Harnessing Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus for Effective Biodegradation of Endocrine Disruptor 4-Nonylphenol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preliminary Bioinformatics Screening of 4-NP-Degrading Bacteria
2.2. Screening of 4-NP-Degrading Bacillus
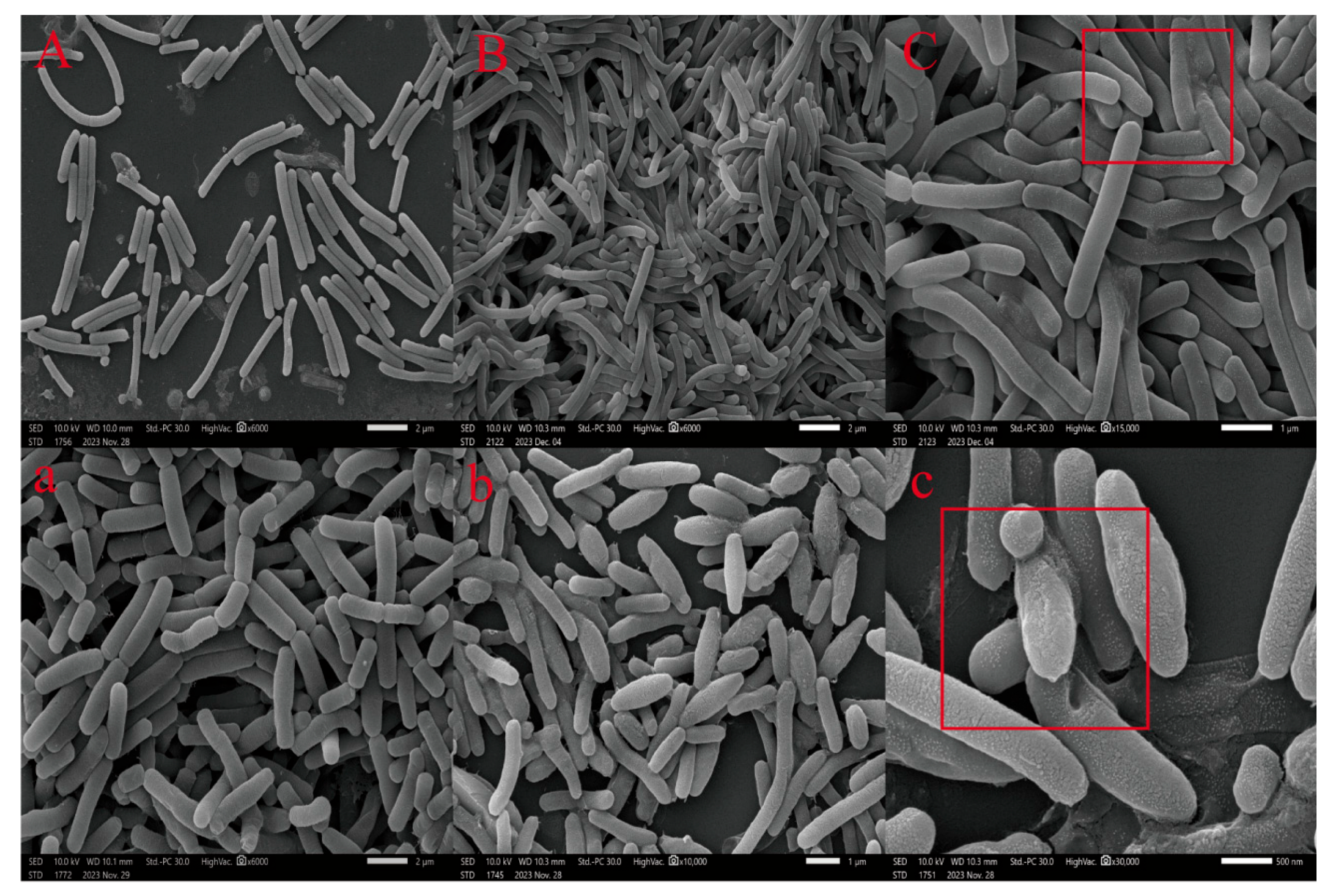
2.3. Effects of 4-NP on the Morphology of Bacillus
2.4. Morphological, Physiological and Biochemical Identification
2.5. Whole-Genome Sequencing to Identify 4-NP-Degrading Bacteria
2.6. Determination of 4-NP Concentration
2.7. Metabolomics Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Primary Screening of 4-NP-Degrading Bacteria
3.2. Screening of Bacillus Under 4-NP
3.3. Effect of 4-NP on Bacillus Morphology
3.4. Morphological Identification Results for 4-NP Degrading Bacteria
3.5. Physiological and Biochemical Identification Results
3.6. 16S rDNA Identification Results
3.7. Whole-Genome Sequencing Results for LY Bacteria
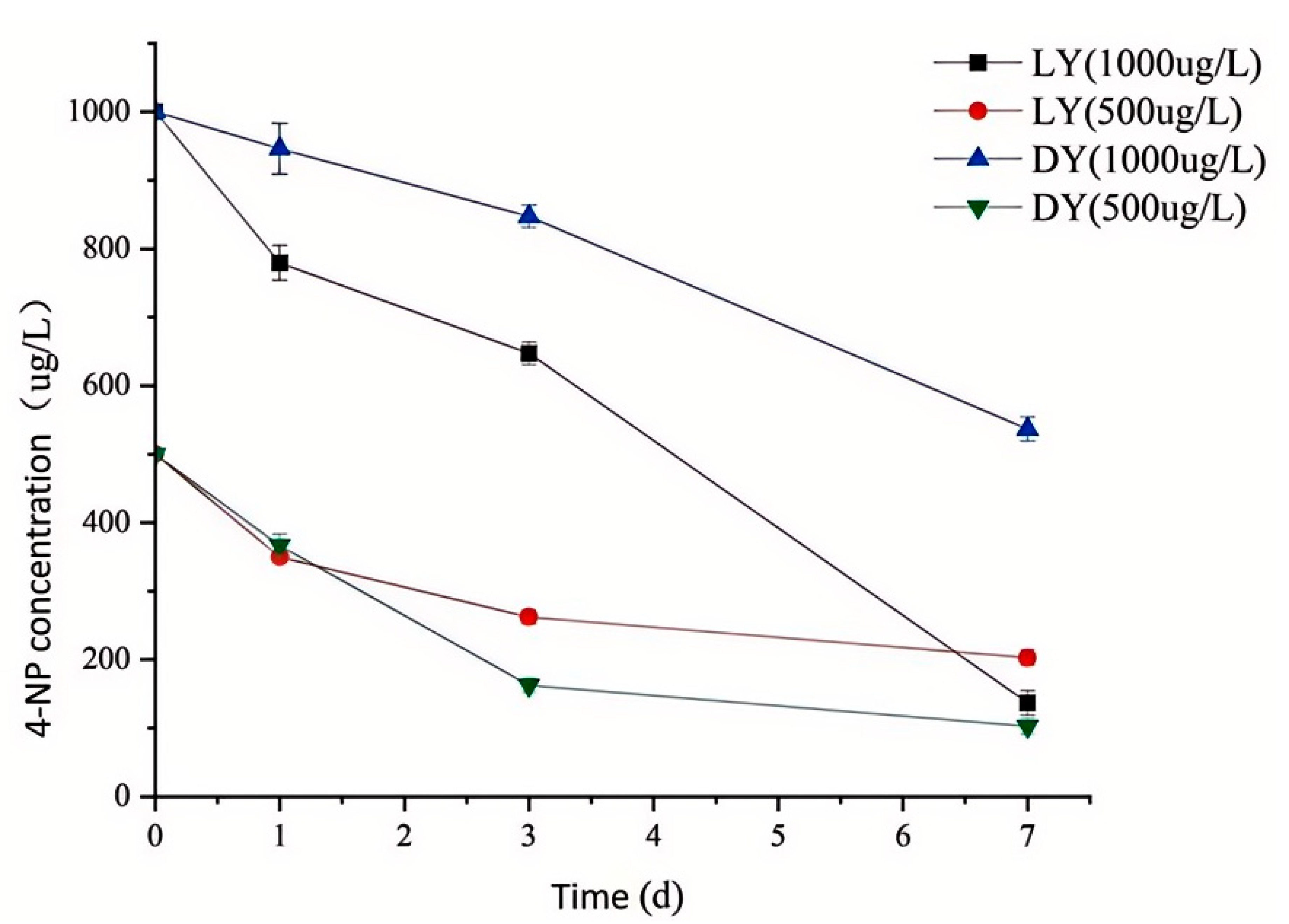
3.8. 4-NP Degradation Rate
3.9. Effect of 4-NP on Metabolites of B. cereus
3.10. Degradation-Related Pathways in Metabolome
3.11. Possible Pathways for 4-NP Biodegradation
4. Discussion
4.1. 4-NP Is Degraded by B. thuringiensis and B. cereus
4.2. Possible Degradation Pathways of B. cereus
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, X.; Li, N.; Yuan, S.; Zhou, X.; Ding, F.; Rao, K.; Ma, M.; Wang, Z. A comparison of endocrine disruption potential of nonylphenol ethoxylate, vanillin ethoxylate, 4-n-nonylphenol and vanillin in vitro. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019, 175, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, B.; Garron, C. NP, OP and Derivatives in Freshwater Sediment Downstream of Textile Associated Municipal Wastewater Discharges. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 86, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.C.; Chao, H.R.; Mansor, W.N.; Peng, C.W.; Hsu, Y.C.; Yu, T.Y.; Chang, W.H.; Fu, L.M. Levels of Phthalates, Bisphenol-A, Nonylphenol, and Microplastics in Fish in the Estuaries of Northern Taiwan and the Impact on Human Health. Toxics 2021, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.; D’Souza, L.C.; Shetty, N.G.; Raghu, S.V.; Sharma, A. Hsp27, a potential EcR target, protects nonylphenol-induced cellular and organismal toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.M.; Chen, C.W.; Huang, C.P.; Dong, C.D. Degradation of 4-nonylphenol in marine sediments using calcium peroxide activated by water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes)-derived biochar. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 113076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lv, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Geng, C.; Bai, N. The unexpected effect of the compound microbial agent NP-M2 on microbial community dynamics in a nonylphenol-contaminated soil: The self-stability of soil ecosystem. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.J.; Li, S.; You, W.D.; Wang, X.Y.; Feng, X.J.; Yang, B.; Ying, G.G. Toxicity assessment of wastewater using a battery of bioassays in two textile wastewater treatment plants from a large industrial park in Guangxi, Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 966, 178766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Xu, D.; Kong, X.; Gong, J.; Yang, Y.; Ran, Y.; Mao, J. Effect of the structure and micropore of activated and oxidized black carbon on the sorption and desorption of nonylphenol. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, E. Recent Advances on Innovative Materials from Biowaste Recycling for the Removal of Environmental Estrogens from Water and Soil. Materials 2022, 15, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isac, L.; Enesca, A. Recent Developments in ZnS-Based Nanostructures Photocatalysts for Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Mudigonda, S.; Dahms, H.U.; Wu, M.C. Assessing the Effects of Ozonation on the Concentrations of Personal Care Products and Acute Toxicity in Sludges of Wastewater Treatment Plants. Toxics 2023, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Oh, S. Removal of Chloroxylenol Disinfectant by an Activated Sludge Microbial Community. Microbes Environ. 2019, 34, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Feng, L.; Yan, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Q. Acidogenic bacteria assisted biodegradation of nonylphenol in waste activated sludge during anaerobic fermentation for short-chain fatty acids production. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Ji, R. Biodegradation of phenolic pollutants and bioaugmentation strategies: A review of current knowledge and future perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mireisz, T.; Horváth, F.B.; Kashaija, N.T.; Farkas, R.; Boldizsár, I.; Tóth, E. Drug-degrading bacteria isolated from the effluent water of a sewage plant. Biol. Futur. 2024, 75, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellan-Schneyder, I.; Matchado, M.S.; Reitmeier, S.; Sommer, A.; Sewald, Z.; Baumbach, J.; List, M.; Neuhaus, K. Primer, Pipelines, Parameters: Issues in 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing. mSphere 2021, 6, e01202-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Li, H. Fast and accurate long-read assembly with wtdbg2. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.Z.; Cai, M.Y. Manual of Common Bacterial Systematic Identification, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 375–403. [Google Scholar]
- Breed, R.S.; Buchanan, R.E.; Gibbons, N.E. Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 8th ed.; Chinese version; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1984; pp. 729–758. [Google Scholar]
- Kuligowski, J.; Moreno-Torres, M.; Quintás, G. Improving insights from metabolomic functional analysis combining multivariate tools. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1323, 343062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelles, H.S.; Motteran, F.; Sakamoto, I.K.; Silva, E.L.; Varesche, M.B.A. 4-Nonylphenol degradation changes microbial community of scale-up Anaerobic Fluidized Bed Reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 267, 110575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidtkunz, C.; Gries, W.; Küpper, K.; Leng, G. A “dilute-and-shoot” column-switching UHPLC-MS/MS procedure for the rapid determination of branched nonylphenol in human urine: Method optimisation and some fundamental aspects of nonylphenol analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 975–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, T.; Zhou, N.N.; Qiao, F.; Du, Z.Y.; Zhang, M.L. Bacillus cereus Alters Bile Acid Composition and Alleviates High-Carbohydrate Diet-Induced Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 4825–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.; Kalsoom, U.; Ahsan, Z.; Bilal, M. Non-magnetic and magnetically responsive support materials immobilized peroxidases for biocatalytic degradation of emerging dye pollutants-A review. J. Basic Microbiol. 2022, 207, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewnowska, J.M.; Stefanska, N.; Czerniecka, M.; Zambrowski, G.; Swiecicka, I. Potential Enterotoxicity of Phylogenetically Diverse Bacillus cereus Sensu Lato Soil Isolates from Different Geographical Locations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e03032-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayolle, E.C.; Noell, A.C.; Johnson, P.V.; Hodyss, R.; Ponce, A. Viability of Bacillus subtilis Spores Exposed to Ultraviolet Light at Ocean World Surface Temperatures. Astrobiology 2020, 20, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Liao, S.; Xing, D.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, D.; Yang, Q. Mechanism of lead adsorption by a Bacillus cereus strain with indole-3-acetic acid secretion and inorganic phosphorus dissolution functions. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Ren, S.; Liu, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. Important role of Bacillus subtilis as a probiotic and vaccine carrier in animal health maintenance. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, A.; Abdelsattar, A.M.; Heikal, Y.M.; El-Esawi, M.A. Synergistic effects of Azospirillum brasilense and Bacillus cereus on plant growth, biochemical attributes and molecular genetic regulation of steviol glycosides biosynthetic genes in Stevia rebaudiana. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 189, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liang, J. A study of highly efficient phenol biodegradation by a versatile Bacillus cereus ZWB3 on aerobic condition. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirozawa, M.T.; Ono, M.A.; Suguiura, I.M.S.; Bordini, J.G.; Ono, E.Y.S. Lactic acid bacteria and Bacillus spp. as fungal biological control agents. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxac083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y. A review on the application of Bacillus as probiotics in aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaycı Kara, A.; Fakıoğlu, Ö.; Kotan, R.; Atamanalp, M.; Alak, G. The investigation of bioremediation potential of Bacillus subtilis and B. thuringiensis isolates under controlled conditions in freshwater. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Du, L.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, J.; Lin, H. Toxicity alleviation and metabolism enhancement of nonylphenol in green algae Dictyosphaerium sp. by NaHCO3. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, J.; Zheng, J.; Yu, Z. iTRAQ-facilitated proteomic analysis of Bacillus cereus via degradation of malachite green. J. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Rensing, C.; Ye, J.; Qiu, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, L.; Lu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Jia, X. Improvement of phenolic acid autotoxicity in tea plantations by Pseudomonas fluorescens ZL22. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Sun, P.; Khan, A.; Zhang, Y. Photochemistry of biochar during ageing process: Reactive oxygen species generation and benzoic acid degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masud, M.A.A.; Kim, D.G.; Shin, W.S. Degradation of phenol using Fe (II)-activated CaO2: Effect of ball-milled activated carbon (ACBM) addition. Environ. Res. 2022, 214 Pt 3, 113882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeo, M.; Prabu, S.K.; Kitamura, C.; Hirai, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kato, D.-I.; Negoro, S. Characterization of alkylphenol degradation gene cluster in Pseudomonas putida MT4 and evidence of oxidation of alkylphenols and alkylcatechols with medium-length alkyl chain. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 102, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Protein Abbreviation | Accessing Number | Function |
|---|---|---|
| PabB | NP_387955.1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=NP_387955.1%20Bacillus accessed on 12 February 2021 | p-aminobenzoic acid synthetase |
| YhbJ | NP_388781.1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=NP_388781.1+Bacillus accessed on 12 February 2021 | Enzymes associated with benzoic acid degradation |
| YhcA | NP_388782.1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=NP_388782.1+Bacillus accessed on 12 February 2021 | Enzymes associated with benzoic acid degradation |
| YhcB | NP_388783.1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=NP_388783.1+Bacillus accessed on 12 February 2021 | Quinone oxidoreductase related to benzoic acid |
| MenC | NP_390956.1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=NP_388783.1+Bacillus accessed on 12 February 2021 | O-Succinylbenzoate-CoA Synthase |
| DhbA | NP_391080.2 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=NP_391080.2+Bacillus accessed on 12 February 2021 | Benzoate dehydrogenase |
| CatD | NP_388704.1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=NP_388704.1+Bacillus accessed on 12 February 2021 | Oxygenase |
| YhjG | NP_388931.1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=NP_388931.1+Bacillus accessed on 12 February 2021 | Aromatic compounds monooxygenase/hydroxylase |
| Steps | Screening Medium | Screening NP Concentration (μg/L) | Inoculation Regimes | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TSA solid medium | 10, 100, 1000 | Streaking | Growth at 100 |
| 2 | TSA solid medium | 100, 300, 600 | Transferred all colonies from Step 1 plate | Growth at 300 |
| 3 | TSA solid medium | 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800 | Washed all colonies from Step 3 plate with saline | Growth at 500 |
| 4 | TSB liquid medium | 100 | Inoculated from Step 1; washed with saline | Turbid, growth |
| 5 | TSB liquid medium | 500 | Inoculated from Step 4; washed with saline | Turbid, growth |
| 6 | Inorganic salt solid medium | 100, 300, 500 | Transferred all colonies from Step 4 plate; inoculated with broth from Step 5 | No growth |
| 7 | Inorganic salt solid medium | 50, 100, 200, 300 | Spread plate (1 μL, 10 μL, 100 μL); washed with saline | No growth |
| 8 | Inorganic salt solid medium | 10, 50, 100, 300 | Transferred all colonies from Step 4 plate; washed with saline | Growth at 300 |
| 9 | Inorganic salt solid medium | 300, 400, 500 | Transferred all colonies from Step 8 plate | Growth at 500 |
| 10 | Inorganic salt solid medium | 500, 600, 700, 800 | Transferred all colonies from Step 9 plate | Growth at 800 |
| 11 | Inorganic salt solid medium | 800, 900, 1000 | Transferred all colonies from Step 10 plate | Growth at 1000 |
| Test Item | Test Result | Test Item | Test Result | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DY | LY | DY | LY | ||
| Xylose | − | − | Urea | − | − |
| Sorbitol | − | − | Hydrogen sulfide | + | − |
| Adonitol | − | − | Phenylalanine deaminase | − | − |
| Raffinose | − | − | Gluconate | − | − |
| Glucose | + | − | Ornithine decarboxylase | − | − |
| Peptone water | − | − | Lysine decarboxylase | − | − |
| Glufosinate water | + | + | Semi-solid agar | + | + |
| Citrate | − | − | |||
| Query ID | Reference ID | ANI | Mapped_Fragment | Query_Fragment | Taxon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY | GCF_002220285 | 96.9227 | 1636 | 1785 | B. cereus strain FORC_047 |
| Mode | Total Ion Number | After Pre-Processing | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| merge | 645 | 645 | 100.00% |
| Metabolite | Structural Formula | Pathway |
|---|---|---|
| 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid |  | Degradation of aromatic compounds Benzoate degradation |
| Benzoic acid |  | Degradation of aromatic compounds Benzoate degradation |
| Phenol |  | Degradation of aromatic compounds Benzoate degradation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Lu, F.; Luo, D.; Dong, R. Harnessing Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus for Effective Biodegradation of Endocrine Disruptor 4-Nonylphenol. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120247
Yang L, Lu F, Luo D, Dong R. Harnessing Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus for Effective Biodegradation of Endocrine Disruptor 4-Nonylphenol. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(12):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120247
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lian, Fanglian Lu, Deqin Luo, and Ranran Dong. 2025. "Harnessing Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus for Effective Biodegradation of Endocrine Disruptor 4-Nonylphenol" Microbiology Research 16, no. 12: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120247
APA StyleYang, L., Lu, F., Luo, D., & Dong, R. (2025). Harnessing Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus for Effective Biodegradation of Endocrine Disruptor 4-Nonylphenol. Microbiology Research, 16(12), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16120247







