Abstract
Background and aim: Over the last few years, SARS-CoV-2 has been reported as a possible cause of acute pancreatitis (AP), but whether it is a relevant clinical–epidemiological entity is still a matter of debate. We aim to evaluate the epidemiological characteristics of AP during the first year of the COVID pandemic (2020) and compare them with the pre-COVID period (2008–2019) to identify any differences and clarify a potential causative role of SARS-CoV-2. Methods: We used a monocentric retrospective study of 132 AP patients during 2020 and 1987 AP patients during 2008–2019. Diagnosis and severity were classified according to the revised Atlanta criteria. Propensity score matching was performed according to clinical–epidemiological features, and outcome analysis was performed on two subgroups of 109 patients. Results: The total number of AP cases in 2020 is one of the lowest in the last 13 years (132 cases, median 161, IQR 146-183). No major epidemiological differences were noted. During 2020, we observed a significant modification of the distribution of etiologies (p < 0.001), mainly based on a decrease in biliary forms (59.6% vs. 43.2%) and an increase in alcoholic forms (6.9% vs. 12.9%). Idiopathic forms remain unchanged (20.5% vs. 21.9%). The proportion of AP of idiopathic etiology and SARS-CoV-2 infection was 0.008%. There were no differences in terms of severity distribution (p = 0.127), length of stay (p = 0.916), need for ICU (p = 0.139), or mortality (p = 0.462). Even among statistically matched groups, there were no differences between the length of stay (9 vs. 10 days, p = 0.890), need for ICU admission (1.8% vs. 3.7%, p = 0.683), or in-hospital mortality (0 vs. 1.8%, p = 0.342). Conclusions: The lower AP diagnoses indicate delayed and likely missed diagnoses, probably because of both hesitancy and organizational problems during the pandemic. The unchanged proportion of idiopathic forms supports the hypothesis that SARS-CoV-2 is not an AP trigger.
1. Introduction
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is one of the most frequent gastrointestinal conditions that result in hospital admission, with an estimated annual incidence of 34 cases per 100,000 people/year [1]. In accordance with the Atlanta classification [2] and the Guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology and the American Pancreatic Association (IAP/APA) [3], an AP diagnosis requires two criteria out of abdominal pain, an increase in lipase, or amylase at least three times the limit of normal and positive imaging. Moreover, according to the revised Atlanta classification of 2012, the severity of AP is defined as follows: mild, in the absence of significant local–regional complications and the absence of organ failure; moderately severe, in the presence of local–regional complications and/or transient organ failure; severe, in the presence of persistent organ failure and/or death [3].
The identification of the etiology is essential for treatment planning, improving the prognosis, and avoiding recurrent forms, and among the various etiologies, the diagnosis of biliary AP is a crucial point for therapeutic choices.
Gallstone disease and alcohol abuse are the two leading causes of AP. The relative percentage of these two main causes varies considerably among different European countries; in Mediterranean countries such as Italy, Spain, and Greece, biliary lithiasis is the most frequent cause of AP (50–60% of cases); in Germany and France, lithiasis and alcohol both cause 35–40% of AP cases; in the countries of Eastern and Northern Europe, alcohol is the most frequent cause, reaching about 55% of cases in Romania, Russia, Finland, and Latvia [4]. Less common causes include hypertriglyceridemia, adverse drug reactions, complications of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), malignant and benign pancreatic neoplasms such as papillary mucinous intraductal neoplasms (IPMN), and other rarer forms.
In the remaining patients, even after an extensive evaluation of history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies, the etiology remains unexplained. In these patients, in whom no underlying condition could be identified, AP is labeled as idiopathic. The diagnosis of idiopathic AP requires the exclusion of known triggers through an accurate anamnesis excluding drug abuse; alcohol abuse; a history of infection; an evaluation of metabolic disorders, including hypertriglyceridemia and hypercalcemia; genetic mutation; and at least two second-level imaging techniques, including endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) to exclude abnormality in the pancreatic gland or pancreatic, biliary, or gallbladder lithiasis. Since this definition, a highly variable incidence of idiopathic AP has been reported, ranging from 8 to 44% [5,6]. This large variability is very likely due to missed diagnoses of underlying conditions that are not immediately evident. Once all possible causes have been explored, the actual incidence of idiopathic AP was recently hypothesized to account for 10% of AP [7]. Despite the body of literature on this condition growing over the last ten years, idiopathic AP is the third most frequent form of AP and still remains a clinical challenge.
Among others, various infectious agents are associated with idiopathic AP, mainly viruses (such as Mumps, Coxsackie B, HSV, CMV, and VZV) but also bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Rigorous criteria for the diagnosis of infective AP have been formulated [8], such as identification via direct staining or culturing the infectious agent in the pancreas or pancreatic ducts (defined); the positive culturing of the organism in blood or pancreatic juice or serological diagnosis in a characteristic epidemiological setting (probable); or the positive culturing of the organism in other anatomic sites or serological diagnosis (possible), in association with the exclusion of lithiasis and alcohol when necessary. Moreover, various other microorganisms can directly infect the pancreas, but without causing a frank AP.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is known to cause gastrointestinal symptoms among 15% of patients [9]. Several studies suggest that SARS-CoV-2 might enter the acinar cells and the islets of Langerhans cells via angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), inducing pancreatic injury [10,11,12]. Several reports and review articles have explored the relationship between COVID-19 and AP [13,14,15,16], but often it remains uncertain whether the pancreatic injury is truly caused by SARS-CoV-2 or whether it is a casual association due to the pandemic. Moreover, insufficient searches for other etiologies, concomitant medication, and critical illness status are advocated as possible biases.
The aim of this study is to evaluate the epidemiological characteristics of AP during the 2020 pandemic and compare them with the pre-COVID period in order to identify any differences in the incidence and distribution of AP etiologies due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Moreover, we evaluated differences in the outcomes of AP patients, such as length of hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and in-hospital mortality, due to the COVID-19 pandemic. If indeed AP can be induced by SARS-CoV-2, an increased incidence of AP, or at least a relative increase in idiopathic forms, should be expected during 2020.
2. Materials and Methods
A retrospective study was conducted using a prospectively maintained database of pancreatic diseases in use at the IRCCS of the S. Orsola-Malpighi Hospital, University of Bologna. The guidelines used for this study were those released by the IAP/APA. We chose these guidelines because a preliminary investigation among our hospital physicians demonstrated that they were the best known.
The Regional Database of Hospital Discharge Forms of our institution was consulted, identifying possible cases of AP through the following diagnosis codes as the first or secondary diagnosis, according to the International Classification of Disease, 9th Edition—Clinical Modification (ICD9-CM): 5770 “Acute pancreatitis”, 5771 “Chronic pancreatitis”, 5772 “Cysts and pseudocysts of the pancreas”, 5778 “Other specified diseases of the pancreas”. Cases of COVID-19 were identified according to the following diagnosis codes (used in Italy in 2020): 07982 “Associated SARS-coronavirus” (a subcategory of group code 0709—virus and chlamydial infections in morbid manifestations classified elsewhere), 4803 “SARS-associated coronavirus pneumonia”.
The database search found 234 cases that matched these criteria from 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2020.
Two authors evaluated, in a blinded manner, all selected records to remove cases that did not meet the revised Atlanta criteria for the diagnosis of AP and patients with incomplete clinical or laboratory data or incorrect diagnoses. The records were considered incomplete when one of the following data was lacking: sex, age, comorbidity, etiology, severity according to the revised Atlanta classification, and outcomes. A total of 132 confirmed cases of AP were identified during 2020. We compared the data of these patients with our historical cohort, namely, the pre-COVID period (from 1 January 2008 to 31 December 2019), which was obtained in the same manner.
For each patient, we collected data regarding sex, age, the presence of comorbidities, and total amylase and lipase levels at diagnosis. Etiology was assessed in agreement with international guidelines. In particular, it was evaluated through personal and family history, imaging, and laboratory tests; in the case of acute idiopathic pancreatitis, EUS and MRCP were performed and were negative. We assessed the severity of AP according to the Atlanta classification, outcome (discharge to home, discharge to long-term care, and death during the hospital stay), need for ICU admission, and length of hospitalization. The diagnosis of COVID-19 was confirmed through a reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test conducted on samples obtained via nasopharyngeal swabbing.
Data are presented as N (%) and median (interquartile range—IQR). Fisher’s test, Chi-square, and t-test were used as appropriate.
Given the considerable difference in the sample size, with the 2008–2019 group containing approximately 15 times the number of cases in the 2020 group, and the heterogeneity of the sample, we performed propensity score statistical matching according to sex, age, comorbidity, amylase and lipase levels, and different etiologies and severities. We performed 1:1 matching of two subgroups of 109 patients. The homogeneity of the groups was tested by measuring the d-value, estimating a low standardized size effect for values <0.2, rather than low standardized size effect for values <0.2: average between 0.2 and 0.5, large between 0.5 and 0.8, and very large if >0.8. All analyses were conducted using STATA 14 (College Station, TX, USA).
The local Ethics Committee (Independent Ethics Committee of the Emilia-Romagna Region—Subsection Center) approved the database with code PANBO 064/2017/U/Oss.
3. Results
The trend of cases of AP admitted to our center from 2008 to 2020 is shown in Figure 1. During the 2008–2019 period, there were 1987 diagnoses of AP, while in 2020, there were 132 cases, which is in the lower quartile of diagnoses per year (median 161, IQR 146-183).
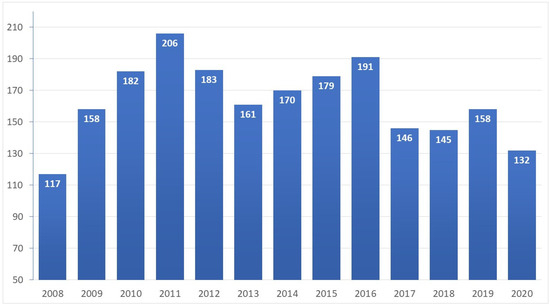
Figure 1.
Cases of AP per year. Number of acute pancreatitis cases per year. Median, 161; interquartile ratio, 146–183.
Epidemiological and clinical features, outcomes, and statistical comparisons between the 2008–2019 period and 2020 are presented in Table 1. Between the two periods, there were no significant differences between sex (61.4% vs. 52.7%, p = 0.058) and age (median 66 years for both, p = 0.669). Most of the patients had at least one comorbidity, although during 2020, a slight decrease was seen (79.5% vs. 93.4%, p < 0.001). The median values of lipases at presentation were similar between the two periods (1339 U/L (360–3085) vs. 1398 U/L (458–4197), p = 0.234), while amylase levels were inferior (677 U/L (200–1168) vs. 823 U/L (307–1876), p = 0.046).

Table 1.
Epidemiological and clinical features, outcomes, and statistical comparisons between the AP cases of 2008–2019 and 2020.
The distribution of the etiologies is presented in Figure 2. Comparing etiologies during 2020 with the pre-COVID period, we observed fewer biliary cases (43.2% vs. 59.6%) and more alcohol-related forms (12.9% vs. 6.9%). Moreover, we observed a slight increase in post-ERCP cases (7.6% vs. 3.2%) and IPMN (9.1% vs. 2.2%). Idiopathic forms remained unchanged comparing 2020 and the 2008–2019 period (20.5% vs. 21.9%).
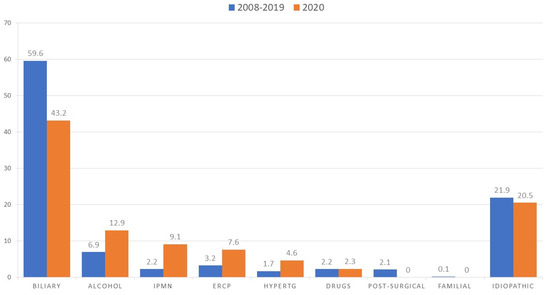
Figure 2.
Distribution of AP etiology during 2008–2019 and 2020. Data are presented as percentages: blue line cases; 2008–2019, orange line cases, 2020. IPMN = intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, ERCP = endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, HyperTG = hypertriglyceridemia.
Between the 2020 and 2008–2019 periods, there were no significant differences between the distribution of severity according to the Atlanta classification, with a prevalence of mild cases (83.3% vs. 79.3%) and lower frequencies of moderately severe (9.6% vs. 15.9%) and severe cases (6.8% vs. 4.8%).
Moreover, there were no differences between the ICU admission rates (6.1% vs. 3.4%, p = 0.139). The median length of stay was comparable (10 days (7–14) vs. 9 days (6–16), p = 0.916). There were no differences between outcomes, with a comparable in-hospital mortality rate (2.3% vs. 4.4%, p = 0.462).
Observational studies are often limited by imbalances that may occur between known and unknown confounding factors. To minimize these potential confounding effects in evaluating the rate of complications and mortality before and during the pandemic, we applied the propensity score matching method. Table 2 presents features of the statistically matched AP cases according to demographics, comorbidity, amylase and lipase levels, different etiology, and severity. The 1:1 analysis included 109 patients from the historical cohort and 109 patients from the COVID period. Patients in the two subgroups presented similar ages (65 vs. 64 years, p = 0.718, d = 0.040), male sex prevalence (45.9% vs. 38.5%, p = 0.337, d = 0.170), comorbidities (77.1% vs. 78%, p = 1.000, d = 0.030), amylase levels at diagnosis (595 U/L vs. 670 U/L, p = 0.857, d = 0.024), and lipase levels at diagnosis (1107 U/L vs. 1309 U/L, p = 0.497, d = 0.090). Regarding etiology, even after the statistical matching, there was a slighter imbalance between alcoholic and biliary forms compared with the historical cohort (biliary 50.5% vs. 42.2%; alcohol 5.5% vs. 14.7%), with p = 0.015 and d = 0.120. Severity distribution was similar in the two groups (mild, 83.5% vs. 85.3%; moderately severe, 14.7% vs. 11%; and severe, 2% vs. 4%), with p = 0.127 and d = 0.039. The epidemiological and clinical features of the statistically matched patients are presented in the Supplementary Materials (Table S1).

Table 2.
Features of the statistically matched AP cases according to demographics, comorbidity, amylase and lipase levels, and different etiologies and severities.
Even after the propensity score analysis, we did not observe any differences in length of stay (9 days vs. 10, p = 0.890), need for ICU admission (1.8% vs. 3.7%, p = 0.683), or in-hospital mortality (0 vs. 1.8%, p = 0.342) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Outcome analysis of statistically matched AP cases according to epidemiological features, comorbidity, amylase and lipase levels, and different etiologies and severities.
During 2020, a total of seven AP patients (5.3%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 using real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) nasopharyngeal swabs. Among these, three patients had biliary etiology; one was secondary to the uremic phase of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and had concomitant severe hypertriglyceridemia; one was suffering from CKD in the uremic phase, and SARS-CoV-2 infection occurred temporally after AP onset (>4 weeks). Of the remaining two cases, initially classified as idiopathic pancreatitis, a grape-like IPMN of the pancreatic head of 18 mm was found in one of the subsequent follow-ups. The prevalence of “possible” SARS-CoV-2-induced AP is, therefore, 0.008% after the accurate exclusion of other causes. During the same year, in our hospital, there were 1218 hospitalizations for COVID-19. In this population, the prevalence of AP was 0.58%, and the prevalence of acute idiopathic pancreatitis was 0.08%.
4. Discussion
SARS-CoV-2 can theoretically infect pancreatic acinar cells by binding to the ACE2 receptor [10]. However, evidence of its real causative role in AP is very poor. A review identified 22 cases of AP associated with COVID-19 in the literature [17]. In five of these, there was an evident triggering cause (biliary, alcohol, hypertriglyceridemia), while in some cases, there was no temporal association between AP and COVID-19. By examining these case reports with the criteria of Parenti et al. [8], in only one case can the etiological role of SARS-CoV-2 be defined as probable. Schepis et al. described a case of a 67-year-old woman with recent AP classified as idiopathic and complicated by a large peripancreatic pseudocyst. After the failure of conservative medical therapy, transgastric drainage of the pseudocyst was performed, and the fluid tested positive in an RT-PCR search for SARS-CoV-2 target genes [18]. In an autopsy study of 11 deceased COVID-19 patients, the immunohistochemistry with monoclonal antibody against SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein was positive in all cases both in the exocrine pancreas and in the islets of Langerhans; however, in neither of them was a previous clinical–laboratory–radiological picture compatible with AP described, nor any histological evidence of AP [19]. It can, therefore, be reasonably stated that SARS-CoV-2 can infect the pancreas and that it could represent a possible causative agent of AP, but whether “SARS-CoV-2-related AP” is a relevant clinical–epidemiological entity is still a matter of debate.
In a large epidemiological study of 63822 cases of COVID-19 admitted to the emergency departments (EDs) of 50 Spanish hospitals, Mirò et al. estimated a prevalence of AP of 0.07%, but no etiology was reported [20]. In another retrospective observational study, the prevalence of AP in patients admitted to 12 US hospitals was 0.27%. In this study, the authors concluded that AP could be one of the possible manifestations of COVID-19 since they found a greater incidence of idiopathic forms among COVID-19 patients (69% vs. 21%) [21]. Furthermore, these results could be affected by several biases. Concomitant drug treatment for COVID-19, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antivirals, antibiotics, corticosteroids, and other immunosuppressants, are associated with drug-induced AP [22,23]. Moreover, severe cases of COVID-19-associated cytokine storm could secondarily affect the pancreas as part of diffuse microthrombosis and multi-organ failure: in a retrospective study, an asymptomatic increase in amylase and lipase was described, respectively, in 17.91% and 16.41% of patients with severe COVID-19 but only in 1.85% of non-severe cases [24]. Moreover, in several studies, the definition of idiopathic AP was not as rigorous as suggested by international guidelines. In our study, in fact, we performed both EUS and CWRM for the diagnosis of idiopathic AP. Finally, it should be noted that the positivity of nasopharyngeal swabs for SARS-CoV-2 is certainly not enough to demonstrate a cause–effect relationship.
In agreement with these observations, a systematic review of the literature by Onoyama et al. highlighted the rarity of this entity and the possible misdiagnosis, as they found that 55.8% of patients had severe or critical COVID-19; 24.6% were under mechanical ventilation; and for over a half (43/82), there were probable causes of AP other than COVID-19 (most relevantly, drug-induced and ischemia–reperfusion), and in almost all cases, a complete work-up for etiology was not carried out [25].
In our study, the prevalence of AP in hospitalized patients with COVID was 0.58%; however, the prevalence of idiopathic AP (or hypothetical SARS-CoV-2-related AP) was 0.08%. On the other hand, the incidence of possible SARS-CoV-2-related AP was 0.008% (1 case out of 132) during the period of January 2020–December 2020.
These data are sufficient to highlight the rarity of hypothetical SARS-CoV-2-related AP, but to confirm it, we performed an analysis of epidemiology and outcomes with the historical cohort of AP up to 2019.
In the first instance, the prevalence of AP in 2020 (or 132 cases) was among the lowest in the last 13 years, ranking below the second quartile. The influence of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic was, therefore, negative on cases of AP, probably because of the reduced access to health services for health problems other than COVID-19 in the most dramatic months of the pandemic.
Comparing the cases of AP collected in 2020 with our historical cohort, no major differences were noted. The epidemiological characteristics were comparable, as was the distribution of the degrees of severity. We observed lower amylase levels at diagnosis, which may be due to later access to the ED given the shorter plasma half-life [26]. The main statistically significant difference lies in the distribution of causes but not for an increase in idiopathic cases in 2020 (as expected if SARS-CoV-2 infection had a real positive epidemiological impact on AP cases) but rather because of a different distribution of the most frequent etiologies. We observed a consistent decrease in biliary AP cases both in relative terms (59.6% vs. 43.2%) and in absolute terms given the context of a lower incidence of AP. This decrease is parallel to a decrease in comorbidity at diagnosis (93.4% vs. 79.5%): this suggests that more comorbid patients, in which biliary forms are most likely [27,28], could be those whose access to care during the months of the pandemic dropped. Parallel to this, we noted an increase in alcoholic AP cases (6.9% vs. 12.9%) during 2020. It has been observed by various studies that, during the pandemic and even more in the months of lockdown, the average consumption of alcohol in Western countries significantly increased [29,30]. In fact, substantial stress from social and economic uncertainty could lead to psychological decompensation and 10%–19% increased drinking compared with the pre-pandemic period [31]. The other most represented etiology in 2020 compared with previous years was the presence of IPMN; this may reflect the increasing attention paid to this relatively recent nosological entity and the progressive refinement and greater availability of second-level diagnostic techniques such as EUS and MRCP [32]. Finally, it is interesting to point out that there have been no post-surgical AP cases in 2020 because of the reduction in elective surgical activity in the first year of the pandemic.
Regarding the outcomes of AP during the pandemic, a metanalysis found that AP in the setting of COVID-19 infection was more frequently severe and had a higher risk of pancreatic necrosis, ICU admission, and mortality. Furthermore, the authors acknowledge the high risk of selection bias that could affect the analysis and address the need for larger-scale studies [33]. Another study evaluated the possibility of a more severe AP prognosis among COVID-19 patients. Through a propensity-score-matched study, the authors compared patients with SARS-CoV-2 infections and AP, patients with AP pre-pandemic, and patients with AP during the pandemic: the major differences demonstrated were a six-fold relative risk of death in patients with AP and SARS-CoV-2 infection compared with those with AP before the pandemic and a three-fold relative risk of death in patients with AP during the pandemic compared with those before the pandemic. Furthermore, the authors believe that these differences were probably due to restrictive measures implemented during the pandemic period, consequent delay in care, and a restriction on surgical treatment indications [34]. Conversely, a more recent study directly compared SARS-CoV-2-positive patients and SARS-CoV-2-negative patients, both diagnosed with AP, and it found no differences regarding mortality rate, severity, or sequelae [35].
Increased mortality during the pandemic was also observed for other gastrointestinal diseases, such as alcoholic liver disease, hepatic failure, and gastrointestinal hemorrhage. In a study based on weekly death counts from the National Vital Statistics System of the USA [36], Han et al. observed increased mortality for AP (measured by excess risk) of 20.6% higher than expected during the March 2020—September 2022 period, with demographic disparities and varied temporal and spatial patterns during the pandemic. In their study, they also confirmed increased mortality due to gastrointestinal hemorrhage and ulcers of 24.8% and 15.1%, respectively, and due to alcoholic liver disease of 19.9%. They concluded that the temporal fluctuation of excess deaths caused by these gastrointestinal conditions might reflect the magnitude of overburdened healthcare services across multiple pandemic waves and the concomitant decrease in endoscopies performed in the early pandemic. Moreover, the changes observed could be related to social isolation, difficulty in accessing regular medical care resources, and other socio-economic issues (such as loss of jobs or insurance), which altogether could affect the outcomes for chronic and acute disorders.
In our analysis, we observed that there were no statistically significant differences in outcomes between AP during 2020 and our historical cohort in the pre-COVID period, neither in the length of stay, the need for ICU, nor in-hospital mortality. Even comparing data between the two more homogeneous subgroups obtained via statistical matching, no significant differences were observed. The heterogeneity of the data in the literature regarding the outcomes of AP during the COVID-19 pandemic probably reflects the heterogeneity of healthcare systems. Also in our context (hub hospital for the treatment of hepato-biliary disorders), some data suggest a reduction of the care for the most fragile patients. In fact, more comorbid patients were hospitalized less frequently, and in agreement with other studies, we observed an increase in alcohol-related AP. However, these epidemiological alterations did not have a negative impact on in-hospital mortality or on other minor outcomes in our reality.
Our study has intrinsic limitations since it is a monocentric retrospective observational study and was not built to record the possibility of mortality after discharge. Moreover, the low number of COVID-19 cases observed in patients hospitalized for AP may affect the statistical analysis; however, this fact supports the rarity of the event. Rigorous population-based studies and active prospective observation are needed to assess the incidence and clinical significance of such observations.
5. Conclusions
Our data do not support the hypothesis that SARS-CoV-2 is a trigger of AP, and they demonstrate that no relevant outcomes were affected during the pandemic. Instead, the lower number of cases during 2020 indicates delayed and likely missed diagnoses, probably due to both the hesitancy of patients and organizational problems due to the pandemic. Even though it is not possible to rule out the role of SARS-CoV-2 in triggering AP, coincidence should not be mistaken for causality given the high burden of possible concomitant causes of AP.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/gastroent14040039/s1, Table S1: Epidemiological and clinical feature of the statistically matched patients for the outcome analysis.
Author Contributions
M.C.: conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; Methodology; writing—original draft. M.F.: conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; writing—original draft. C.E.L.: data curation; investigation; writing—original draft. E.E.: data curation; investigation; writing—original draft. D.M.: data curation; investigation; writing—original draft. E.M.: data curation; investigation; methodology; writing—original draft. C.R.: conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; project administration; software; supervision; validation; writing—review and editing. R.C.: conceptualization; data curation; methodology; supervision; validation; project administration; writing—review and editing. M.M.: conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; project administration; supervision; validation; writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee (Independent Ethics Committee of the Emilia-Romagna Region—Subsection Center) with code PANBO 064/2017/U/Oss.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to ethical restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
ACE2: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; AP: acute pancreatitis; APA: American Pancreatic Association; CKD: chronic kidney disease; ED: emergency department; EUS: endoscopic ultrasound; ERCP: endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; IAP: International Association of Pancreatology; ICD9-CM: International Classification of Disease, 9th Edition—Clinical Modification; ICU: intensive care unit; IPMN: intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; IQR: interquartile range; MRCP: magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography; NSAIDs: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; SARS-CoV-2: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2.
References
- Xiao, A.Y.; Tan, M.L.Y.; Wu, L.M.; Asrani, V.M.; Windsor, J.A.; Yadav, D.; Petrov, M.S. Global incidence and mortality of pancreatic diseases: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of population-based cohort studies. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S.; Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2013, 13 (Suppl. S2), e1–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.E.; Morrison-Rees, S.; John, A.; Williams, J.G.; Brown, T.H.; Samuel, D.G. The incidence and aetiology of acute pancreatitis across Europe. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Enns, R. Review of idiopathic pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 6296–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank, S.; Indaram, A. Causes of acute and recurrent pancreatitis. Clinical considerations and clues to diagnosis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 28, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, P.; Sunkara, T.; Sharma, M. Role of endoscopic ultrasound in idiopathic pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6952–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, D.M.; Steinberg, W.; Kang, P. Infectious Causes of Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 1996, 13, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Qiu, Y.; He, J.S.; Tan, J.Y.; Li, X.H.; Liang, J.; Chen, M.H. Manifestations and prognosis of gastrointestinal and liver involvement in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyerstedt, S.; Casaro, E.B.; Rangel, É.B. COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Q. Pancreatic Injury Patterns in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 19 Pneumonia. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, G.; Fabrizio, C.; Santoro, C.R.; Buccoliero, G.B. Pancreatic injury in the course of coronavirus disease 2019: A not-so-rare occurrence. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 93, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, J.; Gupta, R.; Singh, M.P.; Patnaik, I.; Kumar, A.; Kochhar, R. Coronavirus disease 2019 and the pancreas. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribadi, R.R.; Simadibrata, M. Increased serum amylase and/or lipase in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients: Is it really pancreatic injury? JGH Open 2020, 5, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloysius, M.M.; Thatti, A.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, N.; Bansal, P.; Goyal, H. COVID-19 presenting as acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1026–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinte, L.; Baicus, C. Pancreatic involvement in SARS-CoV-2: Case report and living review. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2020, 29, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sá, T.C.; Soares, C.; Rocha, M. Acute pancreatitis and COVID-19: A literature review. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 13, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepis, T.; Larghi, A.; Papa, A.; Miele, L.; Panzuto, F.; De Biase, L.; Rapaccini, G.L. SARS-CoV2 RNA detection in a pancreatic pseudocyst sample. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1011–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenblock, C.; Richter, S.; Berger, I.; Barovic, M.; Schmid, J.; Schubert, U.; Jarzebska, N.; von Mässenhausen, A.; Linkermann, A.; Schürmann, A.; et al. Viral infiltration of pancreatic islets in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, Ò.; Llorens, P.; Jiménez, S.; Piñera, P.; Burillo-Putze, G.; Martín, A.; Martín-Sánchez, F.J.; del Castillo, J.G. Spanish Investigators in Emergency Situations TeAm (SIESTA) network. Frequency of five unusual presentations in patients with COVID-19: Results of the UMC-19-S1. Epidemiology Infect. 2020, 148, e189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, S.; Benias, P.C.; Liu, Y.; Sejpal, D.V.; Satapathy, S.K.; Trindade, A.J.; The Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Presenting as Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 2226–2228.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badalov, N.; Baradarian, R.; Iswara, K.; Li, J.; Steinberg, W.; Tenner, S. Drug-Induced Acute Pancreatitis: An Evidence-Based Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Hall, O.M.; Kaye, A.M.; Kaye, A.D. Drug-induced acute pancreatitis: A review. Ochsner J. 2015, 15, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Long, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. ACE2 Expression in Pancreas May Cause Pancreatic Damage After SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2128–2130.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoyama, T.; Koda, H.; Hamamoto, W.; Kawahara, S.; Sakamoto, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Kurumi, H.; Kawata, S.; Takeda, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; et al. Review on acute pancreatitis attributed to COVID-19 infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 2034–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, O.Z.; Bhayana, V. Lipase or amylase for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis? Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, R.A.; Braun, D.K.; Patterson, R.E.; Bloomgren, G.L. Increased risk of acute pancreatitis and biliary disease observed in patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-J.; Lai, Y.-C.; Chou, C.-Y.; Yang, H.-W.; Chang, C.-W. Emphysematous Pancreatitis in the Elderly. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 359, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, M.S.; Tucker, J.S.; Green, H.D. Changes in Adult Alcohol Use and Consequences During the COVID-19 Pandemic in the US. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2022942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, I.; Bye, E.K.; Moan, I.S.; Kilian, C.; Bramness, J.G. Changes in Alcohol Consumption during the COVID-19 Pandemic-Small Change in Total Consumption, but Increase in Proportion of Heavy Drinkers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, B.L.; Im, G.Y.; Schiano, T.D. Coronavirus Disease 2019 Hangover: A Rising Tide of Alcohol Use Disorder and Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klibansky, D.A.; Reid–Lombardo, K.M.; Gordon, S.R.; Gardner, T.B. The Clinical Relevance of the Increasing Incidence of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, A.A.; Aziz, M.A.; Omar, N.; Saleem, M.; Pahuja, K.H.; Rasool, M.H.U.; Shah, R. A Meta-analysis of the Severity of Acute Pancreatitis (AP) in COVID-19 Infection. Cureus 2023, 15, e38764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rădulescu, P.M.; Căluianu, E.I.; Traşcă, E.T.; Mercuţ, D.; Georgescu, I.; Georgescu, E.F.; Ciupeanu-Călugăru, E.D.; Mercuţ, M.F.; Mercuţ, R.; Padureanu, V.; et al. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis: A Propensity Score Matched Study Comparing before and during the Pandemic. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, D.; Kang, M.; Li, B.; Su, S. Clinical characteristics and short-term outcomes of acute pancreatitis among patients with COVID-19. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Shi, H.; Li, Y.; Qi, H.; Wang, Y.; Gu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhao, S.; Cao, P.; Xu, L.; et al. Excess Deaths of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases During the COVID-19 Pandemic in the United States. Int. J. Public Health 2023, 68, 1606305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).