Modulation of the Toll-like Receptor 3-Mediated Intestinal Immune Response by Water Kefir
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Water Kefir Elaboration
2.2. Animals, Feeding Procedures, and Administration of Poly(I:C)
2.3. Histological Studies of Small Intestine Injury
2.4. Serum Enzymes Activities
2.5. Intestinal and Serum Cytokines
2.6. Quantitative Expression Analysis by Real-Time PCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
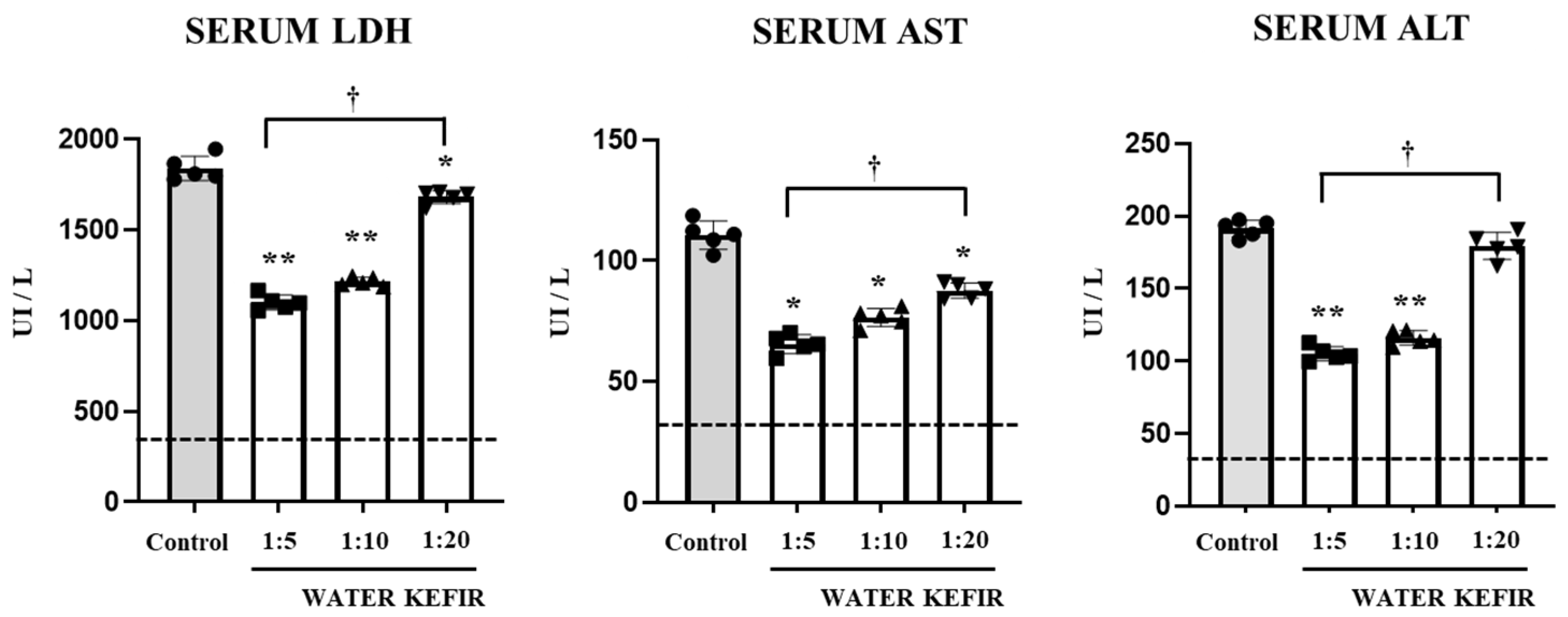
3.1. Water Kefir Reduces Poly(I:C)-Induced Damage
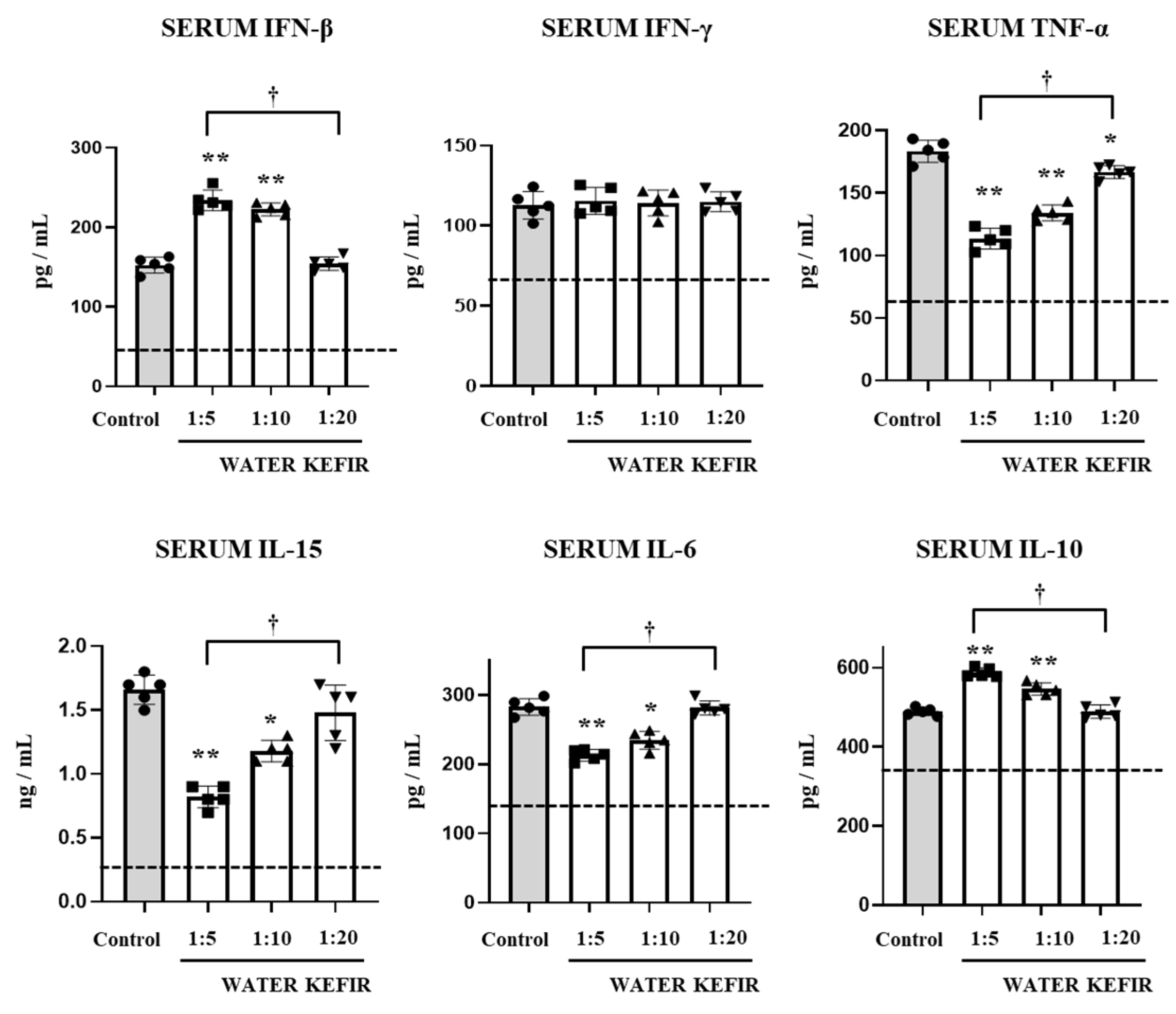
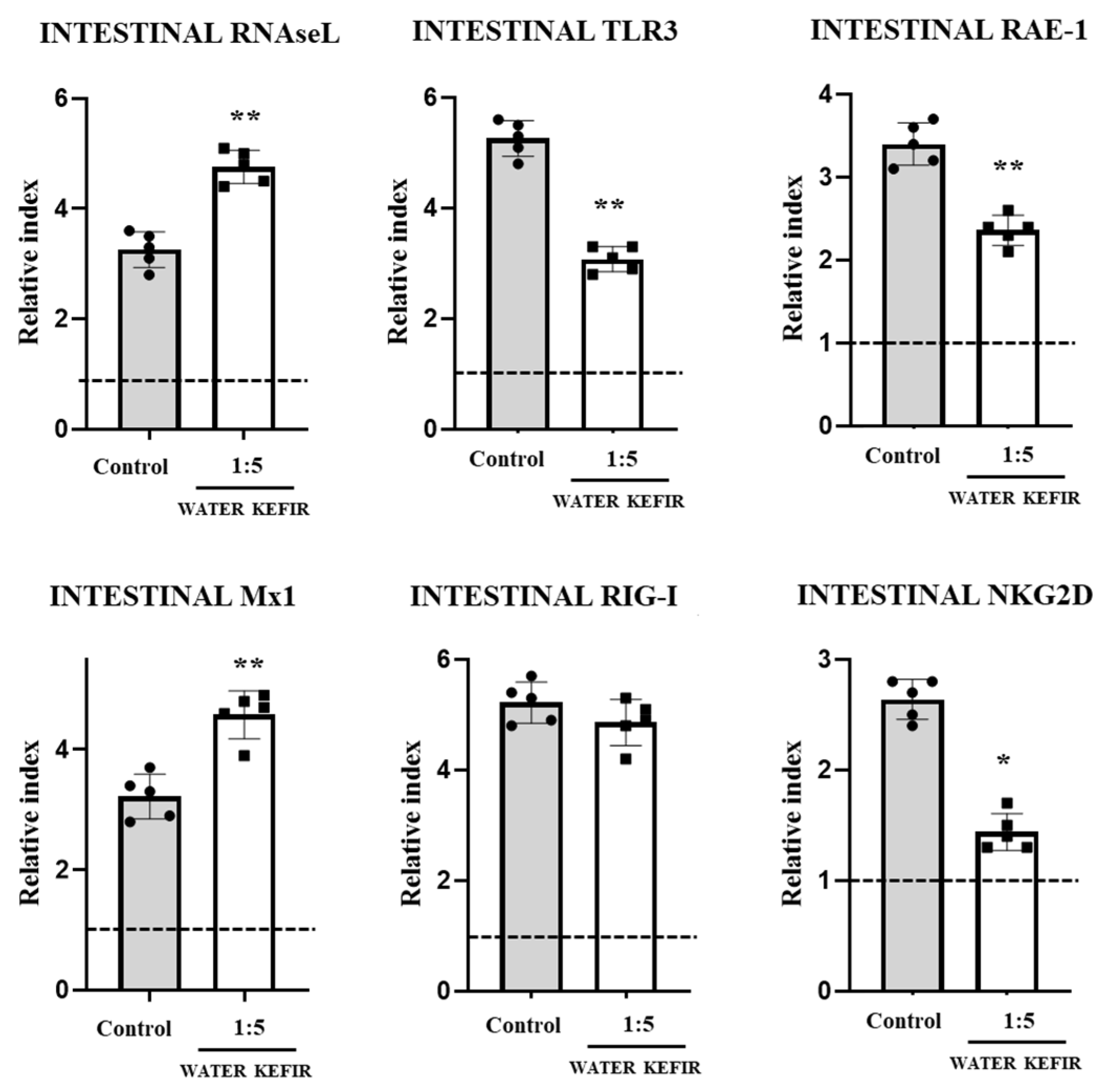
3.2. Water Kefir Differentially Modulates Cytokine Response to Poly(I:C)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luan, X.; Wang, L.; Song, G.; Zhou, W. Innate immune responses to RNA: Sensing and signaling. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1287940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z. Recognition of double-stranded RNA by TLR3 induces severe small intestinal injury in mice. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 4548–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Z. NKG2D recognition mediates Toll-like receptor 3 signaling-induced breakdown of epithelial homeostasis in the small intestines of mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7512–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria. 2001. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/382476b3-4d54-4175-803f-2f26f3526256/content (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Das, T.K.; Pradhan, S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Mondal, K.C.; Ghosh, K. Current status of probiotic and related health benefits. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villena, J.; Li, C.; Vizoso-Pinto, M.G.; Sacur, J.; Ren, L.; Kitazawa, H. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum as a Potential Adjuvant and Delivery System for the Development of SARS-CoV-2 Oral Vaccines. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, A.; Vijayakumar, V.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Ter Haar, J.; Obis, D.; Espadaler, J.; Binda, S.; Desiraju, S.; Day, R. Viral Infections, the Microbiome, and Probiotics. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 596166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, A.; Zelaya, H.; Clua, P.; Salva, S.; Alvarez, S.; Kitazawa, H.; Villena, J. Immunobiotic Lactobacillus strains reduce small intestinal injury induced by intraepithelial lymphocytes after Toll-like receptor 3 activation. Inflamm. Res. 2016, 65, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanmani, P.; Albarracin, L.; Kobayashi, H.; Hebert, E.M.; Saavedra, L.; Komatsu, R.; Gatica, B.; Miyazaki, A.; Ikeda-Ohtsubo, W.; Suda, Y.; et al. Genomic Characterization of Lactobacillus delbrueckii TUA4408L and Evaluation of the Antiviral Activities of its Extracellular Polysaccharides in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarracin, L.; Garcia-Castillo, V.; Masumizu, Y.; Indo, Y.; Islam, M.A.; Suda, Y.; Garcia-Cancino, A.; Aso, H.; Takahashi, H.; Kitazawa, H.; et al. Efficient Selection of New Immunobiotic Strains With Antiviral Effects in Local and Distal Mucosal Sites by Using Porcine Intestinal Epitheliocytes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, H.; Arce, L.; Tomotsune, K.; Albarracin, L.; Funabashi, R.; Vera, D.; Islam, M.A.; Vizoso-Pinto, M.G.; Takahashi, H.; Sasaki, Y.; et al. Lipoteichoic Acid Is Involved in the Ability of the Immunobiotic Strain Lactobacillus plantarum CRL1506 to Modulate the Intestinal Antiviral Innate Immunity Triggered by TLR3 Activation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.M.; Wilkinson, S.; Daenen, L.; Arendt, E.K. An update on water kefir: Microbiology, composition and production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 345, 109128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, N.F.; Kumar, M.R.; Yeap, S.K.; Abdullah, J.O.; Khalid, M.; Omar, A.R.; Alitheen, N.B. Kefir and its biological activities. Foods 2021, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökırmaklı, Ç.; Güzel-Seydim, Z.B. Water kefir grains vs. milk kefir grains: Physical, microbial and chemical comparison. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 4349–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, M.; Moridnia, A.; Mortazavi, D.; Salehi, M.; Bagheri, M.; Sheikhi, A. Kefir: A powerful probiotics with anticancer properties. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluzio, M.D.C.G.; Dias, M.D.M.E.; Martinez, J.A.; Milagro, F.I. Kefir and intestinal microbiota modulation: Implications in human health. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 638740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egea, M.B.; Santos, D.C.D.; Oliveira Filho, J.G.; Ores, J.D.C.; Takeuchi, K.P.; Lemes, A.C. A review of nondairy kefir products: Their characteristics and potential human health benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1536–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinderola, C.G.; Duarte, J.; Thangavel, D.; Perdigón, G.; Farnworth, E.; Matar, C. Immunomodulating capacity of kefir. J. Dairy Res. 2005, 72, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, D.D.; Grześkowiak, Ł.M.; Ferreira, C.L.; Fonseca, A.C.; Reis, S.A.; Dias, M.M.; Siqueira, N.P.; Silva, L.L.; Neves, C.A.; Oliveira, L.L.; et al. Kefir reduces insulin resistance and inflammatory cytokine expression in an animal model of metabolic syndrome. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3390–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinderola, G.; Perdigón, G.; Duarte, J.; Farnworth, E.; Matar, C. Effects of the oral administration of the exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens on the gut mucosal immunity. Cytokine 2006, 36, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahari, A.; Shahabi-Ghahfarrokhi, I.; Koolivand, D. Kefiran ameliorates malfunctions in primary and functional immune cells caused by lipopolysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carasi, P.; Racedo, S.M.; Jacquot, C.; Romanin, D.E.; Serradell, M.A.; Urdaci, M.C. Impact of kefir derived Lactobacillus kefiri on the mucosal immune response and gut microbiota. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 361604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaffová, V.; Mudroňová, D.; Mad’ar, M.; Hrčková, G.; Faixová, D.; Gancarčíková, S.; Ševčíková, Z.; Nemcová, R. Differences in Immune Response and Biochemical Parameters of Mice Fed by Kefir Milk and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Isolated from the Kefir Grains. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.A.; Chang, Y.W.; Lin, W.L.; Yang, Y.C.S.; Chen, W.J.; Huang, F.H.; Liu, Y.R. Modulatory Effects of Heat-Inactivated Streptococcus Thermophilus Strain 7 on the Inflammatory Response: A Study on an Animal Model with TLR3-Induced Intestinal Injury. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Fang, M.; Jones, C.; Minze, L.J.; Xing, J.; Zhang, Z. Mechanisms involved in controlling RNA virus-induced intestinal inflammation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.P.; Nice, T.J. Role of type-I and type-III interferons in gastrointestinal homeostasis and pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2024, 86, 102412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Tacuba, L.; Rojas, M.; Arias, C.F.; López, S. Rotavirus controls activation of the 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetase/RNase L pathway using at least two distinct mechanisms. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12145–12153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Yi, G.; Philip, A.A.; Patton, J.T. Rotavirus NSP1 Subverts the Antiviral Oligoadenylate Synthetase-RNase L Pathway by Inducing RNase L Degradation. mBio 2022, 13, e0299522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKellar, J.; Arnaud-Arnould, M.; Chaloin, L.; Tauziet, M.; Arpin-André, C.; Pourcelot, O.; Blaise, M.; Moncorgé, O.; Goujon, C. An evolutionarily conserved N-terminal leucine is essential for MX1 GTPase antiviral activity against different families of RNA viruses. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, T.; Kanmani, P.; Kobayashi, H.; Miyazaki, A.; Soma, J.; Suda, Y.; Aso, H.; Nochi, T.; Iwabuchi, N.; Xiao, J.Z.; et al. Immunobiotic bifidobacteria strains modulate rotavirus immune response in porcine intestinal epitheliocytes via pattern recognition receptor signaling. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, P.; Nandi, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Bhowmick, R.; Halder, U.C.; Nayak, M.K.; Kobayashi, N.; Chawla-Sarkar, M. Identification of common human host genes involved in pathogenesis of different rotavirus strains: An attempt to recognize probable antiviral targets. Virus Res. 2012, 169, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, C.; Audy, J.; Mathieu, O.; Tompkins, T.A. Multistrain probiotic mod ulation of intestinal epithelial cells’ immune response to a double-stranded RNA ligand, poly(I-C). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidess, E.; Kleerebezem, M.; Brugman, S. Colonizing Microbes, IL-10 and IL-22: Keeping the Peace at the Mucosal Surface. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 729053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Aljamaei, H.M.; Stadnyk, A.W. The Production and Function of Endogenous Interleukin-10 in Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Gut Homeostasis. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.C. Interleukin 15 is a potent stimulant of intraepithelial lymphocytes. Gastroenterology 1998, 115, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerwenka, A.; Bakker, A.B.; McClanahan, T.; Wagner, J.; Wu, J.; Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L. Retinoic acid early inducible genes define a ligand family for the activating NKG2D receptor in mice. Immunity 2000, 12, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dentice Maidana, S.; Ortiz Moyano, R.; Elean, M.; Imamura, Y.; Albarracín, L.; Namai, F.; Suda, Y.; Nishiyama, K.; Villena, J.; Kitazawa, H. Modulation of the Toll-like Receptor 3-Mediated Intestinal Immune Response by Water Kefir. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 1239-1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030083
Dentice Maidana S, Ortiz Moyano R, Elean M, Imamura Y, Albarracín L, Namai F, Suda Y, Nishiyama K, Villena J, Kitazawa H. Modulation of the Toll-like Receptor 3-Mediated Intestinal Immune Response by Water Kefir. Microbiology Research. 2024; 15(3):1239-1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030083
Chicago/Turabian StyleDentice Maidana, Stefania, Ramiro Ortiz Moyano, Mariano Elean, Yoshiya Imamura, Leonardo Albarracín, Fu Namai, Yoshihito Suda, Keita Nishiyama, Julio Villena, and Haruki Kitazawa. 2024. "Modulation of the Toll-like Receptor 3-Mediated Intestinal Immune Response by Water Kefir" Microbiology Research 15, no. 3: 1239-1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030083
APA StyleDentice Maidana, S., Ortiz Moyano, R., Elean, M., Imamura, Y., Albarracín, L., Namai, F., Suda, Y., Nishiyama, K., Villena, J., & Kitazawa, H. (2024). Modulation of the Toll-like Receptor 3-Mediated Intestinal Immune Response by Water Kefir. Microbiology Research, 15(3), 1239-1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030083







