Gastrointestinal Ischemia—Stumbling Stone in COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
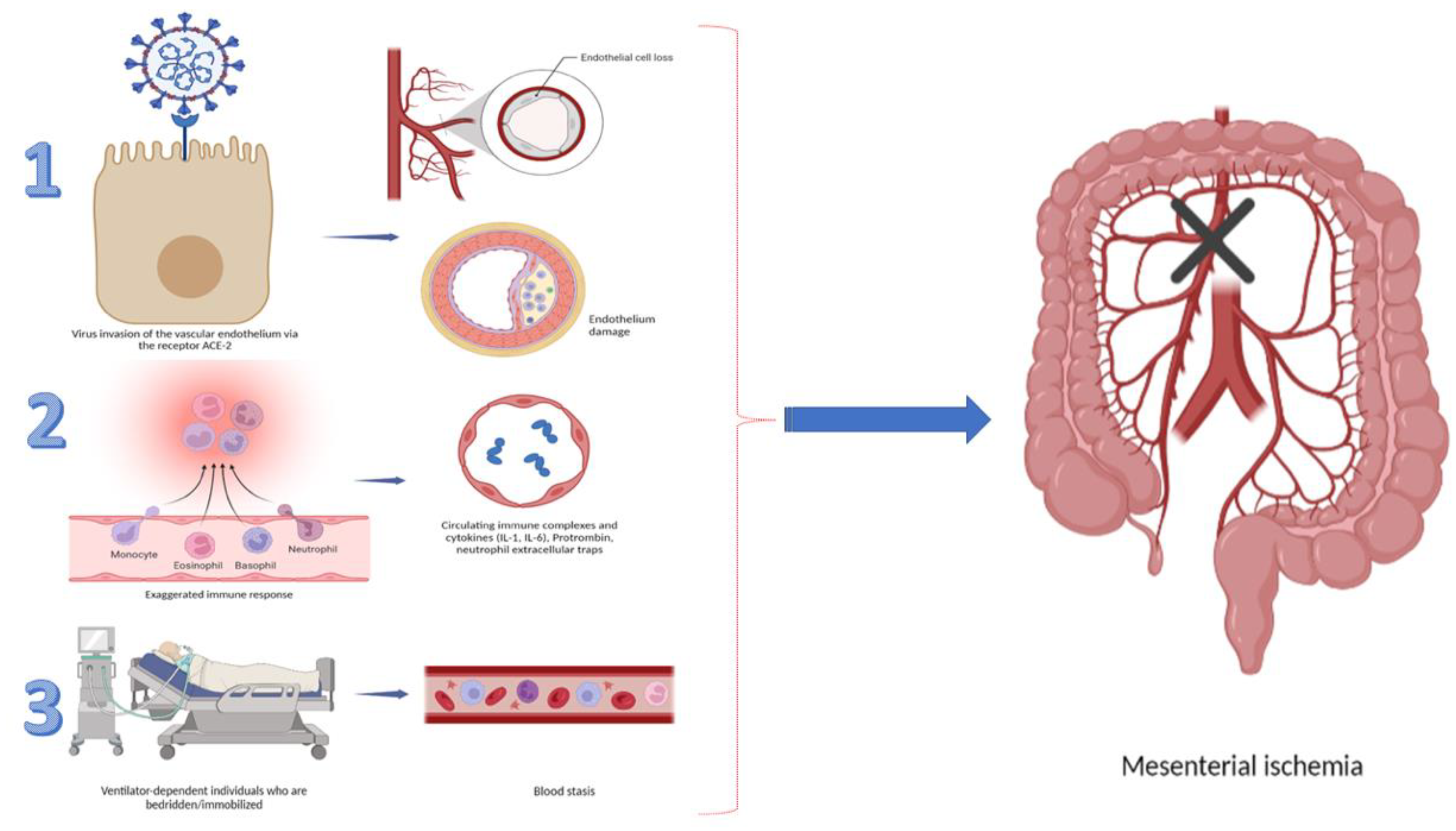
2. Pathogenesis in GI Ischemia
3. Esophageal and Stomach Involvement
4. Colon Ischemia
5. Pancreas
6. Liver
7. Gallbladder
8. Results
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mucino-Bermejo, M.-J. COVID-19 and the Gastrointestinal Tract. Gastroenterol. Insights 2021, 12, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Chen, K.; Zou, J.; Han, P.; Hao, J.; Han, Z. Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keshavarz, P.; Rafiee, F.; Kavandi, H.; Goudarzi, S.; Heidari, F.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. Ischemic gastrointestinal complications of COVID-19: A systematic review on imaging presentation. Clin. Imaging 2021, 73, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadyen, J.D.; Stevens, H.; Peter, K. The Emerging Threat of (Micro)Thrombosis in COVID-19 and Its Therapeutic Implications. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoteit, L.; Deeb, A.-P.; Andraska, E.A.; Kaltenmeier, C.; Yazdani, H.O.; Tohme, S.; Neal, M.D.; Mota, R.I. The Pathobiological Basis for Thrombotic Complications in COVID-19: A Review of the Literature. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2021, 8, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, W. Hypercoagulability in COVID-19: A review of the potential mechanisms underlying clotting disorders. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 20503121211002996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Li, Z.-L.; Zhou, Y.-J.; Tian, G.; Ye, T.; Zeng, Z.-R.; Deng, J.; Wan, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.-B. Gastrointestinal involvement of COVID-19 and potential faecal transmission of SARS-CoV-2. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2020, 21, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.A.F.; De Brito, B.B.; Santos, M.L.C.; Marques, H.S.; Júnior, R.T.D.S.; De Carvalho, L.S.; Vieira, E.S.; Oliveira, M.V.; De Melo, F.F. COVID-19 gastrointestinal manifestations: A systematic review. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2020, 53, e20200714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Moheb, M.; Naar, L.; Christensen, M.A.; Kapoen, C.; Maurer, L.R.; Farhat, M.; Kaafarani, H.M.A. Gastrointestinal Complications in Critically Ill Patients With and Without COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 1899–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascolini, S.; Vannini, A.; Deleonardi, G.; Ciordinik, M.; Sensoli, A.; Carletti, I.; Veronesi, L.; Ricci, C.; Pronesti, A.; Mazzanti, L.; et al. COVID-19 and Immunological Dysregulation: Can Autoantibodies be Useful? Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 14, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Junior, M.A.F.; Augusto, S.D.S.; Elias, Y.G.B.; Costa, C.T.K.; Néder, P.R. Gastrointestinal complications of coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Arq. Bras. Cir. Dig. 2022, 34, e1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Gao, L.; Shi, H.; Mai, L.; et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms of 95 cases with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Gut 2020, 69, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, S.; Lu, J.; Lai, R.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, X.; Zheng, X.; Shan, H. Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Caused by SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1541–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, N.F.; Jafri, N.S.; Holtorf, H.L.; Shah, S.K. Acute oesophageal necrosis in a patient with recent SARS-CoV-2. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e244164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliwala, S.S.; Gurvits, G.E. Acute Esophageal Necrosis in a Patient with COVID-19. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meloy, P.; Bhambri, A. Esophageal Rupture Associated With COVID-19: A Novel Case Report. Cureus 2020, 12, e12256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, F.; Subramanian, S.K.; Larson, S. Case Report of Acute Esophageal Necrosis (Gurvits Syndrome) in Vaccinated, COVID-19-Infected Patient. Cureus 2022, 14, e22241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanella, G.; Capurso, G.; Burti, C.; Fanti, L.; Ricciardiello, L.; Lino, A.S.; Boskoski, I.; Bronswijk, M.; Tyberg, A.; Nair, G.K.K.; et al. Gastrointestinal mucosal damage in patients with COVID-19 undergoing endoscopy: An international multicentre study. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2021, 8, e000578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvits, G.E. Black esophagus: Acute esophageal necrosis syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 3219–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, D. Autopsy Findings and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients With COVID-19. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clair, D.G.; Beach, J.M. Mesenteric Ischemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kärkkäinen, J.M.; Acosta, S. Acute mesenteric ischemia (part I)—Incidence, etiologies, and how to improve early diagnosis. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.-W.; Shi, P.-F.; Qian, S.-X. Acute Mesenteric Ischemia in Patients with COVID-19: Review of the literature. J. Natl. Med Assoc. 2021, 114, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.B.; Mostafavi, K.; Craven, T.E.; Ayerdi, J.; Edwards, M.S.; Hansen, K.J. Clinical course of mesenteric artery stenosis in elderly americans. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 2095–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kärkkäinen, J.M.; Lehtimäki, T.T.; Manninen, H.; Paajanen, H. Acute Mesenteric Ischemia Is a More Common Cause than Expected of Acute Abdomen in the Elderly. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2015, 19, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, F.A.; Kruip, M.J.H.A.; van der Meer, N.J.M.; Arbous, M.S.; Gommers, D.A.M.P.J.; Kant, K.M.; Kaptein, F.H.J.; van Paassen, J.; Stals, M.A.M.; Huisman, M.V.; et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerawala, A.A.; Das, B.; Solangi, A. Mesenteric ischemia in COVID-19 patients: A review of current literature. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, S.; Nilsson, T.K.; Björck, M. D-dimer testing in patients with suspected acute thromboembolic occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery. Br. J. Surg. 2004, 91, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesner, W.; Khurana, B.; Ji, H.; Ros, P.R. CT of acute bowel ischemia. Radiology 2003, 226, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, A.H.; Wani, A.H.; Yaseen, M. Acute Mesenteric Ischemia in Severe Coronavirus-19 (COVID-19): Possible Mechanisms and Diagnostic Pathway. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norsa, L.; Valle, C.; Morotti, D.; Bonaffini, P.A.; Indriolo, A.; Sonzogni, A. Intestinal ischemia in the COVID-19 era. Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 1090–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odun-Ayo, F.; Reddy, L. Gastrointestinal Microbiota Dysbiosis Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Colorectal Cancer: The Implication of Probiotics. Gastroenterol. Insights 2022, 13, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpellini, E.; Scarcella, L.; Romanelli, G.; Basilico, M.; Lattanzi, E.; Rasetti, C.; Abenavoli, L.; Santori, P. Nutritional Status and the Critically Ill Patient: Gut Microbiota and Immuno-Nutrition in I.C.U. at the Time of SARS-COV2 Pandemic. Gastroenterol. Insights 2021, 12, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Q. Pancreatic Injury Patterns in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 19 Pneumonia. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Kang, Z.; Gong, H.; Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Cui, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhan, J.; et al. Digestive system is a potential route of COVID-19: An analysis of single-cell coexpression pattern of key proteins in viral entry process. Gut 2020, 69, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; Sehgal, K.; Nair, N.; Mahajan, S.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Bikdeli, B.; Ahluwalia, N.; Ausiello, J.C.; Wan, E.Y.; et al. Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Long, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. ACE2 Expression in Pancreas May Cause Pancreatic Damage After SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2128–2130.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmon, C.T. Crosstalk between inflammation and thrombosis. Maturitas 2008, 61, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikdeli, B.; Madhavan, M.V.; Jimenez, D.; Chuich, T.; Dreyfus, I.; Driggin, E.; Nigoghossian, C.D.; Ageno, W.; Madjid, M.; Guo, Y.; et al. COVID-19 and Thrombotic or Thromboembolic Disease: Implications for Prevention, Antithrombotic Therapy, and Follow-Up: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2950–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warzecha, Z.; Sendur, P.; Ceranowicz, P.; Dembinski, M.; Cieszkowski, J.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R.; Dembinski, A. Pretreatment with low doses of acenocoumarol inhibits the development of acute ischemia/reperfusion-induced pancreatitis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De-Madaria, E.; Capurso, G. COVID-19 and acute pancreatitis: Examining the causality. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulthuis, M.C.; Boxhoorn, L.; Beudel, M.; Elbers, P.W.G.; Kop, M.P.M.; van Wanrooij, R.L.J.; Besselink, M.G.; Voermans, R.P. Acute pancreatitis in COVID-19 patients: True risk? Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, G.; Fabrizio, C.; Santoro, C.R.; Buccoliero, G.B. Pancreatic injury in the course of coronavirus disease 2019: A not-so-rare occurrence. J. Med Virol. 2020, 93, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, S.; Benias, P.C.; Liu, Y.; Sejpal, D.V.; Satapathy, S.K.; Trindade, A.J.; The Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Presenting as Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 2226–2228.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miró, O.; Llorens, P.; Jiménez, S.; Piñera, P.; Burillo-Putze, G.; Martín, A.; Martín-Sánchez, F.J.; del Castillo, J.G. Frequency of five unusual presentations in patients with COVID-19: Results of the UMC-19-S1. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sá, T.C.; Soares, C.; Rocha, M. Acute pancreatitis and COVID-19: A literature review. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 13, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jothimani, D.; Venugopal, R.; Abedin, M.F.; Kaliamoorthy, I.; Rela, M. COVID-19 and the liver. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fan, Y.; Lai, Y.; Han, T.; Li, Z.; Zhou, P.; Pan, P.; Wang, W.; Hu, D.; Liu, X.; et al. Coronavirus infections and immune responses. J. Med Virol. 2020, 92, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Huang, D.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xia, Z.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, G.; Gou, J.; Qu, J.; et al. COVID-19: Abnormal liver function tests. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Qu, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papic, N.; Pangercic, A.; Vargovic, M.; Barsic, B.; Vince, A.; Kuzman, I. Liver involvement during influenza infection: Perspective on the 2009 influenza pandemic. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2011, 6, e2–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, D.; Du, Q.; Yan, S.; Guo, X.-G.; He, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhao, K.; Ouyang, S. Liver injury in COVID-19: Clinical features and treatment management. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, N.T.N.; Thu, N.T.N.; Barrail-Tran, A.; Duc, N.H.; Lan, N.N.; Laureillard, D.; Lien, T.T.X.; Borand, L.; Quillet, C.; Connolly, C.; et al. Randomised pharmacokinetic trial of rifabutin with lopinavir/ritonavir-antiretroviral therapy in patients with HIV-associated tuberculosis in Vietnam. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagana, S.M.; Kudose, S.; Iuga, A.C.; Lee, M.J.; Fazlollahi, L.; Remotti, H.E.; Del Portillo, A.; De Michele, S.; De Gonzalez, A.K.; Saqi, A.; et al. Hepatic pathology in patients dying of COVID-19: A series of 40 cases including clinical, histologic, and virologic data. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2147–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsoukkary, S.S.; Mostyka, M.; Dillard, A.; Berman, D.R.; Ma, L.X.; Chadburn, A.; Yantiss, R.K.; Jessurun, J.; Seshan, S.V.; Borczuk, A.C.; et al. Autopsy Findings in 32 Patients with COVID-19: A Single-Institution Experience. Pathobiology 2020, 88, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Rizwan, T.; Malik, F.; Akhter, R.; Malik, M.; Ahmad, J.; Khan, A.W.; Chaudhary, M.A.; Usman, M.S. COVID-19 and Liver Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2020, 12, e9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, A.; Garofalo, E.; Zuccalà, V.; Currò, G.; Torti, C.; Navarra, G.; De Sarro, G.; Navalesi, P.; Longhini, F.; Ammendola, M. Histopathological findings in a COVID-19 patient affected by ischemic gangrenous cholecystitis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2020, 15, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhayana, R.; Som, A.; Li, M.D.; Carey, D.E.; Anderson, M.A.; Blake, M.A.; Catalano, O.; Gee, M.S.; Hahn, P.F.; Harisinghani, M.; et al. Abdominal Imaging Findings in COVID-19: Preliminary Observations. Radiology 2020, 297, E207–E215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovece, A.; Asti, E.; Bruni, B.; Bonavina, L. Subtotal laparoscopic cholecystectomy for gangrenous gallbladder during recovery from COVID-19 pneumonia. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 72, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, J.L.; Schenker, S. Acute acalculous cholecystitis: A review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, D.L.; Andrus, C.H.; German, D.; Deshpande, Y.G. The role of prostanoids in the production of acute acalculous cholecystitis by platelet-activating factor. Ann. Surg. 1990, 212, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beccara, L.A.; Pacioni, C.; Ponton, S.A. Arterial Mesenteric Thrombosis as a Complication of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2020, 7, 001690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignat, M.; Philouze, G.; Aussenac-Belle, L.; Faucher, V.; Collange, O.; Mutter, D.; Pessaux, P. Small bowel ischemia and SARS-CoV-2 infection: An underdiagnosed distinct clinical entity. Surgery 2020, 168, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, J.; Tacquard, C.; Severac, F.; Leonard-Lorant, I.; Ohana, M.; Delabranche, X.; Merdji, H.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Schenck, M.; Gandet, F.F.; et al. High risk of thrombosis in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: A multicenter prospective cohort study. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, D.; Rondi, P.; Botturi, E.; Renzulli, M.; Borghesi, A.; Guelfi, D.; Ravanelli, M. Gastrointestinal: Bowel ischemia in a suspected coronavirus disease (COVID-19) patient. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 36, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azouz, E.; Yang, S.; Monnier-Cholley, L.; Arrivé, L. Systemic arterial thrombosis and acute mesenteric ischemia in a patient with COVID-19. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1464–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulliamy, P.; Jacob, S.; Davenport, R.A. Acute aorto-iliac and mesenteric arterial thromboses as presenting features of COVID-19. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 1053–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraissé, M.; Logre, E.; Pajot, O.; Mentec, H.; Plantefève, G.; Contou, D. Thrombotic and hemorrhagic events in critically ill COVID-19 patients: A French monocenter retrospective study. Crit Care 2020, 24, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.; Ranieri, A.J.; Paterniti, G.; Pata, F.; Gallo, G. Acute intestinal ischemia in a patient with COVID-19. Tech. Coloproctol. 2020, 24, 1217–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Carmo Filho, A.; da Silva Cunha, B. Case Report—Inferior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis and COVID-19. Preprints 2020, 2020060282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.M.; Rakheja, D.; Gopal, P. SARS-CoV-2-related Hypercoagulable State Leading to Ischemic Enteritis Secondary to Superior Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 19, e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- English, W.; Banerjee, S. Coagulopathy and mesenteric ischaemia in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. ANZ J. Surg. 2020, 90, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.; Quiwa, J.C.; Pillai, A.; Onwu, C.; Tharayil, Z.J.; Gupta, R. Superior Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis and Acute Intestinal Ischemia as a Consequence of COVID-19 Infection. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e925753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Barry, O.; Mekki, A.; Diffre, C.; Seror, M.; El Hajjam, M.; Carlier, R.-Y. Arterial and venous abdominal thrombosis in a 79-year-old woman with COVID-19 pneumonia. Radiol. Case Rep. 2020, 15, 1054–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, M.; Pellino, G.; Jofra, M.; Sorribas, M.; Solís-Peña, A.; Biondo, S.; Espín-Basany, E. Incidence, features, outcome and impact on health system of de-novo abdominal surgical diseases in patients admitted with COVID-19. Surgeon 2021, 19, e53–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besutti, G.; Bonacini, R.; Iotti, V.; Marini, G.; Riva, N.; Dolci, G.; Maiorana, M.; Spaggiari, L.; Monelli, F.; Ligabue, G.; et al. Abdominal Visceral Infarction in 3 Patients with COVID-19. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1926–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehhat, S.; Talebzadeh, H.; Hakamifard, A.; Melali, H.; Shabib, S.; Rahmati, A.; Larki-Harchegani, A. Acute Mesenteric Ischemia in a Patient with COVID-19: A Case Report. Arch. Iran. Med. 2020, 23, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Roquetaillade, C.; Chousterman, B.; Tomasoni, D.; Zeitouni, M.; Houdart, E.; Guedon, A.; Reiner, P.; Bordier, R.; Gayat, E.; Montalescot, G.; et al. Unusual arterial thrombotic events in COVID-19 patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 323, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Mechineni, A.; Kaur, P.; Ajdir, N.; Maroules, M.; Shamoon, F.; Bikkina, F.S.A.M. Acute Intestinal Ischemia in a Patient with COVID-19 Infection. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 76, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lari, E.; Lari, A.; AlQinai, S.; Abdulrasoul, M.; AlSafran, S.; Ameer, A.; Al-Sabah, S. Severe ischemic complications in COVID-19—A case series. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 75, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuluva, S.K.; Zhu, H.; Tan, M.M.L.; Gupta, S.; Yeong, K.Y.; Wah, S.T.C.; Lin, L.; Yap, E.S. A 29-Year-Old Male Construction Worker from India Who Presented with Left- Sided Abdominal Pain Due to Isolated Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e926785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levolger, S.; Bokkers, R.P.; Wille, J.; Kropman, R.H.; de Vries, J.-P.P. Arterial thrombotic complications in COVID-19 patients. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2020, 6, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Nakamura, R.M.; Gonzalez-Calatayud, M.; Martinez, A.R.M. Acute mesenteric thrombosis in two patients with COVID-19. Two cases report and literature review. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 76, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khesrani, L.S.; Chana, K.; Sadar, F.Z.; Dahdouh, A.; Ladjadj, Y.; Bouguermouh, D. Intestinal ischemia secondary to COVID-19. J. Pediatr. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 61, 101604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucpinar, B.A.; Sahin, C. Superior Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis in a Patient with COVID-19: A Unique Presentation. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2020, 30, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karna, S.T.; Panda, R.; Maurya, A.P.; Kumari, S. Superior Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis in COVID-19 Pneumonia: An Underestimated Diagnosis-First Case Report in Asia. Indian J. Surg. 2020, 82, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, F.B.; Arrabal, E.G.; Delgado, A.B.; Rodríguez, A.J.R. SARS-CoV-2 infection presenting as acute acalculous cholecystitis. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2022, 35, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | Number of Included Patients | Age | Sex | Concomitant Diseases | Type of Ischemia | Symptoms | Intervention | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beccara et al. [62] | 1 | 52 | M | None | Bowel | Fever, diarrhea, vomiting and abdominal pain | Surgery | A |
| Ignat et al. [63] | 3 | 50.3 (mean age) | 2 M; 1 F | 2 DM; 1 HTN; 1 cardiac transplant | Bowel | Vomiting and abdominal pain | Surgery | 2A; 1D |
| Helms et al. [64] | 1 | NA | NA | NA | Bowel | NA | NA | NA |
| Farina et al. [65] | 1 | 70 | M | None | Bowel | Fever, abdominal pain and nausea | Conservative | D |
| Azouz et al. [66] | 1 | 56 | M | None | Bowel | Vomiting and abdominal pain | Surgery | A |
| Vulliamy et al. [67] | 1 | 75 | M | None | Bowel | Vomiting and abdominal pain | Surgery | NA |
| Fraisse et al. [68] | 3 | NA | NA | NA | Bowel | NA | NA | NA |
| Bianco et al. [69] | 1 | 59 | M | None | Bowel | Nausea and abdominal pain | Surgery | D |
| Do Carmo et al. [70] | 1 | 33 | M | Obesity | Bowel | NA | Thrombolytic | A |
| Mitchell et al. [71] | 1 | 69 | M | HTN | Bowel | Epigastric pain, constipation, eructation | Surgery | NA |
| English et al. [72] | 1 | 40 | M | Obesity | Bowel | Abdominal distension | Multiple surgeries | A |
| Cheung et al. [73] | 1 | 55 | M | None | Bowel | Diarrhea, vomiting and abdominal pain | Surgery | A |
| de Barry et al. [74] | 1 | 79 | F | None | Bowel | Diarrhea and abdominal pain | Surgery, embolectomy | D |
| Kraft et al. [75] | 4 | 62.5 (mean age) | 3 F; 1 M | 2 Obesity; 1 COPD | Bowel | NA | Surgery | 2A; 2D |
| Besutti et al. [76] | 1 | 72 | M | CKD, IHD, HTN | Bowel | Fever, dysuria and abdominal pain | Resection, splenectomy | NA |
| Sehhat et al. [77] | 1 | 77 | M | HTN | Bowel | NA | Surgery | D |
| De Roquetaillade et al. [78] | 1 | 65 | M | HTN | Bowel | NA | Surgery | D |
| Singh et al. [79] | 1 | 82 | F | HTN; DM | Bowel | Abdominal distension and tenderness | Surgery | A |
| Lari et al. [80] | 1 | 38 | M | None | Bowel | Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain | Surgery, ECMO | NA |
| Thuluva et al. [81] | 1 | 29 | M | None | Bowel | Abdominal pain | Enoxaparin | A |
| Levolger et al. [82] | 5 | 62 | M | 2 COPD; 1 DM; 1 HTN | Bowel | Abdominal pain | Surgery | 4A; 1D |
| Rodriguez- Nakamura et al. [83] | 2 | 43.5 (mean age) | 1 F; 1 M | 1 Obesity; 1 vitiligo | Bowel | Nausea, mesogastric pain, and diaphoresis | Surgery | 1A; 1D |
| Bhayana et al. [57] | 2 | 49 (mean age) | M | NA | Bowel | Diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain | Surgery | NA |
| Norsa et al. [31] | 1 | 62 | M | Obesity, Cirrhosis, HBV, DM, HTN | Bowel | Abdominal pain and bilious vomiting | Surgery | D |
| Khesrani et al. [84] | 1 | 9 | F | Idiopathic medullar aplasia | Bowel | Vomiting and abdominal pain | Surgery | D |
| Ucpinar et al. [85] | 1 | 82 | F | AF, HTN, CKD | Bowel | Vomiting and abdominal pain | Enoxaparin | D |
| Karna et al. [86] | 1 | 61 | F | HTN; DM | Bowel | Diffuse abdominal pain with distention | Surgery | D |
| Lovece et al. [59] | 1 | 42 | M | NA | Gallbladder | Fever, nausea, and abdominal pain | Surgery | A |
| Berdugo et al. [87] | 2 | 74.5 (mean age) | 1 F; 1 M | NA | Gallbladder | Fever, nausea, and upper abdominal pain | 1 Surgery; 1 conservative | 1D; 1A |
| Bruni et al. [57] | 1 | 59 | M | NA | Gallbladder | Abdominal pain | Surgery | NA |
| Mustafa et al. [14] | 1 | 57 | M | NA | Esophagus | Melena | Endoscopy; conservative | A |
| Deliwala et al. [15] | 1 | 58 | M | Anemia; CKD | Esophagus | Nausea, abdominal pain, and melena | Endoscopy; conservative | A |
| Meloy et al. [16] | 1 | 92 | F | HF; Dementia; Osteoarthritis | Esophagus | Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting | NA | D |
| Rahim et al. [17] | 1 | 72 | M | HTN; DM | Esophagus | Melena | Conservative | D |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peshevska-Sekulovska, M.; Boeva, I.; Sekulovski, M.; Zashev, M.; Peruhova, M. Gastrointestinal Ischemia—Stumbling Stone in COVID-19 Patients. Gastroenterol. Insights 2022, 13, 206-217. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020021
Peshevska-Sekulovska M, Boeva I, Sekulovski M, Zashev M, Peruhova M. Gastrointestinal Ischemia—Stumbling Stone in COVID-19 Patients. Gastroenterology Insights. 2022; 13(2):206-217. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020021
Chicago/Turabian StylePeshevska-Sekulovska, Monika, Irina Boeva, Metodija Sekulovski, Miroslav Zashev, and Milena Peruhova. 2022. "Gastrointestinal Ischemia—Stumbling Stone in COVID-19 Patients" Gastroenterology Insights 13, no. 2: 206-217. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020021
APA StylePeshevska-Sekulovska, M., Boeva, I., Sekulovski, M., Zashev, M., & Peruhova, M. (2022). Gastrointestinal Ischemia—Stumbling Stone in COVID-19 Patients. Gastroenterology Insights, 13(2), 206-217. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020021






