Abstract
Thrombotherapy is an important approach in treatment of various diseases associated with pathologies of the cardiovascular and human hemostasis systems. Screening for producers of modern, specific, and safe thrombolytic substances is an important task for medicine and biotechnology. The aim of this study was to characterize thrombolytic potential of seven strains of micromycete belonging to the genus Tolypocladium, which was obtained from White Sea soils. The Tolypocladium inflatum 62a strain was considered the most promising producer of thrombolytic agent activities suitable for possible use in thrombotherapy or diagnostics of hemostasis pathologies. It demonstrated a high radial growth rate and was characterized not only by a sufficiently high value of enzymatic index in media with fibrin and fibrinogen but also by the highest specificity for fibrillar proteins among all strains. The preparation obtained from it demonstrated pronounced thrombolytic effectiveness and substrate specificity.
1. Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases and their complications occupy the leading position among global causes of death. Every year, 8–9 million deaths are attributed to ischaemic heart disease (IHD). IHD and stroke were the world’s leading causes of death in 2019, according to WHO data [1]. Furthermore, these pathologies of the cardiovascular and hemostasis system are often associated with occurrence and development of thrombotic complications, which could also be potentially fatal.
One of the most effective approaches to treatment of thrombotic complications is plasminogen activator drugs. They are capable of providing a stimulating effect on a patient’s hemostasis system, freeing the bloodstream from blood clots without causing serious complications associated with heavy bleeding or rethrombosis. However, use of thrombolytic drugs such as streptokinase, urokinase, or alteplase, as well as their modern analogues, is still limited due to their rather high cost and risks of intolerance: blood loss, appearance of various hypersensitivity reactions of the body, and extensive hemorrhages in vital organs [2].
A perspective answer to the problem of therapy and diagnosis of thrombosis treatment could be use of drugs based on proteolytic enzymes of microscopic fungi. The search for modern, specific, and safe thrombolytic substances is an important task for modern medicine and biotechnology [3,4]. One promising approach to the treatment of these disorders and expansion of the pool of thrombolytic drugs is use of more specific and safe proteinases obtained from the culture fluid of micromycetes [5,6].
In this study, therapeutic potential of seven micromycete strains from the genus Tolypocladium, isolated from White Sea soils, was examined in comparison to biotechnological and medical potential of the previously studied micromycete strain Tolypocladium inflatum k1, which has already been confirmed as a producer of thrombolytic substances such as plasmin activators [7,8]. The aim of this study was to characterize thrombolytic potential of those seven strains of micromycete. Data obtained could become the basis for the development of new specific thrombotherapeutic substances obtained from those strains for treatment of cardiovascular diseases and their complications, based on preparation of micromycetes from this group as well as diagnostic kits (diagnosticums) for certain pathologies of the hemostasis system.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms and Growth Conditions
Micromycetes were isolated from the bottom soils of the White Sea (depths 0–30 m) on various organic bait substrates. The upper layers (up to 3–5 cm) of the bottom soils from the Kandalaksha Bay, formed by sand and pebbles with an admixture of silt, were studied. Samples were obtained by diving in 3 replications from the littoral zone and from depths 10, 20 and 30 m, and were then placed into sterile plastic vials during the summer season. In places where bottom soils were obtained, algae traces were also detected. Inoculation of fungi was carried out on the sampling day or after several days of storage at +4 °C. Samples were cultivated in 3 probes each in Petri dishes with wort agar, then on wort agar slants containing seawater. Wide-spectrum antibiotics (streptomycin, kanamycin, etc.) were added into the medium to suppress bacterial growth.
2.2. Micromycete Identification
Identification of cultures was carried out according to morphological and cultural characteristics on wort agar and Czapek agar, using manuals of systematics and according to genetic analysis using PCR and further sequencing of the rDNA internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Samples of mycelium were obtained through cultivation of pure cultures on wort agar or liquid wort at 25 °C for 7–20 days, depending on growth dynamics of the fungus. Those samples were then separated from the medium, ground with liquid nitrogen, and transferred into a sterile ceramic mortar. DNA isolation was performed with cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) extracted buffer (0.5 M NaCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 10 mM EDTA, 2% (w/v) CTAB) according to standard extraction protocol [18]. For amplification of rDNA, universal primers ITS1 and ITS4 (TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG/TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC) were used according to standard PCR protocols [19]. PCR was performed with HS Taq DNA polymerase manufactured by Evrogen (Russia). DNA fragments were separated by standard electrophoresis in 1.2% agarose gel with an addition of ethidum bromide (EtBr). Tris-acetate-EDTA buffer (TAE) was used as a buffer system. After electrophoresis, gels were analyzed in UV light with a wavelength of 360 nm. The amplicon was extracted from the gel using a CleanUp Mini kit from Evrogen. Sequencing was performed by Evrogen. DNA was sequenced using a BigDye® Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA) on an Applied Biosystems 3730 xl automated sequencer (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA). Obtained nucleotide sequences were analyzed by GenBank for species identification with the BLASTn program. Multiple-sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree construction were performed using Clustal Omega software.
2.3. Radial Growth Rate Determination
Radial growth rate (Kr) of mycromycetes was determined in Petri dishes with a wort agar medium at different temperatures (4, 12, 20, 28, and 37 °C) and calculated using the formula Kr = ΔR/Δt [20], where R is radial size of colony (mm) and t is time (days). Colony diameter (in mm) was measured daily for 7 days. Growth rate was expressed in mm/h.
2.4. Determination of Enzymatic Index of Micromycetes on Different Substrates
Identification of proteolytic potential in micromycete strains was carried out under surface cultivation conditions in Petri dishes with a Czapek medium and addition of particular substrates (casein, fibrin, fibrinogen). Inoculation was performed by injection of each fungal sample into the center of a dish with a medium. Diameters of hydrolysis zones and colonies were measured after 7 days. Enzymatic index (EI) was calculated based on diameter of micromycete colony (d) and diameter of lysis zone (D) according to the formula EI = D/d.
2.5. Obtaining of Proteinase Preparations
To obtain proteinase preparation, strains were grown in submerged cultivation conditions on orbital shakers (200 rpm) in 750 mL flasks with 100 mL of nutrient medium at 28 °C. Each inoculum was obtained by washing micromycete spores from a Czapek agar medium into a medium containing wort, glucose, and peptone [21], followed by 2 days of cultivation. Further cultivation was carried out in a fermentation medium; inocula (in a 3 mL volume) were separately transferred to cultivation organo-mineral media (medium No. 1) and mineral media (medium No. 2), then cultivated for 3 days. Medium 1 included the following composition (in g/L): glucose, 30.0; glycerol, 70.0; fish meal hydrolyzate, 5.0; NaNO3, 2.0; KH2PO4, 0.5; MgSO4, 0.5. Medium 2 included the following composition (in g/L): glucose, 35.0; starch, 10.0; NH4NO3, 5.0; NaCl, 2.0; KH2PO4, 0.5; MgSO4, 0.5. The culture liquid was separated from the biomass by filtration with a water jet pump through filter paper (FS, Russia). Extracellular proteins from the resulting culture fluid were precipitated with ammonium sulfate at 80% saturation. A precipitate of proteins formed at 4 °C for 12 h. It was then separated by centrifugation at 15,000× g (20 min, 4 °C), dissolved in a minimum volume of 0.01 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.2) containing 0.002 M calcium acetate, and dialyzed in dialysis bags against the same buffer (12 h, 4 °C). The resulting protein solution was centrifuged under the same conditions to remove precipitate and then freeze-dried.
2.6. Evaluation of Thrombolytic Effect
To study thrombolytic effect (effectiveness of thrombolysis) of micromycete preparations, a fibrin clot was formed in Eppendorf-type tubes through addition of 100 µL of human plasma and 20 µL of thrombin to each tube, fixing the mass of the tube before, during (after each stage), and after the experiment. A proteinase preparation was administrated to each fibrin clot sample and change in weight was recorded at regular intervals (30, 60, and 90 min). Residual clot weight (expressed as % of initial clot weight) was used to determine the degree of thrombolysis in samples over time [22].
2.7. Protein Assay
Protein concentration of obtained fractions was determined through measurement of optical density at 562 nm (Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA) Protein Assay) [23] using a NanoDrop One spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Analysis of protein components of fractions was performed using 12.5% SDS-PAGE with Coomassie Blue R250 staining.
2.8. Fibrin Zymography
For fibrin zymography, 0.12% (w/v) fibrinogen and 100 µL of thrombin (10 IU) were mixed in 12% polyacrilamide gel without addition of SDS [24,25]. Electrophoresis was run under native (non-reducing) conditions at 12 mA and room temperature with directional ventilation. After electrophoresis stopped, the gel was gently moved and submerged into 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0, containing 2.5% (v/v) Triton X-100) for 30 min at room temperature, then washed for 30 min in distilled water and incubated for 18 h at 37 °C in a zymogram reaction buffer consisting of 0.02% (w/v) NaN3 and 30 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0). Finally, the gel was stained with Coomassie blue R-250 standard solution for 2 h and washed 3 times with 7% (v/v) acetic acid. Clear bands were detected as fibrin hydrolysis areas.
2.9. Determination of Proteolytic Activity
Proteolytic activity (caseinolytic or fibrinolytic) was determined using the modified Anson–Hagihara method: determination of amount of tyrosine in proteolysis products that were not precipitated by trichloroacetic acid after 10 min of hydrolysis of a solution of 1% casein (or fibrin) solution in 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0–8.2, 37 °C). (C), [26]. Activity was represented in μmoles of tyrosine per minute (ETyr). Specific activity was calculated per mg of protein.
2.10. Determination of Proteolytic Activity toward Particular Proteins of the Hemostasis System
Proteolytic activity in the culture fluid and preparations of micromycetes was determined by hydrolysis of chromogenic peptide substrates (CPS) [27], which had a para-nitroanilide group (-pNA) as a chromophore: plasmin (H-D-Val-Leu-Lys-pNA and For-Ala-Phe-Lys-pNA), thrombin (Tos-Gly-Pro-Arg-pNA and H-D-Phe-Pip-Arg-pNA), factor Xa (Z-D-Arg-Gly-Arg-pNA), urokinase (pGlu-Gly-Arg-pNA), tissue plasminogen activator and serin proteinases (HD-Ile-Pro-Arg-pNA), subtilisin (Z-Ala-Ala-Leu-pNA), elastase (Suc -Ala-Ala-Ala-pNA), and trypsin (Bz-Arg-pNA). To carry out the reaction, 200 µL of a sample, 50 µL of 0.05 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.2), and 100 µL of a 0.05% solution of the corresponding substrate were mixed. The mixture was incubated for 5 min at 37 °C, after which the reaction was stopped through addition of 200 µL of 0.1 N NaOH. The same components were added to the control sample except for the chromogenic substrate. During the reaction, N-nitroaniline (pNA) formed from a colorless chromogenic substrate, had a yellow color, and was detected by the spectrophotometric method of optical absorption at a wavelength of 405 nm. Optical-density measurements were respectively carried out at 405 nm on a Hitachi 200-20 spectrophotometer. The unit of activity (E) in all cases was taken as µM, split from p-nitroaniline.
3. Results
3.1. Micromycete Identification
Isolates of micromycete strains obtained from White Sea soils were identified through PCR and further sequencing of the rDNA ITS region according to morphological, cultural, and genetic characteristics. Isolated strains of DNA fragments, separated by standard electrophoresis in a 1.2% agarose gel with an addition of EtBr, are demonstrated in Figure 1a. According to the 5.8S rRNA sequence analysis, isolated strains were quite similar to some particular, previously described strains of Tolypocladium inflatum and Tolypocladium cylindrosporum, but were not 100% identified as the same types (Table 1, Figure 1b). Furthermore, obtained sequences were aligned with the BLASTn program module, and a phylogenetic tree of the obtained strains (cladogram) was constructed, according to which the obtained strains could be conditionally divided into four subgroups depending on phylogenetic location (phylogenetic proximity to each other). The first group included T. cylindrosporum 150a, the second one T. inflatum 62a, the third one T. inflatum 49a and 126a, and the fourth one three closely related strains: T. inflatum 13a, 14a, and 30a (Figure 1b).
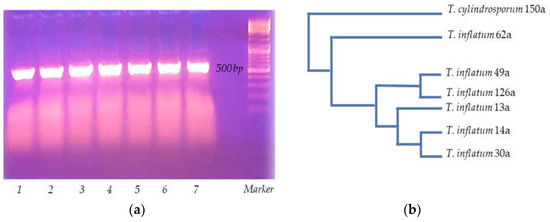
Figure 1.
White Sea micromycete isolate identification (a) PCR analysis 1—13a, 2—14a, 3—126a, 4—49a, 5—150a, 6—62a, 7—30a.; (b) phylogenetic tree of obtained Tolypocladium strains.

Table 1.
Tolypocladium strains obtained from White-Sea-soil identification.
3.2. Radial Growth Rate Determination
According to the results obtained, cultivation temperature significantly affected radial growth rate of all isolated strains of the Tolypocladium genus. At 4 °C and 37 °C, there was actually no growth of mycelium in Petri dishes with the Czapek medium. At temperatures ranging from 12 °C to 20 °C, growth rate reached intermediate values compared to that of 28 °C, at which the most effective growth of all strains was detected. Furthermore, all temperature profiles and radial growth rates of isolated strains comprised a range of fairly close values. In addition, data obtained in the surface cultivation study indicated that the pH optimum for most of the isolated strains of the genus Tolypocladium was in the range from 5.5 to 7.5 (data not shown). At those pH values, the maximum radial growth rate of the strains on the plates was achieved. The maximum possible value of radial growth rate among all strains at an observed optimum temperature of 28 °C and pH~6.5 was revealed for the strain T. inflatum 62a as 0.27 mm/h (Figure 2).
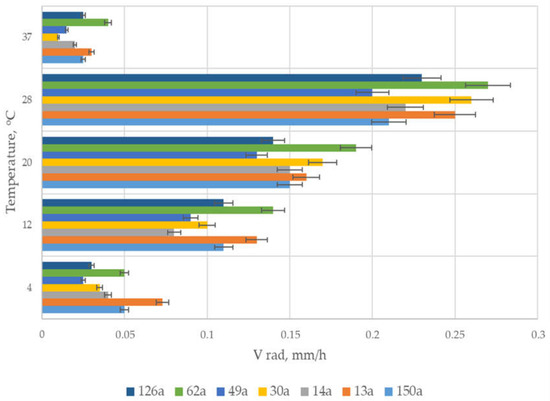
Figure 2.
Radial-growth-rate determination of Tolypocladium strains obtained from White Sea soils.
3.3. Determination of Enzymatic Index of Micromycetes on Different Substrates
The results of determination of mycromycetes’ enzymatic indices in media with different substrates are shown in Table 2 and Figure 3. In addition to determination of enzymatic indices in media with specific substrates, ratios of EI in a medium with casein, EI in a medium with fibrin, and EI in a medium with fibrinogen were also evaluated, making it possible to investigate effectiveness of action of particular micromycete strain proteinases in relation to globular or fibrillar proteins, as casein referred to globular proteins and fibrin and fibrinogen referred to fibrillar ones. For micromycete strains T. inflatum 14a, T. inflatum 49a, and T. cylindrosporum 150a, enzymatic indexes in media with fibrin, casein, and fibrinogen substrates were comparable to each other. It can be supposed that proteolytic activity of these strains was not associated with specificity of the proteinases they produced; they were capable of hydrolyzing globular and fibrillar proteins to an equal extent. The T. inflatum 126a strain demonstrated a greater affinity for globular proteins, since enzymatic index values in the casein medium exceeded those in the fibrin and fibrinogen medium. Furthermore, according to the obtained ratios EIcas/EIfibr and EIcas/EIfg, it can be stated that proteinases of the remaining isolated strains had a pronounced proteolytic activity to fibrillar proteins. Furthermore, the most promising strains for a further study of thrombolytic properties were T. inflatum 30a and T. inflatum 62a, as they were characterized not only by sufficiently high values of enzyme indices in the fibrin and fibrinogen medium but also by the highest specificity with respect to fibrillar proteins. The T. inflatum 13a strain demonstrated comparable enzymatic indices in media with fibrin and casein; nevertheless, it was also selected for further study as a promising producer, since it demonstrated the highest values of enzymatic index in media with fibrin among all isolated strains of micromycetes.

Table 2.
Enzymatic index determination of Tolypocladium strains in media with different substrates.

Figure 3.
Example of enzymatic index determination in a medium with fibrin for T. inflatum (a) 49a, (b) 126a, (c) 13a, and (d) 62a strains.
Further screening-stage experiments were made with preparations obtained from the cultural fluid of Tolypocladium strains during submerged cultivation in medium 1 and medium 2.
3.4. Determination of Caseinolytic and Fibrinolytic Activity of Tolypocladium-Strain Preparations
To determine the most perspective Tolypocladium micromycete (the producer of potentially effective thrombolytic substances from the obtained strains), proteolytic activities (caseinolytic and fibrinolytic) of strain preparations were investigated after being obtained in experiments based on submerged fermentation in media with glycerol and media with starch. Results are represented in Table 3. Experimental data indicated that the most potentially effective preparations were proteolytic substances obtained in media with glycerol from T. inflatum strains 62a (maximum caseinolytic and fibrinolytic activity among all strains), 30a, and 13a. Furthermore, thrombolytic potential of strain 62a was even more pronounced compared to known producer of thrombolytic substances Tolypocladium inflatum k1 (not obtained from the White Sea; taken as the reference-side Tolypocladium strain-producer of thrombolytic substances), which demonstrated almost similar activities in both media with glycerol and with starch, respectively.

Table 3.
Determination of caseinolytic and fibrinolytic activity of Tolypocladium-strain preparations obtained from submerged cultivation in media with glycerin and starch.
3.5. Thrombolytic Effect Evaluation
The study of thrombolysis effectiveness in preparations obtained from Tolypocladium isolates revealed high thrombolytic activity against stable fibrin clots. A proteinase preparation was added to each fibrin clot sample and weight change was detected at regular intervals (30, 60, and 90 min). Extent of thrombolysis in samples over time was determined by residual mass of the clot (expressed as % of initial mass of clot). Proteinases isolated from the culture fluid of strains T. inflatium 62a, 13a, and 49a grown in a starch medium demonstrated the extent of thrombolysis at 78.9%, 76.6%, and 74.8% respectively at the end of the monitoring period. The lowest effectiveness of thrombolysis was detected for the strain of T. inflatium 126a, at 69.4% (Figure 4a). When cultivated in a fermentation medium containing glycerol, preparations obtained from the isolated strains demonstrated a more pronounced thrombolytic effect on fibrin clots (Figure 4b). On average, the extent of thrombolysis of those preparations was 12.3% higher than that of preparations obtained via culture of micromycetes in a medium with starch. The best thrombolytic potential during cultivation of micromycetes in a medium with glycerol was demonstrated by proteinase preparations isolated from the culture fluid of strains T. inflatium 62a, 30a, and 13a, with the extent of thrombolysis being 91.3%, 88.3%, and 87%, respectively. Maximal thrombolytic effectiveness of the T. inflatum k1 strain, already known for its thrombolytic properties, was 86%. Even the lowest value of thrombolysis effectiveness, detected in the T. inflatum 126a strain, was also high (79.7%).
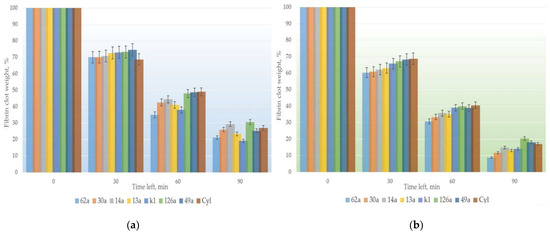
Figure 4.
Determination of thrombolysis effectiveness of micromycete preparations in a fermentation medium with (a) starch and (b) glycerol.
3.6. SDS-PAGE Analysis of Proteinase Preparations and Fibrin Zymography
Preparations obtained from the culture liquid of Tolypocladium isolates were also examined via SDS-PAGE analysis (submerged cultivation of micromycetes was carried out in a medium with glycerol and in a medium with starch). Protein content of the obtained preparation of T. inflatum 62a was revealed to be quite similar to that obtained for known thrombolytic-substance producer Tolypocladium inflatum k1 (Figure 5a). This could indicate similarity of proteins secreted in the culture liquid during submerged cultivation. Furthermore, fibrin zymography of the Tolypocladium inflatum 62a preparation demonstrated pronounced enzymatic activity of proteinases in this strain preparation (Figure 5b). It was also determined that the medium containing glycerol for submerged cultivation of Tolypocladium strains contributed to better production of exoproteinases in comparison to the medium containing starch.
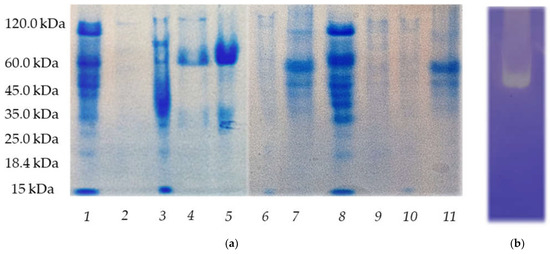
Figure 5.
(a) SDS-PAGE analysis of proteinase preparations obtained from the cultural fluid of micromycetes from Tolypocladium genus 1—k1 (glycerol), 2—126a (starch), 3—49a (glycerol), 4—14a (glycerol), 5—30a (glycerol), 6—49a (starch), 7—13a (glycerol), 8—62a (glycerol), 9—150a (starch), 10—150a (glycerol), and 11—126a (glycerol). (b) Fibrin zymogram of extracellular proteinases of Tolypocladium inflatum 62a.
3.7. Determination of Proteolytic Activity of Tolypocladium inflatum 62a Preparation toward Particular Proteins of the Hemostasis System
According to data obtained in experiments determining substrate specificity of protelytic activity of T. inflatum 62a isolate, plasmin-like (H-D-Val-Leu-Lys-pNA) and subtilizing-like (Z-Ala-Ala-Leu-pNA) were recorded as 27.21 and 14.01 U/mL × 10−3, respectively. The lowest activity was detected with Factor Xa, elastase, and trypsin substrates (Table 4). Therefore, it could be suggested that Tolypocladium inflatum 62a proteinases are capable of cleaving the substrate molecule at the lysine and leucine residues and demonstrate a low ability to cleave the substrate molecule at the arginine residues.

Table 4.
Determination of proteolytic activity toward particular proteins of the hemostasis system.
Comparison to the T. inflatum k1 proteinase preparation revealed differences in substrate specificity; the latter was characterized by pronounced elastase activity, simultaneously demonstrating lower subtilizing and plasmin activity.
4. Discussion
The selection of micromycetes isolated from White Sea soils revealed that the T. inflatum micromycete strain can be used as a promising producer of thrombolytic substances for the creation of new drugs or diagnostic kits based on them.
From a common genetic approach, micromycetes of the species Tolypocladium inflatum are best known as producers of cyclosporine, but recent studies have demonstrated that this species produces other bioactive secondary metabolites, including insecticidal compounds such as ephrapeptins, tolipin, diketopiperazines, and carboxysterol, as well as the antibiotic ergoconin-C and other previously unexplored classes of enzymes [28], which may include compounds with thrombolytic activity. Research of T. inflatum has great potential for production of secondary metabolites. At least 38 gene clusters responsible for synthesis of secondary metabolites for this micromycete were identified [29].
As for thrombolytic potential, among all strains examined in this study, T. inflatum 62a strain demonstrated the most pronounced ability to synthesize thrombolytic substances that were active against proteins of the hemostasis system. The preparation isolated from the culture liquid of micromycetes after cultivation in a medium with glycerol demonstrated high thrombolytic activity against fibrin clots as well as stability in physiological temperature and pH range. This effect can be applied in the development of thrombolytic drugs, both for external use as part of gels used against hematomas and wound dressings and in cases that require use of a thrombolytic agent in order to prevent severe thrombotic conditions, allowing a significant reduction in amount of drug administered and thus reducing the risk of bleeding on application. The use of thrombolytic substances, obtained from T. inflatum 62a, for external use is possible: for example, in combination with heparin to increase substance stability and increase thrombolytic effect. This could be especially relevant to treatment of thrombosis of deep and superficial veins of extremities, phlebothrombosis, and thrombophlebitis, as well as to prevention of pulmonary embolism and myocardial infarction. For instance, a similar approach was used for the preparation of extracellular proteinases of the micromycete Arthrobotrys longa: longolitin. Experiments in vitro and in vivo demonstrated that heparin in combination with longolitin not only exhibited its inherent anticoagulant activity but also accelerated thrombolysis [30,31].
Furthermore, new approaches to therapeutic combinations for thrombotherapy, which consider the differences in substrate specificity of T. inflatum 62a proteinases (subtilisin and plasmin) and substrate specificity of T. inflatum k1 (elastase and plasmins) and thereby allow production of the thrombolytic drug with a wide substrate specificity, could be developed.
During investigation of the obtained strains from the Tolypocladium genus, it became possible to distinguish strains that demonstrated thrombolytic potential.
In the first stage of screening, isolates were identified according to genetic characteristics. As it was clear that all strains belonged to the Tolypocladium genus, further research was considered.
In the second stage, in order to select perspective strain-producers, samples were examined to identify growth conditions of isolates (growth rate at different temperatures and pH) as well as enzymatic indexes in different media to understand potential activity versus particular protein types (fibrillar or globular).
The third stage of screening measured protheolytic and fibrinolytic activities of Tolypocladium-strain preparations obtained in submerged cultivation under conditions with different medium content (starch and glycerol). Furthermore, thrombolytic potential of obtained substances was tested in an experimental model of fibrin clot lysis, and specific protheolytic activity was determined in experiments with chromogenic substrates.
Therefore, seven Tolypocladium isolates obtained from White Sea soils were identified and examined according to thrombolytic characteristics. Throughout screening rounds, it was revealed that the most promising strain-producer of thrombolytic substances was Tolypocladium inflatum 62a, which demonstrated maximal growth rate, proteolytic (caseinolytic) activity, and pronounced fibrinolytic activity among all studied strains and in comparison to known producer of thrombolytic substances Tolypocladium inflatum k1. These thrombolytic properties could have applications in thrombotherapy and diagnostics of hemostasis system pathologies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S.F. and A.A.O.; methodology, N.S.F. and A.A.O.; software, N.S.F. and E.A.P.; validation, N.S.F. and E.A.P.; formal analysis, N.S.F. and A.A.O.; investigation, N.S.F., A.A.O., L.Y.K., A.V.K. and E.A.P.; resources, A.V.K., A.A.O. and L.Y.K.; data curation, N.S.F. and A.A.O.; writing—original draft preparation, N.S.F.; writing—review and editing, N.S.F. and A.A.O.; visualization, N.S.F.; supervision, A.A.O.; project administration, N.S.F. and A.A.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/mortality-and-global-health-estimates (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Baker, W.F., Jr. Thrombolytic therapy. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2002, 8, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balami, J.S.; Chen, R.; Sutherland, B.A.; Buchan, A.M. Thrombolytic agents for acute ischaemic stroke treatment: The past, present and future. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, E. The biotechnological potential of fibrinolytic enzymes in the dissolution of endogenous blood thrombi. Biotechnol. Prog. 2014, 30, 656–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Sabu, A. Fibrinolytic enzymes for thrombolytic therapy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1148, 345–381. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Q.; Dong, B.R.; Yue, J.; Wu, T.; Liu, G.J. Thrombolytic therapy for pulmonary embolism. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkova, T.S.; Matveeva, E.O.; Kreier, V.G.; Osmolovskiy, A.A.; Kurakov, A.V.; Baranova, N.A.; Egorov, N.S. Production of proteinase–plasminogen activators by micromycete tolypocladium inflatum k1. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2016, 52, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokichev, N.S.; Kornienko, E.I.; Sharkova, T.S.; Kreyer, V.G.; Osmolovskiy, A.A. Thrombolytic activity and properties of the proteinase produced by the micromycete tolypocladium inflatum k1. Mycol. Phytopathol. 2021, 55, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.; Gams, W. Cephalosporium-artige Schimmelpilze (Hyphomycetes). J. Basic Microbiol. 1973, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, P.W., Jr.; Kohlmeyer, J.; Kohlmeyer, E. Marine Mycology, the Higher Fungi. Mar. Ecol. 1980, 1, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissett, J. Notes on Tolypocladium and related genera. Can. J. Bot. 1983, 5, 1311–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, R.; Gams, W. A revision of Verticillium sectionProstrata. IV. The genera Lecanicillium and Simplicillium gen. nov. Nova Hedwig. 2001, 73, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klich, M.A. Indentification of Common Aspergillus Species, 1st ed.; Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.V.; Currah, R.S. Oidiodendron: A survey of the named species and related anamorphs of Myxotrichum. Stud. Mycol. 2005, 53, 83–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, P.W.; Braun, U.; Schubert, K.; Groenewald, J.Z. The genus Cladosporium and similar dematiaceous hyphomycetes. Stud. Mycol. 2007, 58, 1–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domsch, K.H.; Gams, W.; Anderson, T.H. Compendium of Soil Fungi, 2nd ed.; IHW-Verlag: Eching, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, K.A.; Gams, W. The genera of Hyphomycetes—2011 update. Pers. Mol. Phylogeny Evol. Fungi 2011, 27, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S.O.; Bendich, A.J. Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol. Biol. 1985, 5, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.D.; Lee, S.B.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics PCR-Protocols and Applications—A Laboratory Manual, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Panikov, N.S. Kinetics of Microorganisms Growth, 1st ed.; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1991; p. 309. [Google Scholar]
- Batomunkueva, B.P.; Egorov, N.S. Isolation, Purification, and Resolution of the Extracellular Proteinase Complex of Aspergillus ochraceus513 with Fibrinolytic and Anticoagulant Activities. Microbiology 2001, 70, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, E.; Helal, G.E.-D.A.; Edries, F.M. Screening for fibrinolytic filamentous fungi and enzymatic properties of the most potent producer, Aspergillus brasiliensis AUMC 9735. Biologia 2015, 70, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.K.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.T.; Mallia, A.K.; Gartner, F.H.; Provenzano, M.D.; Fujimoto, E.K.; Goeke, N.M.; Olson, B.J.; Klenk, D.C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.-M.; Choi, N.S.; Maeng, P.J.; Chun, H.K.; Kim, S.-H. Purification and characterization of a novel fibrinolytic enzyme from chive (Allium tuberosum). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 126, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, Z.; Hou, J.; Tyagi, R.; Liang, Y.; Hu, Y. Purification and characterization of a novel, highly potent fibrinolytic enzyme from Bacillus subtilis DC27 screened from Douchi, a traditional Chinese fermented soybean food. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmolovskiy, A.A.; Popova, E.A.; Kreyer, V.G.; Baranova, N.A.; Egorov, N.S. Fibrinolytic and collagenolytic activity of extracellular proteinases of the strains of micromycetes Aspergillus ochraceus L-1 and Aspergillus ustus 1. Mosc. Univ. Biol. Sci. Bull. 2016, 71, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmolovskiy, A.A.; Zvonareva, E.S.; Kreyer, V.G.; Baranova, N.A.; Egorov, N.S. The effect of micromycete extracellular proteases of the Aspergillus genus on the proteins of haemostatic system. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2014, 40, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaldi, N.; Seifuddin, F.T.; Turner, G.; Haft, D.; Nierman, W.C.; Wolfe, K.H.; Fedorova, N.D. SMURF: Genomic mapping of fungal secondary metabolite clusters. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2010, 47, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushley, K.E.; Raja, R.; Jaiswal, P.; Cumbie, J.S.; Nonogaki, M.; Boyd, A.E.; Owensby, C.A.; Knaus, B.J.; Elser, J.; Miller, D.; et al. The genome of tolypocladium inflatum: Evolution, organization, and expression of the cyclosporin biosynthetic gene cluster. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkova, T.S.; Kornienko, E.I.; Osmolovskiy, A.A.; Kreier, V.G.; Baranova, N.A.; Egorov, N.S. Morphological and Physiological Properties of the Micromycete Arthrobotrys longa, a Producer of Longolytin, a Proteolytic Complex with a Thrombolytic Effect. Mikrobiologiia 2016, 85, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podorol’skaya, L.V.; Serebryakova, T.N.; Sharkova, T.S. Experimental thrombosis in rabbit marginal ear vein and evaluation of the thrombolytic action of longolytin. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 143, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).