Microbial Inoculants and Fertilizer Reduction in Sorghum Cultivation: Implications for Sustainable Agriculture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Determination of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Shoots and Roots
2.2. Chlorophyll Content
3. Statistical Analysis
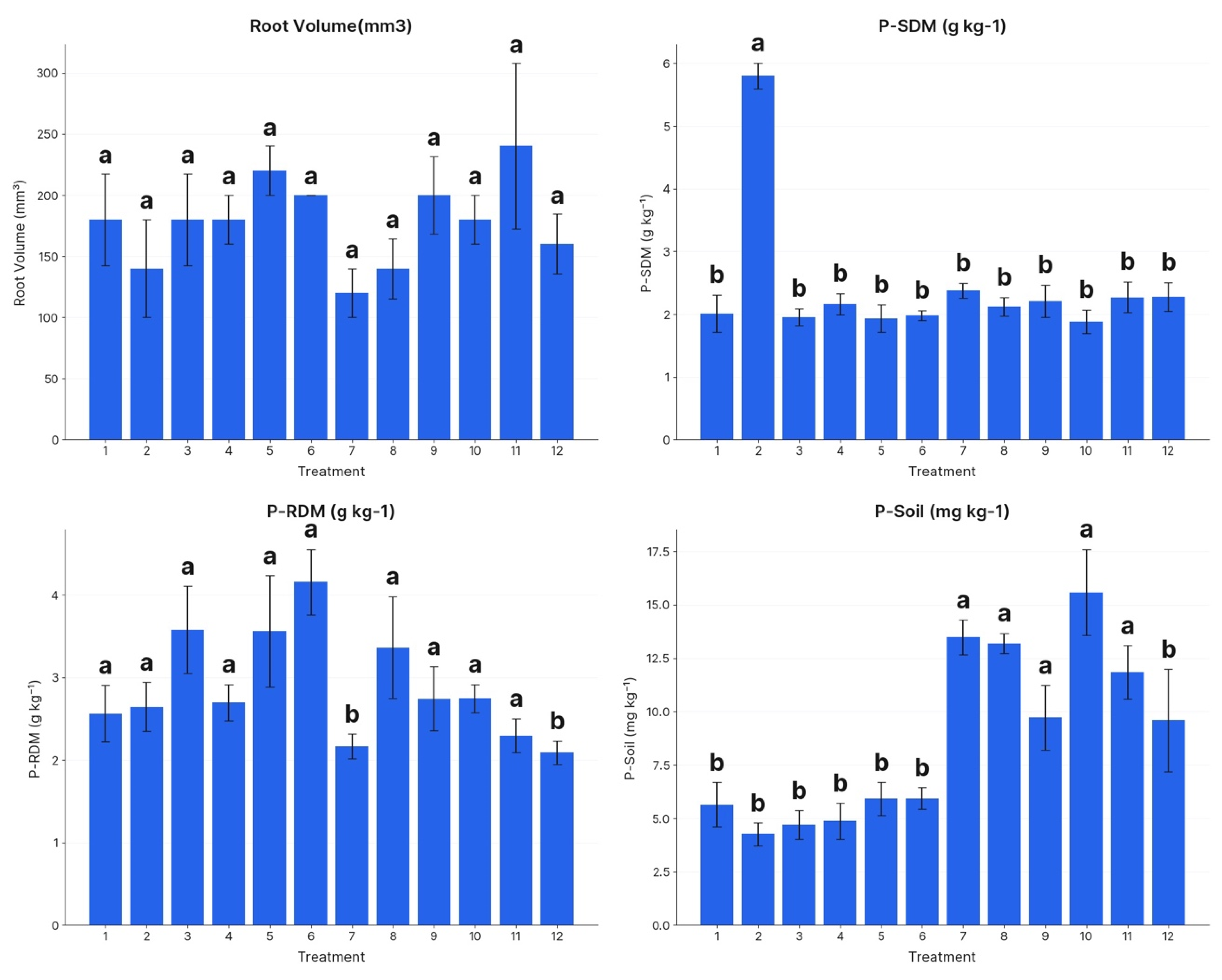
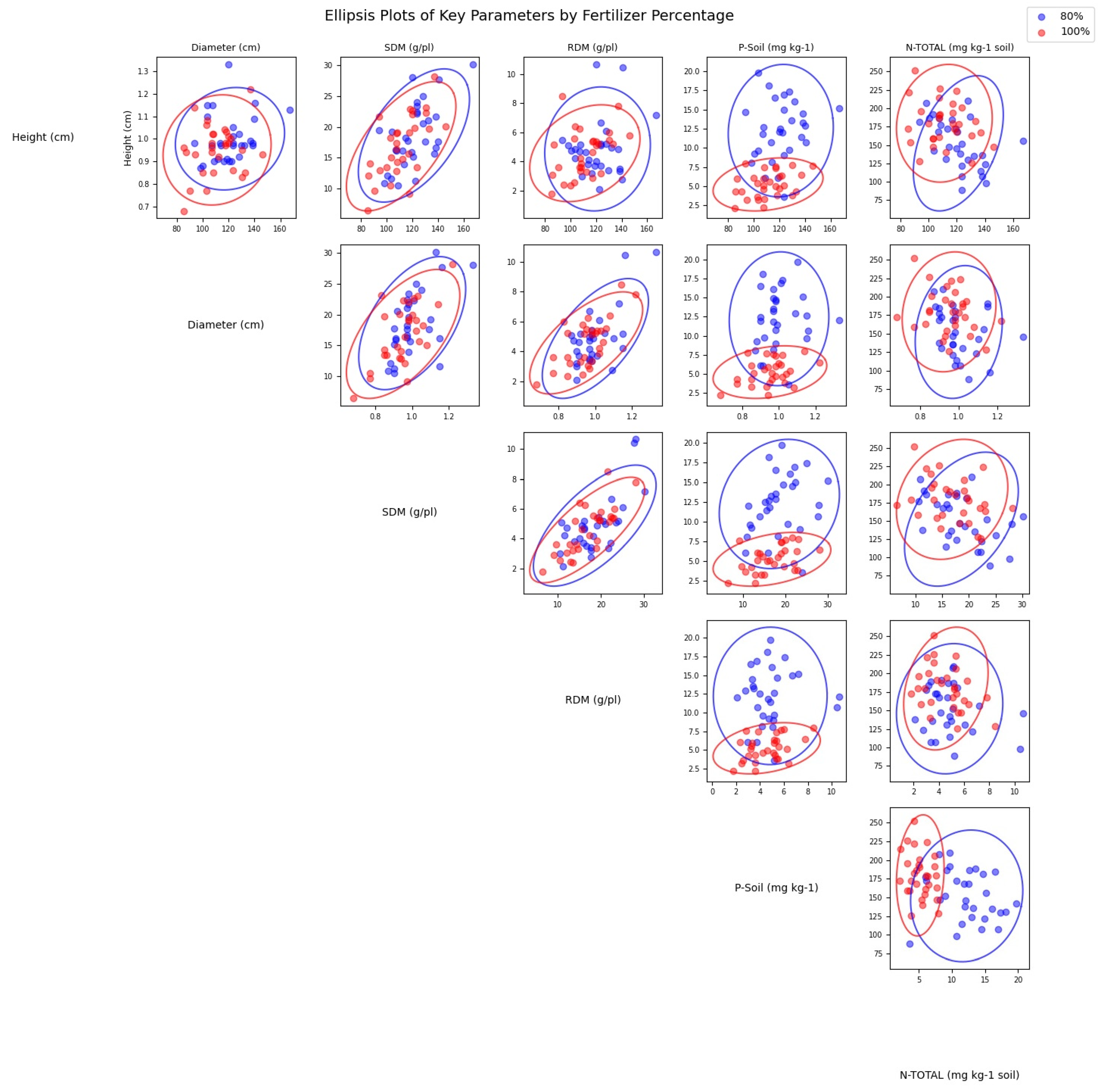
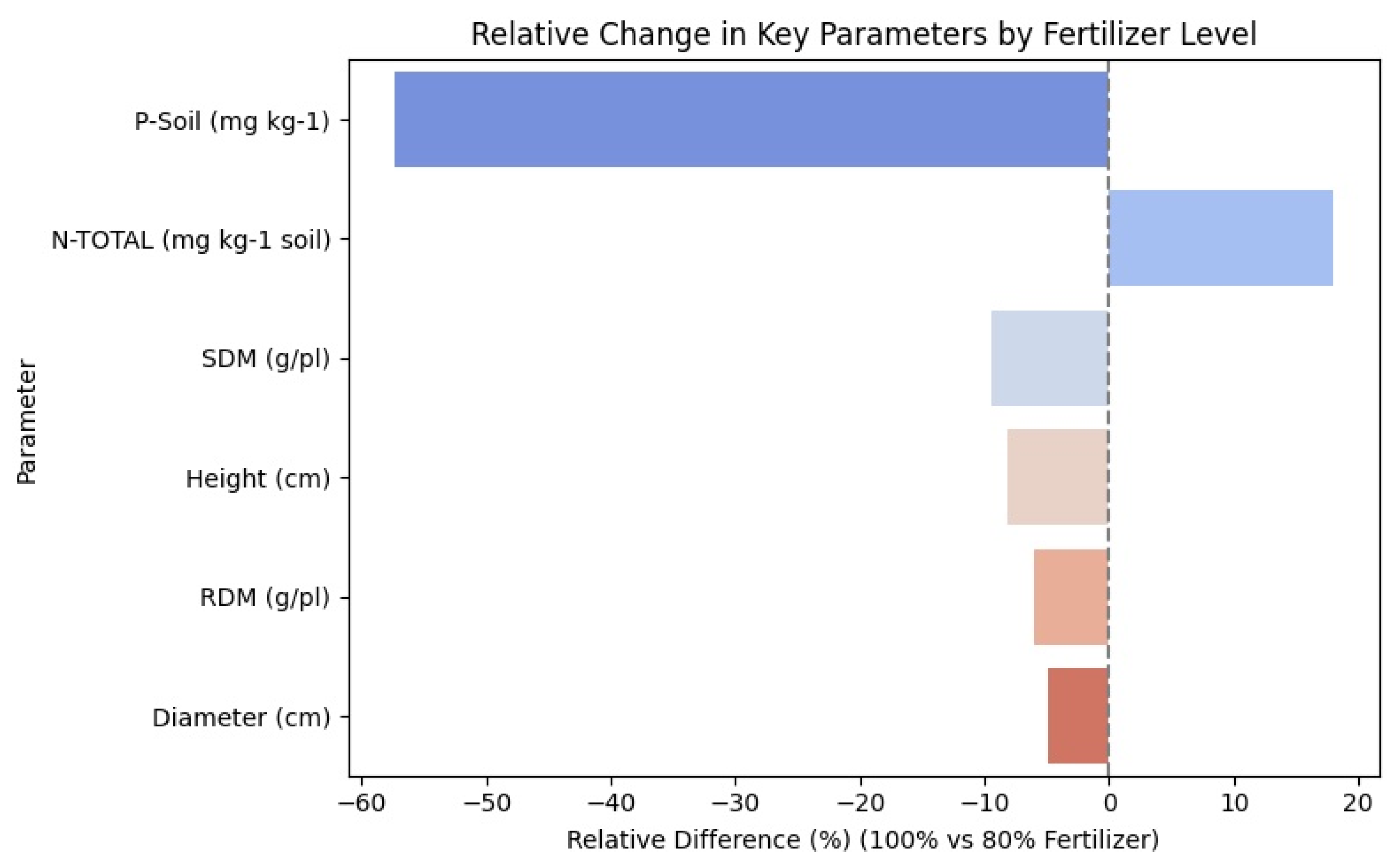
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castro-Jácome, T.P.; Tovar-Pérez, E.G. Biologically Active Peptides from Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] Grain; Bentham Science: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2023; pp. 115–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kazungu, F.K.; Muindi, E.M.; Mulinge, J.M. Overview of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor. L.), its Economic Importance, Ecological Requirements and Production Constraints in Kenya. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2023, 35, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcginnis, M.J.; Painter, J.E. Sorghum. Nutr. Today 2020, 55, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccuistion, K.C.; Selle, P.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Goodband, R.D. Chapter 12—Sorghum as a Feed Grain for Animal Production. In Sorghum and Millets; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 355–391. [Google Scholar]
- Arumugam, Y.; Chinnusamy, K.; Kuppusamy, S.; Chinnusamy, M. Sorghum as Biofuel Crop: Interdisciplinary Methods to Enhance Productivity (Botany, Genetics, Breeding, Seed Technology, and Bioengineering). Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2290, 253–270. [Google Scholar]
- Rooney, L.W.; Rooney, W.L.; Serna Saldivar, S.O. Sorghum. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ronda, V.; Aruna, C.; Visarada, K.B.R.S.; Bhat, B.V. Chapter 14— Sorghum for Animal Feed. In Breeding Sorghum for Diverse End Uses; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Yousuf, A.B.; Ginnidza, M.; Brown, D.; Sismour, E.; Zaid, A.E. Physico-chemical and Nutritional Composition of Ten Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Grain Varieties as Potential Feed for Livestock. J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhao, J.; Feng, X.; Cui, W.; Lu, G. Sorghum Insect Problems and Management. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.M.; Bisht, N.; Singh, T.; Chauhan, P.S. Symphony of survival: Insights into cross-talk mechanisms in plants, bacteria, and fungi for strengthening plant immune responses. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 285, 127762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasusi, O.A.; Babalola, O.O.; Adejumo, T.O. Harnessing of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in agroecosystem sustainability. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2023, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.H.B.; De Andrade, L.A.; Sales, L.R.; Rigobelo, E.C.C.; Frezarin, E.T. Purpureocillium lilacinum for Biocontrol, Bioremediation and Biofertilization. Sustain. Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Timper, P.; Parajuli, G.; Kemerait, R. Improving suppression of Meloidogyne spp. by Purpureocillium lilacinum strain 251. Nematology 2014, 16, 711–717. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Tanaka, K. Purpureocillium lilacinum for plant growth promotion and biocontrol against root-knot nematodes infecting eggplant. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, G.; Copetta, A.; Gamalero, E.; Bona, E.; Cesaro, P.; Scarafoni, A.; D’Agostino, G. Maize development and grain quality are differentially affected by mycorrhizal fungi and a growth-promoting pseudomonad in the field. Mycorrhiza 2014, 24, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreedevi, S.; Padmalatha, P.; Shukla, A. Plant Growth-Promoting Fungi: Mechanisms and Applications; Bentham Science: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2022; pp. 99–122. [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Xu, L.; González-Hernández, A.I.; Camañes, G.; Vicedo, B.; Scalschi, L.; Llorens, E. Harnessing Green Helpers: Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria and Other Beneficial Microorganisms in Plant–Microbe Interactions for Sustainable Agriculture. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, N.C.; Rigobelo, E.C.; Mochi, D.A.; Costa, N.T.A. First report of Aspergillus sydowii and Aspergillus brasiliensis as phosphorus solubilizers in maize. Ann. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, P.A.E.; Baron, N.C.; Rigobelo, E.C. Bacillus spp. as plant growth-promoting bacteria in cotton under greenhouse conditions. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2019, 13, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, B.D.M.S.D.; Rigobelo, E.C.; Chávez, D.W.H.; Silva, M. Genetic and nutritional diversity of Bacillus subtilis isolates demonstrating different aspects related to plant growth promotion. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2020, 14, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchini, G.E.; Malezan, A.; Poletti, M.E.; Soria, E.; Pasqualini, M.; Perez, R.D. Analysis of phosphorous content in cancer tissue by synchrotron micro-XRF. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 179, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellburn, A.R. The Spectral Determination of Chlorophylls a and b, as well as Total Carotenoids, Using Various Solvents with Spectrophotometers of Different Resolution. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 144, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnelutti Filho, A.; Storck, L. Estatísticas de avaliação da precisão experimental em ensaios de cultivares de milho. Pesqui. Agropecuária Bras. 2007, 42, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.P.; De-Bashan, L.E.; Rodriguez, D.J.; Rodriguez, Y.; Bashan, Y. Growth promotion of the freshwater microalga Chlorella vulgaris by the nitrogen-fixing, plant growth-promoting bacterium Bacillus pumilus from arid zone soils. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2008, 45, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, S.; Zhao, X.Q.; Shen, R.F. Bacillus pumilus promotes the growth and nitrogen uptake of tomato plants under nitrogen fertilization. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, K. Study the biochemical and molecular basis of ISR and plant growth promotion in maize under pathogenic stress condition of Rhizoctonia solani. J. Curr. Opin. Crop Sci. 2021, 2, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umapathi, M.; Chandrasekhar, C.N.; Senthil, A.; Kalaiselvi, T.; Kalarani, M.K.; Sivakumar, R.; Karthikeyan, R.; Kuttimani, R.; Anandakumar, S. Bacillus sp. and Pseudacidovorax intermedius colonization effect on biochemical and metabolites expression in drought-stressed Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Moench. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.; Ren, X.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, H.; Han, H.; Chen, Z.-J. Plant growth-promoting bacteria modulate gene expression and induce antioxidant tolerance to alleviate synergistic toxicity from combined microplastic and Cd pollution in sorghum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Pal, G.; Verma, A.; Kumar, D.; Shukla, P.; Verma, S.K. Seed vectored bacterial endophyte Bacillus pumilus protect sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) seedlings from a fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani. Biol. Control 2023, 183, 105249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.C.; Kandasamy, S.; Lazarovits, G.; Rigobelo, E.C. Effect of Chemical Fertilization on the Impacts of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria in Maize Crops. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 3878–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aquino, J.P.A.; de Macedo Junior, F.B.; Antunes, J.E.L.; Figueiredo, M.D.V.B.; de Alcântara Neto, F.; de Araujo, A.S.F. Plant growth-promoting endophytic bacteria on maize and sorghum. Pesqui. Agropecuária Trop. 2019, 49, e56241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fretes, C.E.; Purwestri, Y.A.; Widianto, D.; Nuringtyas, T.R. Plant growth-promoting activity of endophytic bacteria from sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench). Indones. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 26, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigobelo, E.C.; de Carvalho, L.A.L.; Santos, C.H.B.; Frezarin, E.T.; Pinheiro, D.G.; Nicodemo, D.; Babalola, O.O.; Desoignies, N. Growth promotion and modulation of the soybean microbiome INTACTA RR PRO TM with the application of the fungi Trichoderma harzianum and Purpureocillum lilacinum. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhayalan, V.; Sudalaimuthu, K. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in promoting sustainable agriculture. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2021, 7, 401–418. [Google Scholar]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Wirth, S.; Davranov, K.; Hashem, A.; Abd Allah, E.F. Impact of soil salinity on the plant-growth—Promoting and biological control abilities of root associated bacteria. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avis, T.J.; Gravel, V.; Antoun, H.; Tweddell, R.J. Multifaceted beneficial effects of rhizosphere microorganisms on plant health and productivity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukare, A.; Paul, S.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, V. Chapter 13—Microbial-based inoculants in sustainable agriculture: Current perspectives and future prospects. In Biofertilizers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 167–181. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Singh, B.K.; Macdonald, C.A. Microbial inoculants with higher capacity to colonize soils improved wheat drought tolerance. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 2131–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonçalves, L.B.; Santos, C.H.B.; Gonilha, D.B.d.L.; Frezarin, E.T.; da Costa, M.T.P.; Rigobelo, E.C. Microbial Inoculants and Fertilizer Reduction in Sorghum Cultivation: Implications for Sustainable Agriculture. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060115
Gonçalves LB, Santos CHB, Gonilha DBdL, Frezarin ET, da Costa MTP, Rigobelo EC. Microbial Inoculants and Fertilizer Reduction in Sorghum Cultivation: Implications for Sustainable Agriculture. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(6):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060115
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonçalves, Luana Beatriz, Carlos Henrique Barbosa Santos, Dalilla Berlanda de Lima Gonilha, Edvan Teciano Frezarin, Matheus Toller Pires da Costa, and Everlon Cid Rigobelo. 2025. "Microbial Inoculants and Fertilizer Reduction in Sorghum Cultivation: Implications for Sustainable Agriculture" Microbiology Research 16, no. 6: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060115
APA StyleGonçalves, L. B., Santos, C. H. B., Gonilha, D. B. d. L., Frezarin, E. T., da Costa, M. T. P., & Rigobelo, E. C. (2025). Microbial Inoculants and Fertilizer Reduction in Sorghum Cultivation: Implications for Sustainable Agriculture. Microbiology Research, 16(6), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060115





