Evaluation of Predicted siRNA as an Antiviral against MERS-CoV Targeting the Membrane Gene in the Vero Cell Line
Abstract
:1. Introduction
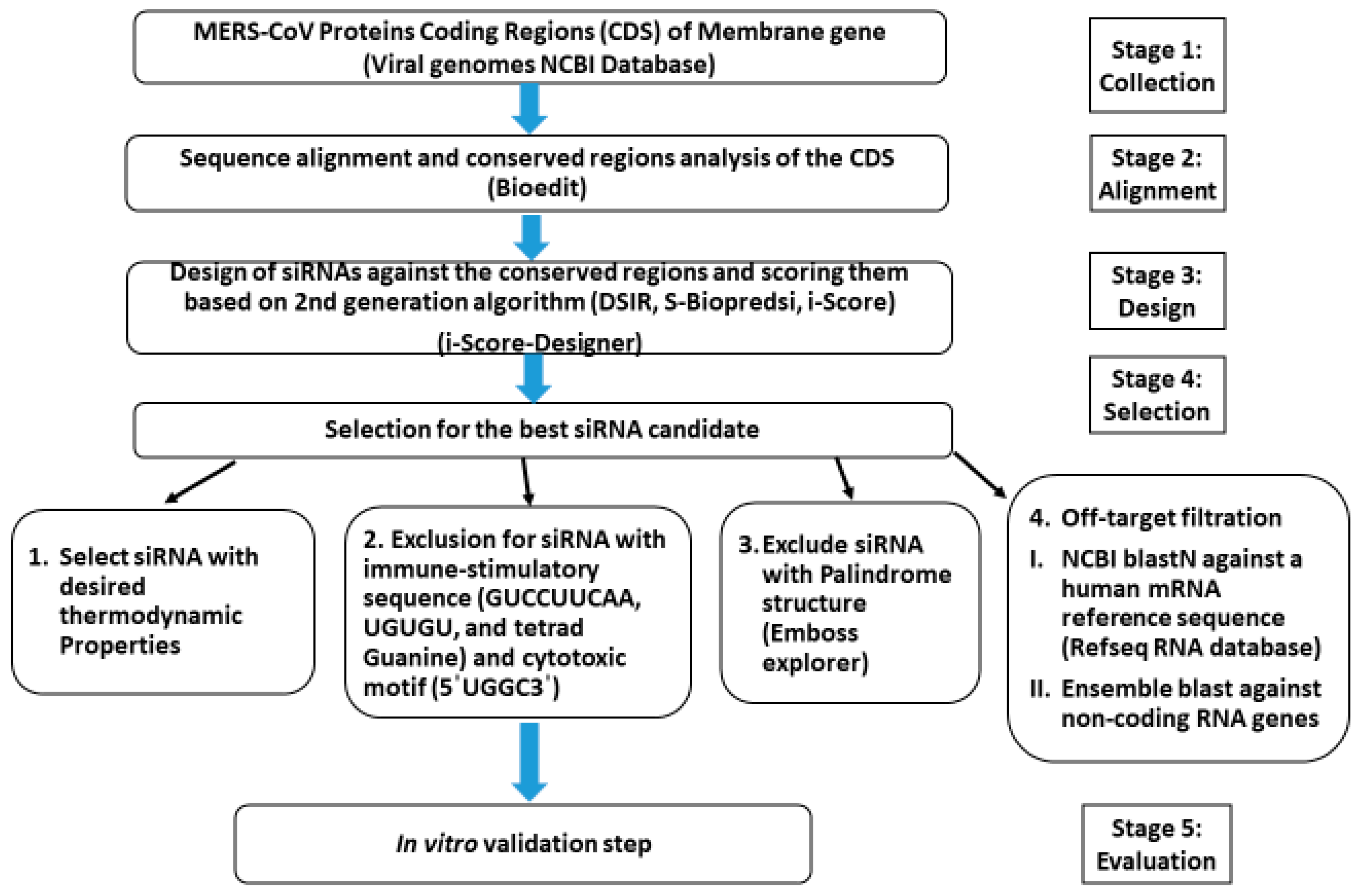
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Silico Prediction
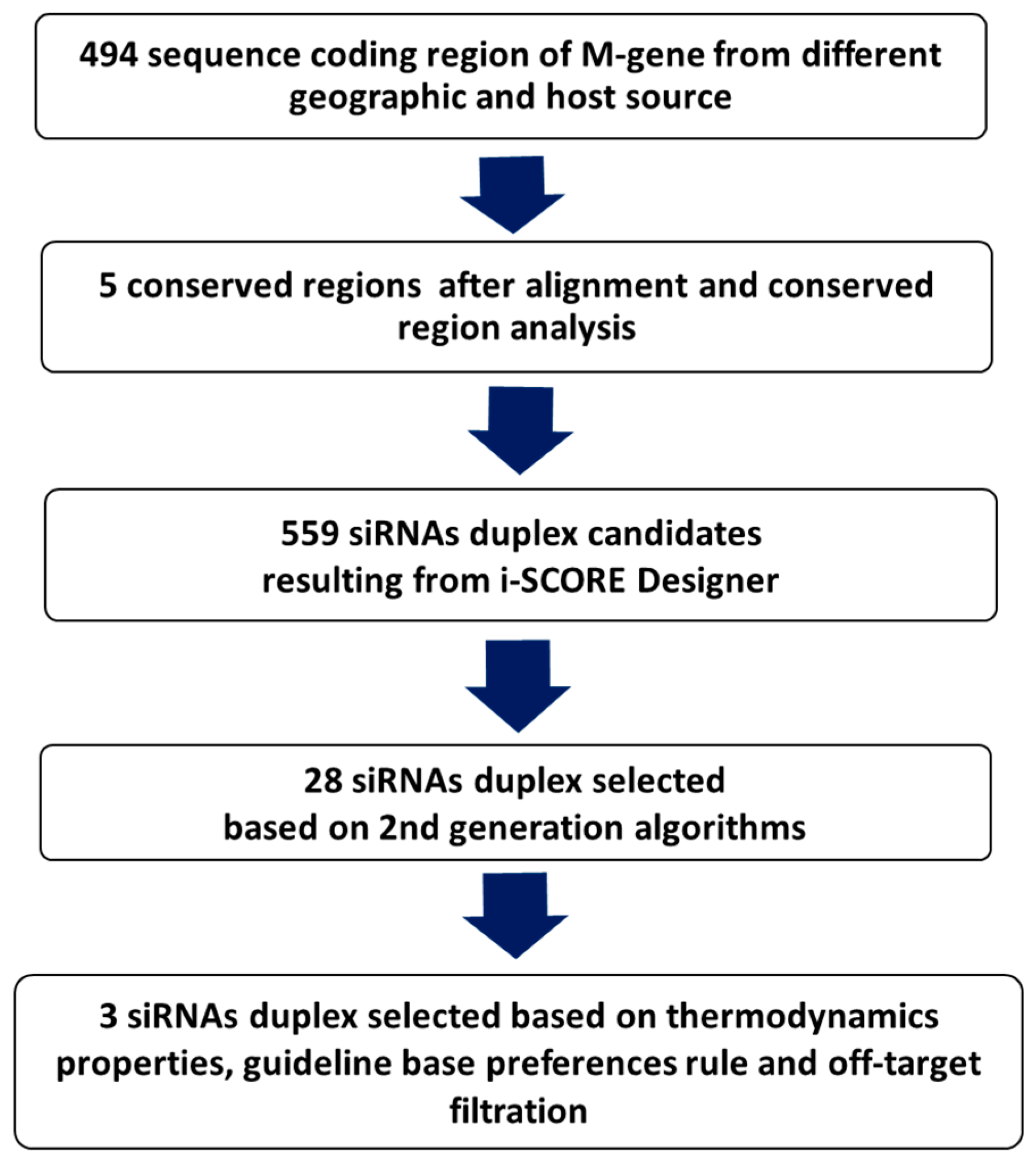
2.1.1. Sequences Collection, Alignments, and Analysis
2.1.2. Design, Prediction, and Selection of siRNA
2.1.3. siRNAs Thermodynamic Properties
2.1.4. Removal of Off-Target siRNAs
2.1.5. Final Selection and Chemical Synthesis
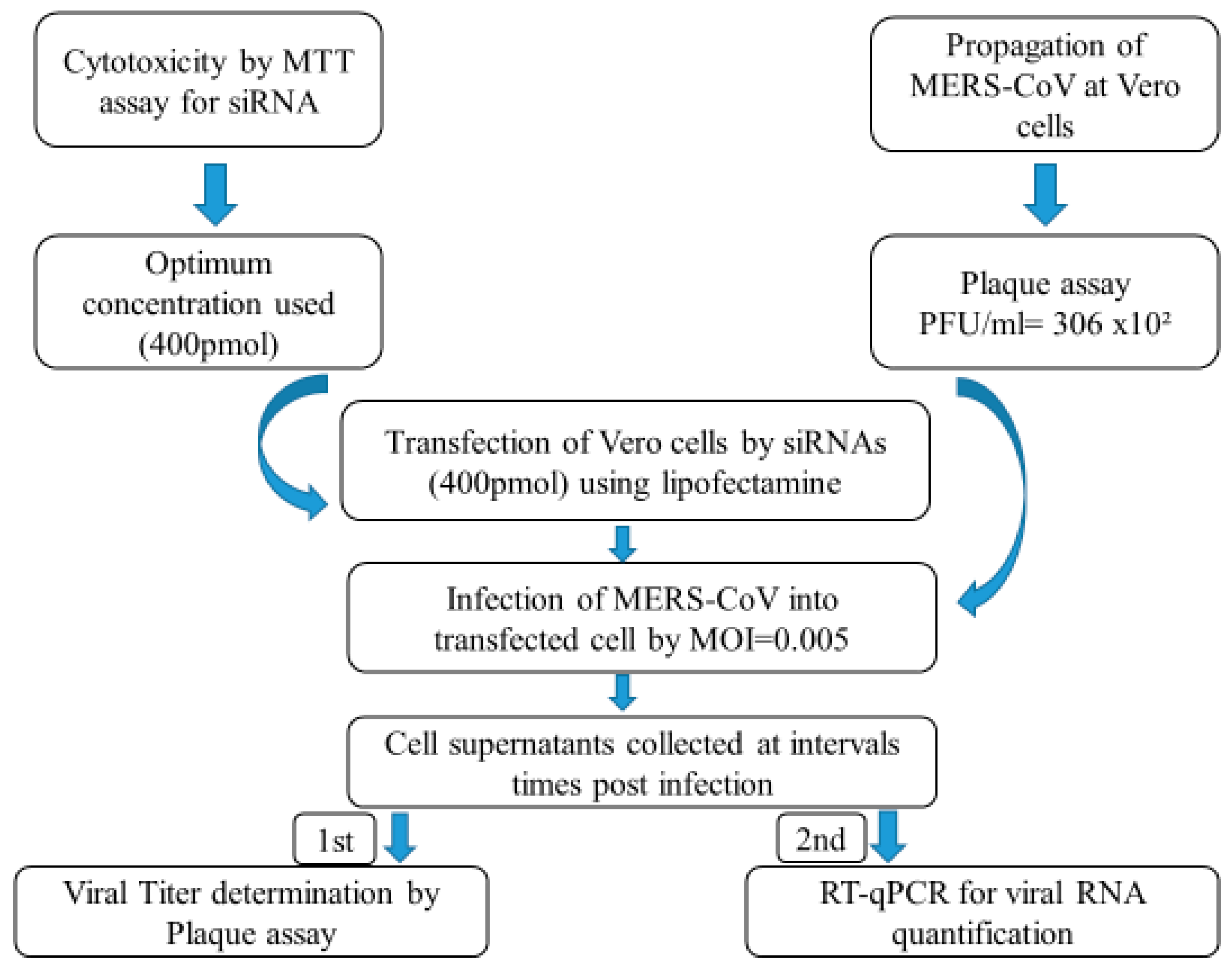
2.2. In Vitro Evaluation
2.2.1. Cells and Virus
2.2.2. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of siRNAs
2.2.3. siRNA Transfection
2.2.4. Evaluation of MERS-CoV Replication Inhibition in Transfected Vero Cells
2.2.5. Plaque Assay for Viral Titer Determination
2.2.6. Total RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
3. Results
3.1. In Silico Scoring, Prediction, and Selection of Potent siRNAs
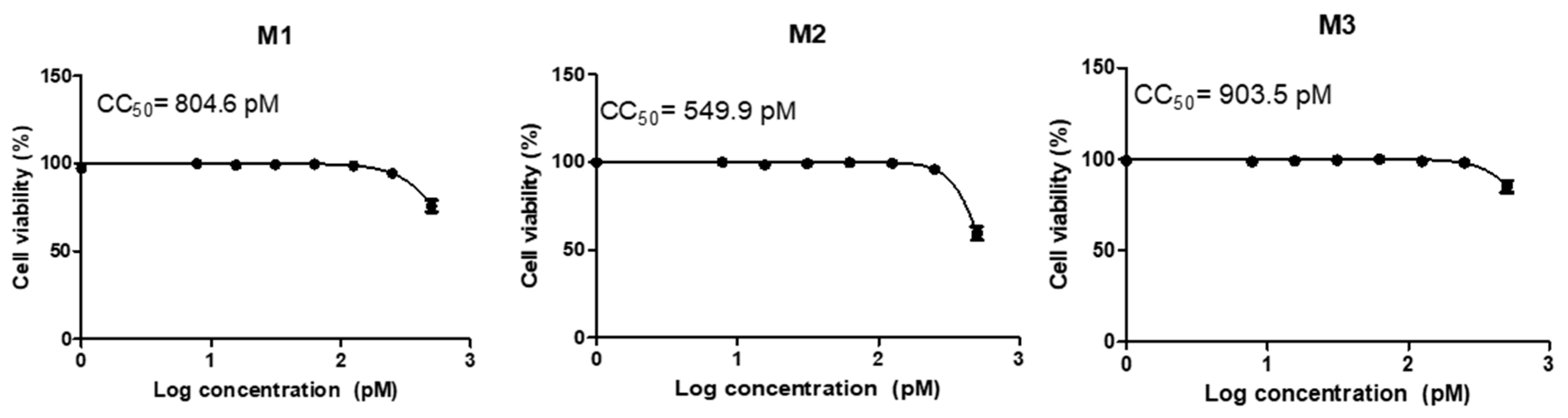
3.2. Cytotoxicity and Transfection
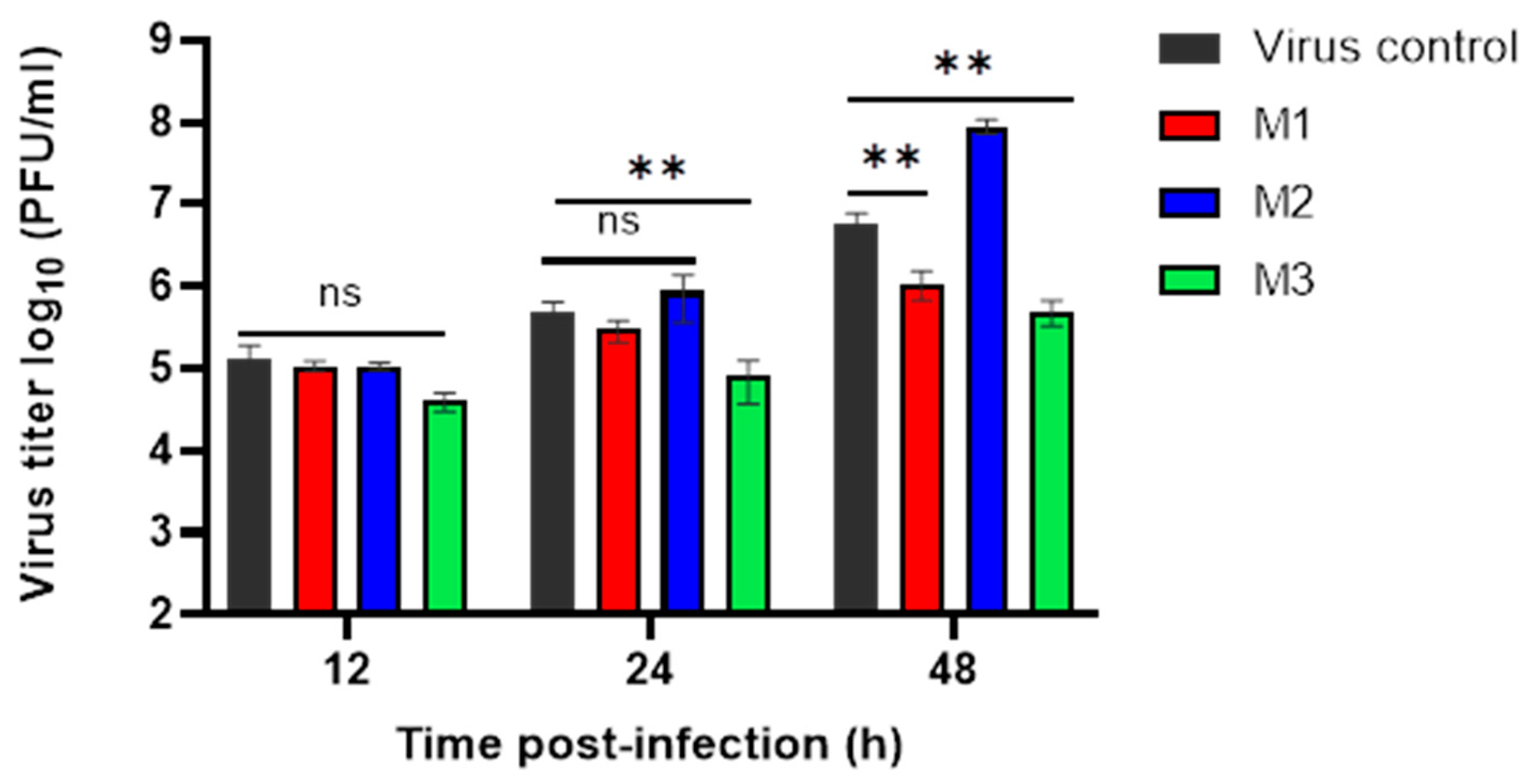
3.3. Evaluation of MERS-CoV Replication Inhibition by Plaque Assay
3.4. Evaluation of MERS-CoV Replication by RT-qPCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaki, A.M.; van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome, Report June 2023; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Al-Ahmed, S.H.; Sah, R.; Alqumber, M.A.; Haque, S.; Patel, S.K.; Pathak, M.; Tiwari, R.; Yatoo, M.I.; Haq, A.U.; et al. MERS-CoV: Epidemiology, molecular dynamics, therapeutics, and future challenges. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, V.S.; Farag, E.A.; Reusken, C.B.; Lamers, M.M.; Pas, S.D.; Voermans, J.; Smits, S.L.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Al-Mawlawi, N.; Al-Romaihi, H.E.; et al. Isolation of MERS coronavirus from a dromedary camel, Qatar, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.K.; Poon, L.L.; Gomaa, M.M.; Shehata, M.M.; Perera, R.A.; Abu Zeid, D.; El Rifay, A.S.; Siu, L.Y.; Guan, Y.; Webby, R.J.; et al. MERS coronaviruses in dromedary camels, Egypt. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar Esam, I.; Hashem Anwar, M.; El-Kafrawy Sherif, A.; Sohrab Sayed, S.; Aburizaiza Asad, S.; Farraj Suha, A.; Hassan Ahmed, M.; Al-Saeed Muneera, S.; Jamjoom Ghazi, A.; Madani Tariq, A. Detection of the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Genome in an Air Sample Originating from a Camel Barn Owned by an Infected Patient. mBio 2014, 5, e01450-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, R.A.; Wang, P.; Gomaa, M.R.; El-Shesheny, R.; Kandeil, A.; Bagato, O.; Siu, L.Y.; Shehata, M.M.; Kayed, A.S.; Moatasim, Y.; et al. Seroepidemiology for MERS coronavirus using microneutralisation and pseudoparticle virus neutralisation assays reveal a high prevalence of antibody in dromedary camels in Egypt, June 2013. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeil, A.; Shehata, M.M.; El Shesheny, R.; Gomaa, M.R.; Ali, M.A.; Kayali, G. Complete Genome Sequence of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Isolated from a Dromedary Camel in Egypt. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, C.F.; Amarasinghe, G.K. Evasion of interferon responses by Ebola and Marburg viruses. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, A.H.; Raj, V.S.; Oudshoorn, D.; Bestebroer, T.M.; van Nieuwkoop, S.; Limpens, R.; Posthuma, C.C.; van der Meer, Y.; Bárcena, M.; Haagmans, B.L.; et al. MERS-coronavirus replication induces severe in vitro cytopathology and is strongly inhibited by cyclosporin A or interferon-α treatment. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D.; Mitchell, H.D.; Cockrell, A.S.; Gralinski, L.E.; Yount, B.L.; Graham, R.L.; McAnarney, E.T.; Douglas, M.G.; Scobey, T.; Beall, A.; et al. MERS-CoV Accessory ORFs Play Key Role for Infection and Pathogenesis. mBio 2017, 8, e00665-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.-Y.R.; Ye, Z.-W.; Lui, P.-Y.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, S.; Zhu, L.; Fung, S.-Y.; Yuen, K.-S.; Siu, K.-L.; Yeung, M.-L.; et al. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus ORF8b Accessory Protein Suppresses Type I IFN Expression by Impeding HSP70-Dependent Activation of IRF3 Kinase IKKε. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 1564–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokri, S.; Mahmoudvand, S.; Taherkhani, R.; Farshadpour, F. Modulation of the immune response by Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Bae, S.; Myoung, J. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-Encoded Accessory Proteins Impair MDA5-and TBK1-Mediated Activation of NF-κB. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, P.-Y.; Wong, L.-Y.R.; Fung, C.-L.; Siu, K.-L.; Yeung, M.-L.; Yuen, K.-S.; Chan, C.-P.; Woo, P.C.-Y.; Yuen, K.-Y.; Jin, D.-Y. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus M protein suppresses type I interferon expression through the inhibition of TBK1-dependent phosphorylation of IRF3. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2016, 5, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Liu Helene, M.; Chang, M.-F.; Chang Shin, C. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein Suppresses Type I and Type III Interferon Induction by Targeting RIG-I Signaling. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00099-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.; Shuai, H.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wen, L.; Huang, X.; Hu, B.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yoon, C.; et al. Targeting highly pathogenic coronavirus-induced apoptosis reduces viral pathogenesis and disease severity. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.K.; Lee, S.I.; Bae, J.-Y.; Park, M.-S.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, H.-J. Production of a Monoclonal Antibody Targeting the M Protein of MERS-CoV for Detection of MERS-CoV Using a Synthetic Peptide Epitope Formulated with a CpG–DNA–Liposome Complex. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 25, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Harborth, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Yalcin, A.; Weber, K.; Tuschl, T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001, 411, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obbard, D.J.; Gordon, K.H.; Buck, A.H.; Jiggins, F.M. The evolution of RNAi as a defence against viruses and transposable elements. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, H.; Chalbatani, G.M.; Mahmoodzadeh, H.; Karimloo, R.; Rezaiean, O.; Moradzadeh, A.; Mehmandoost, N.; Moazzen, F.; Mazraeh, A.; Marmari, V.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms and Biological Functions of siRNA. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 13, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Michler, T.; Merkel, O.M. siRNA Therapeutics against Respiratory Viral Infections-What Have We Learned for Potential COVID-19 Therapies? Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, A.; Løvendorf, M.B.; Kauppinen, S. Development of siRNA Therapeutics for the Treatment of Liver Diseases. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2282, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, L.J.; Keam, S.J. Lumasiran: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Yang, C.F.; Chen, Y.F.; Yang, C.C.; Chou, Y.L.; Chou, H.W.; Chang, T.Y.; Chao, T.L.; Hsu, S.C.; Ieong, S.M.; et al. A siRNA targets and inhibits a broad range of SARS-CoV-2 infections including Delta variant. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e15298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, S.M.; Hasan, M.A.; Amin, M.A.; Hossain, M.; Sharmin, T. Design of Potential RNAi (miRNA and siRNA) Molecules for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) Gene Silencing by Computational Method. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2015, 7, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden-Reid, E.; Ledger, S.; Zhang, Y.; Di Giallonardo, F.; Aggarwal, A.; Stella, A.O.; Akerman, A.; Milogiannakis, V.; Walker, G.; Rawlinson, W.; et al. Novel siRNA therapeutics demonstrate multi-variant efficacy against SARS-CoV-2. Antivir. Res. 2023, 217, 105677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, L.; Yu, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Rong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ning, H.; et al. siRNA targeting the Leader sequence of SARS-CoV inhibits virus replication. Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.; Mottaghitalab, F.; Abdoli, A.; Dinarvand, M.; Esmailie, A.; Kheiri, M.T.; Atyabi, F. Inhibiting influenza virus replication and inducing protection against lethal influenza virus challenge through chitosan nanoparticles loaded by siRNA. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElHefnawi, M.; Hassan, N.; Kamar, M.; Siam, R.; Remoli, A.L.; El-Azab, I.; AlAidy, O.; Marsili, G.; Sgarbanti, M. The design of optimal therapeutic small interfering RNA molecules targeting diverse strains of influenza A virus. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 3364–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljowaie, R.M.; Almajhdi, F.N.; Ali, H.H.; El-Wetidy, M.S.; Shier, M.K. Inhibition of hepatitis C virus genotype 4 replication using siRNA targeted to the viral core region and the CD81 cellular receptor. Cell Stress Chaperones 2020, 25, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togtema, M.; Jackson, R.; Grochowski, J.; Villa, P.L.; Mellerup, M.; Chattopadhyaya, J.; Zehbe, I. Synthetic siRNA targeting human papillomavirus 16 E6: A perspective on in vitro nanotherapeutic approaches. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, K.N.; Abdullah, A.A.; Bala, J.A.; Jesse, F.F.A.; Abdullah, C.A.C.; Noordin, M.M.; Mohd-Azmi, M.L. Immediately early 2 (IE-2) and DNA polymerase SiRNA as virus-specific antiviral against novel transplacental cytomegalovirus strain ALL-03 in vitro. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 90, 104783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.I.; Moazzam, M.; Cho, Y.; Kato, S.; Xu, A.; Way, J.J.; Lohan, S.; Tiwari, R.K. siRNA Therapeutics for the Therapy of COVID-19 and Other Coronaviruses. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 2105–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.; Tantray, V.G.; Kirmani, A.R.; Ahangar, A.G. A review on current status of antiviral siRNA. Rev. Med. Virol. 2018, 28, e1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhong, L.; Weng, Y.; Peng, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, X.-J. Therapeutic siRNA: State of the art. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara, M.; Murakumo, Y.; Masuda, A.; Matsuura, T.; Asai, N.; Jijiwa, M.; Ishida, M.; Shinmi, J.; Yatsuya, H.; Qiao, S.; et al. Thermodynamic instability of siRNA duplex is a prerequisite for dependable prediction of siRNA activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ui-Tei, K.; Naito, Y.; Takahashi, F.; Haraguchi, T.; Ohki-Hamazaki, H.; Juni, A.; Ueda, R.; Saigo, K. Guidelines for the selection of highly effective siRNA sequences for mammalian and chick RNA interference. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarzguioui, M.; Prydz, H. An algorithm for selection of functional siRNA sequences. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 316, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, A.C.; Bo, R.; Manola, J.; Vazquez, F.; Bare, O.; Khvorova, A.; Scaringe, S.; Sellers, W.R. A library of siRNA duplexes targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway: Determinants of gene silencing for use in cell-based screens. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaki, S.; Kotani, S.; Konagaya, A. An effective method for selecting siRNA target sequences in mammalian cells. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huesken, D.; Lange, J.; Mickanin, C.; Weiler, J.; Asselbergs, F.; Warner, J.; Meloon, B.; Engel, S.; Rosenberg, A.; Cohen, D.; et al. Design of a genome-wide siRNA library using an artificial neural network. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, A.; Leake, D.; Boese, Q.; Scaringe, S.; Marshall, W.S.; Khvorova, A. Rational siRNA design for RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, T.; Suzuki, T. Specific residues at every third position of siRNA shape its efficient RNAi activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalina, S.A.; Spiridonov, A.N.; Ogurtsov, A.Y. Computational models with thermodynamic and composition features improve siRNA design. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vert, J.-P.; Foveau, N.; Lajaunie, C.; Vandenbrouck, Y. An accurate and interpretable model for siRNA efficacy prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElHefnawi, M.; Kim, T.; Kamar, M.A.; Min, S.; Hassan, N.M.; El-Ahwany, E.; Kim, H.; Zada, S.; Amer, M.; Windisch, M.P. In silico design and experimental validation of siRNAs targeting conserved regions of multiple hepatitis C virus genotypes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, F.; Sonenberg, N.; Nagar, B. Structural basis for 5′-nucleotide base-specific recognition of guide RNA by human AGO2. Nature 2010, 465, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khvorova, A.; Reynolds, A.; Jayasena, S.D. Functional siRNAs and miRNAs Exhibit Strand Bias. Cell 2003, 115, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysara, M.; Garibaldi, J.M.; ElHefnawi, M. MysiRNA-designer: A workflow for efficient siRNA design. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birmingham, A.; Anderson, E.; Sullivan, K.; Reynolds, A.; Boese, Q.; Leake, D.; Karpilow, J.; Khvorova, A. A protocol for designing siRNAs with high functionality and specificity. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2068–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, S.; Meister, G. siRNA design principles and off-target effects. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 986, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Müller, M.A.; Costabel, U.; Timm, J.; Binger, T.; Meyer, B.; Kreher, P.; Lattwein, E.; Eschbach-Bludau, M.; Nitsche, A.; et al. Assays for laboratory confirmation of novel human coronavirus (hCoV-EMC) infections. Eurosurveillance 2012, 17, 20334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehata, M.M.; Mostafa, A.; Teubner, L.; Mahmoud, S.H.; Kandeil, A.; Elshesheny, R.; Boubak, T.A.; Frantz, R.; Pietra, L.L.; Pleschka, S.; et al. Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles (OMVs)-Based Dual Vaccine for Influenza A H1N1 Virus and MERS-CoV. Vaccines 2019, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reusken, C.B.; Ababneh, M.; Raj, V.S.; Meyer, B.; Eljarah, A.; Abutarbush, S.; Godeke, G.-J.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Zutt, I.; Müller, M.A. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) serology in major livestock species in an affected region in Jordan, June to September 2013. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemida, M.G.; Perera, R.A.; Wang, P.; Alhammadi, M.A.; Siu, L.Y.; Li, M.; Poon, L.L.; Saif, L.; Alnaeem, A.; Peiris, M. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) coronavirus seroprevalence in domestic livestock in Saudi Arabia, 2010 to 2013. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Kandeil, A.; Shehata, M.; El Shesheny, R.; Samy, A.M.; Kayali, G.; Ali, M.A. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV): State of the Science. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharoon, S.; Memish, Z.A. MERS-CoV as an emerging respiratory illness: A review of prevention methods. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 101520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, M.M.; Gomaa, M.R.; Ali, M.A.; Kayali, G. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: A comprehensive review. Front. Med. 2016, 10, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, L.; Gu, X. Evolutionary dynamics of MERS-CoV: Potential recombination, positive selection and transmission. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, V.S.; Mou, H.; Smits, S.L.; Dekkers, D.H.W.; Müller, M.A.; Dijkman, R.; Muth, D.; Demmers, J.A.A.; Zaki, A.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature 2013, 495, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeil, A.; Gomaa, M.; Shehata, M.; El-Taweel, A.; Kayed, A.E.; Abiadh, A.; Jrijer, J.; Moatasim, Y.; Kutkat, O.; Bagato, O.; et al. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection in non-camelid domestic mammals. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeil, A.; Gomaa, M.; Nageh, A.; Shehata, M.M.; Kayed, A.E.; Sabir, J.S.M.; Abiadh, A.; Jrijer, J.; Amr, Z.; Said, M.A.; et al. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) in Dromedary Camels in Africa and Middle East. Viruses 2019, 11, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.S.; Malek, S.S.; Abushahba, M.F. Seroprevalence of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Corona Virus in dromedaries and their traders in upper Egypt. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2020, 14, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.A.; Meyer, B.; Corman, V.M.; Al-Masri, M.; Turkestani, A.; Ritz, D.; Sieberg, A.; Aldabbagh, S.; Bosch, B.J.; Lattwein, E.; et al. Presence of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus antibodies in Saudi Arabia: A nationwide, cross-sectional, serological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkema, R.S.; Farag, E.A.B.A.; Himatt, S.; Ibrahim, A.K.; Al-Romaihi, H.; Al-Marri, S.A.; Al-Thani, M.; El-Sayed, A.M.; Al-Hajri, M.; Haagmans, B.L.; et al. Risk Factors for Primary Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection in Camel Workers in Qatar During 2013–2014: A Case-Control Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1702–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), Fact Sheet; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Memish, Z.A. Update on therapeutic options for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV). Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2017, 15, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.; Aigner, A. Therapeutic siRNA: State-of-the-Art and Future Perspectives. BioDrugs 2022, 36, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawan, M.M.A.K.; Sharma, A.R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Mallik, B.; Akhter, F.; Shakil, M.S.; Hossain, M.M.; Banik, S.; Lee, S.-S.; Hasan, M.A.; et al. Designing an effective therapeutic siRNA to silence RdRp gene of SARS-CoV-2. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 93, 104951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Geng, H.; Deng, Y.; Huang, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tan, W. The structural and accessory proteins M, ORF 4a, ORF 4b, and ORF 5 of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) are potent interferon antagonists. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohrab, S.S.; Aly El-Kafrawy, S.; Mirza, Z.; Hassan, A.M.; Alsaqaf, F.; Azhar, E.I. In silico prediction and experimental validation of siRNAs targeting ORF1ab of MERS-CoV in Vero cell line. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohrab, S.S.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Mirza, Z.; Hassan, A.M.; Alsaqaf, F.; Azhar, E.I. Designing and evaluation of MERS-CoV siRNAs in HEK-293 cell line. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | Value Setup Used |
|---|---|
| Word size | 7 |
| Expect threshold | 1000 |
| Match/Mismatch score | 1, −1 |
| Gap costs | 5, 2 |
| Maximum target sequence | 100 |
| Program selection | Somewhat similar sequences (blastN) |
| Targeted Conserved Regions/(siRNA Name) | Pos. in the Genome | Sense Strand (5′→3′) | Antisense Strand (5′→3′) | Whole ∆G | GC % | DSIR | i-SCORE | s-Biopredsi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 (M1) | 206 to 359 | GAUAAUCUCUGGCAUUGUA | UACAAUGCCAGAGAUUAUCug | −34.3 | 6.8 | 95.2 | 73.8 | 0.869 |
| 3 (M2) | 368 to 437 | UAACUGCUGUUGUAACCAA | UUGGUUACAACAGCAGUUAca | −34.3 | 36.8 | 83.6 | 63.6 | 0.757 |
| 4 (M3) | 439 to 464 | AAAAUGGCUGGCAUGCAUU | AAUGCAUGCCAGCCAUUUUga | −36.3 | 42.1 | 68.1 | 52.3 | 0.631 |
| Time Post Infection (h) | Viral Titer Reduction of M1 (%) | Viral Titer Reduction of M2 (%) | Viral Titer Reduction of M3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 20 | 20 | 70 |
| 24 | 39.45 | −76.87 | 83.67 * |
| 48 | 80.58 * | −1488.23 | 91.17 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Sayed, A.Y.; Shehata, M.; Mahmoud, S.H.; ElHefnawi, M.; Seoudi, D.M.; Ali, M.A. Evaluation of Predicted siRNA as an Antiviral against MERS-CoV Targeting the Membrane Gene in the Vero Cell Line. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 1687-1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14040116
El-Sayed AY, Shehata M, Mahmoud SH, ElHefnawi M, Seoudi DM, Ali MA. Evaluation of Predicted siRNA as an Antiviral against MERS-CoV Targeting the Membrane Gene in the Vero Cell Line. Microbiology Research. 2023; 14(4):1687-1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14040116
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Sayed, Amany Y., Mahmoud Shehata, Sara H. Mahmoud, Mahmoud ElHefnawi, Dina M. Seoudi, and Mohamed A. Ali. 2023. "Evaluation of Predicted siRNA as an Antiviral against MERS-CoV Targeting the Membrane Gene in the Vero Cell Line" Microbiology Research 14, no. 4: 1687-1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14040116
APA StyleEl-Sayed, A. Y., Shehata, M., Mahmoud, S. H., ElHefnawi, M., Seoudi, D. M., & Ali, M. A. (2023). Evaluation of Predicted siRNA as an Antiviral against MERS-CoV Targeting the Membrane Gene in the Vero Cell Line. Microbiology Research, 14(4), 1687-1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14040116





