Effect of Two Strains of Beauveria bassiana on the Fecundity of Nezara viridula L. (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nezara Viridula Colony
2.2. Beauveria Bassiana Spore Powder
2.3. Bioassay Procedure to Determine Survival and Fecundity of N. viridula
2.4. Statistical Analysis
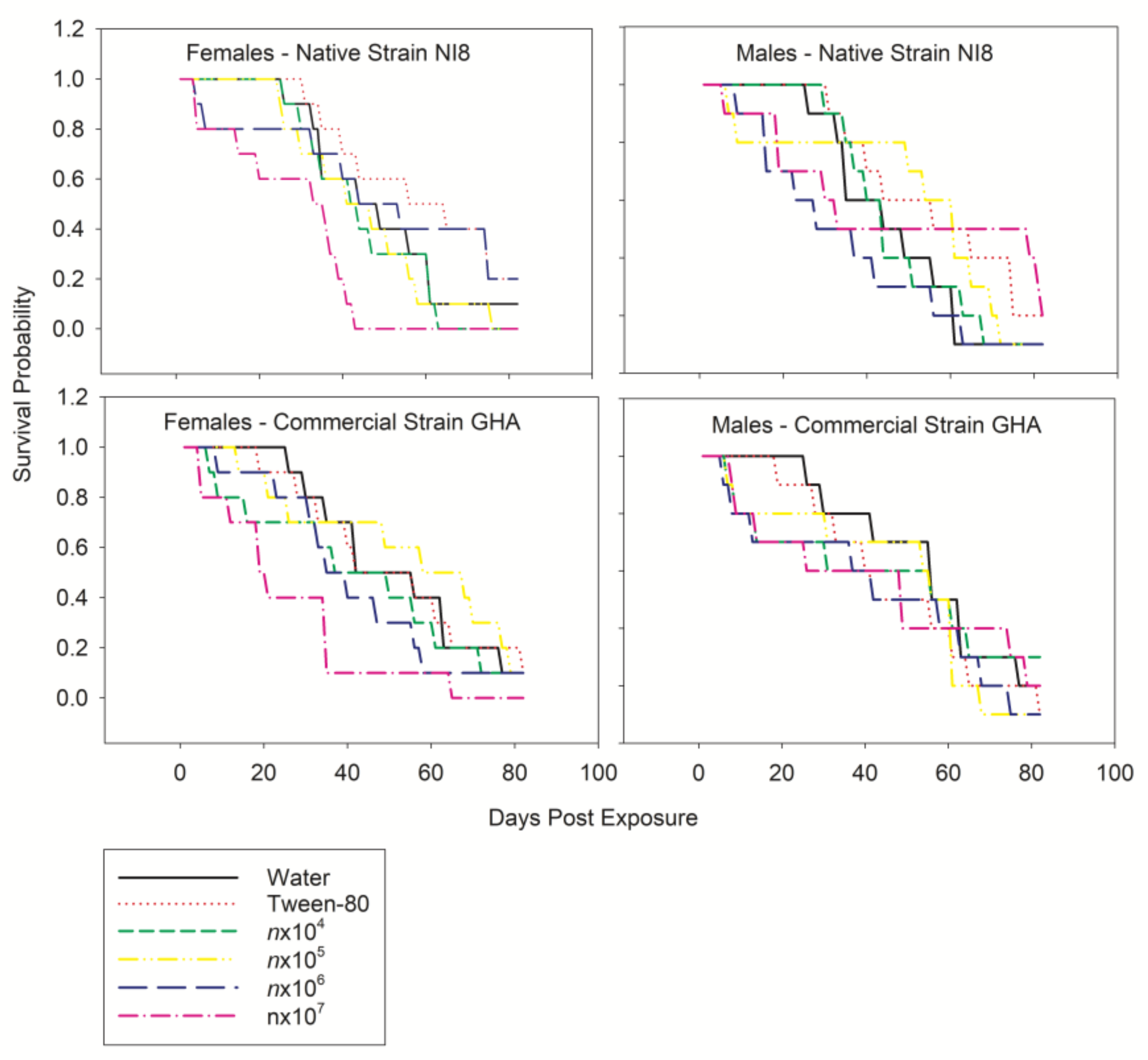
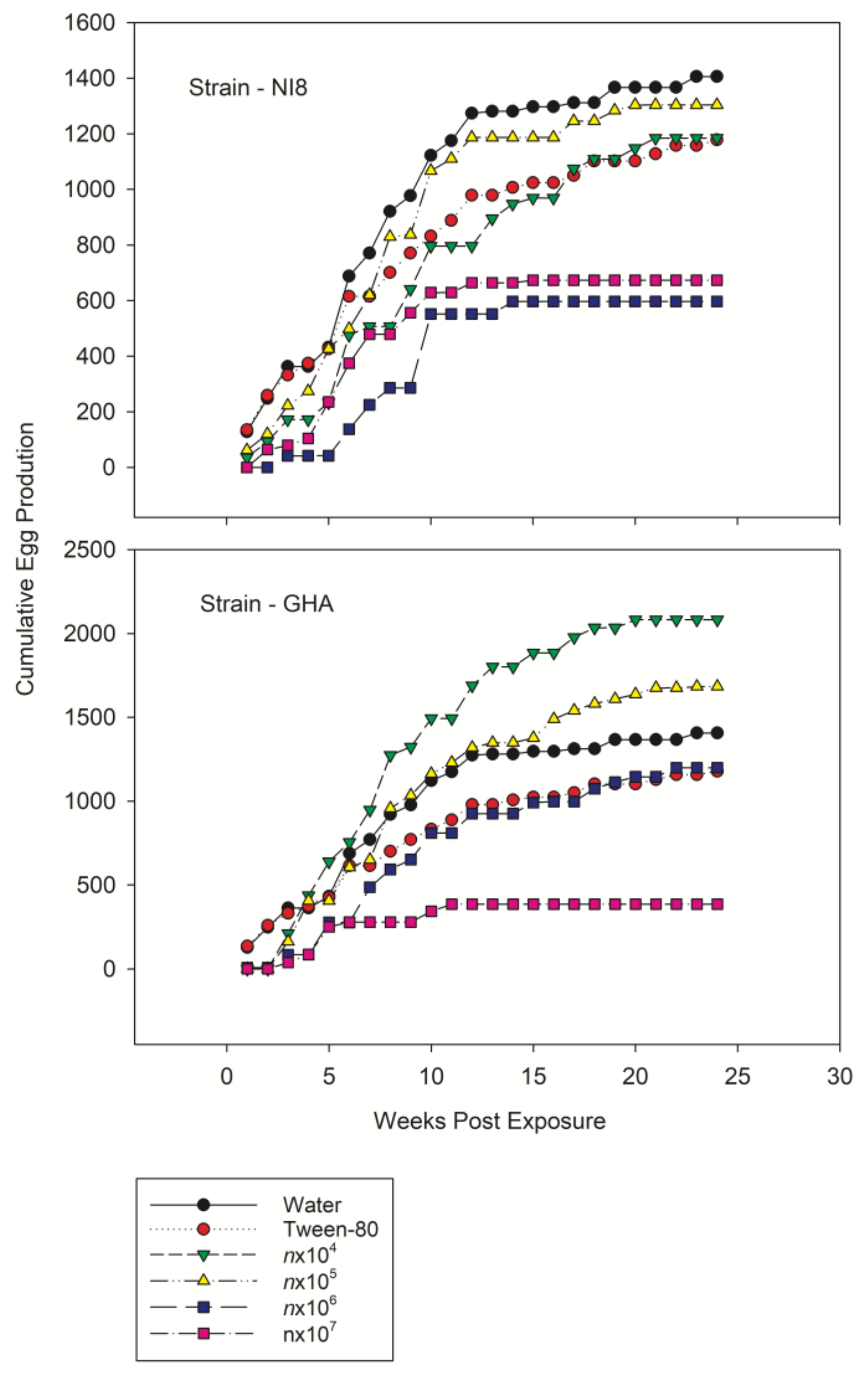
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giacometti, R.; Jacobi, V.; Kronberg, F.; Panagos, C.; Edison, A.; Zavala, J. Digestive activity and organic compounds of Nezara viridula watery saliva induce defensive soybean seed responses. Nat. Res. 2020, 10, 15468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musser, F.R.; Conley, S.P.; Davis, J.A.; Lorenz, G. 2019 soybean insect losses in the United States. MidSouth Entomol. 2020, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, D.R.; Threet, M. 2019 Cotton Insect Losses Estimates, Proceedings of the 2020 Beltwide Cotton Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 8–10 January 2020; National Cotton Council: Memphis, TN, USA, 2019; pp. 679–721. [Google Scholar]
- Gad, A.A.; Nada, M. Effect of the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana on the cellular immunity and biochemistry of green bug Nezara viridula L. J. Biopestic. 2021, 13, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass, G.L.; Scott, W.P.; Abel, C.A.; Robbins, J.T.; Gore, J.; Hardee, D.D. Suppression of tarnished plant bugs (Heteroptera: Miridae) in cotton by control of early season wild host plants with herbicides. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, M. Biological control as an alternative measure for tarnished plant bug control in Mississippi. MidSouth Entomol. 2014, 7, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, H.; Endo, N. Insecticide susceptibility of Nezara viridula (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) and three other stink bug species composing a soybean pest complex in Japan. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sosa-Gomez, D.; Correa-Ferreira, B.; Kraemer, B.; Pasini, A.; Husch, P.E.; Vieira, C.E.D.; Martinez, C.B.; Lopes, I.O. Prevalence, damage, management, and insecticide resistance of stink populations (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in commodity crops. J. Agric. For. Entomol. 2020, 22, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permadi, M.A. Efication of Some Entomopatogen Fungus on Green Ladybug Imago (Nezara Viridula Linnaeus) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Bp. Int. Res. Exact Sci. (BirEx) J. 2019, 1, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, M.; Snodgrass, G.L.; Luttrell, R.G. Mississippi Delta native strain Beauveria bassiana for control of tarnished plant bug (Lygus lineolaris). MidSouth Entomol. 2014, 7, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, R.B.; Lauman, R.A.; Blassioli-Moraes, M.C.; Borges, M.; Faria, M. The fungistatic and fungicidal effects of volatiles from metathoracic glands of soybean-attacking stink bugs (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) on the entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 132, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnah, S.; Sably, H. Effectiveness of Fungus Beauveria bassiana on Mortality of Nezara viridula on Stadia Nymphs and Imago. J. Floratek 2012, 7, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nada, M. Response of green stinkbug Nezara viridula (Linnaeus), to the activity of entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae. J. Plant Prot. Path. 2015, 6, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pushnya, M.; Rodionova, E.; Snesareva, E. Development of elements of the biological system for protecting crops against the southern green stink bug Nezara viridula L. (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in Krasnodar Krai. BIO Web. Conf. 2020, 21, 00037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Gomez, D.R.; Moscardi, F. Laboratory and field study on the infection of stink bugs, Nezara viridula, Piezodorus guildinii, and Euschistus heros (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) with Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana in Brazil. J. Inverterb. Pathol. 1998, 71, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, M.; Reddy, G.V.P. Development of a method for Rearing Nezara viridula (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) on a Semi-solid Artificial Diet. J. Insect Sci. 2021, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, M.; Luttrell, R.; Snodgrass, G.; Zhu, Y.C.; Riddick, E. Lethality of the Entomogenous Fungus Beauveria bassiana Strain NI8 on Lygus lineolaris (Hemiptera: Miridae) and its Possible Impact on Beneficial Arthropods. J. Entomol. Sci. 2017, 52, 352–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappione, A.; Crossley, E.; Thirumalapura, N.; Hoover, D. Immuno-Monitoring Using the Sceptertm 2.0 Cell Counter and Software Pro; Application Note; EMD Millipore: Darmstadt, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Parys, K.; Portilla, M. Effectiveness of Beauveria bassiana against Piezodorus guildinii (hemiptera: Pentatomidae), a key pest of soybeans in the neotropics. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2020, 30, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, M.; Abbas, H.K.; Accinelli, C.; Luttrell, R. Laboratory and Field Investigation on Compatibility of Beauveria bassiana (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae) Spores with a Sprayable Bioplastic Formulation for Application in the Biocontrol of Tarnished Plant Bug in Cotton. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 112, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbot, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.L.; Priestler, H.K. Pesticide Bioassay with Arthropods. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- SAS Institute. SAS/STAT User’s Manual; Version 9.4; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Noma, T.; Strickler, K. Factors affecting Beauveria bassiana for control of lygus bugs (Hemiptera: Miridae) in alfalfa seed fields. J. Agric. Urban Entomol. 1999, 16, 215–234. [Google Scholar]
- Boucias, D.G.; Stokes, C.; Storey, G.; Pendland, C. The effect of imidacloprid on the termite Reticulitermes flavipes and its interaction with the mycopathogen Beauveria bassiana. Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. Bayer 1996, 49, 103–144. [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Kloger, E.; Stein, W. Gewachshausversuche mit Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuellimin zur infection von Sitona lineatus L. (Col. Curculionidae) im Boden. Z. Angew. Entomol. 1970, 65, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Doye, M.B. Influence d’une infection a Beauveria bassiana sur les survivant et la descendance de Chilo suppressalis (Lep: Pyralidae). Entomophaga 1976, 21, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargues, J.; Delmas, J.C.; Auge, J.; Lebrun, R.A. Fecundity and eggs fertility in the adult Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata) surviving larva infection by the fungus Beauveria bassiana. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1991, 61, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, M.; Snodgrass, G.; Luttrell, R. Lethal and sub-lethal effects of Beauveria bassiana (Cordycipitaceae) strain NI8 on Chrysoperla rufilabris (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Fla. Entomol. 2017, 100, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, D.E.N.; Alston, D.G.; Roberts, D.W. Effects of physical and nutritional stress conditions during mycelial growth on conidial gemination speed, adhesion to host cuticle, and virulence of Metarhizium anisopliae, an entomopathogenic fungus. Mycol. Res. 2008, 112, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Feng, M.G.; Fan, Y.H.; Lou, Z.B.; Yang, X.Y.; Wu, D. A cuticle-degrading protease (CDEP-1) of Beauveria bassiana enhance virulence. Bio. Sci. Technol. 2008, 6, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrini, N.; Ortiz-Urquiza, A.; Huarte-Bonnet, C.; Zhang, S.; Keyhani, N.O. Targeting of insect epicuticular lipids by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana: Hydrocarbon oxidation within the context of a hist-pathogen interaction. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Gomez, D.R.; Boucias, D.G.; Nation, J.L. Attachment of Metarhizium anisopliae to the Southern Green Stink Bug Nezara viridula Cuticle and Fungistatic Effect of Cuticular Lipids and Aldehydes. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1997, 69, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, G.D.; Goettel, M.; Butt, T.M.; Strasser, H. Use of Hyphomycetous Fungi for Managing Insect Pest. In Fungi as Biocontrol Agents Progress, Problems and Potential; Butt, T.M., Jackson, C., Managan, N., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 23–69. [Google Scholar]


| Concentration Response ((μg/vial or Diet Cup) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | n | Slope ± SE | LC50(95%CI) (1) | Probit Trend | RR50 (95%CI) (4) | |||
| Test for Slope (2) | Test for GoF (3) | |||||||
| X2 | p > X2 | X2 | p > X2 | |||||
| 15 Days | ||||||||
| F (5)-NI8 | 60 | 0.79 ± 0.33 | 323 (163–9693) | 5.81 | 0.0159 | 2.05 | 0.1293 | 6.2 × 1010 (4.2 × 10115–9.3 × 10135) |
| F-GHA | 60 | 0.21 ± 0.25 | 15,310 (-) | 0.61 | 0.4350 | 1.22 | 0.2940 | 2.9 × 1012 (1.5 × 10−9–2.8 × 1016) |
| M (6)-NI8 | 60 | −0.04 ± 0.21 | 5.2 × 109(-) | 0.03 | 0.8711 | 1.23 | 0.2927 | 1 |
| M-GHA | 60 | 0.05 ± 0.21 | 5.2 × 106(-) | 0.05 | 0.8149 | 0.00 | 1.000 | 1.0 × 1015 (3.3 × 10117–3.0 × 10146) |
| 20 Days | ||||||||
| F (5)-NI8 | 60 | 0.97 ± 0.36 | 236 (148–1239) | 7.17 | 0.0074 | 1.97 | 0.1397 | 1 |
| F-GHA | 60 | 0.52 ± 0.25 | 326 (102–4.6 × 109) | 4.28 | 0.0385 | 1.48 | 0.2265 | 1.24 (0.26–5.97) |
| M (6)-NI8 | 60 | 0.05 ± 0.42 | 1.1 × 107(-) | 0.01 | 0.9042 | 3.14 | 0.0429 | 1.1 × 104 (8.5 × 1087–1.61 × 1096) |
| M-GHA | 60 | 0.48 ± 0.21 | 5.2 × 105(-) | 4.07 | 0.0437 | 0.44 | 0.6400 | 1.9 × 104 (1.1 × 10−36–3.4 × 1044) |
| Test * | Female NI8 | Female GHA | Male NI8 | Male GHA | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X2 | DF | p > X2 | X2 | DF | p > X2 | X2 | DF | p > X2 | X2 | DF | p > X2 | |
| Log-Rank | 10.6448 | 5 | 0.8423 | 6.0283 | 5 | 0.3035 | 5.1194 | 5 | 0.4015 | 4.0621 | 5 | 0.5405 |
| Wilcoxon | 7.7946 | 5 | 0.1679 | 5.3465 | 5 | 0.3751 | 5.6568 | 5 | 0.3411 | 5.1611 | 5 | 0.3965 |
| (LR)-2 Log | 11.1875 | 5 | 0.0478 | 8.3178 | 5 | 0.1396 | 5.8850 | 5 | 0.3176 | 5.9121 | 5 | 0.3149 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Portilla, M.; Reddy, G.V.P.; Tertuliano, M. Effect of Two Strains of Beauveria bassiana on the Fecundity of Nezara viridula L. (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 514-522. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13030035
Portilla M, Reddy GVP, Tertuliano M. Effect of Two Strains of Beauveria bassiana on the Fecundity of Nezara viridula L. (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Microbiology Research. 2022; 13(3):514-522. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13030035
Chicago/Turabian StylePortilla, Maribel, Gadi V. P. Reddy, and Moukaram Tertuliano. 2022. "Effect of Two Strains of Beauveria bassiana on the Fecundity of Nezara viridula L. (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae)" Microbiology Research 13, no. 3: 514-522. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13030035
APA StylePortilla, M., Reddy, G. V. P., & Tertuliano, M. (2022). Effect of Two Strains of Beauveria bassiana on the Fecundity of Nezara viridula L. (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Microbiology Research, 13(3), 514-522. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13030035







