Isolation of Bacillus paralichenifromis BL-1 and Its Potential Application in Producing Bioflocculants Using Phenol Saline Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Culture Medium
2.2. Strain Isolation
2.3. Determination of Flocculating Activity
2.4. Quantification of γ-PGA
2.5. Determination of Phenol Concentration
2.6. Genome Analysis of Isolate BL-1
2.7. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
3. Results
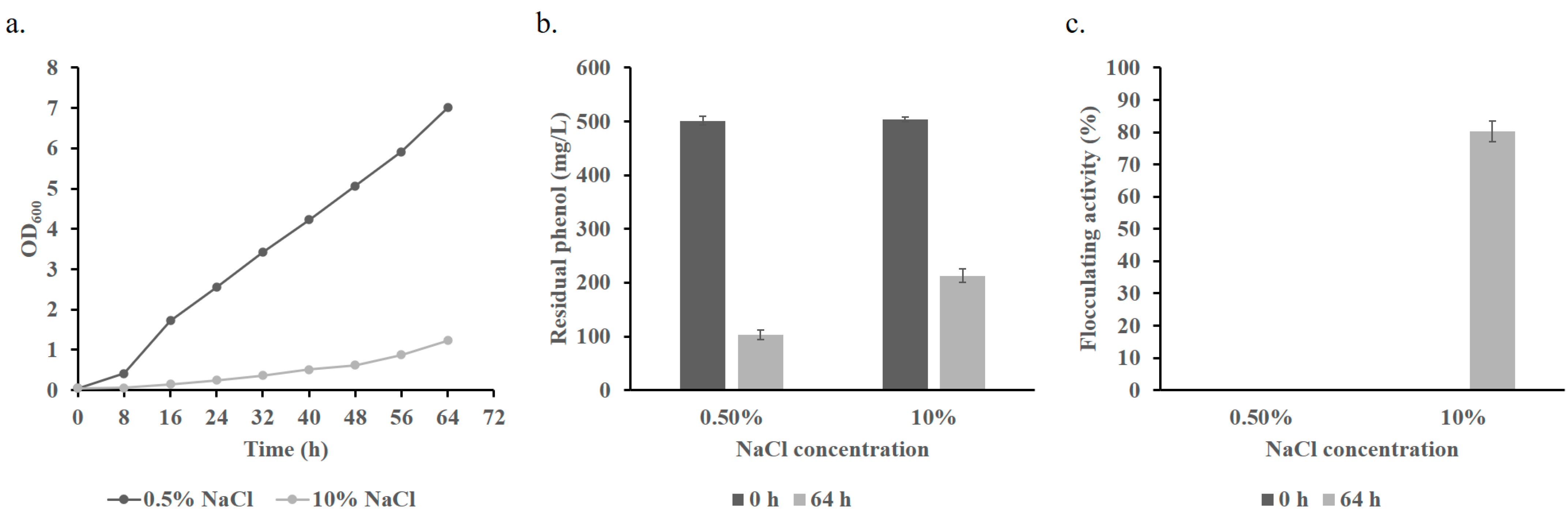
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Bioflocculant-Producing Strain
3.2. Genome Analysis of Strain BL-1
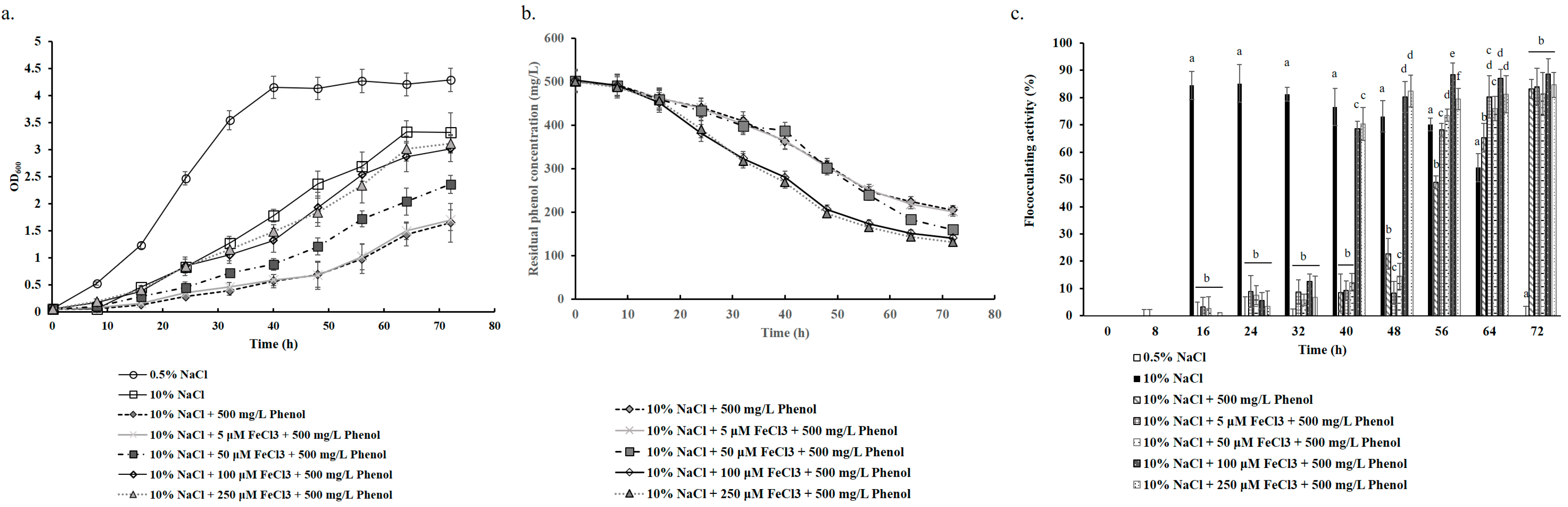
3.3. Phenol Degradation of B. paralicheniformis BL-1
3.4. Poly-γ-glutamate Is the Main Flocculating Substance
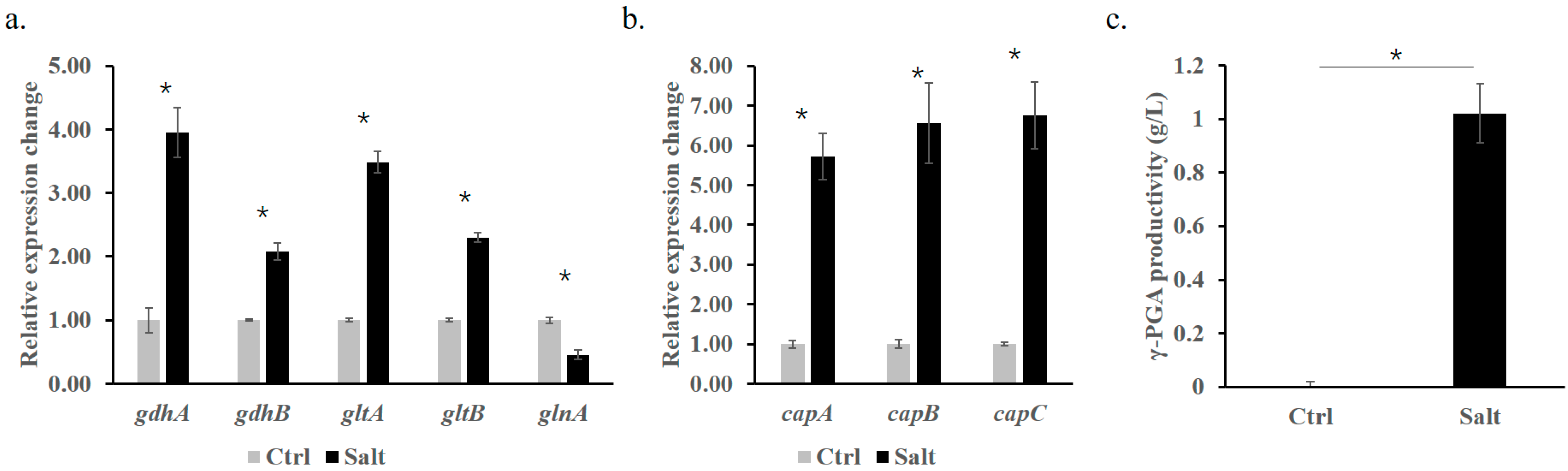
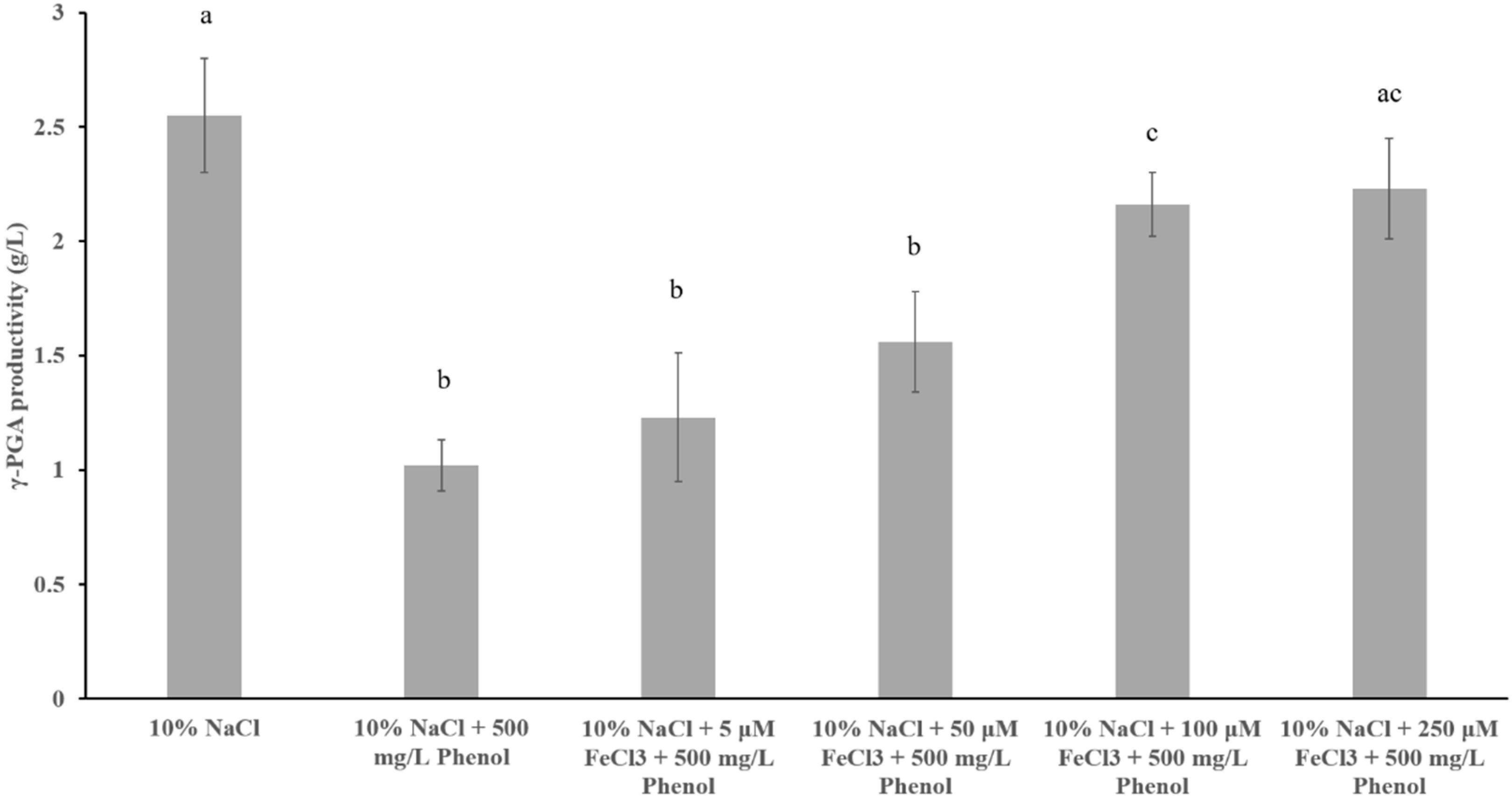
3.5. Alleviation of Iron Starvation Improves Salinity Adaptation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grace Pavithra, K.; Sundar Rajan, P.; Arun, J.; Brindhadevi, K.; Hoang Le, Q.; Pugazhendhi, A. A review on recent advancements in extraction, removal and recovery of phenols from phenolic wastewater: Challenges and future outlook. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 117005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phenol Market Size, Industry Share & Forecasts Report 2032. Available online: https://www.persistencemarketresearch.com/market-research/phenol-market.asp (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Careghini, A.; Mastorgio, A.F.; Saponaro, S.; Sezenna, E. Bisphenol A, nonylphenols, benzophenones, and benzotriazoles in soils, groundwater, surface water, sediments, and food: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 5711–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M.; Mishra, S.R.; Gadore, V.; Yadav, G.; Roy, S.; Bhattacharjee, B.; Bhuyan, A.; Hazarika, B.; Darabdhara, J.; Kumari, K. Phenolic compounds in water: From toxicity and source to sustainable solutions—An integrated review of removal methods, advanced technologies, cost analysis, and future prospects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Meng, F.; Duan, W.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Y. Biodegradation of phenol in saline or hypersaline environments by bacteria: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viggor, S.; Joesaar, M.; Soares-Castro, P.; Ilmjarv, T.; Santos, P.M.; Kapley, A.; Kivisaar, M. Microbial metabolic potential of phenol degradation in wastewater treatment plant of crude oil refinery: Analysis of metagenomes and characterization of isolates. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmetwalli, A.; Allam, N.G.; Hassan, M.G.; Albalawi, A.N.; Shalaby, A.; El-Said, K.S.; Salama, A.F. Evaluation of Bacillus aryabhattai B8W22 peroxidase for phenol removal in waste water effluents. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.S.; Goradia, B.; Saxena, A. Bacterial laccase: Recent update on production, properties and industrial applications. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, O.; Moletta, R. Treatment of organic pollution in industrial saline wastewater: A literature review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3671–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Ahmad, S.; Sung, S.; Ni, S.Q. Biotreatment of high-salinity wastewater: Current methods and future directions. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Carvajal, L.C.; Sanz-Martin, J.L.; Barragan-Huerta, B.E. Biodegradation of organic pollutants in saline wastewater by halophilic microorganisms: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 9578–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zeng, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, N.; Xin, J.; Yang, H.; Lei, L.; Khalique, A.; Rajput, D.S.; Pan, K.; et al. Analysis of miRNA Expression in the ileum of broiler chickens during Bacillus licheniformis H2 supplementation against subclinical necrotic enteritis. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, R.; He, N. Production and characterization of a novel bioflocculant from Bacillus licheniformis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2778–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhong, S.; Lei, H.Y.; Chen, R.W.; Yu, Q.; Li, H.L. Production of a novel bioflocculant by Bacillus licheniformis X14 and its application to low temperature drinking water treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3650–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermlim, W.; Prasertsan, P.; Doelle, H. Screening and characterization of bioflocculant produced by isolated Klebsiella sp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 52, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liu, J.; Qiu, H.; Zhao, M.; Zou, W.; Li, S. Microbial synthesis of poly-gamma-glutamic acid: Current progress, challenges, and future perspectives. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 2016, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmschlag, B.; Putri, S.P.; Fukusaki, E.; Blank, L.M. Poly-gamma-glutamic acid production by Bacillus subtilis 168 using glucose as the sole carbon source: A metabolomic analysis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 130, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yun, Y.Q.; Xing, L.; Song, L. Novel bioflocculant produced by salt-tolerant, alkaliphilic strain Oceanobacillus polygoni HG6 and its application in tannery wastewater treatment. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Ji, Z.; Chen, S. Isolation of halotolerant Bacillus licheniformis WX-02 and regulatory effects of sodium chloride on yield and molecular sizes of poly-gamma-glutamic acid. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Ghoshal, A.K. Phenol degradation by Bacillus cereus: Pathway and kinetic modeling. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5501–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, J.; Ding, F.; Shao, C.; Guo, R. Isolation of a novel multiple-heavy metal resistant Lampropedia aestuarii GYF-1 and investigation of its bioremediation potential. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadalin, F.; Vezzi, F.; Policriti, A. GapFiller: A de novo assembly approach to fill the gap within paired reads. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13 (Suppl. S14), S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massouras, A.; Hens, K.; Gubelmann, C.; Uplekar, S.; Decouttere, F.; Rougemont, J.; Cole, S.T.; Deplancke, B. Primer-initiated sequence synthesis to detect and assemble structural variants. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarailo-Graovac, M.; Chen, N. Using RepeatMasker to identify repetitive elements in genomic sequences. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2009, 25, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galperin, M.Y.; Kristensen, D.M.; Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Microbial genome analysis: The COG approach. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairoch, A.; Apweiler, R. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence database and its supplement TrEMBL in 2000. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S.; Sato, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Bono, H.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T.; Brown, G.R.; Maglott, D.R. NCBI Reference Sequences (RefSeq): Current status, new features and genome annotation policy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D130–D135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Carbasse, J.S.; Peinado-Olarte, R.L.; Goker, M. TYGS and LPSN: A database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Stefanic, P.; Miao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Xun, W.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.; Mandic-Mulec, I. Housekeeping gene gyrA, a potential molecular marker for Bacillus ecology study. AMB Express 2022, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chris Felshia, S.; Aswin Karthick, N.; Thilagam, R.; Chandralekha, A.; Raghavarao, K.; Gnanamani, A. Efficacy of free and encapsulated Bacillus lichenformis strain SL10 on degradation of phenol: A comparative study of degradation kinetics. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, A.; Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Cao, M.; He, N. Advanced strategies for metabolic engineering of Bacillus to produce extracellular polymeric substances. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023, 67, 108199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.; Schutz, A.; Brosius, M.; Volker, A.; Volker, U.; Bremer, E. High-salinity-induced iron limitation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achak, M.; Elayadi, F.; Boumya, W. Chemical coagulation/flocculation processes for femoval of phenolic compounds from olive mill wastewater: A comprehensive review. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2019, 16, 59–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahadat, M.; Teng, T.T.; Rafatullah, M.; Shaikh, Z.A.; Sreekrishnan, T.R.; Ali, S.W. Bacterial bioflocculants: A review of recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Ding, P.; Xu, M.J.; Zhang, C.M.; Xing, K.; Qin, S. Biodegradation of phenol by a halotolerant versatile yeast Candida tropicalis SDP-1 in wastewater and soil under high salinity conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, J. Sustained degradation of phenol under extreme conditions by polyurethane-based Bacillus sp. ZWB3. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bing, W.; Hu, T.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Liang, J.; Li, Y. Enhanced biodegradation of phenol by microbial collaboration: Resistance, metabolite utilization, and pH stabilization. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhong, J.; Lei, Q.; Song, H.; Chen, S.F.; Wahla, A.Q.; Bhatt, K.; Chen, S. New roles for Bacillus thuringiensis in the removal of environmental pollutants. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, M.; Sliwakowski, W.; Kowalczyk, P.; Kramkowski, K.; Dobrzynski, J. Bioremediation of heavy metals by the genus Bacillus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.A.; Jabeen, S. Degradation kinetics and pathway of phenol by Pseudomonas and Bacillus species. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2015, 29, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, G.; Boll, M.; Heider, J. Microbial degradation of aromatic compounds—From one strategy to four. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.T.; Feng, M.; Liu, C.L.; Liu, C.Z.; Guo, C. Efficient phenol degradation by laccase immobilized on functional magnetic nanoparticles in fixed bed reactor under high-gradient magnetic field. Eng. Life Sci. 2021, 21, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Deng, Z.; Borham, A.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Bohu, T. Significance of soil siderophore-producing bacteria in evaluation and elevation of crop yield. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, A.; Roy, S.; Bellenger, J.P.; Beauregard, P.B. Iron homeostasis in Bacillus subtilis requires siderophore production and biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02439-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, G.; Wang, L.; Chen, A.; Xie, X.; Huang, X.; Hu, W. Improved production of poly-γ-glutamic acid with low molecular weight under high ferric ion concentration stress in Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 9945a. Process Biochem. 2017, 56, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, Z.; Xia, W.; Chen, Y.; Cao, M.; He, N. Molecular weight control of poly-gamma-glutamic acid reveals novel insights into extracellular polymeric substance synthesis in Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 2024, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovley, D.R.; Lonergan, D.J. Anaerobic oxidation of toluene, phenol, and p-cresol by the dissimilatory iron-reducing organism, GS-15. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1858–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewale, P.; Lang, A.; Huang, F.; Zhu, D.; Sun, J.; Ngadi, M.; Yang, T.C. A novel Bacillus ligniniphilus catechol 2,3-dioxygenase shows unique substrate preference and metal requirement. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, B.; Liu, M.; Liu, M.; Shi, C.; Feng, X.; Fu, Y.; Shi, D.; et al. Phenolic compounds induce ferroptosis-like death by promoting hydroxyl radical generation in the Fenton reaction. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Phenol (mg/L) | 0 | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 | 1200 | 1400 | 1600 | 1800 | 2000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5% NaCl | +++ a | +++ a | +++ a | +++ a | +++ a | +++ a | +++ a | +++ a | +++ a | ++ a | / b |
| 10% NaCl | +++ a | ++ b | +++ b | ++ b | + b | + b | / b | / b | / b | / b | / b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Guo, R.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Shao, C.; Zhou, J.; Ding, F.; Yu, L. Isolation of Bacillus paralichenifromis BL-1 and Its Potential Application in Producing Bioflocculants Using Phenol Saline Wastewater. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16010023
Zhang T, Guo R, Liu F, Zhang L, Li L, Zhang R, Shao C, Zhou J, Ding F, Yu L. Isolation of Bacillus paralichenifromis BL-1 and Its Potential Application in Producing Bioflocculants Using Phenol Saline Wastewater. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tao, Rongkai Guo, Fanshu Liu, Lei Zhang, Linxiao Li, Rongfei Zhang, Chaogang Shao, Junbo Zhou, Fan Ding, and Lan Yu. 2025. "Isolation of Bacillus paralichenifromis BL-1 and Its Potential Application in Producing Bioflocculants Using Phenol Saline Wastewater" Microbiology Research 16, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16010023
APA StyleZhang, T., Guo, R., Liu, F., Zhang, L., Li, L., Zhang, R., Shao, C., Zhou, J., Ding, F., & Yu, L. (2025). Isolation of Bacillus paralichenifromis BL-1 and Its Potential Application in Producing Bioflocculants Using Phenol Saline Wastewater. Microbiology Research, 16(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16010023






