Microbiota of the Whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) by 16S rDNA Illumina Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling of Bemisia tabaci and Total DNA Extraction
2.2. Determining the Biotypes of Bemisia tabaci
2.3. Diagnostic Assays for the L925I and F331W Resistance Mutations and Diversity of Resistance Alleles
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis of Microbiota Based on 16 rDNA Gene Sequencing
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Identification of Bemisia tabaci Biotypes
3.2. Detection of L925i (kdr) and F331W (ace) Mutations
3.3. Gut Microbiota Associated with Bemisia tabacii Biotypes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Barro, P.J.; Liu, S.-S.; Boykin, L.M.; Dinsdale, A.B. Bemisia tabaci: A Statement of Species Status. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navas-Castillo, J.; Fiallo-Olivé, E.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Emerging Virus Diseases Transmitted by Whiteflies. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 219–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perring, T.M. The Bemisia tabaci species complex. Crop Prot. 2001, 20, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; De Barro, P.J.; Xu, J.; Zang, L.S.; Ruan, Y.M.; Qiu, B.L. Asymmetric mating interactions between two cryptic species of Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius). Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, I.D.; Briddon, R.W.; Brown, J.K.; Rosell, R.C.; Markham, P.G. Geminivirus Transmission and Biological Characterisation of Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) Biotypes from Different Geographic Regions. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1994, 125, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boykin, L.M. Bemisia tabaci Nomenclature: Lessons Learned. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiza Chikoti, P.; Tembo, M.; Peter Legg, J.; Rufini Shirima, R.; Mugerwa, H.; Sseruwagi, P. Genetic Diversity of Mitochondrial DNA of Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) Associated with Cassava and the Occurrence of Cassava Mosaic Disease in Zambia. Insects 2020, 11, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakala, S.; Ghanim, M. Global Genetic Diversity and Geographical Distribution of Bemisia tabaci and Its Bacterial Endosymbionts. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongnikong, W.; Van Brunschot, S.L.; Hereward, J.P.; De Barro, P.J.; Walter, G.H. Testing Mate Recognition through Reciprocal Crosses of Two Native Populations of the Whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) in Australia. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2020, 110, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbertson, A.; Vänninen, I. The Importance of Maintaining Protected Zone Status against Bemisia tabaci. Insects 2015, 6, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Abdelkrim, A.; Hattab, T.; Fakhfakh, H.; Belkadhi, M.S.; Gorsane, F. A Landscape Genetic Analysis of Important Agricultural Pest Species in Tunisia: The Whitefly Bemisia tabaci. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, T.G.E.; Field, L.M.; Usherwood, P.N.R.; Williamson, M.S. DDT, Pyrethrins, Pyrethroids and Insect Sodium Channels. IUBMB Life 2007, 59, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberemok, V.V.; Laikova, K.V.; Gninenko, Y.I.; Zaitsev, A.S.; Nyadar, P.M.; Adeyemi, T.A. A Short History of Insecticides. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2015, 55, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.G. resistance of drosophila to toxins. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2001, 46, 545–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alon, M.; Alon, F.; Nauen, R.; Morin, S. Organophosphates’ Resistance in the B-Biotype of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) Is Associated with a Point Mutation in an Ace1-Type Acetylcholinesterase and Overexpression of Carboxylesterase. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roditakis, E.; Tsagkarakou, A.; Vontas, J. Identification of Mutations in the Para Sodium Channel of Bemisia tabaci from Crete, Associated with Resistance to Pyrethroids. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2006, 85, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boykin, L.M.; Shatters, R.G., Jr.; Rosell, R.C.; McKenzie, C.L.; Bagnall, R.A.; De Barro, P.; Frohlich, D.R. Global Relationships of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) Revealed Using Bayesian Analysis of Mitochondrial COI DNA Sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 44, 1306–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostant, W.G.; Wedell, N.; Hosken, D.J. Transposable Elements and Insecticide Resistance. In Advances in Genetics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 78, pp. 169–201. ISBN 978-0-12-394394-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hollingworth, R.M.; Dong, K. The Biochemical and Molecular Genetic Basis of Resistance to Pesticides in Arthropods. In Global Pesticide Resistance in Arthropods; Whalon, M.E., Mota-Sanchez, D., Hollingworth, R.M., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2008; pp. 40–89. ISBN 978-1-84593-353-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bergé, J.B.; Chevillon, C.; Raymond, M.; Pasteur, N. Resistance of insects to insecticides. Molecular mechanisms and epidemiology. C R Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 1996, 190, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Boush, M.G.; Matsumura, F. Insecticidal Degradation by Pseudomonas Melophthora, the Bacterial Symbiote of the Apple Maggot. J. Econ. Entomol. 1967, 60, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Hayatsu, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Nagayama, A.; Tago, K.; Fukatsu, T. Symbiont-Mediated Insecticide Resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8618–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, N.; Li, R.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, L.; Liang, P.; Gao, X. The Gut Symbiont Sphingomonas Mediates Imidacloprid Resistance in the Important Agricultural Insect Pest Aphis Gossypii Glover. BMC Biol. 2023, 21, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, J.; Qin, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, X.; Hou, M.; Chen, J. Reduced Insecticide Susceptibility of the Wheat Aphid SITOBION MISCANTHI after Infection by the Secondary Bacterial Symbiont Hamiltonella Defensa. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 1936–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, R.; Chen, M.; Yue, L.; Xing, K.; Li, T.; Kang, K.; Liang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, W. A Distinct Strain of Arsenophonus Symbiont Decreases Insecticide Resistance in Its Insect Host. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaljac, M.; Kirfel, P.; Grotmann, J.; Vilcinskas, A. Fitness Costs of Infection with Serratia Symbiotica Are Associated with Greater Susceptibility to Insecticides in the Pea Aphid ACYRTHOSIPHON PISUM. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thao, M.L.; Baumann, P. Evolutionary Relationships of Primary Prokaryotic Endosymbionts of Whiteflies and Their Hosts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3401–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.-M.; Guo, L.; Tao, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Wan, F.-H.; Chu, D. Effects of Host Plant Factors on the Bacterial Communities Associated with Two Whitefly Sibling Species. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, S.; Chen, X.; Hypsa, V. Phylogeny and Potential Transmission Routes of Midgut-associated Endosymbionts of Tsetse (Diptera: Glossinidae). Insect Mol. Biol. 1997, 6, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugerwa, H.; Colvin, J.; Alicai, T.; Omongo, C.A.; Kabaalu, R.; Visendi, P.; Sseruwagi, P.; Seal, S.E. Genetic Diversity of Whitefly (Bemisia spp.) on Crop and Uncultivated Plants in Uganda: Implications for the Control of This Devastating Pest Species Complex in Africa. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 1307–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, Y.; Ghanim, M.; Chiel, E.; Gerling, D.; Portnoy, V.; Steinberg, S.; Tzuri, G.; Horowitz, A.R.; Belausov, E.; Mozes-Daube, N.; et al. Identification and Localization of a Rickettsia Sp. in Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3646–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, S.; Williamson, M.S.; Goodson, S.J.; Brown, J.K.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Dennehy, T.J. Mutations in the Bemisia tabaci Para Sodium Channel Gene Associated with Resistance to a Pyrethroid plus Organophosphate Mixture. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, N.; Clouet, C.; Perrakis, A.; Kapantaidaki, D.; Peterschmitt, M.; Tsagkarakou, A. Genetic Structure of Bemisia tabaci Med Populations from Home-range Countries, Inferred by Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Markers: Impact on the Distribution of the Insecticide Resistance Genes. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1477–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeshima, T.; Mori, A.; Kozaki, T.; Iwata, Y.; Hidoh, O.; Harada, S.; Kasai, S.; Severson, D.W.; Kono, Y.; Tomita, T. An Amino Acid Substitution Attributable to Insecticide-Insensitivity of Acetylcholinesterase in a Japanese Encephalitis Vector Mosquito, Culex Tritaeniorhynchus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 313, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Status of Insecticide Resistance and Associated Mutations in Q-Biotype of Whitefly, Bemisia tabaci, from Eastern China. Crop Prot. 2012, 31, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, D.; Laarif, A.; Clouet, C.; Gauthier, N. Spatial and Host-plant Partitioning between Coexisting Bemisia tabaci Cryptic Species in Tunisia. Popul. Ecol. 2012, 54, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei-Poku, J.; Mbogo, C.M.; Palmer, W.J.; Jiggins, F.M. Deep Sequencing Reveals Extensive Variation in the Gut Microbiota of Wild Mosquitoes from K Enya. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 5138–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P. biology of bacteriocyte-associated endosymbionts of plant sap-sucking insects. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 59, 155–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delalibera, I.; Handelsman, J.; Raffa, K.F. Contrasts in Cellulolytic Activities of Gut Microorganisms Between the Wood Borer, Saperda vestita (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), and the Bark Beetles, Ips pini and Dendroctonus frontalis (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ. Entomol. 2005, 34, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werren, J.H. Symbionts Provide Pesticide Detoxification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8364–8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, D.B.; Moran, N.A. Genome Reduction and Co-Evolution between the Primary and Secondary Bacterial Symbionts of Psyllids. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 3781–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarzewicz, T.; Moskal, A. Ultrastructure, Distribution, and Transmission of Endosymbionts in the whitefly Aleurochiton aceris Modeer (Insecta, Hemiptera, Aleyrodinea). Protoplasma 2001, 218, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.-T.; Cai, L.; Shen, Y.; Du, Y.-Z. Diversity and Evolution of the Endosymbionts of Bemisia tabaci in China. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, M.; Samanta, S.; Thakur, H.; Chakraborty, S.; Samanta, A.; Ghosh, A.; Tarafdar, J. Effect of Neonicotinoids on Bacterial Symbionts and Insecticide-Resistant Gene in Whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. Insects 2021, 12, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueguen, G.; Rolain, J.M.; Zchori-Fein, E.; Vavre, F.; Fleury, F.; Raoult, D. Molecular Detection and Identification of Rickettsia Endosymbiont in Different Biotypes of Bemisia tabaci. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontsedalov, S.; Zchori-Fein, E.; Chiel, E.; Gottlieb, Y.; Inbar, M.; Ghanim, M. The Presence of Rickettsia Is Associated with Increased Susceptibility of Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) to Insecticides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, X.; Ruan, Y.; Rao, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, S. Diversity of Secondary Endosymbionts among Different Putative Species of the Whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Insect Sci. 2013, 20, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierry, M.; Becker, N.; Hajri, A.; Reynaud, B.; Lett, J.-M.; Delatte, H. Symbiont Diversity and Non-Random Hybridization among Indigenous (Ms) and Invasive (B) Biotypes of Bemisia tabaci: Symbionts of hybridizing B. tabaci biotypes. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 2172–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.-W.; Luan, J.-B.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Douglas, A.E.; Liu, S.-S. The Inherited Bacterial Symbiont Hamiltonella Influences the Sex Ratio of an Insect Host. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20191677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, G.K.; Frohlich, D.R.; Veneti, Z.; Braig, H.R.; Miller, T.A.; Bedford, I.D.; Markham, P.G.; Savakis, C.; Bourtzis, K.; Nirgianaki, A. Wolbachia Infections of the Whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Curr. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zchori-Fein, E.; Brown, J.K. Diversity of Prokaryotes Associated with Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2002, 95, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, A.R.; Velten, R.; Stouthamer, R. Incidence of a New Sex–Ratio–Distorting Endosymbiotic Bacterium among Arthropods. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 270, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzoni, O.; Sabaneyeva, E.; Modeo, L.; Castelli, M.; Lebedeva, N.; Verni, F.; Schrallhammer, M.; Potekhin, A.; Petroni, G. Diversity and Environmental Distribution of the Cosmopolitan Endosymbiont “Candidatus Megaira”. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, K.D.E.; Thao, M.; Horn, M.; Dyszynski, G.E.; Baumann, P. Novel Chlamydiae in Whiteflies and Scale Insects: Endosymbionts ‘Candidatus Fritschea Bemisiae’ Strain Falk and ‘Candidatus Fritschea Eriococci’ Strain Elm. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


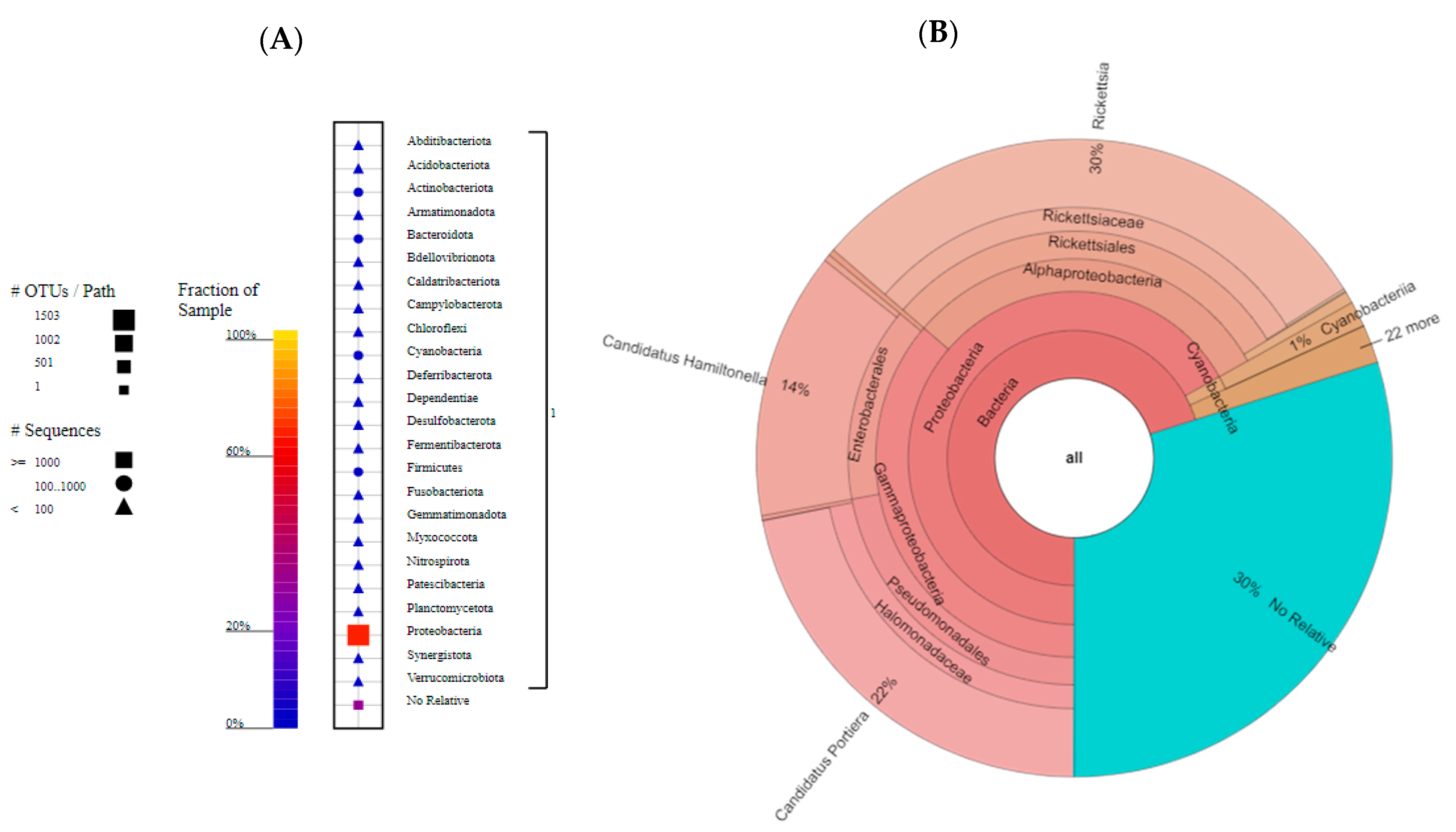
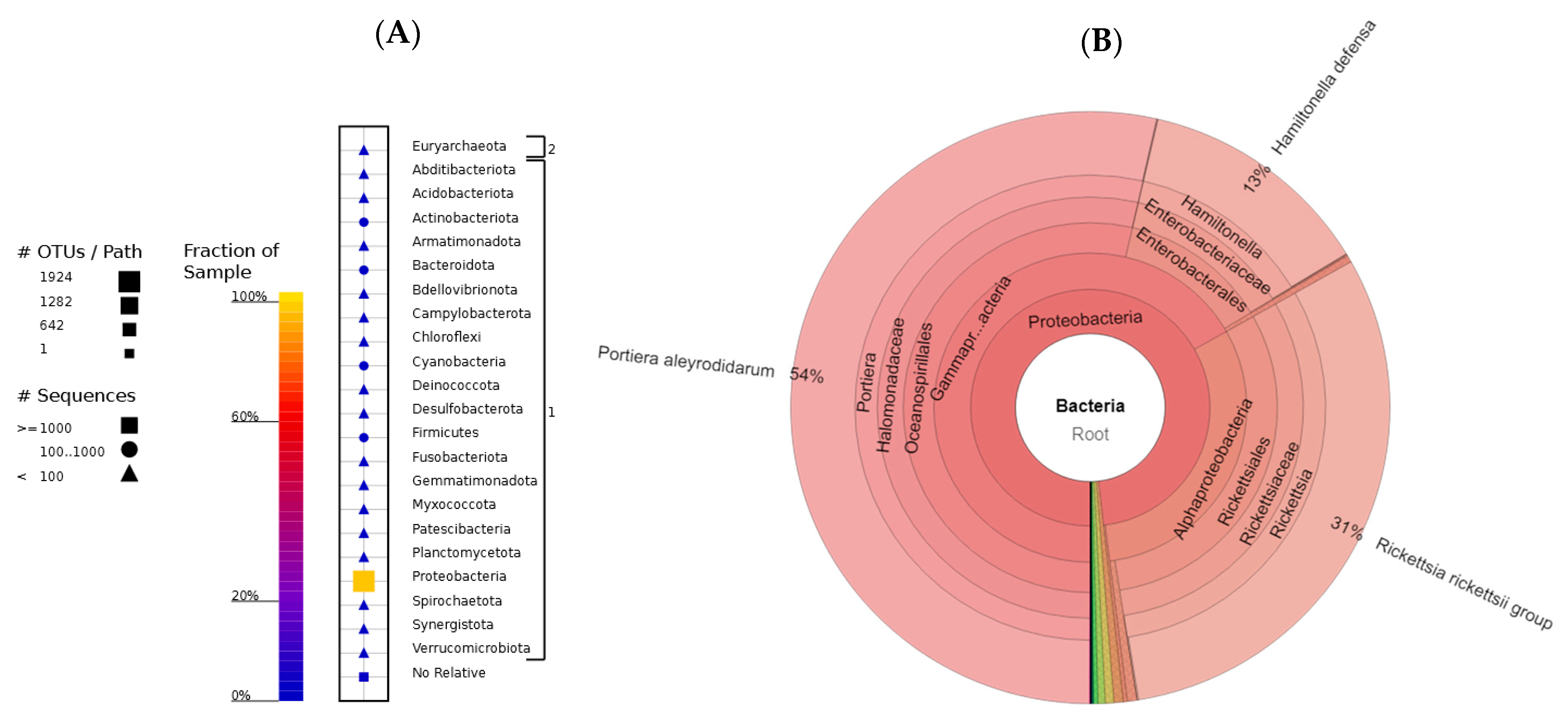
| Biotypes | Raw Reads | Valid Reads | Average Reads Length | OTUs | Classified OTUs | Chao-1 | ACE | Simpson | Shannon | Good’s Coverage of Library (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bt_lantana-Q | 35.057 | 34.999 | 419 | 2154 | 70% | 857.91 | 1028.00 | 0.40 | 1.25 | 99.05 |
| Bt_pepper-B | 49.754 | 49.439 | 419 | 2558 | 97% | 844.16 | 1455.33 | 0.40 | 1.16 | 99.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Najjari, A.; Naccache, C.; Abdelkefi, N.; Djebbi, S.; Souii, A.; Chermiti, B.; Elloumi, M.; Mezghani Khemakhem, M. Microbiota of the Whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) by 16S rDNA Illumina Sequencing. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16070163
Najjari A, Naccache C, Abdelkefi N, Djebbi S, Souii A, Chermiti B, Elloumi M, Mezghani Khemakhem M. Microbiota of the Whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) by 16S rDNA Illumina Sequencing. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(7):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16070163
Chicago/Turabian StyleNajjari, Afef, Chahnez Naccache, Nour Abdelkefi, Salma Djebbi, Amira Souii, Brahim Chermiti, Mourad Elloumi, and Maha Mezghani Khemakhem. 2025. "Microbiota of the Whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) by 16S rDNA Illumina Sequencing" Microbiology Research 16, no. 7: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16070163
APA StyleNajjari, A., Naccache, C., Abdelkefi, N., Djebbi, S., Souii, A., Chermiti, B., Elloumi, M., & Mezghani Khemakhem, M. (2025). Microbiota of the Whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) by 16S rDNA Illumina Sequencing. Microbiology Research, 16(7), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16070163








