Identification, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Clinical Significance of Klebsiella variicola Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
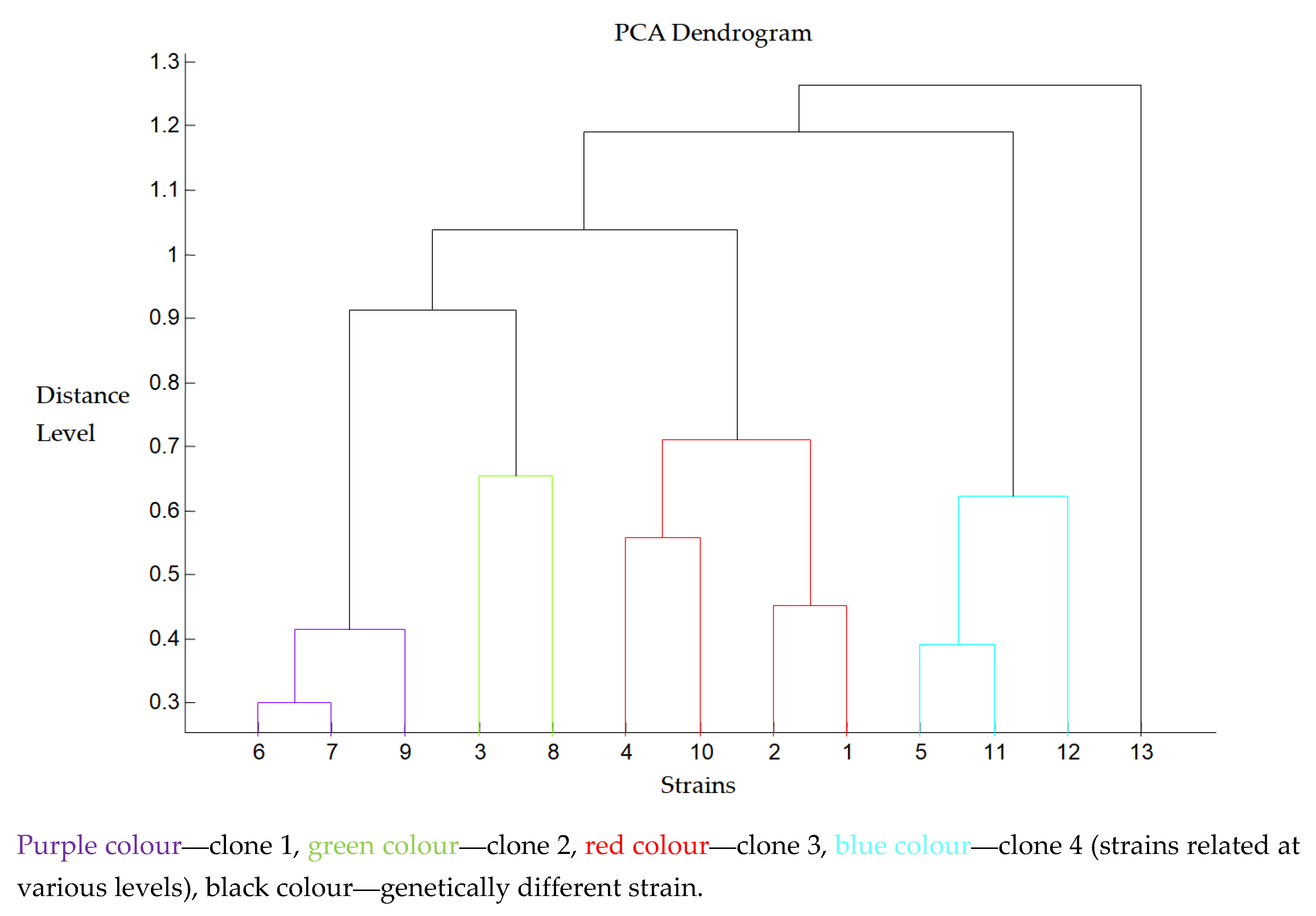
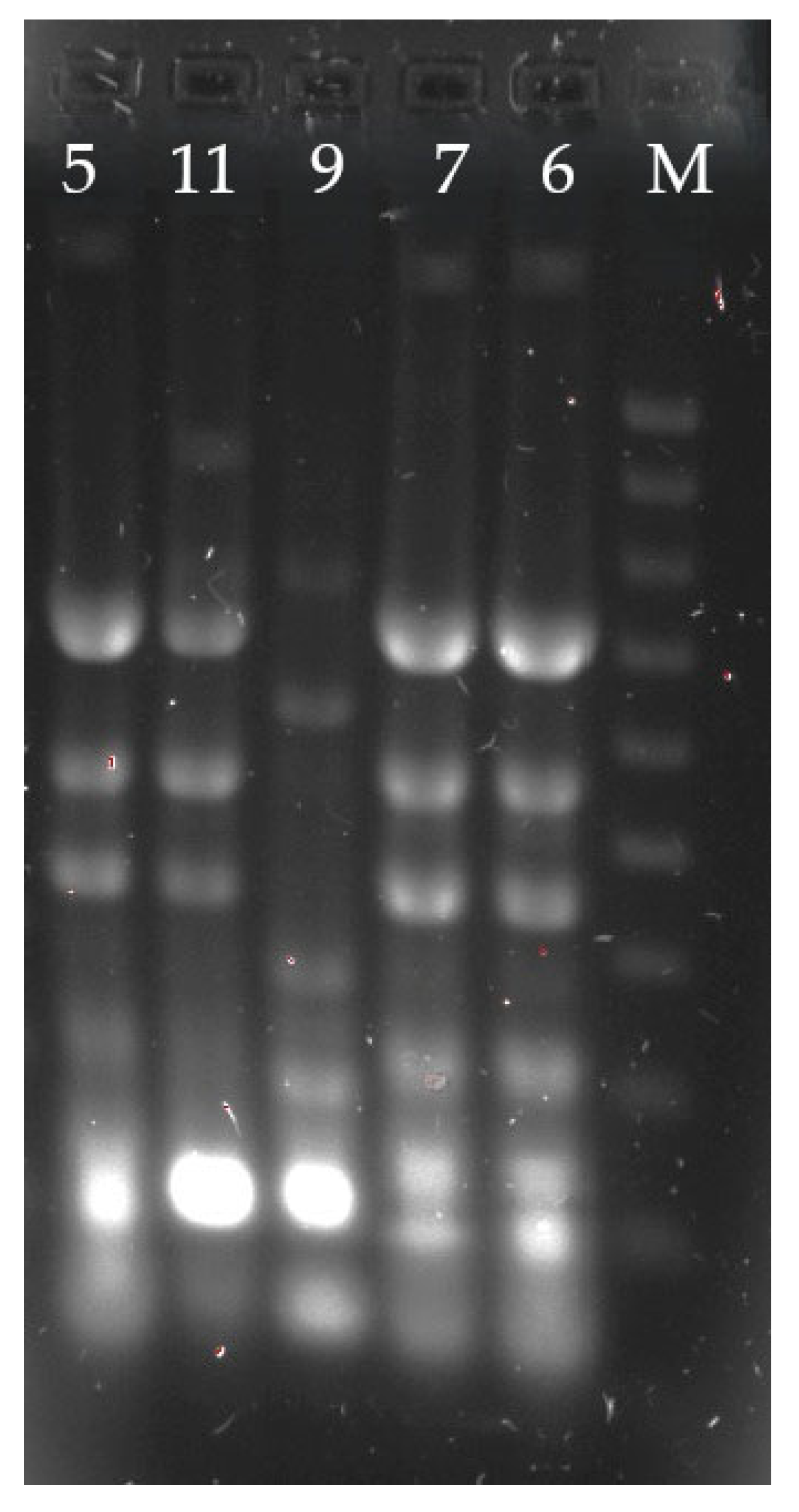
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, N.; Yang, X.; Chan, E.W.-C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Klebsiella Species: Taxonomy, Hypervirulence and Multidrug Resistance. EBioMedicine 2022, 79, 103998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.S.; da Silva Dias, R.C.; de Castro, A.C.D.; Riley, L.W.; Moreira, B.M. Identification of Clinical Isolates of Indole-Positive and Indole-Negative Klebsiella spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3640–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, R.F.; Lainhart, W.; Twentyman, J.; Wallace, M.A.; Wang, B.; Burnham, C.A.; Rosen, D.A.; Dantas, G. Population Structure, Antibiotic Resistance, and Uropathogenicity of Klebsiella variicola. mBio 2018, 9, e02481-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Medina, N.; Barrios-Camacho, H.; Duran-Bedolla, J.; Garza-Ramos, U. Klebsiella variicola: An Emerging Pathogen in Humans. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Fu, L.; Hu, X.; Liang, X.; Gong, G.; Xie, C.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Co-Occurrence of Klebsiella variicola and Klebsiella pneumoniae Both Carrying Bla KPC from a Respiratory Intensive Care Unit Patient. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 4503–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiley, J.L.; Mende, K.; Beckius, M.L.; Kaiser, S.J.; Carson, M.L.; Lu, D.; Whitman, T.J.; Petfield, J.L.; Tribble, D.R.; Blyth, D.M. Resistance Patterns and Clinical Outcomes of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Invasive Klebsiella variicola in Trauma Patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.; Masud, S.; Deans, G.D. Pyelonephritis and Bacteremia Caused by Klebsiella variicola Following Renal Transplantation. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2021, 2021, 9988396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Ishibashi, N.; Kodana, M.; Tarumoto, N.; Sakai, J.; Kawamura, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Taji, Y.; Ebihara, Y.; Ikebuchi, K.; et al. Correction to: Clinical Characteristics in Blood Stream Infections Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella variicola, and Klebsiella quasipneumoniae: A Comparative Study, Japan, 2014–2017. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Watari, T.; Otsuka, Y.; Yamagata, K.; Fujioka, M. Clinical Characteristics and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella variicola and Klebsiella quasipneumoniae Isolated from Human Urine in Japan. J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 71, 001546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legese, M.H.; Asrat, D.; Swedberg, G.; Hasan, B.; Mekasha, A.; Getahun, T.; Worku, M.; Shimber, E.T.; Getahun, S.; Ayalew, T.; et al. Sepsis: Emerging Pathogens and Antimicrobial Resistance in Ethiopian Referral Hospitals. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2022, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.-Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Dong, F.; Ji, Y.-Q.; Yao, K.-H.; Gang, L. The First Community-Acquired Klebsiella variicola Bacterial Meningitis Identified by Metagenomic Next Generation Sequencing. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 42, e186–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura-Silva, R.; Macedo, L.M.D.; Cerdeira, L.; Oliveira-Silva, M.; Silva-Sousa, Y.T.C.; Pitondo-Silva, A. First Report of Hypermucoviscous Klebsiella variicola Subsp. Variicola Causing Primary Endodontic Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eucast: EUCAST. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/ (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- van der Zwaluw, K.; de Haan, A.; Pluister, G.N.; Bootsma, H.J.; de Neeling, A.J.; Schouls, L.M. The Carbapenem Inactivation Method (CIM), a Simple and Low-Cost Alternative for the Carba NP Test to Assess Phenotypic Carbapenemase Activity in Gram-Negative Rods. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemima, S.A.; Verghese, S. Multiplex PCR for Bla(CTX-M) & Bla(SHV) in the Extended Spectrum Beta Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Gram-Negative Isolates. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bali, E.B.; Açık, L.; Sultan, N. Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of SHV, TEM, CTX-M and Extended-Spectrum-Lactamase Produced by Escherichia coli, Acinobacter baumannii and Klebsiella Isolates in a Turkish Hospital. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 650–654. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblueth, M.; Martínez, L.; Silva, J.; Martínez-Romero, E. Klebsiella variicola, a Novel Species with Clinical and Plant-Associated Isolates. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 27, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Ramos, U.; Silva-Sánchez, J.; Martínez-Romero, E.; Tinoco, P.; Pina-Gonzales, M.; Barrios, H.; Martínez-Barnetche, J.; Gómez-Barreto, R.E.; Tellez-Sosa, J. Development of a Multiplex-PCR Probe System for the Proper Identification of Klebsiella variicola. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, S.; van Himbergen, T.; Kusters, K.; Verhoef, J. Development of a Rapid Identification Method for Klebsiella pneumoniae Phylogenetic Groups and Analysis of 420 Clinical Isolates. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, S.S.; Thorsteinsson, M.; Lambine, T.-L.; Penninga, L. Severe Sepsis Caused by a Gas-Forming Clostridium perfringens and Klebsiella variicola Liver Abscess Following Total Pancreatectomy. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e238896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.-L.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, J.-L.; Mu, S.-J.; Chen, L.; Shi, X.-Q.; Li, J.-Q. Fatal Community-Acquired Bloodstream Infection Caused by Klebsiella variicola: A Case Report. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-León, F.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; Caro, C.; Lincopan, N.; Cardenas-Arias, A.; Esposito, F.; Illesca, V.; Rioseco, M.L.; Domínguez-Yévenes, M.; Lima, C.A.; et al. Hypervirulent and Hypermucoviscous Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsiella variicola in Chile. Virulence 2021, 12, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, S.; Aoki, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Ishii, Y.; Sekiya, N.; Kurai, H.; Furukawa, K.; Doi, A.; Tochitani, K.; Kubo, K.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Causing Bloodstream Infections in Japan: Occurrence of Hypervirulent Infections in Health Care. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01206-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzana, R.; Jones, L.S.; Rahman, M.A.; Andrey, D.O.; Sands, K.; Portal, E.; Watkins, W.J.; Pervin, M.; Banerjee, M.; Walsh, T.R. Outbreak of Hypervirulent Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella variicola Causing High Mortality in Neonates in Bangladesh. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 1225–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepenbrock, E.; Higgins, P.G.; Wille, J.; Xanthopoulou, K.; Zweigner, J.; Jahn, P.; Reuter, S.; Skov, R.; Eichhorn, J.; Seifert, H. Klebsiella variicola Causing Nosocomial Transmission among Neonates—An Emerging Pathogen? J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohama, Y.; Nomura, Y.; Mizoguchi, M.; Higurashi, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Harada, S. Accurate Identification of Klebsiella variicola by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Microbiology Laboratories. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0284422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Jo, J.; Ko, K.S. Lipid A Modification-Induced Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella variicola from Healthy Adults. J. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 72, 001680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukada, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Aoki, K.; Yoshizawa, S.; Kondo, Y.; Sawa, T.; Murakami, H.; Sato, E.; Tomida, M.; Otani, M.; et al. The Outbreak of Multispecies Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales Associated with Pediatric Ward Sinks: IncM1 Plasmids Act as Vehicles for Cross-Species Transmission. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2024, 52, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voellmy, I.K.; Lang, C.; Gasser, M.; Kronenberg, A.; Swiss Centre for Antibiotic Resistance (ANRESIS). Antibiotic Resistance Surveillance of Klebsiella pneumoniae Complex Is Affected by Refined MALDI-TOF Identification, Swiss Data, 2017 to 2022. Eurosurveillance 2022, 27, 2200104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.W.; Linson, S.E.; Ojeda Saavedra, M.; Cantu, C.; Davis, J.J.; Brettin, T.; Olsen, R.J. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Human Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Reveals Misidentification and Misunderstandings of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella variicola, and Klebsiella quasipneumoniae. mSphere 2017, 2, e00290-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurfluh, K.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P.; Klumpp, J.; Stephan, R. First Detection of Klebsiella variicola Producing OXA-181 Carbapenemase in Fresh Vegetable Imported from Asia to Switzerland. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2015, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antimicrobial | Percentage of Strains (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Susceptible | Susceptible (High Exposure) | Resistant | |
| Amoxicillin-clavulanate | 57.1 | 16.2 | 26.6 |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 82.4 | 0.9 | 16.7 |
| Cefuroxime | 23.6 | 50.0 | 26.6 |
| Cefotaxime | 87.9 | - | 12.1 |
| Ceftazidime | 85.5 | 1.8 | 13.0 |
| Cefepime | 85.2 | 0.9 | 13.9 |
| Imipenem | 99.1 | - | 0.9 |
| Meropenem | 96.3 | 0.9 | 2.8 |
| Ertapenem | 94.5 | - | 5.5 |
| Gentamicin | 92.6 | - | 7.4 |
| Amikacin | 96.3 | - | 3.7 |
| Tobramycin | 88.6 | - | 10.4 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 89.8 | 2.7 | 7.7 |
| Levofloxacin | 90.5 | 1.8 | 7.7 |
| Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | 85.0 | - | 15.0 |
| Strain | Standard PCR | CRE Test |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SHV | CTX-M 1 |
| 2 | SHV | - |
| 3/5/11 | CTX-M, SHV | CTX-M 1 |
| 4 | CTX-M, TEM | CTX-M 1 |
| 6/7/9/13 | CTX-M, SHV, TEM | CTX-M 1 |
| 8 | CTX-M | CTX-M 1 |
| 10 | CTX-M, TEM | - |
| 12 | TEM | CTX-M 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sękowska, A.; Konechnyi, Y.; Carrazco-Montalvo, A. Identification, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Clinical Significance of Klebsiella variicola Strains. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060123
Sękowska A, Konechnyi Y, Carrazco-Montalvo A. Identification, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Clinical Significance of Klebsiella variicola Strains. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(6):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060123
Chicago/Turabian StyleSękowska, Alicja, Yulian Konechnyi, and Andrés Carrazco-Montalvo. 2025. "Identification, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Clinical Significance of Klebsiella variicola Strains" Microbiology Research 16, no. 6: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060123
APA StyleSękowska, A., Konechnyi, Y., & Carrazco-Montalvo, A. (2025). Identification, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Clinical Significance of Klebsiella variicola Strains. Microbiology Research, 16(6), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060123








