Tick Diversity and Distribution of Hard (Ixodidae) Cattle Ticks in South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geographical Distribution of Ixodidae in South Africa
3. Predominant Tick Species on Cattle in South Africa
3.1. Amblyomma
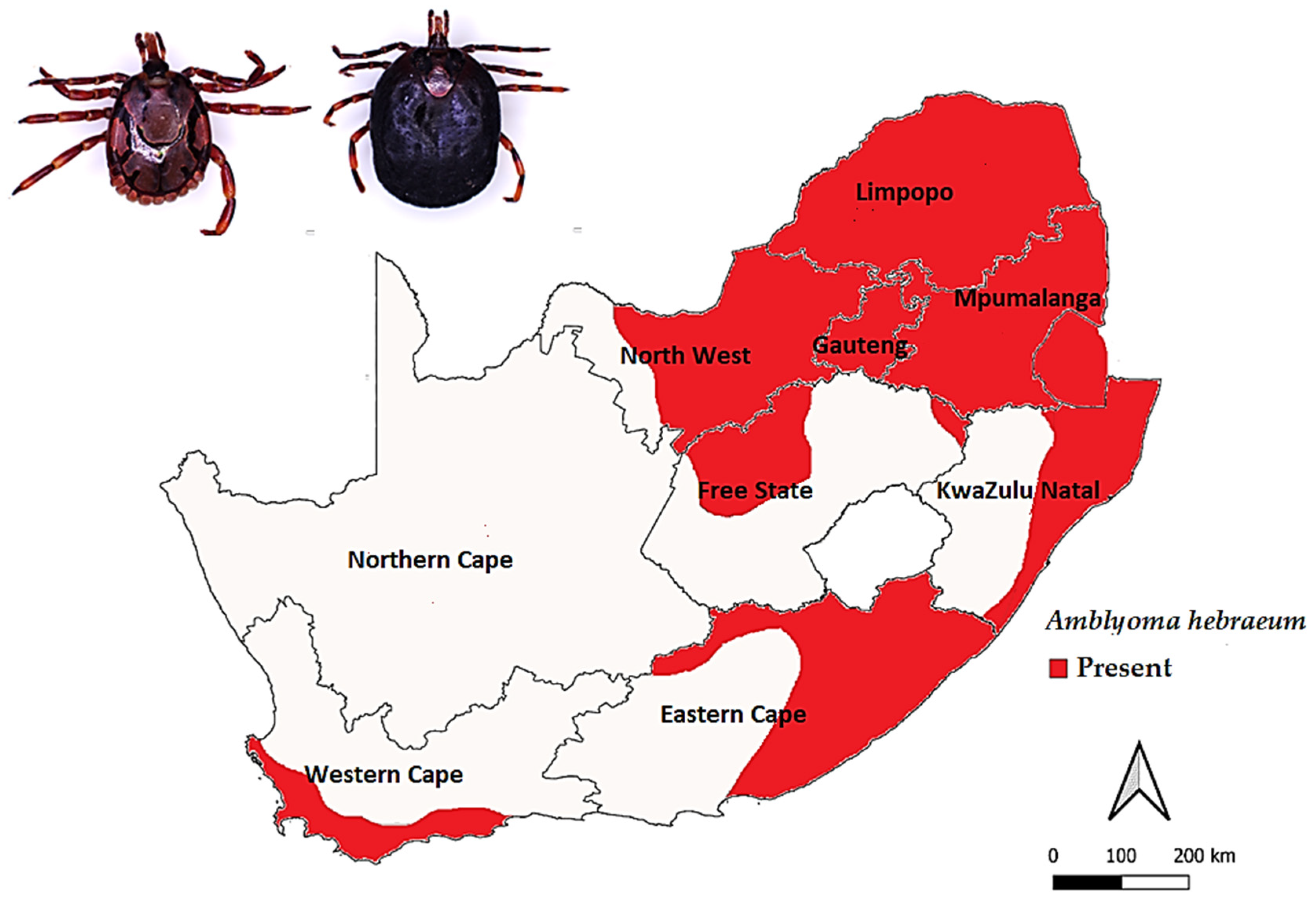
Amblyomma hebraeum Koch, 1844
3.2. Hyalomma
3.2.1. Hyalomma truncatum Koch, 1844
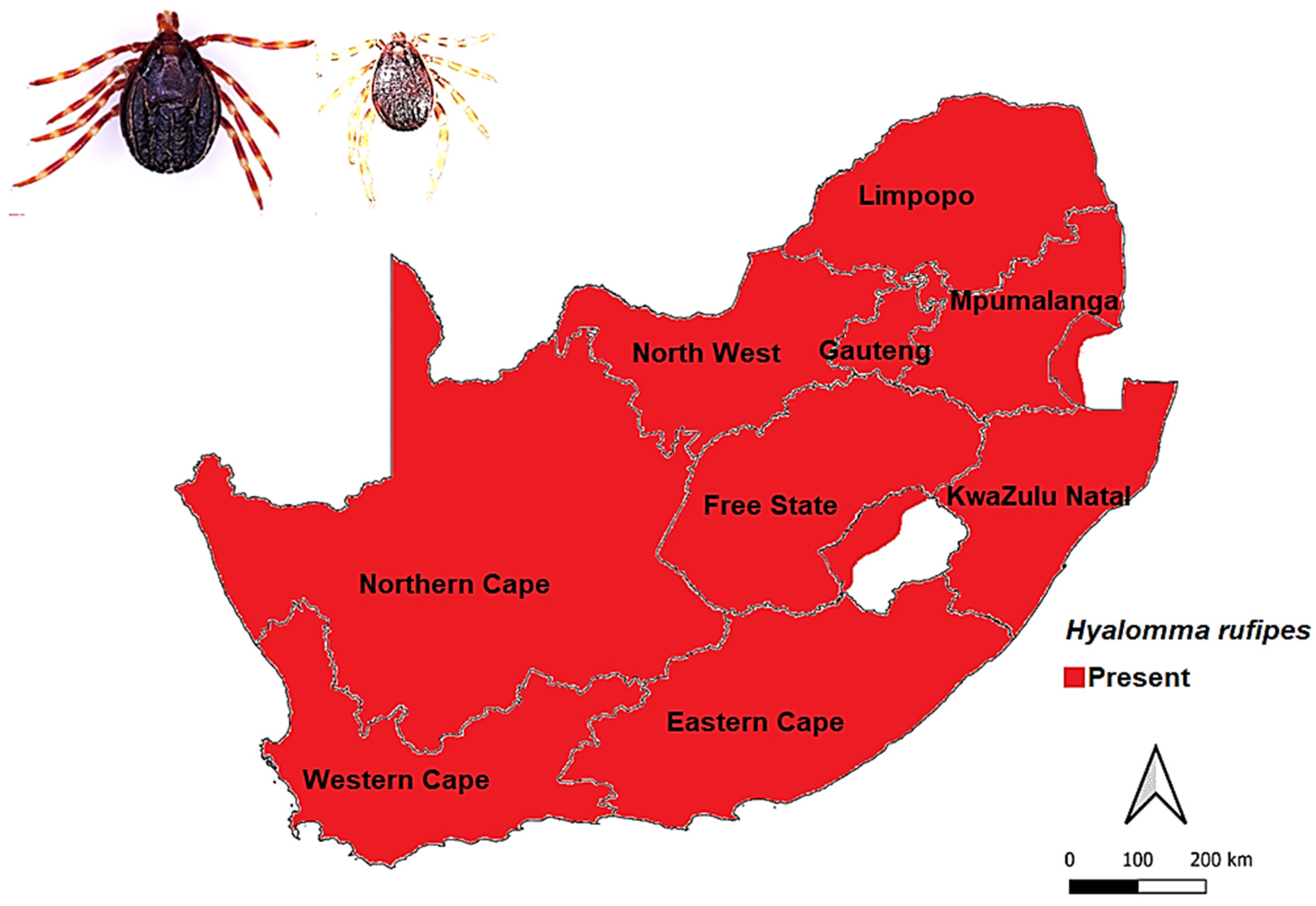
3.2.2. Hyalomma rufipes Koch, 1844
3.3. Rhipicephalus
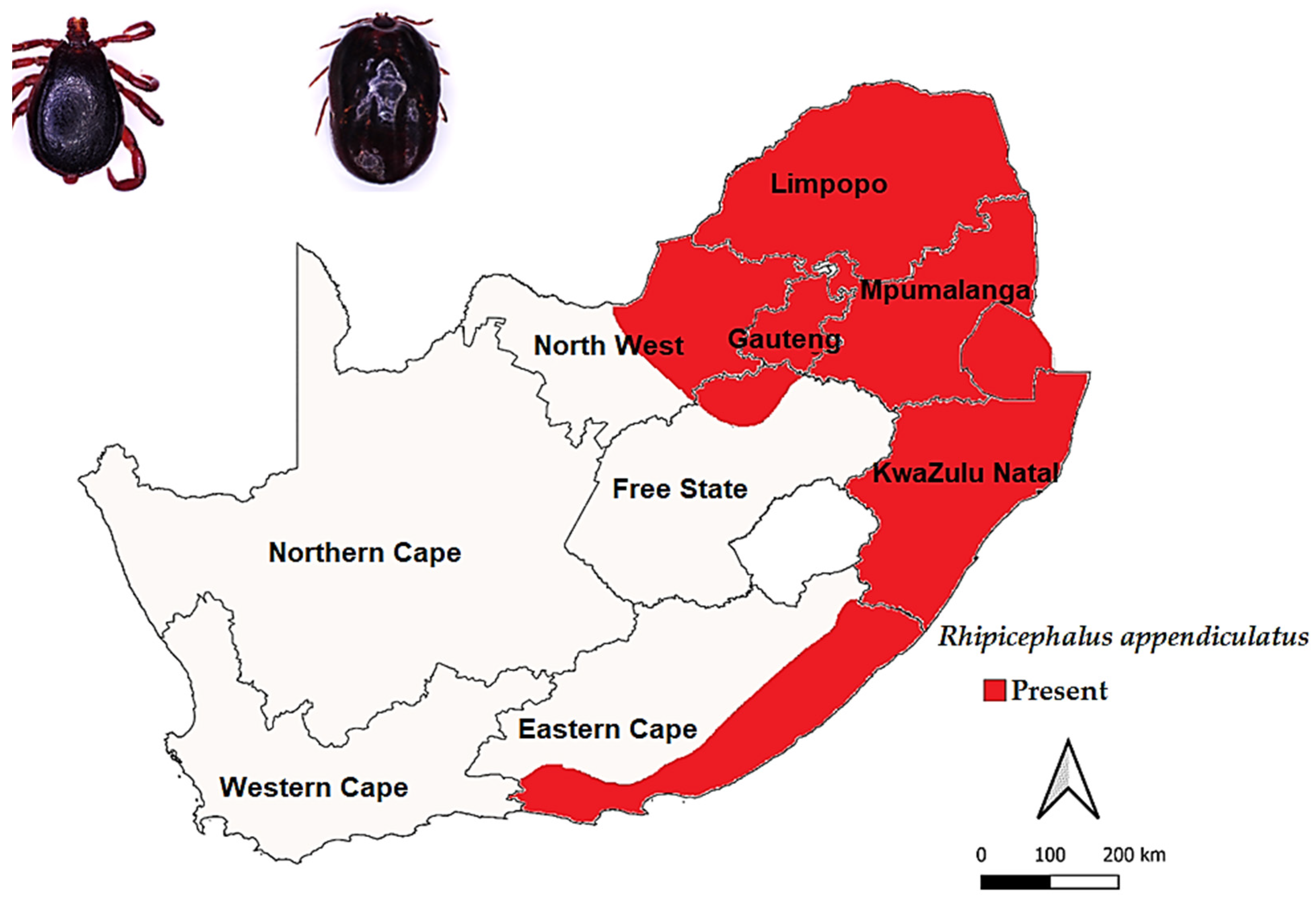
3.3.1. Rhipicephalus appendiculatus Neumann, 1901
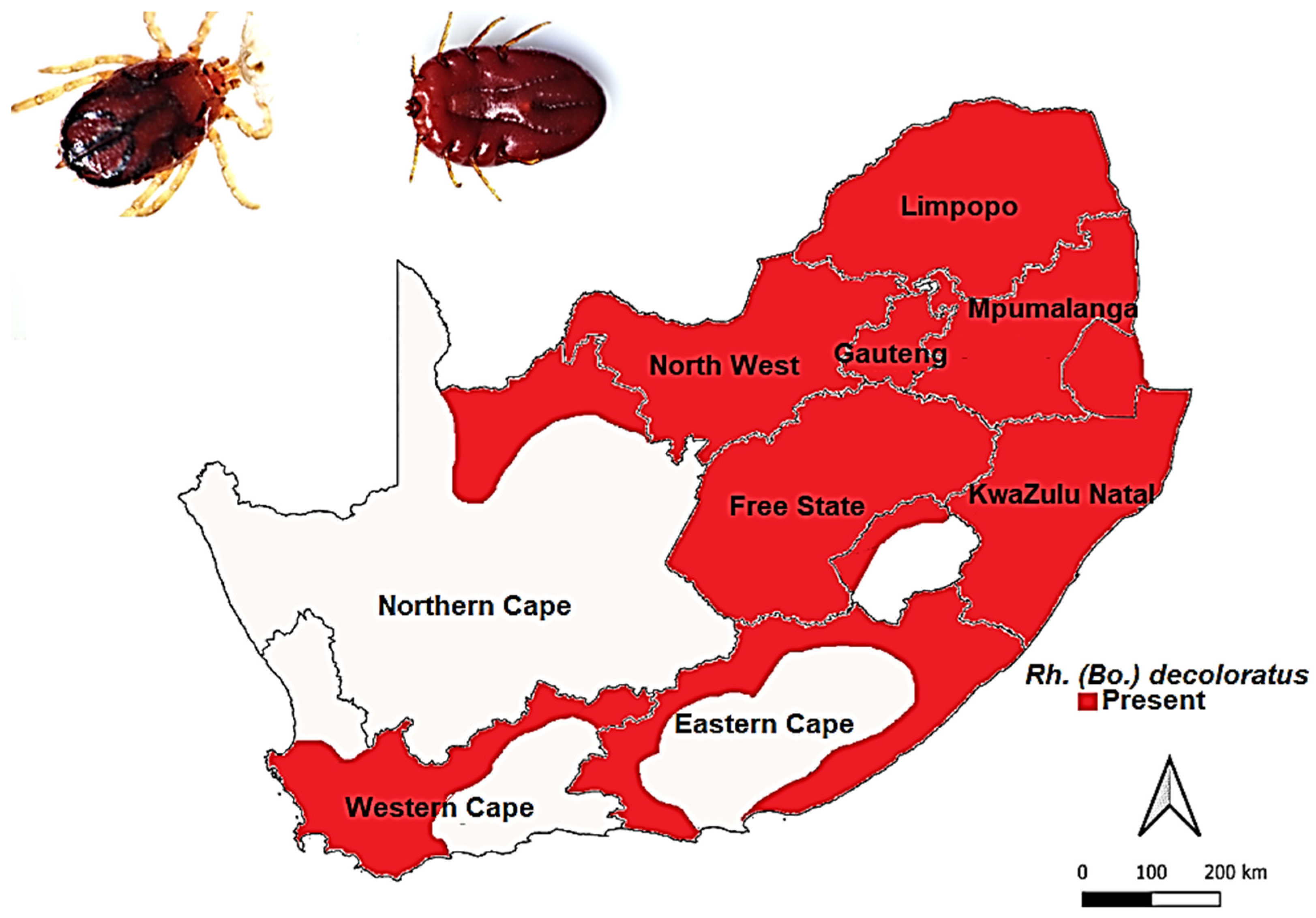
3.3.2. Rhipicephalus (Bo.) decoloratus (Koch, 1844)
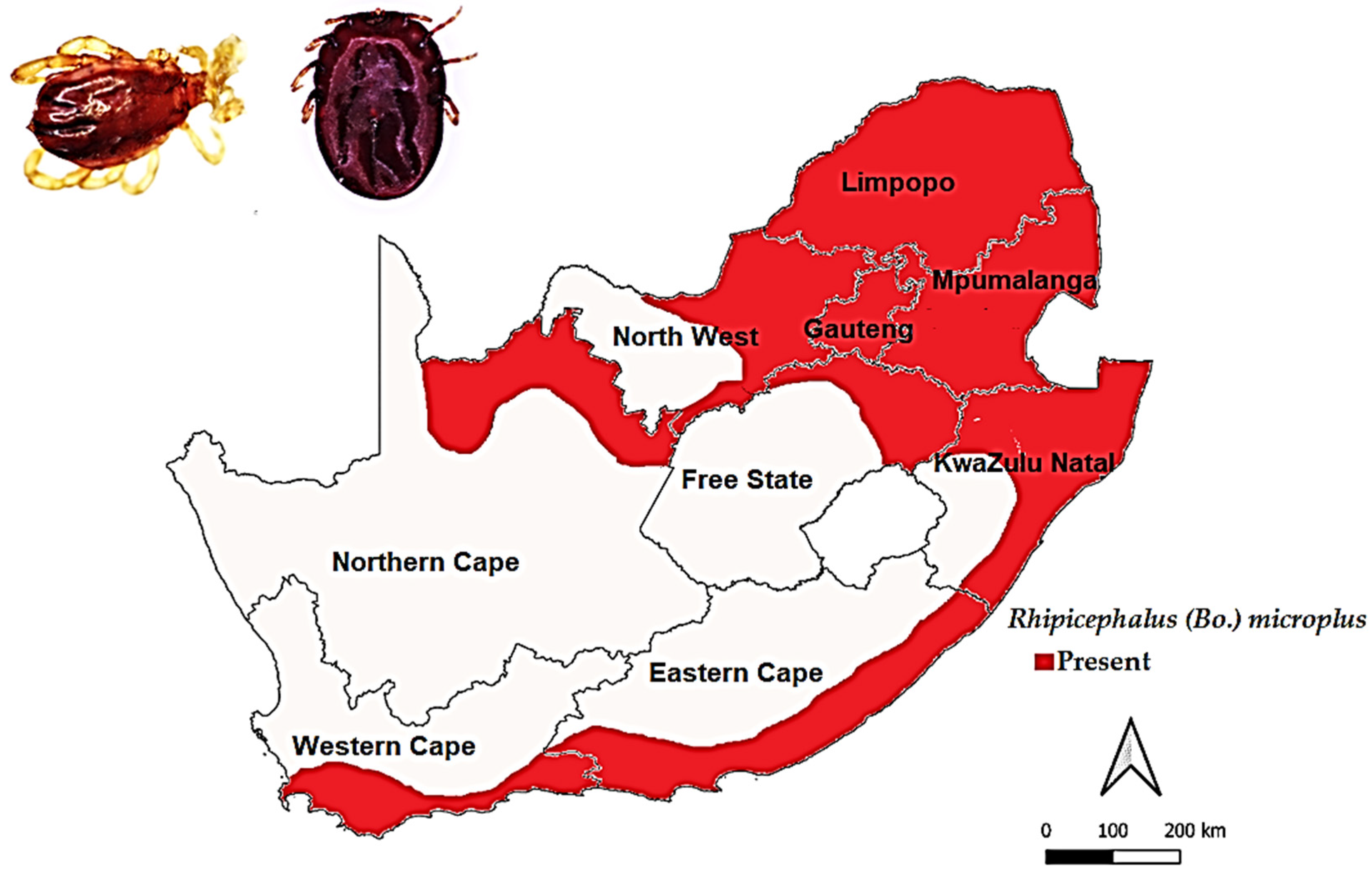
3.3.3. Rhipicephalus (Bo.) microplus (Canestrini, 1888)
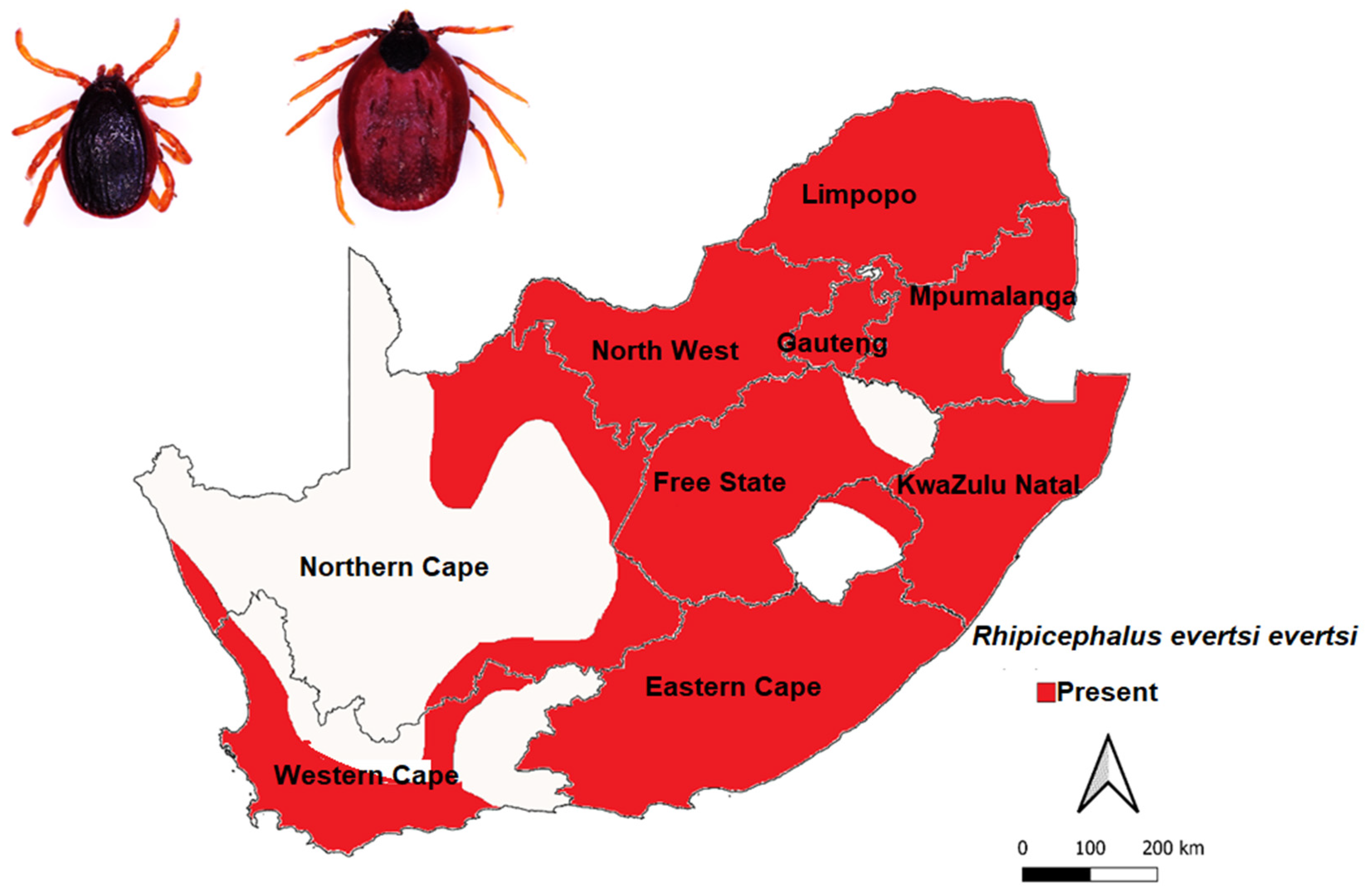
3.3.4. Rhipicephalus evertsi evertsi Neumann, 1897
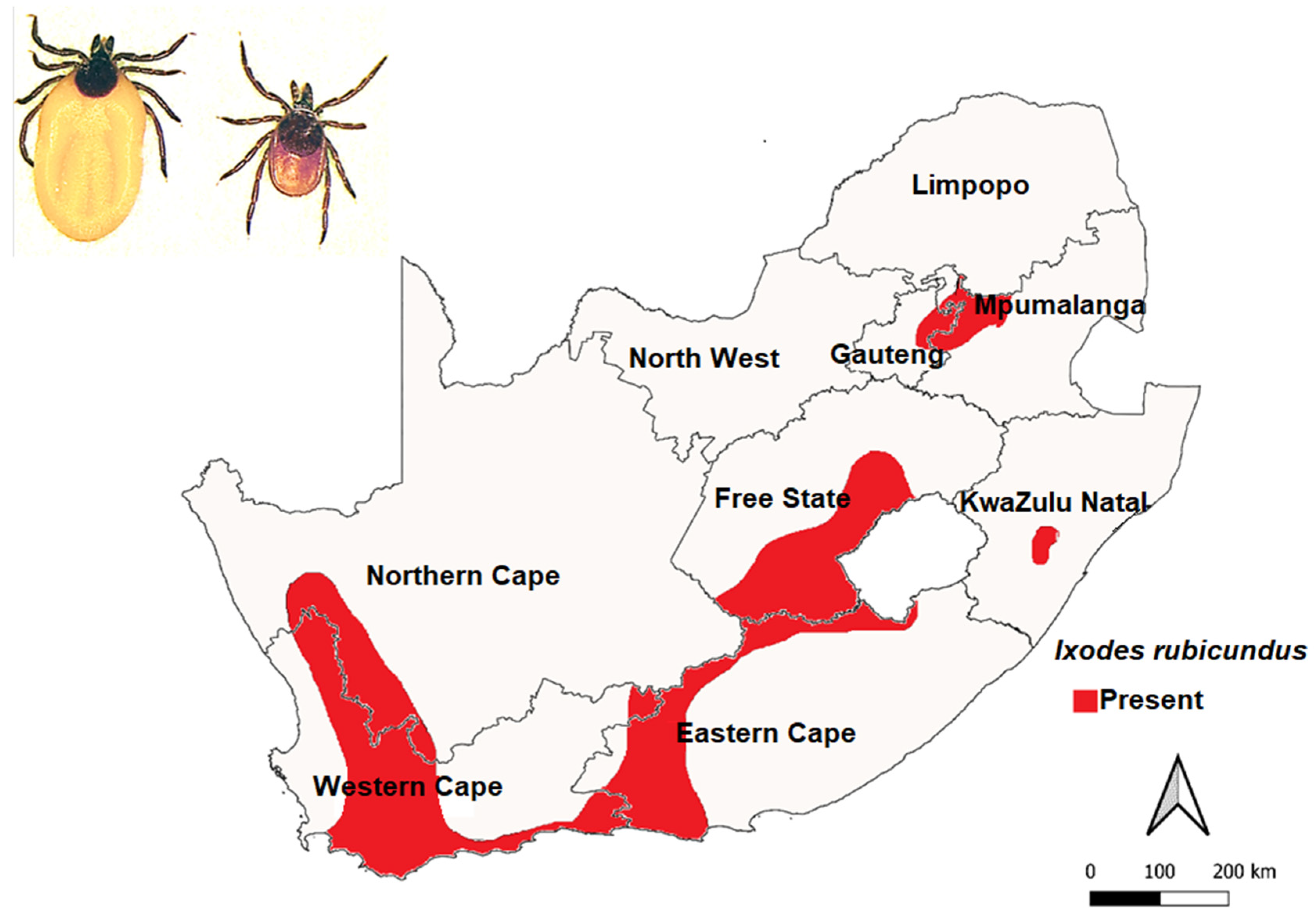
3.4. Ixodes rubicundus Neumann, 1904
4. The Economic Impact of Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases on Cattle Production
5. Control of Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases
5.1. Control of Ticks in South Africa
5.1.1. Control of Ticks with Vaccines
5.1.2. Other Methods of Tick Control
Manual Removal
Husbandry Practices That Support Tick Control
5.2. Host Resistance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De la Fuente, J.; Estrada-Pena, A.; Venzal, J.M.; Kocan, K.M.; Sonenshine, D.E. Overview: Ticks as vectors of pathogens that cause disease in humans and animals. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2008, 13, 6938–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klompen, J.; Keirans, J.; Oliver, J., Jr. Evolution of ticks. Annu. Rev. Ent. 1996, 41, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Robbins, R.G.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Petney, T.N.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Horak, I.G.; Shao, R.; Barker, S.C. The Argasidae, Ixodidae and Nuttalliellidae (Acari: Ixodida) of the world: A list of valid species names. Zootaxa 2010, 2528, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, G. Nuttalliella namaqua, a new genus and species of tick. Parasitology 1931, 23, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.A.; Putterill, J.F.; De Klerk, D.G.; Pienaar, R.; Mans, B.J. Nuttalliella namaqua (Ixodoidea: Nuttalliellidae): First description of the male, immature stages and re-description of the female. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogstraal, H.; Aeschlimann, A. Tick-host specificity. Bull. Société Entomol. Suisse 1982, 55, 5–32. [Google Scholar]
- Horak, I.G.; Camicas, J.-L.; Keirans, J.E. The Argasidae, Ixodidae and Nuttalliellidae (Acari: Ixodida): A world list of valid tick names. Ticks Tick-Borne Pathog. 2003, 28, 27–54. [Google Scholar]
- Nava, S.; Guglielmone, A.A.; Mangold, A.J. An overview of systematics and evolution of ticks. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2009, 14, 2857–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, R.A.; Bonamo, P.M.; Grierson, J.D.; Shear, W.A. Oribatid mite fossils from a terrestrial Devonian deposit near Gilboa, New York. J. Paleontol. 1988, 62, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M. Biology of Ticks Volume 2; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Chomel, B.B.; Otranto, D. Ticks and tick-borne diseases: A One Health perspective. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, J. Physician’s Guide to Arthropods of Medical Importance, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tabor, A.E.; Ali, A.; Rehman, G.; Rocha Garcia, G.; Zangirolamo, A.F.; Malardo, T.; Jonsson, N.N. Cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus-host interface: A review of resistant and susceptible host responses. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongejan, F.; Uilenberg, G. The global importance of ticks. Parasitology 2004, 129, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediannikov, O.; Fenollar, F. Looking in ticks for human bacterial pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2014, 77, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, S.C.; Walker, A.R. Ticks of Australia. The species that infest domestic animals and humans. Zootaxa 2014, 3816, 1–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Rani, P.A.M.; Irwin, P.J.; Coleman, G.T.; Gatne, M.; Traub, R.J. A survey of canine tick-borne diseases in India. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, E.; Kock, R.; McKeever, D.; Gakuya, F.; Musyoki, C.; Chege, S.M.; Mutinda, M.; Kariuki, E.; Davidson, Z.; Low, B. Prevalence of Theileria equi and Babesia caballi as well as the identification of associated ticks in sympatric Grevy’s zebras (Equus grevyi) and donkeys (Equus africanus asinus) in northern Kenya. J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagel Van Zee, J.; Geraci, N.S.; Guerrero, F.D.; Wikel, S.K.; Stuart, J.J.; Nene, V.M.; Hill, C.A. Tick genomics: The Ixodes genome project and beyond. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Shehla, S.; Zahid, H.; Ullah, F.; Zeb, I.; Ahmed, H.; da Silva Vaz, I., Jr.; Tanaka, T. Molecular survey and spatial distribution of Rickettsia spp. in ticks infesting free-ranging wild animals in Pakistan (2017–2021). Pathogens 2022, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senbill, H.; Tanaka, T.; Karawia, D.; Rahman, S.; Zeb, J.; Sparagano, O.; Baruah, A. Morphological identification and molecular characterization of economically important ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) from North and North–Western Egypt. Acta Trop. 2022, 231, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, W.M.A.; Moustafa, M.A.M.; Kelava, S.; Barker, D.; Matsuno, K.; Nonaka, N.; Shao, R.; Mans, B.J.; Barker, S.C.; Nakao, R. Reconstruction of mitochondrial genomes from raw sequencing data provides insights on the phylogeny of Ixodes ticks and cautions for species misidentification. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, J.; Kocan, K. Strategies for development of vaccines for control of ixodid tick species. Parasite Immunol. 2006, 28, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnarelli, L.A. Global importance of ticks and associated infectious disease agents. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2009, 31, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoryeva, L.A.; Shatrov, A. Life cycle of the tick Ixodes ricinus (L.)(Acari: Ixodidae) in the North-West of Russia. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2022, 27, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tälleklint, L.; Jaenson, T.G. Relationship between Ixodes ricinus density and prevalence of infection with Borrelia-like spirochetes and density of infected ticks. J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 33, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongejan, F.; Uilenberg, G. Infectious Diseases of Livestock; Coetzer, J.A.W., Thomson, G.R., Maclachlan, N.J., Penrith, M.-L., Eds.; Anipedia; Oxford University Press: Cape Town, South Africa, 2018; Available online: http://www.anipedia.org/ (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Horak, I.G.; Jordaan, A.J.; Nel, P.J.; van Heerden, J.; Heyne, H.; van Dalen, E.M. Distribution of endemic and introduced tick species in Free State Province, South Africa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2015, 86, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabaja, M.F.; Tempesta, M.; Bayan, A.; Vesco, G.; Greco, G.; Torina, A.; Blanda, V.; La Russa, F.; Scimeca, S.; Lelli, R. Diversity and distribution of ticks from domestic ruminants in Lebanon. Vet. Ital. 2017, 53, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Horak, I.G.; Heyne, H.; Williams, R.; Gallivan, G.J.; Spickett, A.M.; Bezuidenhout, J.D.; Estrada-Peña, A. The Ixodid Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) of Southern Africa; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mapholi, N.O.; Marufu, M.C.; Maiwashe, A.; Banga, C.B.; Muchenje, V.; MacNeil, M.D.; Chimonyo, M.; Dzama, K. Towards a genomics approach to tick (Acari: Ixodidae) control in cattle: A review. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangiwe, N.; Goni, S.; Hervé-Claude, L.P.; Ruddat, I.; Horak, I.G. Ticks on pastures and on two breeds of cattle in the Eastern Cape province, South Africa. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2011, 78, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, I.G.; Gallivan, G.J.; Spickett, A.M. The dynamics of questing ticks collected for 164 consecutive months off the vegetation of two landscape zones in the Kruger National Park (1988–2002). Part I. Total ticks, Amblyomma hebraeum and Rhipicephalus decoloratus. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2011, 78, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bryson, N.; Horak, I.; Venter, E.; Yunker, C. Collection of free-living nymphs and adults of Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae) with pheromone/carbon dioxide traps at 5 different ecological sites in heartwater endemic regions of South Africa. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2000, 24, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoult, D.; Roux, V. Rickettsioses as paradigms of new or emerging infectious diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 694–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maina, A.N.; Jiang, J.; Omulo, S.A.; Cutler, S.J.; Ade, F.; Ogola, E.; Feikin, D.R.; Njenga, M.K.; Cleaveland, S.; Mpoke, S. High prevalence of Rickettsia africae variants in Amblyomma variegatum ticks from domestic mammals in rural western Kenya: Implications for human health. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.S.; Janovy, J.; Schmidt, G.; Larry, S. Roberts’ Foundations of Parasitology; Mcgraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Norval, R.; Horak, I. Vectors: Ticks. Infect. Dis. Livest. 2004, 1, 3–42. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, J.B. A review of the ixodid ticks (Acari, Ixodidae) occurring in southern Africa. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1991, 58, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horak, I.; Anthonissen, M.; Krecek, R.; Boomker, J. Arthropod parasites of springbok, gemsbok, kudus, giraffes and Burchell’s and Hartmann’s zebras in the Etosha and Hardap Nature Reserves, Namibia. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1992, 59, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biggs, H.; Langenhoven, J. Seasonal Prevelance of Ixodid Ticks on Cattle in the Windhoek District of South West Africa/Namibia. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1984, 51, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horak, I.G.; Londt, J.; De Villiers, I. Parasites of domestic and wild animals in South Africa. XIII. The seasonal incidence of adult ticks (Acarina: Ixodidae) on cattle in the northern Transvaal. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1979, 46, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mapholi, N.; Maiwashe, A.; Matika, O.; Riggio, V.; Banga, C.; MacNeil, M.D.; Muchenje, V.; Nephawe, K.; Dzama, K. Genetic parameters for tick counts across months for different tick species and anatomical locations in South African Nguni cattle. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, I.G.; Boshoff, C.R.; Cooper, D.V.; Foggin, C.M.; Govender, D.; Harrison, A.; Hausler, G.; Hofmeyr, M.; Kilian, J.W.; MacFadyen, D.N.; et al. Parasites of domestic and wild animals in South Africa. XLIX. Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting white and black rhinoceroses in southern Africa. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2017, 84, e1–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Walker, A.R. Ticks of Domestic Animals in Africa: A Guide to Identification of Species; Bioscience Reports Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Keirans, J. Systematics of the Ixodida (Argasidae, Ixodidae, Nuttalliellidae): An overview and some problems. In Tick Vector Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, J.B.; Keirans, J.E.; Horak, I.G. The genus Rhipicephalus (Acari, Ixodidae)—A guide to the brown ticks of the world. Rostrum Newsl. Entomol. Soc. South. Afr. 2000, 2000, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Nijhof, A.M.; Balk, J.A.; Postigo, M.; Jongejan, F. Selection of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR studies in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Rhipicephalus appendiculatus ticks and determination of the expression profile of Bm86. BMC Mol. Biol. 2009, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, R.E.; Cote, M.; Le Naour, E.; Bonnet, S.I. Environmental factors influencing tick densities over seven years in a French suburban forest. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessard, P.; l’Eplattenier, R.; Norval, R.; Kundert, K.; Dolan, T.; Croze, H.; Walker, J.; Irvin, A.; Perry, B.D. Geographical information systems for studying the epidemiology of cattle diseases caused by Theileria parva. Vet. Rec. 1990, 126, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mapholi, N.O.; Maiwashe, A.; Matika, O.; Riggio, V.; Bishop, S.; MacNeil, M.; Banga, C.; Taylor, J.; Dzama, K. Genome-wide association study of tick resistance in South African Nguni cattle. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madder, M.; Horak, I.; Stoltsz, H. Tick identification. Pretoria Fac. Vet. Sci. Univ. Pretoria 2014, 58, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-Peña, A. The relationships between habitat topology, critical scales of connectivity and tick abundance Ixodes ricinus in a heterogeneous landscape in northern Spain. Ecography 2003, 26, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangiwe, N.; Harrison, A.; Horak, I.G. Displacement of Rhipicephalus decoloratus by Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2013, 61, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, K.; Fourie, L.; Kok, D. Tick diversity, abundance and seasonal dynamics in a resource-poor urban environment in the Free State Province. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1998, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, M.; Ducasse, F. Tick infestation of livestock in Natal. I. The predilection sites and seasonal variations of cattle ticks. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1967, 38, 447–453. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, M.; Ducase, F.; Sutherst, R.W.; Maywald, G. The seasonal tick populations on traditional and commercial cattle grazed at four altitudes in Natal. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1989, 60, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Terkawi, M.A.; Huyen, N.X.; Shinuo, C.; Inpankaew, T.; Maklon, K.; Aboulaila, M.; Ueno, A.; Goo, Y.-K.; Yokoyama, N.; Jittapalapong, S. Molecular and serological prevalence of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in water buffaloes in the northeast region of Thailand. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 178, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spickett Arthur, M. Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases Monograph 1—Ixodid Ticks of Major Economic Importance and Their Distribution in South Africa, 1st ed.; Agri Connect: Pretoria, South Africa, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Temeyer, K.B.; Davey, R.B.; Chen, A.C. Identification of a third Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) cDNA presumptively encoding an acetylcholinesterase. J. Med. Entomol. 2004, 41, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, E.M.; Leta, S.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Madder, M.; Adehan, S.; Vanwambeke, S.O. Species distribution modelling for Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) in Benin, West Africa: Comparing datasets and modelling algorithms. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 118, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottinger, M. The distribution of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) decoloratus on a Farm in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa; University of the Free State: Free State, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yessinou, R.E.; Adoligbe, C.; Akpo, Y.; Adinci, J.; Youssao Abdou Karim, I.; Farougou, S. Sensitivity of Different Cattle Breeds to the Infestation of Cattle Ticks Amblyomma variegatum, Rhipicephalus microplus, and Hyalomma spp. on the Natural Pastures of Opkara Farm, Benin. J. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.A.; Norval, R. The ticks of Zimbabwe. I. The genus Boophilus. Zimb. Vet. J. 1980, 11, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- De Matos, C.; Sitoe, C.; Neves, L.; Nöthling, J.; Horak, I.G. The comparative prevalence of five ixodid tick species infesting cattle and goats in Maputo Province, Mozambique. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2009, 76, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanepoel, R.; Coetzer, J.; Tustin, R. Infectious Diseases of Livestock with Special Reference to Southern Africa; Oxford University Press: Cape Town, South Africa, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- de Castro, J.J. Sustainable tick and tickborne disease control in livestock improvement in developing countries. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 71, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangiwe, N.; Horak, I.G.; Van der Mescht, L.; Matthee, S. Range expansion of the economically important Asiatic blue tick, Rhipicephalus microplus, in South Africa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2017, 88, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fivaz, B.; De Waal, D. Towards strategic control of ticks in the eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 1993, 25, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaija, P.D.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Contreras, M.; Kirunda, H.; de la Fuente, J. Cattle ticks and tick-borne diseases: A review of Uganda’s situation. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minjauw, B.; McLeod, A. Tick-Borne Diseases And Poverty: The Impact of Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases on the Livelihoods of Small-Scale and Marginal Livestock Owners in India and Eastern and Southern Africa; Centre for Tropical Veterinary Medicine, University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yawa, M.; Nyangiwe, N.; Kadzere, C.; Muchenje, V.; Mpendulo, T.; Marufu, M.C. In search of the Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in the western-central regions of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyangiwe, N.; Matthee, C.; Horak, I.; Matthee, S. First record of the pantropical blue tick Rhipicephalus microplus in Namibia. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2013, 61, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourie, L.; Petney, T.; Horak, I.; De Jager, C. Seasonal incidence of Karoo paralysis in relation to the infestation density of female Ixodes rubicundus. Vet. Parasitol. 1989, 33, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theiler, G. Zoological Survey of the Union of South Africa. Tick Survey. Part IV. Distribution of Rhipicephalus Capensis, the Cape Brown Tick. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Sci. Anim. Ind. 1950, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Fourie, L.; Horak, I. The life cycle of Ixodes rubicundus (Acari: Ixodidae) and its adaptation to a hot, dry environment. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1994, 18, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourie, L.; Kok, O. The role of host behaviour in tick-host interactions: A domestic host-paralysis tick model. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1992, 13, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.J. Principles of Cattle Production, 3rd ed.; CAB International: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; p. 271. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, S.N.U.A.; Khan, A.; Niaz, S.; Aktas, M.; Ozubek, S.; Farooq, M.; Adil, M.M.; Zając, Z.; Iqbal, F.; Alhimaidi, A.R. Prevalence of Anaplasma marginale in cattle blood samples collected from two important livestock regions in Punjab (Pakistan) with a note on epidemiology and phylogeny of parasite. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Heever, M.; Lombard, W.; Bahta, Y.; Maré, F. The economic impact of heartwater on the South African livestock industry and the need for a new vaccine. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 203, 105634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.F.; Matika, O.; Djikeng, A.; Mapholi, N.; Burrow, H.M.; Yokoo, M.J.I.; Campos, G.S.; Gulias-Gomes, C.C.; Riggio, V.; Pong-Wong, R. Multiple country and breed genomic prediction of tick resistance in beef cattle. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, B.; Masika, P. Tick control methods used by resource-limited farmers and the effect of ticks on cattle in rural areas of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2009, 41, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troyo, A.; Moreira-Soto, R.D.; Calderon-Arguedas, Ó.; Mata-Somarribas, C.; Ortiz-Tello, J.; Barbieri, A.R.; Avendaño, A.; Vargas-Castro, L.E.; Labruna, M.B.; Hun, L. Detection of rickettsiae in fleas and ticks from areas of Costa Rica with history of spotted fever group rickettsioses. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-PeñA, A. Distribution, abundance, and habitat preferences of Ixodes ricinus (Acari: Ixodidae) in northern Spain. J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano-Román, R.; Díaz-Martín, V.; de la Fuente, J.; Pérez-Sánchez, R. Soft ticks as pathogen vectors: Distribution, surveillance and control. Parasitology 2012, 7, 125–162. [Google Scholar]
- Muchenje, V.; Dzama, K.; Chimonyo, M.; Raats, J.; Strydom, P. Tick susceptibility and its effects on growth performance and carcass characteristics of Nguni, Bonsmara and Angus steers raised on natural pasture. Animal 2008, 2, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Vivas, R.I.; Jonsson, N.N.; Bhushan, C. Strategies for the control of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks in a world of conventional acaricide and macrocyclic lactone resistance. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, J.; Contreras, M. Tick vaccines: Current status and future directions. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 14, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willadsen, P.; Riding, G.; McKenna, R.; Kemp, D.; Tellam, R.; Nielsen, J.; Lahnstein, J.; Cobon, G.; Gough, J. Immunologic control of a parasitic arthropod. Identification of a protective antigen from Boophilus microplus. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 1346–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, S.; Kemp, D. Insecticides and acaricides: Resistance and environmental impact. Rev. Sci. Et Tech. (Int. Off. Epizoot.) 1994, 13, 1249–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Vivas, R.; Rivas, A.; Chowell, G.; Fragoso, S.; Rosario, C.; García, Z.; Smith, S.; Williams, J.; Schwager, S. Spatial distribution of acaricide profiles (Boophilus microplus strains susceptible or resistant to acaricides) in southeastern Mexico. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 146, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Tipacamu, G.; Rodriguez-Vivas, R. Effect of moxidectin against natural infestation of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus (Acarina: Ixodidae) in the Mexican tropics. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 111, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, J. Chemical control of ticks on cattle. In Tick Vector Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Vivas, R.I.; Rosado-Aguilar, J.A.; Ojeda-Chi, M.M.; Pérez-Cogollo, L.C.; Trinidad-Martínez, I.; Bolio-González, M.E. Control integrado de garrapatas en la ganadería bovina. Ecosistemas Y Recur. Agropecu. 2014, 1, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Vivas, R.I.; Pérez-Cogollo, L.C.; Rosado-Aguilar, J.A.; Ojeda-Chi, M.M.; Trinidad-Martinez, I.; Miller, R.J.; Li, A.Y.; de León, A.P.; Guerrero, F.; Klafke, G. Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus resistant to acaricides and ivermectin in cattle farms of Mexico. Rev. Bras. De Parasitol. Veterinária 2014, 23, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, S.J.; Neitzel, D.; Reed, K.D.; Belongia, E.A. Coinfections acquired from Ixodes ticks. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 708–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbati, P.A.; Hlatshwayo, M.; Mtshali, M.S.; Mogaswane, K.R.; Waal, T.D.D.; Dipeolu, O.O. Ticks and tick-borne diseases of livestock belonging to resource-poor farmers in the eastern Free State of South Africa. In Ticks and Tick-Borne Pathogens; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Merino, O.; Alberdi, P.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; de la Fuente, J. Tick vaccines and the control of tick-borne pathogens. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitz, W.; Alexander, R. Immunization of Cattle Against Heartwater and the Control of the Tick-Borne Diseases, Redwater, Gallsickness and Heartwater. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1945, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Allsopp, B. Trends in the control of heartwater: Tick-borne diseases. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2009, 76, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweygarth, E.; Josemans, A.I.; Steyn, H.C. Experimental use of the attenuated Ehrlichia ruminantium (Welgevonden) vaccine in Merino sheep and Angora goats. Vaccine 2008, 26, G34–G39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, I.; Gomara, M.J. Design of synthetic peptidic constructs for the vaccine development against viral infections. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2004, 5, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.B.; Rangel, C.P.; de Azevedo Baêta, B.; da Fonseca, A.H. Analysis of the risk factors relating to cows’ resistance to Rhipicephalus microplus ticks during the peripartum. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2014, 63, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masika, P.; Sonandi, A.; Van Averbeke, W. Tick control by small-scale cattle farmers in the central Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1997, 68, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamboko, T.; Mukhebi, A.; Callaghan, C.; Peter, T.; Kruska, R.; Medley, G.; Mahan, S.; Perry, B.D. The control of heartwater on large-scale commercial and smallholder farms in Zimbabwe. Prev. Vet. Med. 1999, 39, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, L.; Sutherst, R.; Kerr, J. Trapping of larvae of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus by Stylosanthes scabra under grazing conditions. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1989, 40, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.Z.; Zaman, M.A.; Colwell, D.D.; Gilleard, J.; Iqbal, Z. Acaricide resistance in cattle ticks and approaches to its management: The state of play. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 203, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, J.; Knott, S.; Kearnan, J. A coordinated approach to control of the cattle tick (Boophilus microplus) in south east Queensland, Australia. CABI 1983, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Girona-García, A.; Zufiaurre Galarza, R.; Mora, J.L.; Armas-Herrera, C.M.; Martí, C.; Ortiz-Perpiñá, O.; Badía-Villas, D. Effects of prescribed burning for pasture reclamation on soil chemical properties in subalpine shrublands of the Central Pyrenees (NE-Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikel, S. Ticks and tick-borne pathogens at the cutaneous interface: Host defenses, tick countermeasures, and a suitable environment for pathogen establishment. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyobela, J.; Nkunika, P.O.Y.; Mwase, E.T. In vitro acaricidal activity of Bobgunnia madagascariensis Desv. against Amblyomma variegatum (Fabricius) (Acari: Ixodidae). Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, H.; Cilek, J.; Oz, E.; Aydin, L.; Deveci, O.; Yanikoglu, A. Acaricidal activity of Satureja thymbra L. essential oil and its major components, carvacrol and γ-terpinene against adult Hyalomma marginatum (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 170, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikel, S.K. Host immunity to ticks. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1996, 41, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, J.; Newson, R. Host resistance in cattle tick control. Parasitol. Today 1993, 9, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechav, Y.; Kostrzewski, M. The relative resistance of six cattle breeds to the tick Boophilus decoloratus in South Africa. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1991, 58, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sutherst, R.; Wharton, R.; Utech, K. Guide to Studies on Tick Ecology; CSIRO: Melbourne, Australia, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Shyma, K.; Gupta, J.P.; Singh, V. Breeding strategies for tick resistance in tropical cattle: A sustainable approach for tick control. J. Parasit. Dis. 2015, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Genus | Species |
|---|---|
| Amblyomma | Amblyomma hebraeum Koch, 1844 |
| Amblyomma lepidum Dönitz, 1909 | |
| Amblyomma variegatum Fabricius, 1794 | |
| Hyalomma | Hyalomma rufipes Koch, 1844 |
| Hyalomma truncatum Koch, 1844 | |
| Ixodes rubicundus | Ixodes rubicundus Neumann, 1904 |
| Rhipicephalus | Rhipicephalus (Bo.) annulatus Say, 1821 |
| Rhipicephalus appendiculatus Neumann, 1901 | |
| Rhipicephalus (Bo.) decoloratus Koch, 1844 | |
| Rhipicephalus evertsi Neumann, 1897 | |
| Rhipicephalus (Bo.) geigyi Aeschliman & Morel, 1965 | |
| Rhipicephalus (Bo.) microplus Canestrini, 1888 | |
| Rhipicephalus zambeziensis Walker, Norval, and Corwin, 1981 |
| Compound | First Used | Resistance 1st Reported |
|---|---|---|
| Arsenic | 1893 | Du Toit and Bekker [98] |
| DDT | 1948 | Whitehead [99] |
| BHC and Toxaphene | 1950 | Whitnall, Thorburn [100] |
| Carbamates | 1960 | Shaw [101] |
| Organophosphates | 1960 | Shaw [101] |
| Synthetic Pyrethroids | 1981 | Coetzee, Stanford [102] |
| Growth regulators | 2000 | Whitehead [99] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makwarela, T.G.; Nyangiwe, N.; Masebe, T.; Mbizeni, S.; Nesengani, L.T.; Djikeng, A.; Mapholi, N.O. Tick Diversity and Distribution of Hard (Ixodidae) Cattle Ticks in South Africa. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 42-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010004
Makwarela TG, Nyangiwe N, Masebe T, Mbizeni S, Nesengani LT, Djikeng A, Mapholi NO. Tick Diversity and Distribution of Hard (Ixodidae) Cattle Ticks in South Africa. Microbiology Research. 2023; 14(1):42-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakwarela, Tsireledzo G., Nkululeko Nyangiwe, Tracy Masebe, Sikhumbuzo Mbizeni, Lucky T. Nesengani, Appolinaire Djikeng, and Ntanganedzeni O. Mapholi. 2023. "Tick Diversity and Distribution of Hard (Ixodidae) Cattle Ticks in South Africa" Microbiology Research 14, no. 1: 42-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010004
APA StyleMakwarela, T. G., Nyangiwe, N., Masebe, T., Mbizeni, S., Nesengani, L. T., Djikeng, A., & Mapholi, N. O. (2023). Tick Diversity and Distribution of Hard (Ixodidae) Cattle Ticks in South Africa. Microbiology Research, 14(1), 42-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010004






