40 Years of Helicobacter pylori: A Revolution in Biomedical Thought
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Historical Helicobacter pylori Traces
2.2. The Biomolecular Knowledge Developments
2.3. The Associated Diseases
2.4. Microbiota and H. pylori Interactions
2.5. The Diagnosis Over Time
2.6. New Therapeutic Issues
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salama, N.R.; Hartung, M.L.; Müller, A. Life in the human stomach: Persistence strategies of the bacterial pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, M. Antibiotic overuse: Stop the killing of beneficial bacteria. Nature 2011, 476, 393–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josenhans, C.; Eaton, K.A.; Thevenot, T.; Suerbaum, S. Switching of flagellar motility in Helicobacter pylori by reversible length variation of a short homopolymeric sequence repeat in fliP, a gene encoding a basal body protein. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4598–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertsethtakarn, P.; Ottemann, K.M.; Hendrixson, D.R. Motility and chemotaxis in Campylobacter and Helicobacter. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 65, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomb, J.F.; White, O.; Kerlavage, A.R.; Clayton, R.A.; Sutton, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.D.; Ketchum, K.A.; Klenk, H.P.; Gill, S.; Dougherty, B.A.; et al. The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 1997, 388, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.D.; Kling-Bäckhed, H.; Giannakis, M.; Xu, J.; Fulton, R.S.; Fulton, L.A.; Cordum, H.S.; Wang, C.; Elliott, G.; Edwards, J.; et al. The complete genome sequence of a chronic atrophic gastritis Helicobacter pylori strain: Evolution during disease progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9999–10004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, A.H. Use of pan-genome analysis for the identification of lineage-specific genes of Helicobacter pylori. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, fnw296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, N.S.; Ahlawat, R. Helicobacter pylori. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534233/ (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- Logan, R.P. Adherence of Helicobacter pylori. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 10 (Suppl. 1), 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, M.J.; Atherton, J.C. Helicobacter pylori persistence: Biology and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; el-Zimaity, H.M.; Gutierrez, O.; Osato, M.S.; Graham, D.Y. Importance of Helicobacter pylori oipA in clinical presentation, gastric inflammation, and mucosal interleukin 8 production. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.D.; Mitchell, H.M.; Tobias, V. Acute Helicobacter pylori infection in an infant, associated with gastric ulceration and serological evidence of intra-familial transmission. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1992, 87, 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, J.; Thiberg, J.M.; Chevalier, C.; Kalach, N.; Bergeret, M.; Labigne, A.; Dauga, C. Genetic and transmission analysis of Helicobacter pylori strains within a family. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topi, S.; Santacroce, L.; Bottalico, L.; Ballini, A.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Dipalma, G.; Charitos, I.A.; Inchingolo, F. Gastric Cancer in History: A Perspective Interdisciplinary Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Topi, S.; Haxhirexha, K.; Hidri, S.; Charitos, I.A.; Bottalico, L. Medicine and healing in the pre-Socratic thought. A brief analysis of magics and rationalism in ancient herbal therapy. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charitos, I.A.; Gagliano-Candela, R.; Santacroce, L.; Bottalico, L. Venoms and poisonings during the centuries. A narrative review. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, B. Lessons from the history of light microscopy. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2000, 2, E151–E152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gest, H. The Discovery of Microorganisms by Robert Hooke and Antoni van Leeuwenhoek, Fellows of the Royal Societ. Notes Rec. R. Soc. Lond. 2004, 58, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Bottalico, L.; Topi, S.; Castellaneta, F.; Charitos, I.A. The “Scourge of the Renaissance”. A Short Review About Treponema pallidum infection. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, M.; Modlin, I.M. A century of Helicobacter pylori: Paradigms lost-paradigms regained. Digestion 1998, 59, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Warren, R.; Marshall, B. Helicobacter Pylori; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarello, P.; Calligaro, A.L.; Calligaro, A. Giulio Bizzozero: A pioneer of cell biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 2, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, S. Helicobacter pylori: The story continues. Lancet 2001, 357, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Link, A.; Selgrad, M. Helicobacter pylori: Perspectives and time trends. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriani, R.; Mazzucco, D.; Venturini, I.; Mazzarello, M.G.; Zanella, D.; Orso Giacone, G. Helicobacter Pylori: Stato, dell’arte. Caleidosc. Riv. Mens. Med. 2020, 159, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, B. Helicobacter connections. ChemMedChem 2006, 1, 783–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.J.; Warren, J.R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet 1984, 16, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megraud, F.; Bonnet, F.; Gamier, M.; Lamouliatte, H. Characterization of “Campylobacter pyloridis” by culture, enzymatic profile, and protein content. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1985, 22, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaniuk, P.J.; Zoltowska, B.; Trust, T.J.; Lane, D.J.; Olsen, G.J.; Pace, N.R.; Stahl, D.A. Campylobacter pylori, the spiral bacterium associated with human gastritis, is not a true Campylobacter sp. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 2137–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.J.; Armstrong, J.A.; McGechie, D.B.; Glancy, R.J. Attempt to fulfill Koch’s postulates for pyloric Campylobacter. Med. J. Aust. 1985, 142, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.; Nicholson, G. Ingestion of Campylobacter pyloridis causes gastritis and raised fasting gastric pH. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1987, 82, 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, D.A.; Li, C.; Patel, N.R.; Mayberry, W.R.; Chi, D.S.; Thomas, E. Isolation of Helicobacter pylori from saliva. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 2802–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.M.; Engstrand, L.; Genta, R.M.; Graham, D.Y.; el-Zaatari, F.A. Detection of Helicobacter pylori in dental plaque by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snaith, A.; El-Omar, E.M. Helicobacter pylori: Host genetics and disease outcomes. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 2, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, L.; Figueras, M.J. Taxonomy, epidemiology, and clinical relevance of the genus Arcobacter. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.G. The non-H pylori helicobacters: Their expanding role in gastrointestinal and systemic diseases. Gut 2002, 50, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusters, J.G.; van Vliet, A.H.; Kuipers, E.J. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 449–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, L.; Cagiano, R.; Del Prete, R.; Bottalico, L.; Sabatini, R.; Carlaio, R.G.; Prejbeanu, R.; Vermesan, H.; Dragulescu, S.I.; Vermesan, D.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric MALTomas: An up-to-date and therapy highlight. Clin. Ter. 2008, 159, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moodley, Y.; Linz, B. Helicobacter pylori Sequences Reflect Past HumanMigrations. Genome Dyn. 2009, 6, 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, K.J.; Correa, P. The transmission of Helicobacter pylori. A critical review of the evidence. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 24, 875–887, . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.Y.; Yamaoka, Y.; Malaty, H.M. Thoughts about populations with unexpected low prevalences of Helicobacter pylori infection. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 101, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alm, R.A.; Bina, J.; Andrews, B.M.; Doig, P.; Hancock, R.E.; Trust, T.J. Comparative genomics of Helicobacter pylori: Analysis of the outer membrane protein families. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4155–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Survival of Helicobacter pylori in gastric acidic territory. Helicobacter 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenbreit, S.; Swoboda, K.; Barwig, I.; Ruhl, S.; Borén, T.; Koletzko, S.; Haas, R. Outer membrane protein expression profile in Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3782–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxen, M.A.; Sisson, G.; Melano, R.; Hoffman, P.S. The Helicobacter pylori chemotaxis receptor TlpB (HP0103) is required for pH taxis and for colonization of the gastric mucosa. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 2656–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 46. Williams, S.M.; Chen, Y.T.; Andermann, T.M.; Carter, J.E.; McGee, D.J.; Ottemann, K.M. Helicobacter pylori chemotaxis modulates inflammation and bacterium-gastric epithelium interactions in infected mice. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 3747–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, G.; Kombrabail, M.; Raninga, N.; Sau, A.K. Arginase of Helicobacter Gastric Pathogens Uses a Unique Set of Non-catalytic Residues for Catalysis. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 1120–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kao, C.Y.; Sheu, B.S.; Wu, J.J. Helicobacter pylori infection: An overview of bacterial virulence factors and pathogenesis. Biomed. J. 2016, 39, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, K.P.; Gaddy, J.A. Helicobacter pylori: Genomic Insight into the Host-Pathogen Interaction. Int. J. Genom. 2015, 2015, 386905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilver, D.; Arnqvist, A.; Ogren, J.; Frick, I.M.; Kersulyte, D.; Incecik, E.T.; Berg, D.E.; Covacci, A.; Engstrand, L.; Borén, T. Helicobacter pylori adhesin binding fucosylated histo-blood group antigens revealed by retagging. Science 1998, 279, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Soyfoo, D.M.; Wu, Y.; Xu, S. Virulence of Helicobacter pylori outer membrane proteins: An updated review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benktander, J.; Barone, A.; Johansson, M.M.; Teneberg, S. Helicobacter pylori SabA binding gangliosides of human stomach. Virulence 2018, 9, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suerbaum, S.; Thiberge, J.M.; Kansau, I.; Ferrero, R.L.; Labigne, A. Helicobacter pylori hspA-hspB heat-shock gene cluster: Nucleotide sequence, expression, putative function and immunogenicity. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 14, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miehlke, S.; Yu, J.; Schuppler, M.; Frings, C.; Kirsch, C.; Negraszus, N.; Morgner, A.; Stolte, M.; Ehninger, G.; Bayerdörffer, E. Helicobacter pylori vacA, iceA, and cagA status and pattern of gastritis in patients with malignant and benign gastroduodenal disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantuya, B.; El Serag, H.B.; Saruuljavkhlan, B.; Azzaya, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Uchida, T.; Oyuntsetseg, K.; Oyunbileg, N.; Davaadorj, D.; Yamaoka, Y. Advantage of 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing in Helicobacter pylori diagnosis. Helicobacter 2021, 17, e12790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidpour, A. CagA-mediated pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 93, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskito, L.A.; Yih-Wu, J.; Yamaoka, Y. The role of integrating conjugative elements in Helicobacter pylori: A review. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censini, S.; Lange, C.; Xiang, Z.; Crabtree, J.E.; Ghiara, P.; Borodovsky, M.; Rappuoli, R.; Covacci, A. cag, a pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type I-specific and disease-associated virulence factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14648–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, A.; Blum, G.; Emody, L.; Kerenyi, M.; Bock, A.; Neuhierl, B.; Rabsch, W.; Scheutz, F.; Hacker, J. tRNA genes and pathogenicity islands: Influence on virulence and metabolic properties of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 17, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, G.; Falbo, V.; Caprioli, A.; Hacker, J. Gene clusters encoding the cytotoxic necrotizing factor type 1, Prs-fimbriae and alpha-hemolysin form the pathogenicity island II of the uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain J96. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 126, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbreit, S.; Puls, J.; Sedlmaier, B.; Gerland, E.; Fischer, W.; Haas, R. Translocation of Helicobacter pylori CagA into gastric epithelial cells by type IV secretion. Science 2000, 287, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.; Rappuoli, R.; Covacci, A. The cag Pathogenicity Island. In Helicobacter pylori: Physiology and Genetics; Mobley, H.L.T., Mendz, G.L., Hazell, S.L., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; Chapter 31. [Google Scholar]
- Higashi, H.; Tsutsumi, R.; Muto, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Azuma, T.; Asaka, M.; Hatakeyama, M. SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase as an intracellular target of Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Science 2002, 295, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kita, M.; Kodama, T.; Sawai, N.; Imanishi, J. Helicobacter pylori cagA gene and expression of cytokine messenger RNA in gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.; Argent, R.H.; Atherton, J.C. The inflammatory and immune response to Helicobacter pylori infection. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 21, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedrud, J.G.; Blanchard, S.S.; Czinn, S.J. Helicobacter pylori inflammation and immunity. Helicobacter 2002, 7 (Suppl. 1), 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noto, J.M.; Peek, R.M., Jr. The Helicobacter pylori cag Pathogenicity Island. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 921, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Pacchiani, N.; Censini, S.; Buti, L.; Covacci, A. Echoes of a distant past: The cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, J.; Chen, N.; Amenta, P.S.; Fukui, H.; Oshima, T.; Tomita, T.; Miwa, H.; Lim, K.J.; Das, K.M. Helicobacter pylori associated chronic gastritis, clinical syndromes, precancerous lesions, and pathogenesis of gastric cancer development. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5461–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, A.; Furuta, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; O’Morain, C. Review—Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection 2020. Helicobacter 2020, 25 (Suppl. 1), e12743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, M.; Higashi, H. Helicobacter pylori CagA: A new paradigm for bacterial carcinogenesis. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumrese, C.; Slomianka, L.; Ziegler, U.; Choi, S.S.; Kalia, A.; Fulurija, A.; Lu, W.; Berg, D.E.; Benghezal, M.; Marshall, B.; et al. The secreted Helicobacter cysteine-rich protein A causes adherence of human monocytes and differentiation into a macrophage-like phenotype. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiotani, A.; Graham, D.Y. Pathogenesis and therapy of gastric and duodenal ulcer disease. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 86, 1447–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.F. Patterns of inflammation linked to ulcer disease. Bailliere’s Best Practice & Research. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2000, 14, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorer, M.S.; Cohen, I.E.; Sessler, T.H.; Fero, J.; Salama, N.R. Natural competence promotes Helicobacter pylori chronic infection. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Hu, J.; Su, R.; Zhang, J.; Han, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. Molecular mechanism of Helicobacter pylori-induced autophagy in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 6221–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, F.; Roper, J.; Joseph, N.; Pei, Z.; Chhada, A.; Shak, J.R.; de Perez, A.Z.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Blaser, M.J. The effect of H. pylori eradication on meal-associated changes in plasma ghrelin and leptin. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, E.J. Review article: Exploring the link between Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 13 (Suppl. 1), 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Report on Cancer: Setting Priorities, Investing Wisely and Providing Care for All; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Koeppel, M.; Garcia-Alcalde, F.; Glowinski, F.; Schlaermann, P.; Meyer, T.F. Helicobacter pylori Infection Causes Characteristic DNA Damage Patterns in Human Cells. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, M.A.; Canales, J.; Corvalán, A.H.; Quest, A.F. Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation and epigenetic changes during gastric carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12742–12756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, Y.; Khan, A.; Farooqui, A.; Mubarak, M.; Facista, A.; Akhtar, S.S.; Khan, S.; Kazi, J.I.; Bernstein, C.; Kazmi, S.U. Oxidative DNA damage as a potential early biomarker of Helicobacter pylori associated carcinogenesis. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganuma, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ono, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Hayashi, T.; Ogawa, T.; Imai, K.; Kuzuhara, T.; Nishizono, A.; Fujiki, H. TNF-alpha-inducing protein, a carcinogenic factor secreted from H. pylori, enters gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, S.; Kawai, N.; Tsujii, M.; Kawano, S.; Hori, M. Review article: Inflammation-related promotion of gastrointestinal carcinogenesis-a perigenetic pathway. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 89 (Suppl. 1), 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, T.; Miwa, K.; Inokuchi, M.; Nakagawara, H.; Tajima, H.; Takamura, H.; Ninomiya, I.; Kitagawa, H.; Fushida, S.; Fujimura, T.; et al. Spontaneous clearance of Helicobacter pylori after pylorus-preserving gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Baas, I.O.; van Rees, B.P.; Musler, A.; Craanen, M.E.; Tytgat, G.N.; van den Berg, F.M.; Offerhaus, G.J. Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus infection and the p53 tumour suppressor pathway in gastric stump cancer compared with carcinoma in the non-operated stomach. J. Clin. Pathol. 1998, 51, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genta, R.M.; Hamner, H.W.; Graham, D.Y. Gastric lymphoid follicles in Helicobacterpylori infection: Frequency, distribution, and response totriple therapy. Hum. Pathol. 1993, 24, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotherspoon, A.C. Gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue and Helicobacter pylori. Annu. Rev. Med. 1998, 49, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, A.; Thiede, C.; Morgner, A.; Alpen, B.; Ritter, M.; Neubauer, B.; Wündisch, T.; Ehninger, G.; Stolte, M.; Bayerdörffer, E. Cure of Helicobacter pylori infection and duration of remission of low-grade gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1997, 89, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Losacco, T.; Cagiano, R.; Bottalico, L.; Carlaio, R.G.; Prejbeanu, R.; Vermesan, H.; Dragulescu, S.I.; Vermesan, D.; Motoc, A.; Santacroce, L. Our experience in Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric MALToma. Clin. Ter. 2008, 159, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach, G.; Ford, R.; Glober, G.; Sample, D.; Hagemeister, F.B.; Lynch, P.M.; McLaughlin, P.W.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Romaguera, J.E.; Sarris, A.H.; et al. Antibiotic treatmen t of gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 131, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Mégraud, F.; O’Morain, C.; Hungin, A.P.; Jones, R.; Axon, A.; Graham, D.Y.; Tytgat, G. European Helicobacter pylori Study Group (EHPSG). Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection—The Maastricht 2-2000 Consensus Report. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 16, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, A.G.; Zagari, R.M.; De Musis, C.; Romano, L.; Loguercio, C.; Romano, M. Helicobacter pylori and extragastric diseases: A review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3204–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasceri, V.; Cammarota, G.; Patti, G.; Cuoco, L.; Gasbarrini, A.; Grillo, R.L.; Fedeli, G.; Gasbarrini, G.; Maseri, A. Association of virulent Helicobacter pylori strains with ischemic heart disease. Circulation 1998, 97, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceti, A.; Are, R.; Sabino, G.; Fenu, L.; Pasquazzi, C.; Quaranta, G.; Zechini, B.; Terrosu, P. Helicobacter pylori active infection in patients with acute coronary heart disease. J. Infect. 2004, 49, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousoulis, D.; Davies, G.; Stefanadis, C.; Toutouzas, P.; Ambrose, J.A. Inflammatory and thrombotic mechanisms in coronary atherosclerosis. Heart 2003, 89, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yu, M.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S.; Xi, Y.; Duan, G. A meta-analysis of the association between Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.J.; Sanderson, J.E. Hyperhomocysteinaemia, Helicobacter pylori, and coronary heart disease. Heart 1996, 76, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Baek, H.; Park, J.S.; Kim, S.; Kyung, C.; Baik, S.J.; Lee, B.K.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, C.W.; Kim, K.R.; et al. Current Helicobacter pylori infection is significantly associated with subclinical coronary atherosclerosis in healthy subjects: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, M.V.; Kandulski, A.; Schreiber, J.; Malfertheiner, P. Helicobacter pylori infection and the respiratory system: A systematic review of the literature. Digestion 2011, 84, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaselli, M.; Zaffoni, E.; Ruina, M.; Sartori, S.; Trevisani, L.; Ciaccia, A.; Alvisi, V.; Fabbri, L.; Papi, A. Helicobacter pylori and chronic bronchitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 34, 828–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, S.J.; Jorgensen, T.; Andersen, L.P.; Bonnevie, O. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with lifestyle, chronic disease, body indices and age at menarche in Danish adults. Scand. J. Public Health 2000, 28, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, P. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and chronic bronchitis: A meta-analysis of 16 studies. Infect. Dis. 2015, 47, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitz, H.S.; Farber, S.S. Demonstration of Helicobacter pylori intracheal secretions. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 1993, 93, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedi, B.; Kapp, A. Helicobacter pylori infection in skin diseases: A critical appraisal. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 3, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.; Rodrigues, J.; Delgado, L.; Fonseca, J.; Vaz, M. Is Helicobacter pylori infection associated with chronic idiopathic urticaria? Allergol. Immunopathol. 2003, 31, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyk, D.S.; Koutsoumpas, A.L.; Mytilinaiou, M.G.; Rigopoulou, E.I.; Sakkas, L.I.; Bogdanos, D.P. Helicobacter pylori and autoimmune disease: Cause or bystander. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabelo-Gonçalves, E.M.; Roesler, B.M.; Zeitune, J.M. Extragastric manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection: Possible role of bacterium in liver and pancreas diseases. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2968–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, H.O.; Taneera, J.; Castedal, M.; Glatz, E.; Olsson, R.; Wadstrom, T. Identification of Helicobacter pylori and other Helicobacter species by PCR, hybridization, and partial DNA sequencing in human liver samples from patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis or primary biliary cirrhosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Shen, Z.; Feng, Y.; Taylor, N.S.; Paster, B.J.; Ericson, R.L.; Lau, C.N.; Correa, P.; Araya, J.C.; et al. Hepatic Helicobacter speciesia identified in bile and gallbladder tissue from Chileans with chronic cholecystitis. Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, R.W.; Sung, J.J. Review article: Helicobacter species and hepatobiliary diseases. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 16, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottalico, L.; Castellaneta, F.; Charitos, I.A. From hydrotherapy to the discovery of the gut microbiota: The historical gastrointestinal health concept. Pharmacophore 2020, 11, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Santacroce, L.; Charitos, I.A.; Ballini, A.; Inchingolo, F.; Luperto, P.; De Nitto, E.; Topi, S. The Human Respiratory System and its Microbiome at a Glimpse. Biology 2020, 9, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, A.; Ciurea, C.N.; Pasaroiu, D.; Savin, A.I.; Toma, F.; Sular, F.; Santacroce, L.; Mare, A. New perspectives on the nutritional factors influencing growth rate of Candida albicans in diabetics. An in vitro study. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2017, 112, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbey, G.; Sproston, E.; Hanafiah, A. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastric Microbiota. Euroasian J. Hepatogastroenterol. 2020, 10, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charitos, I.A.; Castellaneta, F.; Santacroce, L.; Bottalico, L. Historical anecdotes and breakthroughs of histamine: From discovery to date. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Inchingolo, F.; Topi, S.; Del Prete, R.; Di Cosola, M.; Charitos, I.A.; Montagnani, M. Potential beneficial role of probiotics on the outcome of COVID-19 patients: An evolving perspective. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, L.; Sardaro, N.; Topi, S.; Pettini, F.; Bottalico, L.; Cantore, S.; Cascella, G.; Del Prete, R.; Dipalma, G.; Inchingolo, F. The pivotal role of oral microbiota in health and disease. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, L.; Mavaddati, S.; Hamedi, J.; Zeinali, B.; Ballini, A.; Bilancia, M. Expressive Analysis of Gut Microbiota in Pre- and Post- Solid Organ Transplantation Using Bayesian Topic Models Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polimeno, L.; Barone, M.; Mosca, A.; Viggiani, M.T.; Leo, A.; Debellis, L.; Troisi, M.; Daniele, A.; Santacroce, L. Gut Microbiota Imbalance is Related to Sporadic Colorectal Neoplasms. A Pilot Study. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, A.; Scacco, S.; Boccellino, M.; Santacroce, L.; Arrigoni, R. Microbiota and Obesity: Where Are We Now? Biology 2020, 9, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Serio, F.; Lovero, R.; D’Agostino, D.; Nisi, L.; Miragliotta, G.; Contino, R.; Man, A.; Ciccone, M.M.; Santacroce, L. Evaluation of procalcitonin, Vitamin D and C-reactive protein levels in septic patients with positive emocoltures. Our preliminary experience. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2016, 32, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; D’agostino, D.; Charitos, I.A.; Bottalico, L.; Ballini, A. A short review about electrophysiology and bioimpedance: History and perspectives. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2018, 9, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isacco, C.G.; Ballini, A.; De Vito, D.; Nguyen, K.C.D.; Cantore, S.; Bottalico, L.; Quagliuolo, L.; Boccellino, M.; Di Domenico, M.; Santacroce, L.; et al. Rebalance the oral microbiota as efficacy tool in endocrine, metabolic, and immune disorders. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polimeno, L.; Barone, M.; Mosca, A.; Viggiani, M.T.; Joukar, F.; Mansour-Ghanaei, F.; Mavaddati, S.; Daniele, A.; Debellis, L.; Bilancia, M.; et al. Soy Metabolism by Gut Microbiota from Patients with Precancerous Intestinal Lesions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, F.; Kacprowski, T.; Rühlemann, M.; Bang, C.; Franke, A.; Zimmermann, K.; Nauck, M.; Völker, U.; Völzke, H.; Biffar, R.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection associates with fecal microbiota composition and diversity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, N.R.; Khoder, G.; Nada, A.M.; Al Bataineh, M.T. Exploring the impact of Helicobacter pylori on gut microbiome composition. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.M.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, C.M.; Fang, Y.J.; Bair, M.J.; Chen, P.Y.; Chang, C.Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Chen, M.J.; Chen, C.C.; et al. Taiwan Gastrointestinal Disease and Helicobacter Consortium. Long-term changes of gut microbiota, antibiotic resistance, and metabolic parameters after Helicobacter pylori eradication: A multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.; Schütte, K.; Mayerle, J.; Malfertheiner, P. The role of the gastric bacterial microbiome in gastric cancer: Helicobacter pylori and beyond. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 1756284819894062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazirzadeh, J.; Falahi, J.; Moghim, S.; Narimani, T.; Rafiei, R.; Karbasizadeh, V. Molecular Assessment of Resistance to Clarithromycin in Helicobacter pylori Strains Isolated from Patients with Dyspepsia by Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization in the Center of Iran. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2304173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajbakhsh, S.; Samarbaf-Zadeh, A.R.; Moosavian, M. Comparison of fluorescent in situ hybridization and histological method for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in gastric biopsy samples. Med. Sci. Monit. 2008, 14, BR183–BR187. [Google Scholar]
- Makristathis, A.; Hirschl, A.M.; Mégraud, F.; Bessède, E. Review: Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2019, 24 (Suppl. 1), e12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atherton, J.C. Non-endoscopic tests in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 11 (Suppl. 1), 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Yamaoka, Y. Diagnostic Methods of Helicobacter pylori Infection for Epidemiological Studies: Critical Importance of Indirect Test Validation. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4819423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Gonzalez, E.; Bosques-Padilla, F.J.; Tijerina-Menchaca, R.; Flores-Gutierrez, J.P.; Maldo-nado-Garza, H.J.; Perez-Perez, G.I. Comparison of endoscopy-basedand serum-based methods for the diagnosis ofHel icobacterpylori. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 17, 101–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cutler, A.F.; Prasad, V.M. Long-term follow-up of Helicobacter pylori serology after successful eradication. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1996, 91, 85–843. [Google Scholar]
- Fallone, C.A.; Moss, S.F.; Malfertheiner, P. Reconciliation of Recent Helicobacter pylori Treatment Guidelines in a Time of Increasing Resistance to Antibiotics. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. European Helicobacter and Microbiota Study Group and Consensus panel. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, N.; Howden, C.W. Update on the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2020, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, L.; Charitos, I.A.; Bottalico, L. A successful history: Probiotics and their potential as antimicrobials. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2019, 17, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signorini, L.; De Leonardis, F.; Santacroce, L.; Haxhirexha, K.; Topi, S.; Fumarola, L.; Dipalma, G.; Coscia, M.F.; Inchingolo, F. Probiotics may modulate the impact of aging on adults. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballini, A.; Santacroce, L.; Cantore, S.; Bottalico, L.; Dipalma, G.; Topi, S.; Saini, R.; De Vito, D.; Inchingolo, F. Probiotics Efficacy on Oxidative Stress Values in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Randomized Double-Blinded Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 19, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchingolo, F.; Santacroce, L.; Cantore, S.; Ballini, A.; Del Prete, R.; Topi, S.; Saini, R.; Dipalma, G.; Arrigoni, R. Probiotics and EpiCor® in human health. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 1973–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchingolo, F.; Dipalma, G.; Cirulli, N.; Cantore, S.; Saini, R.S.; Altini, V.; Santacroce, L.; Ballini, A.; Saini, R. Microbiological results of improvement in periodontal condition by administration of oral probiotics. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Ballini, A.; Gnoni, A.; De Vito, D.; Dipalma, G.; Cantore, S.; Gargiulo Isacco, C.; Saini, R.; Santacroce, L.; Topi, S.; Scarano, A.; et al. Effect of probiotics on the occurrence of nutrition absorption capacities in healthy children: A randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled pilot study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8645–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, L.; Santacroce, L.; Dipalma, G.; Haxhirexha, K.; Topi, S.; Cantore, S.; Altini, V.; Pacifici, A.; De Vito, D.; Pettini, F.; et al. Gender medicine: The impact of probiotics on male patients. Clin. Ter. 2021, 171, e8–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signorini, L.; Ballini, A.; Arrigoni, R.; De Leonardis, F.; Saini, R.; Cantore, S.; De Vito, D.; Coscia, M.F.; Dipalma, G.; Santacroce, L.; et al. Evaluation of a nutraceutical product with probiotics, vitamin d, plus banaba leaf extracts (Lagerstroemia speciosa) in glycemic control. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, D.; Valenzano, A.; Grande, G.; Santacroce, L. Interazioni farmaco-alimentari: Un problema terapeutico sempre più attuale [Drug/food interactions: An actual therapeutic outcome]. Clin. Ter. 2004, 155, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhou, X.; Wang, F.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, H.; Lv, N. Efficacy and safety of probiotics as adjuvant agents for Helicobacter pylori infection: A meta-analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesbros-Pantoflickova, D.; Corthésy-Theulaz, I.; Blum, A.L. Helicobacter pylori and probiotics. J. Nutr. 2007, 137 (Suppl. 2), 812S–818S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj, J.; Forma, A.; Sitarz, M.; Portincasa, P.; Garruti, G.; Krasowska, D.; Maciejewski, R. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors-Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogenicity in the Gastric Microenvironment. Cells 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larussa, T.; Leone, I.; Suraci, E.; Imeneo, M.; Luzza, F. Helicobacter pylori and T Helper Cells: Mechanisms of Immune Escape and Tolerance. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 981328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroblewski, L.E.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Wilson, K.T. Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: Factors that modulate disease risk. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 713–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, G.; Beckloff, N.; Weinberg, A.; Kisich, K.O. The roles of antimicrobial peptides in innate host defense. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2377–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Bufo, P.; Latorre, V.; Losacco, T. Ruolo dei mastociti nella fisiopatologia delle lesioni gastriche indotte da Helicobacter pylori [Role of mast cells in the physiopathology of gastric lesions caused by Helicobacter pylori]. Chir. Ital. 2000, 52, 527–531. [Google Scholar]
- De Luca, A.; Baldi, A.; Russo, P.; Todisco, A.; Altucci, L.; Giardullo, N.; Pasquale, L.; Iaquinto, S.; D’Onofrio, V.; Parodi, M.C.; et al. Coexpression of Helicobacter pylori’s proteins CagA and HspB induces cell proliferation in AGS gastric epithelial cells, independently from the bacterial infection. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6350–6356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Loguercio, S.; Dian, C.; Flagiello, A.; Scannella, A.; Pucci, P.; Terradot, L.; Zagari, A. In HspA from Helicobacter pylori vicinal disulfide bridges are a key determinant of domain B structure. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3537–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Yokota, K.; Ayada, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Okada, T.; Shen, L.; Oguma, K. Helicobacter pylori heat-shock protein 60 induces interleukin-8 via a Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathway in human monocytes. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56 Pt 2, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, Y.; Yokota, K.; Mizuno, M.; Yunoki, N.; Uesu, T.; Okada, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Hirai, Y.; Oguma, K.; Tsuji, T. Antibodies to human gastric epithelial cells and heat shock protein 60 in Helicobacter pylori positive mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. Gut 1999, 45, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.S.; He, P.J.; Tsai, N.M.; Li, C.H.; Yang, S.C.; Hsu, W.T.; Wu, M.S.; Wu, C.J.; Cheng, T.L.; Liao, K.W. A potential role for Helicobacter pylori heat shock protein 60 in gastric tumorigenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 392, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kita, M.; Kodama, T.; Sawai, N.; Tanahashi, T.; Kashima, K.; Imanishi, J. Chemokines in the gastric mucosa in Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 1998, 42, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, B.; Chen, C.; Yi, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Zheng, S.; Li, N.; She, F. N-terminal region of Helicobacter pylori CagA induces IL-8 production in gastric epithelial cells via the β1 integrin receptor. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, M.; Eguchi, H.; Goto, Y.; Kondo, T.; Nishio, K.; Ishida, Y.; Kawai, S.; Okada, R.; Hishida, A.; Wakai, K.; et al. Associations of plasma IL-8 levels with Helicobacter pylori seropositivity, gastric atrophy, and IL-8 T-251A genotypes. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucchelli, L.; Blaser, A.; Kappeler, A.; Schärli, P.; Laissue, J.A.; Baggiolini, M.; Uguccioni, M. BCA-1 is highly expressed in Helicobacter pylori-induced mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue and gastric lymphoma. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, R49–R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
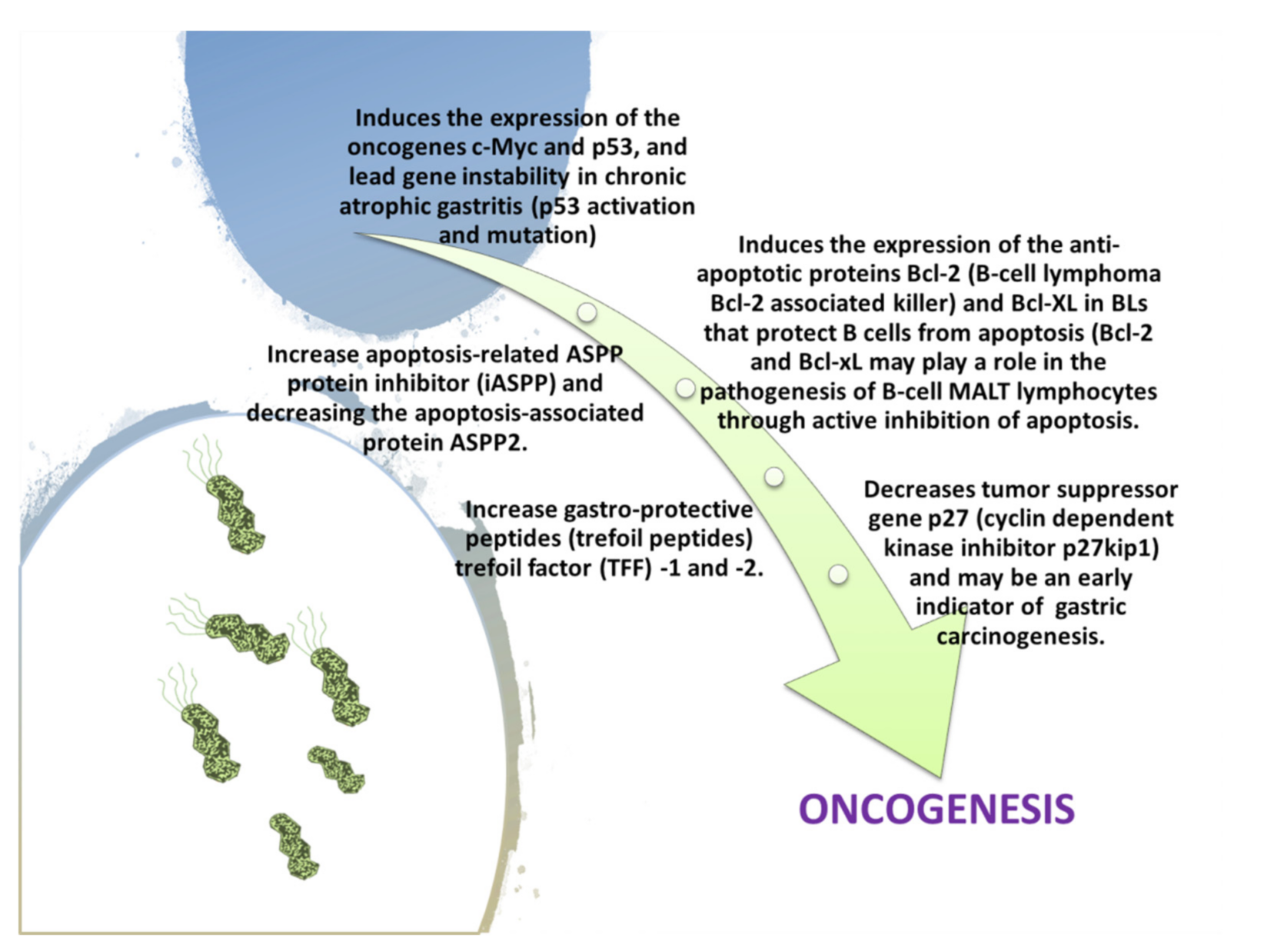
- Michelis, R.; Sela, S.; Sbeit, W.; Cohen, H.I.; Reshef, R. Decreased TFF2 expression in the gastric antrum in patients infected with CagA-positive Helicobacter pylori. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2009, 11, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peterson, A.J.; Menheniott, T.R.; O’Connor, L.; Walduck, A.K.; Fox, J.G.; Kawakami, K.; Minamoto, T.; Ong, E.K.; Wang, T.C.; Judd, L.M.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection promotes methylation and silencing of trefoil factor 2, leading to gastric tumor development in mice and humans. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 2005–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, H.; Takaishi, S.; Menheniott, T.R.; Yang, X.; Shibata, W.; Jin, G.; Betz, K.S.; Kawakami, K.; Minamoto, T.; Tomasetto, C.; et al. Inhibition of gastric carcinogenesis by the hormone gastrin is mediated by suppression of TFF1 epigenetic silencing. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Liu, J.; Lin, B.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Huang, G. A meta-analysis of interleukin8- 251 promoter polymorphism associated with gastric cancer risk. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e28083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukri, A.; Hanafiah, A.; Mohamad Zin, N.; Kosai, N.R. Epidemiology and role of Helicobacter pylori virulence factors in gastric cancer carcinogenesis. APMIS 2020, 128, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, J.W.T.; Wilson, R.B. Pathways of Gastric Carcinogenesis, Helicobacter pylori Virulence and Interactions with Antioxidant Systems, Vitamin C and Phytochemicals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
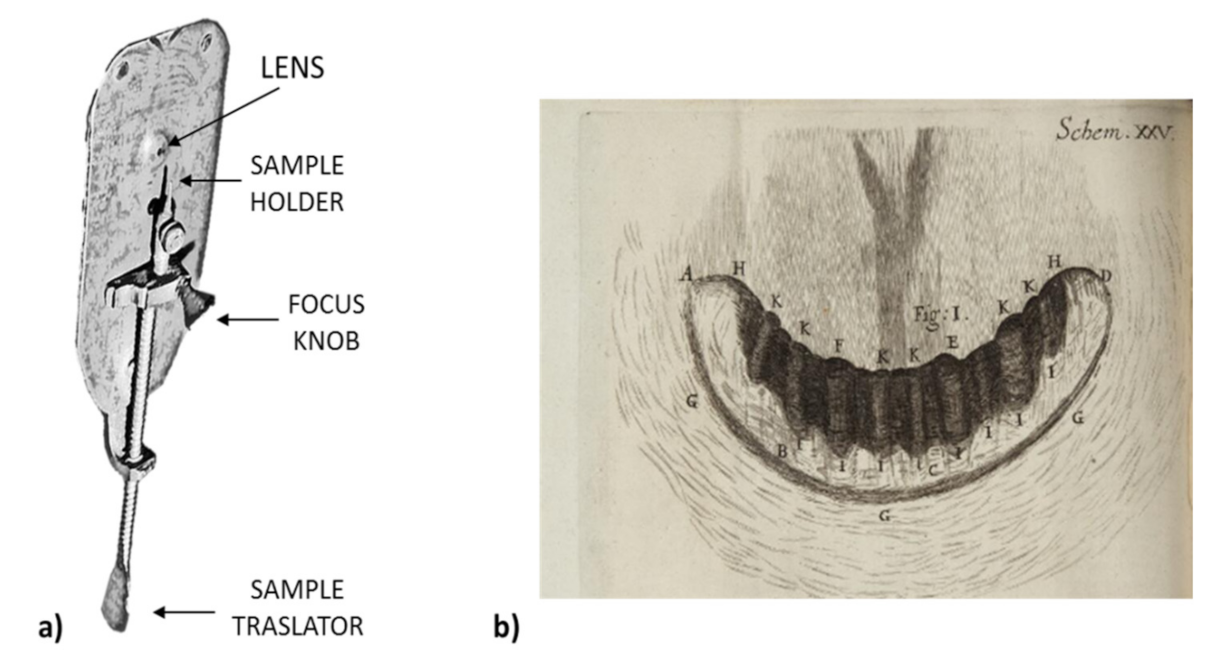
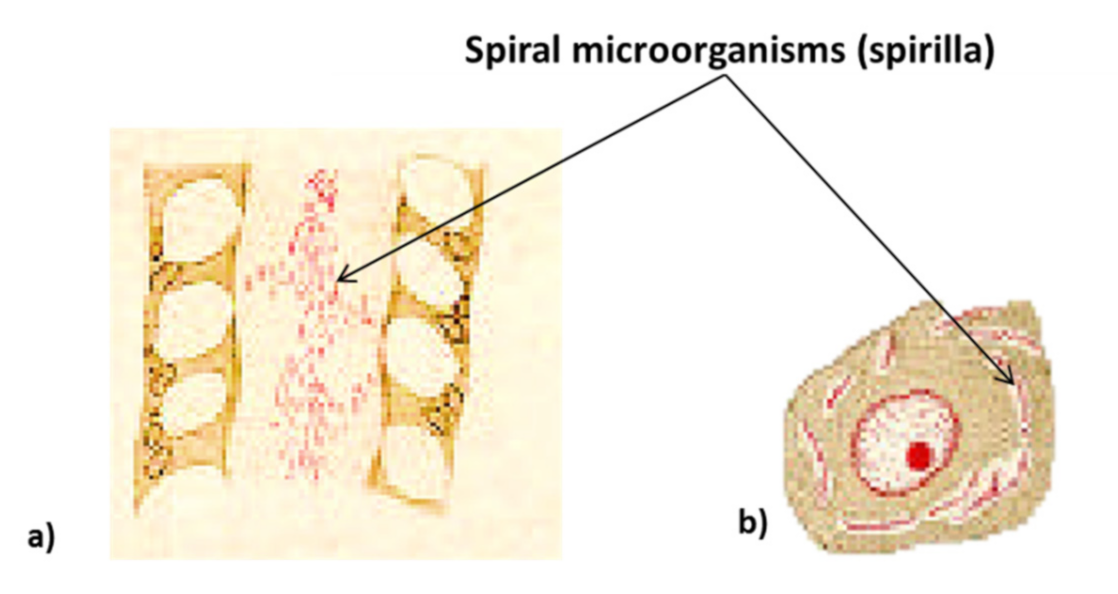
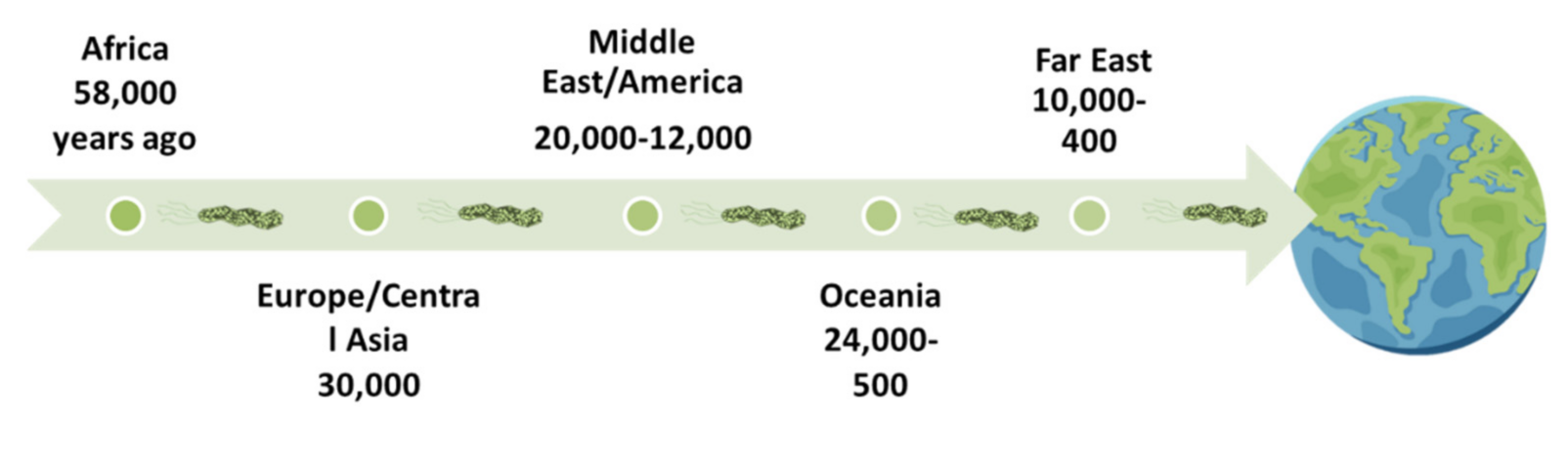


| Gastric Bacteria Discoveries—Historical Timeline | |
|---|---|
| Year | Researchers |
| 1875 | G. Bottcher/M. Letulle (demonstrated bacteria in ulcer margins) |
| 1881 | C. Klebs (indentified bacterial colonization and inter-glandular small cell infiltration) |
| 1889 | W. Jaworski (noticed spiral organisms, Vibrio rugula, in gastric washings) |
| 1893 | G. Bizzozero (identified spirochetes in gastric mucosa of dogs) |
| 1896 | H. Salomon (spirochetes noted in gastric mucosa and experimentally transferred to mice) |
| 1906 | W.Krienitz (noticed spirochetes in gastric contents of a patient with gastric carcinoma) |
| 1916 | E.C. Rosenow (described Streptococcus-induced gastric ulcers) |
| 1917 | L.R. Dragstedt (bacteria in experimental ulcers, no significant role identified) |
| 1924 | J.M. Luck (discovered gastric mucosal urease-1 in dogs) |
| 1925 | B. Hoffma (described B. hoffmani as a putative ulcerous agent) |
| 1938 | J.L. Doenge (Spirochetes in gastric glands of Macacus rhesus and humans) |
| 1940 | S.Freedberg (note spirochaetes in biopsies of patients operated on for ulcer or stomach cancer) and F.D. Gorham (postulated gastric acidophilic bacteria as etiologic agents in ulcer disease) |
| 1983 | J.R. Warren (identified Campylobacter pylori in human gastritis) |
| 1967 | S.Ito (in his “Handbook of physiology” reported an image of a spiral bacterium with flagella such as the Helicobacter pylori from samples taken from own stomach) |
| 1981 | R.Warren (after biopsy noticed curved bacteria in the stomach of some patients) and B.Marshall (begins the pilot study for this) |
| 1982 | B. Marshall (isolated and cultured Helicobacter pylori) |
| 1983 | B. Marshall and R. Warren (they describe H. pylori as a new species on Lancet) |
| 1985/1987 | B. Marshall/A. Morris (ingested and proved the infectivity of H. pylori according to the Koch’s 3rd criterium postulate) |
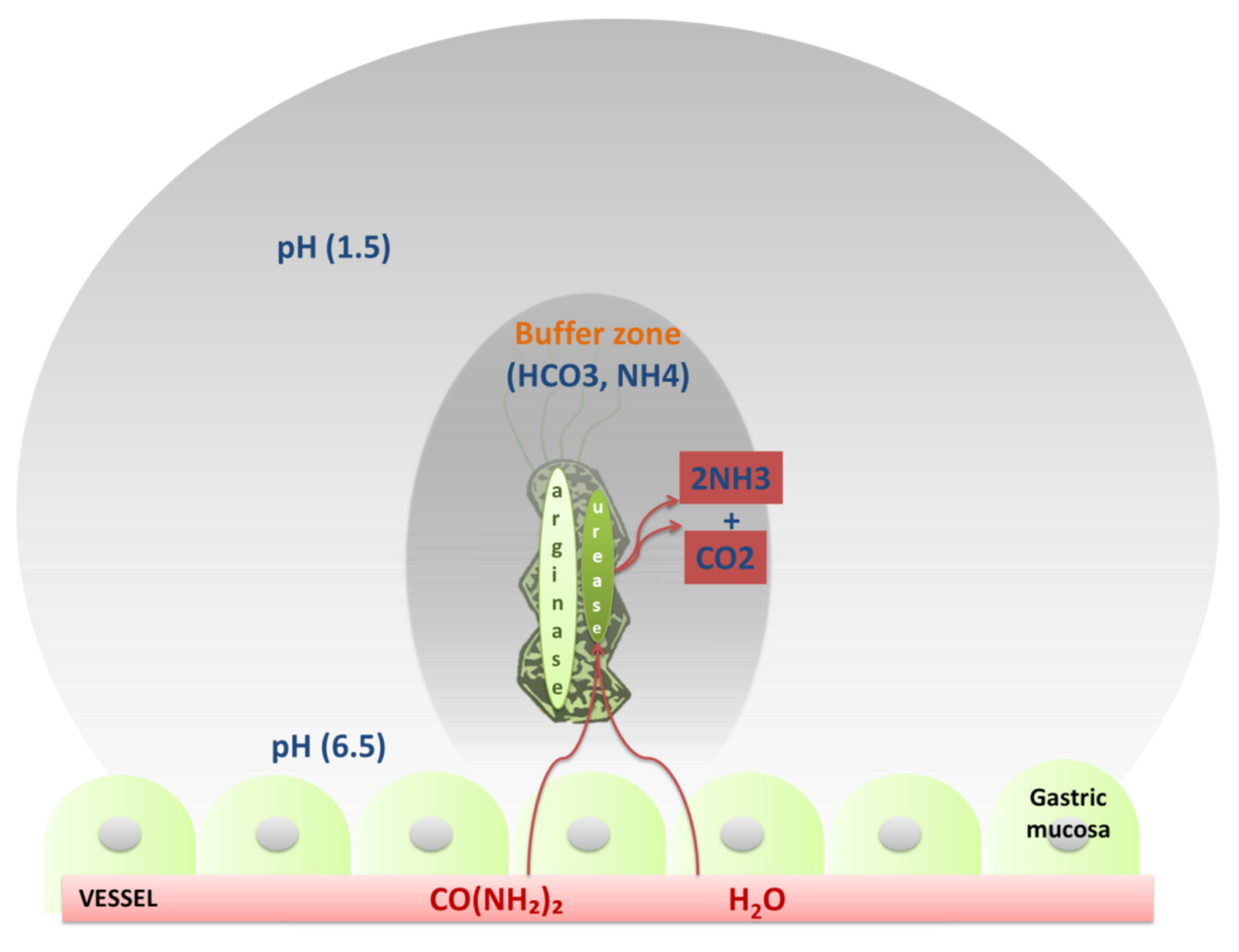
| Virulence Factors in H. pylori | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
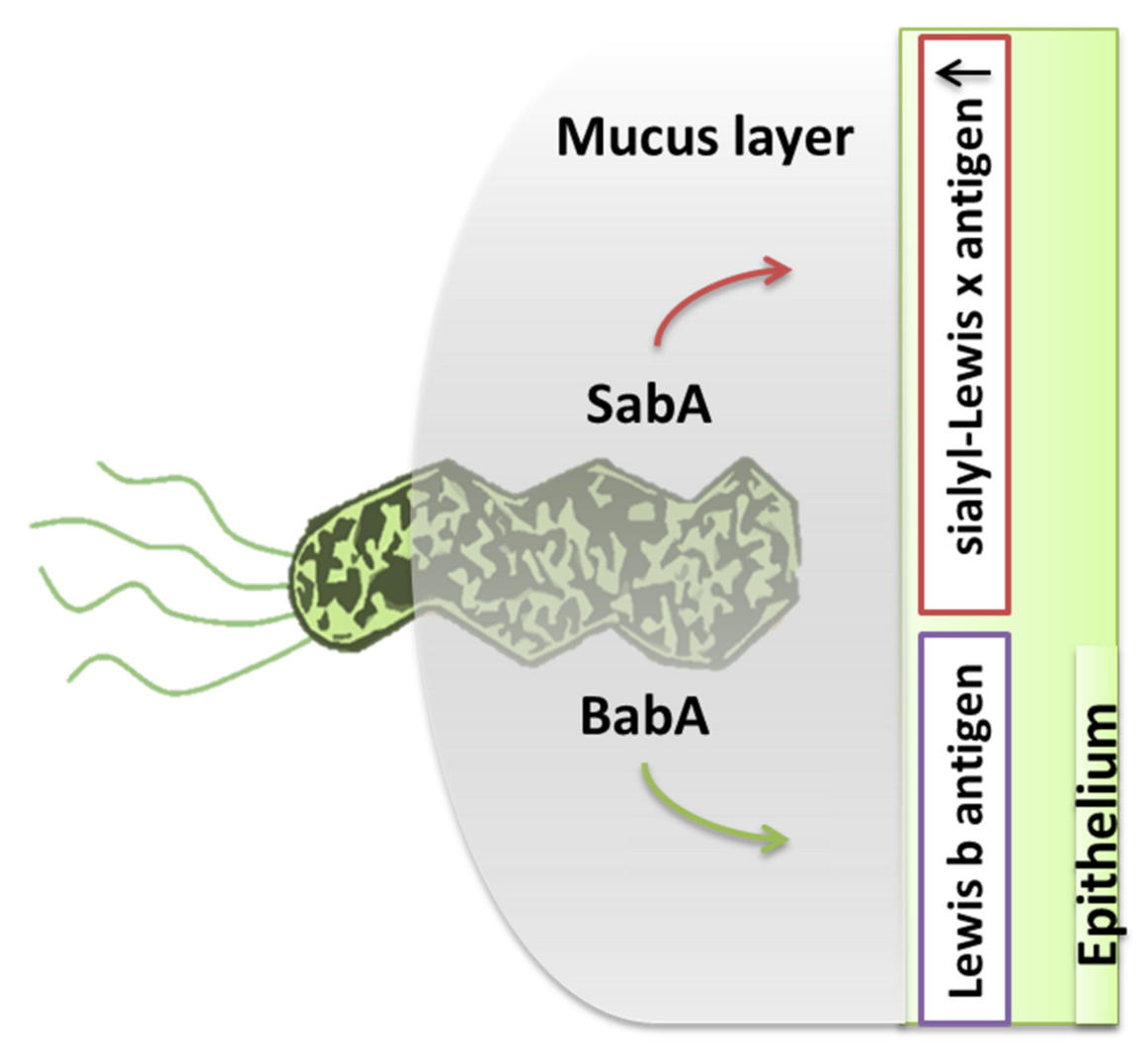
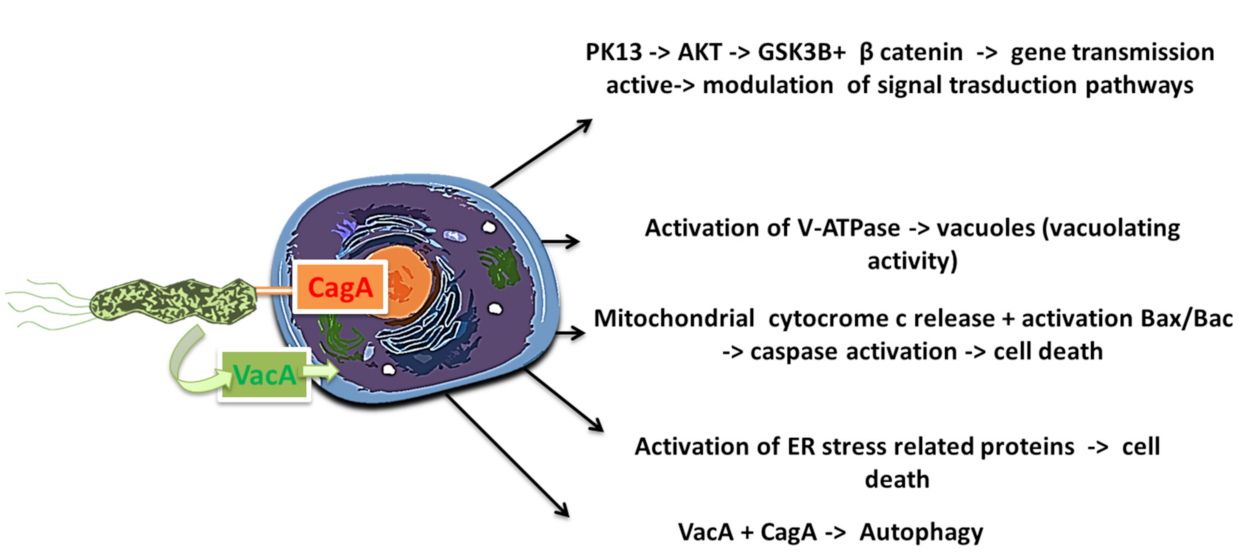
| Flagella | Urease | Lipopolysaccharides | Adhesins | Type IV Secretion System | Exotoxins | Lytic Enzymes | Heat Shock Proteins (Hsps) |
| Chemotaxis | Buffer the gastric acidic pH (creates mucosal damage through ammonia production) | Cell adhesion andinflammation | Cell adhesion, inflammation, stimulates the increase of sialyl-Lewis x antigen on the gastric mucosa. | Inject CagA and other factors. It causes the production of pro-inflammatory factors with subsequent cell apoptosis | VacA causes mucosal damage | Mucinases, proteases, lipases that cause damage to the mucosa | HSP-A and HSP-B proteins lead to inflammation |
| H. pylori Infection Associated Diseases | |
|---|---|
| Digestive Tract | Extra-Digestive |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charitos, I.A.; D’Agostino, D.; Topi, S.; Bottalico, L. 40 Years of Helicobacter pylori: A Revolution in Biomedical Thought. Gastroenterol. Insights 2021, 12, 111-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent12020011
Charitos IA, D’Agostino D, Topi S, Bottalico L. 40 Years of Helicobacter pylori: A Revolution in Biomedical Thought. Gastroenterology Insights. 2021; 12(2):111-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent12020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharitos, Ioannis Alexandros, Donato D’Agostino, Skender Topi, and Lucrezia Bottalico. 2021. "40 Years of Helicobacter pylori: A Revolution in Biomedical Thought" Gastroenterology Insights 12, no. 2: 111-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent12020011
APA StyleCharitos, I. A., D’Agostino, D., Topi, S., & Bottalico, L. (2021). 40 Years of Helicobacter pylori: A Revolution in Biomedical Thought. Gastroenterology Insights, 12(2), 111-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent12020011





