Abstract
The study of the metagenomes of bacterial communities in saline areas is relevant in connection with the global salinization of agricultural lands. The aim of this study was to investigate the biodiversity and structure of rhizobacterial communities associated with the halophyte S. marina from low and moderate sulfate–chloride salinity habitats. The bacterial community of bulk and rhizosphere soil was analyzed using high-throughput sequencing of the V1–V9 region of 16S rRNA by Oxford Nanopore Technologies. Alpha and beta diversity indices were calculated. A total of 55 phyla and 309 genera of bacteria were identified, among which Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes dominated. The occurrence of Planctomycetes, Verrucomicrobia, and Acidobacteria in the rhizosphere was higher than in the bulk soil. Bacterial alpha diversity in the bulk soil decreased with increasing salinity, while it increased in the rhizosphere. The proportion of the halotolerant bacteria of Flavobacterium and Alteromonas genera significantly grew with increasing salinity both in the bulk and rhizosphere soil. In addition, in the rhizosphere, the percentage of Comamonas, Methylibium, Lysobacter, Planctomyces, Sphingomonas, Stenotrophomonas, and Lewinella genera increased. Among them, several genera included plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). In the more saline bulk soil, the proportion of halotolerant genera Bacillus, Salinimicrobium, Marinobacter, Clostridium, Euzebya, KSA1, Marinobacter, Clostridium, Salinimicrobium, and Halorhodospira was also higher compared to the low saline site. Thus, increasing the salinity changed the taxonomic structure of the bacterial communities of both bulk soil and rhizosphere.
1. Introduction
One of the global problems is large-scale soil salinization and, as a consequence, a decrease in the productivity of ecosystems and the yield of food, forage industrial crops, and other plants [1]. Soil microorganisms can make a significant contribution to plant resistance to salinization [2]. Among the bacterial communities of saline areas, halotolerant (growing with salt concentrations less than 0.2 M or 1%) and halophilic bacteria (growing at high salt concentrations of 0.34–5.1 M NaCl) [3] can be distinguished, and some of them can stimulate plant growth [2,4,5,6,7]. Both rhizosphere and endophytic bacteria facilitate acclimation to salt stress in plants by improving soil fertility and structure, degrading organic soil components, releasing exopolysaccharides and phytohormones, secreting osmolytes, and producing antibiotics [3,4,5,6,7]. Thus, the study of the taxonomic composition and structure of the rhizosphere bacterial communities of halophyte plants is important for understanding the role of these bacteria in plant resistance to salinity [2,6,7].
Microbial consortia of a particular habitat or the set of microbial genes of such a community is known as the microbiome [8]. Its characteristics are influenced by both the environmental factors, such as the granulometric and chemical composition of the soil, acidity, and humidity [9,10] and metabolites of the soil biota, including plants. The role of the bacterial community of the rhizosphere in increasing plant tolerance to salinity has been shown earlier in many halophyte species such as Aster tripolium L., Borsczowia aralocaspica Bunge., Glaux maritima L., Kalidium foliatum (Pall.) Moq., Limonium sinense (Girard) Kuntze, Messerschmidia sibirica (L.) L., Salicornia europaea L., and others [2,9,11,12,13,14]. These studies demonstrate the taxonomic diversity of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere, and the dominant phyla of Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, and Firmicutes [2,9,13]. Genera containing PGP bacteria (Bacillus, Marinomonas, Pseudomonas, Sphingomonas, Streptomyces, and Rhizobium) have been also identified in the rhizosphere of halophyte plants [2,9,13,14]. Such communities can be considered as a bioresource for the development of phytoremediation technologies and the development of complex bacterial fertilizers for glycophytes [4,5,6].
There are data on bacterial communities of saline soils of natural and anthropogenically disturbed ecosystems obtained by high-throughput sequencing methods [2,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. In Russia, the most studied bacterial communities are known for the saline areas of the Caspian Lowland, the chernozem regions in the Central, Volga, and Southern Federal Districts [16,17,18]. The metagenome of the soils of the Southern Urals has not been sufficiently studied, although unique ecosystems with a saline upper horizon have formed along the shores of solonetzic and salt lakes with different types of mineralization [19]. These soils are widely used for agricultural purposes. Based on the geobotanical description, we found that in the Southern Urals, there is only one rare halophyte species S. marina (Caryophyllaceae family) that grows exclusively in saline habitats and is unknown to non-saline soils. It is an obligatory halophyte, growing in soils with high salinity [20]. It was found in marine marshes, salt lake shores, and saline agricultural lands [21]. The adaptations to salinity were described in this plant [20], but unlike other halophytes, the rhizosphere metagenome of this species has not been studied. Therefore, it is of interest to study the rhizosphere metagenome of S. marina, which allows this species to grow in saline conditions. We hypothesize that the degree of soil salinity, moderate or low, determines the taxonomic structure and, accordingly, the functional properties of the microbiome of both bulk and rhizosphere soils of S. marina. In our research, we describe the diversity and structure of rhizosphere bacterial communities in habitats with low and moderate salinity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Sample Collection
The study areas are located in Chelyabinsk region, Russian Federation (Figure 1). The first site is the gently sloping shore of the brackish lake Kurgi (N 55°43′ and E 61°18′). The second site is an agricultural land covered with grassy vegetation (N 55°43′, E 61°17′). In the sampling sites along the shore of Lake Kurgi, the predominant species were Salicornia perennans Willd., S. marina, Atriplex prostrata Boucher ex DC., and Suaeda prostrata Pall. The projective plant cover was 80–100%. In site 2, S. prostrata, Limonium gmelinii (Willd.) Kuntze, Plantago salsa Pall., S. marina, and grasses were identified. The projective plant cover was 50–60%.

Figure 1.
Study site location (a). Red point—site 1; green point—site 2. Bar 1.5 km. Photo—S. marina (b).
Halophyte plants grew at these sites, indicating soil salinity. The samples were collected in August 2024. The moisture content of the soil samples was 18.4 ± 1.9% at site 1 and 20.6 ± 0.8% at site 2. Soil samples were collected at depths of 15 cm of topsoil. At each site, both bulk soil (S1 and S2), which did not contain plant parts, and S. marina rhizosphere soil samples (SM1 and SM2) were randomly collected in sterile plastic bags or 50 mL sterile Falcon tubes and transported to the laboratory on the ice. The collected soil samples were stored in tubes at –76 °C (ARA M80, Ara Refrigeration, Seoul, Republic of Korea) and processed for DNA isolation and sequencing. The mixed soil sample for each plot was used for analysis in five replicates.
2.2. Assessment of Physicochemical Properties of Soil
The soil samples were dried, homogenized using a mortar and pestle, and sifted through a sieve with a pore diameter of 2 mm to achieve uniform fractions [22]. Soil to water extract 1:2.5 (w/v) was used to study the composition of the ions [23].
The contents of water–soluble sodium, potassium, and ammonium cations, chloride and nitrate anions, and pH were determined ionometrically [24]. Sodium, ammonium, and nitrate ions were determined using ion-selective electrodes and a silver chloride reference electrode filled with 3 M potassium chloride; potassium and chloride ions—by ion-selective electrodes and a silver chloride reference electrode filled with 3 M ammonium nitrate. The concentration of ions was calculated according to calibration curves ranged from 10−5 to 10−1 M tested ions. Electrode preparation, calibration, and measurements were made in accordance with the recommendations of the electrode and ion meter manufacturer I-160MI (Izmeritelnaya tehnika, Moscow, Russia).
The sulfate content in the soil extracts was determined turbidimetrically [25] with the following modifications: 0.1 mL of 10% hydrochloric acid, 0.2 mL of 20% barium chloride, and 0.2 mL of 1% soluble starch were added to 2 mL of the extract. The mixture was shaken for 30 min, and the turbidity of the solution was determined at wavelength 650 nm (Apel PD-303 UV-VIS spectrophotometer, Apel Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Calibration was performed using a potassium sulfate solution ranging from 0.01 to 0.5 mg/mL (approximation coefficient was 0.996). Statistical data processing was carried out in STATISTICA 13 (StatSoft Incorporated, Tulsa, OK, USA) using Mann–Whitney U-test, with asterisks indicating significant differences (p < 0.05). All laboratory experiments were carried out at the Department of Experimental Biology and Biotechnology of the Institute of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, Yekaterinburg.
2.3. DNA Extraction
Total DNA from soil sample was isolated using SKYamp Soil DNA Kit (EDC336, SkyGen NA, Moscow, Russia, https://kits.skygen.com/tproduct/655797264-807745184481-nabor-skyamp-soil-dna-kit, accessed on 18 February 2025.) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality and quantity of DNA was examined by 1.0% (v/v) agarose gel electrophoresis and using Shimadzu UV-1800 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) at 260, 280 and 235 nm. DNA was stored at –76 °C. For the analysis aliquot of DNA, it was diluted approximately 40 times to a final concentration 10 ng/μL with sterile nuclease-free water.
2.4. PCR Amplification and Nanopore Sequencing
To identify bacterial communities, V1–V9 region of 16S rRNA gene sequencing was performed. The following two primers for amplification were used: 27F (forward primer) 5’-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3’and 1492R (reverse primer) 5’-ACGGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3’ [26].
PCR was performed in a T100 Thermal cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, California, USA) using the following polymerase chain reaction program: 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 34 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 55.8 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 90 s; and 72 °C for 5 min as a final extension. Amplifications were performed using the HS Taq DNA-polymerase Kit (PK018, Evrogen, Moscow, Russia), as follows: 2.5 µL of each 10 µM primers, 5 µL 10X Taq Turbo, 1 µL dNTP mix, 0.5 µL HS Taq DNA-polymerase (5 U μL− 1) and 2 µL DNA per 50 µL reaction volume. Amplicon size was 1465 base pair. The PCR product was purified by AMPure XP Beads (Beckman Coulter, Brea, California, USA). Equal concentration of amplicon (approximately 8 ng) for each sample was used for library preparation.
The sequencing library was prepared according to the Ligation Sequencing amplicon SQK-LSK109 (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Oxford, UK). Barcodes from the Native Barcoding Expansion 1–11 (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Oxford, UK) were ligated to purified amplicons using NEBNext Quick Ligation Module E6056 (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, Massachusetts, USA). The library was sequenced using flow cell R9.4.1 (FLO-MIN106D, Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Oxford, UK) until the desired number of reads was achieved. Basecalling was performed on MinION Mk1C (version 22.10.7) using Guppy (version 6.3.9) with high-accuracy basecalling model and read filtering of min_score = 9. Estimated N50 was 1.47 kb. Each sample was sequenced in triplicate.
2.5. Bioinformatic and Statistical Analyses
The reads obtained from sequencing of each replicate were combined into one FASTA file. Read quality was checked using FastQC (version 0.12.1) and SeqKit (version 2.4.0). Trimmomatic (version 0.39) was used for trimming low quality and short reads. Sequences with a mean quality score < 9 were filtered out. Vsearch (version 2.29.2) was used for chimeras’ search and remove [27]. Then, the Kraken 2 software (version 2.1.1) with Greengenes reference database were used for taxonomic annotation. Bracken (version 3.0) was used for estimation genus abundance in each sample with relative abundance threshold 0.05% [28]. KrakenTools (version 1.2) was used for calculation of the alpha diversity index, as follows: Berger Parker’s, Simpson’s, Inverse Simpson’s, and Shannon’s [28,29]. Beta diversity (Sørensen–Dice Index and Jaccard Index) was calculated in Microsoft Excel [30]. Bray–Curtis dissimilarity was calculated in R using “Phyloseq” package [31,32]. Venn Diagram was built in R (version 4.4.1) using “VennDiagram” R package. Rarefaction curves were reconstructed using iNEXT Online (https://chao.shinyapps.io/iNEXTOnline/, accessed on 10 November 2024) [33].
Heat maps were constructed in Heatmapper (http://heatmapper.ca/expression/, accessed on 14 November 2024), and Spearman’s test was used to calculate correlations between the abundance of bacterial taxonomic groups in different samples [34]. Heat maps were constructed for taxonomic groups with an abundance of more than 1% in any of the 4 samples.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties
The soil of site 1, located on the gently sloping shore of the brackish lake Kurgi, belongs to the low saline sandy soil according to the content of water–soluble sulfates and chlorides (Table 1).

Table 1.
Hydrogen potential (pH), electric conductivity (EC), and the content of water-soluble ions (g/kg) in bulk soil of sites 1 and 2.
Clay soil of site 2 belongs to the moderately saline soil according to the electrical conductivity and content of water-soluble salts by the classification of soil salinity based on EC [35] and the classification of Ismayilov et al. [36]. The total amount of water-soluble components was 1.43 ± 0.14 g/kg soil for site 1 and 14.08 ± 0.41 g/kg soil for site 2. The ratio of the water-soluble chlorides to sulfates was 0.31 ± 0.09 and 0.53 ± 0.01 for sites 1 and 2, respectively. The concentration of the hydrocarbonate anion in the soil extracts was low—8.1 ± 0.6 mg/kg soil at site 1 and 15.5 ± 2.4 mg/kg soil at site 2.
Thus, on both sites, the soil had a sulfate–chloride type of salinization. Site 1—sandy soil—had a flushing type of water regime; therefore, the content of water-soluble ions in the soil extract was not high—the soil was slightly saline. The soils of site 2 were characterized by a higher content of sodium ions, chloride and sulfate anions, and electrical conductivity and were defined as moderately saline [35,36,37].
3.2. Analysis of the Taxonomic Structure of Bacterial Communities
The taxonomic composition was characterized based on the data of sequencing 16S rRNA. After filtering the reads by quality and length, 14876 reads were taken to an account for SM1 with an average length of 1215 base, 27105 for SM2 with an average length of 1172 base, 7597 reads for S1 with an average length of 1297 base, and 6903 reads for S2 with an average length of 1233 base. From 46 to 51% of all reads had a quality score of Q20; from 7.4 to 9.5% of reads had a quality score of Q30. The obtained data were used for taxonomic classification. Since the samples had different numbers of reads, the sequencing depth was determined using saturation curves (Figure S1) at the level of identified bacterial genera. Analysis of sample coverage showed that the saturation curves almost reached a plateau for all soil samples. The saturation curves indicate enough reads to identify the main bacterial taxa of studied soil samples. Since the soil has a heterogeneous structure and is characterized by the complexity of the spatial and species structure of microbial communities, the saturation curves showing the dependence of community diversity on the number of reads, located closer to the top of the exponential phase, i.e., they practically reach a plateau.
These data were used for the annotation of the bacterial community in the rhizosphere of S. marina and bulk soil samples using the Kraken2 program and the 16S rRNA Greengenes database. The most common taxonomic groups of bacteria (occurrence ≥ 1%) at the phylum level are presented in Figure 2.
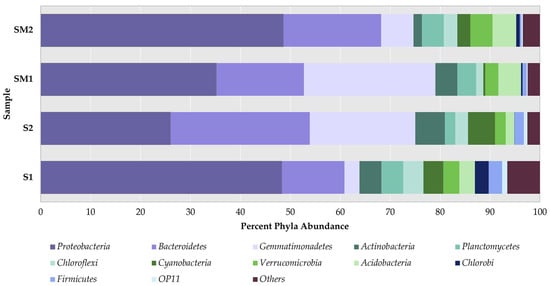
Figure 2.
Percentage of the most abundant bulk soil and rhizosphere bacteria at the phylum level. Note: S1—bulk soil, site 1; S2—bulk soil, site 2; SM1—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 1; SM2—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 2. The x-axis shows the percentage of taxon occurrence.
The Proteobacteria phylum was a dominant group in all analyzed samples—its occurrence ranged from 26 to 49%. The number of occurrence records by the Bacteroidetes phylum was 17 and 19% in the rhizosphere; in bulk soil—12% in S1 and 28% in S2. The Gemmatimonadetes phylum was also found in all samples and accounted for 3 to 26% of all phyla. It included predominantly uncultured bacteria, which were identified only at class level (Figure S2). In all samples, the occurrence of Actinobacteria was 1.7–5.9%, Acidobacteria—1.7–4.8%, and Chloroflexi was found in 1.4–4.0%. The percent of Planctomycetes phylum was 2.1–4.4% for bulk soil and 3.8–4.4% for rhizosphere; Verrucomicrobia, coordinately, 2.1–3.2% and 2.6–4.4%. Cyanobacteria was higher in bulk soil and accounted for 4.0–5.4%, while in the rhizosphere it was 0.4–2.6%. The occurrence of Firmicutes was higher in bulk soil than in rhizosphere, namely, 1.8–2.7%, versus less than 1%.
To identify the most common bacterial families and genera, taxonomic groups with a relative abundance threshold of less than 0.05% at the genus level were discarded using the Bracken program. The data obtained are presented in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure S2.
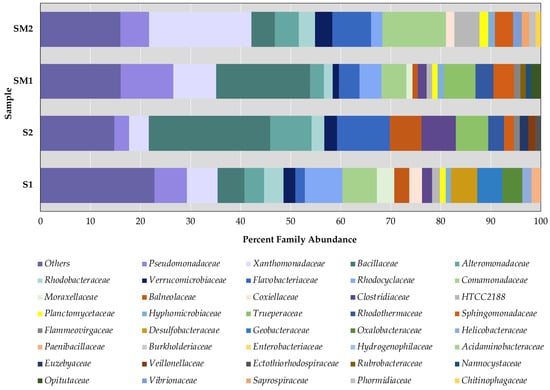
Figure 3.
Percentage of the most abundant bulk soil and rhizosphere bacteria (more than 1%) at the family level. Note: S1—bulk soil, site 1; S2—bulk soil, site 2; SM1—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 1; SM2—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 2. The x-axis shows the percentage of taxon occurrence.
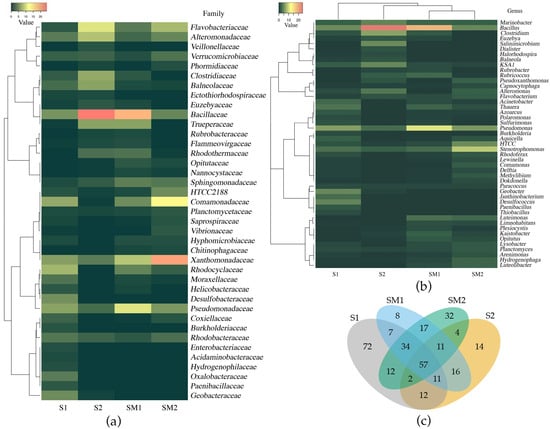
Figure 4.
Clustering of bacteria at family level (a) and genus level (b); Venn diagram of the number of common and unique bacteria from bulk soil and rhizosphere at the genus level (c). Note: S1—bulk soil, site 1; S2—bulk soil, site 2; SM1—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 1; SM2—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 2.
In the first site, 106 bacteria families were identified in bulk soil and 80 families in the plant rhizosphere. In the more saline site (S2), the number of identified families in bulk soil and in the rhizosphere decreased and amounted to 69 families.
In both habitats, the occurrence of Rhodocyclaceae, Desulfobacteraceae, Geobacteraceae, and Oxalobacteraceae families was higher in the bulk soil compared to the rhizosphere. In the more saline site, in the bulk soil among the major taxa (occurrence more than 1%), the proportion of Alteromonadaceae, Flavobacteriaceae, Bacillaceae, Balneolaceae, Clostridiaceae, Trueperacea, Rhodothermaceae, Euzebyaceae, Veillonellaceae, and Ectothiorhodospiraceae families increased (Figure 3).
In both habitats, the proportion of the families Pseudomonadaceae, Xanthomonadaceae, and Sphingomonadaceae increased in the rhizosphere compared to the bulk soil. In addition, in site 2, in the rhizosphere soil, the proportion of Alteromonadaceae, Flavobacteriaceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Verrucomicrobiaceae, marine gamma proteobacterium HTCC2188, Planctomycetaceae, and Comamonadaceae was higher than in site 1. In the lower salinity habitat (site 1), the rhizosphere also had an increased abundance of the families Bacillaceae, Rhodocyclaceae, Trueperaceae, and Rhodothermaceae. In this habitat, both in the rhizosphere and in the bulk soil, the proportion of Rhodocyclaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, and Moraxellaceae families was greater than in the habitat with higher salinity. In contrast, at the more saline site, the proportion of Alteromonadaceae and Flavobacteriaceae families was higher.
Based on the Venn diagram analysis, the total number of bacterial genera and the number of unique genera were identified. In the bulk soil, 207 and 127 bacterial genera were identified, respectively, in the S1 and S2 samples; among them, 82 genera were common to both habitats (Figure 4c). In the rhizosphere soil, 161 and 169 bacterial genera were identified for SM1 and SM2, respectively; 119 genera were common for both sites. Fifty-seven common bacterial genera were identified across all samples. For the bulk soil and rhizosphere, 109 common bacterial genera were identified in site 1; 74 common genera were identified in site 2.
Among the genera, common for all samples, 12 belonged to the phylum Proteobacteria (Agrobacterium, Bdellovibrio, Bradyrhizobium, Capnocytophaga, Erythrobacter, Legionella, Pseudomonas, Rhizobium, Rhodobacter, Rhodoplanes, Sphingomonas, and Stenotrophomonas) and two genera belonged to Bacteroidetes (Prevotella and Flavobacterium). Among these taxonomic groups, several typical soil bacteria were identified, namely, nitrogen fixing bacteria—Bradyrhizobium, Rhizobium, and Azospirillum; decomposers—Bacillus, Streptomyces, and Pseudomonas; and bacteria involved in environmental cycling—Geobacter, Sphingomonas, Devosia, Fulvivirga, Opitutus, and Phaeobacter.
In all samples, more than 80 genera are known to possess halotolerant species. The percent of such genera was 45.7–64.8% from the total amount. Among them, Gram-negative bacteria resistant to moderate salinity included Flavobacterium, Ectothiorhodospira, Erythrobacter, Lutibacterium, Marinobacter, Paracoccus, Pseudomonas, Rhodobacter, Salinimicrobium, Spirochaeta, Sphingomonas, Vibrio, and others (Table S1). Gram-positive halotolerant bacteria included Bacillus, Clostridium, and Streptomyces. Extreme halophytes (bacteria resistant to 15–20% NaCl) were performed by Halomonas, Halorhodospira, Halothiobacillus, Salinibacter, Gillisia, and Salisaeta.
Among the major bacterial genera (occurrence more than 1% of the total number of reads), Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Stenotrophomonas, and Marinobacter predominated in both habitats both in the bulk soil and in the rhizosphere (Figure 4a and Table S1).
In the more saline bulk soil, the percentage of Salinimicrobium, Marinobacter, Clostridium, Euzebya, KSA1, Flavobacterium, Bacillus, and Alteromonas increased. At site 1, a low salinity site, a high occurrence of Phodoplanes (including low halotolerant species) and moderately halotolerant genera Octadecabacter, Planctomyces, and Pseudomonas were detected compared to site 2. In the rhizosphere of S. marina, the frequency of these bacterial genera was higher in habitat 1 compared to habitat 2.
In rhizosphere soils from both sites, 119 common genera of bacteria were found, which is 74% of all identified genera in sample SM1 and 70% in sample SM2. With the increasing salinity of the environment, the proportion of halotolerant bacteria increased significantly in the SM2 rhizosphere soil: for Stenotrophomonas—from 3 to 10% from the total number of reads, Alteromonas—from 0 to 2.4%, Flavobacterium—from 1.1 to 2.1%, Comamonas—from 0.2 to 2.2%, Luteolibacter—from 1.1 to 2.4%, Methylibium—from 0.3 to 1,8%, Lysobacter—from 1.1 to 1.9%, Planctomyces—from 1.1 to 1.7%, and Sphingomonas—from 0.5 to 0.9%. The part of minor halotolerant genera Afifella, Aequorivita, Azoarcus, Erythrobacter, and Halomonas (occurrence less than 1%) and major Marinobacter (occurrence more than 1% of the total number of bacterial genera) did not change. The occurrence of other major genera decreased significantly—Pseudomonas from 10.6 to 5.7% and Bacillus from 18.8 to 4.7%. In sample SM2, nitrogen-fixing bacteria (Nostoc), sulfate-reducing bacteria (Rubritalea), plant-associated bacteria (Xylella and Zhouia), and siderophore-producing bacteria Flectobacillus were identified among the unique rhizosphere bacteria, which accounted in sum for less than 4% of the total reads.
In the bulk soil and in the rhizosphere of S. marina plants, 16 genera capable for plant growth promotion were found: Achromobacter, Acinetobacter, Azospirillum, Azoarcus, Bacillus, Bradyrhizobium, Burkholderia, Mesorhizobium, Methylibium, Ochrobactrum, Pseudomonas, Phodoplanes, Rhizobium, Serratia, Sinorhizobium, and Variovorax (Table S2). Additionally, Arthrobacter and Methylobacterium were found in the rhizosphere soil.
Among the bacteria unique to the S1 site, sulfate-reducing bacteria (Desulfobacca, Desulfobacter, Desulfocapsa, Desulfococcus, Desulfomicrobium, Desulfosarcina, Desulfosporosinus, Desulfotignum, Dethiosulfatibacter, Sulfuricurvum, Sulfuritalea, Thioalkalivibrio, Thiobacillus, Thiocystis, Thiofaba, Thiomicrospira, Thiorhodococcus, Thiorhodospira, and Thiothrix), sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (Halochromatium, Halomicronema, Halothiobacillus, Ectothiorhodospira, Thiorhodospira, and Thiomicrospira), and iron-reducing and iron-oxidizing bacteria (Gallionella, Thiorhodococcus, and Thiorhodospira) were identified (Table S1). The number of unique sulfate-reducing bacteria was 9.18%; sulfur-oxidizing bacteria was 0.98%; and iron-reducing and iron-oxidizing bacteria was 0.88%. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria included Cupriavidus, Klebsiella, Paenibacillus, and Marivita genera; the total amount was 2.28%.
To assess the diversity of bacterial communities in general, several indices were calculated. The alpha diversity was estimated at the level of bacterial genera and was characterized by Berger Parker’s, Simpson’s, Inverse Simpson’s, and Shannon’s indices (Table A1). The value of the indices allows us to conclude that in bulk soil from the more saline site (S2) the taxonomic diversity decreased compared to the less saline (S1), and in rhizosphere soil, on the contrary, it increased. In site 1, the alpha diversity of the S. marina rhizosphere was slightly lower, compared to the bulk soil. In site 2, the taxonomic richness of bacterial genera in the rhizosphere was higher than in the bulk soil.
The Simpson’s diversity index indicates the distribution of the number of taxonomic groups in the community. In our case, a high index value in all samples indicated many low-numbered bacterial genera, i.e., high taxonomic diversity, which is generally characteristic for soil metagenomes. The Berger Parker’s diversity index increased with the number of dominant taxa. Low index values in the studied samples indicated a high taxonomic diversity of bacterial communities at the genera level. The differences between samples were identified using beta diversity indices. The Sørensen–Dice Index and Jaccard Index consider the number of common taxa in two groups, and the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity index consider the abundance of taxa. The results are presented as matrices in Figure A1. The highest similarity of taxonomic diversity at the genus level was found for rhizosphere bacterial communities.
4. Discussion
To expand our understanding of bacterial microbiome associated with halophytes, we studied both the taxonomic structure and diversity of the bacterial communities in the bulk soil and rhizosphere of S. marina. Two habitats in the Kurgi Lake area of the Chelyabinsk region, Russian Federation, differing in soil types and salinity levels, were chosen (Table 1). It is known that the structure of soil bacterial communities is determined by the physicochemical factors such as soil acidity, electrical conductivity, ionic composition, the amount of carbon and nitrogen, etc. [38,39]. The abundance and diversity of bacteria in the soil and plant rhizosphere are affected by the concentration of sodium, potassium, sulfates, and carbonates [12,38,39]. Our study revealed that the bacterial diversity, including potential candidates for halotolerant PGPR, was significantly influenced by the site conditions, as the studied habitats differed in the content of sodium, chloride, and sulfate ions by more than 4–5 times (Table 1). According to the data obtained, the diversity of soil microbiomes was different in moderate saline and low saline sites.
Table S1 shows the functional characteristics of the bacterial genera identified in our research, according to the literature data. Microbial diversity analysis showed that Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Gemmatimonadetes were the dominant phyla in the bulk and rhizosphere soil. Several species of Proteobacteria are known to be involved in nitrogen fixation, production, and excretions of osmoprotectants, of auxins and cytokinins, and phosphate solubilization [39,40]. Among Gemmatimonadetes, salt tolerant bacteria are widely represented [41]. They degrade organic matter, contributing to the carbon cycle and solubilization of inorganic phosphates. Bacteroidetes in saline soil can produce extracellular polymeric compounds, which help to aggregate soil particles and retain moisture, indirectly mitigating the adverse effects of salinity on soil structure. They also degrade complex organic materials that are critical in nutrient cycling and carbon turnover under high salt stress. So, they can help to maintain microbial diversity and resilience under stressful conditions [42]. Similar results on the taxonomic diversity and abundance of phyla in bacterial communities in the rhizosphere of several halophyte plants such as Aster tripolium L., Glaux maritima, Salicornia europaea, Messerschmidia sibirica, and Limonium sinense were published earlier by other authors [2,9,11,12,13,14].
Salinization changed the taxonomic structure of soil microbiomes. With increasing salinity of the environment, the structure of communities changed at the phylum level. The ratio of the major phyla Bacteroidetes and Gemmatimonadetes in communities increased in bulk soil, which can be explained by their ability to tolerate a wide range of environmental salinity [38], but the proportion of the phylum Proteobacteria decreased. In the bulk soil, the proportion of halophilic bacteria belonged to the Bacillus, Salinimicrobium, Alterenomonas, and Pseudonomas genera increased (Figure 4), which led to a decrease in the genera evenness in the community and, therefore, to a decrease in alpha diversity. These trends have also been shown for other soil communities of saline habitats [9,12,14,16]. According to our data, under more saline conditions, the bacterial diversity of and the bacterial genera displayed more evenness,
One possible reason for the higher taxonomic diversity in the rhizosphere compared to bulk soil is the secretion of exudates by plant roots. Exudates contain a variety of organic substances, including polysaccharides, sugars, amino acids, and organic acids [43,44]. The rise of environmental salinity can affect the composition of root exudates produced by halophyte plants, and bacteria can use these compounds as osmoprotectors [45]. Another possible reason for the more diverse rhizosphere microbiome is the higher occurrence of genera Acidobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, and Planctomycetes in the rhizosphere compared to bulk soil. In addition, in the more saline site, the proportion of Proteobacteria and Cyanobacteria phyla in rhizosphere soil increased. Acidobacteria play a key role in the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles through mineralization of organic compounds and solubilization of phosphates [42]. Some Acidobacteria and Verrucomicrobia can increase plant resistance to adverse environmental factors by improving nutrient availability, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, in poor soils [42]. Also, they produce phytohormones, such as auxins, which can enhance root growth and improve the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients, thereby helping them cope with salt stress [42,46]. Planctomycetes contribute to nitrogen cycling and improving soil structure through production of extracellular polymeric compounds that are crucial for plant survival under osmotic stress [47].
In the rhizosphere of S. marina, halotolerant nitrogen-fixing bacteria belonged to the genera Achromobacter, Azospirillum, Bradyrhizobium, Mesorhizobium, Rhodoplanes, and Nostoc were identified These bacteria can increase the content of available nitrogen in the soil and thereby stimulate plant growth [48,49]. The availability of phosphates for plants could be increased by Bacillus and Pseudomonas [48,49] that were also found in the rhizosphere. Among the halophyte bacteria we determined Methylobacterium, which produce ACC-deaminase [44], and Halomonas, which improve soil conditions in saline environments by exopolysaccharide production and have a potential plant growth-promoting ability [50]. It is known that bacteria of the genera Acinetobacter, Bacillus, and Pseudomonas can secrete the phytohormones auxin, indole-3-acetic acid, cytokinins, and jasmonic acid, which promote the proliferation of root cells, slow down the aging of plant organs, and stimulate the biosynthesis of secondary and primary metabolites, including components of the antioxidant defense system [48,49,50,51,52]. Thus, the rhizosphere soil of the studied habitats may be of interest as a source of bacterial isolates for the development of biofertilizers for use on the soils of saline agricultural areas.
In both the rhizosphere and bulk soil, among the major groups of bacteria, Actinobacteria, Cyanobacteria, and Firmicutes phyla were found. In the bulk soil, their percentage was higher than in the rhizosphere. It is known that bacteria of these phyla improve soil structure and fertility. Actinobacteria and Cyanobacteria are capable of nitrogen fixation and so increase nitrogen in the soil; Firmicutes carry out phosphate solubilization and suppress phytopathogens [48,49,52]. Chloroflexi and Chlorobi bacteria that are capable of photosynthesis were identified in all samples. Some Chloroflexi species are known to degrade chlorinated organic pollutants, such as polychlorinated biphenyls, that makes them interesting for bioremediation. They also contribute to the decomposition of lignin, cellulose, and other biopolymers [53]. Chlorobi convert inorganic carbon into organic matter in anaerobic habitats so they could be effective producers in flooded or waterlogged soils. They also play a key role in the sulfur cycle by oxidizing reduced sulfur compounds into sulfate [54]. In our study, sulfate-reducing and sulfite-oxidizing bacteria were found in the soils near Lake Kurgi as the sulfate concentration was high in both habitats. However, having low salt tolerance [39], these bacteria were detected only in the slightly saline soil of the first habitat. The presence of sulfate-reducing and sulfite-oxidizing bacteria is of high interest, as many of them can reduce hydrocarbons [55], so they can be considered promising for use on soils contaminated with fuel and oil products.
5. Conclusions
For the first time, the metagenome of bulk soil and rhizosphere of the halophyte S. marina was studied in habitats with low and moderate sulfate–chloride salinity near Lake Kurgi in the Southern Urals. The molecular genetic analysis revealed the characteristics of bacterial communities from bulk and rhizosphere soils under different salinity conditions. Dominant bacterial phyla, common to both bulk soil and plant rhizosphere were identified as Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Gemmatimonadetes. It was shown that the proportion of Acidobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, and Planctomycetes was higher in the rhizosphere soil. With increasing salinity, the number of bacterial genera in the rhizosphere also increased, including halophilic and halotolerant, as well as PGPR bacteria, so the community became more complex. This could contribute to the salinity resistance of halophyte S. marina. Thus, the rhizosphere of this plant has the potential to isolate salt-tolerant bacteria capable of stimulating plant growth on saline soils, including agricultural ones. In the bulk soil of the studied habitats, bacterial diversity was higher in the case of less saline soil. Such soils have the potential to isolate sulfate-reducing and sulfite-oxidizing bacteria, which are promising for ecobiotechnologies aimed at improving the quality of agricultural lands.
Thus, the communities of bulk soil and rhizosphere of S. marina plants from habitats near Lake Kurgi in the Southern Urals include halophilic and halotolerant bacteria, among which there are potential PGPR bacteria. Future studies should aim to obtain isolates of salt-tolerant bacteria that will be promising for creating bacterial fertilizers and bioformulations for saline agricultural soils.
The limitation of this study is that in the Chelyabinsk region, S. marina was found only in two saline habitats and being an obligatory halophyte could not grow in non-saline soils. Non-saline soils of this region are characterized by another type and plant communities.
Our work provides a preliminary functional characterization of microbial communities. For a better understanding of functions, it is necessary to apply whole-genome sequencing and metabolomic analysis methods.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microbiolres16030064/s1, Figure S1: rarefaction and extrapolation curves of soil samples for sample coverage (a) and diversity (b). Note: S1—bulk soil, site 1; S2—bulk soil, site 2; SM1—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 1; SM2—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 2; Figure S2: percentage of the most abundant bulk soil and rhizosphere bacteria at the class level (more than 1%). Note: S1—bulk soil, site 1; S2—bulk soil, site 2; SM1—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 1; SM2—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 2.; Table S1: functional characteristics and abundance of bacterial genera in bulk soil and rhizosphere of S. marina.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.T. and I.S.K.; methodology, A.S.T. and A.A.E.; software, A.S.T.; validation, A.S.T., A.A.E. and I.S.K.; formal analysis, A.S.T.; investigation, A.S.T., A.A.E. and G.I.S.; resources, A.S.T. and I.S.K.; data curation, A.S.T. and I.S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.T. and A.A.E.; writing—review and editing, A.S.T., A.A.E., G.I.S. and I.S.K.; visualization, A.S.T. and A.A.E.; supervision, I.S.K.; project administration, A.S.T.; funding acquisition, A.S.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, grant number 24-76-10062, https://rscf.ru/project/24-76-10062/, accessed on 22 January 2025.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PGPR | Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria |
| S1 | Bulk soil from site 1 |
| S2 | Bulk soil from site 2 |
| SM1 | S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 1 |
| SM2 | S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 2 |
Appendix A
Table A1 shows Alpha diversity indices, Figure A1 shows Beta diversity indices of bacterial communities of the bulk soil and rhizosphere soil of S. marina plants.

Table A1.
Alpha diversity indices of bacterial communities of the bulk and rhizosphere soil of S. marina plants.
Table A1.
Alpha diversity indices of bacterial communities of the bulk and rhizosphere soil of S. marina plants.
| Sample 1 | Berger Parker’s Diversity | Simpson’s Diversity | Inverse Simpson’s | Shannon’s Diversity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.06 | 0.98 | 49.26 | 4.50 |
| S2 | 0.24 | 0.92 | 12.35 | 3.45 |
| SM1 | 0.19 | 0.94 | 17.08 | 3.84 |
| SM2 | 0.09 | 0.97 | 39.63 | 4.30 |
1 S1—bulk soil, site 1; S2—bulk soil, site 2; SM1—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 1; SM2—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 2.
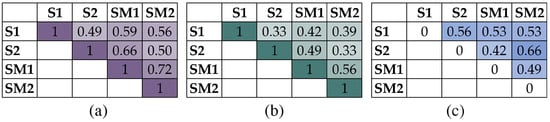
Figure A1.
Beta diversity indices of bacterial communities of the bulk soil and rhizosphere soil of S. marina plants: Sørensen–Dice Index (a), Jaccard Index (b) and Bray–Curtis dissimilarity (c). Note: S1—bulk soil, site 1; S2—bulk soil, site 2; SM1—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 1; SM2—S. marina rhizosphere soil, site 2.
References
- Singh, A. Soil salinization management for sustainable development: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Feng, W.-W.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Wang, T.-T.; Xiong, Y.-W.; Xing, K. Diversity of bacterial Microbiota of coastal Halophyte Limonium sinense and Amelioration of salinity stress damage by symbiotic plant growth-promoting Actinobacterium Glutamicibacter halophytocola KLBMP 5180. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01533-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, H. Halophilism. The Biology of Halophilic Bacteria; Vreeland, R.H., Hochstein, L.I., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Druzhinina, I.S.; Pan, X.; Yuan, Z. Microbially mediated plant salt tolerance and microbiome-based solutions for saline agriculture. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1245–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Druzhinina, I.S.; Labbé, J.; Redman, R.; Qin, Y.; Rodriguez, R.; Zhang, C.; Tuskan, G.A.; Lin, F. Specialized microbiome of a halophyte and its role in helping non-host plants to withstand salinity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppel, S.; Franken, P.; Witzel, K. Properties of the halophyte microbiome and their implications for plant salt tolerance. Funct. Plant Biol. 2013, 40, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.B.; Vogel, C.; Bai, Y.; Vorholt, J.A. The plant microbiota: Systems-level insights and perspectives. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2016, 50, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Vergès, M.-C.C.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Corral, G.H.; et al. Microbiome definition re-visited: Old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Shiwa, Y.; Ishige, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Tanaka, K.; Uchino, M.; Tanaka, N.; Oguri, S.; Saitoh, H.; Tsushima, S. Bacterial diversity associated with the Rhizosphere and Endosphere of two Halophytes: Glaux maritima and Salicornia europaea. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, R.; Mapelli, F.; Rolli, E.; Mosqueira, M.J.; Fusi, M.; Bariselli, P.; Reddy, M.; Cherif, A.; Tsiamis, G.; Borin, S.; et al. Salicornia strobilacea (Synonym of Halocnemum strobilaceum) grown under different tidal regimes selects rhizosphere bacteria capable of promoting plant growth. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, S.; Płociniczak, T.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z.; Złoch, M.; Ruppel, S.; Hrynkiewicz, K. Metabolic potential and community structure of endophytic and rhizosphere bacteria associated with the roots of the halophyte Aster tripolium L. Microbiol Res. 2016, 182, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mohamed, O.A.A.; Fan, X.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Ma, J. Bacterial Community Structure and Potential Microbial Coexistence Mechanism Associated with Three Halophytes Adapting to the Extremely Hypersaline Environment. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.Y.; Zhang, C.S. Illumina-based analysis of endophytic and rhizosphere bacterial diversity of the coastal halophyte Messerschmidia sibirica. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.W.; Lou, K.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhao, S.; Tian, C.Y. Illumina-based analysis of bacterial diversity related to halophytes Salicornia europaea and Sueada aralocaspica. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, P.P.; Carrillo, Y.; Pino, V.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B. Soil Properties Drive Microbial Community Structure in a Large Scale Transect in South Eastern Australia. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.I.; Ivanova, E.A.; Samylina, O.S.; Kurbanova, F.G.; Gruzdev, D.S.; Kanapatskiy, T.A.; Pimenov, N.V. Prokaryotic Communities in Saline Soils of the Lake Elton Area in a Soil Catena along the Khara River. Microbiology 2020, 89, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poshvina, D.V.; Balkin, A.S.; Teslya, A.V.; Dilbaryan, D.S.; Stepanov, A.A.; Kravchenko, S.V.; Vasilchenko, A.S. Structural and Functional Differences in the Bacterial Community of Chernozem Soil Under Conventional and Organic Farming Conditions. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, T.I.; Tkhakakhova, A.K.; Kutovaya, O.V. Assessment of diversity indices for the characterization of the soil prokaryotic community by metagenomic analysis. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernousenko, G.I.; Kalinina, N.V.; Khitrov, N.B.; Pankova, E.I.; Rukhovich, D.I.; Yamnova, I.A.; Novikova, A.F. Quantification of the areas of saline and solonetzic soils in the Ural Federal Region of the Russian federation. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2011, 44, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcin, T.A.; Akcin, A.; Yalcin, E. Anatomical Adaptations to Salinity in Spergularia marina (Caryophyllaceae) from Turkey. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 85, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliszko, A. A new record of Spergularia marina (Caryophyllaceae) from southern Poland. Acta Mus. Siles. Sci. Nat. 2017, 66, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, K.; Sharma, J.C.; Dahiya, S.S.; Dhankar, J.S. Collection and preparation of soil samples. In Research Methods in Plant Sciences: Allelopathy. Volume 1. Soil Analysis; Narwal, S.S., Dahiya, S.S., Singh, J.P., Eds.; Scientific Publishers: Jodhpur, India, 2004; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Haldar, A.; Sahoo, A.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Das, K.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Dwivedi, B. Comparison of different methods of electrical conductivity determination for assessment of salinity in soils of coastal region, West Bengal. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2021, 9, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadağ, S.; Eren, E.; Çetinkaya, E.; Özen, S.; Deveci, S. Optimization of sodium extraction from soil by using a central composite design (CCD) and determination of soil sodium content by ion selective electrodes. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2016, 5, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kolmert, A.; Wikström, P.; Hallberg, K.B. A fast and simple turbidimetric method for the determination of sulfate in sulfate-reducing bacterial cultures. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 41, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Methé, B.A.; Nelson, K.E.; Pop, M.; Creasy, H.H.; Giglio, M.G.; Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Petrosino, J.F.; Abubucker, S.; Mannon, P.J.; et al. A framework for human microbiome research. Nature 2012, 486, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ. 2016, 2016, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Rincon, N.; Wood, D.E.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Pockrandt, C.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L.; Steinegger, M. Metagenome analysis using the Kraken software suite. Nat Protoc. 2022, 17, 2815–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thukral, A.K. A review on measurement of Alpha diversity in biology. Agric. Res. J. 2017, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildi, O. Data Analysis in Vegetation Ecology, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2010; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Gotelli, N.J.; Hsieh, T.C.; Sander, E.L.; Ma, K.H.; Colwell, R.K.; Ellison, A.M. Rarefaction and extrapolation with Hill numbers: A framework for sampling and estimation in species diversity studies. Ecol. Monogr. 2014, 84, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babicki, S.; Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.R.; Maciejewski, A.; Wishart, D.S. Heatmapper: Web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.W.; Hayward, H.E.; Richards, A.; Bernstein, L.; Hatcher, J.T.; Reeve, R.C.; Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Agriculture Handbook No. 60; US Government Printing Office: Washington DC, USA, 1954.
- Ismayilov, A.I.; Mamedov, A.I.; Fujimaki, H.; Tsunekawa, A.; Levy, G.J. Soil Salinity Type Effects on the Relationship between the Electrical Conductivity and Salt Content for 1:5 Soil-to-Water Extract. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazilevich, N.I.; Pankova, E.I. An experience of soil classification according to the concentration of toxic salts and ions. Byull. Pochv. Inst. Im. V.V. Dokuchaeva 1972, 5, 36–49. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Z.; Jia, A.; Li, H.; Wang, M.; Qu, S. Explore the soil factors driving soil microbial community and structure in Songnen alkaline salt degraded grassland. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1110685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Zhai, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, W.; Hu, X. Microbial diversity and functions in saline soils: A review from a biogeochemical perspective. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 59, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, R.; Rokem, J.S.; Ilangumaran, G.; Lamont, J.; Praslickova, D.; Ricci, E.; Subramanian, S.; Smith, D.L. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria: Context, Mechanisms of Action, and Roadmap to Commercialization of Biostimulants for Sustainable Agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, G.; Tang, X.; Shao, K.; Gong, Y. Pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial communities in Lake Bosten, a large brackish inland lake in the arid northwest of China. Can. J. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsbrink, J.; McKee, L.S. Bacteroidetes bacteria in the soil: Glycan acquisition, enzyme secretion, and gliding motility. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 110, 63–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Hao, H.; Qi, Y.; Bai, H.; Li, H.; Shi, Z.; Shi, L. Effect of Salt Stress on Microbiome Structure and Diversity in Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.) Rhizosphere Soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haichar, F.Z.; Marol, C.; Berge, O.; Rangel-Castro, J.I.; Prosser, J.I.; Balesdent, J.; Heulin, T.; Achouak, W. Plant host habitat and root exudates shape soil bacterial community structure. ISME J. 2008, 2, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, C.; Kumar, A.; Parshad, J.; Sharma, S.S.; Patra, A.; Dogra, P.; Yadav, G.K.; Dadhich, S.K.; Verma, R.; Kumawat, G.L. Microbial Diversity and Adaptation under Salt-Affected Soils: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Cho, Y.G. Plant hormones in salt stress tolerance. J. Plant Biol. 2015, 58, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Teeseling, M.C.; Mesman, R.J.; Kuru, E.; Espaillat, A.; Cava, F.; Brun, Y.V.; VanNieuwenhze, M.S.; Kartal, B.; van Niftrik, L. Anammox Planctomycetes have a peptidoglycan cell wall. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Godínez, L.J.; Aguirre-Noyola, J.L.; Martínez-Romero, E.; Arteaga-Garibay, R.I.; Ireta-Moreno, J.; Ruvalcaba-Gómez, J.M. A Look at Plant-Growth-Promoting Bacteria. Plants 2023, 12, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zishan, M.; Manzoor, U. Promoting crop growth with symbiotic microbes in agro-ecosystems—II. In Microbes and Microbial Biotechnology for Green Remediation; Malik, J.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, R.; Kumar, V.; Gupta, P. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria-assisted bioremediation of toxic contaminant: Recent advancements and applications. In Microbial Biodegradation and Bioremediation; Das, S., Dash, H.R., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzer, M.; Ahmad, N.; Nielsen, B.L. Halophilic Plant-Associated Bacteria with Plant-Growth-Promoting Potential. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Asaf, S.; Khan, A.L.; Adhikari, A.; Jan, R.; Ali, S.; Imran, M.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, I.J. Halotolerant Rhizobacterial Strains Mitigate the Adverse Effects of NaCl Stress in Soybean Seedlings. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 20, 9530963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freches, A.; Fradinho, J.C. The biotechnological potential of the Chloroflexota phylum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e0175623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, L.H.; Bryant, D.A.; Frigaard, N.-U. Mechanisms and evolution of oxidative sulfur metabolism in green sulfur bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, L.L.; Fauque, G.D. Biochemistry, physiology and biotechnology of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 68, 41–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).