Point Shear Wave Elastography and 2-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography as a Non-Invasive Method in Differentiating Benign from Malignant Liver Lesions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
AIM
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Methods
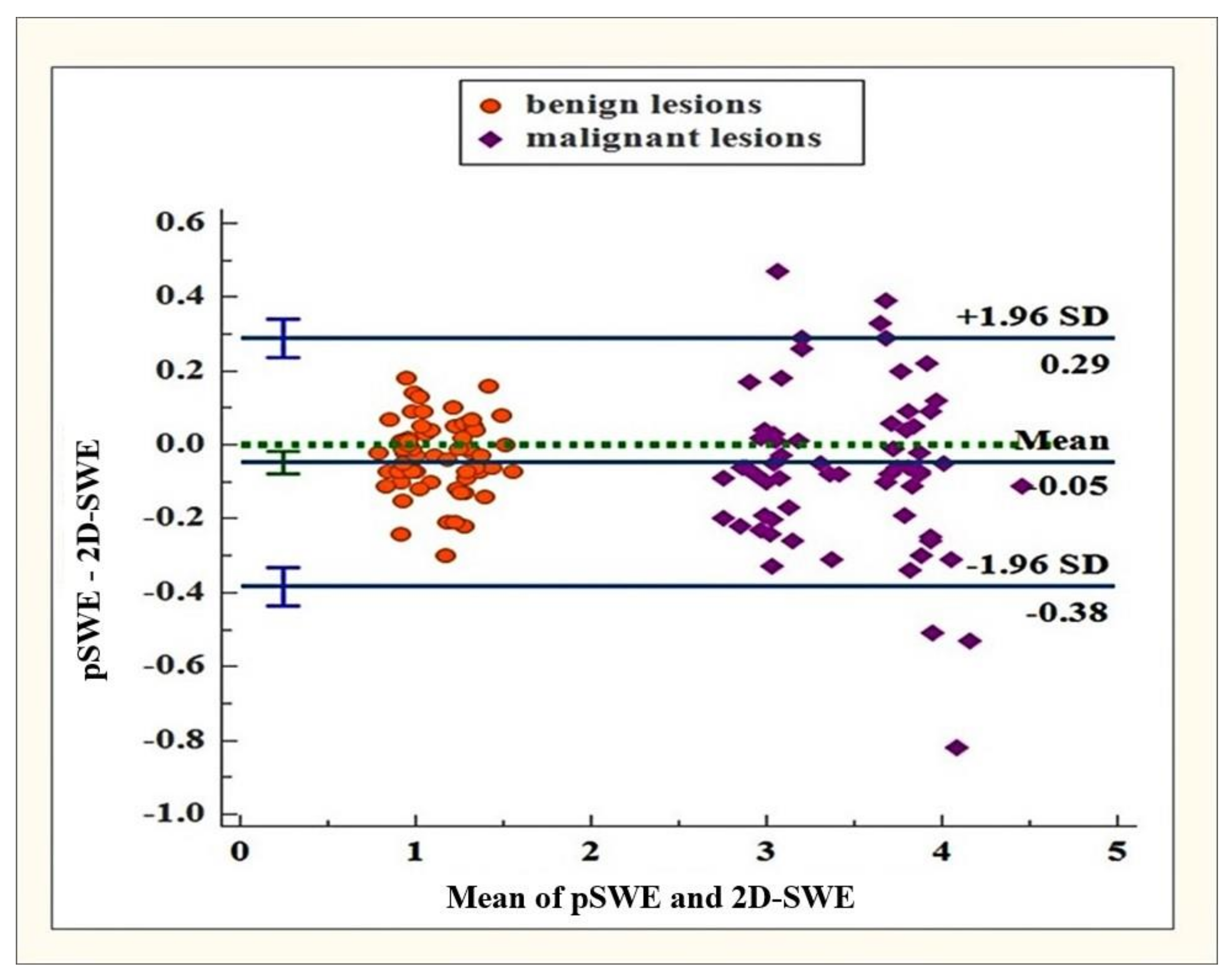
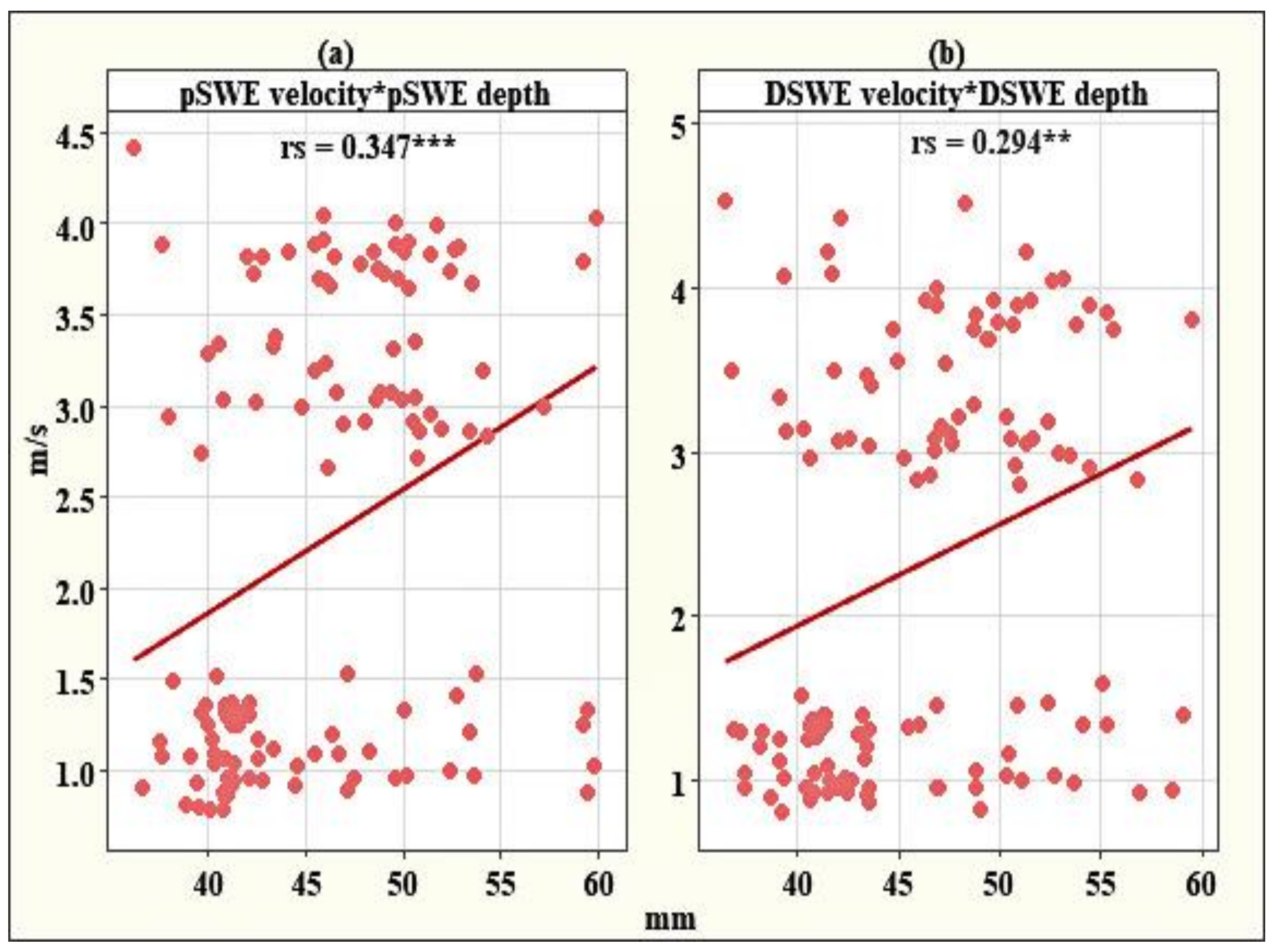
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
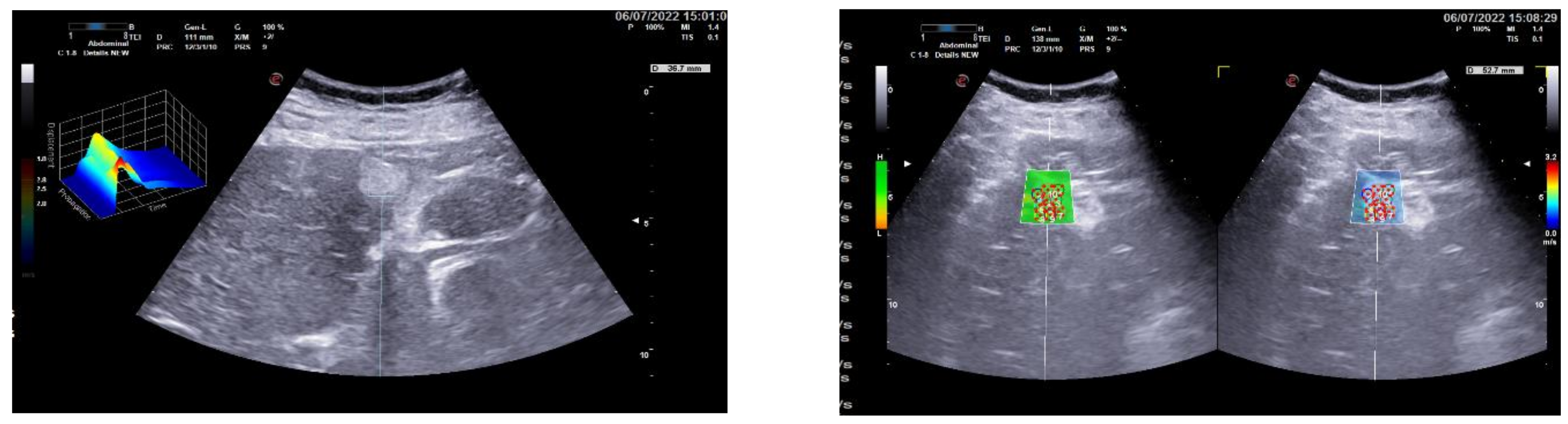
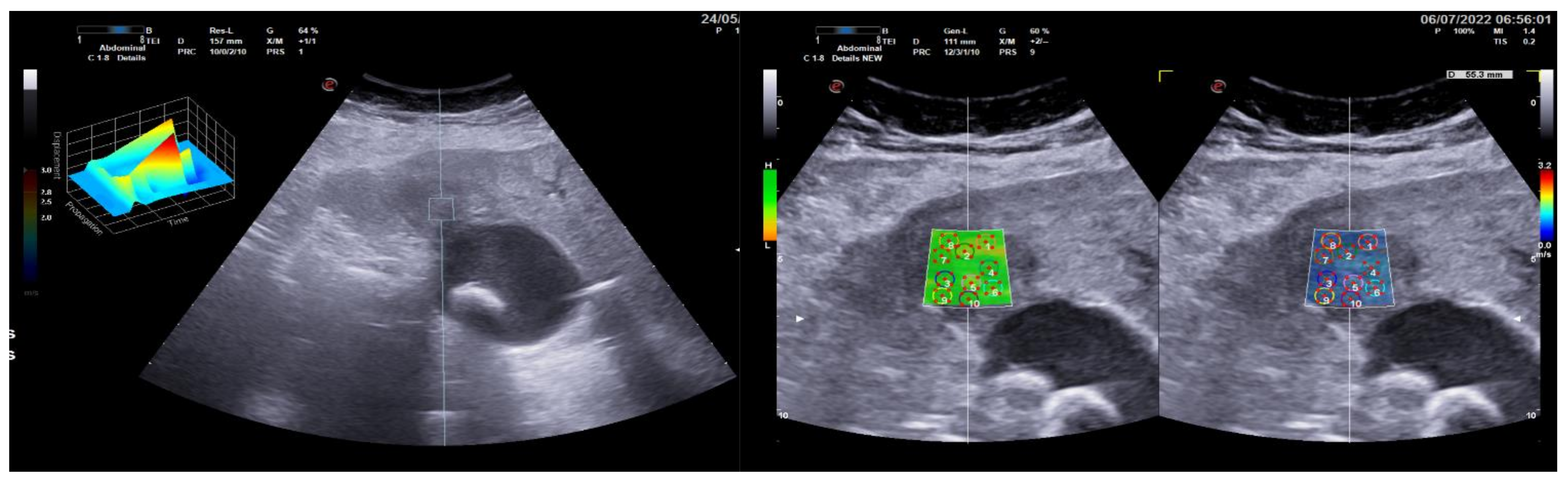
3.1. Group 1: Benign Focal Liver Lesions (Hemangiomas)
3.2. Group 2: Malignant Focal Liver Lesions (Hepatocellular Carcinoma)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merritt, C.R.B.; Foreman, M.; Bluth, E.I.; Sullivan, M.A. Abdominal ultrasound: Clinical application of realtime. Appl. Radiol. 1981, 10, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hadzhidekov, G.; Grudeva, V. Ultrasound elastography in breast. Rentgenol. Radiol. 2010, 1, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilska, A.; Doykov, M.; Kumchev, E. Changes in renal stiffness, measured by ultrasound elastography in chronic kidney disease, Nephrology. Hemo Dial. Transplant. 2022, 1, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Castera, L. Invasive and non-invasive methods for the assessment of fibrosis and disease progression in chronic liver disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Joo, I.; Lee, E.S.; Sohn, J.Y.; Jang, S.K.; Lee, K.B.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Hepatic fibrosis: Prospective comparison of MR elastography and US shear-wave elastography for evaluation. Radiology 2014, 273, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, K.B.; Yoon, J.H.; Shin, C.I.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B viral infection using magnetic resonance elastography. Korean J. Radiol. 2014, 15, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochatzis, E.A.; Gurusamy, K.S.; Ntaoula, S.; Cholongitas, E.; Davidson, B.R.; Burroughs, A.K. Elastography for the diagnosis of severity of fibrosis in chronic liver disease: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbing, J.; Farouk, L.; Panos, G.; Anderson, M.; Jiao, L.R.; Mandalia, S.; Bower, M.; Gazzard, B.; Nelson, M. A meta-analysis of transient elastography for the detection of hepatic fibrosis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxbury, M.S.; Garden, O.J. Giant haemangiona of the liver: Observation or resection? Dig. Surg. 2010, 27, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, J.; Azevedo, A.M. Splenomegaly; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gersak, M.M.; Sorantin, E.; Windhaber, J.; Dudea, S.M.; Riccabona, M. The influence of acute physical effort on liver stiffness estimation using Virtual Touch Quantification (VTQ). Preliminary results. Med. Ultrason. 2016, 18, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiina, T.; Nightingale, K.R.; Palmeri, M.L.; Hall, T.J.; Bamber, J.C.; Barr, R.G.; Castera, L.; Choi, B.I.; Chou, Y.H.; Cosgrove, D.; et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: Part 1: Basis principals and terminology. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 1126–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Filice, C.; Castera, L.; Choi, B.I.; Sporea, I.; Wilson, S.R.; Cosgrove, D.; Dietrich, C.F.; Amy, D.; Bamber, J.C.; et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: Part 3: Liver. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 1161–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Yu, M.H.; Jung, S.I.; Jeon, H.J. Shear Wave Elastography of Focal Liver Lesion: Intraobserver Reproducibility and Elasticity Characterization. Ultrasound Q. 2015, 31, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibal, A.; Boularan, C.; Bruce, M.; Vallin, M.; Pilleul, F.; Walter, T.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Boublay, N.; Dumortier, J.; Lefort, T. Evaluation of shearwave elastography for the characterisation of focal liver lesions on ultrasound. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, T.; Guibal, A.; Boularan, C.; Ducerf, C.; Mabrut, J.Y.; Bancel, B.; Boussel, L.; Rode, A. Focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatocellular adenoma: The value of shear wave elastography for differential diagnosis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 2059–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, B.J.; Nightingale, K.R.; Nelson, R.C.; Palmeri, M.L.; Trahey, G.E. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging of the abdomen: Demonstration of feasibility and utility. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2005, 31, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frulio, N.; Laumonier, H.; Carteret, T.; Laurent, C.; Maire, F.; Balabaud, C.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Trillaud, H. Evaluation of liver tumors using acoustic radiation force impulse elastography and correlation with histologic data. J. Ultrasound Med. Off. J. Am. Inst. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Suh, C.H.; Kim, K.W.; Pyo, J.; Park, C.; Jung, S.C. Technical Performance of Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography for Measuring Liver Stiffness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraquelli, M.; Rigamonti, C.; Casazza, G.; Conte, D.; Donato, M.F.; Ronchi, G.; Colombo, M. Reproducibility of transient elastography in the evaluation of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease. Gut 2007, 56, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffer, O.S.; Lung, P.F.C.; Bosanac, D.; Patel, V.M.; Ryan, S.M.; Heneghan, M.A.; Quaglia, A.; Sidhu, P.S. Acoustic radiation force impulse quantification: Repeatability of measurements in selected liver segments and influence of age, body mass index and liver capsule-to-box distance. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, e858–e863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Konstantatou, E.; Romanos, O.; Yusuf, G.T.; Quinlan, D.J.; Sidhu, P.S. Reproducibility of 2-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography Assessment of the Liver: A Direct Comparison with Point Shear Wave Elastography in Healthy Volunteers. J. Ultrasound Med. 2017, 36, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraioli, G.; Tinelli, C.; Lissandrin, R.; Zicchetti, M.; Dal Bello, B.; Filice, G.; Filice, C. Point shear wave elastography method for assessing liver stiffness. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 4787–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinino, F.; Sagnelli, E.; Pasquale, G.; Giusti, G. Complications following percutaneous liver biopsy. A multicentre retrospective study on 68,276 biopsies. J. Hepatol. 1986, 2, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, D.B.; Rakela, J.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Ott, B.J. A 21-year experience with major hemorrhage after percutaneous liver biopsy. Gastroenterology 1990, 99, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedossa, P.; Dargère, D.; Paradis, V. Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, M.; Palmentieri, B.; Vecchione, R.; Torella, R.; De Sio, I. Diagnosis of chronic liver disease: Reproducibility and validation of liver biopsy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 491–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Total (n = 62) | Men (n = 39) | Women (n = 23) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| Mean (±SD) | 69.30 ± 6.37 | 70.41 ± 5.66 | 67.43 ± 7.16 | 0.075 t |
| Minimum-maximum | 56–81 | 59–80 | 56–81 | 0.075 t |
| WD-HCC | 37 (59.67%) | 25 (67.56%) | 12 (32.43%) | 0.155 χ2 |
| MD-HCC | 17 (27.42%) | 13 (76.40%) | 4 (23.60%) | 0.155 χ2 |
| PD-HCC | 8 (12.90%) | 7 (87.50%) | 1 (12.50%) | 0.155 χ2 |
| BMI | ||||
| Mean (±SD) | 22.36 ± 1.35 | 22.50 ± 1.34 | 22.12 ± 1.36 | 0.286 t |
| Minimum-maximum | 19.90 to 25.10 | 19.90 to 25.10 | 19.90 to 24.80 | 0.286 t |
| Median (IQR) | 3.50 (0.80) | 3.65 (0.77) | 3.35 (0.95) | 0.590 U |
| Minimum-maximum | 2.65 to 4.40 | 2.74 to 4.40 | 2.65 to 4.03 | 0.590 U |
| 2D-SWE (m/s) | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 3.48(0.01) | 3.49 (0.80) | 3.33 (0.92) | 0.278 U |
| Minimum-maximum | 2.80 to 4.51 | 2.83 to 4.51 | 2.80 to 4.21 | 0.278 U |
| pSWE depth (mm) | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 48.68 (5.45) | 48.65 (4.75) | 49.62 (7.87) | 0.565 U |
| Minimum-maximum | 36.26 to 59.88 | 36.26 to 59.88 | 40.06 to 57.27 | 0.565 U |
| 2-D-SWE depth (mm) | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 48.15 (7.62) | 47.60 (7.20) | 49.30 (8.20) | 0.555 U |
| Minimum-maximum | 36.50 to 59.40 | 36.50 to 59.40 | 39.10 to 56.80 | 0.555 U |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nacheva-Georgieva, E.L.; Doykov, D.I.; Andonov, V.N.; Doykova, K.A.; Tsvetkova, S.B. Point Shear Wave Elastography and 2-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography as a Non-Invasive Method in Differentiating Benign from Malignant Liver Lesions. Gastroenterol. Insights 2022, 13, 296-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13030030
Nacheva-Georgieva EL, Doykov DI, Andonov VN, Doykova KA, Tsvetkova SB. Point Shear Wave Elastography and 2-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography as a Non-Invasive Method in Differentiating Benign from Malignant Liver Lesions. Gastroenterology Insights. 2022; 13(3):296-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13030030
Chicago/Turabian StyleNacheva-Georgieva, Emiliya Lyubomirova, Daniel Ilianov Doykov, Vladimir Nikolov Andonov, Katya Angelova Doykova, and Silviya Bogdanova Tsvetkova. 2022. "Point Shear Wave Elastography and 2-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography as a Non-Invasive Method in Differentiating Benign from Malignant Liver Lesions" Gastroenterology Insights 13, no. 3: 296-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13030030
APA StyleNacheva-Georgieva, E. L., Doykov, D. I., Andonov, V. N., Doykova, K. A., & Tsvetkova, S. B. (2022). Point Shear Wave Elastography and 2-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography as a Non-Invasive Method in Differentiating Benign from Malignant Liver Lesions. Gastroenterology Insights, 13(3), 296-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13030030






