Abstract
Introduction. Ultrasound-guided (US-guided) percutaneous drainage (PD) of abdominal collections represents the first-choice alternative to surgical intervention. The aim of our study was to assess the efficacy and safety of PD of visceral and non-visceral abdominal collections by reviewing our personal experience over a period of 5 years. Material and methods. The present study included 66 patients who underwent PD under ultrasound guidance. We analyzed clinical variables (collection size, catheter diameter, collection type, microbiological analysis, antibiotic regimens) along with the outcomes of the procedure. Results. Visceral collections were predominant, encompassing 38 hepatic abscesses and 1 splenic hematoma. Microbiological analysis showed that the majority (54%) were monomicrobial. The most encountered pathogens were Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli. Technical success was achieved in all cases and clinical success was observed in 84.6% of the cases. No immediate procedural complications were detected. There were 6 patients who needed reinterventions, either by catheter replacement or by surgical treatment. The mortality rate was 4.5%, due to patients’ poor overall status and oncological comorbidities. Conclusions. Percutaneous drainage under ultrasound guidance is a safe and effective procedure in the management of abdominal collections.
1. Introduction
Abdominal collections represent a complex pathology bearing significant morbidity and mortality rates. Left untreated, abdominal collections associate a mortality rate varying between 45% to 100%. However, in the last two decades, due to advancement of minimally invasive techniques such as percutaneous drainage, this rate decreased substantially to less than 15% [1,2].
Regarding their etiology, abdominal collections result from inflammatory conditions (cholecystitis, appendicitis, diverticulitis, pancreatitis etc.), surgical interventions or traumatic lesions. The wide spectrum of abdominal collections could be classified according to their origin and location. Collections may be visceral (hepatic, splenic, pancreatic, renal) or non-visceral (subphrenic, subhepatic, paracolic, mesenteric), intraperitoneal or retroperitoneal [3,4].
Depending on their content, collections may be fluid (such as seroma, lymphocele, hematoma, bilioma) or may become infected, leading to abscess formation. The distinction between infected and noninfected collection is crucial in order to guide the treatment. The gold-standard method is the microbiological analysis of the content obtained by aspiration. Nevertheless, imagistic, laboratory and clinical information might also be helpful and most of the times sufficient to decide the appropriate treatment strategy [5]. For example, uninfected fluid collections have well-defined walls and few internal echoes. Whereas, abscesses have irregular margins, with highly echogenic interior and gas within the collection [2]. In the case of a highly suggestive appearance of an abscess, besides antibiotics, a more aggressive approach is recommended. Apart from infection, there are other indications for drainage such as large or increasing diameter of the collection and symptoms attributable to it. Drainage of abdominal collections may be performed by three methods: surgically, endoscopically or percutaneously.
2. Aim and Objectives
The main purpose of this study was to assess the indications, efficacy and safety of percutaneous drainage performed under ultrasound guidance for the treatment of abdominal collections. Secondary, we aimed to review our personal experience with percutaneous drainages by analyzing demographic data and various parameters regarding collections such as size, location, etiology, bacterial cultures, antimicrobial therapy. Patients were followed to assess the outcome of the percutaneous treatment and development of any complications. Ultrasound was performed every third day during hospitalization. After discharge of the patient, periodic clinical and sonographic examinations were carried out until total resolution of the collection was achieved.
3. Materials and Methods
Study design. This is a single-center retrospective study conducted from the start of January 2016 until the end of January 2021 and was approved by the hospital’s ethics committee. Inclusion criteria for study enrolment were patients older than 18 years, with single abdominal collections, visceral and non-visceral, regardless of their etiology (previous surgery, inflammatory conditions etc.). Further inclusion criteria were collections diagnosed by a least one imagistic method (ultrasound, CT and/or magnetic resonance imaging), and managed by ultrasound-guided percutaneous drainage as first-choice treatment. We excluded patients with multiple abdominal collections, who refused the procedure or underwent percutaneous drainage under CT-guidance. Thus, we included a total of 66 patients totalizing a number of 68 procedures.
Procedure description. All patients signed an informed written consent before the procedure. We previously checked the coagulation parameters and corrected where was necessary. Patients with antiplatelets or oral anticoagulants were discontinued 5–7 days a priori to procedure. All patients received antibiotics before and after procedure. All procedures were performed by the same gastroenterologist under local anesthesia with 2% Lidocaine and under aseptic conditions. In some cases, we used intravenous consciously sedation and analgesia. We used a double-step procedure called the Seldinger technique. First, we identified the collection by using the Siemens Acuson S3000™ Ultrasound System in B-mode combined with Doppler and in selected cases we performed contrast enhanced-ultrasound for differential diagnosis (Figure 1).
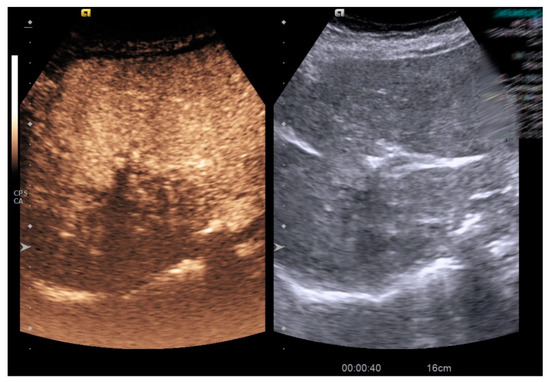
Figure 1.
Contrast enhanced-ultrasound in a patient with hepatic abscess.
Afterwards, we established its features regarding: content (hypoechoic, hyperechoic, mixt), rim, boundaries (nearby organs, structures etc.), distance from skin, interposing vessels. Afterwards, we punctured the collection using an 18-Gauge Chiba needle under real-time sonographic guidance. We aspired a small quantity of fluid to confirm position and we sent it for microbiological analysis. The next step was the insertion of a 0.035-inch guidewire, while the needle (trocar) was slowly withdrawn. We dilated the incision site by using dilators with progressive diameters. Finally, we inserted a pigtail catheter which was sutured to skin and connected to a bag. Some of the ultrasound images can be seen below, in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
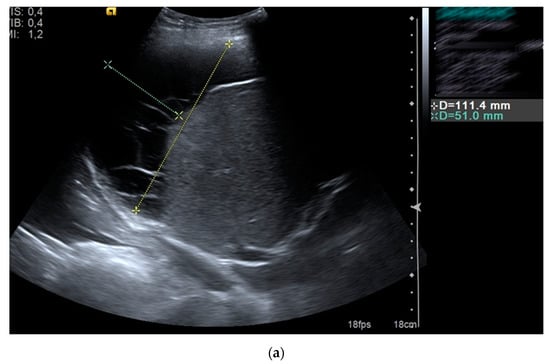
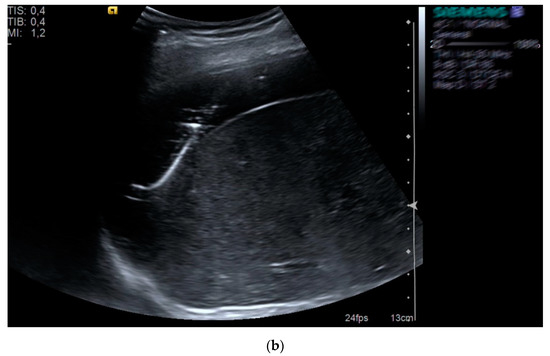
Figure 2.
Subhepatic fluid collection (a) drained with pigtail catheter (b) under ultrasound guidance in a patient who underwent abdominal surgery.
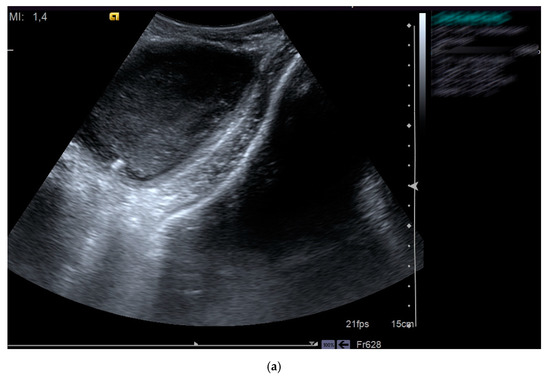
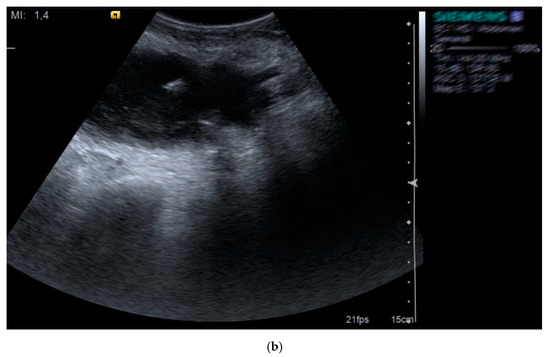
Figure 3.
Pelvic abscess (a) drained with pigtail catheter (b) under ultrasound guidance in a patient with HIV infection.
Outcomes. We defined technical success as successful placement of drainage catheter and clinical success according to the following criteria: clinical and paraclinical status improvement (e.g., subsidence of fever, local and systemic signs and symptoms, decrease in leukocyte counts, resolution of the collection at follow-up imaging or reduction in size to less than 3 cm), no evidence of relapse or recurrence after drain removal, no need for further surgical intervention.
Statistical analysis. For statistical analysis we used IBM SPSS v.20 software package and considered statistically significant a p value below 0.05. Descriptive statistical results were expressed as means ± standard deviations and ranges or as medians and ranges for continuous variables. In addition, categorical variables were expressed as frequencies/absolute numbers with percentages. To test statistical hypothesis, we performed several tests according to our databases: Chi-Square test and ANOVA unifactorial test.
4. Results
A total of 66 patients who underwent ultrasound-guided percutaneous drainage were identified in the databases of Clinical Emergency Hospital of Bucharest, between January 2016 and January 2021.
There were 37 (56.1%) men and 29 (43.9%) females with a mean ± SD age of 64.03 ± 13.87 years. Collections had an average size of 88.26 mm and were drained using pigtail catheters with mean± SD diameter of 11.89 ± 1.906 Fr. More than half of the collections were drained using 12 Fr catheter, while the 20 Fr catheter was used in 2 patients for large collections, over 150 mm. Fluid culture was negative in 8 collections (12.1%) from the total of 66 patients. Most patients (54.5%) had monomicrobial cultures and 33.3% of the patients had cultures with ≥ 2 bacteria growth.
Table 1 summarizes the demographic and clinical variables of the patients included in the study.

Table 1.
Demographic and Clinical Variables of Patients with Abdominal Collections.
The great majority of the patients had visceral collections (38 hepatic abscesses and one splenic hematoma), while the rest had non-visceral collections (27 patients), related to inflammatory conditions such as diverticulitis and pancreatitis or occurred after surgical interventions (perisplenic seroma, subphrenic abscess, bilioma). According to their cultures results, approximately half of the hepatic abscesses were polymicrobial, while postsurgery bilioma and seroma were aseptic. This correlation between the type of the collection and its microbiological analysis (Table 2) proved to have statistical significance (p = 0.001 < 0.05, Chi-Square test).

Table 2.
Classification of abdominal collections and their microbiological classification.
In addition, we studied the types of pathogens encountered inside collections by bacteriological analysis. Thus, Klebsiella pneumoniae was the leading organism present in 26 patients (in 15 cultures as unique pathogen, in 11 cultures associated with one or more pathogens). Secondly most frequently seen was Escherichia coli which was found in 23 patients (in 12 cultures as unique pathogen, in 11 cultures associated with one or more pathogens). Other microorganisms encountered were included anaerobic species (13 patients), Staphylococcus aureus (5 patients), Proteus spp. (5 patients), Enterococcus spp. (5 patients), Citrobacter spp. (4 patients), Enterobacter spp. (2 patients), Pseudomonas spp. (2 patients), Acinetobacter spp. (1 patient) and Candida spp. (1 patient).
We observed that germs were highly antibiotic-resistant, probably because many of them were opportunistic responsible for hospital-acquired infection. The most used antibiotic regimens included 3rd generation cephalosporines and metronidazole, administered in 20 patients and 21, respectively. Secondly, we used carbapenems, namely Imipenem/Cilastatin in 12 patients and Meropenem in 6 patients. Other regimens included large broad-spectrum antibiotics such as Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Tigecycline, Colistin and Vancomycin, but also an antifungal drug named Fluconazole.
When referring to outcomes, the technical success was achieved in all cases of ultrasound-guided drainage, while the overall clinical success was 86.4% (57 patients). There were 6 patients (9.1%) who required reintervention and 3 patients (4.5%) who died before catheter removal due to their poor overall status and oncological comorbidities. There were no major complications recorded periprocedural. Related to reintervention, there were 2 patients to whom the catheter had to be replaced to another one with larger diameter because of insufficient drainage of thick and viscous content. The rest 4 patients with reintervention required surgical treatment for enlargement of hepatic abscess, 2 of them due to unresolved peripancreatic necrosis and one for bilioma caused by biliary fistula following surgery. Furthermore, collection type did not influence the outcome as the statistical analysis showed no significant difference. The data regarding mortality and reintervention can be observed in Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 3.
Reintervention and mortality according to the collection type.

Table 4.
Possible predictor parameters for outcome.
Furthermore, we divided the patients into 3 groups in accordance with the evolution of their collection (resolution/reintervention/mortality). In order to see if there are any differences between the 3 groups, we used the ANOVA Unifactorial test to compare means for age, collection size and catheter diameter. Surprisingly, neither of these parameters influenced the outcome (p > 0.05, ANOVA Unifactorial test) (Table 4). We observed that mean age was higher for patients who died, but not statistically significant. The largest collections required reintervention, while catheter diameter was similar among all 3 groups. In addition, on overall group analysis, we found no statistical association between microbiological results and the outcomes of the procedure (p = 0.231 > 0.05, Chi-Square test). However, we observed that all aseptic collections resolved per primam by percutaneous approach, while polymicrobial collections required reintervention more frequently than monomicrobial ones and also bared a higher mortality rate. Therefore, infections which are polymicrobial expose the patient to a higher chance of reintervention and mortality.
5. Discussion
Imagistic techniques are important not only to localize the collection, characterize and establish its relation to nearby structures, but also to guide the percutaneous drainage procedure in selected cases. Both ultrasonography (US) and computed tomography (CT) may be used for guidance, but the former has a series of advantages. Ultrasound provides real-time imaging during the procedure, has no ionizing radiation, is widely available, less expansive and can be performed at the bedside. US-guidance is the preferred method for drainage of superficially and unilocular collections. CT is reserved mostly for the drainage of multiple collections or whenever US guidance is not considered safe enough [2].
Percutaneous catheter drainage of abdominal collections is considered an effective and safe procedure with more than 80% success rates among various studies [1,2,6]. Similarly, we obtained an 86.4% success rate in our study conducted over a period of 5 years.
Cinat et al. [6] studied multiple predictors of outcome with percutaneous catheter drainage (age, sex, APACHE II score, postoperative abscess, the presence of yeast on a gram stain or culture, the number of organisms identified, pancreatic origin). The results showed that postoperative abscess was the only independent predictor of successful outcome, while negative predictors of successful outcome included the presence of yeast and pancreatic origin [6]. In our study, variables such as age, collection size, type or catheter dimensions could not predict the further treatment and outcome occurred. In a comprehensive study among patients with hepatic abscesses, Lardière-Deguelte and his colleagues [7] observed that early criteria for effective treatment are apyrexia, disappearance of pain, normalization of leukocytosis and C-Reactive protein. These clinical and paraclinical criteria along with imagistic characterization of residual contents are also necessary for drain removal which commonly happens after 7–15 days [7,8].
Several researchers have compared outcomes in terms of success and complication rates between different drainage methods [1,9,10]. It has been recently observed a positive trend towards endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage because of higher clinical success, lower complication rates, less mortality related to the procedure and shorter hospital stay [9,10,11,12]. However, percutaneous drainage is still the preferred intervention when compared to surgical treatment. In a large prospective study over 13-year period, Politano et al. [13] revealed that open surgery drainage is associated with increased mortality compared to percutaneous drainage (14.6% versus 4.2%) even after adjusting for severity of illness and other variables independently associated with death such as intensive care unit, immunosuppression, dialysis.
Mortality after percutaneous drainage ranges between 1.4% and 15% and is seldomly determined by the procedure, mostly being caused by the critical status or serious comorbidities of the patient [14]. Complications are estimated at 10% and may be related to the procedure, to the catheter or to the drained collection [6,8]. Complications related to the procedure may occur due to inappropriate puncture of interposing bowel loops, solid organs or vessels [8]. Usually, complications related to the drain such as obstruction or misposition can be managed by repositioning or replacing the catheter. Other rare complications include cellulitis surrounding the drain entry, fistula formation, bleeding [6]. In addition, multiloculated and complex collections may need prolonged drainage predisposing to infections, fistulas or may require multiple exchange procedures [15].
Percutaneous drainage is curative in 80–100% of cases depending on availability, operator expertise, body habitus, presence of adjacent structures, size and location of the collection, and presence of intracavitary or enteric gas [6,8,14,16,17,18]. Antibiotic treatment should be started promptly to limit the systemic complications. Antibiotic selection is initially empirical, directed at the microorganisms typically suspected and afterwards is adjusted based on culture and sensitivities. The duration of antibiotic therapy is not clearly established but is generally between 2 and 6 weeks [7]. In a series of 107 patients, Hope et al. [17] reported a 100% clinical success rate with antibiotics alone for unilocular hepatic abscesses smaller than 3 cm, while another literature review of 465 abscesses revealed a success rate of medical treatment alone of 80% for collections smaller than 5 cm [18]. Regarding interventional approach, there were studies which compared repeated needle aspiration with catheter aspiration and concluded that the two techniques were similar in terms of success, morbidity, mortality and hospital stay [19,20]. Collections smaller than 3 cm [21,22], or smaller than 5 cm by some authors [16,23] may be solved by aspiration and lavage only, while larger, multiloculated collections with symptoms need continuous percutaneous catheter drainage [23]. However, in some cases, the collections cannot be solved by percutaneous drainage only. In our study, we observed that bilioma due to post-surgery fistula, hepatic abscesses or pancreatic necrosis with thick content need reintervention either surgically or percutaneously.
Overall, percutaneous drainage is a safe procedure with only few contraindications, mostly relative, not absolute (for example: severe coagulopathies, anticoagulation or a bleeding diathesis, hemodynamic and cardiopulmonary instability, unavailable safe percutaneous access) [24].
6. Conclusions
Improvements in imaging modalities associated with broad-spectrum antibiotics and drainage catheters, have changed the treatment of abdominal collections that previously required an urgent, invasive intervention. Collections that traditionally were treated with open surgical drainage and debridement, can now, almost always, be resolved with percutaneous drainage guided by ultrasonography and with antibiotic treatment. In selected cases, especially in critically ill patients, percutaneous drainage may represent a “bridge” to more invasive approaches that will allow for preparation of the patient for a later elective and definitive operation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S.-I. and G.C.; methodology, A.S.-U.; software, A.S.-U.; validation, E.R., V.S. and A.B.; formal analysis, O.-M.P.; investigation, G.G.; data curation, A.M.O.; writing—original draft preparation, O.-M.P.; writing—review and editing, C.C.D.; visualization, B.P.; supervision, G.C. and M.S.-I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee from Clinical Emergency Hospital of Bucharest.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Téllez-Ávila, F.; Carmona-Aguilera, G.J.; Valdovinos-Andraca, F.; Sanchez, L.E.C.; González-Aguirre, A.; Casanovasanchez, I.E.; Elizondo-Rivera, J.; Ramírez-Luna, M. Postoperative abdominal collections drainage: Percutaneous versus guided by endoscopic ultrasound. Dig. Endosc. 2015, 27, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, S.; Akhan, O.; Köroğlu, M. Percutaneous drainage of abdominal abcess. Eur. J. Radiol. 2002, 43, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menichetti, F.; Sganga, G. Definition and classification of intra-abdominal infections. J. Chemother. 2009, 21 (Suppl. 1), 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, A.I.; Mueller, P.; Thabet, A.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.; Fagenholz, P. A Step-Up Approach to Infected Abdominal Fluid Collections: Not Just for Pancreatitis. Surg. Infect. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnannt, R.; Fischer, M.A.; Baechler, T.; Clavien, P.-A.; Karlo, C.; Seifert, B.; Lesurtel, M.; Alkadhi, H. Distinguishing infected from noninfected abdominal fluid collections after surgery: An imaging, clinical, and laboratory-based scoring system. Investig. Radiol. 2015, 50, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinat, M.E.; Wilson, S.E.; Din, A.M. Determinants for successful percutaneous image-guided drainage of intra-abdominal abscess. Arch. Surg. 2002, 137, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardière-Deguelte, S.; Ragot, E.; Amroun, K.; Piardi, T.; Dokmak, S.; Bruno, O.; Appere, F.; Sibert, A.; Hoeffel, C.; Sommacale, D.; et al. Hepatic abscess: Diagnosis and management. J. Visc. Surg. 2015, 152, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, B.; Yzet, T.; Regimbeau, J.M. Radiologic drainage of post-operative collections and abscesses. J. Visc. Surg. 2013, 150 (Suppl. 3), S11–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, M.; Opriţă, R.; Șandru, V.; Berceanu, D.; Plotogea, O.; Constantinescu, A.; Diaconescu, D.; Negoi, I.; Constantinescu, G. EUS-Guided Transgastric Drainage of Intraabdominal Fluid Collections. Chirurgia 2018, 113, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Efishat, M.; Attiyeh, M.A.; Eaton, A.A.; Gönen, M.; Covey, A.M.; D’Angelica, M.I.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Kingham, T.P.; Balachandran, V.; Jarnagin, W.R.; et al. Endoscopic versus percutaneous drainage of post-operative peripancreatic fluid collections following pancreatic resection. HPB 2019, 21, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, B.; Varadarajulu, S. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pelvic abscess drainage (with video). J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Sci. 2015, 22, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, M. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Drainage of Pancreatic Fluid Collections. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 28, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politano, A.D.; Hranjec, T.; Rosenberger, L.H.; Sawyer, R.G.; Tache Leon, C.A. Differences in morbidity and mortality with percutaneous versus open surgical drainage of postoperative intra-abdominal infections: A review of 686 cases. Am. Surg. 2011, 77, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinci, D.; Akhan, O.; Ozmen, M.N.; Karabulut, N.; Ozkan, O.; Cil, B.E.; Karcaaltincaba, M. Percutaneous drainage of 300 intraperitoneal abscesses with long-term follow-up. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2005, 28, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.Y.; Varadarajulu, S. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided drainage of postoperative abdominal fluid collections: What should we do to improve outcomes? Dig. Endosc. 2015, 27, 726–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, J.M.; Al-Refaie, W.B.; Cash, B.D.; Gaba, R.C.; Gervais, D.A.; Gipson, M.G.; Kolbeck, K.J.; Kouri, B.E.; Marshalleck, F.E.; Nair, A.V.; et al. ACR appropriateness criteria radiologic management of infected fluid collections. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2015, 12, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, W.W.; Vrochides, D.V.; Newcomb, W.L.; Mayo-Smith, W.W.; Iannitti, D.A. Optimal treatment of hepatic abscess. Am. Surg. 2008, 74, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamberger, D.M. Outcome of medical treatment of bacterial abscesses without therapeutic drainage: Review of cases reported in the literature. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 23, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulku, G.; Mohan, G.; Samuelson, S.; Ferguson, J.; Tibballs, J. Percutaneous aspiration versus catheter drainage of liver abscess: A retrospective review. Australas. Med. J. 2015, 8, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.C.; Ho, S.S.; Lau, W.Y.; Yeung, D.T.; Yuen, E.H.; Lee, P.S.; Metreweli, C. Treatment of pyogenic liver abscess: Prospective randomized comparison of catheter drainage and needle aspiration. Hepatology 2004, 39, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.R.; Kim, J.T.; Haukoos, J.S.; Macias, L.H.; Dixon, M.R.; Stamos, M.J.; Konyalian, V.R. Factors affecting the successful management of intra-abdominal abscesses with antibiotics and the need for percutaneous drainage. Dis. Colon Rectum. 2006, 49, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siewert, B.; Tye, G.; Kruskal, J.; Sosna, J.; Opelka, F. Impact of CT-guided drainage in the treatment of diverticular abscesses: Size matters. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 186, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abusedera, M.A.; Magdy, K.; Ali, A.M.A.; Hassan, A.E. Percutaneous image-guided aspiration versus catheter drainage of abdominal and pelvic collections. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2013, 44, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lorenz, J.; Thomas, J.L. Complications of percutaneous fluid drainage. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 23, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).