Abstract
Increasing evidence suggests that the gut microbiota, through the “microbiota–gut–brain axis”, can regulate anxiety, mood, and cognitive abilities such as memory and learning processes. Consistently with this, treatments altering the gut microbiota, such as antibiotics and probiotics, may influence brain function and impact behavior. The mechanisms that underlie the interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain have been intensively studied. We aimed to investigate the effects of two probiotic lactobacilli strains, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus 12L and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 8PA3, on behavioral disorders in mice induced by a two-week parenteral treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics. On completion of the treatment, the mice were subjected to behavioral tests, including the open field test (OFT), novel object recognition test (ORT), and T-maze test. Antibiotic-treated mice demonstrated anxiety-related behavior, decreased cognition, and retarded exploratory activity that were ameliorated by the administration of probiotics. As was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), both tested strains produced serotonin and its metabolite 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), as well as dopamine, which was further metabolized into norepinephrine by L. plantarum 8PA3 and epinephrine by L. rhamnosus 12L. Moreover, these lactobacilli were found to harbor catecholamines and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) in their biomass when grown on MRS broth. Additionally, L. plantarum 8PA3 and L. rhamnosus 12L were able to impact oxidative stress via H2O2 production and antioxidant activity, as determined in this study by the ferrous oxidation–xylenol orange (FOX) assay and the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging assay, respectively. The results obtained in this study support the role of probiotics as a promising therapeutic for neurological disorders. However, more investigations are required to confirm the clinical significance of this finding.
Keywords:
antibiotics; probiotics; lactobacilli; mice; gut dysbiosis; microbiota; behavior; neurotransmitters; hydrogen peroxide 1. Introduction
Probiotics, according to the conventional definition, are “live microorganisms which, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host” [1]. Probiotics favorably alter the host microbiota composition, primarily due to the competitive exclusion of pathogens and the promotion of intestinal epithelial barrier function, and they regulate immune function, participate in digestion, produce vitamins, inactivate toxic and mutagenic compounds, exert antioxidant activity, and play an essential role in gut–brain communication [2]. The latter constitutes the “microbiota–gut–brain axis”, a complex multidirectional cross-talk system between the gut microbiota and the nervous, immune, and endocrine systems. It acts as an integral network for the regulation of many physiological systems in the human body through neural, immune, metabolic, and endocrine pathways [3,4,5]. Alterations in the abundance and variety of the intestinal microbiota under different neurological disorders have been the focus of recent research. The pathophysiological role of microbiota disruption has been reported in anxiety, depression, stress susceptibility, autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease [5]. Experimental evidence indicates that dysbiosis can influence memory, exploratory behavior, and cognition [3,6]. An ambitious goal of studies in the field of the “microbiota–gut–brain axis” is to unravel the therapeutic potential of certain microbial taxa against neurological disorders, which gives rise to the concept of psychobiotics, probiotics that influence and benefit the mental health of the host [7]. Over the past decade, there has been growing evidence that probiotic supplementation can favorably modulate the neurophysiology of mice [8,9,10,11]. Several experimental and clinical studies have confirmed the efficiency of probiotic treatment in depression [4,12], autism [13], Alzheimer’s disease [14], and multiple sclerosis [15]. The neuroregulatory activity of probiotics is based on several mechanisms: the production and modulation of neurotransmitters such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), serotonin (5-HT), dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE), glutamate (Glu), histamine, and acetylcholine (ACh) [16]; brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); the vagus and enteric nerves; the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis, and the immune and endocrine systems [4]. Moreover, recent studies have shown that the intestinal microbiota may affect neuronal function through the modulation of the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which plays an important role in the proper functioning of the nervous system [17].
Here, we investigated the effects of two probiotic lactobacilli strains on behavioral disorders in mice induced by parenteral treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics. To determine their possible mechanisms of action, we further investigated their ability to produce H2O2 and neurotransmitters.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Three-week-old (postnatal day (PND) 25–26) male outbred NMRI mice were purchased from the Pushchino Nursery of Laboratory Animals (Pushchino, Russia). Male mice were used to avoid any effects of the estrous cycle and related hormonal changes in female mice. The mice were housed in polypropylene cages (32 × 40 × 18 cm3) under a controlled temperature (22–24 °C) with a 12 h light/dark cycle (lights on at 7:00 a.m.) and had ad libitum access to food and water. The animals were adapted to the laboratory conditions for 2 weeks before the onset of the experiment. This study was carried out in accordance with EU Directive 2010/63/EU for animal experiments and approved by the Local Ethics Committee of Kazan Federal University (Protocol No. 33, 25 November 2021).
2.2. Probiotics
The probiotic used was a 1:1 (v/v) mixture of two lactobacilli strains: Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 8PA3, isolated from the probiotic preparation “Lactobacterin dry” (Biomed, Perm, Russia) [18], and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus 12L, purchased from the Russian National Collection of Industrial Microorganisms (VKPM B-8238). The bacteria were cultured in De Man, Rogosa, Sharpe (MRS) broth [19] under microaerophilic conditions at 37 °C for 24 h; harvested by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 10 min; washed three times with saline; and reconstituted in saline solution to a final concentration of 4 × 106 CFU/mL.
2.3. Experimental Design
The animals were weighed and subjected to a series of behavioral tests at baseline. Then, the mice were randomly divided into three groups with five mice per group. AB received injections of the antibiotic cocktail; AB + LB received injections of the antibiotic cocktail and an oral gavage of probiotics; CON received injections and an oral gavage of saline. Intraperitoneal injections of antibiotics or saline (200 μL) and the oral gavage of probiotics (1 mL) were administered every second day for two weeks. Antibiotics were purchased from PAO Kraspharma (Krasnoyarsk, Russia) and OAO Sintez (Kurgan, Russia). The antibiotic cocktail was prepared fresh in saline solution, and the dose administered was 2 mg ampicillin, 0.2 mg amphotericin-B, 2 mg neomycin, 4 mg vancomycin, and 1 mg metronidazole [20]. Over the course of the experiments, the body weights of the animals were recorded every second day. Behavioral tests, except for the estimation of the integral anxiety score (IAS), were applied on the 13th day of the experiment to obtain data from 2/3 of the group (n = 4). During the experimental procedure, the mice’s feces was collected every second day and the fecal microbiota was assessed by the plate count method.
2.4. Fecal Microbiota Analysis
First, 5 g of freshly collected mouse feces was thoroughly washed with 10 mL of sterile saline for 30 min at 37 °C and 180–200 rpm. The resulting suspension was serially diluted and plated onto different nutrient agars in Petri dishes as follows. Nonselective nutrient agar for the cultivation of “BTN” microorganisms (obtained from “Biotechnovacia”, Moscow, Russia) was used as plate count agar to assess the total microbial growth. For the detection of Lactobacillus spp., MRS agar [19] was implemented. These plates were incubated in anaerobic conditions (Anaerogas GasPak, NIKI MLT, St. Petersburg, Russia) at 37 °C for 72 h. Bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae were inoculated onto Endo agar and incubated aerobically at 37 °C for 24 h. The bacterial colonies were counted and identified based on their morphological properties. For a statistical analysis, we performed at least three seedings of five fecal samples harvested per caged group of mice.
2.5. Behavioral Testing
2.5.1. Open Field Test (OFT) and Integral Anxiety Score (IAS)
The OFT was used to measure general locomotor activity, anxiety, and exploration. Mice were placed in the center of a circular arena (60 cm (d) × 36 cm (h)) with 13 through holes (diameter 10 mm) evenly spaced across the area of the arena, which was divided into squares (10 × 10 cm2) and equipped with a video system (Open Science, Moscow, Russia). The animals were placed into the apparatus for 3 min, and the square crossings, rearings, head-dippings, grooming and defecation episodes, and time spent in the center square were recorded [21]. The arena was cleaned with 70% ethanol after each trial, and the next animal was placed in the apparatus only after the ethanol had completely evaporated. The study was carried out in a specially equipped, well-ventilated room under standard conditions with uniform lighting and no noise.
The dynamics of the anxiety-phobic state of mice during the period of treatment were evaluated by the integral anxiety score (IAS), determined on the 3rd, 5th, 7th, 9th, 11th, and 13th days of the experiment by assessing the reaction of each animal placed in the center of the open field to the slowly approaching hand of the experimenter. Avoidance (moving back from the experimenter’s hand), vocalization, freezing (when the animal was immobile in a strained pose), and the flattening of the ears were recorded. The IAS was calculated as follows: 0, when there was no reaction; 1, when a reaction appeared after stroking (contact with the experimenter’s hand); 2, when the reaction was preserved after the removal of the hand; and 3, when a spontaneous reaction was detected. The test was carried out in triplicate, and the average of the three approaches was calculated. A larger score corresponded to a higher anxiety-phobic level [22].
2.5.2. T-Maze
The T-maze was used to assess the spatial working memory and cognitive abilities of the mice. The T-maze, a T-shaped enclosed apparatus in the form of a T placed horizontally, was composed of non-reflective, odor-resistant material and equipped with a video-tracking system (Open Science, Moscow, Russia). The animals started from the base of the T and were allowed to choose one of the two lateral goal arms (left and right) and explore it for 30 s. Then, after the mouse had entered a goal arm, it was closed for 30 s. Each mouse was tested in three 3 min trials with 10 min breaks. An alternation was considered when the rodent tended to choose the arm not visited before, reflecting its memory of the first choice, and was scored as 33.3% [23,24].
2.5.3. Novel Object Recognition Test (ORT)
The ORT was applied to evaluate attention, learning, and memory retention in the mice. The procedure is based on the natural proclivity of rodents to explore novelty. The mice were allowed to explore two identical objects (wooden cubes with 5 cm sides) for 15 min. For the testing trial, one of the previously used objects was replaced with a novel one (100 mL glass jar). The duration of exploration of each object was scored by trained observers blinded to the experimental treatments. The ORT score was calculated as (time spent exploring the novel object/time spent exploring a familiar object) × 100% [25].
2.6. Study of Physiological Traits of Probiotics
2.6.1. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
Antibiotic susceptibility was assessed by the disk diffusion method, as described earlier [26]. In brief, overnight cultures of the tested lactobacilli strains were diluted in saline to obtain turbidity equivalent to McFarland scale 0.5, and aliquots were pour-plated on MRS agar plates. Whatman antibiotic assay disks (diameter 6 mm) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) were placed on the surfaces of the inoculated plates and loaded with stock antibiotic solutions to give the following concentrations (µg/disk): amphotericin-B—40; metronidazole—5; neomycin—30. Ampicillin and vancomycin disks were purchased from the Scientific Research Centre of Pharmacotherapy (St. Petersburg, Russia). After 48 h incubation in anaerobic conditions (Anaerogas GasPak, NIKI MLT, St. Petersburg, Russia) at 37 °C, the inhibition halos were measured in mm (means ± SD of 3 trials) and interpreted as susceptible (S), moderately susceptible (MS), or resistant (R) according to [26].
2.6.2. Determination of H2O2 Production
Overnight cultures of the tested lactobacilli strains were harvested by centrifugation; bacterial cells were washed twice with PBS and resuspended in 500 µL Lysogeny broth (LB). After 4 h incubation with shaking at 200 rpm at 37 °C, the suspension was centrifuged for 3 min at 7000 rpm, and the H2O2 concentration was measured in the resulting supernatant with the ferrous oxidation–xylenol orange (FOX) assay. The FOX assay relies on the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+ in acidic conditions. The assay solution containing 250 µM ferrous ammonium sulfate, 100 mM sorbitol, 125 µM xylenol orange, and 25 mM H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) and the supernatant were mixed 1:10 (v/v) in a 96-well microplate. The reaction mixtures were incubated at room temperature for 30 min. The absorbance was measured at 595 nm by a microplate absorbance spectrophotometer, the xMarkTM (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA). The H2O2 content was calculated from a standard curve prepared using a series of diluted solutions of commercial 3% H2O2 [27].
2.6.3. Assessment of Antioxidant Activity
The antioxidant activity of the tested lactobacilli strains was determined using the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging assay [28], with some modifications. Bacteria were cultured in MRS broth at 37 °C for 24 h and then harvested by centrifugation. Then, 0.1 mM DPPH (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) solution prepared in ethanol and the resulting supernatant of each strain were mixed 1:1 (v/v) in a 96-well microplate. After incubation at 25 °C for 30 min in a dark environment, the absorbance at 517 nm was measured using a microplate absorbance spectrophotometer, the xMarkTM (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA). The DPPH scavenging activity was calculated as (%) = [1 − (Asample)/Acontrol] × 100%, where Asample is the A at 517 nm of the sample after incubation and Acontrol is the absorbance of a 0.1 mM DPPH solution in ethanol.
2.6.4. Measurement of Bacterial Neurotransmitters
The content of monoamines and their metabolites was determined in culture fluids and in cells. For this, bacteria were grown and separated from the medium as described above. Culture fluids and cell suspensions in saline were filtered with membrane filters (0.1 μm, Merk-Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA), frozen, and stored at −5–18 °C until chromatographic studies for no longer than 1 month. The content of neurotransmitters was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a LC-304E chromatographic apparatus (BAC, West Lafayette, IN, USA), followed by fluorimetric detection. To 400 μL of each solution, 50 μL of 1.0 N HClO4 and 50 μL of 3,4-dioxibenzylamine (DOBA) solution (5.0 nmol/mL in 0.1 N HClO4) were added as an internal standard. The samples were centrifuged at 15,000 g for 10 min. Then, 20 μL of the supernatant was applied to the analytical column by direct injection. Norepinephrine (NE), 3,4-dioxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAA), dopamine (DA), homovanilinic acid (GVA), 5-oxyindoleacetic acid (5-OIAA), and serotonin or 5-hydroxytyramine (5-HT) were divided in a reverse-phase YMC-Triart C18 column, 3 × 150 mm2, particle size 3 μm, using 0.1 M citrate-phosphate buffer containing 0.3 mM sodium octanesulfonate, 0.1 mM EDTA, and 10% acetonitrile as the mobile phase (pH 2.9), on an isocratic chromatograph using a PM-80 pump and an LC-4B electrochemical detector (Bioanalytical Systems, West Lafayette, IN, USA). Monoamines and their metabolites were detected on a glass carbon electrode at a potential of +0.85 V against an Ag/AgCl reference electrode. The flow rate of the mobile phase was 0.4 mL/min. The registration of the samples was carried out using the MULTICHROM 1.5 software (AMPERSEND).
All reagents used for analysis were of analytical grade. To calibrate the chromatograph, mixtures of the analyzed substances were used at a concentration of 500 pmol/mL (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The concentration of monoamines in the experimental samples was calculated by the “internal standard” method, based on the ratio of the peak area in the standard mixture and in the sample. The results obtained were statistically processed as the averages of 3 to 5 independent measurements. The experimental data scatter was the average of the absolute values of the deviation of the data points from the average and did not exceed 5%.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The normality of the sample data was evaluated with the Shapiro–Wilk test (sample size less than 25) for equal variance using the F-test and Origin Pro software 2015 (8.5) (OriginLab Corp., Northampton, MA, USA). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM, unless otherwise specified. Statistical significance between medians was calculated using the nonparametric ANOVA Kruskal–Wallis test and Mann–Whitney test in Origin Pro 2015 (8.5) (OriginLab Corp., Northampton, MA, USA). The chi-square test was used to analyze the mortality of the mice (p < 0.05). The Wilcoxon signed rank test (pw) for related paired data was used to compare the resulting meanings with the baseline. Differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05; n indicates the number of animals.
3. Results
3.1. Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Antibiotics and Lactobacilli
To examine the effects of antibiotics and probiotics on the gut microbiota, the bacterial community from the fecal samples of each experimental group was analyzed (Table 1). During the experimental procedure, the total microbial abundance and lactose-negative Enterobacteriaceae increased, while lactose-positive Enterobacteriaceae, in contrast, decreased in all groups. It is likely that these fecal microbiota dynamics reflect age-related changes in the murine gut microbiota [29,30]. However, upon completion of the treatment, the overall bacterial density and lactose-positive Enterobacteria were lower and lactose-negative Enterobacteria were higher in the AB group as compared to the other experimental groups, but these differences were not statistically significant. Surprisingly, in the AB + LB group, the lactobacilli population was not affected by the oral administration of lactobacilli-based probiotics and was as abundant as in the other experimental groups. This may have resulted from the antibiotic resistance of the probiotic strains [31,32]. To test this prediction, we studied the resistance of two probiotic strains to the antimicrobials used in this study using the disk diffusion method. Ampicillin inhibited both bacterial strains used in this study; moreover, L. plantarum 8PA3 demonstrated sensitivity to neomycin and vancomycin (Table 2).

Table 1.
Fecal microbiota dynamics in test groups of mice (lg CFU/g, mean ± SD).

Table 2.
Physiological characteristics of lactobacilli strains: antibiotic resistance, H2O2 production, and antioxidant activity.
3.2. Probiotics Ameliorated Antibiotics’ Toxicity and Antibiotic-Induced Mortality
Significant mortality was found in the AB group compared to the other experimental groups (p < 0.001). The survival rate in the antibiotic-treated AB group was 16.7%, while, in the AB + LB group treated with both antibiotics and probiotics, it was 83.3% and identical to that of the control group (Figure 1A). Thus, the probiotics reversed the mortality induced by the antibiotics. The injury and subsequent death of one of the six animals in the CON and AB + LB groups could be explained by the aggression and the establishment of hierarchical connections during juvenile development [33]. The input data in the behavioral tests of these dead animals were not taken into account.
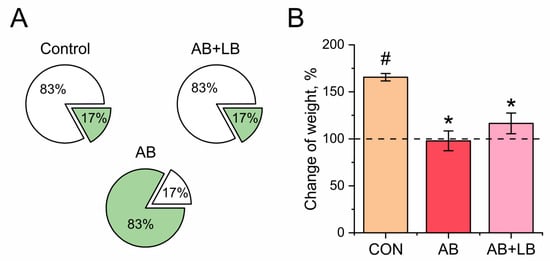
Figure 1.
Effects of treatment with antibiotics (AB) and antibiotics together with probiotics (AB + LB) on mortality (A) and weight (B) of mice. (A) The white part is the percentage of surviving animals and the green part is the percentage of dead animals after two weeks of treatment. (B) The initial weight of the mice before treatment was assumed to be 100%. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM; n = 5; * p < 0.05 compared to the control untreated group, # p < 0.05 compared to the initial values.
In the control group, we registered a significant weight gain during the period of the experiment (165.0 ± 1.3%, p = 0.007). The AB + LB (116.5 ± 11.0%, p = 0.655) and AB (97.8 ± 10.0%, p = 0.494) groups showed a similar weight gain, which did not notably exceed the baseline state but was significantly lower compared to the control group (Figure 1B).
3.3. Probiotics Ameliorated Antibiotic-Induced Changes in Mouse Behavior
It is known that exposure to antibiotics leading to an altered gut microbiota can induce changes in behavior reflective of increased depression and anxiety [20,34]. To study the ability of probiotics to correct this neuropsychological dysfunction, after two weeks of treatment with antibiotics alone or combined with probiotics, the mice were subjected to a panel of behavioral tests. Figure 2 shows the anxiety-related behavior of the mice. In the control group, the integral anxiety score (IAS) was low throughout the experiment, indicating the non-anxious mood of the animals (Figure 2A). At the beginning of the treatment (day 3), the animals from both experimental groups demonstrated anxiety-related behavior in line with their enhanced scores (AB: 2.6 ± 0.6 points (p = 0.048); AB + LB: 1.5 ± 0.5 points (p = 0.140)) compared to the baseline state (0.50 ± 0.34 points). After 5 days, in the AB + LB group, the IAS decreased to the basal level (1.0 ± 0.5 point: p = 0.390 against the baseline state and p = 0.373 against the control) and was preserved throughout the experiment. In the AB group, the anxiety also tended to decrease on days 5 and 7 (1.0 ± 0.1 point: p = 0.231 against the baseline state and p = 0.009 against the control) but never recovered to the baseline state and remained increased (1.0 ± 0.1 point, p = 0.016) above the control level (Figure 2A).
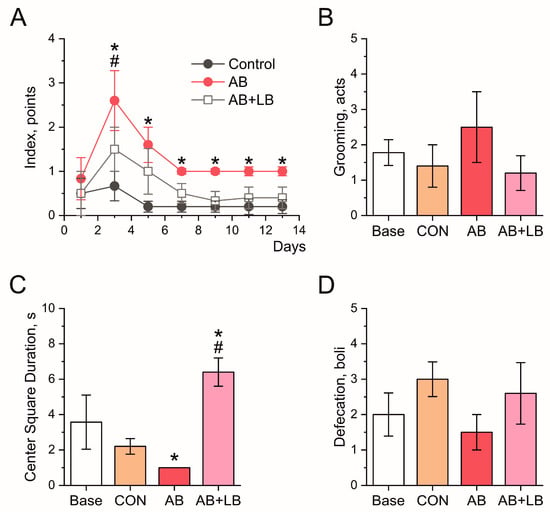
Figure 2.
Effects of treatment with antibiotics (AB) and antibiotics together with probiotics (AB + LB) on anxiety levels of mice. (A) The integral anxiety score of the mice during the two-week treatment. In (B–D), the parameters of the anxiety levels of the mice are given for the open field test upon the completion of the treatment. (B) The frequency of grooming activity in the mice. (C) The time spent by the mice in the center square of the arena. (D) The number of fecal boli produced by the mice. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM; n = 5. * p < 0.05 compared to the control untreated group, # p < 0.05 compared to the initial values.
In the open field test, the quantifiable parameters used as a measure of anxiety included grooming behaviors, the time spent in the center of the open field, and the number of fecal boli produced by the animals. The mice in the AB group tended to demonstrate an increased level of grooming and a decreased level of defecation, indicative of anxiety-like behavior, although these findings did not quite reach statistical significance. The administration of antibiotics together with probiotics did not affect their anxiety, as indicated by the equal frequency of grooming activity and number of defecation boli compared to the control group (Figure 2B,D). However, the time spent in the center of the open field decreased in the AB group to 1 ± 0 s as compared with the control group (2.2 ± 0.4 s, p = 0.031). We observed that the AB + LB mice spent longer periods of time than all other tested animals in the stressful, highly lit central square of the arena (6.4 ± 0.8 s, p = 0.028), indicating their anxiolytic and antidepressive behavior (Figure 2C).
Locomotor activity like square crossings (horizontal activity) and rearings (vertical activity) was measured in the open field test and were considered aspects of exploratory behavior (Figure 3). Upon the completion of the treatment, in the AB group, both characteristics of locomotor activity remained at the same level as that prior to the experiment (94 ± 16 square crossings, p = 0.186; 7.5 ± 2.1 rearings, p = 0.638), while, in the control (116 ± 12 square crossings, 16 ± 9 rearings) and AB + LB groups, they increased (114 ± 16 square crossings, p = 0.180; 18 ± 4 rearings, p = 0.290) compared with the baseline state (71 ± 4 square crossings, 7.9 ± 1.0 rearings). Figure 3C shows the total locomotor activity of the mice, which was calculated as the sum of the horizontal activity (square crossings) and vertical activity (number of rearings) measured in the open field test. Hence, the antibiotic treatment disrupted the age-specific development of locomotory activity in the mice, which could be restored by the probiotics.
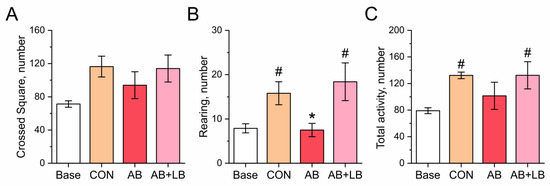
Figure 3.
Effects of treatment with antibiotics (AB) and antibiotics together with probiotics (AB + LB) on locomotory activity of mice, measured in open field test upon completion of treatment. (A) The number of crossed squares, i.e., horizontal activity. (B) The number of rearings, i.e., vertical activity. (C) The total locomotor activity of the mice, calculated as the sum of the horizontal activity (square crossings) and vertical activity (number of rearings). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM; n = 5; * p < 0.05 compared to the control untreated group, # p < 0.05 compared to the initial values.
Figure 4 shows the cognitive function of the mice. The amount of time that the animals spent exploring the holes in the open field by dipping their noses into the holes was quantified as a measure of their willingness to examine the novel environment. As seen from Figure 4A, the number of head dips did not change in the AB group (3.5 ± 1.5, p = 0.581) and increased significantly in the control (7.8 ± 2.2, p = 0.148, pw = 0.264) and AB + LB (7.8 ± 1.7, p = 0.151, pw = 0.500) groups but exhibited no statistical significance as compared to the amount prior to the experiment (3.7 ± 1.3).
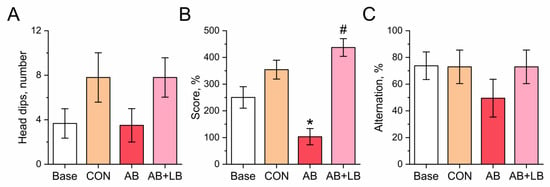
Figure 4.
Effects of treatment with antibiotics (AB) and antibiotics together with probiotics (AB + LB) on cognitive function of mice, measured upon completion of treatment. (A) Head dips. (B) Novel object recognition (NOR) score. (C) Percentage of alternation in the T-maze. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM; n = 5; * p < 0.05 compared to the initial values, # p < 0.05 compared to the control untreated group.
The novel object recognition test (ORT) demonstrated that the levels of cognition tended to increase with age in the control and AB + LB groups. Upon completion of the treatment, the results in the novel ORT in the AB group (103 ± 30%) were significantly decreased compared with the control mice (354 ± 35%, p = 0.019), while the level of cognition in the AB + LB group (437 ± 33%, p = 0.144) was similar to the latter (Figure 4B). No statistical differences in memory retention were found among the tested groups in the T-maze (Figure 4C).
Thus, the antibiotic-treated mice had signs of increased anxiety and decreased cognition and demonstrated retarded exploratory activity, which were ameliorated by the administration of probiotics.
3.4. Lactobacilli’s Potential to Modulate Neurotransmitter Levels and Oxidative Stress
Figure 5 presents the levels of neurotransmitters mediated by the two lactobacilli strains. In the MRS broth used for the cultivation of the bacteria, we detected significant amounts of DOPA, noradrenaline, adrenaline, dopamine, DOPAC, serotonin, and 5-HIAA, which might have originated from the yeast extract [35]. The lactobacilli’s ability to absorb the neurotransmitters from the nutrient medium was assessed as the difference between its amount in the pure MRS broth and that in the 24 h culture medium. Negative values indicate the absorbance of the neurotransmitter from the medium and, in some cases, its further transubstantiation into the other neurotransmitters. Positive values denote the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter by lactobacilli. L. rhamnosus 12L showed the ability to synthesize DOPA, while L. plantarum 8PA3 accumulated it from the growth medium. In both strains, DOPA was further oxidized to dopamine, but the pathways of its oxidation into HVA were not well developed. L. rhamnosus 12L further converted dopamine into adrenaline, while L. plantarum 8PA3 converted it into noradrenaline. Both tested lactobacilli strains were able to synthesize serotonin and oxidize it to 5-HIAA.
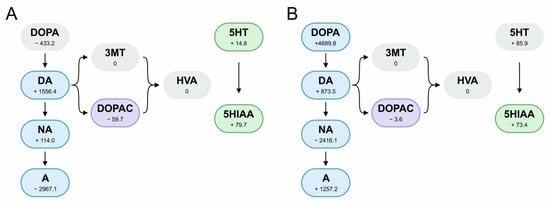
Figure 5.
Production and processing of neurotransmitters by L. plantarum 8PA3 (A) and L. rhamnosus 12L (B). Numbers indicate the amount produced during growth in MRS broth (pmol/mL). Negative values indicate an inability to synthesize the neurotransmitter and absorption from the nutrient medium. Frames indicate the secretion of the neurotransmitter into the saline.
The lactobacilli cultures grown in MRS broth were washed and resuspended in saline. In line with the levels of the neurotransmitters in the saline, L. rhamnosus 12L was able to produce DOPA, dopamine, noradrenaline, adrenaline, DOPAC, and 5-HIAA. In the saline solution with L. plantarum 8PA3, these neurotransmitters were also released, with the exception of serotonin instead of DOPA (Figure 5).
Both tested lactobacilli strains were able to produce H2O2, as was detected in the FOX assays, and demonstrated antioxidant activity since their cell-free supernatants were able to scavenge DPPH free radicals (Table 2). While H2O2 production can contribute to the antagonistic activity of the producing strains [36], the radical scavenging activity is likely to protect them from oxygen radical injury.
4. Discussion
Antibiotics have revolutionized the human fight against many deadly and infectious diseases. However, they may also exert negative effects on the body, like toxicity and allergies. Among the unfavorable effects of antibiotic treatment, the most common is dysbiosis, i.e., the disruption of the normal microbiota’s homeostasis [37]. Probiotics normalize the microbiota of the body and are therefore often used together or immediately after antibiotic therapy to reduce its negative effects on the normal microbiota [38]. The nervous system responds to intestinal dysbiosis with behavioral disorder, in accordance with the “microbiota–gut–brain axis” [39]. It has been shown that exposure to antibiotics can provoke anxiety- and depression-like behavior and impair sociability, social novelty preferences, recognition memory, and spatial cognition in rodents [34]. There are still a number of discrepancies in the current state of knowledge regarding the influence of antibiotic-induced dysbiosis on brain function and behavior, apparently due to the large variations in the antibiotics used, the administration mode, the age of the animals, and the behavioral tests applied. In this study, the parenteral administration of the cocktail of antibiotics induced high mortality, inappetence, and weight loss in the mice (Figure 1). Moreover, the antibiotic-treated mice tended to demonstrate increased anxiety and decreased cognition (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4). Surprisingly, the simultaneous administration of probiotics reversed the negative consequences of the antibiotic treatment, not only regarding behavioral disorders but also mortality and general toxicity (Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4).
In order to identify the mechanism by which lactobacilli exert their impressive effects on antibiotic-treated mice, we analyzed the changes in the mouse fecal microbiota during the experiment. A cocktail of broad-spectrum antibiotics consisting of ampicillin, amphotericin-B, neomycin, vancomycin, and metronidazole was chosen based on a previous report that this combination was able to deplete the gut microbiota in adolescent mice [20]. Amphotericin-B is an antifungal medication; metronidazole is highly active against anaerobic microorganisms, including bacteria and protozoa; ampicillin and vancomycin usually kill Gram-positive bacteria; and neomycin is cytotoxic to both Gram-positive and Gram-negative aerobic bacteria [20,40]. However, under treatment with this antibiotic cocktail, the fecal microbiota in the AB group demonstrated only a slight difference in the ratio of lactose-positive/-negative Enterobacteria compared with the control and AB + LB groups. The other parameters of the intestinal microbiota in all three groups were coequal (Table 1).
It is known that dysbiosis is characterized by a decrease in Lactobacillus spp. in the gut [41,42], which may originate from their massive discharge in the feces or death under antibiotics [43]. L. plantarum 8PA3 was shown to be sensitive to ampicillin, neomycin, and vancomycin, while L. rhamnosus 12L demonstrated susceptibility only to ampicillin among the antibiotics used in this study (Table 2). The administration of antibiotics alone (AB group) or in combination with probiotics (AB + LB group) had no effect on the content of lactobacilli in the murine feces. Similar to our findings, Beck et al. showed that among three groups of mice treated with different Lactobacillus strains, only one group revealed a significant increase in the Lactobacillaceae population [44]. Apparently, the abundance of lactobacilli in the fecal microbiota in all three groups resulted from the low selectivity of MRS agar, a medium that, although considered selective, is able to support the growth of many other lactic acid bacteria [45].
Thus, we demonstrated that the parenteral administration of antibiotics induced certain changes in the microbiota of the mice, the limited scale of which does not correspond to the significant disturbances in nervous activity and the drastic decrease in the survival of such rodents. When administered parenterally, antibiotics may exert a neurotoxic effect directly, rather than through the disruption of the intestinal microbiota. Changes in body weight, a global vitality marker, also suggest a direct effect of circulating antibiotics on the brain. Thus, cognitive and behavioral impairments represent a systemic antibiotic response rather than a consequence of gut dysbiosis. More surprising is the observed beneficial effect of probiotics in this case. The results of the disk diffusion method suggest that both lactobacilli strains did not survive the ampicillin treatment (Table 2). According to the concept of postbiotics, bacteria-derived cell components and metabolites can generate beneficial host responses and specifically affect the nervous system [46,47]. Postbiotics can act in many ways, and, currently, we can only speculate regarding how L. plantarum 8PA3 and L. rhamnosus 12L improved both the nervous function and general survival of the mice.
The gut microbiota can interact with the central nervous system via the modulation of neurotransmitters such as GABA, glutamate (Glu), serotonin (5-HT), DA, NE, histamine, and acetylcholine (ACh). Several studies have demonstrated their fundamental roles in the regulation of the brain and cognitive processes [48]. Lactobacillus spp. are known to produce multiple neurotransmitters in a species-dependent manner in vitro [4,49]. Herein, we also detected the ability of the two lactobacilli strains to modulate the levels of neurotransmitters, especially catecholamines, in vitro. Both tested strains produced DA, which is a precursor for other catecholamines like norepinephrine and epinephrine. Moreover, DA is involved in motor control and reward-motivated behavior [48]. L. plantarum 8PA3 was shown to further metabolize DA into norepinephrine, while L. rhamnosus 12L produced predominantly epinephrine. In the central nervous system, norepinephrine induces arousal and alertness, increases aggression and anxiety, and plays a role in cognitive functions, like memory, learning, and attention. Epinephrine functions in the fight-or-flight response, primarily by increasing the cardiac output and blood glucose level [16,48]. The synthesis of epinephrine is a rare property in bacteria and has not been shown in Lactobacillus before. Serotonin is involved in the regulation of appetite; sleep; mood; cognition, including learning and memory; and numerous physiological processes [48]. Both tested Lactobacillus strains produced serotonin and its metabolite, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), during growth in MRS medium and secreted them into the saline solution (Figure 5).
The oxidative balance is an important prerequisite for the normal and proper functioning of the central nervous system. Along with the “microbiota–gut–brain axis”, intestinal dysbiosis can lead to oxidative stress, which is a key factor in the pathogenesis of many neurodegenerative disorders [50]. Growing evidence suggests that H2O2, a reactive oxygen species (ROS), may act as a neuromodulator in the brain [51,52]. It has been documented that H2O2 is involved in intracellular signaling and induces neuronal loss in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases [53]. Instead, H2O2, generated by Limosilactobacillus reuteri, reduces the plasma levels of the depression-associated metabolite kynurenine (KYN) by inhibiting the expression of the enzyme IDO1, which usually converts tryptophan to KYN [54]. In this study, we demonstrated that L. plantarum 8PA3 and L. rhamnosus 12L were able to produce H2O2, as detected in the FOX assay (Table 2). H2O2-producing lactobacilli (Lactobacillus johnsonii, L. jensenii, L. crispatus, L. gasseri, and L. acidophilus) are typical of the vaginal microbiota, where the production of H2O2 is considered to be a non-specific antimicrobial defense mechanism [55,56]. According to the literature, the ability to synthesize H2O2 is a rare property for L. plantarum and L. rhamnosus, although the mechanism of H2O2 generation via the transformation of oxygen by flavoprotein oxidase in the absence of catalase does not counter the physiology of these taxa [57]. The potential of L. plantarum 8PA3 and L. rhamnosus 12L to impact the balance of oxidants and antioxidants and thus modulate the host’s central nervous system is also based on their antioxidant activity (Table 2). Oxidative stress is considered to be associated with anxiety, cognitive disorders, motor deficits, hippocampal neuronal damage, and many other neurological disorders [11,50].
Thus, our findings demonstrate that probiotic supplementation with L. plantarum 8PA3 and L. rhamnosus 12L had favorable effects on the cognitive and behavioral functions impaired in response to the antibiotic treatment. An important limitation of this study is the limited number of mice included in each group. Secondly, it is known that the probiotic properties of lactobacilli are strain-specific [58], while the effects of antibiotics are dependent on the class, dose, route, and duration of administration [34]. Therefore, the results should be interpreted with caution and cannot be extrapolated to other combinations of probiotics and antibiotics. We elucidated several properties of L. plantarum 8PA3 and L. rhamnosus 12L that may potentially impact the nervous system, namely the production and modulation of neurotransmitters, the biosynthesis of H2O2, and antioxidant activity. However, our in vitro studies did not consider all of the biochemical and physiological variables involved in the host–microbe interactions within the host organism. Additional animal studies analyzing gene expression and sensitive biochemical in vivo assays are needed to establish the specific mechanisms driven by probiotics that mediate their neuroprotective and anxiolytic effects. Considering the probable role of probiotics as a promising therapeutic for neurological disorders, further investigations should confirm their clinical significance.
5. Conclusions
Our study indicated that the two-week parenteral administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics induced anxiety-related behavior and a reduction in locomotor activity in mice, as assessed with the open field test. As was demonstrated in the novel object recognition and open field tests, cognition and exploratory activity were also diminished in antibiotic-treated mice. We used a classical culture method to assess the fecal microbiota and found that the only change caused by antibiotic administration was an insignificant increase in lactose-negative Enterobacteria and a decrease in lactose-positive Enterobacteria, as compared with untreated control mice and mice treated with antibiotics in combination with a mixture of two probiotic lactobacilli strains, L. plantarum 8PA3 and L. rhamnosus 12L. In addition, in the antibiotic-treated group, we detected high mortality and no weight gain, suggesting that there might have been a systemic antibiotic response, rather than antibiotic-induced gut dysbiosis, that caused the cognitive and behavioral impairments in the mice. Surprisingly, the administration of probiotics together with the antibiotics reversed the negative consequences of the antibiotic treatment regarding behavioral and cognitive disturbances, as well as the mortality and general toxicity, in the mice. To elucidate the mechanisms by which lactobacilli exert their beneficial effects on the nervous system, we studied their ability to modulate the levels of neurotransmitters. As was determined by HPLC, both tested strains produced serotonin and its metabolite, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), as well as dopamine (DA), which was further metabolized into norepinephrine (NE) by L. plantarum 8PA3 and epinephrine by L. rhamnosus 12L. Moreover, these lactobacilli were found to harbor catecholamines and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) in their biomass when grown on MRS broth. Additionally, L. plantarum 8PA3 and L. rhamnosus 12L were able to impact oxidative stress via H2O2 production and antioxidant activity, as determined in this study by the FOX and DPPH assays, respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.Y., O.Y., Y.N. and G.S.; methodology, D.Y., O.Y. and V.K.; formal analysis, D.Y., O.Y. and G.E.-R.; investigation, A.A. (Anastasia Alexandrova), V.N., A.A. (Alisa Arslanova) and V.K.; data curation, D.Y., O.Y. and Y.N.; visualization, I.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A. (Anastasia Alexandrova), V.N., A.A. (Alisa Arslanova), I.S. and V.K.; writing—review and editing, D.Y., O.Y., Y.N., G.E.-R. and G.S.; supervision, G.S.; project administration, G.S. and D.Y.; funding acquisition, D.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation (grant No. 22-16-00040).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was carried out in accordance with EU Directive 2010/63/EU for animal experiments and approved by the Local Ethics Committee of Kazan Federal University (Protocol No. 33, 25 November 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Acknowledgments
The work was performed with the framework of the Kazan Federal University Strategic Academic Leadership Program (PRIORITY-2030).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation. Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria. 2001. Available online: http://www.fao.org/tempref/docrep/fao/meeting/009/y6398e.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2024).
- Latif, A.; Shehzad, A.; Niazi, S.; Zahid, A.; Ashraf, W.; Iqbal, M.W.; Rehman, A.; Riaz, T.; Aadil, R.M.; Khan, I.M.; et al. Probiotics: Mechanism of action, health benefits and their application in food industries. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1216674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.B.; Keating, D.J.; Young, R.L.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J.; Wesselingh, S. From gut dysbiosis to altered brain function and mental illness: Mechanisms and pathways. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.J.; Tong, T.; Chew, J.; Lim, W.L. Antidepressive mechanisms of probiotics and their therapeutic potential. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Arbab, S.; Tian, Y.; Liu, C.Q.; Chen, Y.; Qijie, L.; Khan, M.I.U.; Hassan, I.U.; Li, K. The gut microbiota-brain axis in neurological disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1225875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, E.; Guzzardi, M.A.; Tripodi, M.; Panetta, D.; Selma-Royo, M.; Zega, A.; Telleschi, M.; Collado, M.C.; Iozzo, P. Microbiota signatures relating to reduced memory and exploratory behaviour in the offspring of overweight mothers in a murine model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Psychobiotics: A novel class of psychotropic. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, M.; Lalonde, R.; Violle, N.; Javelot, H.; Desor, D.; Nejdi, A.; Bisson, J.F.; Rougeot, C.; Pichelin, M.; Cazaubiel, M.; et al. Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohland, C.L.; Kish, L.; Bell, H.; Thiesen, A.; Hotte, N.; Pankiv, E.; Madsen, K.L. Effects of Lactobacillus helveticus on murine behavior are dependent on diet and genotype and correlate with alterations in the gut microbiome. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emge, J.R.; Huynh, K.; Miller, E.N.; Kaur, M.; Reardon, C.; Barrett, K.E.; Gareau, M.G. Modulation of the microbiota-gut-brain axis by probiotics in a murine model of inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G989–G998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanova, A.; Tarasova, A.; Alexandrova, A.; Novoselova, V.; Shaidullov, I.; Khusnutdinova, D.; Grigoryeva, T.; Yarullina, D.; Yakovleva, O.; Sitdikova, G. Protective effects of probiotics on cognitive and motor functions, anxiety level, visceral sensitivity, oxidative stress and microbiota in mice with antibiotic-induced dysbiosis. Life 2021, 11, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkasheh, G.; Kashani-Poor, Z.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Jafari, P.; Akbari, H.; Taghizadeh, M.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Asemi, Z.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic administration in patients with major depressive disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrition 2016, 32, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, E. A review of probiotics in the treatment of autism spectrum disorders: Perspectives from the gut-brain axis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1123462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, E.; Asemi, Z.; Daneshvar Kakhaki, R.; Bahmani, F.; Kouchaki, E.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Hamidi, G.A.; Salami, M. Effect of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function and metabolic status in Alzheimer’s disease: A randomized, double-blind and controlled trial. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchaki, E.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Salami, M.; Bahmani, F.; Daneshvar Kakhaki, R.; Akbari, E.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Jafari, P.; Asemi, Z. Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic supplementation in patients with multiple sclerosis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleskin, A.V.; El’-Registan, G.I.; Shenderov, B.A. Role of neuromediators in the functioning of the human microbiota: “Business talks” among microorganisms and the microbiota-host dialogue. Mikrobiologiia 2016, 85, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandilya, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar Jha, N.; Kumar Kesari, K.; Ruokolainen, J. Interplay of gut microbiota and oxidative stress: Perspective on neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 38, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsapieva, A.; Duplik, N.; Suvorov, A. Structure of plantaricin locus of Lactobacillus plantarum 8P-A3. Benef. Microbes 2011, 2, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Man, J.C.; Rogosa, M.; Sharpe, M.T. A medium for the cultivation of lactobacilli. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1960, 23, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbonnet, L.; Clarke, G.; Traplin, A.; O’Sullivan, O.; Crispie, F.; Moloney, R.D.; Cotter, P.D.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut microbiota depletion from early adolescence in mice: Implications for brain and behaviour. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.; Pabst, R.; von Hörsten, S. Behavioral phenotyping of mice in pharmacological and toxicological research. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 55, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodina, V.I.; Krupina, N.A.; Kryzhanovskiĭ, G.N.; Oknina, N.B. A multiparameter method for the complex evaluation of anxiety-phobic states in rats. Zhurnal Vyss. Nervn. Deiatelnosti Im. IP Pavlova 1993, 43, 1006–1017. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Deacon, R.M.; Rawlins, J.N. T-maze alternation in the rodent. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.C.; Lerner, F.M.; Couto E Silva, A.; Possoit, H.E.; Hsieh, T.H.; Neumann, J.T.; Minagar, A.; Lin, H.W.; Lee, R.H.C. Utilizing the modified T-maze to assess functional memory outcomes after cardiac arrest. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 131, 56694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sandhir, R. Hydrogen sulfide suppresses homocysteine-induced glial activation and inflammatory response. Nitric Oxide 2019, 90, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, E.A.; Yarullina, D.R. Antibiotic resistance of LACTOBACILLUS strains. Curr. Microbiol. 2019, 76, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Woollard, A.C.; Wolff, S.P. Hydrogen peroxide production during experimental protein glycation. FEBS Lett. 1990, 268, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blois, M.S. Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature 1958, 181, 1199–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.; Meehan, C.J.; Koenig, J.E.; Dhanani, A.S.; Rose, R.A.; Howlett, S.E.; Beiko, R.G. Microbial shifts in the aging mouse gut. Microbiome 2014, 2, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Lugt, B.; Rusli, F.; Lute, C.; Lamprakis, A.; Salazar, E.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Hooiveld, G.J.; Müller, M.; Vervoort, J.; Kersten, S.; et al. Integrative analysis of gut microbiota composition, host colonic gene expression and intraluminal metabolites in aging C57BL/6J mice. Aging 2018, 10, 930–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campedelli, I.; Mathur, H.; Salvetti, E.; Clarke, S.; Rea, M.C.; Torriani, S.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C.; O’Toole, P.W. Genus-wide assessment of antibiotic resistance in Lactobacillus spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 85, e01738-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, E.; Gorokhova, I.; Karimullina, G.; Yarullina, D. Alarming antibiotic resistance of lactobacilli isolated from probiotic preparations and dietary supplements. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, E.M.; Zidar, J.; Ewaldsson, B.; Askevik, K.; Udén, E.; Svensk, E.; Törnqvist, E. Aggression in group-housed male mice: A systematic review. Animals 2022, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayer, S.S.; Hwang, S.; Clayton, J.B. Antibiotic-induced gut dysbiosis and cognitive, emotional, and behavioral changes in rodents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1237177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, K.; Hallam, K.; Stojanovska, L.; Apostolopoulos, V. Yeast based spreads improve anxiety and stress. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atassi, F.; Servin, A.L. Individual and co-operative roles of lactic acid and hydrogen peroxide in the killing activity of enteric strain Lactobacillus johnsonii NCC933 and vaginal strain Lactobacillus gasseri KS120.1 against enteric, uropathogenic and vaginosis-associated pathogens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 304, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, D.C. Facing a new challenge: The adverse effects of antibiotics on gut microbiota and host immunity. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Éliás, A.J.; Barna, V.; Patoni, C.; Demeter, D.; Veres, D.S.; Bunduc, S.; Erőss, B.; Hegyi, P.; Földvári-Nagy, L.; Lenti, K. Probiotic supplementation during antibiotic treatment is unjustified in maintaining the gut microbiome diversity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Mahony, S.M. The microbiome-gut-brain axis: From bowel to behavior. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Feng, S.; Huo, F.; Liu, H. Effects of four antibiotics on the diversity of the intestinal microbiota. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0190421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tu, K.; Cao, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, X.T.; Zhang, M.M.; Wu, X.J.; Yang, H.; Chen, T. Antibiotics-induced intestinal dysbacteriosis caused behavioral alternations and neuronal activation in different brain regions in mice. Mol. Brain 2021, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvers, K.T.; Wilson, V.J.; Hammond, A.; Duncan, L.; Huntley, A.L.; Hay, A.D.; van der Werf, E.T. Antibiotic-induced changes in the human gut microbiota for the most commonly prescribed antibiotics in primary care in the UK: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.; Baloch, Z.; Shah, Z.; Cui, X.; Xia, X. The intestinal microbiota: Impacts of antibiotics therapy, colonization resistance, and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, B.R.; Park, G.S.; Jeong, D.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Im, S.; Song, W.H.; Kang, J. Multidisciplinary and comparative investigations of potential psychobiotic effects of Lactobacillus strains isolated from newborns and their impact on gut microbiota and ileal transcriptome in a healthy murine model. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Kumai, S.; Ogawa, M.; Benno, Y.; Nakase, T. Characterization and identification of Pediococcus species isolated from forage crops and their application for silage preparation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2901–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, A.; Shu, X.; Huang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, R.; Yue, M.; Yang, C. Lactobacillus plantarum-derived postbiotics prevent Salmonella-induced neurological dysfunctions by modulating gut-brain axis in mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 946096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijová, E. Postbiotics as metabolites and their biotherapeutic potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Debs, L.H.; Patel, A.P.; Nguyen, D.; Patel, K.; O’Connor, G.; Grati, M.; Mittal, J.; Yan, D.; Eshraghi, A.A.; et al. Neurotransmitters: The critical modulators regulating gut-brain axis. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 2359–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleskin, A.; Zhilenkova, O.; Shenderov, B.; Amerhanova, A.; Kudrin, V.; Klodt, P. Lactic-acid bacteria supplement fermented dairy products with human behavior-modifying neuroactive compounds. J. Pharm. Nutr. Sci. 2014, 4, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, L.; Popescu-Olaru, I.; Cozma, L.; Tulbă, D.; Hinescu, M.E.; Ceafalan, L.C.; Gherghiceanu, M.; Popescu, B.O. Oxidative stress and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 2406594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.C.; Rice, M.E. Classification of H2O2 as a neuromodulator that regulates striatal dopamine release on a subsecond time scale. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.R.; Patel, J.C.; O’Neill, B.; Rice, M.E. Inhibitory and excitatory neuromodulation by hydrogen peroxide: Translating energetics to information. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 3431–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rio, M.; Velez-Pardo, C. The hydrogen peroxide and its importance in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Med. Chem. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents 2004, 4, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.A.; Goertz, J.E.; Ren, T.; Rich, S.S.; Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Farber, E.; Wu, M.; Overall, C.C.; Kipnis, J.; Gaultier, A. Microbiota alteration is associated with the development of stress-induced despair behavior. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, R.; Suárez, J.E. Biosynthesis and degradation of H2O2 by vaginal lactobacilli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertzberger, R.; Arents, J.; Dekker, H.L.; Pridmore, R.D.; Gysler, C.; Kleerebezem, M.; de Mattos, M.J. H2O2 production in species of the Lactobacillus acidophilus group: A central role for a novel NADH-dependent flavin reductase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2229–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, L.M.; Daniele, M.B.; Pájaro, C.; Barberis, L. Lactobacillus species isolated from the vagina: Identification, hydrogen peroxide production and nonoxynol-9 resistance. Contraception 2006, 73, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, R.; van Hemert, S.; Baffone, W. Strain-specific probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria and their interference with human intestinal pathogens invasion. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).