ESBL Displace: A Protocol for an Observational Study to Identify Displacing Escherichia coli Strain Candidates from ESBL-Colonized Travel Returners Using Phenotypic, Genomic Sequencing and Metagenome Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aim and Objectives
The Detailed Aims Include
3. Patients and Public Involvement
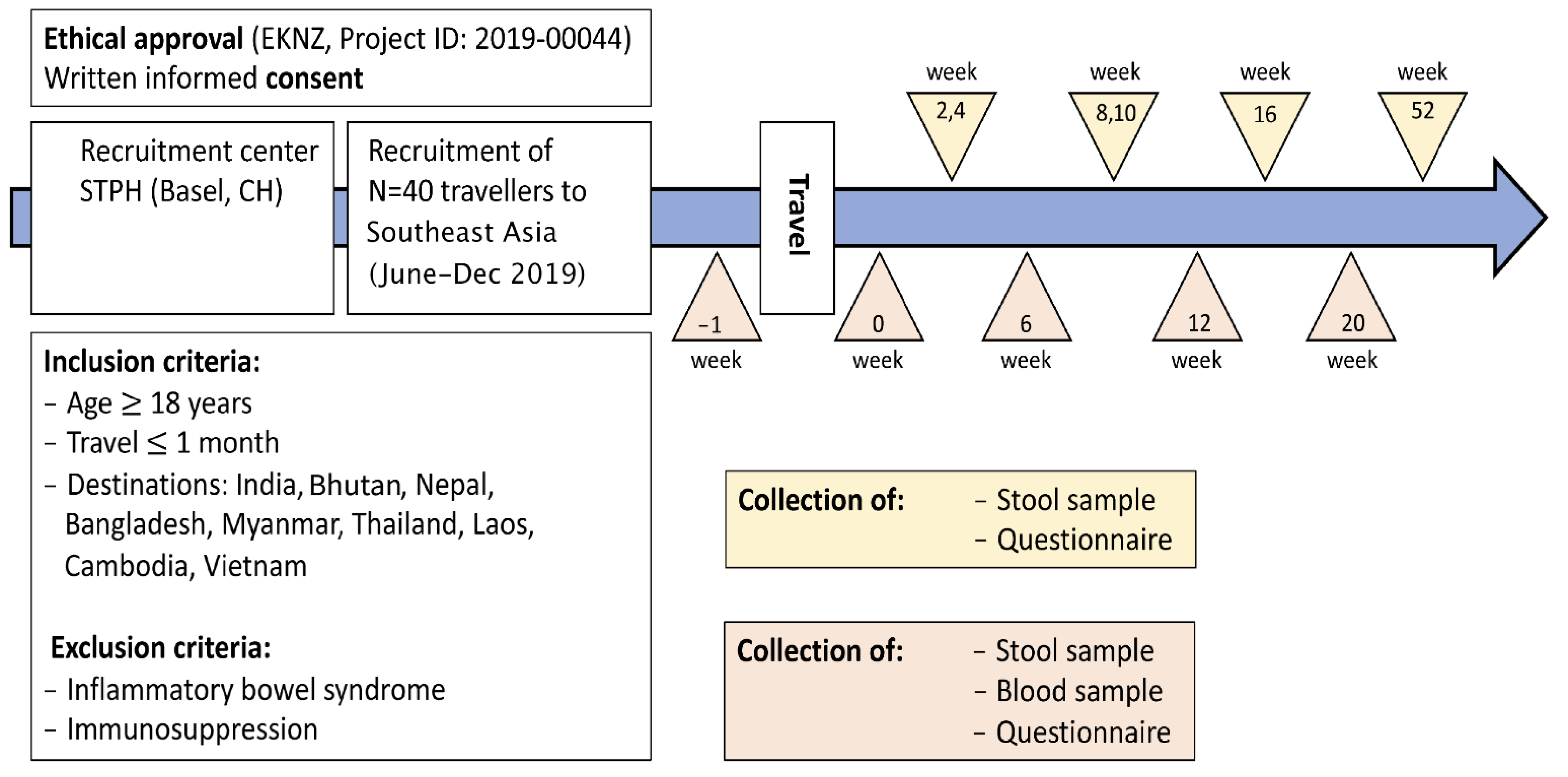
4. Methods/Design
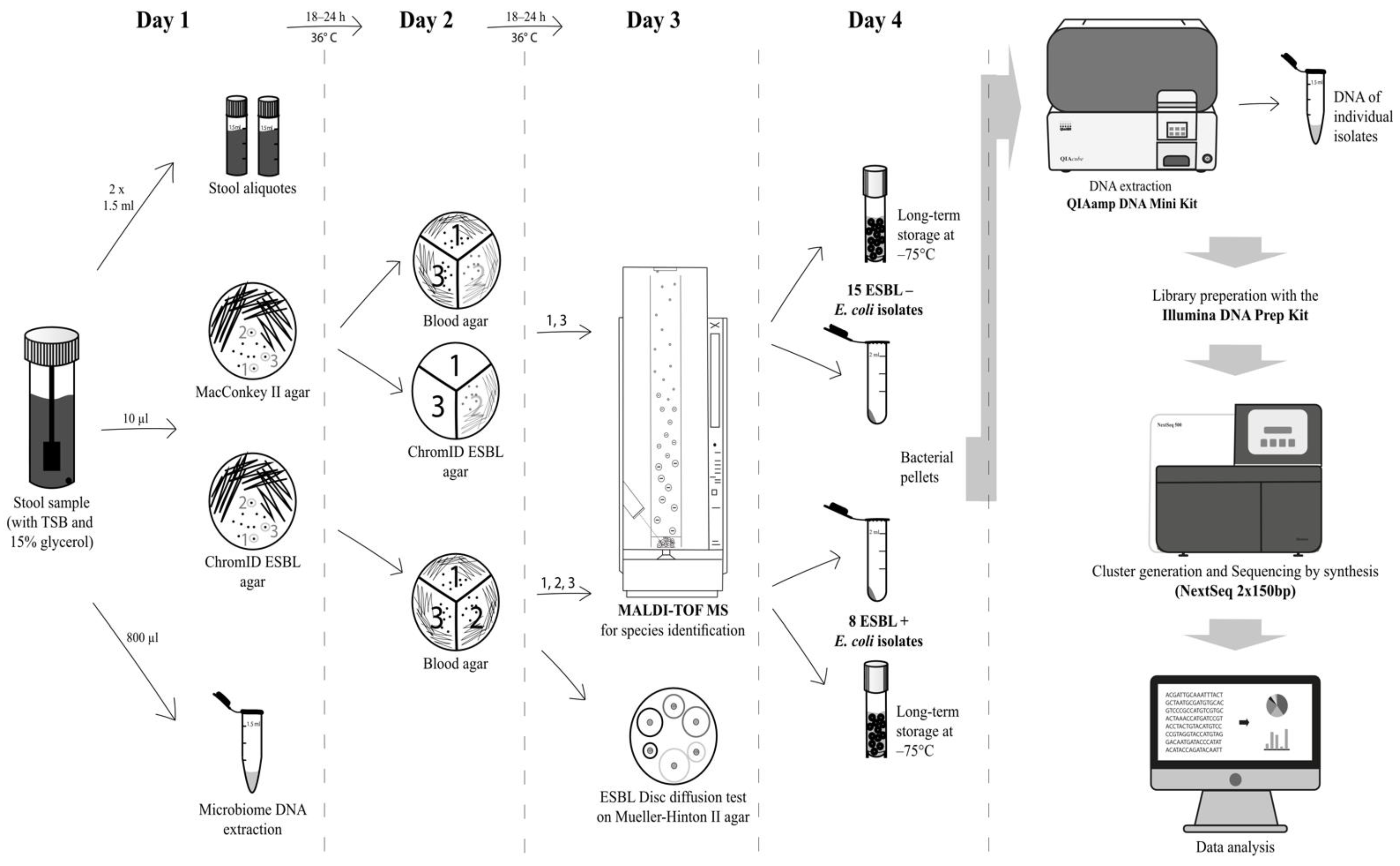
5. Phenotypic Characterisation
6. Genotypic Characterisation
7. Questionnaires
8. Data Analysis
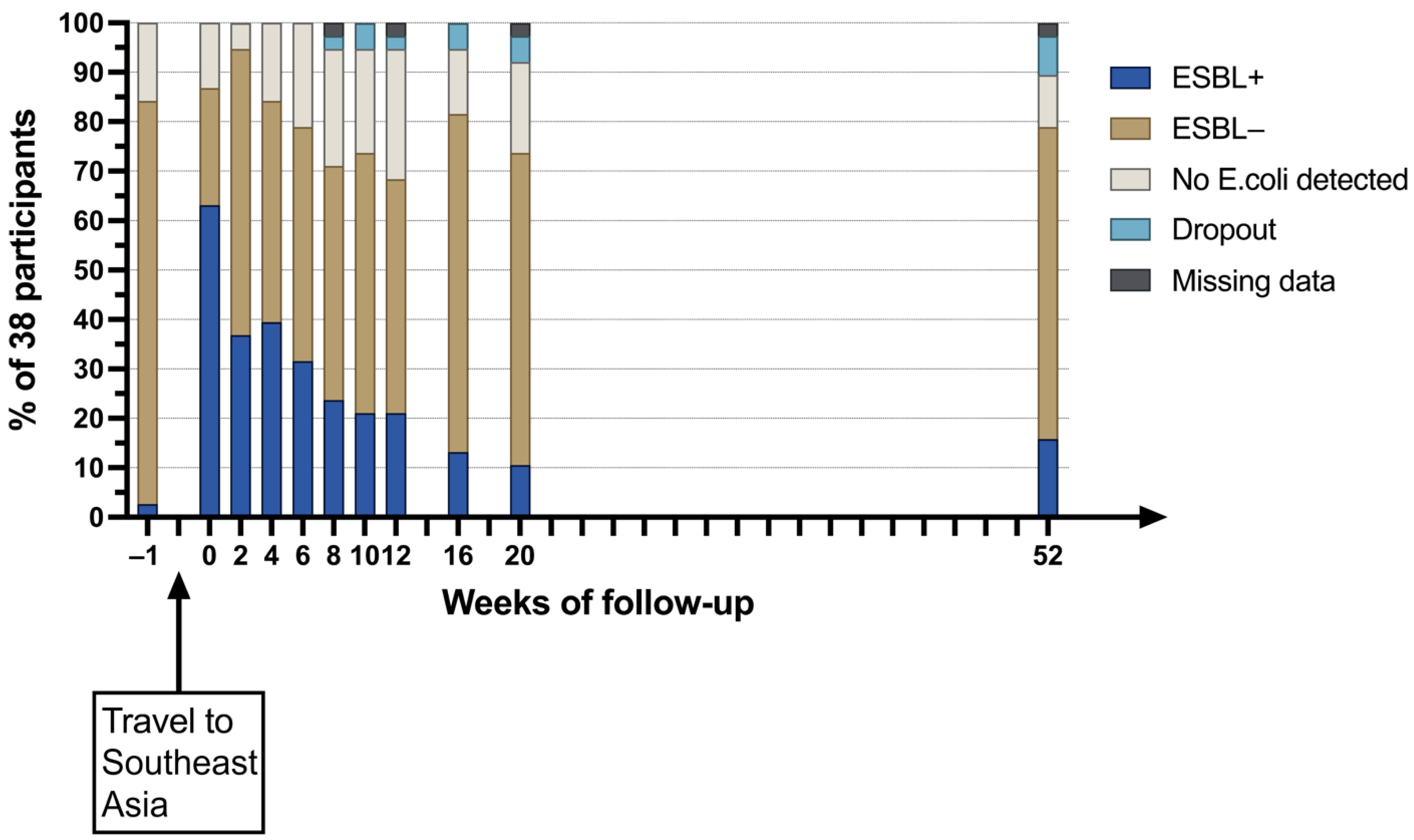
9. Preliminary Results
10. Discussion
11. Strengths and Limitations of the Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, B.N.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, M.N.; Ryu, J.; Kim, Y.S. Clinical implications of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteraemia. J. Hosp. Infect. 2002, 52, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaber, M.J.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Kaye, K.S.; Ben-Ami, R.; Schwartz, D.; Carmeli, Y. Clinical and economic impact of bacteremia with extended- spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, S.E. The relationship between antimicrobial resistance and patient outcomes: Mortality, length of hospital stay, and health care costs. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42 (Suppl. S2), S82–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steptoe, A.; Shankar, A.; Demakakos, P.; Wardle, J. Social isolation, loneliness, and all-cause mortality in older men and women. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5797–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, J.A.; Hornung-Winter, C.; Radicke, I.; Hug, B.L.; Biedert, M.; Abshagen, C.; Battegay, M.; Widmer, A.F. Direct Costs of a Contact Isolation Day: A Prospective Cost Analysis at a Swiss University Hospital. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2018, 39, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschudin-Sutter, S.; Lucet, J.C.; Mutters, N.T.; Tacconelli, E.; Zahar, J.R.; Harbarth, S. Contact Precautions for Preventing Nosocomial Transmission of Extended-Spectrum beta Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli: A Point/Counterpoint Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, A.J.; Peirano, G.; Pitout, J.D. Escherichia coli ST131: The quintessential example of an international multiresistant high-risk clone. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 90, 109–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttner, B.; Haustein, T.; Uckay, I.; Renzi, G.; Stewardson, A.; Schaerrer, D.; Agostinho, A.; Andremont, A.; Schrenzel, J.; Pittet, D.; et al. Decolonization of intestinal carriage of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae with oral colistin and neomycin: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Iovleva, A.; Bonomo, R.A. The ecology of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs) in the developed world. J. Travel Med. 2017, 24, S44–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezabih, Y.M.; Sabiiti, W.; Alamneh, E.; Bezabih, A.; Peterson, G.M.; Bezabhe, W.M.; Roujeinikova, A. The global prevalence and trend of human intestinal carriage of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli in the community. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitout, J.D.; Laupland, K.B. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: An emerging public-health concern. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassing, R.J.; Alsma, J.; Arcilla, M.S.; van Genderen, P.J.; Stricker, B.H.; Verbon, A. International travel and acquisition of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: A systematic review. Euro Surveill. 2015, 20, 30074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuerz, T.C.; Kassim, S.S.; Atkins, K.E. Acquisition of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (ESBL-PE) carriage after exposure to systemic antimicrobials during travel: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 37, 101823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzli, E.; Jaeger, V.K.; Frei, R.; Neumayr, A.; DeCrom, S.; Haller, S.; Blum, J.; Widmer, A.F.; Furrer, H.; Battegay, M.; et al. High colonization rates of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli in Swiss travellers to South Asia—A prospective observational multicentre cohort study looking at epidemiology, microbiology and risk factors. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangden, T.; Cars, O.; Melhus, A.; Lowdin, E. Foreign travel is a major risk factor for colonization with Escherichia coli producing CTX-M-type extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: A prospective study with Swedish volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3564–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcilla, M.S.; van Hattem, J.M.; Haverkate, M.R.; Bootsma, M.C.J.; van Genderen, P.J.J.; Goorhuis, A.; Grobusch, M.P.; Lashof, A.M.O.; Molhoek, N.; Schultsz, C.; et al. Import and spread of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae by international travellers (COMBAT study): A prospective, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostholm-Balkhed, A.; Tarnberg, M.; Nilsson, M.; Nilsson, L.E.; Hanberger, H.; Hallgren, A.; Travel Study Group of Southeast, S. Travel-associated faecal colonization with ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae: Incidence and risk factors. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuland, E.A.; Sonder, G.J.; Stolte, I.; Al Naiemi, N.; Koek, A.; Linde, G.B.; van de Laar, T.J.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.; van Dam, A.P. Travel to Asia and traveller’s diarrhoea with antibiotic treatment are independent risk factors for acquiring ciprofloxacin-resistant and extended spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae-a prospective cohort study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 731.e1–731.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltansing, S.; Vlot, J.A.; Kraakman, M.E.; Mesman, R.; Bruijning, M.L.; Bernards, A.T.; Visser, L.G.; Veldkamp, K.E. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing enterobacteriaceae among travelers from the Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhary, H.; Pangesti, K.N.A.; Rashid, H.; Abd El Ghany, M.; Hill-Cawthorne, G.A. Travel-Related Antimicrobial Resistance: A Systematic Review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Bano, J.; Lopez-Cerero, L.; Navarro, M.D.; Diaz de Alba, P.; Pascual, A. Faecal carriage of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli: Prevalence, risk factors and molecular epidemiology. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mughini-Gras, L.; Dorado-Garcia, A.; van Duijkeren, E.; van den Bunt, G.; Dierikx, C.M.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Bootsma, M.C.J.; Schmitt, H.; Hald, T.; Evers, E.G.; et al. Attributable sources of community-acquired carriage of Escherichia coli containing beta-lactam antibiotic resistance genes: A population-based modelling study. Lancet Planet. Health 2019, 3, e357–e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calbo, E.; Freixas, N.; Xercavins, M.; Riera, M.; Nicolas, C.; Monistrol, O.; Sole Mdel, M.; Sala, M.R.; Vila, J.; Garau, J. Foodborne nosocomial outbreak of SHV1 and CTX-M-15-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology and control. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Cobas, A.E.; Moya, A.; Gosalbes, M.J.; Latorre, A. Colonization Resistance of the Gut Microbiota against Clostridium difficile. Antibiotics 2015, 4, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekirov, I.; Tam, N.M.; Jogova, M.; Robertson, M.L.; Li, Y.; Lupp, C.; Finlay, B.B. Antibiotic-induced perturbations of the intestinal microbiota alter host susceptibility to enteric infection. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4726–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecher, B.; Hardt, W.D. Mechanisms controlling pathogen colonization of the gut. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, M.; Van Belkum, A.; Girard, V.; Charrier, J.P.; Pincus, D. An update on the routine application of MALDI-TOF MS in clinical microbiology. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2019, 16, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. EUCAST Disk Diffusion Method for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Disk_test_documents/2021_manuals/Reading_guide_v_8.0_EUCAST_Disk_Test_2021.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Hinic, V.; Ziegler, J.; Straub, C.; Goldenberger, D.; Frei, R. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) detection directly from urine samples with the rapid isothermal amplification-based eazyplex(R) SuperBug CRE assay: Proof of concept. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 119, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenod, A.; Wuthrich, D.; Seth-Smith, H.M.B.; Ott, C.; Gehringer, C.; Foucault, F.; Mouchet, R.; Kassim, A.; Revathi, G.; Vogt, D.R.; et al. Whole-genome sequence-informed MALDI-TOF MS diagnostics reveal importance of Klebsiella oxytoca group in invasive infections: A retrospective clinical study. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Haft, D.H.; Prasad, A.B.; Slotta, D.J.; Tolstoy, I.; Tyson, G.H.; Zhao, S.; Hsu, C.H.; McDermott, P.F.; et al. Validating the AMRFinder Tool and Resistance Gene Database by Using Antimicrobial Resistance Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in a Collection of Isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00483-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.P.; Raphenya, A.R.; Lau, T.T.Y.; Tsang, K.K.; Bouchard, M.; Edalatmand, A.; Huynh, W.; Nguyen, A.V.; Cheng, A.A.; Liu, S.; et al. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D517–D525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Jin, Q.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2019: A comparative pathogenomic platform with an interactive web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D687–D692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwan, C.L.; Lomonaco, S.; Bastos, L.M.; Cook, P.W.; Maher, J.; Trinetta, V.; Bhullar, M.; Phebus, R.K.; Gragg, S.; Kastner, J.; et al. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica Strains Isolated From Cambodian Informal Markets. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 711472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, J.; Nash, J.H.E. MOB-suite: Software tools for clustering, reconstruction and typing of plasmids from draft assemblies. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Estimating the population size for capture-recapture data with unequal catchability. Biometrics 1987, 43, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, Y.H.; Deng, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, B.Y.; Xue, K.; Wu, L.; He, Z.; Yang, Y. Random sampling process leads to overestimation of beta-diversity of microbial communities. mBio 2013, 4, e00324-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Foundation Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 7 February 2022).
- Shaffer, M.; Thurimella, K.; Lozupone, C.A. SCNIC: Sparse Correlation Network Investigation for Compositional Data. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. CoNet app: Inference of biological association networks using Cytoscape. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Yoseph, H.; Hussein, K.; Braun, E.; Paul, M. Natural history and decolonization strategies for ESBL/carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae carriage: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2729–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woerther, P.L.; Lepeule, R.; Burdet, C.; Decousser, J.W.; Ruppe, E.; Barbier, F. Carbapenems and alternative beta-lactams for the treatment of infections due to extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: What impact on intestinal colonisation resistance? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffie, C.G.; Pamer, E.G. Microbiota-mediated colonization resistance against intestinal pathogens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, S. Microbiota Replacement Therapies: Innovation in Gastrointestinal Care. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 103, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamer, E.G. Resurrecting the intestinal microbiota to combat antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Science 2016, 352, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George Kerry, R.; Patra, J.K.; Gouda, S.; Park, Y.; Shin, H.S.; Das, G. Benefaction of probiotics for human health: A review. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tannock, G.W.; Tiong, I.S.; Priest, P.; Munro, K.; Taylor, C.; Richardson, A.; Schultz, M. Testing probiotic strain Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (Mutaflor) for its ability to reduce carriage of multidrug-resistant E. coli by elderly residents in long-term care facilities. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szajewska, H.; Canani, R.B.; Guarino, A.; Hojsak, I.; Indrio, F.; Kolacek, S.; Orel, R.; Shamir, R.; Vandenplas, Y.; van Goudoever, J.B.; et al. Probiotics for the Prevention of Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea in Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 62, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; DuPont, H.L. New approaches for bacteriotherapy: Prebiotics, new-generation probiotics, and synbiotics. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60 (Suppl. S2), S108–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecher, B.; Chaffron, S.; Kappeli, R.; Hapfelmeier, S.; Freedrich, S.; Weber, T.C.; Kirundi, J.; Suar, M.; McCoy, K.D.; von Mering, C.; et al. Like will to like: Abundances of closely related species can predict susceptibility to intestinal colonization by pathogenic and commensal bacteria. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, S.H. Antibiotic resistance in the absence of selective pressure. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2001, 17, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
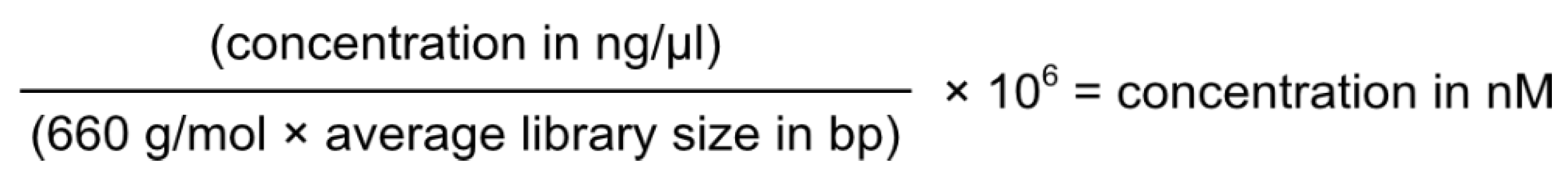
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schweitzer, M.; Mari, A.; Roloff, T.; Künzli, E.; Heller, S.; Albertos Torres, D.; Meola, M.; Nogarth, D.; Laganenka, L.; Prampolini, L.; et al. ESBL Displace: A Protocol for an Observational Study to Identify Displacing Escherichia coli Strain Candidates from ESBL-Colonized Travel Returners Using Phenotypic, Genomic Sequencing and Metagenome Analysis. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 177-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010015
Schweitzer M, Mari A, Roloff T, Künzli E, Heller S, Albertos Torres D, Meola M, Nogarth D, Laganenka L, Prampolini L, et al. ESBL Displace: A Protocol for an Observational Study to Identify Displacing Escherichia coli Strain Candidates from ESBL-Colonized Travel Returners Using Phenotypic, Genomic Sequencing and Metagenome Analysis. Microbiology Research. 2023; 14(1):177-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchweitzer, Michael, Alfredo Mari, Tim Roloff, Esther Künzli, Stefanie Heller, Diana Albertos Torres, Marco Meola, Danica Nogarth, Leanid Laganenka, Lisa Prampolini, and et al. 2023. "ESBL Displace: A Protocol for an Observational Study to Identify Displacing Escherichia coli Strain Candidates from ESBL-Colonized Travel Returners Using Phenotypic, Genomic Sequencing and Metagenome Analysis" Microbiology Research 14, no. 1: 177-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010015
APA StyleSchweitzer, M., Mari, A., Roloff, T., Künzli, E., Heller, S., Albertos Torres, D., Meola, M., Nogarth, D., Laganenka, L., Prampolini, L., Seth-Smith, H. M. B., Grüninger, O., Gensch, A., Reist, J., Bonhoeffer, S., Hardt, W.-D., & Egli, A. (2023). ESBL Displace: A Protocol for an Observational Study to Identify Displacing Escherichia coli Strain Candidates from ESBL-Colonized Travel Returners Using Phenotypic, Genomic Sequencing and Metagenome Analysis. Microbiology Research, 14(1), 177-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010015





