A Rare Case of Disseminated Nocardia transvalensis in an Immunocompetent Host
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Taxonomy and Microbiological Description
1.2. Epidemiology
1.3. Transmission
1.4. Diagnosis
1.5. Disease Spectrum and Previous Rare Cases
1.6. Treatment Modalities
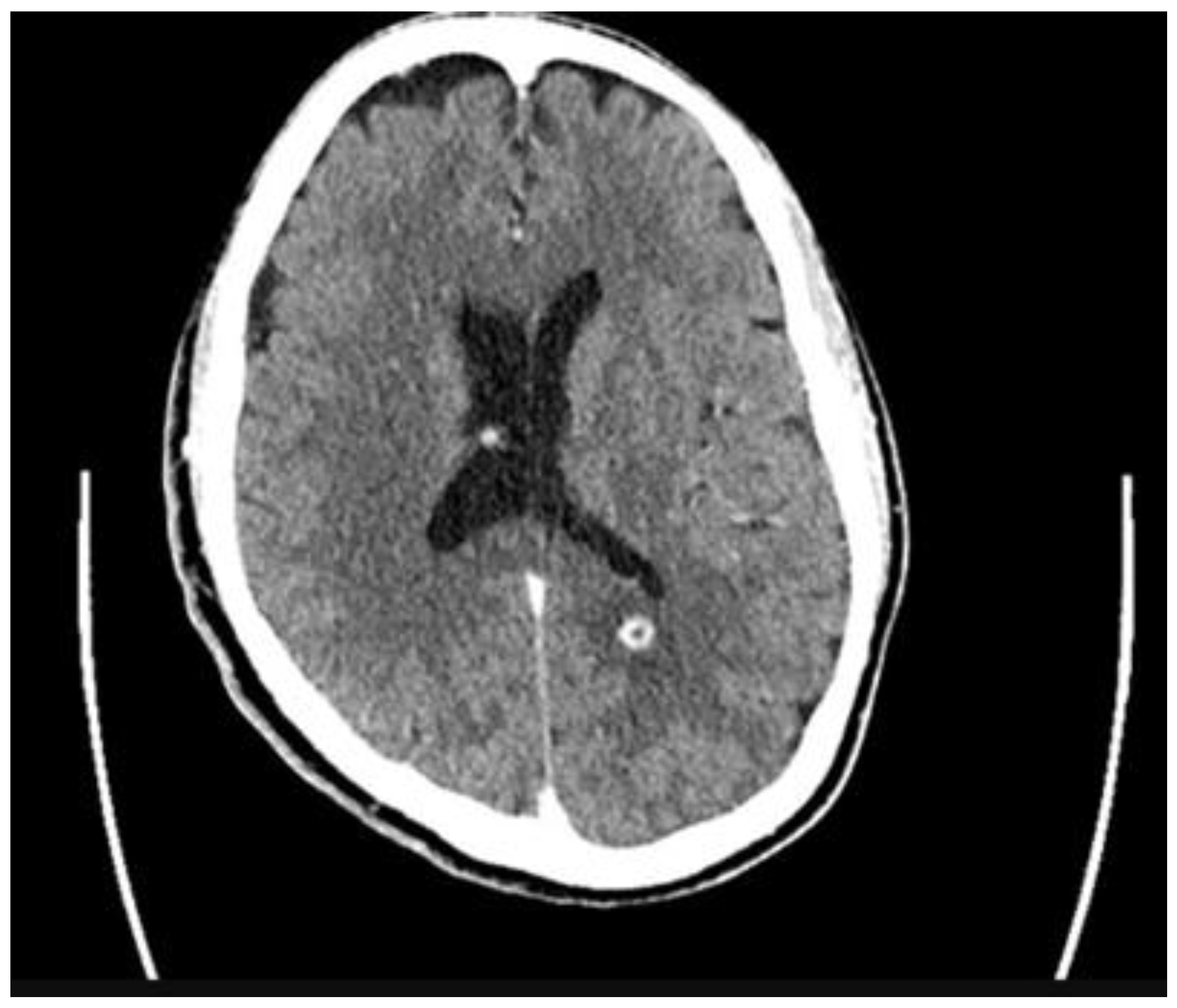
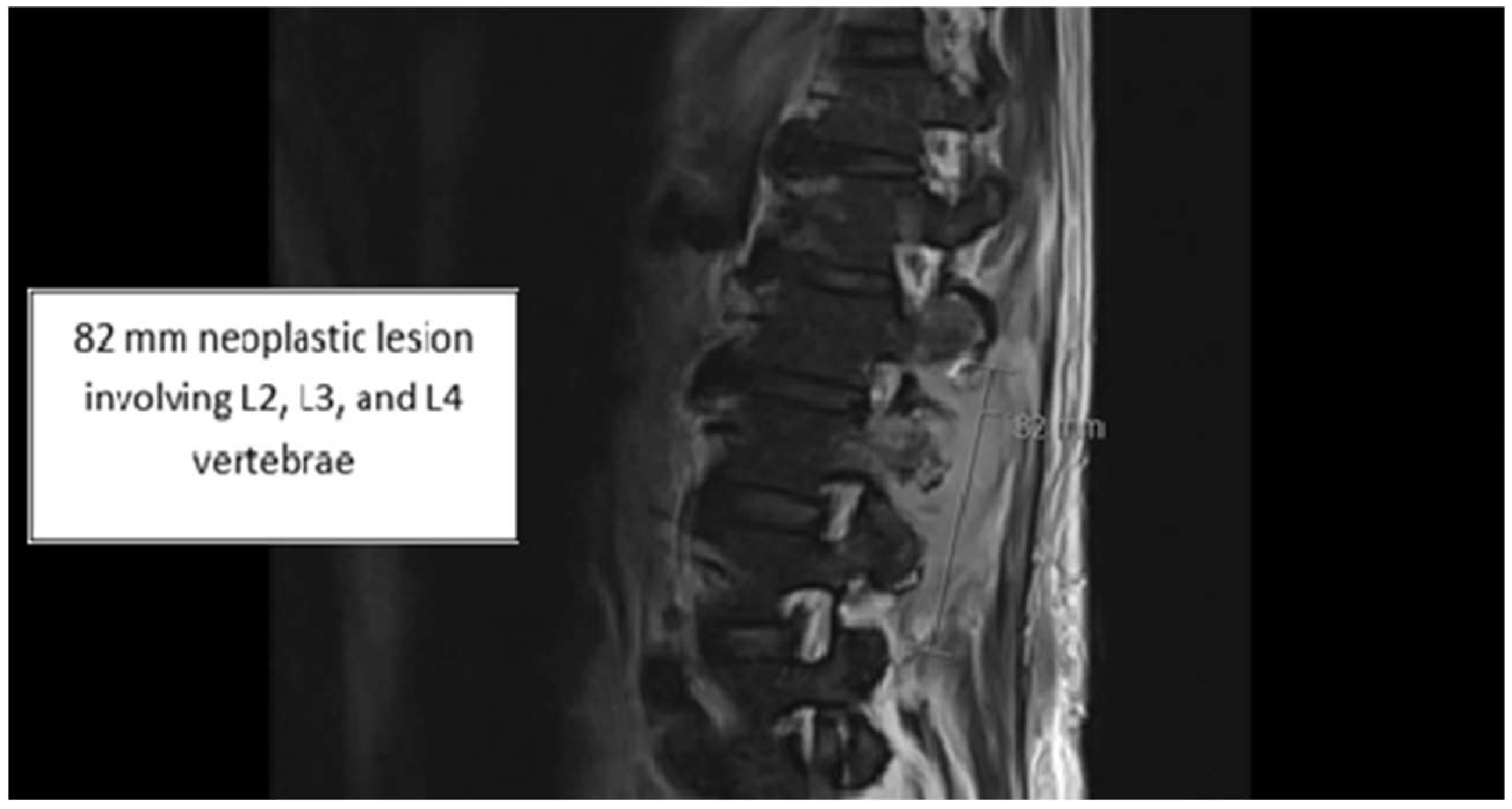
2. Case
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, J.W. Nocardiosis: Updates and clinical overview. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Diallo, A.; Dembele, Y.; Yaya, I.; Niang, M.; Benoit-Cattin, T.; Meliani, P.; Permal, S. Disseminated Nocardia transvalensis complex and farcinica: First case in an immunocompetent. New Microbes New Infect. 2023, 53, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- García-Méndez, J.; Carrillo-Casas, E.M.; Rangel-Cordero, A.; Leyva-Leyva, M.; Xicohtencatl-Cortes, J.; Arenas, R.; Hernández-Castro, R. Nocardia transvalensis Disseminated Infection in an Immunocompromised Patient with Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2016, 2016, 3818969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conville, P.S.; Brown, J.M.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Brown-Elliott, B.A.; Witebsky, F.G. Nocardia wallacei sp. nov. and Nocardia blacklockiae sp. nov., Human Pathogens and Members of the “Nocardia transvalensis Complex”. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical Overview of Nocardiosis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nocardiosis/hcp/clinical-overview/index.html (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Bafghi, M.F.; Eshraghi, S.S.; Heidarieh, P.; Habibnia, S.; Nasab, M.R. Nocardiosis in immune disorder disease. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 21, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Singh, S.; Samant, R.; Rodrigues, C. Nocardiosis in a patient with common variable immunodeficiency. J. Assoc. Physicians India. 2006, 54, 495–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fatahi-Bafghi, M. Nocardiosis from 1888 to 2017. Microb Pathog. 2018, 114, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdezate, S.; Garrido, N.; Carrasco, G.; Medina-Pascual, M.J.; Villalón, P.; Navarro, A.M.; Saéz-Nieto, J.A. Epidemiology and susceptibility to antimicrobial agents of the main Nocardia species in Spain. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, S.Y.; Deng, J.; Zhuang, K.W.; Tang, Y.; Wu, N.; Kang, M. Application of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for identification of Nocardia species. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provost, F.; Laurent, F.; Blanc, M.V.; Boiron, P. Transmission of nocardiosis and molecular typing of Nocardia species: A short review. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 13, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boell, K.; Gotoff, R.; Foltzer, M.; Storm, R.; Bourbeau, P.P. Implantable defibrillator pocket infection and bacteremia caused by Nocardia nova complex isolate. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5325–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Beaman, B.L.; Beaman, L. Nocardia species: Host-parasite relationships. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 7, 213–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chow, E.; Moore, T.; Deville, J.; Nielsen, K. Nocardia asteroides brain abscesses and meningitis in an immunocompromized 10-year-old child. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 37, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijper, A.; Pullinger, B.D. South African nocardiosis. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1927, 27, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger, M.; Eid, A.; Schreiber, L.; Shapiro, M.; Ilan, Y.; Libson, E.; Tur-Kaspa, R. Disseminated Nocardia transvalensis infection resembling pulmonary infarction in a liver transplant recipient. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1995, 14, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeil, M.M.; Brown, J.M.; Georghiou, P.R.; Allworth, A.M.; Blacklock, Z.M. Infections due to Nocardia transvalensis: Clinical spectrum and antimicrobial therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 15, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, P.I.; Baum, G.L. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Nocardia species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1973, 4, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gombert, M.E.; Aulicino, T.M.; duBouchet, L.; Silverman, G.E.; Sheinbaum, W.M. Therapy of experimental cerebral nocardiosis with imipenem, amikacin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and minocycline. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1986, 30, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McTaggart, L.R.; Doucet, J.; Witkowska, M.; Richardson, S.E. Antimicrobial susceptibility among clinical Nocardia species identified by multilocus sequence analysis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Toyokawa, M.; Ohana, N.; Ueda, A.; Imai, M.; Tanno, D.; Honda, M.; Shimura, H. Identification and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Nocardia species clinically isolated in Japan. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gram Stain: Few gram positive branching bacilli | |
| Results: Many Nocardia sp. transvalensis | |
| Method: MIC reference susceptibility | |
| Antibiotic | Susceptibility (µg/mL) |
| Amikacin | 16: Resistant |
| Amoxicillin/clavulanate | 32: Resistant |
| Ceftriaxone | 4: Susceptible |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.5: Susceptible |
| Clarithromycin | 0.5: Susceptible |
| Doxycycline | 4: Intermediate |
| Imipenem | 0.5: Susceptible |
| Linezolid | 1: Susceptible |
| Minocycline | 2: Intermediate |
| Moxifloxacin | 0.12: Susceptible |
| Tobramycin | 32: Resistant |
| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | 1: Susceptible |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ragunanthan, B.; Wunderly, K.; Kleshinski, J.; Hollingshead, C. A Rare Case of Disseminated Nocardia transvalensis in an Immunocompetent Host. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060140
Ragunanthan B, Wunderly K, Kleshinski J, Hollingshead C. A Rare Case of Disseminated Nocardia transvalensis in an Immunocompetent Host. Infectious Disease Reports. 2025; 17(6):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060140
Chicago/Turabian StyleRagunanthan, Branavan, Kevin Wunderly, James Kleshinski, and Caitlyn Hollingshead. 2025. "A Rare Case of Disseminated Nocardia transvalensis in an Immunocompetent Host" Infectious Disease Reports 17, no. 6: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060140
APA StyleRagunanthan, B., Wunderly, K., Kleshinski, J., & Hollingshead, C. (2025). A Rare Case of Disseminated Nocardia transvalensis in an Immunocompetent Host. Infectious Disease Reports, 17(6), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060140





