Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia in Pediatric Age: Focus on Genetics and Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
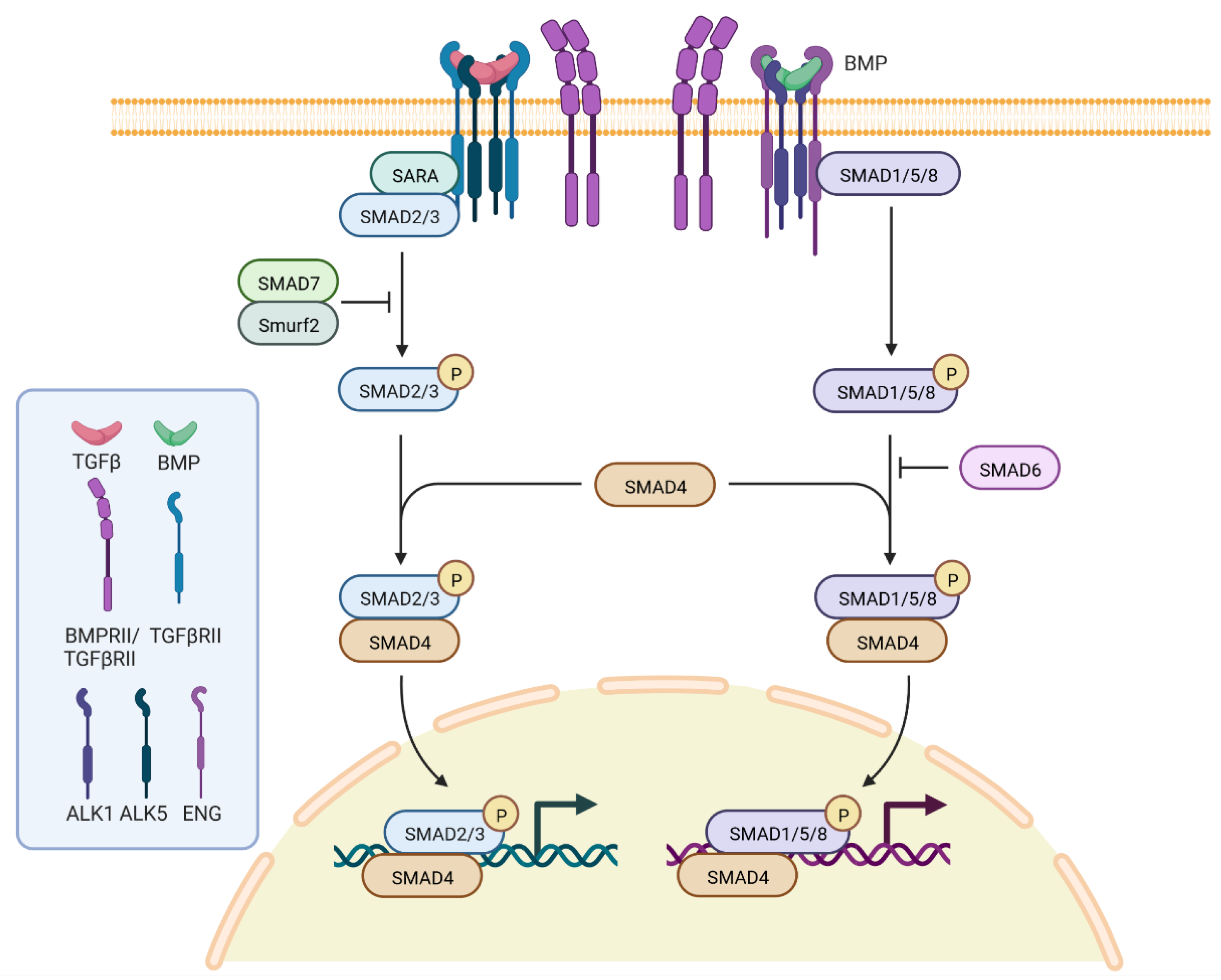
3. Genetics, Molecular Genetics and Pathogenesis
4. Diagnosis and Clinical Presentation
5. Epistaxis (Nosebleeds)
6. Telangiectases
7. Arterovenous Malformations (AVM)
8. Heritable Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Polymicrogyria in HHT
9. Pregnancy and Prenatal Diagnosis
10. Genetic Counseling
11. Guidelines
12. Molecular Testing
13. Surveillance
14. Therapy
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadick, H.; Sadick, M.; Götte, K.; Naim, R.; Riedel, F.; Bran, G.; Hörmann, K. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: An update on clinical manifestations and diagnostic measures. Wien Klin. Wochenschr. 2006, 118, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babington, B.G. Hereditary epistaxis. Lancet 1865, 2, 362–363. [Google Scholar]
- Rendu, H. Epistaxis répétées chez un sujet porteur de petits angiomes cutanées et muqueux. Gaz. Des Hôpitaux Civ. Et Mil. 1896, 69, 1322–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Osler, W. On family form of recurring epistaxis, associated with multiple telangiectases of skin and mucous membranes. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1901, 12, 333–337. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, E.P. Multiple hereditary developmental angiomata (telangiectasia) of the skin and mucous membranes associated with recurring hemorrhages. Lancet 1907, 2, 160–162. [Google Scholar]
- Hanes, F.M. Multiple hereditary telangiectases causing hemorrhage (hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia). Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1909, 20, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, J.; Stevenson, D.A. Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. In GeneReviews; Updated 24 November 2021; Adam, M.P., Everman, D.B., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993–2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1351/ (accessed on 2 August 2022).
- Plauchu, H.; de Chadarevian, J.P.; Bideau, A.; Robert, J.M. Age-related clinical profile of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia in an epidemiologically recruited population. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1989, 32, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallione, C.J.; Scheessele, E.A.; Reinhardt, D.; Duits, A.J.; Berg, J.N.; Westermann, C.J.; Marchuk, D.A. Two common endoglin mutations in families with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia in the Netherlands Antilles: Evidence for a founder effect. Hum. Genet. 2000, 107, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbalchiero, A.; Hweij, Y.A.; Mazza, T.; Buscarini, E.; Scotti, C.; Pagella, F.; Manfredi, G.; Matti, E.; Spinozzi, G.; Olivieri, C. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: First demonstration of a founder effect in Italy; The ACVRL1 c.289_294del variant originated in the country of Bergamo 200 years ago. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2022, 10, e1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faughnan, M.E.; Palda, V.A.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Geisthoff, U.W.; McDonald, J.; Proctor, D.D.; Spears, J.; Brown, D.H.; Buscarini, E.; Chesnutt, M.S.; et al. International Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 48, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, K.A.; Grogg, K.M.; Johnson, D.W.; Gallione, C.J.; Baldwin, M.A.; Jackson, C.E.; Helmbold, E.A.; Markel, D.S.; McKinnon, W.C.; Murrell, J.; et al. Endoglin, a TGF-beta binding protein of endothelial cells, is the gene for hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1. Nat. Genet. 1994, 8, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.W.; Berg, J.N.; Baldwin, M.A.; Gallione, C.J.; Marondel, I.; Yoon, S.J.; Stenzel, T.T.; Speer, M.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Diamond, A.; et al. Mutations in the activin receptor-like kinase 1 gene in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.; Wooderchak-Donahue, W.; VanSant Webb, C.; Whitehead, K.; Stevenson, D.A.; Bayrak-Toydemir, P. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Genetics and molecular diagnostics in a new era. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ARUP Database. Available online: https://arup.utah.edu/database/HHT/ (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- Lesca, G.; Burnichon, N.; Raux, G.; Tosi, M.; Pinson, S.; Marion, M.J.; Babin, E.; Gilbert-Dussardier, B.; Rivière, S.; Goizet, C.; et al. Distribution of ENG and ACVRL1 (ALK1) mutations in French HHT patients. Hum. Mutat. 2006, 27, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyries, M.; Coulet, F.; Girerd, B.; Montani, D.; Humbert, M.; Lacombe, P.; Chinet, T.; Gouya, L.; Roume, J.; Axford, M.; et al. ACVRL1 germinal mosaic with two mutant alleles in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Clin. Genet. 2012, 82, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallione, C.J.; Repetto, G.M.; Legius, E.; Rustgi, A.K.; Schelley, S.L.; Tejpar, S.; Mitchell, G.; Drouin, E.; Westermann, C.J.; Marchuk, D.A. A combined syndrome of juvenile polyposis and hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia associated with mutations in MADH4 (SMAD4). Lancet 2004, 363, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooderchak-Donahue, W.L.; McDonald, J.; O’Fallon, B.; Upton, P.D.; Li, W.; Roman, B.L.; Young, S.; Plant, P.; Fulop, G.T.; Langa, C.; et al. BMP9 mutations cause a vascular-anomaly syndrome with phenotypic overlap with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, S.A.; Letarte, M. Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: Current views on genetics and mechanisms of disease. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Guttmacher, A.E.; Buscarini, E.; Faughnan, M.E.; Hyland, R.H.; Westermann, C.J.; Kjeldsen, A.D.; Plauchu, H. Diagnostic criteria for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome). Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 91, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, K.S.; Choudhury, A.; Wusik, K.; Hammill, A.; White, A.; Henderson, K.; Pollak, J.; Kasthuri, R.S. Applicability of the Curaçao Criteria for the Diagnosis of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia in the Pediatric Population. J. Pediatr. 2018, 197, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faughnan, M.E.; Mager, J.J.; Hetts, S.W.; Palda, V.A.; Lang-Robertson, K.; Buscarini, E.; Deslandres, E.; Kasthuri, R.S.; Lausman, A.; Poetker, D.; et al. Second International Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matti, E.; Lizzio, R.; Ugolini, S.; Maiorano, E.; Zaccari, D.; De Silvestri, A.; De Sando, E.; Marseglia, G.L.; Benazzo, M.; Olivieri, C.; et al. Nasal Endoscopy in the Clinical Diagnosis of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. J. Pediatr. 2021, 238, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baugh, T.P.; Chang, C.W.D. Epidemiology and Management of Pediatric Epistaxis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 159, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.; Porteous, M.; Reinhardt, D.; Gallione, C.; Holloway, S.; Umasunthar, T.; Lux, A.; McKinnon, W.; Marchuk, D.; Guttmacher, A. Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: A questionnaire-based study to delineate the different phenotypes caused by endoglin and ALK1 mutations. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C.D.; Mcdonald, J.; Stevenson, D.A.; Whitehead, K.J.; Petersen, M.G.; Presson, A.P.; Ding, Q.; Wilson, K.F. Epistaxis in children and adolescents with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, J.D.; Li, Q.; Hester, S.T.; Leitner, O.; Smith, K.L.; Kasthuri, R.S. Integration of clinical parameters, genotype and epistaxis severity score to guide treatment for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia associated bleeding. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.M.; Kallogjeri, D.; Spitznagel, E.; Chakinala, M.M.; Schneider, J.S.; Piccirillo, J.F. Development and Validation of the Nasal Outcome Score for Epistaxis in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (NOSE HHT). JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagella, F.; Maiorano, E.; Ugolini, S.; Lizzio, R.; Sovardi, F.; Mirabella, R.; Nanfito, L.; Tinelli, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Olivieri, C. Epidemiological, clinical and endoscopic features of epistaxis severity and quality of life in Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: A cross-sectional study. Rhinology 2021, 59, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, C.D.; Cipriano, S.D.; Topham, C.A.; Stevenson, D.A.; Whitehead, K.J.; Vanderhooft, S.; Presson, A.P.; McDonald, J. Localization and age distribution of telangiectases in children and adolescents with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: A retrospective cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei-Zahav, M.; Letarte, M.; Faughnan, M.E.; Abdalla, S.A.; Cymerman, U.; MacLusky, I.B. Symptomatic children with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: A pediatric center experience. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2006, 160, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krings, T.; Ozanne, A.; Chng, S.M.; Alvarez, H.; Rodesch, G.; Lasjaunias, P.L. Neurovascular phenotypes in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia patients according to age. Review of 50 consecutive patients aged 1 day-60 years. Neuroradiology 2005, 47, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krings, T.; Chng, S.M.; Ozanne, A.; Alvarez, H.; Rodesch, G.; Lasjaunias, P.L. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia in children: Endovascular treatment of neurovascular malformations: Results in 31 patients. Neuroradiology 2005, 47, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Castilla, L.; Russin, J.J.; Martinez-Del-Campo, E.; Soriano-Baron, H.; Spetzler, R.F.; Nakaji, P. Molecular and cellular biology of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: A review of current concepts and future trends in treatment. Neurosurg. Focus. 2014, 37, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Valero, S.F.; Bortolotti, C.; Sturiale, C.; Lanzino, G. Are parenchymal AVMs congenital lesions? Neurosurg. Focus. 2014, 37, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, Y.; Osanai, T.; Nakayama, N.; Ushikoshi, S.; Hokari, M.; Shichinohe, H.; Abumiya, T.; Kazumata, K.; Houkin, K. De novo arteriovenous malformation in a patient with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2016, 17, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eker, O.F.; Boccardi, E.; Sure, U.; Patel, M.C.; Alicante, S.; Alsafi, A.; Coote, N.; Droege, F.; Dupuis, O.; Fialla, A.D.; et al. European Reference Network for Rare Vascular Diseases (VASCERN) position statement on cerebral screening in adults and children with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT). Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesca, G.; Olivieri, C.; Burnichon, N.; Pagella, F.; Carette, M.F.; Gilbert-Dussardier, B.; Goizet, C.; Roume, J.; Rabilloud, M.; Saurin, J.C.; et al. Genotype-Phenotype correlations in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Data from the French-Italian HHT network. Genet. Med. 2007, 9, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocran, K.; Rickes, S.; Heukamp, I.; Wermke, W. Sonographic findings in hepatic involvement of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Ultraschall Med. 2004, 25, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscarini, E.; Danesino, C.; Olivieri, C.; Lupinacci, G.; De Grazia, F.; Reduzzi, L.; Blotta, P.; Gazzaniga, P.; Pagella, F.; Grosso, M.; et al. Doppler ultrasonographic grading of hepatic vascular malformations in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia—Results of extensive screening. Ultraschall Med. 2004, 25, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianora, A.A.; Memeo, M.; Sabba, C.; Cirulli, A.; Rotondo, A.; Angelelli, G. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Multi-detector row helical CT assessment of hepatic involvement. Radiology 2004, 230, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, P.; Nigro, A.; Lenato, G.M.; Guanti, G.; Suppressa, P.; Lastella, P.; De Mattia, D.; Sabbà, C. Screening for children from families with Rendu-Osler-Weber disease: From geneticist to clinician. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saleh, S.; John, P.R.; Letarte, M.; Faughnan, M.E.; Belik, J.; Ratjen, F. Symptomatic liver involvement in neonatal hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Pediatrics 2011, 127, e1615–e1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfa, M.N.; Bouzaiene, H.; Ben Farhat, L.; Gharbi, L.; Ghariani, B.; Mestiri, H.; Hendaoui, L.; Khalfallah, M.T. Intrahepatic Osler’s disease: Report of two cases and review of the literature. Hepatogastroenterology 2003, 50 (Suppl. S2), ccx–ccxiii. [Google Scholar]
- Bross, D.A.; Perez-Atayde, A.; Mandell, V.S.; Hyams, J.S.; Jonas, M.M. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia presenting in early childhood. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1994, 18, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merves, M.; Parsons, K.; Alazraki, A.; Meisel, J.; Sauer, C.; Li, H. Significant Hematochezia and Intracranial Bleeding in Neonatal Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. AJP Rep. 2019, 9, e10–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Miron, I.; Al-Rukban, H.; Chitayat, D.; Nezarati, M.M. Prenatal presentation of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia—A report of two sibs. Prenat. Diagn. 2016, 36, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.; Bevilacqua, E.; Badr, D.A.; Cannie, M.M.; Sanchez, T.C.; Segers, V.; Keymolen, K.; Jani, J.C. An ACVRL1 gene mutation presenting as vein of Galen malformation at prenatal diagnosis. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 1255–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorselaars, V.; Hosman, A.E.; Westermann, C.; Snijder, R.J.; Mager, J.J.; Goumans, M.J.; Post, M.C. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoot, L.B.; Obler, D.; McElhinney, D.B.; Boardman, K.; Wu, B.L.; Lip, V.; Mullen, M.P. Clinical features of pulmonary arterial hypertension in young people with an ALK1 mutation and hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Arch. Dis. Child. 2009, 94, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, C.; Lanzarini, L.; Pagella, F.; Semino, L.; Corno, S.; Valacca, C.; Plauchu, H.; Lesca, G.; Barthelet, M.; Buscarini, E.; et al. Echocardiographic screening discloses increased values of pulmonary artery systolic pressure in 9 of 68 unselected patients affected with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Genet. Med. 2006, 8, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, D.; Cinnante, C.; Valcamonica, G.; Manenti, G.; Lanfranconi, S.; Colombi, A.; Ghione, I.; Saetti, M.C.; D’Amico, M.; Bonato, S.; et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia associated with cortical development malformation due to a start loss mutation in ENG. BMC Neurol. 2020, 26, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palagallo, G.J.; McWilliams, S.R.; Sekarski, L.A.; Sharma, A.; Goyal, M.S.; White, A.J. The Prevalence of Malformations of Cortical Development in a Pediatric Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Population. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klostranec, J.M.; Chen, L.; Mathur, S.; McDonald, J.; Faughnan, M.E.; Ratjen, F.; Krings, T. A theory for polymicrogyria and brain arteriovenous malformations in HHT. Neurology 2019, 92, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuis, O.; Delagrange, L.; Dupuis-Girod, S. Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia and pregnancy: A review of the literature. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Sodhi, V.; McCarthy, A.; Lasjaunias, P.; Jackson, J.E.; Sheppard, M.N. Estimates of maternal risks of pregnancy for women with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome): Suggested approach for obstetric services. BJOG 2008, 115, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, P.; Lemoine, J.; Trotter, C.; Rakova, I.; Billings, P.; Peacock, S.; Kao, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, F.; Eng, C.M.; et al. Clinical experience with non-invasive prenatal screening for single-gene disorders. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 59, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucassen, A.; Clancy, T.; Montgomery, J.; Clarke, A.; Hall, A.; Fryer, A.; Fenwick, A.; Parker, M. Report on the Genetic Testing of Children; Wellcome Trust Symposium; British Society for Human Genetics: Birmingham, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lebrin, F.; Srun, S.; Raymond, K.; Martin, S.; van den Brink, S.; Freitas, C.; Bréant, C.; Mathivet, T.; Larrivée, B.; Thomas, J.L.; et al. Thalidomide stimulates vessel maturation and reduces epistaxis in individuals with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, R.; Quaglia, F.; Klersy, C.; Pagella, F.; Ornati, F.; Chu, F.; Matti, E.; Spinozzi, G.; Plumitallo, S.; Grignani, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of thalidomide for the treatment of severe recurrent epistaxis in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: Results of a non-randomised, single-centre, phase 2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e465–e473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscarini, E.; Botella, L.M.; Geisthoff, U.; Kjeldsen, A.D.; Mager, H.J.; Pagella, F.; Suppressa, P.; Zarrabeitia, R.; Dupuis-Girod, S.; Shovlin, C.L.; et al. Safety of thalidomide and bevacizumab in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Sharp, H.; Weisdorf-Schindele, S. Argon plasma coagulation: Clinical experience in pediatric patients. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2003, 57, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, J.; Lamin, S.; Thomas, A.; Walsh, A.R.; Rodrigues, D.; Lo, W.B.; Solanki, G.A. Clinical features and outcome in pediatric arteriovenous malformation: Institutional multimodality treatment. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowers, K.L.; Sekarski, L.; White, A.J.; Grady, R.M. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations in children with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: A longitudinal study. Pulm. Circ. 2018, 8, 2045894018786696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Danesino, C.; Cantarini, C.; Olivieri, C. Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia in Pediatric Age: Focus on Genetics and Diagnosis. Pediatr. Rep. 2023, 15, 129-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15010011
Danesino C, Cantarini C, Olivieri C. Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia in Pediatric Age: Focus on Genetics and Diagnosis. Pediatric Reports. 2023; 15(1):129-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleDanesino, Cesare, Claudia Cantarini, and Carla Olivieri. 2023. "Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia in Pediatric Age: Focus on Genetics and Diagnosis" Pediatric Reports 15, no. 1: 129-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15010011
APA StyleDanesino, C., Cantarini, C., & Olivieri, C. (2023). Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia in Pediatric Age: Focus on Genetics and Diagnosis. Pediatric Reports, 15(1), 129-142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15010011





