 (−0.33, −0.04) | 0.014951 | |||
| Cocaine | 0.32 (0.16, 0.49) | 0.0002 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 1.66 × 10−5 | |||
| Parameter Values | Model Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate (C.I.) | p-Value | Parameter | Value | Significance |
| Additive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + Alcohol + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income) | |||||
| Tobacco | 0.06 (0.03, 0.09) | 7.85 × 10−6 | rho | −0.2466 | 0.1750 |
| Alcohol | 0.16 (0.1, 0.21) | 7.80 × 10−9 | lambda | 0.2035 | 0.2040 |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | −2.08 (−3.75, −0.41) | 0.0146 | S.D. | 0.4193 | |
| Herb | 4.39 (1.45, 7.33) | 0.0035 | Log.Lik | −63.7327 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 3.86 (1.74, 5.98) | 0.0003 | |||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | −7.12 (−11.06, −3.18) | 0.0004 | |||
| Amphetamines | −0.31 (−0.44, −0.18) | 1.55 × 10−6 | |||
| Cocaine | 0.41 (0.21, 0.61) | 7.76 × 10−5 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 7.22 × 10−8 | |||
| Interactive | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco * Herb + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Tobacco | 0.14 (0.08, 0.19) | 1.90 × 10−7 | rho | −0.2964 | 0.0830 |
| Herb | 25.8 (12.3, 39.3) | 0.0002 | lambda | 0.2477 | 0.0959 |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 4.13 (2.11, 6.15) | 5.65 × 10−5 | |||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | −1.58 (−3.19, 0.03) | 0.053753 | |||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | −8.65 (−12.49, −4.81) | 9.86 × 10−6 | |||
| Alcohol | 0.2 (0.14, 0.26) | 1.60 × 10−11 | |||
| Amphetamines | −0.36 (−0.49, −0.24) | 1.32 × 10−8 | |||
| Cocaine | 0.54 (0.33, 0.74) | 4.82 × 10−7 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 4.93 × 10−5 | |||
| Tobacco: Herb | −0.88 (−1.42, −0.34) | 0.0014 | |||
| 2 Lags | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco * LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Herb + LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC + LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Tobacco | 0.04 (0.01, 0.07) | 9.22 × 10−3 | rho | −0.4671 | 0.0021 |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 5 (1.71, 8.29) | 0.0029 | lambda | 0.3779 | 0.0091 |
| Herb | 4.95 (1.01, 8.89) | 0.0137 | |||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | −4.14 (−7.28, −1) | 0.0098 | |||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | −5.9 (−9.8, −2) | 0.0030 | |||
| Alcohol | 0.14 (0.09, 0.19) | 2.04 × 10−8 | |||
| Amphetamines | −0.25 (−0.36, −0.13) | 3.03 × 10−5 | |||
| Cocaine | 0.33 (0.13, 0.54) | 0.0014 | |||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 3.79 × 10−3 | |||
| Parameter Values | Model Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate (C.I.) | p-Value | Parameter | Value | Significance |
| Additive Model without Cannabis Terms | |||||
| Rate ~ Tobacco + Alcohol + Amphetamines + Cocaine + Income | |||||
| Income | 0 (0, 0) | 2.57 × 10−12 | Least Squares | ||
| S.D. | 0.6399 | ||||
| Log.Lik. | −106.99 | ||||
| Spatial Hausman Test | |||||
| Chi.Squared | 184.20 | ||||
| Deg.Freedom | 2 | ||||
| p-Value | <2.2 × 10−16 | ||||
| Anomaly | Term | p-Value | E-Value Estimate | Lower Bound E-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Anomalies | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0001 | 1.75 | 1.45 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | <2.2 × 10−16 | 212.22 | 106.93 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 7.81 × 10−15 | 5.67 | 4.29 | |
| 1 Lag | ||||
| Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | <2.2 × 10−16 | 1.42 | 1.38 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | <2.2 × 10−16 | 1.69 | 1.62 | |
| 2 Lags | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0176 | 4.47 × 1015 | 1.76 × 103 | |
| Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 2.66 × 10−8 | 1.77 | 1.57 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0303 | 73.47 | 2.36 | |
| VACTERL | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.52 × 10−12 | 230.82 | 72.72 | |
| Herb | 0.0042 | 1.42 × 104 | 37.93 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 4.72 × 10−5 | 1.26 | 1.18 | |
| 1 Lag | ||||
| Daily.Interpol. | 0.0185 | 3.32 × 1059 | 1.67 × 1011 | |
| 4 Lags | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0009 | 5.93 × 1038 | 1.56 × 1017 | |
| FAS | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.44 × 10−13 | 17.04 | 10.05 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0020 | 1.57 × 104 | 61.02 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0016 | 4.78 | 2.31 | |
| 2 Lags | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 6.97 × 10−7 | 1.00 × 1018 | 3.56 × 1011 | |
| Herb | 0.0070 | 4.29 × 104 | 36.32 | |
| Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.31 × 10−5 | 6.65 | 3.61 | |
| Situs Inversus | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0034 | 8.35 | 2.86 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC | 5.44 × 10−6 | 7.97 × 1010 | 6.73 × 105 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0061 | 50.05 | 4.74 | |
| Tobacco: Resin | 1.26 × 10−5 | 3.01 | 2.15 | |
| 2 Lags | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.88 × 10−7 | 1.38 × 1016 | 4.79 × 1010 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC | 0.0030 | 2.55 × 1013 | 1.07 × 104 | |
| Daily.Interpol. | 0.0056 | 9.76 × 1021 | 1.20 × 107 | |
| Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.36 × 10−5 | 7.48 | 3.88 | |
| Lateralization | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| Resin | 0.0003 | 186.86 | 16.72 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0039 | 892.53 | 15.10 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0061 | 263.18 | 9.83 | |
| Tobacco: Resin | 1.26 × 10−5 | 75.09 | 10.63 | |
| 2 Lags | ||||
| Resin | 7.39 × 10−6 | 50.49 | 13.06 | |
| Teratogenic Syndromes | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | <2.2 × 10−16 | 356.29 | 145.49 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 6.64 × 10−8 | 1.86 × 104 | 850.04 | |
| Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | <2.2 × 10−16 | 2.10 | 1.95 | |
| 2 Lags | ||||
| lag(LpmResinDailyInt, 2) | 5.52 × 10−9 | 39.30 | 15.60 |
| Anomaly | Term | p-Value | E-Value Estimate | Lower Bound E-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Anomalies | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 8.96 × 10−6 | 8.49 × 103 | 213.85 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| Herb | 8.09 × 10−6 | 2.87 × 104 | 1.08 × 103 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 2.23 × 10−2 | 1.92 | 1.34 | |
| 2 Lags | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 0.0037 | 18.72 | 3.60 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0198 | 1.65 | 1.20 | |
| VACTERL | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| Daily.Interpol. | 0.0205 | 2.61 × 1016 | 647.17 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| Daily.Interpol. | 0.0006 | Infinity | 2.53 × 1067 | |
| 2 Lags | ||||
| Daily.Interpol. | 6.56 × 10−6 | Infinity | 6.52 × 10138 | |
| 4 Lags | ||||
| Daily.Interpol. | 6.81 × 10−12 | Infinity | Infinity | |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC | 0.0022 | 1.65 × 1011 | 1.76 × 104 | |
| 6 Lags | ||||
| Daily.Interpol. | 8.10 × 10−10 | Infinity | Infinity | |
| FAS | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| Herb | 0.0004 | 1.41 × 104 | 104.35 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| Herb | 0.0004 | 1.41 × 104 | 104.35 | |
| 2 Lags | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0034 | 23.51 | 1.53 | |
| Situs Inversus | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| Herb | 0.0019 | 9.61 × 104 | 107.71 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| Herb | 0.0019 | 9.61 × 104 | 107.71 | |
| 1 Lags | ||||
| Herb | 0.0299 | 1.05 × 104 | 4.10 | |
| Lateralization | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 0.0006 | 1.83 × 103 | 36.69 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0476 | 149.75 | 1.29 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 0.0006 | 1.83 × 103 | 36.69 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0476 | 149.75 | 1.29 | |
| 2 Lags | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 0.0134 | 54.61 | 3.41 | |
| Teratogenic Syndromes | ||||
| Additive | ||||
| Herb | 0.0035 | 1.77 × 105 | 155.66 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0003 | 2.91 × 103 | 33.76 | |
| Interactive | ||||
| Herb | 0.0002 | 7.54 × 1017 | 2.85 × 105 | |
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 5.65 × 10−5 | 2.63 × 103 | 29.12 | |
| 2 Lags | ||||
| LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0029 | 2.02 × 105 | 21.03 | |
| Herb | 0.0137 | 2.28 × 105 | 107.43 |
| No. | E-Value Estimate | Lower Bound E-Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Infinity | Infinity |
| 2 | Infinity | Infinity |
| 3 | Infinity | 6.52 × 10138 |
| 4 | Infinity | 2.53 × 1067 |
| 5 | 3.32 × 1059 | 1.56 × 1017 |
| 6 | 5.93 × 1038 | 3.56 × 1011 |
| 7 | 9.76 × 1021 | 1.67 × 1011 |
| 8 | 1.00 × 1018 | 4.79 × 1010 |
| 9 | 7.54 × 1017 | 1.20 × 107 |
| 10 | 2.61 × 1016 | 6.73 × 105 |
| 11 | 1.38 × 1016 | 2.85 × 105 |
| 12 | 4.47 × 1015 | 1.76 × 104 |
| 13 | 2.55 × 1013 | 1.07 × 104 |
| 14 | 1.65 × 1011 | 1.76 × 103 |
| 15 | 7.97 × 1010 | 1.08 × 103 |
| 16 | 2.28 × 105 | 850.04 |
| 17 | 2.02 × 105 | 647.17 |
| 18 | 1.77 × 105 | 213.85 |
| 19 | 9.61 × 104 | 155.66 |
| 20 | 9.61 × 104 | 145.49 |
| 21 | 4.29 × 104 | 107.71 |
| 22 | 2.87 × 104 | 107.71 |
| 23 | 1.86 × 104 | 107.43 |
| 24 | 1.57 × 104 | 106.93 |
| 25 | 1.42 × 104 | 104.35 |
| 26 | 1.41 × 104 | 104.35 |
| 27 | 1.41 × 104 | 72.72 |
| 28 | 1.05 × 104 | 61.02 |
| 29 | 8.49 × 103 | 37.93 |
| 30 | 2.91 × 103 | 36.69 |
| 31 | 2.63 × 103 | 36.69 |
| 32 | 1.83 × 103 | 36.32 |
| 33 | 1.83 × 103 | 33.76 |
| 34 | 892.53 | 29.12 |
| 35 | 356.29 | 21.03 |
| 36 | 263.18 | 16.72 |
| 37 | 230.82 | 15.60 |
| 38 | 212.22 | 15.10 |
| 39 | 186.86 | 13.06 |
| 40 | 149.75 | 10.63 |
| 41 | 149.75 | 10.05 |
| 42 | 75.09 | 9.83 |
| 43 | 73.47 | 4.74 |
| 44 | 54.61 | 4.29 |
| 45 | 50.49 | 4.10 |
| 46 | 50.05 | 3.88 |
| 47 | 39.30 | 3.61 |
| 48 | 23.51 | 3.60 |
| 49 | 18.72 | 3.41 |
| 50 | 17.04 | 2.86 |
| 51 | 8.35 | 2.36 |
| 52 | 7.48 | 2.31 |
| 53 | 6.65 | 2.15 |
| 54 | 5.67 | 1.95 |
| 55 | 4.78 | 1.62 |
| 56 | 3.01 | 1.57 |
| 57 | 2.10 | 1.53 |
| 58 | 1.92 | 1.45 |
| 59 | 1.77 | 1.38 |
| 60 | 1.75 | 1.34 |
| 61 | 1.69 | 1.29 |
| 62 | 1.65 | 1.29 |
| 63 | 1.42 | 1.20 |
| 64 | 1.26 | 1.18 |
| No. | Anomaly | Regression | Model Type | Term | p-Value | E-Value Estimate | Lower Bound E-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | All Anomalies | Panel | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0176 | 4.47 × 1015 | 1.76 × 103 |
| 2 | All Anomalies | Spatial | Interactive | Herb | 8.09 × 10−6 | 2.87 × 104 | 1.08 × 103 |
| 3 | All Anomalies | Spatial | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 8.96 × 10−6 | 8.49 × 103 | 213.85 |
| 4 | All Anomalies | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | <2.2 × 10−16 | 212.22 | 106.93 |
| 5 | All Anomalies | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 7.81 × 10−15 | 5.67 | 4.29 |
| 6 | All Anomalies | Spatial | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 0.0037 | 18.72 | 3.60 |
| 7 | All Anomalies | Panel | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0303 | 73.47 | 2.36 |
| 8 | All Anomalies | Panel | 1 Lag | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | <2.2 × 10−16 | 1.69 | 1.62 |
| 9 | All Anomalies | Panel | 2 Lags | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 2.66 × 10−8 | 1.77 | 1.57 |
| 10 | All Anomalies | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0001 | 1.75 | 1.45 |
| 11 | All Anomalies | Panel | 1 Lag | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | <2.2 × 10−16 | 1.42 | 1.38 |
| 12 | All Anomalies | Spatial | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 2.23 × 10−2 | 1.92 | 1.34 |
| 13 | All Anomalies | Spatial | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0198 | 1.65 | 1.20 |
| 14 | FAS | Panel | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 6.97 × 10−7 | 1.00 × 1018 | 3.56 × 1011 |
| 15 | FAS | Spatial | Additive | Herb | 0.0004 | 1.41 × 104 | 104.35 |
| 16 | FAS | Spatial | Interactive | Herb | 0.0004 | 1.41 × 104 | 104.35 |
| 17 | FAS | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0020 | 1.57 × 104 | 61.02 |
| 18 | FAS | Panel | 2 Lags | Herb | 0.0070 | 4.29 × 104 | 36.32 |
| 19 | FAS | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.44 × 10−13 | 17.04 | 10.05 |
| 20 | FAS | Panel | 2 Lags | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.31 × 10−5 | 6.65 | 3.61 |
| 21 | FAS | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0016 | 4.78 | 2.31 |
| 22 | FAS | Spatial | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0034 | 23.51 | 1.53 |
| 23 | Lateralization | Panel | Additive | Resin | 0.0003 | 186.86 | 16.72 |
| 24 | Lateralization | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0039 | 892.53 | 15.10 |
| 25 | Lateralization | Panel | 2 Lags | Resin | 7.39 × 10−6 | 50.49 | 13.06 |
| 26 | Lateralization | Panel | Interactive | Tobacco: Resin | 1.26 × 10−5 | 75.09 | 10.63 |
| 27 | Lateralization | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0061 | 263.18 | 9.83 |
| 28 | Lateralization | Spatial | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 0.0006 | 1.83 × 103 | 36.69 |
| 29 | Lateralization | Spatial | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 0.0006 | 1.83 × 103 | 36.69 |
| 30 | Lateralization | Spatial | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | 0.0134 | 54.61 | 3.41 |
| 31 | Lateralization | Spatial | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0476 | 149.75 | 1.29 |
| 32 | Lateralization | Spatial | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0476 | 149.75 | 1.29 |
| 33 | Situs Inversus | Panel | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.88 × 10−7 | 1.38 × 1016 | 4.79 × 1010 |
| 34 | Situs Inversus | Panel | 2 Lags | Daily.Interpol. | 0.0056 | 9.76 × 1021 | 1.20 × 107 |
| 35 | Situs Inversus | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC | 5.44 × 10−6 | 7.97 × 1010 | 6.73 × 105 |
| 36 | Situs Inversus | Panel | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC | 0.0030 | 2.55 × 1013 | 1.07 × 104 |
| 37 | Situs Inversus | Spatial | Additive | Herb | 0.0019 | 9.61 × 104 | 107.71 |
| 38 | Situs Inversus | Spatial | Interactive | Herb | 0.0019 | 9.61 × 104 | 107.71 |
| 39 | Situs Inversus | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0061 | 50.05 | 4.74 |
| 40 | Situs Inversus | Spatial | 1 Lags | Herb | 0.0299 | 1.05 × 104 | 4.10 |
| 41 | Situs Inversus | Panel | 2 Lags | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.36 × 10−5 | 7.48 | 3.88 |
| 42 | Situs Inversus | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0034 | 8.35 | 2.86 |
| 43 | Situs Inversus | Panel | Interactive | Tobacco: Resin | 1.26 × 10−5 | 3.01 | 2.15 |
| 44 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | Interactive | Herb | 0.0002 | 7.54 × 1017 | 2.85 × 105 |
| 45 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 6.64 × 10−8 | 1.86 × 104 | 850.04 |
| 46 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | Additive | Herb | 0.0035 | 1.77 × 105 | 155.66 |
| 47 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | <2.2 × 10−16 | 356.29 | 145.49 |
| 48 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | 2 Lags | Herb | 0.0137 | 2.28 × 105 | 107.43 |
| 49 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0003 | 2.91 × 103 | 33.76 |
| 50 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 5.65 × 10−5 | 2.63 × 103 | 29.12 |
| 51 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0029 | 2.02 × 105 | 21.03 |
| 52 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Panel | 2 Lags | lag(LpmResinDailyInt, 2) | 5.52 × 10−9 | 39.30 | 15.60 |
| 53 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Panel | Interactive | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | <2.2 × 10−16 | 2.10 | 1.95 |
| 54 | VACTERL | Spatial | 4 Lags | Daily.Interpol. | 6.81 × 10−12 | Infinity | Infinity |
| 55 | VACTERL | Spatial | 6 Lags | Daily.Interpol. | 8.10 × 10−10 | Infinity | Infinity |
| 56 | VACTERL | Spatial | 2 Lags | Daily.Interpol. | 6.56 × 10−6 | Infinity | 6.52 × 10138 |
| 57 | VACTERL | Spatial | Interactive | Daily.Interpol. | 0.0006 | Infinity | 2.53 × 1067 |
| 58 | VACTERL | Panel | 4 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 0.0009 | 5.93 × 1038 | 1.56 × 1017 |
| 59 | VACTERL | Panel | 1 Lag | Daily.Interpol. | 0.0185 | 3.32 × 1059 | 1.67 × 1011 |
| 60 | VACTERL | Spatial | 4 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC | 0.0022 | 1.65 × 1011 | 1.76 × 104 |
| 61 | VACTERL | Spatial | Additive | Daily.Interpol. | 0.0205 | 2.61 × 1016 | 647.17 |
| 62 | VACTERL | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 1.52 × 10−12 | 230.82 | 72.72 |
| 63 | VACTERL | Panel | Additive | Herb | 0.0042 | 1.42 × 104 | 37.93 |
| 64 | VACTERL | Panel | Interactive | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | 4.72 × 10−5 | 1.26 | 1.18 |
| Anomaly | Number | Mean Minimum E-Value | Median Minimum E-Value | Minimum Minimum E-Value | Maximum Minimum E-Value | Mean E-Value Estimate | Median E-Value Estimate | Minimum E-Value Estimate | Maximum E-Value Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VACTERL | 11 | 2.73 × 10306 | 1.67 × 1011 | 1.18 | 1.50 × 10307 | 5.45 × 10306 | 5.93 × 1038 | 1.26 | 1.50 × 10307 |
| Situs Inversus | 11 | 4.36 × 109 | 107.71 | 2.15 | 4.79 × 1010 | 8.87 × 1020 | 9.61 × 104 | 3.01 | 9.76 × 1021 |
| Teratogenic Syndromes | 10 | 2.86 × 104 | 70.595 | 1.95 | 285,000 | 7.54 × 1016 | 10,755.00 | 2.10 | 7.54 × 1017 |
| FAS | 9 | 3.96 × 1010 | 36.32 | 1.53 | 3.56 × 1011 | 1.11 × 1017 | 14,100.00 | 4.78 | 1.00 × 1018 |
| Lateralization | 10 | 14.471 | 11.845 | 1.29 | 36.69 | 548.226 | 168.31 | 50.49 | 1830 |
| All Anomalies | 13 | 244.58 | 2.36 | 1.2 | 1760 | 3.44 × 1014 | 5.67 | 1.42 | 4.47 × 1015 |
| No. | Anomaly | Regression | Model Type | Term | Group | p-Value | E-Value Estimate | Lower Bound E-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VACTERL | Spatial | 4 Lags | Daily.Interpol. | Daily | 6.81 × 10−12 | Infinity | Infinity |
| 2 | VACTERL | Spatial | 6 Lags | Daily.Interpol. | Daily | 8.10 × 10−10 | Infinity | Infinity |
| 3 | VACTERL | Spatial | 2 Lags | Daily.Interpol. | Daily | 6.56 × 10−6 | Infinity | 6.52 × 10138 |
| 4 | VACTERL | Spatial | Interactive | Daily.Interpol. | Daily | 0.0006 | Infinity | 2.53 × 1067 |
| 5 | VACTERL | Panel | 1 Lag | Daily.Interpol. | Daily | 0.0185 | 3.32 × 1059 | 1.67 × 1011 |
| 6 | Situs Inversus | Panel | 2 Lags | Daily.Interpol. | Daily | 0.0056 | 9.76 × 1021 | 1.20 × 107 |
| 7 | VACTERL | Spatial | Additive | Daily.Interpol. | Daily | 0.0205 | 2.61 × 1016 | 647.17 |
| 8 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | Interactive | Herb | Herb | 0.0002 | 7.54 × 1017 | 2.85 × 105 |
| 9 | All Anomalies | Spatial | Interactive | Herb | Herb | 8.09 × 10−6 | 2.87 × 104 | 1.08 × 103 |
| 10 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | Additive | Herb | Herb | 0.0035 | 1.77 × 105 | 155.66 |
| 11 | Situs Inversus | Spatial | Additive | Herb | Herb | 0.0019 | 9.61 × 104 | 107.71 |
| 12 | Situs Inversus | Spatial | Interactive | Herb | Herb | 0.0019 | 9.61 × 104 | 107.71 |
| 13 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | 2 Lags | Herb | Herb | 0.0137 | 2.28 × 105 | 107.43 |
| 14 | FAS | Spatial | Additive | Herb | Herb | 0.0004 | 1.41 × 104 | 104.35 |
| 15 | FAS | Spatial | Interactive | Herb | Herb | 0.0004 | 1.41 × 104 | 104.35 |
| 16 | VACTERL | Panel | Additive | Herb | Herb | 0.0042 | 1.42 × 104 | 37.93 |
| 17 | FAS | Panel | 2 Lags | Herb | Herb | 0.0070 | 4.29 × 104 | 36.32 |
| 18 | Situs Inversus | Spatial | 1 Lags | Herb | Herb | 0.0299 | 1.05 × 104 | 4.10 |
| 19 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Panel | 2 Lags | lag (LpmResinDailyInt, 2) | Herb | 5.52 × 10−9 | 39.30 | 15.60 |
| 20 | Situs Inversus | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC | Herb | 5.44 × 10−6 | 7.97 × 1010 | 6.73 × 105 |
| 21 | VACTERL | Spatial | 4 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC | Herb | 0.0022 | 1.65 × 1011 | 1.76 × 104 |
| 22 | Situs Inversus | Panel | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC | Herb | 0.0030 | 2.55 × 1013 | 1.07 × 104 |
| 23 | VACTERL | Panel | 4 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 0.0009 | 5.93 × 1038 | 1.56 × 1017 |
| 24 | Situs Inversus | Panel | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 1.88 × 10−7 | 1.38 × 1016 | 4.79 × 1010 |
| 25 | All Anomalies | Panel | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 0.0176 | 4.47 × 1015 | 1.76 × 103 |
| 26 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 6.64 × 10−8 | 1.86 × 104 | 850.04 |
| 27 | All Anomalies | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | <2.2 × 10−16 | 212.22 | 106.93 |
| 28 | Lateralization | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 0.0039 | 892.53 | 15.10 |
| 29 | Lateralization | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 0.0061 | 263.18 | 9.83 |
| 30 | Situs Inversus | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 0.0061 | 50.05 | 4.74 |
| 31 | Situs Inversus | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 0.0034 | 8.35 | 2.86 |
| 32 | All Anomalies | Spatial | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 2.23 × 10−2 | 1.92 | 1.34 |
| 33 | Lateralization | Spatial | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 0.0476 | 149.75 | 1.29 |
| 34 | Lateralization | Spatial | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 0.0476 | 149.75 | 1.29 |
| 35 | All Anomalies | Spatial | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | Resin | 8.96 × 10−6 | 8.49 × 103 | 213.85 |
| 36 | Lateralization | Spatial | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | Resin | 0.0006 | 1.83 × 103 | 36.69 |
| 37 | Lateralization | Spatial | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | Resin | 0.0006 | 1.83 × 103 | 36.69 |
| 38 | All Anomalies | Spatial | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | Resin | 0.0037 | 18.72 | 3.60 |
| 39 | Lateralization | Spatial | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC | Resin | 0.0134 | 54.61 | 3.41 |
| 40 | FAS | Panel | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 6.97 × 10−7 | 1.00 × 1018 | 3.56 × 1011 |
| 41 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | <2.2 × 10−16 | 356.29 | 145.49 |
| 42 | VACTERL | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 1.52 × 10−12 | 230.82 | 72.72 |
| 43 | FAS | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 0.0020 | 1.57 × 104 | 61.02 |
| 44 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 0.0003 | 2.91 × 103 | 33.76 |
| 45 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 5.65 × 10−5 | 2.63 × 103 | 29.12 |
| 46 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Spatial | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 0.0029 | 2.02 × 105 | 21.03 |
| 47 | FAS | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 1.44 × 10−13 | 17.04 | 10.05 |
| 48 | FAS | Spatial | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 0.0034 | 23.51 | 1.53 |
| 49 | All Anomalies | Panel | Additive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 0.0001 | 1.75 | 1.45 |
| 50 | All Anomalies | Spatial | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 0.0198 | 1.65 | 1.20 |
| 51 | All Anomalies | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 7.81 × 10−15 | 5.67 | 4.29 |
| 52 | All Anomalies | Panel | 2 Lags | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 0.0303 | 73.47 | 2.36 |
| 53 | FAS | Panel | Interactive | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 0.0016 | 4.78 | 2.31 |
| 54 | All Anomalies | Panel | 1 Lag | LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol.: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | <2.2 × 10−16 | 1.69 | 1.62 |
| 55 | Lateralization | Panel | Additive | Resin | Resin | 0.0003 | 186.86 | 16.72 |
| 56 | Lateralization | Panel | 2 Lags | Resin | Resin | 7.39 × 10−6 | 50.49 | 13.06 |
| 57 | FAS | Panel | 2 Lags | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Herb.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Herb | 1.31 × 10−5 | 6.65 | 3.61 |
| 58 | Situs Inversus | Panel | 2 Lags | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 1.36 × 10−5 | 7.48 | 3.88 |
| 59 | Teratogenic Syndromes | Panel | Interactive | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | <2.2 × 10−16 | 2.10 | 1.95 |
| 60 | All Anomalies | Panel | 2 Lags | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 2.66 × 10−8 | 1.77 | 1.57 |
| 61 | All Anomalies | Panel | 1 Lag | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | <2.2 × 10−16 | 1.42 | 1.38 |
| 62 | VACTERL | Panel | Interactive | Tobacco: LM.Cannabis × Resin.THC × Daily.Interpol. | Resin | 4.72 × 10−5 | 1.26 | 1.18 |
| 63 | Lateralization | Panel | Interactive | Tobacco: Resin | Resin | 1.26 × 10−5 | 75.09 | 10.63 |
| 64 | Situs Inversus | Panel | Interactive | Tobacco: Resin | Resin | 1.26 × 10−5 | 3.01 | 2.15 |
| Group | Number | Mean Minimum E-Value | Median Minimum E-Value | Minimum Minimum E-Value | Maximum Minimum E-Value | Mean E-Value Estimate | Median E-Value Estimate | Minimum E-Value Estimate | Maximum E-Value Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | 7 | 4.29 × 10306 | 2.53 × 1067 | 647.17 | 1.50 × 10307 | 8.57 × 10306 | 1.50 × 10307 | 2.61 × 1016 | 1.50 × 10307 |
| Herb | 28 | 5.57 × 1015 | 105.64 | 1.29 | 1.56 × 1017 | 2.12 × 1037 | 16,400 | 1.92 | 5.93 × 1038 |
| Resin | 29 | 1.23 × 1010 | 4.29 | 1.18 | 3.56 × 1011 | 3.45 × 1016 | 50.49 | 1.26 | 1.00 × 1018 |
| Comparison | W-Statistic | Alternative | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lower E-Value, Daily_v_Herb | 184 | two.sided | 4.20 × 10−4 |
| Lower E-Value, Daily_v_Resin | 200 | two.sided | 8.94 × 10−5 |
| Lower E-Value, Herb_v_Resin | 592 | two.sided | 3.06 × 10−3 |
| E-Value Estimate, Daily_v_Herb | 193 | two.sided | 9.59 × 10−5 |
| E-Value Estimate, Daily_v_Resin | 202 | two.sided | 6.34 × 10−5 |
| E-Value Estimate, Herb_v_Resin | 642 | two.sided | 1.70 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reece, A.S.; Hulse, G.K. Patterns of Cannabis- and Substance-Related Congenital General Anomalies in Europe: A Geospatiotemporal and Causal Inferential Study. Pediatr. Rep. 2023, 15, 69-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15010009
Reece AS, Hulse GK. Patterns of Cannabis- and Substance-Related Congenital General Anomalies in Europe: A Geospatiotemporal and Causal Inferential Study. Pediatric Reports. 2023; 15(1):69-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleReece, Albert Stuart, and Gary Kenneth Hulse. 2023. "Patterns of Cannabis- and Substance-Related Congenital General Anomalies in Europe: A Geospatiotemporal and Causal Inferential Study" Pediatric Reports 15, no. 1: 69-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15010009
APA StyleReece, A. S., & Hulse, G. K. (2023). Patterns of Cannabis- and Substance-Related Congenital General Anomalies in Europe: A Geospatiotemporal and Causal Inferential Study. Pediatric Reports, 15(1), 69-118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15010009







