Supporting Breastfeeding in 2021 and Beyond—Lessons from the Pandemic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. COVID Pandemic and Maternal–Infant Health
2.1. Uncertainties over Vertical Transmission of SARS-CoV-2
2.2. Breastfeeding and COVID-19 Infection
2.3. Breast Milk and Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2
2.4. COVID-19 and Kangaroo Mother Care
2.5. Uncertainties Regarding Discharge Planning and Homecare
2.6. Uncertainties Regarding Vaccination of Pregnant and Lactating Mothers
2.7. Comprehensive National Paid Maternity Leave Policy to Promote Breastfeeding
2.8. Maternal Health and Breastfeeding
3. Innovative Solutions to Support Breastfeeding
3.1. Telemedicine Support for Promoting Maternal Health and Breastfeeding
3.2. NICU Visitation Policy and COVID-19
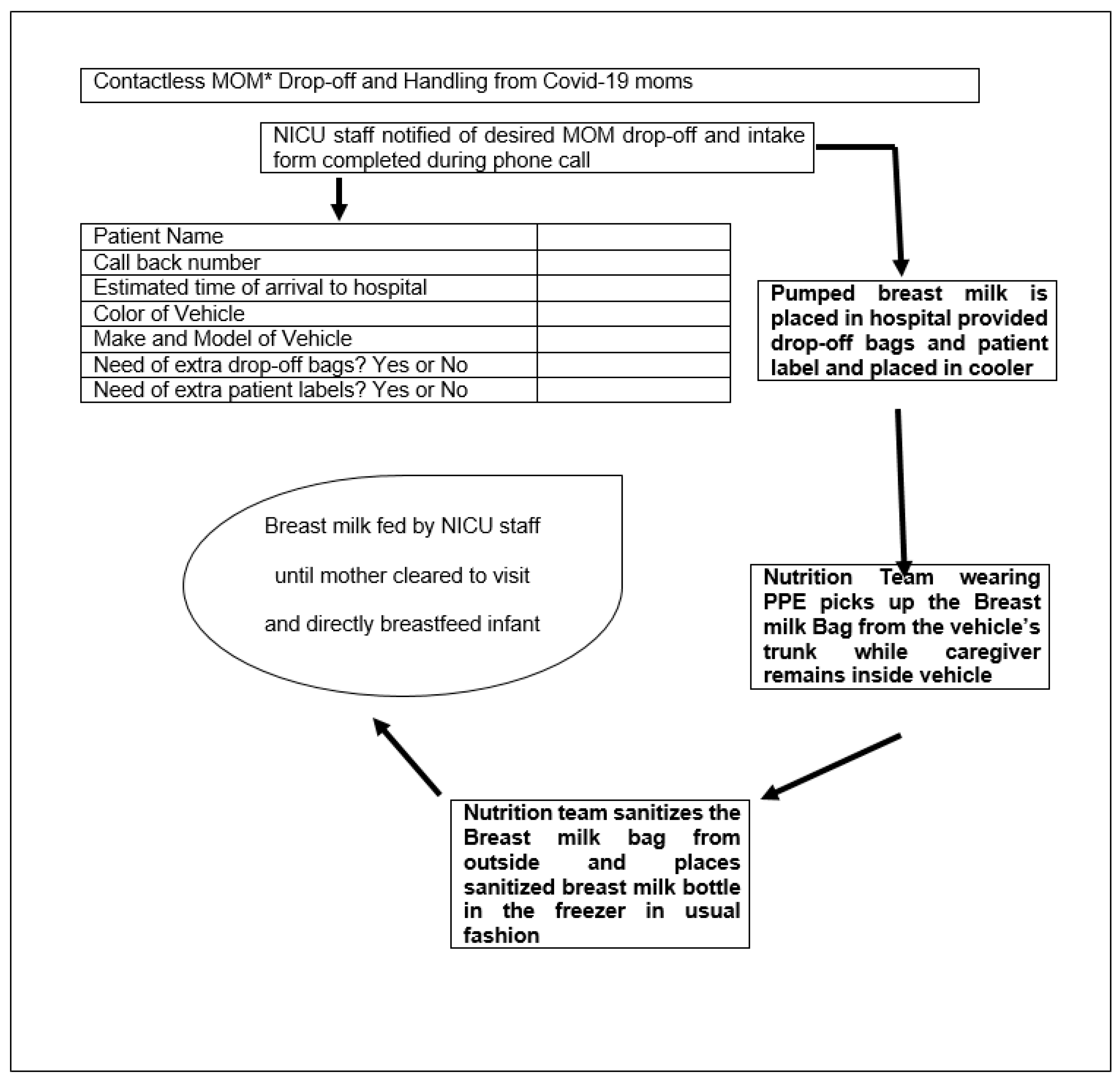
3.3. Contactless Delivery of Breast Milk
3.4. Telelactation
3.5. Antenatal Counseling and Breastfeeding Education
3.6. Evolution of the Lactation Consultant
4. Unanswered Questions and Further Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kickbusch, I.; Leung, G.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Matsoso, M.P.; Ihekweazu, C.; Abbasi, K. Covid-19: How a virus is turning the world upside down. BMJ 2020, 369, m1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Shenker, N. Experiences of breastfeeding during COVID-19: Lessons for future prac-tical and emotional support. Mater. Child. Nutr. 2021, 17, e13088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e827–e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Jackson, M.A.; Long, S.S. (Eds.) Transmission of Infectious Agents via Human Milk. In American Academy of Pediatrics, Red Book: 2018 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 31st ed.; American Academy of Pediatrics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease C: Contraindications to Breastfeeding or Feeding Expressed Breast Milk to Infants. 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/breastfeeding-special-circumstances/contraindications-to-breastfeeding.html (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- Centers for Disease C: Pregnancy, Breastfeeding, and Caring for Newborns. December 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/pregnancy-breastfeeding (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- Pediatrics AAP: Management of Infants Born to Mothers with Suspected or Confirmed COVID-19. July, 2020. Available online: https://services.aap.org/en/pages/2019-novel-coronavirus-covid-19-infections/clinical-guidance/faqs-management-of-infants-born-to-covid-19-mothers/ (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- Colaizy, T.T.; Bartick, M.C.; Jegier, B.J.; Green, B.D.; Reinhold, A.G.; Schaefer, A.J.; Bogen, D.L.; Schwarz, E.B.; Stuebe, A.M.; Jobe, A.H.; et al. Impact of Optimized Breastfeeding on the Costs of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Extremely Low Birthweight Infants. J. Pediatr. 2016, 175, 100–105.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartick, M. Breastfeeding and the U.S. economy. Breastfeed. Med. 2011, 6, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, S.; Teng, X.; Lewis, P.; Shaman, J. Optimizing respiratory virus surveillance networks using uncertainty propagation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhidin, S.; Moghadam, Z.B.; Vizheh, M. Analysis of Maternal Coronavirus Infections and Neonates Born to Mothers with 2019-nCoV; a Systematic Review. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2020, 8, e49. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Tian, J.; He, S.; Zhu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, J. Possible Vertical Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 From an Infected Mother to Her Newborn. JAMA 2020, 323, 1846–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenizia, C.; Biasin, M.; Cetin, I.; Vergani, P.; Mileto, D.; Spinillo, A.; Gismondo, M.R.; Perotti, F.; Callegari, C.; Mancon, A.; et al. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 vertical transmission during pregnancy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirjian, A.; Singh, C.; Tebruegge, M.; Herbert, R.; Draz, N.; Mirfenderesky, M.; Jones, V.; Hinstridge, P.; Seneviratne, R.; Myers, R.; et al. Probable Vertical Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, e257–e260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Xia, S.; Yuan, W.; Yan, K.; Xiao, F.; Shao, J.; Zhou, W. Neonatal Early-Onset Infection With SARS-CoV-2 in 33 Neonates Born to Mothers With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piersigilli, F.; Carkeek, K.; Hocq, C.; van Grambezen, B.; Hubinont, C.; Chatzis, O.; Van der Linden, D.; Danhaive, O. COVID-19 in a 26-week preterm neonate. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivanti, A.J.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Prevot, S.; Zupan, V.; Suffee, C.; Do Cao, J.; Benachi, A.; De Luca, D. Transplacental transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitriu, D.; Emeruwa, U.N.; Hanft, E.; Liao, G.V.; Ludwig, E.; Walzer, L.; Arditi, B.; Saslaw, M.; Andrikopoulou, M.; Scripps, T.; et al. Outcomes of Neonates Born to Mothers With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection at a Large Medical Center in New York City. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Puopolo, K.M. Balancing Risks in the Time of COVID-19. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, C.; Li, X. The SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 expression of maternal-fetal interface and fetal organs by single-cell transcriptome study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230295. [Google Scholar]
- Dumitriu, D.; Gyamfi-Bannerman, C. Understanding Risk for Newborns Born to SARS-CoV-2-Positive Mothers. JAMA 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, M.; Naver, L.; Soderling, J.; Ahlberg, M.; Hervius Askling, H.; Aronsson, B.; Bystrom, E.; Jonsson, J.; Sengpiel, V.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; et al. Association of Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pregnancy With Neonatal Outcomes. JAMA 2021, e215775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, V.A.; Assis, A.M.; da Costa RJúnior, H. Protective effect of human lactoferrin in the gastrointestinal tract. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2013, 31, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska-Zimny, M.; Kamińska-El-Hassan, E.; Wróbel, E. Milk Therapy: Unexpected Uses for Human Breast Milk. Nutrients 2019, 11, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, C.M.; Han, J.Y.; Acker, K.P.; Tiwari, P.; Jin, J.; Brandler, M.; Cangemi, C.; Gordon, L.; Parow, A.; Di-Pace, J.; et al. Neonatal management and outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic: An obser-vation cohort study. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, P.C.K.; Ly, K.M.; Kernich, M.L.; Spurrier, N.; Lawrence, D.; Gordon, D.L.; Tucker, E.C. Detectable Se-vere Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Human Breast Milk of a Mildly Symptomatic Patient With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 128–130. [Google Scholar]
- Bastug, A.; Hanifehnezhad, A.; Tayman, C.; Ozkul, A.; Ozbay, O.; Kazancioglu, S.; Bodur, H. Virolactia in an Asymptomatic Mother with COVID-19. Breastfeed. Med. 2020, 15, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, C.; Krogstad, P.; Bertrand, K.; Contreras, D.; Tobin, N.H.; Bode, L.; Aldrovandi, G. Evaluation for SARS-CoV-2 in Breast Milk From 18 Infected Women. JAMA 2020, 324, 1347–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, R.M.; Williams, J.E.; Jarvinen, K.M.; Belfort, M.B.; Pace, C.D.; Lackey, K.A.; Gogel, A.C.; Nguyen-Contant, P.; Kanagaiah, P.; Fitzgerald, T.; et al. COVID-19 and human milk: SARS-CoV-2, antibodies, and neutralizing capacity. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, D.D.; Puopolo, K.M. Perinatal COVID-19: Guideline development, implementation, and challenges. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2021, 33, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzelmann, C.; Gross, R.; Meister, T.L.; Todt, D.; Krawczyk, A.; Dittmer, U.; Stenger, S.; Munch, J.; Stein-mann, E.; Muller, J.A.; et al. Pasteurization Inactivates SARS-CoV-2-Spiked Breast Milk. Pediatr. 2021, 147, e2020031690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Agudelo, A.; Diaz-Rossello, J.L.; Belizan, J.M. Kangaroo mother care to reduce morbidity and mortality in low birthweight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2003, CD002771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minckas, N.; Medvedev, M.M.; Adejuyigbe, E.A.; Brotherton, H.; Chellani, H.; Estifanos, A.S.; Ezeaka, C.; Go-bezayehu, A.G.; Irimu, G.; Kawaza, K.; et al. Preterm care during the COVID-19 pandemic: A com-parative risk analysis of neonatal deaths averted by kangaroo mother care versus mortality due to SARS-CoV-2 infection. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 33, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuppa, A.A.; Sindico, P.; Orchi, C.; Carducci, C.; Cardiello, V.; Catenazzi, P.; Romagnoli, C. Safety and Efficacy of Galactogogues: Substances that Induce, Maintain and Increase Breast Milk Production. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 13, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, L.D.; Ellington, S.; Strid, P.; Galang, R.R.; Oduyebo, T.; Tong, V.T.; Woodworth, K.R.; Nahabedian, J.F., 3rd; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Gilboa, S.M.; et al. Update: Characteristics of Symptomatic Women of Reproductive Age with Laboratory-Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Pregnancy Status-United States, January 22-October 3, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allotey, J.; Stallings, E.; Bonet, M.; Yap, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Kew, T.; Debenham, L.; Llavall, A.C.; Dixit, A.; Zhou, D.; et al. Clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes of corona-virus disease 2019 in pregnancy: Living systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 370, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimabukuro, T.T.; Kim, S.Y.; Myers, T.R.; Moro, P.L.; Oduyebo, T.; Panagiotakopoulos, L.; Marquez, P.L.; Olson, C.K.; Liu, R.; Chang, K.T.; et al. Preliminary Findings of mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine Safety in Pregnant Persons. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blehar, M.C.; Spong, C.; Grady, C.; Goldkind, S.F.; Sahin, L.; Clayton, J.A. Enrolling Pregnant Women: Issues in Clinical Research. Womens Health Issues 2013, 23, e39–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illamola, S.M.; Bucci-Rechtweg, C.; Costantine, M.M.; Tsilou, E.; Sherwin, C.M.; Zajicek, A. Inclusion of pregnant and breastfeeding women in research-efforts and initiatives. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 84, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gynecologists ACOG: Vaccinating Pregnant and Lactating Patients against COVID-19: Practice Advisory. 2020. Available online: https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/practice-advisory/articles/2020/12/vaccinating-pregnant-and-lactating-patients-against-covid-19 (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Pediatrics. AAP: Interim Guidance for COVID-19 Vaccination in Children and Adolescents. 2021. Available online: https://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/early/2021/05/11/peds.2021-052336 (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Prevention. CDC: COVID-19 Vaccines: Interim Clinical Considerations for Use of COVID-19 Vaccines Currently Authorized in the United States. 2021. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/info-by-product/clinical-considerations.html (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Mirkovic, K.R.; Perrine, C.G.; Scanlon, K.S. Paid Maternity Leave and Breastfeeding Outcomes. Birth 2016, 43, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, A.; Jahagirdar, D.; Dimitris, M.C.; Labrecque, J.A.; Strumpf, E.C.; Kaufman, J.; Vincent, I.; Atabay, E.; Harper, S.; Earle, A.; et al. The Impact of Parental and Medical Leave Policies on Socioeconomic and Health Outcomes in OECD Countries: A Systematic Review of the Empirical Literature. Milbank Q. 2018, 96, 434–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Nandi, A.; Heymann, J. Does extending the duration of legislated paid maternity leave improve breastfeeding practices? Evidence from 38 low-income and middle-income coun-tries. BMJ Glob. Health 2018, 3, e001032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleni, X. Karageorge Ubols: COVID-19 Recession is Tougher on Women. 2020. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/2020/beyond-bls/covid-19-recession-is-tougher-on-women.htm. (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Titan Alon MD, Jane Olmstead-Rumsey & Michèle Tertilt, National Bureau of Economic Research The Impact of COVID-19 on Gender Equality. 2020. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/p/bon/boncrc/crctr224_2020_163.html (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Burtle, A.; Bezruchka, S. Population Health and Paid Parental Leave: What the United States Can Learn from Two Decades of Research. Healthcare 2016, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease C: The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Support Breastfeeding. 2011. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/resources/calltoaction.htm (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- Racine, N.; Hetherington, E.; McArthur, B.A.; McDonald, S.; Edwards, S.; Tough, S.; Madigan, S. Maternal depressive and anxiety symptoms before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada: A longitudinal analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessami, K.; Romanelli, C.; Chiurazzi, M.; Cozzolino, M. COVID-19 pandemic and maternal mental health: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebel, C.; MacKinnon, A.; Bagshawe, M.; Tomfohr-Madsen, L.; Giesbrecht, G. Elevated depression and anxiety symptoms among pregnant individuals during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitelson, E.; Kim, S.; Baker, A.S.; Leight, K. Treatment of postpartum depression: Clinical, psycho-logical and pharmacological options. Int. J. Womens Health 2010, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bashshur, R.; Doarn, C.R.; Frenk, J.M.; Kvedar, J.C.; Woolliscroft, J.O. Telemedicine and the COVID-19 Pandemic, Lessons for the Future. Telemed. e-Health 2020, 26, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portnoy, J.; Waller, M.; Elliott, T. Telemedicine in the Era of COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2020, 8, 1489–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollander, J.E.; Carr, B.G. Virtually Perfect? Telemedicine for Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1679–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Dai, P.; Qin, Y.; Wu, M.; Yang, B.; Yu, X. Effectiveness of telemedicine for pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus: An updated meta-analysis of 32 randomized controlled tri-als with trial sequential analysis. BMC Pregnancy Child. 2020, 20, 198. [Google Scholar]
- Kalafat, E.; Benlioglu, C.; Thilaganathan, B.; Khalil, A. Home blood pressure monitoring in the ante-natal and postpartum period: A systematic review meta-analysis. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2020, 19, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, A.; Hedderson, M.M.; Brown, S.D.; Ehrlich, S.F.; Tsai, A.-L.; Feng, J.; Galarce, M.; Marcovina, S.; Catalano, P.; Quesenberry, C.P. A telehealth lifestyle intervention to reduce excess gestational weight gain in pregnant women with overweight or obesity (GLOW): A randomised, parallel-group, controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, D.; Dholakia, N.; Gopalan, R.; Venkatraman, S.; Dave, K.; Shah, S.; Desai, G.; Qazi, S.A.; Sinha, A.; Pandey, R.M.; et al. mHealth intervention “ImTeCHO” to improve delivery of maternal, neonatal, and child care services-A cluster-randomized trial in tribal areas of Gujarat, India. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ippolito, A.; De Falco, M.; Triassi, M.; Di Lieto, A. A cost study of prenatal telemedicine. J. Telemed. Telecare 2003, 9, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guille, C.; Newman, R.; Fryml, L.D.; Lifton, C.K.; Epperson, C.N. Management of postpartum depres-sion. J. Midwifery Womens Health 2013, 58, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darcy Mahoney, A.; White, R.D.; Velasquez, A.; Barrett, T.S.; Clark, R.H.; Ahmad, K.A. Impact of re-strictions on parental presence in neonatal intensive care units related to coronavirus dis-ease 2019. J. Perinatol. 2020, 40 (Suppl. 1), 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.D.; Swanson, J.R. Visitation restrictions: Is it right and how do we support families in the NICU during COVID-19? J. Perinatol. 2020, 40, 1576–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.; Chyou, P.-H.; Tirmizi, Z.; Gross, J. Web Camera Use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: Impact on Nursing Workflow. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, E.G.; Arechiga, J.; Dancy, M.; Simon, J.; Wilson, D.; Alhusen, J.L. Integrative Review of Tech-nology to Support Communication With Parents of Infants in the NICU. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. JOGNN 2017, 46, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Clinical Management of Severe Acute Respiratory Infection (SARI) When COVID-19 Disease is Suspected. 2020. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331446. (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Steele, C. Best Practices for Handling and Administration of Expressed Human Milk and Donor Human Milk for Hospitalized Preterm Infants. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglash, A.; Simon, L. Academy of Breastfeeding M: ABM Clinical Protocol #8: Human Milk Stor-age Information for Home Use for Full-Term Infants, Revised 2017. Breastfeed. Med. 2017, 12, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuen, J.W.; Loke, A.Y.; Gohel, M.D. Nutritional and immunological characteristics of fresh and re-frigerated stored human milk in Hong Kong: A pilot study. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y. Contactless Healthcare. Heal. Informatics Res. 2020, 26, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Milstein, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Illuminating the dark spaces of healthcare with ambient intelli-gence. Nature 2020, 585, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapinos, K.; Kotzias, V.; Bogen, D.; Ray, K.; Demirci, J.; Rigas, M.A.; Uscher-Pines, L. The Use of and Ex-periences With Telelactation Among Rural Breastfeeding Mothers: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2019, 21, e13967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, E.A.; Armenti, K.; Henning, M.; Sirois, L. Identifying Barriers and Supports to Breastfeeding in the Workplace Experienced by Mothers in the New Hampshire Special Supplemental Nutri-tion Program for Women, Infants, and Children Utilizing the Total Worker Health Framework. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmquist, A.E.L.; Parry, K.C.; Wouk, K.; Lawless, G.C.; Smith, J.L.; Smetana, A.R.; Bourg, J.F.; Hendricks, M.J.; Sullivan, C.S. Ready, Set, BABY Live Virtual Prenatal Breastfeeding Education for COVID-19. J. Hum. Lact. 2020, 36, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Supporting Breastfeeding in Year 2021 and Beyond |
|---|
Supportive Legislations
|
Innovative solutions to support breastfeeding
|
| Pairing proactive virus surveillance with breastfeeding research. |
| Combating misinformation. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, A.P.; Kumar, V.H.; Panda, S. Supporting Breastfeeding in 2021 and Beyond—Lessons from the Pandemic. Pediatr. Rep. 2021, 13, 289-301. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric13020037
Singh AP, Kumar VH, Panda S. Supporting Breastfeeding in 2021 and Beyond—Lessons from the Pandemic. Pediatric Reports. 2021; 13(2):289-301. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric13020037
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Ajay Pratap, Vasantha HS Kumar, and Sanjeet Panda. 2021. "Supporting Breastfeeding in 2021 and Beyond—Lessons from the Pandemic" Pediatric Reports 13, no. 2: 289-301. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric13020037
APA StyleSingh, A. P., Kumar, V. H., & Panda, S. (2021). Supporting Breastfeeding in 2021 and Beyond—Lessons from the Pandemic. Pediatric Reports, 13(2), 289-301. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric13020037






