Bioremediation of Azo Dye Brown 703 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An Effective Treatment Technique for Dye-Polluted Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Brown 703 Dye
2.3. Isolation of Bacterial Strains
2.4. Brown 703 Degradation Analyses
2.5. Brown 703 Degradation and Effect of Different Physiochemical Parameters
2.5.1. Effect of Brown 703 Concentrations
2.5.2. Effect of pH on Degradation of Brown 703
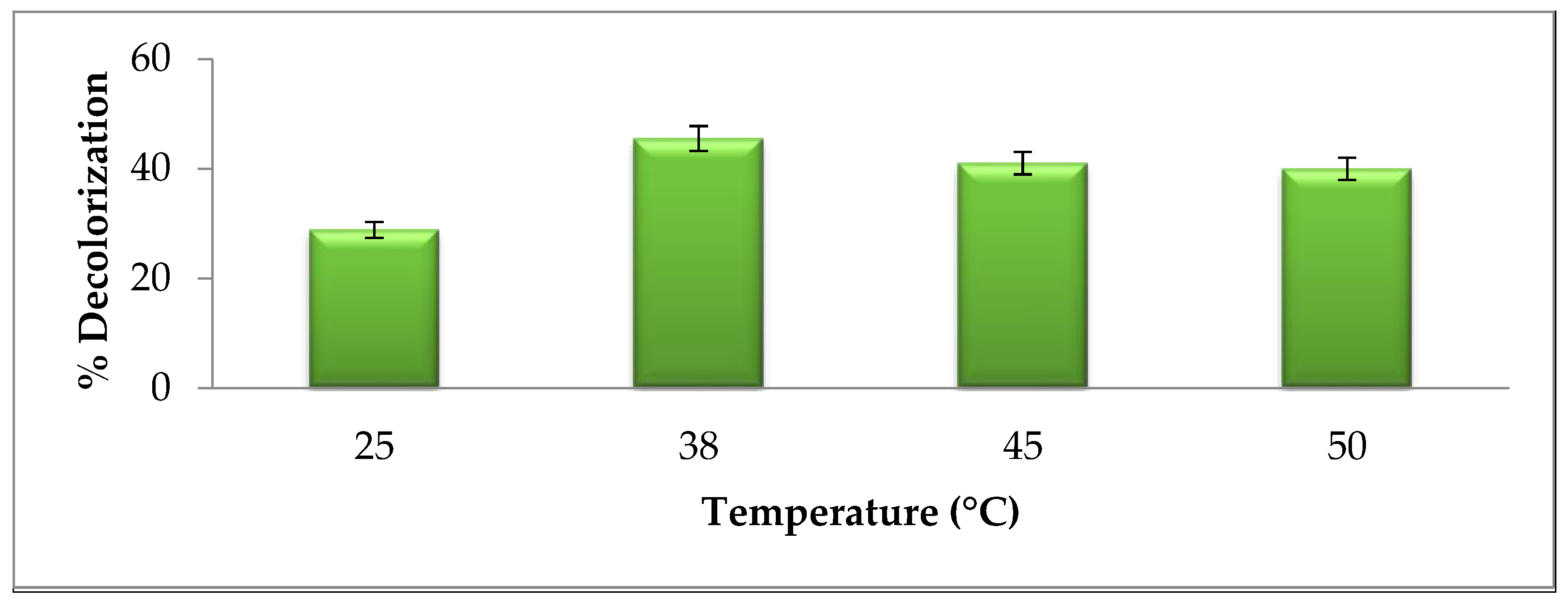
2.5.3. Temperature Effect on Brown 703 Degradation
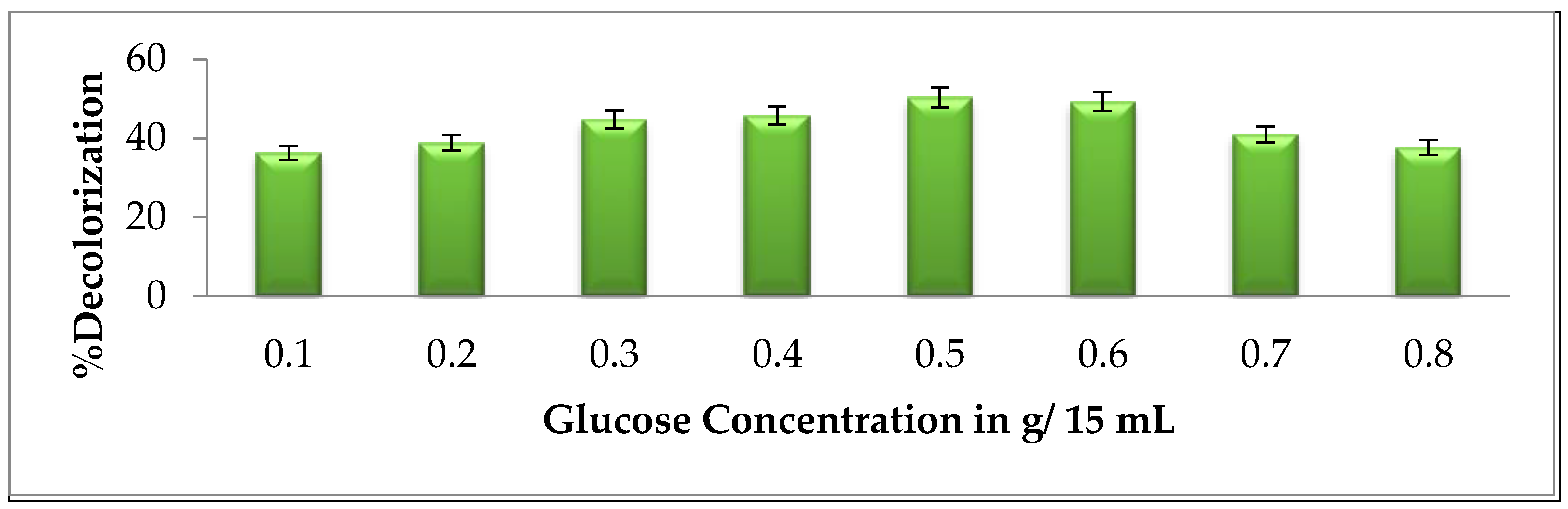
2.5.4. Effect of Glucose
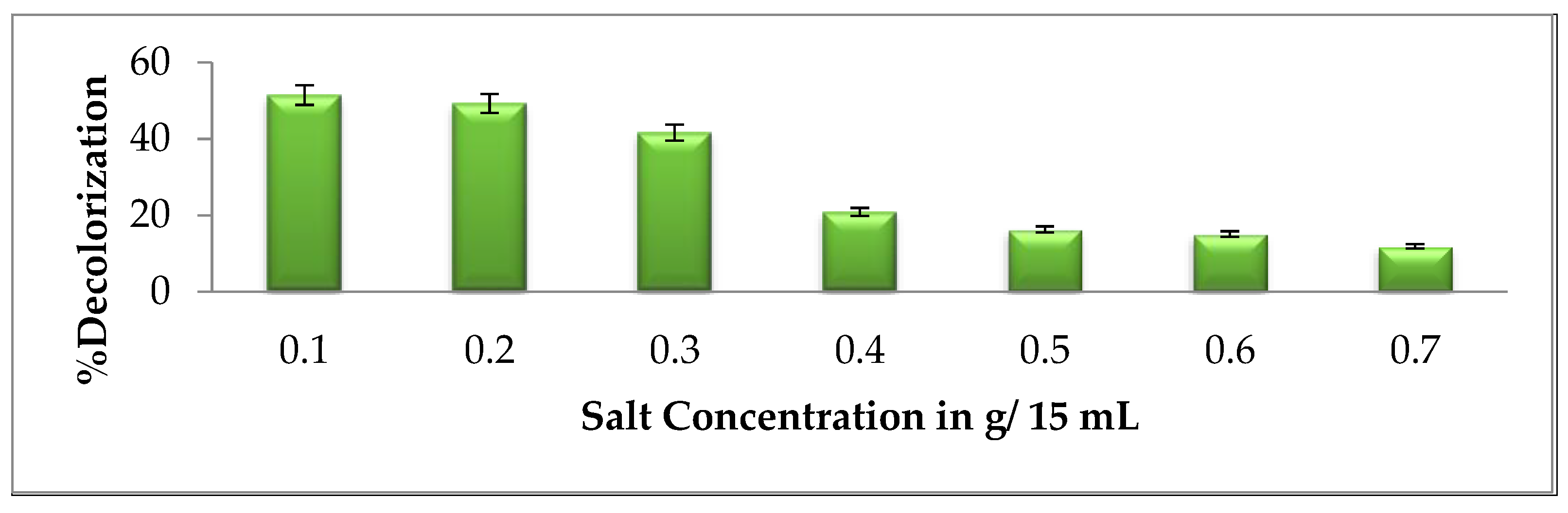
2.5.5. Effect of NaCl (Salt)
2.5.6. Effect of Time
2.6. Brown 703 Biodegradation under Optimal Conditions
2.7. Brown 703 Degradation Metabolite Extraction, Isolation, and Identification
2.7.1. Brown 703 FT-IR Analysis
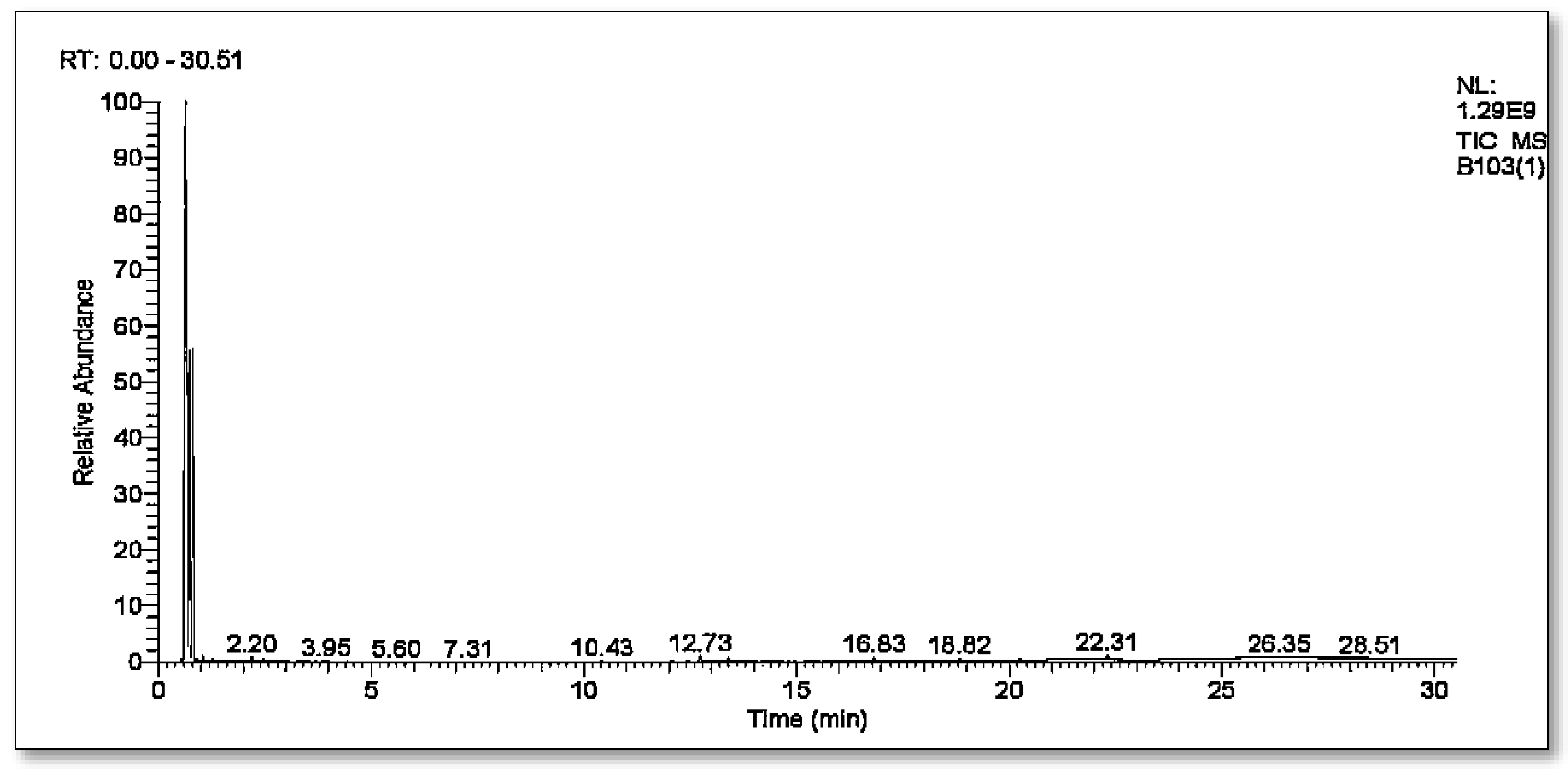
2.7.2. Brown 703 GC-MS Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
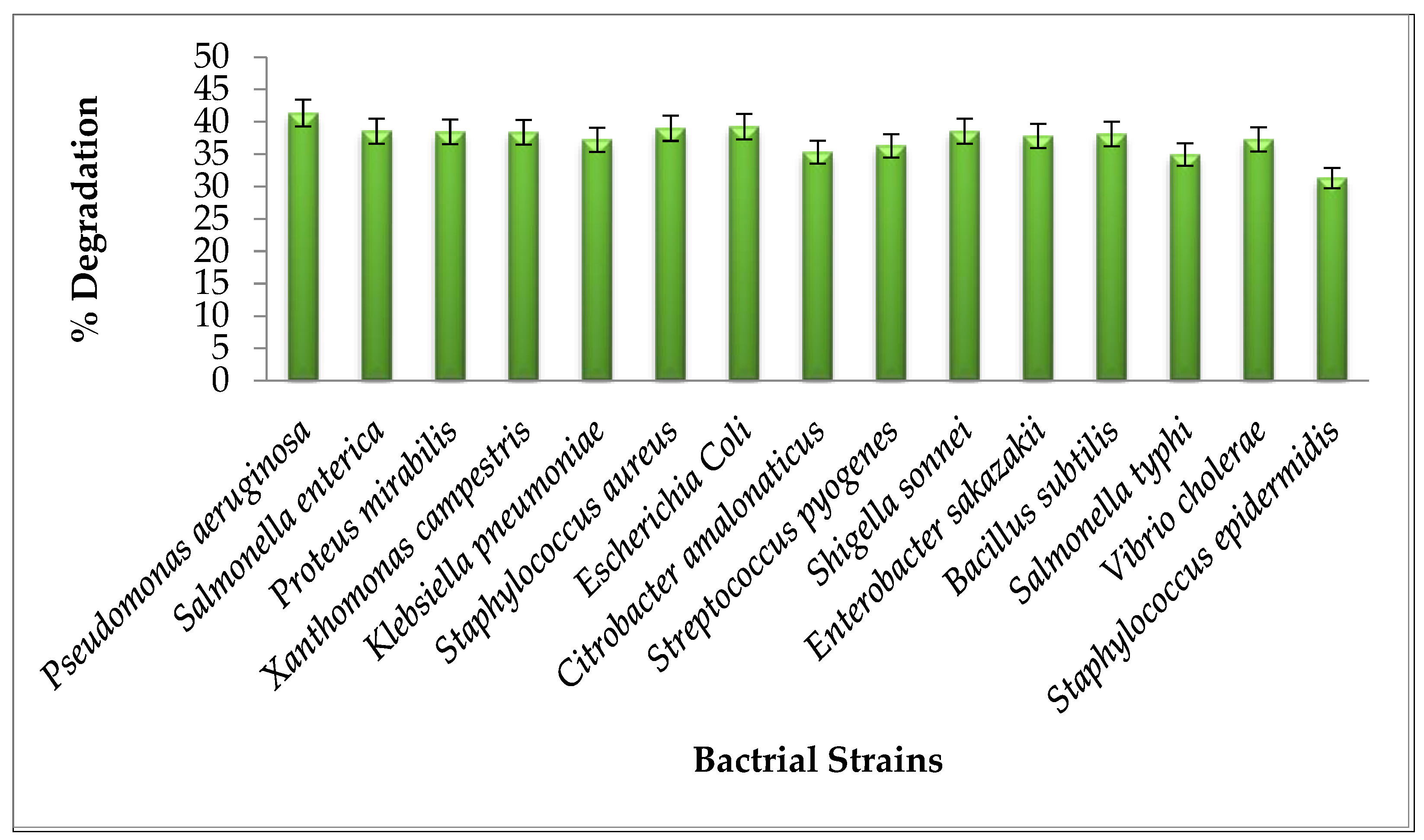
3.1. Bacterial Strains Isolation and Identification from Dye Contaminated Water
3.2. Different Parameters and Their Effects on Brown 703 Biodegradation
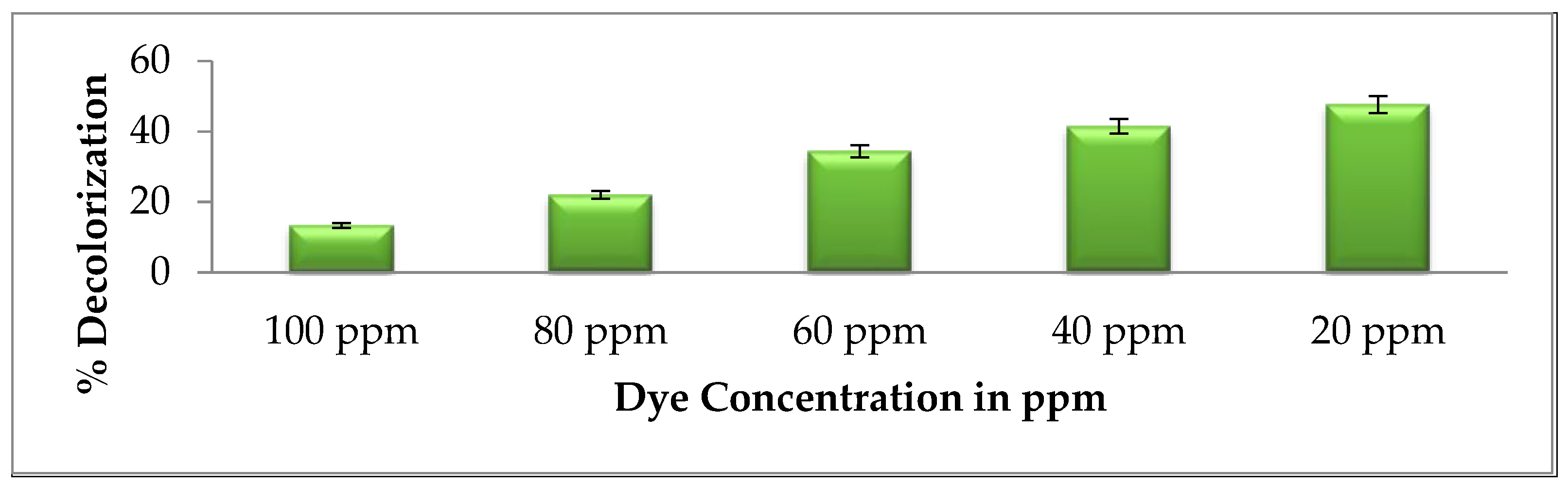
3.2.1. Effect of Brown 703 Dye Concentration
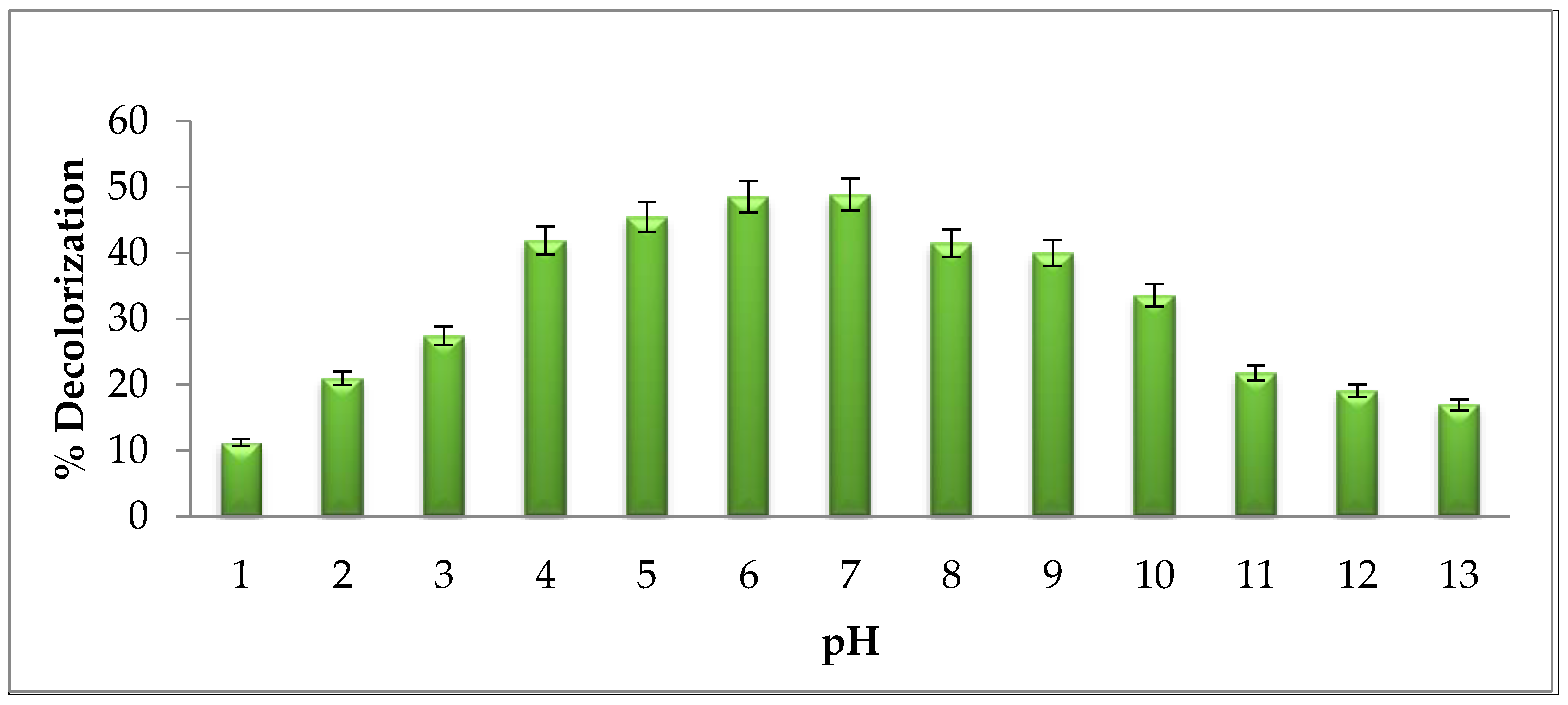
3.2.2. Effect of pH
3.2.3. Effect of Temperature
3.2.4. Effect of Glucose Concentration on Brown 703 Degradation
3.2.5. Effect of NaCl Salt Concentration on Brown 703 Degradation
3.2.6. Effect of Time (in Days) on Dye Degradation
3.3. Biodegradation of Brown 703 at Optimum Conditions
3.4. Characterization of Brown 703 Degraded Metabolites
3.4.1. FT-IR Analysis of Brown 703 Metabolites
3.4.2. GC-MS Analysis of Brown 703 Metabolites
3.4.3. Brown 703 Dye NMR Spectra of Metabolites
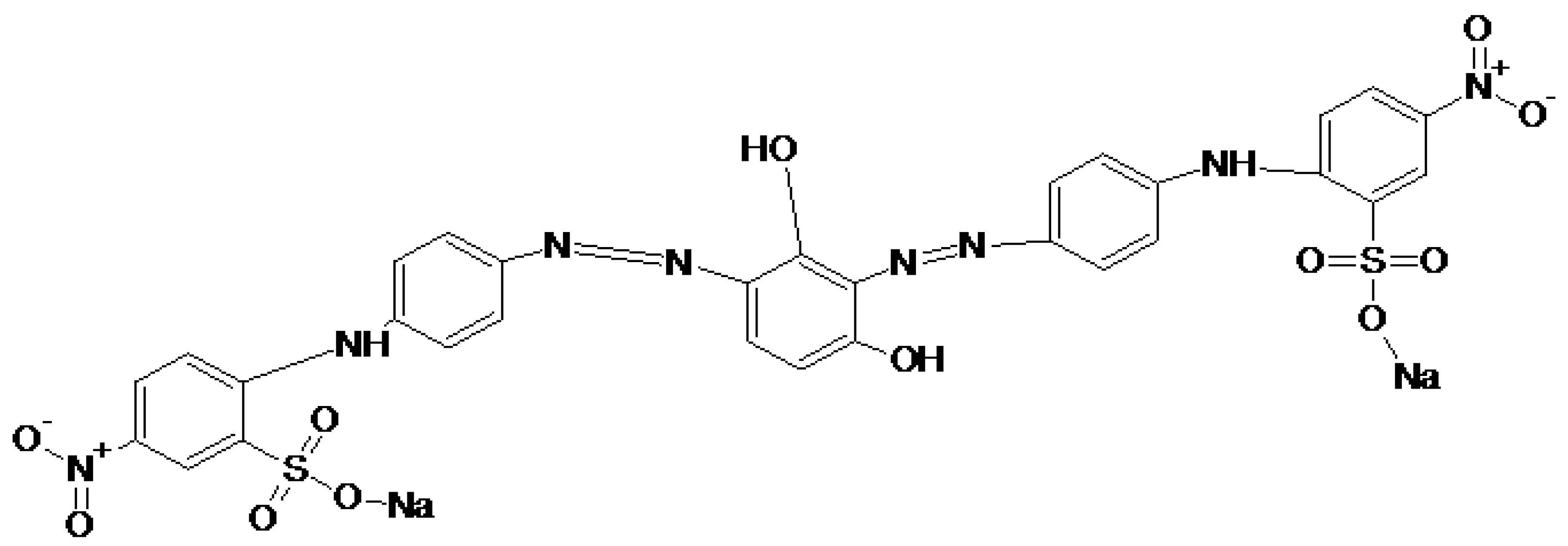
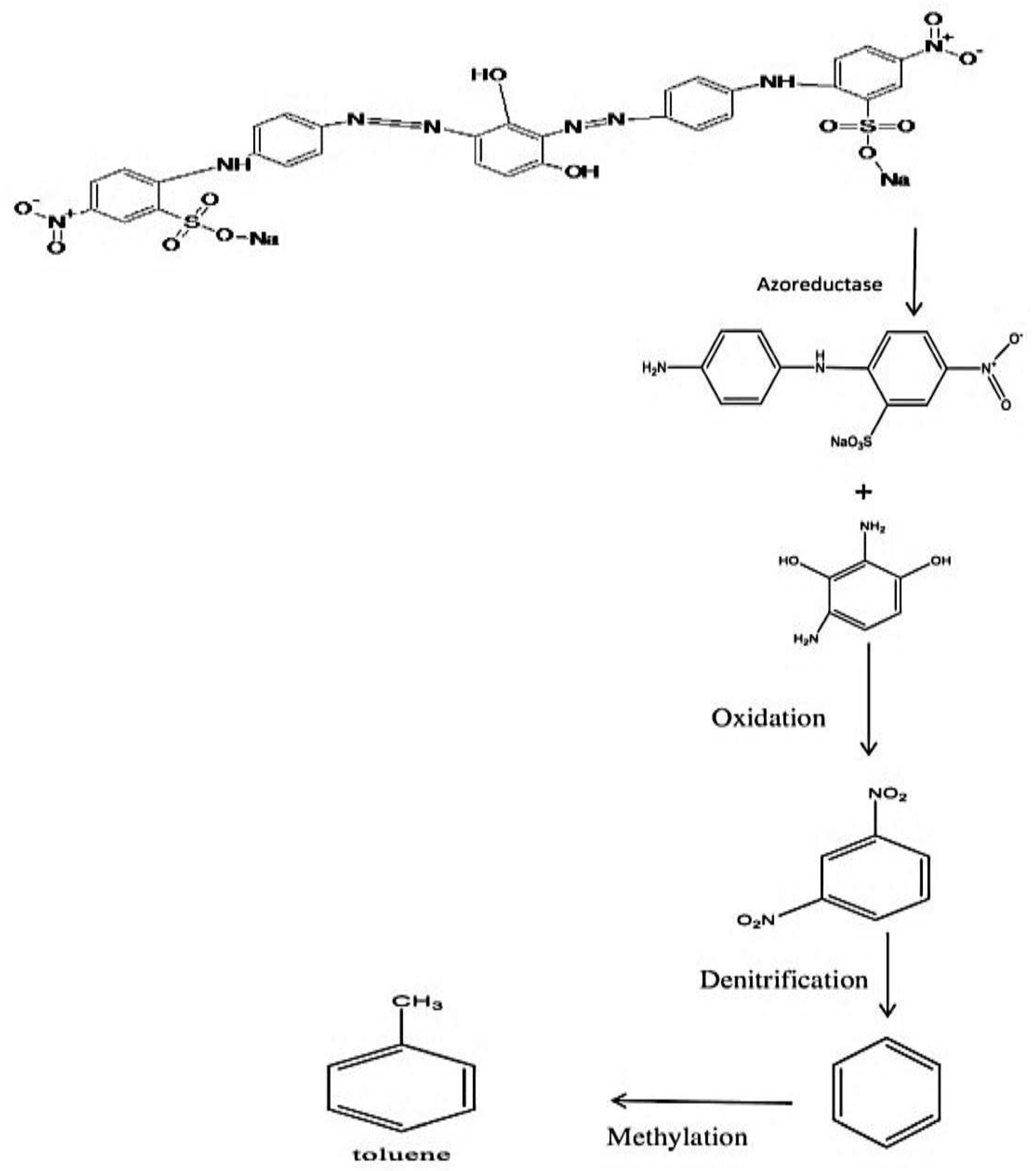
3.5. Proposed Mechanism Responsible for the Biodegradation of Brown 703
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oyekanmi, A.A.; Ahmad, A.; Mohd Setapar, S.H.; Alshammari, M.B.; Jawaid, M.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Vaseashta, A. Sustainable Durio zibethinus-Derived Biosorbents for Congo Red Removal from Aqueous Solution: Statistical Optimization, Isotherms and Mechanism Studies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Shukla, S.P. Hazardous consequences of textile mill effluents on soil and their remediation approaches. Clean Eng.Technol. 2022, 7, 100434. [Google Scholar]
- Ikram, M.; Naeem, M.; Zahoor, M.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Oyekanmi, A.A.; Islam, N.U.; Ullah, M.; Mahnashi, M.H.; Ali, A.A.; Jalal, N.A.; et al. Bacillus subtilis: As an Efficient Bacterial Strain for the Reclamation of Water Loaded with Textile Azo Dye, Orange II. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, R.; Purchase, D.; Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Bilal, M.; Chandra, R.; Bharagava, R.N. Eco toxicological and health concerns of persistent coloring pollutants of textile industry wastewater and treatment approaches for environmental safety. J. Environ.Chem.Eng. 2021, 9, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thite, V.D.; Giripunje, S.M. Adsorption and photo catalytic performance of ZnAl layered double hydroxide nanoparticles in removal of methyl orange dye. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2022, 7, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Zahoor, M.; Din, W.U.; Muhammad, M.; Khan, F.A.; Sohail, A.; Ullah, R.; Ali, E.A.; Murthy, H.C. Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution Using Black Tea Wastes: Used as Efficient Adsorbent. Adsorp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 5713077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Zahoor, M.; Batiha, G.E.S. Biodegradation and decolorization of textile dyes by bacterial strains: A biological approach for wastewater treatment. Z. Phy. Chem. 2021, 235, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Kumar, P.; Rawat, D.; Garg, S.; Mukherjee, P.; Farooqi, F.; Roy, A.; Sundaram, S.; Sharma, R.S.; Mishra, V. Microbial fuel cells for mineralization and decolorization of azo dyes: Recent advances in design and materials. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 826, 154038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dihom, H.R.; Al-Shaibani, M.M.; Mohamed, R.M.S.R.; Al-Gheethi, A.A.; Sharma, A.; Khamidun, M.H.B. Photocatalytic degradation of disperse azo dyes in textile wastewater using green zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized in plant extract: A critical review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 47, 102705. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, G.; Zahid, M.T.; Ihsan, S.; Zia, I.; Abbas, S.Z.; Rafatullah, M. Bacterial Extracellular Polymeric Substances for Degradation of Textile Dyes. In Polymer Technology in Dye-Containing Wastewater; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 175–191. [Google Scholar]
- Gayathiri, E.; Prakash, P.; Selvam, K.; Awasthi, M.K.; Gobinath, R.; Karri, R.R.; Ragunathan, M.G.; Jayanthi, J.; Mani, V.; Poudineh, M.A.; et al. Plant microbe based remediation approaches in dye removal: A review. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 7798–7828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Madliya, S.; Khare, A.; Subudhi, I.; Bhaskara Rao, K.V. Enzymatic biodegradation, kinetic study, and detoxification of Reactive Red-195 by Halomonas meridiana isolated from Marine Sediments of Andaman Sea, India. Environ. Technol. 2022, 44, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Christina, E. Mechanism and Techniques of Dye Removal by Microflora. In Dye Biodegradation, Mechanisms and Techniques; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 87–112. [Google Scholar]
- Basharat, Z.; Yasmin, A. Sulphonated azo dye decolorization by Alcaligenes faecalis subsp. phenolicus MB207: Insights from laboratory and computational analysis. Biophy. Chem. 2022, 286, 106806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikram, M.; Zahoor, M.; Khan, E.; Khayam, S.M.U. Biodegradation of Novacron Turqueiose (Reactive Blue 21) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Che. Soc. Pak. 2020, 42, 737–745. [Google Scholar]
- Thakor, R.; Mistry, H.; Tapodhan, K.; Bariya, H. Efficient biodegradation of Congo red dye using fungal consortium incorporated with Penicillium oxalicum and Aspergillus tubingensis. Folia Microbiol. 2022, 67, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H. Biodegradation of Synthetic Dyes-A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 213, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Zahoor, M.; Naeem, M.; Islam, N.U.; Shah, A.B.; Shahzad, B. Bacterial oxidoreductive enzymes as molecular weapons for the degradation and metabolism of the toxic azo dyes in wastewater: A review. Z. Phys. Chem. 2023, 137, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, J.M.; Alyahya, S.A.; Govindan, R.; Chelliah, C.K.; Maruthupandy, M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Issac, R.; Murugan, S.; Li, W.J. Laccase producing bacteria influenced the high decolorization of textile azo dyes with advanced study. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, A.; Muhammad, G.; Raza, M.A.; Iqbal, M.M.; Aslam, M.S.; Ashraf, A.; Saif, T. Aerobic Biological Units in Dye Removal. In Biological Approaches in Dye-Containing Wastewater; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 57–94. [Google Scholar]
- Velusamy, K.; Periyasamy, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Jayaraj, T.; Gokulakrishnan, M.; Keerthana, P. Transformation of aqueous methyl orange to green metabolites using bacterial strains isolated from textile industry effluent. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 25, 102126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, L.R.S.; Gradíssimo, D.G.; Xavier, L.P.; Santos, A.V. Degradation of Azo Dyes: Bacterial potential for bioremediation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.; Anbarasu, A.; Pasupuleti, R.R.; Sekar, M.; Praveenkumar, T.R.; Kumar, J.A. Treatment of heavy metals containing wastewater using biodegradable adsorbents: A review of mechanism and future trends. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadia, M.; Ahmad, I.; Saleheen, Z.U.; Zubair, M.; Zahoor, M.; Ullah, R.; Bari, A.; Zekker, I. Synthesis and Characterization of MIPs for Selective Removal of Textile Dye Acid Black-234 from Wastewater Sample. Molecules 2023, 28, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, N.T.; Dave, S.R. Optimisation for enhanced decolourization and degradation of Reactive Red BS CI 111 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa NGKCTS. Biodegradation 2009, 20, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Shi, M.; Pan, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Shen, T.; Tian, Y. Decolourization and biodegradation of methylene blue dye by a ligninolytic enzyme-producing Bacillus thuringiensis: Degradation products and pathway. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2022, 156, 109999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.L.; Chaudhary, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Yadav, A. Biodegradation of Reactive Yellow-145 azo dye using bacterial consortium: A deterministic analysis based on degradable Metabolite, phytotoxicity and genotoxicity study. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.T.; Danish, M.; Singh, R.S.; Rafatullah, M.; HPS, A.K. Exploiting microbial biomass in treating azo dyes contaminated wastewater: Mechanism of degradation and factors affecting microbial efficiency. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 43, 102255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, N.; Patel, K.C.; Keharia, H.; Madamwar, D. Decolorization of diazo-dye reactive blue 172 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa NBAR12. J. Basic Microbiol. 2005, 45, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yang, Y.; Sun, F.; Liu, Y.; Tang, M.; Chen, J. Rapid degradation of Congo red wastewater by Rhodopseudomonas palustris intimately coupled carbon nanotube-Silver modified titanium dioxide photocatalytic composite with sodium alginate. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerbergen, K.; Willems, K.A.; Dewil, R.; Van Impe, J.; Appels, L.; Lievens, B. Isolation and screening of bacterial isolates from wastewater treatment plants to decolorize azo dyes. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 125, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayam, S.M.U.; Zahoor, M.; Khan, E.; Shah, M. Reduction of keto group in drimarene blue by Aspergillus niger; a predominant reason for subsequent decolorization. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 1397–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.U.; Zahoor, M.; Rehman, M.U.; Shah, A.B.; Zekker, I.; Khan, F.A.; Ullah, R.; Albadrani, G.M.; Bayram, R.; Mohamed, H.R.H. Biological Mineralization of Methyl Orange by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water 2022, 14, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyasa, I.; Sudiartha, G.A.W. Treatment of Fabric Dye Wastewater from Household Industries Using Fixed Bed Reactor (FBR) With Local Microbial Isolates from Water Channel Sediment in Denpasar City, Bali Province, Indonesia. EnvironmentAsia 2022, 15, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, S.; Banerjee, A.; Halder, U.; Biswas, R.; Bandopadhyay, R. Degradation of synthetic azo dyes of textile industry: A sustainable approach using microbial enzymes. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Rehman, M.U.; Zahoor, M.; Shah, A.B.; Zekker, I. Biodegradation of Brown 706 Dye by Bacterial Strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water 2021, 13, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Naeem, M.; Zahoor, M.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Oyekanmi, A.A.; Ullah, R.; Farraj, D.A.A.; Elshikh, M.S.; Zekker, I.; Gulfam, N. Biological Degradation of the Azo Dye Basic Orange 2 by Escherichia coli: A Sustainable and Ecofriendly Approach for the Treatment of Textile Wastewater. Water 2022, 14, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolekar, Y.M.; Nemade, H.N.; Markad, V.L.; Adav, S.S.; Patole, M.S.; Kodam, K.M. Decolorization and biodegradation of azo dye, reactive blue 59 by aerobic granules. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikram, M.; Naeem, M.; Zahoor, M.; Rahim, A.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Oyekanmi, A.A.; Shah, A.B.; Mahnashi, M.H.; Al Ali, A.; Jalal, N.A.; et al. Biodegradation of Azo Dye Methyl Red by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Optimization of Process Conditions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Singh, P.; Iyengar, L. Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 59, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


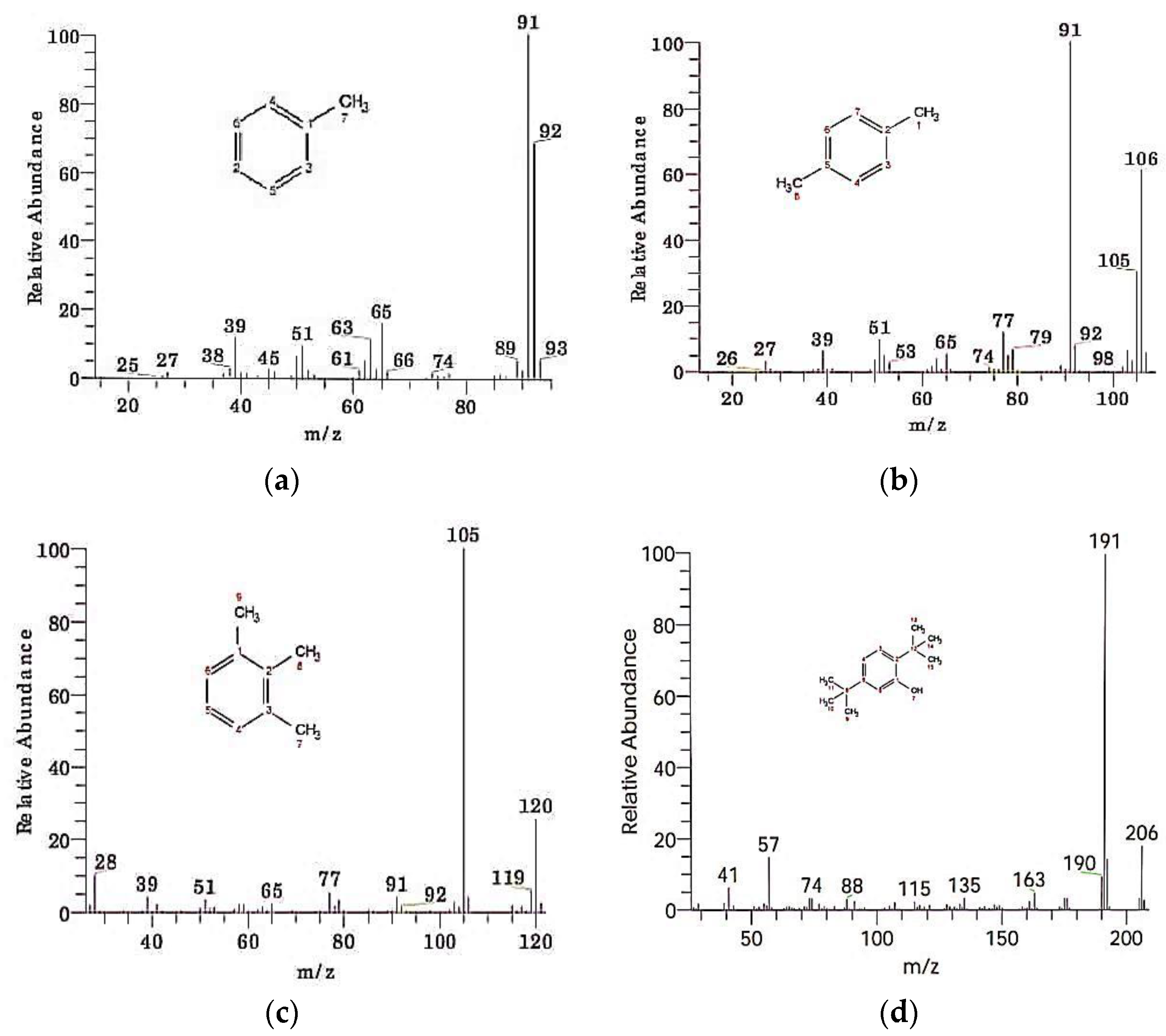
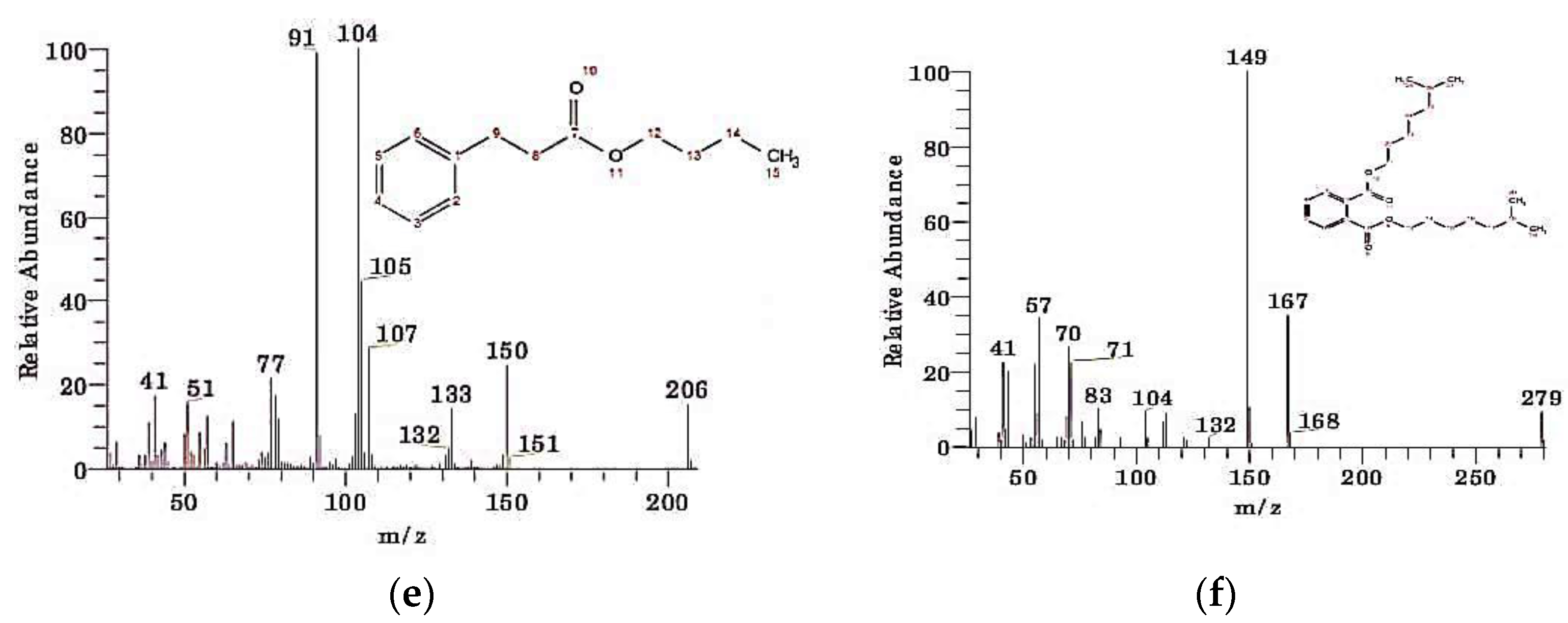


| S. No. | Compound Name | Retention Time | Peak Area | Chemical Formula | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Toluene | 1.30 | 0.26 | C7H8 | 92 |
| 2 | p-Xylene | 2.18 | 0.39 | C8H10 | 106 |
| 3 | Benzene, 1,2,3-triMethyl | 3.42 | 0.03 | C9H12 | 120 |
| 4 | Phenol, 2,5-bis(1,1-diMethylethyl) | 12.30 | 0.07 | C14H22O | 206 |
| 5 | Benzenepropanoic acid, butyl ester | 12.75 | 0.50 | C13H18O2 | 206 |
| 6 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, diisooctyl ester | 22.31 | 0.51 | C24H38O4 | 390 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah Khan, A.; Zahoor, M.; Ur Rehman, M.; Ikram, M.; Zhu, D.; Naveed Umar, M.; Ullah, R.; Ali, E.A. Bioremediation of Azo Dye Brown 703 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An Effective Treatment Technique for Dye-Polluted Wastewater. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 1049-1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14030070
Ullah Khan A, Zahoor M, Ur Rehman M, Ikram M, Zhu D, Naveed Umar M, Ullah R, Ali EA. Bioremediation of Azo Dye Brown 703 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An Effective Treatment Technique for Dye-Polluted Wastewater. Microbiology Research. 2023; 14(3):1049-1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14030070
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah Khan, Asad, Muhammad Zahoor, Mujaddad Ur Rehman, Muhammad Ikram, Daochen Zhu, Muhammad Naveed Umar, Riaz Ullah, and Essam A. Ali. 2023. "Bioremediation of Azo Dye Brown 703 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An Effective Treatment Technique for Dye-Polluted Wastewater" Microbiology Research 14, no. 3: 1049-1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14030070
APA StyleUllah Khan, A., Zahoor, M., Ur Rehman, M., Ikram, M., Zhu, D., Naveed Umar, M., Ullah, R., & Ali, E. A. (2023). Bioremediation of Azo Dye Brown 703 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An Effective Treatment Technique for Dye-Polluted Wastewater. Microbiology Research, 14(3), 1049-1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14030070







