Abstract
This study examined the effects of Bacillus probiotic strains on red abalone Haliotis rufescens reproductive performance. We supplemented plant- and fish-based feeds and compared them to fresh giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera as a control diet. Over 180 days, abalone fed the plant–probiotic diet reached higher female gonadal maturation, with 56% of females attaining the maximum Visual Gonad Index (VGI 3). Additionally, plant-based treatment showed a female-biased sex ratio (1.5:1 female-to-male ratio, F:M) compared with the kelp control treatment (0.8:1 F:M). These results suggest that probiotics can improve nutrient utilization from soybean meal and may enhance the bioavailability of phytoestrogens and other bioactive compounds, contributing to reproductive outcomes. Although the mechanisms remain to be confirmed, this approach provides a promising strategy to reduce reliance on fishmeal and wild macroalgae while supporting faster reproductive cycles in abalone aquaculture. Future research should focus on biochemical validation, molecular pathways, and multigenerational trials to ensure the long-term safety and sustainability of probiotic–plant-based feeds.
1. Introduction
Probiotics represent promising biotechnological advances in modern aquaculture, offering sustainable solutions to traditional nutritional and health challenges. Among probiotics, Bacillus species have emerged as particularly valuable due to their Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status, spore-forming capabilities, and enzymatic repertoire [1,2,3]. The benefits of Bacillus supplementation have been documented across commercially important aquatic species, including Lithopennaeus vanamei [4,5,6], Totoaba mcdonaldi [7,8], Oreochromis niloticus [9,10,11], and Haliotis diversicolor [12], Haliotis discuss hannai [13,14], and Haliotis asinina [15]. Bacillus enhances survival rates, improves growth performance, modulates gut microbiota, and strengthens overall organism health while simultaneously reducing aquaculture operation costs [1,3,16].
The enzymatic capacity of Bacillus extends beyond traditional nutritional benefits, particularly through the production of carbohydrase, protease and lipase enzymes [17]. Among carbohydrases, galactosidase enzymes are essential for liberating proteins from a complex carbohydrates’ matrix breaking down oligosaccharides, which, at the same time, release other soy essential ingredients [18]. This enzymatic liberation seems to enhance isoflavones bioavailability—compounds with potent phytoestrogenic activity that can influence reproductive development through estrogen receptor interactions [19,20].
In abalone aquaculture, reproductive management represents a key factor in the success of this industry. Consistent and programmable gonadal maturation is essential for maintaining year-round production cycles, ensuring stable market supply, and producing high-quality larvae with superior survival and settlement rates [21]. Traditional approaches in abalone nutrition have relied primarily on fresh macroalgae or fishmeal-based feeds. Both present escalating economic and environmental challenges [22,23,24,25]. Fishmeal production raises serious concerns regarding marine ecosystem disruption and overfishing, with market prices reaching $1600 USD per ton [26,27,28]. Similarly, macroalgae resources face multiple constraints including declining wild populations, unpredictable seasonal availability, and costs approaching $800 USD per ton [29,30,31,32].
Plant ingredients, particularly soybean meal ($400 USD/ton), offer substantial economic advantages while providing nutritional consistency and enhanced scalability [28,33]. Remarkably, soy contains the highest concentration of isoflavones among all plant sources—compounds with proven phytoestrogenic activity that could potentially enhance reproductive development in aquatic species [19,20,34,35]. In that sense, formulated feed containing soybean meal may benefit abalone reproductive development; however, previous studies using soybean meal in formulated feed have not demonstrated enhanced gonadal maturation in abalone [35,36]. This is likely due to insufficient endogenous enzymatic capacity in abalone digestive systems to release phytoestrogens from soy oligosaccharides [37,38]. Additionally, high inclusions of soybean meal in formulated feed introduce challenges, primarily due to antinutritional factors such as protease inhibitors and toxic oligosaccharides [7,39]. These antinutritional factors can impair digestion, reduce nutrient absorption, and ultimately lead to decreased growth and survivorship of cultured organisms [1,17,18]. Hence, strategies to mitigate these soy antinutritional properties while preserving plant-based ingredients’ economic and environmental benefits are urgently needed.
To address these enzymatic limitations, Bacillus probiotic strains represent a promising strategy as they produce peptidase and galactosidase enzymes that enhance nutrients and phytoestrogens bioavailability by breaking down proteases inhibitors and toxic oligosaccharides, respectively [18,40,41]. This transforms toxic ingredients into assimilable nutrients and biologically active compounds like phytoestrogens, capable of influencing reproductive pathways [40,41]. Bacillus supplementation could mitigate antinutritional factors while enhancing overall feed digestibility and organism health [1,16,42,43]. However, despite these findings, research examining probiotic-supplemented plant-based feed’s effects on abalone reproductive performance remains limited.
The present study addresses this gap by evaluating the effects of a plant-based diet with soybean meal supplemented with Bacillus probiotic strains Sp1 and Sp3 on gonadal maturation, sex differentiation, and survival in red abalone Haliotis rufescens. We hypothesize that Bacillus-mediated enhancement of phytoestrogen bioavailability from soybean meal will significantly improve reproductive development compared to fishmeal-based diet with same Bacillus strains but without soybean meal or fresh giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera used as control. This research aims to provide practical insights for improving reproductive management in abalone aquaculture while demonstrating the broader potential of probiotic-enhanced plant-based nutrition in sustainable aquaculture systems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtention and Phylogenetic Identification of Bacillus Probiotic Strains
Bacillus Sp1 and Sp3 strains were obtained from a culture collection at the Ensenada Center for Scientific Research and Higher Education (CICESE; Ensenada, Baja California, Mexico). The phylogenetic identification and growth conditions of Sp1 and Sp3 strains were previously described by Mercado et al. [8] and Macías et al. [9]. Sp1 and Sp3 were identified as B. velezensis and B. amyloliquefaciens, respectively. Therefore, both strains are recognized within the GRAS classification. Strains were cultured at 37 °C and 250 rpm in Shaeffer medium until T4 sporulation phase was reached; later strains were kept at 4 °C until use.
2.2. Antibiotic Resistance of Bacillus Probiotic Strains
Antibiotic resistance of Bacillus strains Sp1 and Sp3 were determined according to the methodology described by Mercado et al. [8] and Macias et al. [9], following CSLI (Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute, Berwyn, IL, USA) and EFSA (European Food Safety Authorities, Parma, Italy) guidelines. Bacillus strains were inoculated onto LB agar plates containing amoxicillin, ampicillin, cefaclor, cephalexin, chloramphenicol, clindamycin, doxycycline, erythromycin, oxytetracycline, and streptomycin clinical-grade antibiotics at standard therapeutic concentrations. Plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h and colonies were reported as present (+) or absent (−) growth.
2.2.1. Enzymatic Activity of Bacillus Probiotic Strains
Proteases
Protease production was evaluated using solid media containing soy protein concentrate (SPC), soybean meal (SBM) and wheat flour (WHF) at 10 g L−1. Plates were inoculated with sterile swabs and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Following incubation, colony diameter and the surrounding degradation halo were measured using a vernier caliper. Enzymatic activity was quantified by calculating the ratio of the degradation area in cm2 with respect to the colony area [8].
Carbohydrases
Carbohydrase activity was assessed using plates containing starch (STR) and WHF at 10 g L−1. After 48 h incubation at 37 °C, plates were stained with iodine crystals. Amylase production was determined by the presence (+) or absence (−) of a transparent degradation halo and area in cm2 of this halo. Measurements of the degradation halo and colony size were performed as described for protease activity [8].
α-Galactosidase and Lipase Activity
α-Galactosidase production was evaluated using plates containing the chromogenic substrate α-X-Gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-galactoside) in agar supplemented with melibiose and raffinose. Plates were inoculated with the bacterial strains using sterile swabs and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. After incubation, α-galactosidase production was determined by the presence (+) or absence (−) of blue coloration in the colonies. Lipase production was assessed using media containing 1.6% (w/v) soybean oil supplemented with 0.001% (w/v) rhodamine B. Plates were inoculated and incubated for 24 h, after which lipase production was characterized by the presence (+) or absence (−) of pink coloration in the colonies [8].
2.3. Probiotic-Enhanced Feed Formulation and Preparation
2.3.1. Feed Composition and Design
The CICESE prepared feeds (Table 1), which we refer to as plant diet and fish diet, are non-commercial proprietary recipes, and ingredient composition cannot be provided. Both formulated diets were nutritionally equivalent in macro and macronutrient. The fish diet had 30% fishmeal as its primary source of protein, and no soybean meal was added. In the plant-based diet, only 10% of fishmeal was included; soybean meal and other plant meals were used to accomplish the same amount of protein. Fresh M. pyrifera served as a naturally occurring control diet commonly used in red abalone aquaculture. Both formulated diets maintained macronutrient profiles: 21% protein, 55% carbohydrates, and 5% lipids to ensure nutritional equivalence and isolate the effects of ingredient source and probiotic enhancement. Pellets were produced and dried at 64 °C for 4 h. Fishmeal was obtained from a local supplier (Procesadora Mar de Ensenada, S. de R.L. de C.V., Ensenada, Baja California, Mexico). Vitamin and mineral premix (Brovel S.A. de C.V., Mexico City, Mexico), soybean meal (Soyarin®, FRACA S.A. de C.V., Tepatitlan, Meixco), and wheat flour (El Rosal® Molinera del Valle S.A. de C.V., Mexicali, Mexico) were obtained from national suppliers.

Table 1.
Proximal composition of experimental diets and control.
2.3.2. Probiotic Incorporation and Processing
A standardized combination of Bacillus strains Sp1 and Sp3 (1:1 ratio) was incorporated into both experimental diets at a concentration of 2 × 106 CFU/g of feed based on previous aquafeed production [7,8,9]. Macro and micronutrient ingredients were thoroughly mixed using a ribbon mixer for 15 min to ensure homogeneous distribution. The probiotic inoculum was then added as a liquid suspension and mixed for an additional 10 min. Pellets were formed using a laboratory-scale pelletizer and subsequently dried at 64 °C for 4 h. The thermal processing conditions were specifically chosen to maintain probiotic viability, as Sp1 and Sp3 strains demonstrate thermostability, surviving temperatures up to 80 °C for extended periods [8,9]. The probiotic concentrations used (106–109 CFU/g) match those in human supplements [45]. This confirms their safety profile for food-production animals.
Probiotic viability in processed feeds was confirmed using plate count methodology. Dried feed samples (0.1 g) were weighed in triplicate into sterile tubes and homogenized with 1 mL of Luria–Bertani (LB) medium using sterile pestles. Samples were incubated at 30 °C for 1 h with periodic vortex mixing to facilitate spore germination and bacterial recovery. Serial dilutions (102 to 109) were prepared in sterile LB medium, and 100 μL aliquots from each dilution were plated in triplicate onto LB agar plates. Plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h, and colonies were enumerated for dilutions yielding 30–100 colonies per plate to ensure statistical accuracy. Final bacterial concentrations were calculated as CFU/g of feed by multiplying colony counts by the dilution factor and adjusting the initial sample weight. Post-processing viability analysis confirmed that both Bacillus strains maintained concentrations of 1.8–2.2 × 106 CFU/g in dried feeds.
2.4. Experimental Design and Animal Husbandry
A 180-day feeding trial was conducted from 25 October 2024, to 23 April 2025, at CICESE’s Marine Biotechnology department. The study evaluated three dietary treatments using a completely randomized design: (1) plant-based diet + probiotics, (2) fish-based diet + probiotics, and (3) control: fresh giant kelp M. pyrifera collected weekly from local coastal waters.
A total of 297 juvenile H. rufescens with mean (± SD) shell length of 48.51 ± 4.64 mm and body weight of 16.01 ± 5.51 g were obtained from CICESE’s Aquaculture Department. Animals used in this study and all experimental procedures complied with institutional animal welfare guidelines certified by the bioethics committee from CICESE (Ensenada, Baja California, Mexico, ORGA_ACUA_2025_03). Abalone were randomly distributed across nine 200 L circular fiberglass tanks (n = 33 per tank) in a factorial design with three dietary treatments and three replicate tanks per treatment. Each tank was equipped with two corrugated 30 × 30 cm plastic refuge plates to provide habitat. A flow-through seawater system maintained optimal water quality with 30% daily water exchange rate. Water quality parameters were monitored daily and maintained within optimal ranges for red abalone cultivation: temperature (17 ± 1 °C), dissolved oxygen (>6 mg/L), pH (8.0–8.2), and salinity (33–35‰). Natural photoperiod was maintained (approximately 14:10 light/dark during experimental months) without artificial illumination. Abalone were fed the three diets ad libitum and uneaten feed removed every two days by siphoning debris from the bottom of each tank before the addition of new food.
2.5. Biometric Sampling and Reproductive Assessment
Biometric and reproductive assessments were conducted at 0, 90, and 180 days. All organisms were measured for shell length using digital calipers (Mitutoyo 500-196-30, precision ±0.1 mm) and body weight using an analytical balance (precision ±0.01 g). Sex determination was performed visually based on gonad coloration: males (white/cream gonads) and females (olive green/dark gonads), with indeterminate classification for immature specimens (Figure 1). Gonadal development was assessed using the Visual Gonad Index (VGI) according to established protocols [46,47]: 0 = sex indistinguishable; 1 = sex distinguishable, thin gonad <40% colored with pointed tip; 2 = gonad partially enlarged 40–70% colored with pointed tip; 3 = gonad swollen >80% colored with rounded tip (Figure 1). All assessments were conducted by trained personnel following standardized protocols to ensure consistent evaluation across treatments and sampling periods.
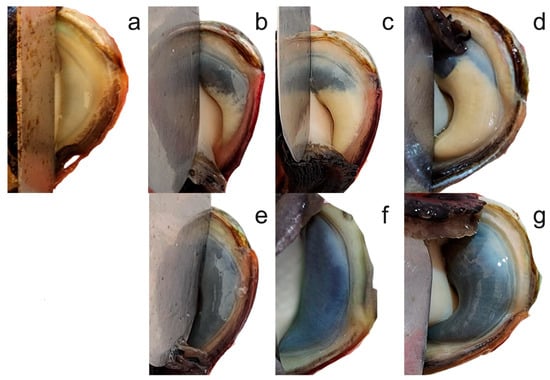
Figure 1.
Abalone Visual Gonad Index (VGI) and sex differentiation. 0 = sex indistinguishable (a); 1 = sex distinguishable, thin gonad <30% colored with pointed tip, (b) = male, (e) = female; 2 = gonad partially enlarged 40–70% colored with pointed tip, (c) = male, (f) = female; 3 = gonad swollen >80% colored with rounded tip, (d) = male, (g) = female.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Each dietary treatment started with 99 abalone (n = 297 total). At the end of the 180-day feeding trial, the number of surviving animals per treatment was: fish-based diet = 93, control fresh kelp = 96, and plant-based diet = 96, corresponding to survival rates of 93.9–97.0%. Mortalities were removed but not replaced, and all statistical analyses were conducted with the actual numbers of animals per treatment and sex at each time point.
Statistical analyses were performed using R (version 4.0.5) with tidyverse and multicomp packages. Data normality was assessed using Shapiro–Wilk tests, and homogeneity of variance was evaluated using Levene’s test. For VGI analysis, a two-phase approach was employed: two-way ANOVA examining dietary treatment × time interactions, followed by Tukey’s HSD post hoc comparisons with Bonferroni adjustment. Sex-specific analyses used one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD tests. Sex ratio distributions were analyzed using Pearson’s chi-square tests with Fisher’s exact tests for small sample sizes. Size-maturation correlations were assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients, with strength interpreted according to Cohen’s guidelines: weak (0.1–0.3), moderate (0.3–0.5), and strong (>0.5). Growth parameters were analyzed using repeated-measures ANOVA accounting for temporal dependence. All visualizations were created using ggplot2, with error bars representing SEM. Statistical significance was established at p < 0.05 for all analyses.
3. Results
3.1. Probiotic Safety Profile and Enzymatic Activity
Strains Sp1 (B. velezensis) and Sp3 (B. amyloliquefaciens) belong to B. subtilis subgroup, demonstrating safety profiles essential for probiotic applications in food-producing animals. Strain Sp1 showed complete susceptibility to all tested antibiotics, while strain Sp3 exhibited resistance only to ampicillin at 100 μg/mL. Both strains produce no hemolytic activity, confirming their non-pathogenic characteristics and GRAS status suitability. Enzymatic activity of both strains is summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Enzymatic activity profile of Bacillus probiotic strains.
3.2. Probiotic-Enhanced Reproductive Development
Probiotic supplementation in plant-based diet produced significant effects on gonadal maturation over the 180-day experimental period. At day 90, no significant differences were observed between treatments in either males (F = 1.013, df = 2, p = 0.365) or females (F = 1.998, df = 2, p = 0.142). By day 180, significant differences emerged. Two-way ANOVA revealed significant effects of treatment (F = 21.85, df = 2, p < 0.001), time (F = 261.91, df = 2, p < 0.001), and their interaction (F = 26.01, df = 4, p < 0.001). Post hoc analysis showed the plant-based diet significantly enhanced gonadal development. It outperformed both fish-based diets and fresh kelp controls (Figure 2).
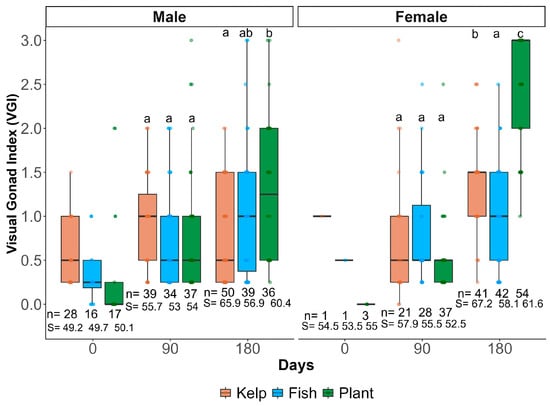
Figure 2.
Visual gonad index (VGI) in male and female Haliotis rufescens fed three dietary treatments over 180 days. Treatments: fresh kelp (Macrocystis pyrifera, orange), fish-based diet + probiotics (blue), and plant-based diet + probiotics (green). Different letters (a–c) above boxplots indicate significant differences between treatments within the same time point and sex (Tukey’s HSD, p < 0.05). n = sample size per treatment and sex at each time point. S = the average size (mm) of male or female abalone per treatment and sampling point.
Males across all treatments exhibited earlier initial maturation but plateaued at VGI levels of 1.5 for fish-based diet and control, while plant-based treatment enabled males to achieve VGI level 2. Females demonstrated even more pronounced responses, with plant-based probiotic treatment producing maximum VGI level 3 maturation, compared to level 1.5 achieved in other treatments (Figure 2).
3.3. Sex-Specific Maturation Responses at 180 Days
After 180 days, 30 females (55.6% of females in this treatment group) achieved full VGI level 3 maturation. Remarkably, zero females in fish-based probiotic treatment or fresh kelp control achieved this advanced maturation level. Chi-square analysis confirmed significant association with plant-based diet and attainment of VGI 3 (χ2 = 59.04, df = 2, p < 0.001), with Fisher’s exact test corroborating this finding (p < 0.001). Males in plant-based probiotic treatment showed more moderate but still significant responses, with 27.8% achieving VGI level 2 compared to 7.7% in fish-based and 4.0% in kelp treatments (Table 3).

Table 3.
Summary of dietary effects on red abalone reproductive performance and survival.
3.4. Relationship Between Size and Gonadal Maturation at 180 Days
On day 180, diet treatment had an effect between size and maturation (Figure 3). In fish and control treatments, females exhibited expected positive correlations between size and gonadal maturation: fresh kelp (r = 0.348, p = 0.026) and fish-based with probiotic diet (r = 0.424, p = 0.005). These correlations reflect traditional energy allocation models where reproductive investment scales with body size and available resources. Remarkably, females in plant-based treatment showed no significant correlation between size and reproductive maturity (r = 0.207, p = 0.134), despite having the largest sample size (n = 54) and highest proportion of fully mature individuals. Males demonstrated no significant size-maturation correlations in any treatment, indicating that male reproductive development may be inherently less size-dependent than female development in red abalone (Table 3).
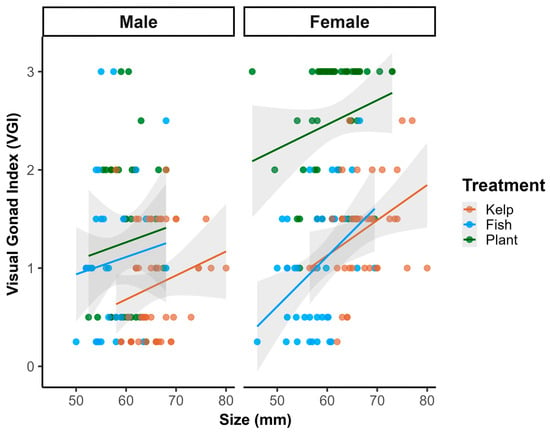
Figure 3.
Correlation between size (mm) and visual gonad index (VGI) in male and female H. rufescens after 180 days of dietary treatments. Treatments: fresh kelp M. pyrifera (orange), fish-based diet + probiotics (blue), and plant-based diet + probiotics (green). Solid lines represent linear regression fits; shaded areas indicate 95% confidence intervals. Pearson correlation coefficients (r) Females—Kelp: r = 0.348, p = 0.026; Fish: r = 0.424, p = 0.005; Plant: r = 0.207, p = 0.134. Males—all treatments non-significant (p > 0.05).
3.5. Dietary Effects on Sex Ratios
The temporal progression of sex differentiation showed that at the beginning of the experiment, most specimens (>70%) exhibited indeterminate gonads, consistent with their initial size range (48.51 ± 4.64 mm) [48]. By day 90, approximately 65% of individuals across all treatments had differentiated to either male or female (Figure 4). Abalone in plant-based diet resulted in a female-biased sex ratio of 1.5:1 female-to-male ratio (F:M), with differences from 0.8:1 F:M in kelp diet (χ2 = 4.02, df = 2, p = 0.0445), and no differences from the 1.1:1 in the fishmeal-based diet (χ2 = 1.15, df = 2, p = 0.284) on day 180. The emergence of diet-specific effects on sex ratios by day 180 suggests that dietary influence on sex differentiation may be exerted during a specific window of sexual differentiation in juvenile red abalone (Figure 4).
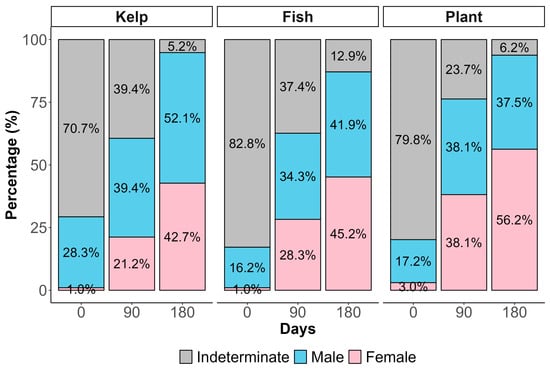
Figure 4.
Temporal changes in sex distribution of red abalone H. rufescens fed different dietary treatments over 180 days. Treatments: Control fresh kelp M. pyrifera, fish-based diet + probiotics, and plant-based diet + probiotics. Gray bars represent indeterminate sex, blue bars represent males, and pink bars represent females. F:M = female-to-male sex ratio. Differences among treatments were tested by chi-square analysis with Fisher’s exact test for small sample sizes (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
This study evaluated the effects of a plant and fish-based diet supplemented with Bacillus probiotic strains Sp1 and Sp3 compared to a control with fresh kelp M. pyrifera on gonadal maturation, sex ratios, and survival in red abalone H. rufescens. In that sense, plant diet induced higher gonadal development compared to both fish diet and control, especially in females. After 180 days of experimentation two key findings emerged: (1) 56% of females fed plant-based diet achieved full gonadal maturation (VGI level 3) compared to none in fish diet and control (Figure 1; Table 3); and (2) a female-biased sex ratio also occurred in plant treatment producing a 1.5:1 F:M, compared to 0.8:1 F:M obtained in control (Figure 4; Table 3). The reproductive outcomes produced by plant-based diet likely result from interaction between probiotic enzymes, dietary phytoestrogens contained in soy oligosaccharides, and other bioactive compounds not contained in fish diet or control. These findings represent a novel approach to reproductive management in abalone aquaculture using sustainable plant-based feeds and Bacillus.
4.1. Bacillus Safety, Enzymatic Mechanisms, and Phytoestrogen Liberation
The GRAS status confirmation of Bacillus strains Sp1 and Sp3 provides regulatory foundation for application in aquafeed. Strain Sp1′s complete antibiotic susceptibility and Sp3′s resistance limited to ampicillin align with EFSA guidelines for probiotic safety, while both strains produced no hemolytic activity, confirming their non-pathogenic characteristics [1,8,9] (Table 2). This safety profile, combined with their spore-forming capability and thermostability, establishes these strains as ideal candidates for commercial aquafeed applications.
The enzymatic repertoire of these Bacillus strains may explain their reproductive enhancement effects. While both strains demonstrated robust proteolytic and carbohydrase activities essential for plant-based feed degradation, their α-galactosidase production is key for oligosaccharides breakdown, enabling phytoestrogen liberation [18,40,41].
Previous studies investigating soybean meal effects on abalone reproductive development yielded inconclusive results, with both Meusel et al. [35] and Wu et al. [36] reporting no significant reproductive enhancement in Haliotis midae fed soybean-containing diets. A key distinction between our study and previous investigations lies principally in the incorporation of Bacillus probiotic into aquafeeds produced and assessed in this assay. Therefore, even when red abalone enzymatic activity (β-glucuronidase, N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase, α-fucosidase, etc.) is useful to digest a great profile of complex carbohydrates (fucoidans, alginates, carrageenans) from sea algae origin, it seems that they have constraints in fully digesting terrestrial plant-derived macromolecules [38]. In that sense, while H. rufescens possesses an evolutionary adaptation for degrading proteins and complex polysaccharides from their natural macroalgal diet—it has a relatively low concentration of proteases and carbohydrases essentials for plant-derived macronutrients degradation [37,49,50].
Bacillus Sp1 and Sp3 strains’ enzymatic analysis demonstrated capacity to degrade plant-derived macronutrients, including proteases inhibitors and oligosaccharides from soybean (Table 2) [8,18,51]. In that sense, Bacillus addition is critical to release essential nutrients and bioactive compounds like amino acids, sugars, lipids, carotenoids and phytoestrogens. Therefore, complex macronutrients degradation by Bacillus enzymes avoids antinutritional effects that could be induced by plant-based formulations [1,14,52].
The specificity of this mechanism is supported by the absence of reproductive enhancement in fish-based diet supplemented with identical probiotic strains but without soybean meal. Despite producing the same Bacillus Sp1 and Sp2 enzymatic profile, fish-based treatment showed minimal reproductive development. This suggests that the availability of soy oligosaccharides-phytoestrogens, rather than probiotic supplementation alone, drives the observed reproductive effects. Additionally, previous studies have documented phytoestrogen enzymatic liberation mechanism by Bacillus enhancing isoflavone bioavailability in mammals [40,41,51,53].
Our findings are consistent with a probiotic-mediated release of soy phytoestrogens, although we recognize this evidence remains indirect. Bacillus species are known to hydrolyze isoflavone glycosides into aglycones with greater bioavailability and estrogenic activity [40]. In mammals, fermented soybean products rich in Bacillus have been shown to improve metabolic and bone parameters through increased isoflavone activity [41,53]. In contrast, abalone studies where soybean meal was included without probiotic supplementation did not observe similar reproductive effects [35,36], suggesting that soy alone may be insufficient unless enzymatic liberation occurs. While this supports the plausibility of our proposed mechanism, alternative explanations remain possible, including other soy bioactive compounds, direct modulation of the abalone microbiome by Bacillus, or host enzymatic contributions. To verify the mechanism, future studies should include direct quantification of isoflavones in feed and tissues, receptor activation assays, and combined microbiome–transcriptomic analyses to determine how probiotics and soy interact to influence reproduction.
4.2. Sex-Specific Maturation Patterns in H. rufescens
The response to dietary treatments exhibited distinct maturation patterns between male and female red abalone. Females demonstrated a remarkable response to the plant-based diet, with 56% achieving maximum gonadal maturity (VGI 3) after 180 days. In contrast, no females in fishmeal or kelp diets reached this advanced developmental stage (Figure 2; Table 3). The underlying mechanism likely involves probiotic-liberated isoflavones binding to estrogen receptors and stimulating vitellogenesis pathways essential for oocyte development. Phytoestrogens demonstrate structural similarity to endogenous estrogens, enabling them to activate reproductive signaling cascades while providing molecular signals that accelerate energy mobilization toward gonadal tissue development [19,20,34]. This hormonal stimulation appears well-suited to the substantial maternal investment required for abalone’s lecithotrophic developmental strategy, where females must provide eggs with extensive nutrient reserves for successful larval development [54].
The sexually dimorphic response pattern—with females showing higher maturation than males—could reflect differences in gametogenic energy requirements between sexes. Oogenesis demands significantly greater energetic investment than spermatogenesis in mollusks, making female reproductive development more responsive to nutritional and hormonal enhancement [55,56]. The limited reproductive development observed in abalone fed fresh M. pyrifera, despite feeding during the natural reproductive season (October-March), highlights important limitations of monospecific diets in aquaculture [48]. In natural habitats, abalone consumes a diverse array of macroalgae, including various Laminariales, green algae, and red algae species [57]; potentially producing synergistic combinations of bioactive compounds that could increase the reproductive capacity of H. rufescens. The reproductive capacity induced by the plant-based diet supplemented with Bacillus Sp1 and Sp3 strains could provide commercial advantages for operations focused on maximizing egg production and breeding efficiency.
The probiotic-mediated reproductive enhancement mechanism represents a novel application of functional nutrition in aquaculture. Demonstrating how microbial enzymes, in addition to feed degradation, can unlock bioactive compound potential in sustainable and economically viable plant-based ingredients. This approach addresses multiple industry challenges simultaneously: reducing dependency on marine-derived feeds, lowering production costs, and providing solutions for abalone reproductive management.
4.3. Size-Maturation Decoupling Through Probiotic Enhancement
Traditional abalone reproductive biology assumes strong correlations between body size and reproductive capacity, reflecting conventional energy allocation models where reproductive investment scales with somatic growth and available energy reserves [58,59]. Our findings suggest that probiotic-enhanced phytoestrogen bioavailability can decouple reproductive development from size constraints.
In fish and control treatments, females exhibited expected positive correlations between size and reproductive maturity (kelp control: r = 0.348; fish + probiotics: r = 0.424), consistent with established reproductive biology principles. However, females receiving plant-based diet with probiotics showed no significant size-maturation correlation (r = 0.207, p = 0.134) despite achieving the highest reproductive success rates (Figure 3; Table 3). This decoupling suggests that probiotic-liberated phytoestrogens activate reproductive pathways through direct endocrine mechanisms rather than traditional energy-dependent processes. This mechanism, where bioactive compounds affect reproductive pathways, has been observed in fish [20,60,61], reptiles [62], and other organisms [63,64]. This result of diet-induced decoupling between size and reproductive development represents a novel finding in abalone reproductive management with significant applications for aquaculture production. The ability to manipulate reproductive development through diet formulation, independent of size, provides abalone farmers with a valuable tool to optimize production cycles and improve breeding efficiency [65].
4.4. Effects on Sex Ratio
Our results suggest that plant-based feed supplemented with Bacillus probiotic strains influenced not only gonadal maturation but also sex ratio in red abalone (Figure 4; Table 3). The shift in sex ratios toward a female-biased population (1.5:1 F:M) in abalone fed plant-based diet with Bacillus, compared to 0.8:1 F:M with fresh kelp, indicates a potential dietary influence on sex differentiation processes. This result contrasts with Meusel et al. [35], who obtained 0.9:1 F:M in abalone fed with fishmeal and soybean meal combination. This finding is relevant considering that at the beginning of the experiment, red abalone were <50 mm in shell length and could not be sexually differentiated [42] (Figure 4).
The timing of this sex ratio manipulation suggests that probiotic-liberated phytoestrogens may influence developmental switches during sexual differentiation. Endocrine disruption effects have been documented in fish, amphibians, and reptiles [66,67]. For example, El-Sayed et al. [68] obtained 77% females in Oreochromis niloticus larvae fed soybean meal compared to 52% when fed fishmeal. Similar results were observed with Anguilla anguilla, where treatments exposed to phytoestrogens achieved 56–88% females [69].
Phytoestrogens’ bioavailability by probiotic enzymes aligns with studies demonstrating increased concentration of plant phytochemicals through microbial fermentation [40,41]. The enzymatic activity from Bacillus strains used likely facilitated isoflavones release from soybean meal, increasing their bioavailability with consequent effects on H. rufescens sex ratio. Synergistic effects obtained from dietary soy-phytoestrogens and probiotics supplementation offer a novel perspective on nutritional strategies for reproductive management in abalone aquaculture. However, caution must be exercised in attributing causality to phytoestrogens alone. Controlled experiments targeting isolated phytoestrogens’ effects would be necessary to establish a direct causal relationship between specific phytoestrogens and the observed sex differentiation outcomes.
From an ecological and evolutionary perspective, abalone in the wild consume a wide variety of macroalgae rich in polysaccharides, carotenoids, phlorotannins, and sterols that can influence physiology and reproduction [57]. In contrast, soybean meal introduces high concentrations of isoflavones ranging from 1.2 to 4.2 mg·kg−1 dry matter [70]. These compounds provide an estrogenic chemical signal not normally encountered in natural abalone diets, which may help explain the female-biased sex ratios observed in this study. However, the ecological relevance and long-term consequences of this effect remain uncertain. Phytoestrogen supplementation has been associated in other taxa with endocrine disruption, altered sex differentiation, and reduced male fertility across generations [66,67]. Similar risks could emerge in abalone if reproductive pathways are overstimulated or persistent female bias compromises fertilization success.
Finally, the lipid composition of formulated diets differs from that of wild kelp, with higher total lipids and altered sterol profiles that may increase substrate availability for steroidogenesis and transport of lipophilic hormones [71], which has been documented in mollusks [72]. Taken together, these compositional differences suggest that (a) soybean-derived phytoestrogens act through pathways distinct from natural algal bioactive compounds, and (b) dietary lipids and sterols may interact with these compounds to further modulate reproductive physiology. Future studies should therefore quantify isoflavones in feeds and tissues, characterize sterol and lipid classes, and evaluate their combined impact on endocrine gene expression, fertility, and multigenerational reproductive performance to ensure that the benefits of probiotic–soy supplementation do not come at the cost of long-term reproductive capacity.
5. Conclusions
This study provides evidence that supplementing a plant-based diet with Bacillus probiotic strains can enhance reproductive performance in red abalone H. rufescens. The enzymatic activities of Bacillus—particularly carbohydrases, proteases and lipases—are likely to improve bioavailability of essential nutrients, bioactive compounds and phytoestrogens from soybean meal. In addition, probiotics may reduce antinutritional factors of soybean meal added to plant-based feed. This mechanism possibly resulted in two major outcomes with substantial commercial implications: enhanced female gonadal maturation with 56% females achieving maximum maturity level (VGI 3) and a shift toward female-biased sex differentiation (1.5:1 F:M).
From an applied perspective, these results indicate a potential strategy for reproductive management in abalone aquaculture. For example, practitioners could: (1) program reproductive cycles rather than relying solely on natural seasonal cycles; and (2) obtain higher quality larvae, as eggs from fully mature females may contain superior nutritional reserves leading to enhanced settlement and survival rates. Additionally, this approach could offer economic advantages by replacing fishmeal with soybean meal supplemented with Bacillus, reducing dependency on marine-derived ingredients. Reduced reliance on wild macroalgae, whose nutritional quality fluctuates seasonally and depends on environmental conditions, may provide operational stability and predictable feed costs. This study opens new research avenues in molluscan reproductive endocrinology and the role of dietary bioactive compounds in influencing sex differentiation pathways. Future research should evaluate the persistence of these effects across successive generations and employ biochemical, microbiome, transcriptomic, and proteomic approaches to confirm the underlying mechanisms ensuring their safe application in sustainable aquaculture.
The broader implications extend beyond abalone aquaculture to encompass the future of sustainable aquaculture nutrition. By demonstrating how probiotic biotechnology can transform plant-based ingredients into functionally superior alternatives to traditional marine-derived feeds, this research contributes to the development of sustainable aquaculture capable of meeting growing global protein demands without compromising marine ecosystem integrity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.O.; Methodology, J.O., M.A.-R. and F.L.-D.l.C.; Formal analysis, J.B.; Investigation, J.O., M.A.-R. and F.L.-D.l.C.; Resources, J.O., M.A.-R. and F.L.-D.l.C.; Writing—original draft, J.O.; Writing—review & editing, J.O., M.A.-R. and J.B.; Visualization, J.B.; Supervision, J.O. and M.A.-R.; Project administration, J.O. and M.A.-R.; Funding acquisition, J.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Partial financial support was received from the Secretaría de Ciencia, Humanidades, Tecnología e Innovación (SECIHTI) with a postdoctoral grant to Jeremie Bauer (CVU #830611).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Comité de Bioética del CICESE (Bioethics Committee of CICESE ORGA_ACUA_2025_03 2025-07-09).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgments to Jazmine Gutierrez Castañeda and Jesús Mariscal Medina for their invaluable time, effort, and support throughout this project. Their dedication, insights, and collaborative spirit were essential to the completion of this work. We also acknowledge the Secretaría de Ciencia, Humanidades, Tecnología e Innovación (SECIHTI) for the postdoctoral grant to Jeremie Bauer (CVU #830611).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| VGI | Visual Gonad Index |
| SBM | Soybean Meal |
| SPC | Soy Protein Concentrate |
| STR | Starch |
| WHF | Wheat Flour |
References
- Olmos Soto, J.; Paniagua-Michel, J.d.J.; Lopez, L.; Ochoa, L. Functional Feeds in Aquaculture. In Springer Handbook of Marine Biotechnology; Kim, S.K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1237–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.-Z.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Z. Probiotics as means of diseases control in aquaculture, a review of current knowledge and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, J.; Acosta, M.; Mendoza, G.; Pitones, V. Bacillus subtilis, an ideal probiotic bacterium to shrimp and fish aquaculture that increase feed digestibility, prevent microbial diseases, and avoid water pollution. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmos, J.; Ochoa, L.; Paniagua-Michel, J.; Contreras, R. Functional feed assessment on Litopenaeus vannamei using 100% fish meal replacement by soybean meal, high levels of complex carbohydrates and Bacillus probiotic strains. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, J.O. Feed intake improvement, gut microbiota modulation and pathogens control by using Bacillus species in shrimp aquaculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Dai, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Dong, F.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, T. Effects of Bacillus subtilis-fermented soybean meal replacing fish meal on antioxidant activity, immunity, endoplasmic reticulum stress and hepatopancreas histology in Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1449066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, J.; López, L.M.; Gorriño, A.; Galaviz, M.A.; Mercado, V. Bacillus subtilis Effects on Growth Performance and Health Status of Totoaba macdonaldi Fed with High Levels of Soy Protein Concentrate. Animals 2022, 12, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, V.; Olmos, J.; López, L.M.; Galaviz, M.A. First report of significant growth improvement of Totoaba macdonaldi using Bacillus and soy. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, L.; Mercado, V.; Olmos, J. Assessment of Bacillus species capacity to protect Nile tilapia from A. hydrophila infection and improve growth performance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1354736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Dakar, A.Y.; Elgamal, A.A.; Amer, M.A.B.; Mohammed, A.S.; Abdel-Aziz, M.F. Evaluation of fermented soybean meal by Bacillus subtilis as an alternative to fishmeal on the growth, and physiological status of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus fingerlings. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonmee, T.; Deevong, P.; Rinthong, P.-O.; Yuangsoi, B. Improvement of nutritive value of soybean meal by microbial hydrolysis with Bacillus subtilis Hs-2 for use as raw material in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) diet. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 35, 101943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ling, Y.; Zhang, R.; Ke, C.-H.; Hong, G. Effects of dietary supplementation of probiotics on growth, immune responses, and gut microbiome of the abalone Haliotis diversicolor. Aquaculture 2018, 493, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaolong, G.; Caihuan, K.; Fucun, W.; Xian, L.; Ying, L. Effects of Bacillus lincheniformis feeding frequency on the growth, digestion and immunity of Haliotis discus hannai. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 96, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadangin, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Jeon, C.-Y.; Lee, E.-S.; Moon, J.-S.; Park, S.-J.; Hur, S.-W.; Jang, W.-J.; Choi, Y.-H. Effects of dietary supplementation of Bacillus, β-glucooligosaccharide and their synbiotic on the growth, digestion, immunity, and gut microbiota profile of abalone, Haliotis discus hannai. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 35, 102027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Bolch, C.J.S.; Adams, M.B.; Burke, C.M. Growth enhancement of tropical abalone, Haliotis asinina L, through probiotic supplementation. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, J.; Mercado, V. Use of alternative ingredients and probiotics in aquafeeds formulation. In Sustainable Aquafeeds; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 21–56. [Google Scholar]
- Olmos, J.; Paniagua-Michel, J. Bacillus subtilis a potential probiotic bacterium to formulate functional feeds for aquaculture. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2014, 6, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Solano, J.L.; Olmos-Soto, J. The functional property of Bacillus for shrimp feeds. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederroth, C.R.; Nef, S. Soy, phytoestrogens and metabolism: A review. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 304, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.P.; Nirmal, T.; Prabhakaran, A.; Varghese, T. Phytoestrogens as endocrine-disrupting agents in aquaculture. In Xenobiotics in Aquatic Animals; Rather, M.A., Amin, A., Hajam, Y.A., Jamwal, A., Ahmad, I., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Teruel, M.N.; Millamena, O.M.; Fermin, A.C. Reproductive performance of hatchery-bred donkey’s ear abalone, Haliotis asinina, Linne, fed natural and artificial diets. Aquac. Res. 2001, 32, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, D.; Pan, M.; Sahandi, J.; Wu, Z.; Mai, K.; Zhang, W. Nutrition and feeds for abalone: Current knowledge and future directions. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 1555–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Beas-Luna, R.; Emeterio-Cerecero, M.; Vaca-Rodríguez, J.; Montaño-Moctezuma, G.; Lorda, J. Growth and survival of juvenile red abalone (Haliotis rufescens) fed invasive macroalgae. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2025, 59, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Lorda, J.; Beas-Luna, R.; Malpica-Cruz, L.; Lafarga-De la Cruz, F.; Micheli, F.; Searcy-Bernal, R.; Rogers-Bennett, L.; Bracamontes-Peralta, M. The effects of depth and diet on red abalone growth and survival in cage mariculture at San Jeronimo Island, Baja California, Mexico. Cienc. Mar. 2020, 46, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Beas-Luna, R.; Searcy-Bernal, R.; Micheli, F.; Vázquez-Vera, L.; Boch, C.; Carpizo-Ituarte, E.; la Cruz, F.L.-D.; Montaño-Moctezuma, G.; Lorda, J. Growth of juvenile red abalone (Haliotis rufescens) co-cultivated with two densities of warty sea cucumber (Apostichopus parvimensis). N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2025, 59, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Metian, M. Feed matters: Satisfying the feed demand of aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2015, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; D’Abramo, L.R.; Glencross, B.D.; Huyben, D.C.; Juarez, L.M.; Lockwood, G.S.; McNevin, A.A.; Tacon, A.G.J.; Teletchea, F.; Tomasso, J.R., Jr.; et al. Achieving sustainable aquaculture: Historical and current perspectives and future needs and challenges. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 578–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indexmundi. Commodity Prices—Price Charts, Data, and News. 2025. Available online: https://www.indexmundi.com/commodities/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- IMARC Group. Seaweed Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2024–2032. 2024. Available online: https://www.imarcgroup.com/seaweed-market (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Cai, J.; Lovatelli, A.; Aguilar-Manjarrez, J.; Cornish, L.; Dabbadie, L.; Desrochers, A.; Yuan, X. Seaweeds and Microalgae: An Overview for Unlocking Their Potential in Global Aquaculture Development; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular 1229; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eger, A.M.; Marzinelli, E.M.; Beas-Luna, R.; Blain, C.O.; Blamey, L.K.; Byrnes, J.E.K.; Carnell, P.E.; Choi, C.G.; Hessing-Lewis, M.; Kim, K.Y.; et al. The value of ecosystem services in global marine kelp forests. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Beas-Luna, R.; Malpica-Cruz, L.; Abadía-Cardoso, A.; Filz, P.; Bonilla, J.C.; Lorda, J. Community-led management maintains higher predator biomass supporting kelp forests persistence in Baja California. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, N.L.; Klinger, D.H.; Sims, N.A.; Yoshioka, J.-R.; Kittinger, J.N. Nutritional attributes, substitutability, scalability, and environmental intensity of an illustrative subset of current and future protein sources for aquaculture feeds: Joint consideration of potential synergies and trade-offs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5532–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liggins, J.; Bluck, L.J.C.; Runswick, S.; Atkinson, C.; Coward, W.A.; Bingham, S.A. Daidzein and genistein contents of vegetables. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 84, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meusel, E.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Naylor, M.; Kaiser, H.; El-Matbouli, M. Gonad development in farmed male and female South African abalone, Haliotis midae, fed artificial and natural diets under a range of husbandry conditions. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Kaiser, H.; Jones, C.L.W. A first study on the effect of dietary soya levels and crystalline isoflavones on growth, gonad development and gonad histology of farmed abalone, Haliotis midae. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, B., Jr.; Thanassi, N.; Nakada, H.I. Hepatopancreas glycosidases of the abalone (Haliotus rufescens). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1971, 40, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp-Valdez, M.A.; Galindo-Sánchez, C.E.; Ventura-López, C.; Cicala, F.; Montes-Orozco, V.; Lafarga-De la Cruz, F. Diet-driven transcriptional changes in weaning red abalone (Haliotis rufescens) and its hybrid (H. rufescens [♀] x H. fulgens [♂]). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom.—Proteom. 2025, 55, 101484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.; Makkar, H.P.S.; Becker, K. Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their effects in fish. Aquaculture 2001, 199, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, L.-C.; Cheng, W.-Y.; Wu, R.-Y.; Huang, C.-J.; Lee, K.-T. Hydrolysis of black soybean isoflavone glycosides by Bacillus subtilis natto. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 73, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yue, Y.; Jeong, S.-J.; Ryu, M.-S.; Wu, X.; Yang, H.-J.; Li, C.; Jeong, D.-Y.; Park, S. Improvement of estrogen deficiency symptoms by the intake of long-term fermented soybeans (doenjang) rich in Bacillus species through modulating gut microbiota in estrogen-deficient rats. Foods 2023, 12, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Koshio, S.; Yokoyama, S.; Dossou, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Shadrack, R.S.; Mzengereza, K.; Zhu, K.; et al. Optimization of Soybean Meal Fermentation for Aqua-Feed with Bacillus subtilis natto Using the Response Surface Methodology. Fermentation 2021, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, M.A.B.; Julien, B.B.; Islam, S.M.M.; Francis, D.S. Fermentation in aquafeed processing: Achieving sustainability in feeds for global aquaculture production. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 1244–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Montesinos, Y.; Hernández-Carmona, G. Seasonal and geographic variations of Macrocystis pyrifera chemical composition at the western coast of Baja California. Cienc. Mar. 1991, 17, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutting, S.M. Bacillus probiotics. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubert, M.A.; Ritar, A.J. Temperature effects on the dynamics of gonad and oocyte development in captive wild-caught blacklip (Haliotis rubra) and greenlip (H. laevigata) abalone. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2004, 45, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Botwright, N.A.; Zhao, M.; Wang, T.; McWilliam, S.; Colgrave, M.L.; Hlinka, O.; Li, S.; Suwansa-Ard, S.; Subramanian, S.; McPherson, L.; et al. Greenlip Abalone (Haliotis laevigata) Genome and Protein Analysis Provides Insights into Maturation and Spawning. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2019, 9, 3067–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers-Bennett, L.; Dondanville, R.F.; Moore, J.D.; Vilchis, L.I. Size specific fecundity of red abalone (Haliotis rufescens): Evidence for reproductive senescence. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 553–560. [Google Scholar]
- Erasmus, J.H.; Cook, P.A.; Coyne, V.E. The role of bacteria in the digestion of seaweed by the abalone Haliotis midae. Aquaculture 1997, 155, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serviere-Zaragoza, E.; Navarrete del Toro, M.; García-Carreño, F. Protein-hydrolyzing enzymes in the digestive systems of the adult Mexican blue abalone, Haliotis fulgens (Gastropoda). Aquaculture 1997, 157, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulsara, J.; Soni, A.; Patil, P.; Halpati, K.; Desai, S.; Acharya, S. Bio-enhancement of Soy Isoflavones (Genistein & Daidzein) Using Bacillus coagulans in Letrozole Induced Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome by Regulating Endocrine Hormones in Rats. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 14, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, J.O. Bacillus Probiotic Enzymes: External Auxiliary Apparatus to Avoid Digestive Deficiencies, Water Pollution, Diseases, and Economic Problems in Marine Cultivated Animals. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 80, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-J.; Zhang, T.; Yue, Y.; Jeong, S.-J.; Ryu, M.-S.; Wu, X.; Li, C.; Jeong, D.-Y.; Park, S. protective effect of long-term fermented soybeans with abundant Bacillus subtilis on glucose and bone metabolism and memory function in ovariectomized rats: Modulation of the gut microbiota. Foods 2023, 12, 2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeckle, W.B.; Manahan, D.T. Growth and energy imbalance during the development of a lecithotrophic molluscan larva (Haliotis rufescens). Biol. Bull. 1989, 177, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llodra, E.R. Fecundity and life-history strategies in marine invertebrates. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2002, 43, 87–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaay, M.; De Silva, S.S. Spawning season, fecundity and proximate composition of the gonads of wild-caught blacklip abalone (Haliotis rubra) from Port Fairy waters, south eastern Australia. Aquat. Living Resour. 2003, 16, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullon, N.; Seyfoddin, A.; Alfaro, A.C. The role of aquafeeds in abalone nutrition and health: A comprehensive review. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2023, 54, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, K. Toward a new paradigm for growth modeling in fisheries stock assessments: Embracing plasticity and its consequences. Fish. Res. 2016, 180, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Lu, L.; Chen, S.; Lin, F.; Chang, L. A dynamic energy budget model for abalone, Haliotis discus hannai Ino. Ecol. Model. 2021, 451, 109569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdehi, A.Y.; Sudagar, M.; Bahmani, M.; Hosseini, S.A.; Dehghani, A.A.; Yazdani, M.A. Comparative study of dietary soy phytoestrogens genistein and equol effects on growth parameters and ovarian development in farmed female beluga sturgeon, Huso huso. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 40, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohreh, P.; Mohammadzadeh, S.; Mood, S.M.; Ahmadifar, E.; Naiel, M.A.E.; Chandran, D. the potentials of phytoestrogen compounds in aquaculture—A Review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2024, 24, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnarowski, K.; Podobiński, P.; Cholewińska, P.; Smoliński, J.; Dorobisz, K. Impact of estrogens present in environment on health and welfare of animals. Animals 2021, 11, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirotkin, A.V.; Harrath, A.H. Phytoestrogens and their effects. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 741, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ha, D.; Yoshitake, R.; Chan, Y.S.; Sadava, D.; Chen, S. Exploring the biological activity and mechanism of xenoestrogens and phytoestrogens in cancers: Emerging methods and concepts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morash, A.J.; Alter, K. Effects of environmental and farm stress on abalone physiology: Perspectives for abalone aquaculture in the face of global climate change. Rev. Aquac. 2016, 8, 342–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, E.F.; Guillette, L.J. Sexual dimorphic responses in wildlife exposed to endocrine disrupting chemicals. Environ. Res. 2007, 104, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, M.R. Clover root exudate produces male-biased sex ratios and accelerates male metamorphic timing in wood frogs. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, A.-F.M.; Abdel-Aziz, E.-S.H.; Abdel-Ghani, H.M. Effects of phytoestrogens on sex reversal of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) larvae fed diets treated with 17α-Methyltestosterone. Aquaculture 2012, 360–361, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzchori, I.; Degani, G.; Elisha, R.; Eliyahu, R.; Hurvitz, A.; Vaya, J.; Moav, B. The influence of phytoestrogens and oestradiol-17beta on growth and sex determination in the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Aquac. Res. 2004, 35, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzer, M.S.; Xu, X. Dietary Phytoestrogens. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1997, 17, 353–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, I.; Markov, G.V.; Yañez-Guerra, L.A.; Elekes, K.; Pollák, E.; Molnár, L.; Pirger, Z. Istv Cholesterol and sterols in molluscan endocrinology: Past, present, future. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1627166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitiphuree, T.; Nagasawa, K.; Osada, M. Molecular identification of steroidogenesis-related genes in scallops and their potential roles in gametogenesis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 186, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).