Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Brucella melitensis Phylogeny and Virulence Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search and Accession of Sequences
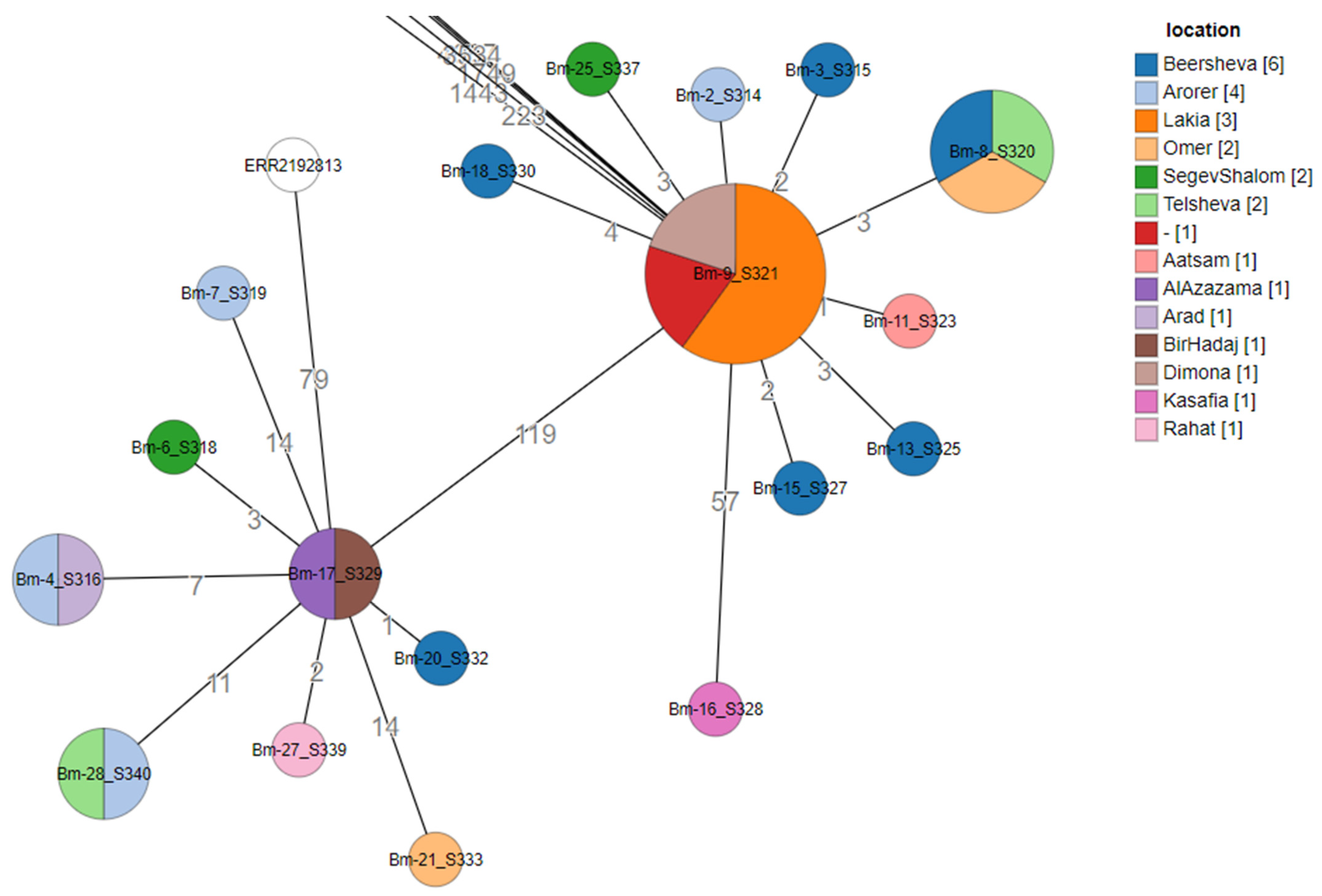
2.2. Brucella Isolates Recovered in Israel
2.3. Assembly of Whole Genomes
Raw Reads QC, Filtering, and Assembly
2.4. Phylogenomic Analyses
2.5. Analysis of Virulence Genes
2.6. Visualizations
2.6.1. Pangenome Analysis
2.6.2. SNP Variation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome Assembly
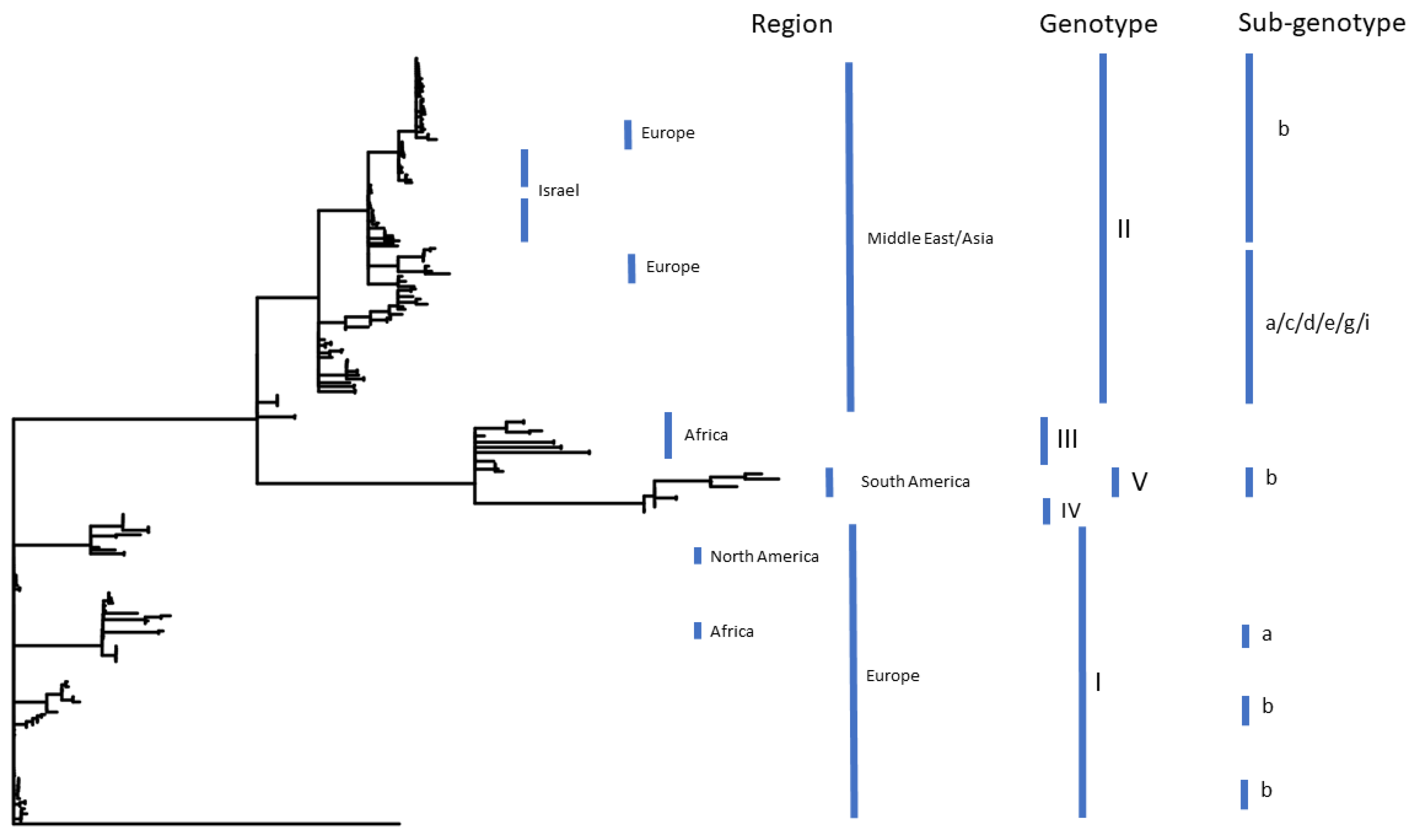
3.2. Segregation by Genotype and Region
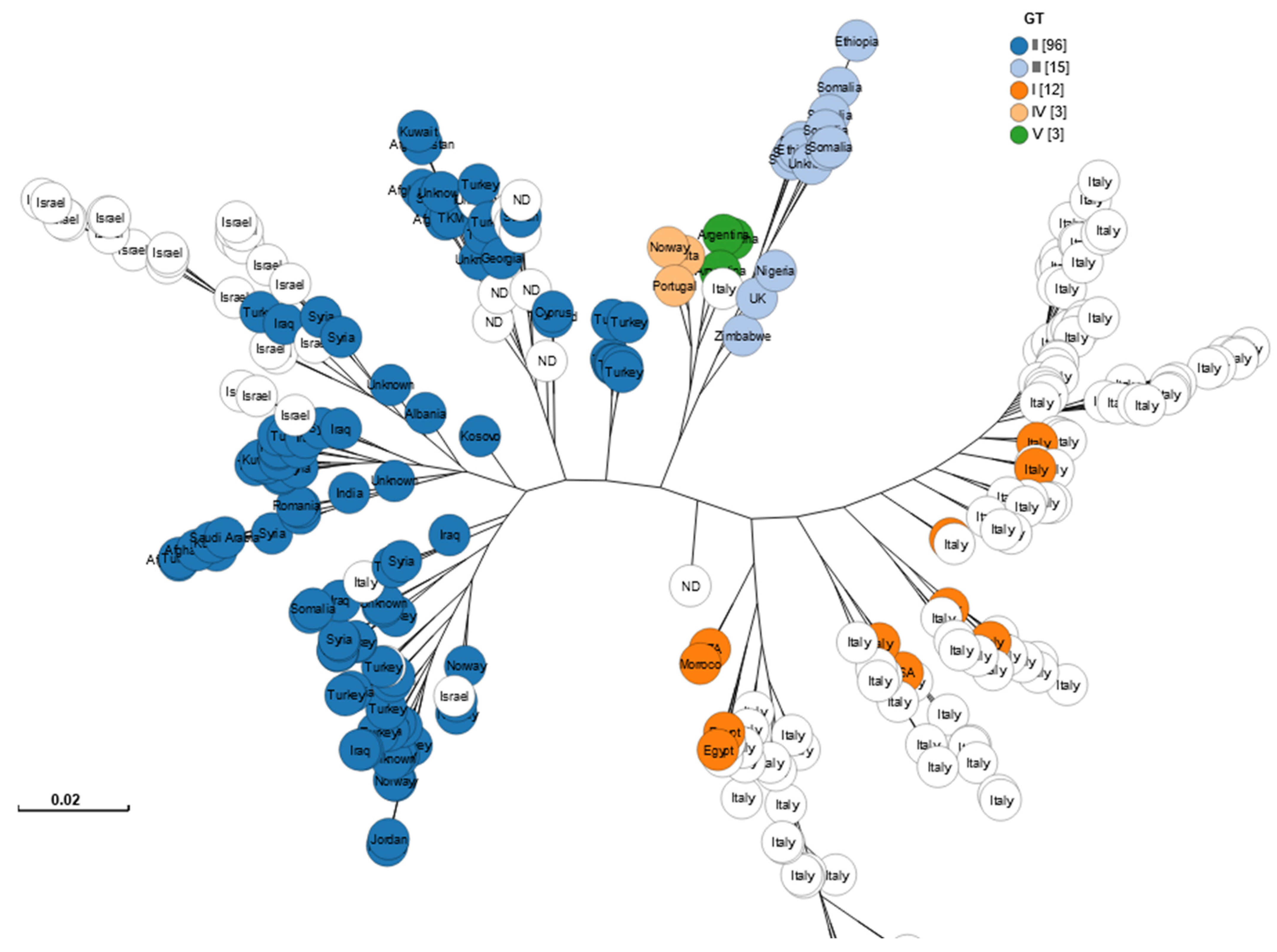
3.2.1. Global Clustering of Genotypes I–V
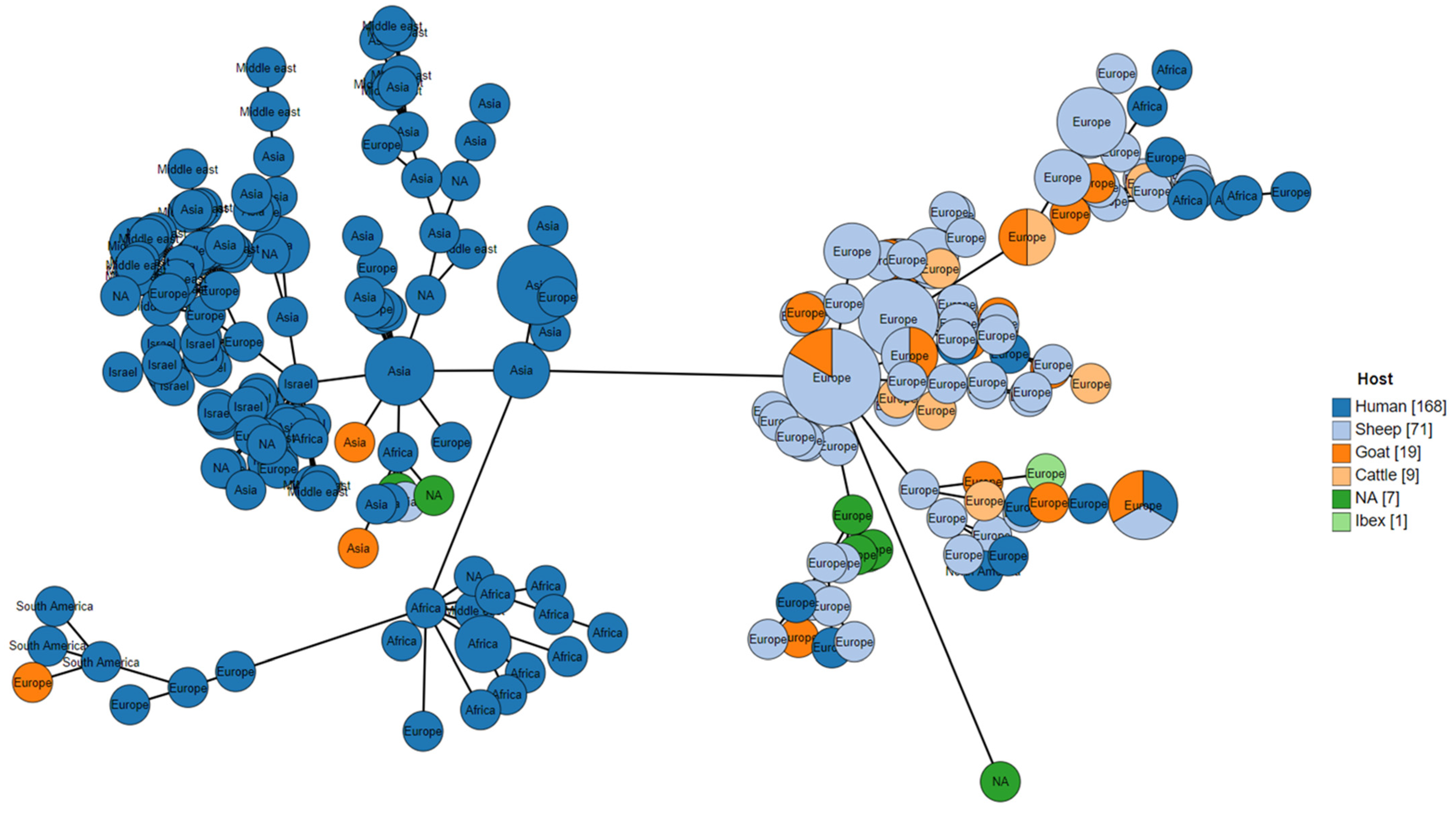
3.2.2. Host Species
3.2.3. Local Variation
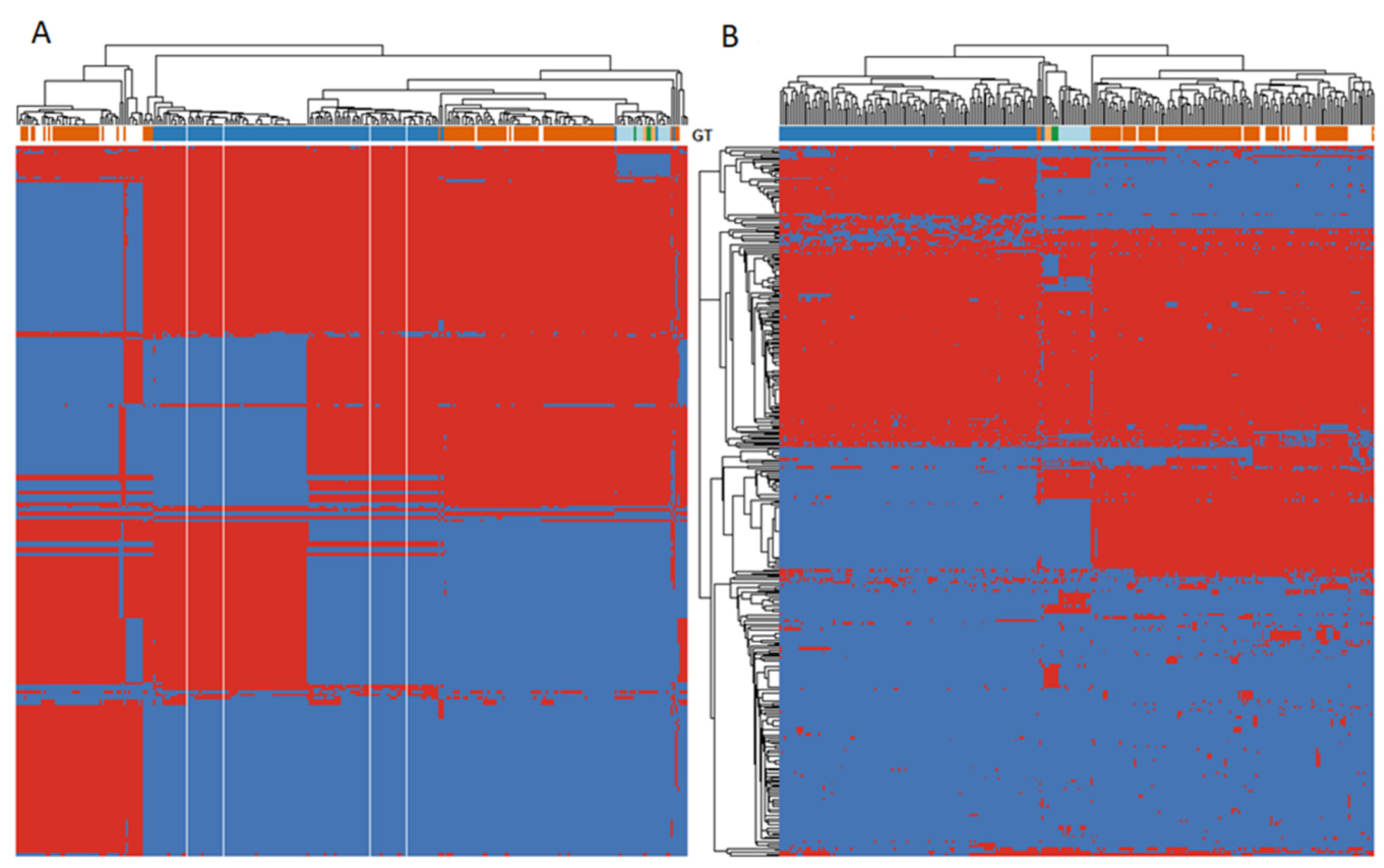
3.3. Pangenome Analysis
3.4. Virulome Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dean, A.S.; Crump, L.; Greter, H.; Hattendorf, J.; Schelling, E.; Zinsstag, J. Clinical Manifestations of Human Brucellosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doganay, G.D.; Doganay, M. Brucella as a Potential Agent of Bioterrorism. Recent Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, A.S.; Crump, L.; Greter, H.; Schelling, E.; Zinsstag, J. Global Burden of Human Brucellosis: A Systematic Review of Disease Frequency. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bechtol, D.; Carpenter, L.R.; Mosites, E.; Smalley, D.; Dunn, J.R. Brucella melitensis Infection Following Military Duty in Iraq. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, S.C.; Palmer, M.V. Advancement of Knowledge of Brucella Over the Past 50 Years. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemifar, I.; Yadegar, A.; Jazi, F.M.; Amirmozafari, N. Molecular prevalence of putative virulence-associated genes in Brucella melitensis and Brucella abortus isolates from human and livestock specimens in Iran. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancilla, M. Smooth to Rough Dissociation in Brucella: The Missing Link to Virulence. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzapfel, M.; Girault, G.; Keriel, A.; Ponsart, C.; O’Callaghan DM, V. Comparative Genomics and in vitro Infection of Field Clonal Isolates of Brucella melitensis Biovar 3 Did Not Identify Signature of Host Adaptation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Piao, D.; Mao, L.; Pang, B.; Zhao, H.; Tian, G.; Jiang, H.; Kan, B. Whole-genome sequencing of rough Brucella melitensis in China provides insights into its genetic features. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głowacka, P.; Żakowska, D.; Naylor, K.; Niemcewicz, M.; Bielawska-Drózd, A. Brucella—Virulence Factors, Pathogenesis and Treatment. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Callaghan, D.; Whatmore, A.M. Brucella genomics as we enter the multi-genome era. Brief. Funct. Genomics 2011, 10, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brambila-Tapia, A.J.; Armenta-Medina, D.; Rivera-Gomez, N.; Perez-Rueda, E. Main functions and taxonomic distribution of virulence genes in Brucella melitensis 16 M. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cannella, A.P.; Tsolis, R.M.; Liang, L.; Felgner, P.; Saito, M.; Gotuzzo, E.; Sette, A.; Vinetz, J.M. Antigen-specific acquired immunity in human brucellosis: Implications for diagnosis, prognosis, and vaccine development. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sangari, F.J.; Cayón, A.M.; Seoane, A.; García-Lobo, J.M. Brucella abortus ure2 region contains an acid-activated urea transporter and a nickel transport system. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancilla, M.; López-Goñi, I.; Moriyón, I.; Zárraga, A.M. Genomic Island 2 is an unstable genetic element contributing to Brucella lipopolysaccharide spontaneous smooth-to-rough dissociation. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 6346–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, J.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, J.; Liu, T.; Qin, N.; Yang, Y.; Cui, B.; Chen, C.; Liu, C.; et al. Whole genome sequences of four Brucella strains. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 3674–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirnejad, R.; Jazi, F.M.; Mostafaei, S.; Sedighi, M. Molecular investigation of virulence factors of Brucella melitensis and Brucella abortus strains isolated from clinical and non-clinical samples. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 109, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgi, E.; Walter, M.C.; Pfalzgraf, M.T.; Northoff, B.H.; Holdt, L.M.; Scholz, H.C.; Zoeller, L.; Zange, S.; Antwerpen, M.H. Whole genome sequencing of Brucella melitensis isolated from 57 patients in Germany reveals high diversity in strains from Middle East. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janowicz, A.; De Massis, F.; Ancora, M.; Cammà, C.; Patavino, C.; Battisti, A.; Prior, K.; Harmsen, D.; Scholz, H.; Zilli, K.; et al. Core genome multilocus sequence typing and single nucleotide polymorphism analysis in the epidemiology of Brucella melitensis infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00517-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pelerito, A.; Nunes, A.; Núncio, M.S.; Gomes, J.P. Genome–scale approach to study the genetic relatedness among Brucella melitensis strains. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, S.; Guo, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z. Brucella melitensis, a latent “travel bacterium,” continual spread and expansion from Northern to Southern China and its relationship to worldwide lineages. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1618–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.K.; Tan, Y.C.; Chang, L.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Nore, S.S.; Yee, W.Y.; Isa, M.N.; Jafar, F.L.; Hoh, C.C.; AbuBakar, S. Full genome SNP-based phylogenetic analysis reveals the origin and global spread of Brucella melitensis. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johansen, T.B.; Scheffer, L.; Jensen, V.K.; Bohlin, J.; Feruglio, S.L. Whole-genome sequencing and antimicrobial resistance in Brucella melitensis from a Norwegian perspective. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarenko, S.V.; Kovalev, D.A.; Volynkina, A.S.; Ponomarenko, D.G.; Rusanova, D.V.; Zharinova, N.V.; Khachaturova, A.A.; Tokareva, L.E.; Khvoynova, I.G.; Kulichenko, A.N. Global evolution and phylogeography of Brucella melitensis strains. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Cao, X.A.; Wang, M.; Piao, D.R.; Zhao, H.Y.; Cui, B.Y.; Jiang, H.L.Z. Whole-Genome Sequencing of a Brucella melitensis Strain (BMWS93) Isolated from a Bank Clerk and Exhibiting Complete Resistance to Rifampin. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e01645-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salmon-Divon, M.; Yeheskel, A.; Kornspan, D. Genomic analysis of the original elberg Brucella melitensis rev.1 vaccine strain reveals insights into virulence attenuation. Virulence 2018, 9, 1436–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C.J. BIGSdb: Scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinformatics 2010, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, M.; Machado, M.P.; Silva, D.N.; Rossi, M.; Moran-Gilad, J.; Santos, S.; Ramirez, M.; Carriço, J.A. chewBBACA: A complete suite for gene-by-gene schema creation and strain identification. Microb. Genomics 2018, 4, e000166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHC Key Laboratory of Systems Biology of Pathogens. VFDB Virulence Factors Database [Internet]. 2003. Available online: http://www.mgc.ac.cn (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Slater, G.S.C.; Birney, E. Automated generation of heuristics for biological sequence comparison. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonkin-Hill, G.; MacAlasdair, N.; Ruis, C.; Weimann, A.; Horesh, G.; Lees, J.A.; Gladstone, R.A.; Lo, S.; Beaudoin, C.; Floto, R.A.; et al. Producing polished prokaryotic pangenomes with the Panaroo pipeline. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushey, K.; Lin, L.; Finak, G. COMPASS: Combinatorial Polyfunctionality Analysis of Single Cells. Available online: https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/COMPASS.html (accessed on 9 March 2021).
- Nakamura, T.; Yamada, K.D.; Tomii, K.; Katoh, K. Parallelization of MAFFT for Large-Scale Multiple Sequence Alignments. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2490–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, A.J.; Taylor, B.; Delaney, A.J.; Soares, J.; Seemann, T.; Keane, J.A.; Harris, S.R. SNP-Sites: Rapid Efficient Extraction of SNPs from Multi-FASTA Alignments. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve Years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Jing, Z.; Di, D.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Ni, B.; Sun, X.; et al. Multiple locus variable-number tandem-repeat and single-nucleotide polymorphism-based Brucella typing reveals multiple lineages in Brucella melitensis currently endemic in China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Base Position in Gene | Genotype (GT) | Note | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | |||
| ure | 169 | T | G | G | G | G | |
| 328 | C | T | C | C | C | ||
| 515 | C | A | C | C | C | ||
| 785 | C | T | C | C | C | in GTIIb (Israeli/Middle East) sub-genotype | |
| 863 | C | T | C | C | C | ||
| 1188 | G | G | A | A | A | ||
| mviN | 104 | A | G | G | G | G | |
| 211 | G | A | A | A | A | ||
| vceC | 216 | G | C | G | G | G | In GTIIa sub-genotype |
| omp19 | none | ||||||
| prpA | none | ||||||
| betB | none | ||||||
| bpe275 | none | ||||||
| bspB | none | ||||||
| perA | none | ||||||
| manA | none | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabinowitz, P.; Zilberman, B.; Motro, Y.; Roberts, M.C.; Greninger, A.; Nesher, L.; Ben-Shimol, S.; Yagel, Y.; Gdalevich, M.; Sagi, O.; et al. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Brucella melitensis Phylogeny and Virulence Factors. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 698-710. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12030050
Rabinowitz P, Zilberman B, Motro Y, Roberts MC, Greninger A, Nesher L, Ben-Shimol S, Yagel Y, Gdalevich M, Sagi O, et al. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Brucella melitensis Phylogeny and Virulence Factors. Microbiology Research. 2021; 12(3):698-710. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12030050
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabinowitz, Peter, Bar Zilberman, Yair Motro, Marilyn C. Roberts, Alex Greninger, Lior Nesher, Shalom Ben-Shimol, Yael Yagel, Michael Gdalevich, Orly Sagi, and et al. 2021. "Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Brucella melitensis Phylogeny and Virulence Factors" Microbiology Research 12, no. 3: 698-710. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12030050
APA StyleRabinowitz, P., Zilberman, B., Motro, Y., Roberts, M. C., Greninger, A., Nesher, L., Ben-Shimol, S., Yagel, Y., Gdalevich, M., Sagi, O., Davidovitch, N., Kornspan, D., Bardenstein, S., & Moran-Gilad, J. (2021). Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Brucella melitensis Phylogeny and Virulence Factors. Microbiology Research, 12(3), 698-710. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12030050







